[68Ga]FAPI PET for Imaging and Treatment Monitoring in a Preclinical Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Comparison to [18F]FDG PET and CT
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
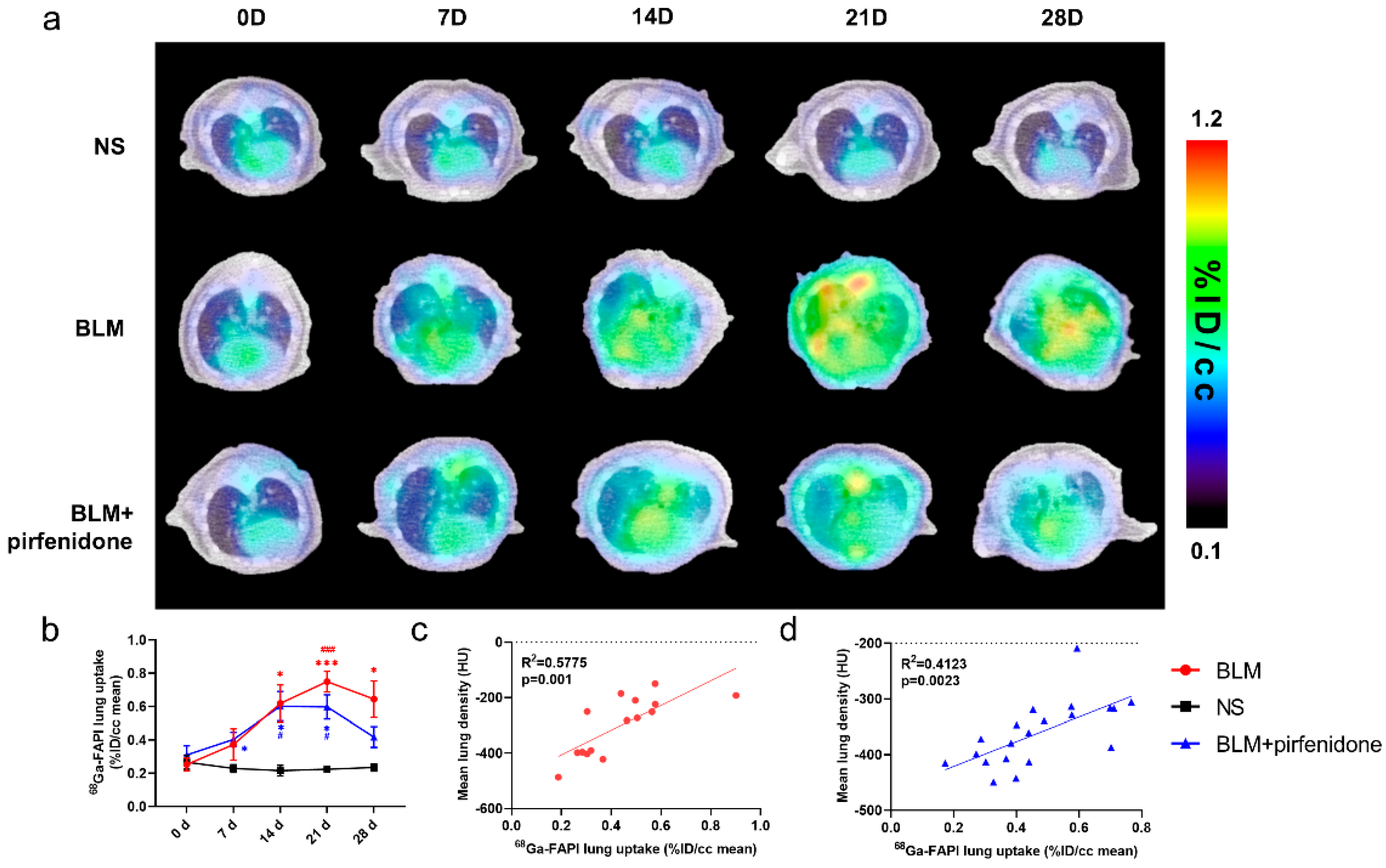
2.1. [68Ga]FAPI PET Detects BLM-Induced Lung Fibrosis
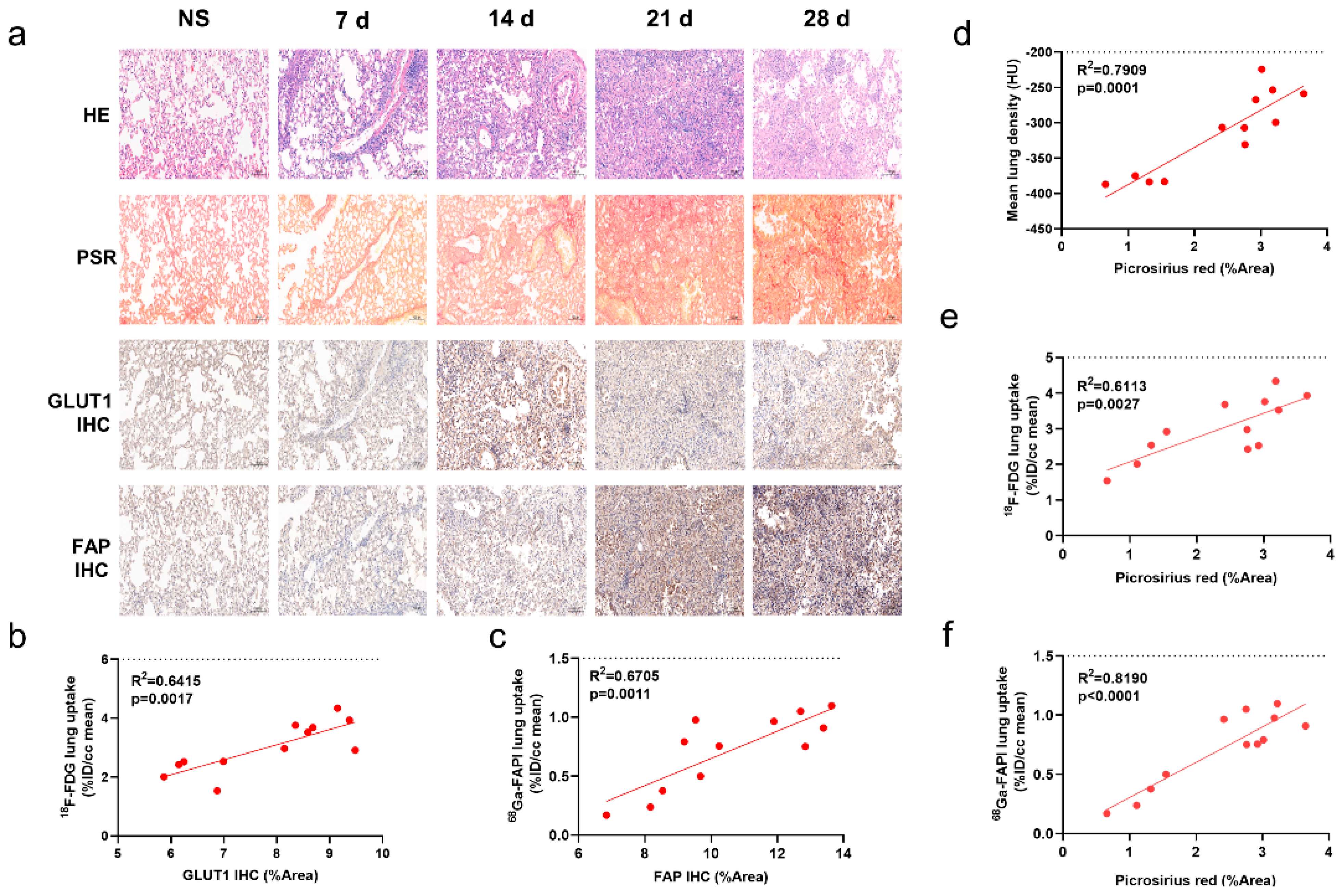
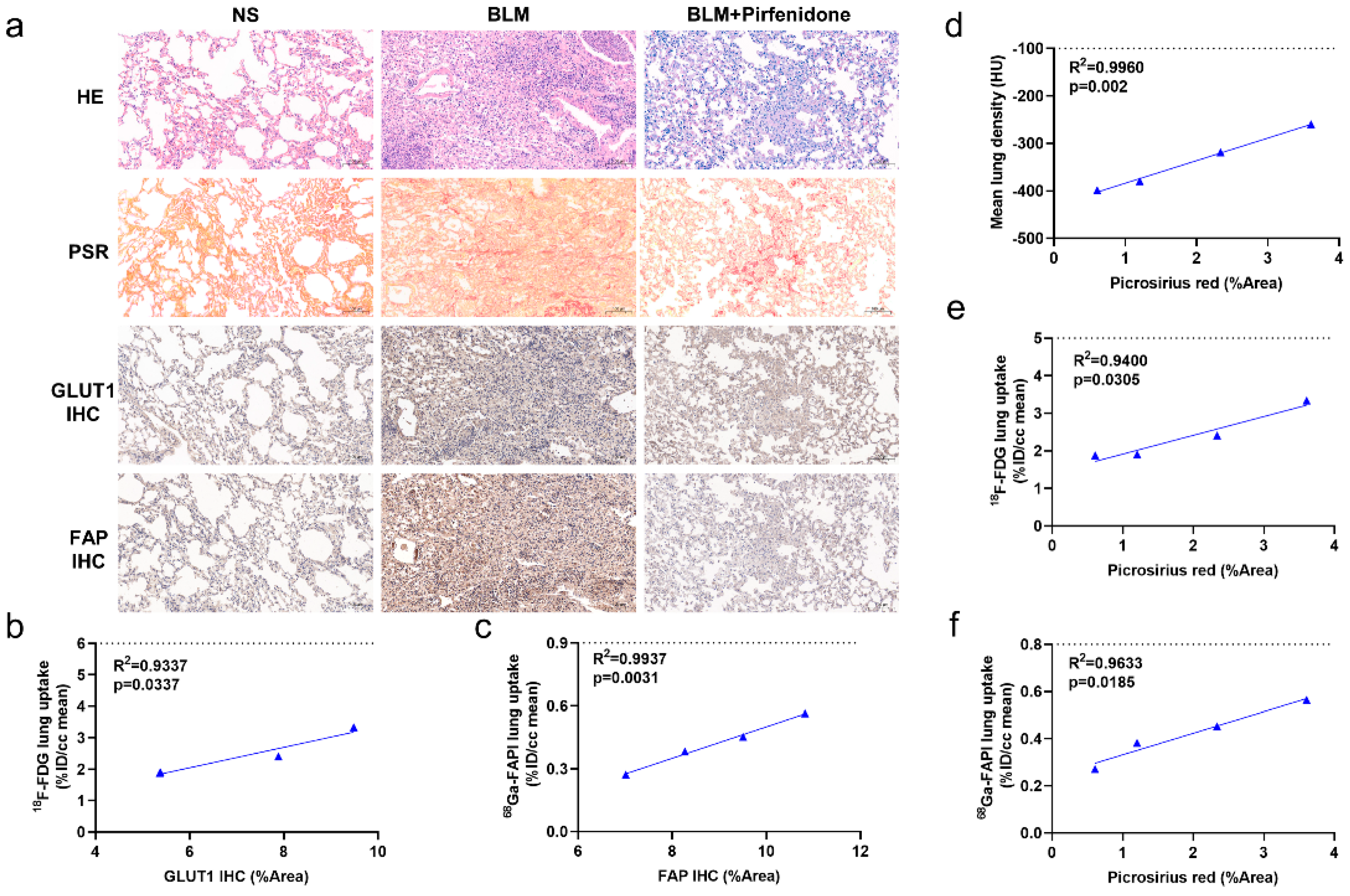
2.2. [68Ga]FAPI PET Correlates with Pathological Findings
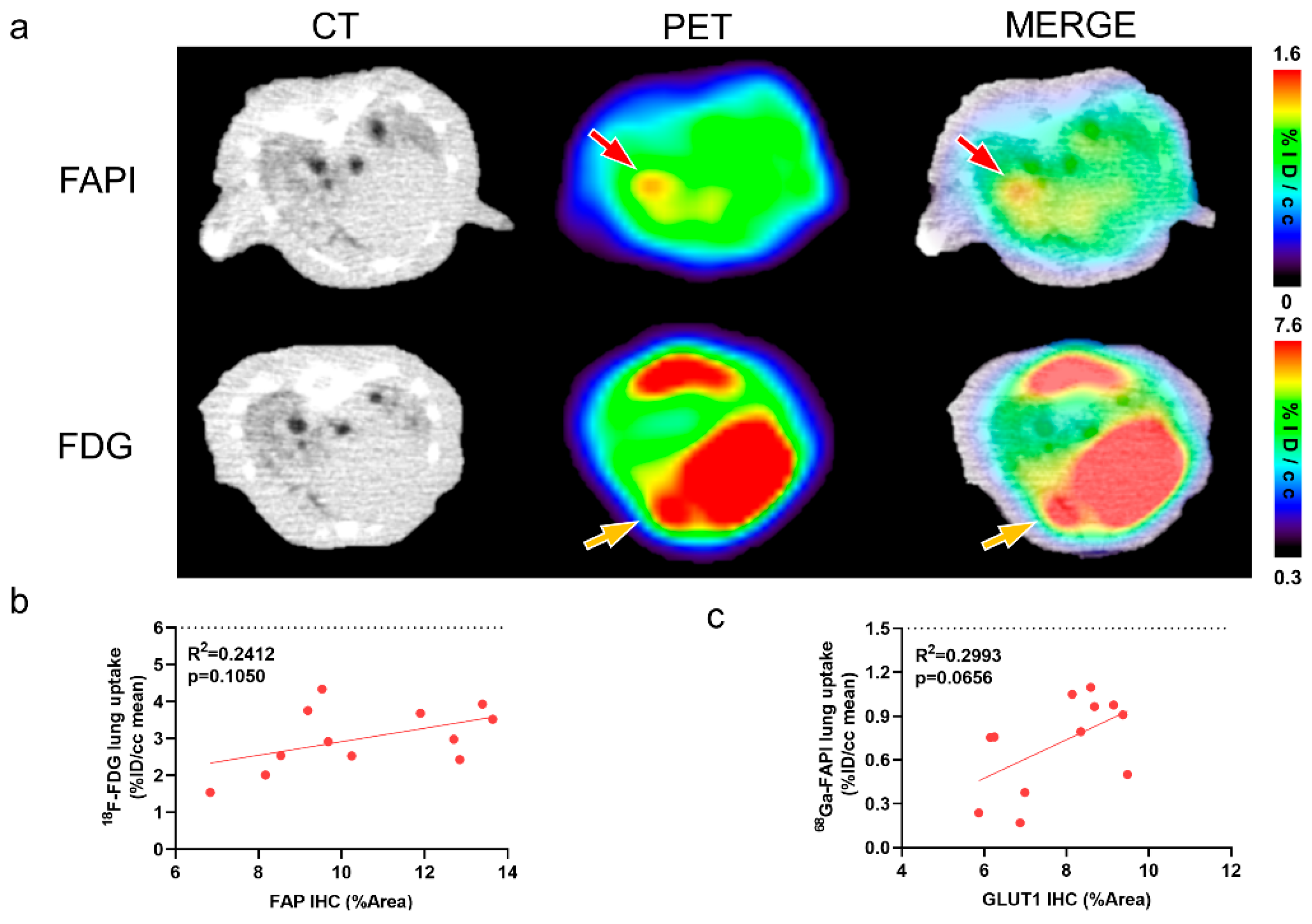
2.3. [68Ga]FAPI and [18F]FDG PET Reflects Different Pathological Changes of Pulmonary Fibrosis
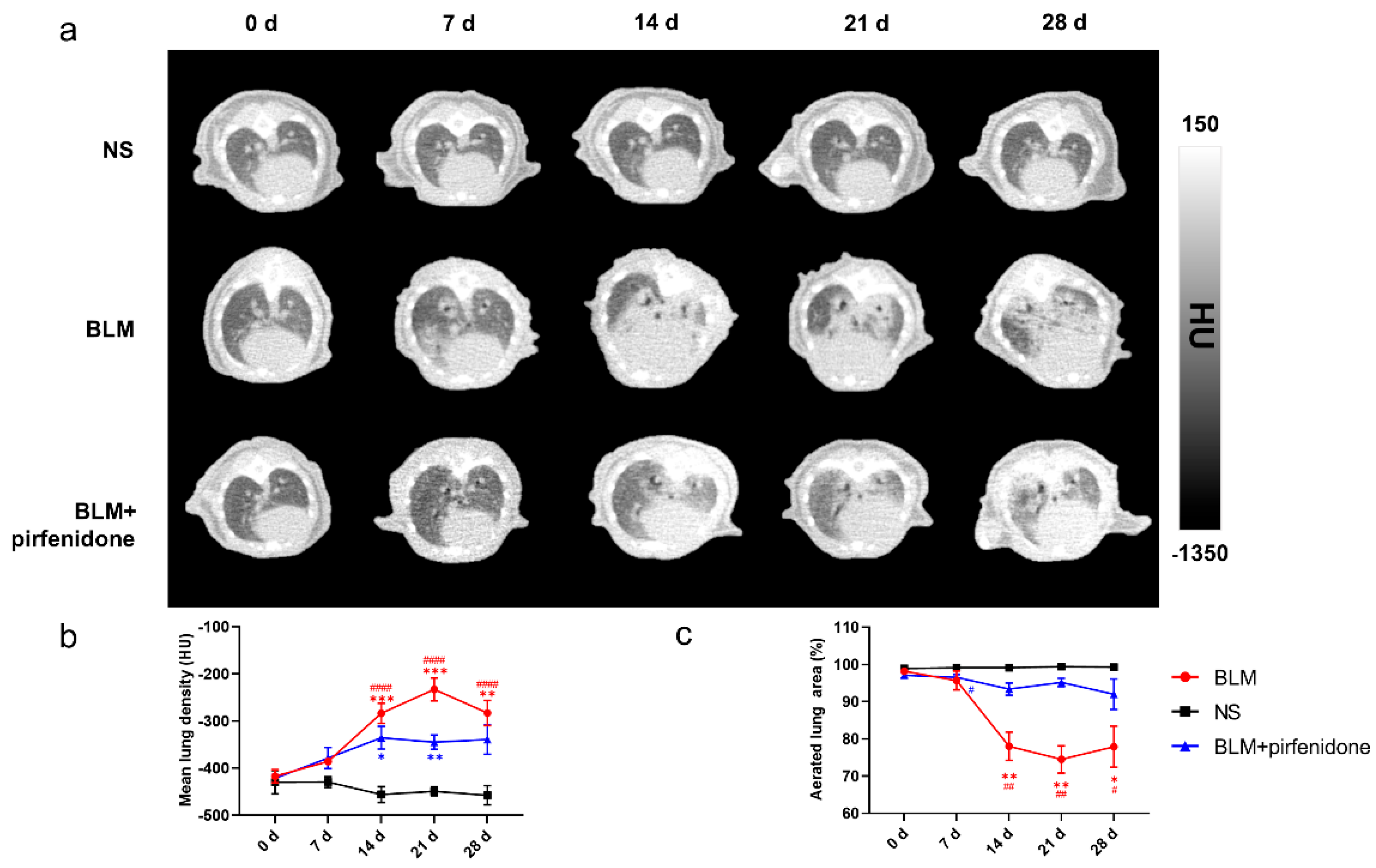
2.4. CT Imaging Confirms Effective Pirfenidone Treatment
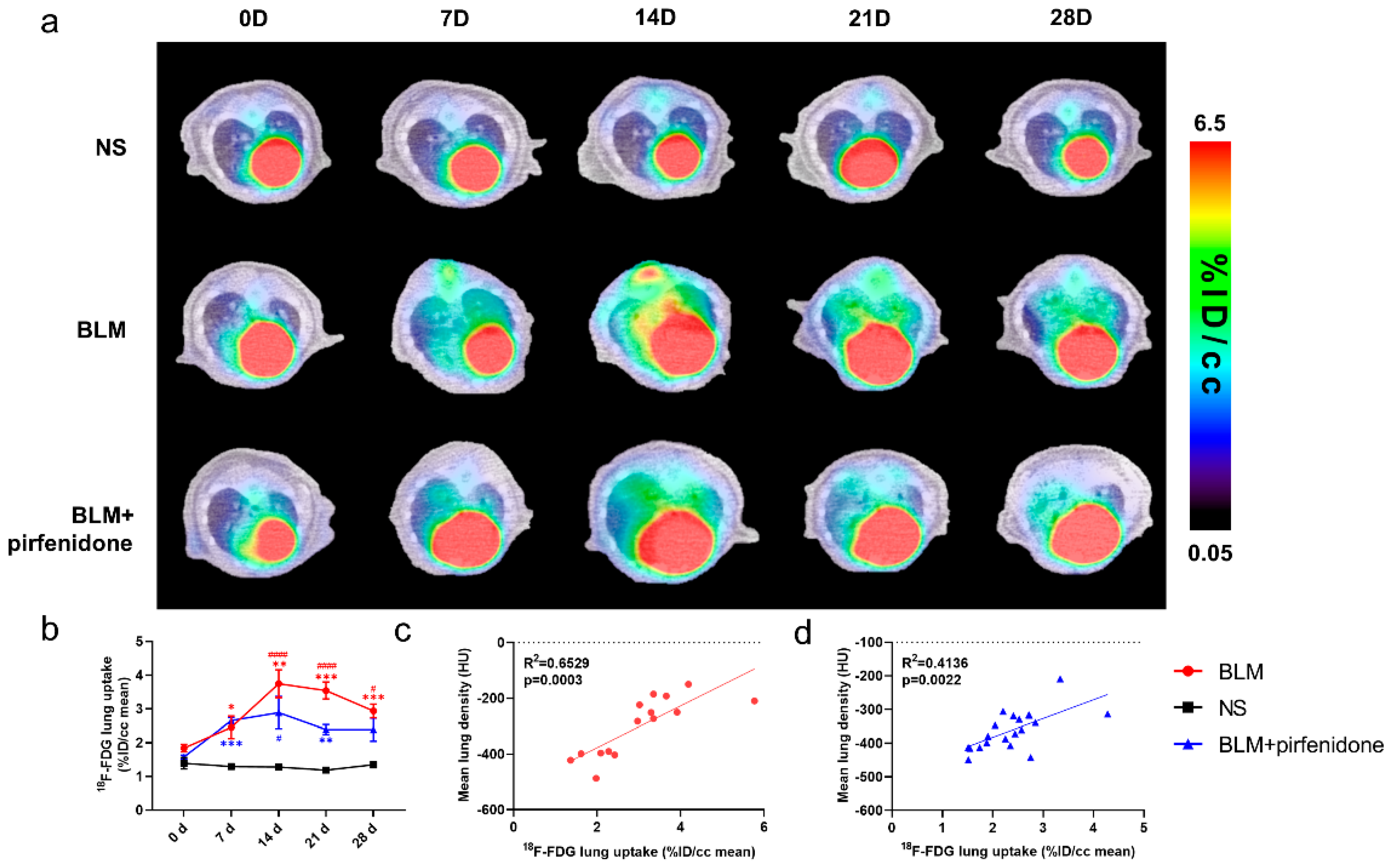
2.5. [18F]FDG PET Reflects Pirfenidone Treatment
2.6. [68Ga]FAPI PET Accurately Reflects Efficacy of Pirfenidone
2.7. Pathological Findings Confirm Imaging Results and Validate Pirfenidone Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiments
4.2. PET Imaging and Biodistribution Studies
4.3. Imaging Analysis
4.4. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining, Immunohistochemistry, and Quantification
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, T.E., Jr.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2011, 378, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalysnyk, L.; Cid-Ruzafa, J.; Rotella, P.; Esser, D. Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Review of the literature. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2012, 21, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Bois, R.M. Strategies for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, D.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Bagiella, E.; Philip, N.; Arcasoy, S.M.; Lederer, D.J. Delayed access and survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A cohort study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansell, D.M.; Goldin, J.G.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Richeldi, L.; Wells, A.U. CT staging and monitoring of fibrotic interstitial lung diseases in clinical practice and treatment trials: A position paper from the Fleischner Society. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraioli, F.; Lyasheva, M.; Porter, J.C.; Bomanji, J.; Shortman, R.I.; Endozo, R.; Wan, S.; Bertoletti, L.; Machado, M.; Ganeshan, B.; et al. Synergistic application of pulmonary (18)F-FDG PET/HRCT and computer-based CT analysis with conventional severity measures to refine current risk stratification in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, J. The diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2013, 110, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Win, T.; Thomas, B.A.; Lambrou, T.; Hutton, B.F.; Screaton, N.J.; Porter, J.C.; Maher, T.M.; Endozo, R.; Shortman, R.I.; Afaq, A.; et al. Areas of normal pulmonary parenchyma on HRCT exhibit increased FDG PET signal in IPF patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Wong, C.S.; Fung, S.L.; Yan, P.K.; Ho, J.C. SUV as an adjunct in evaluating disease activity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis—A pilot study. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2014, 35, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, Y.; Demura, Y.; Morikawa, M.; Anzai, M.; Kadowaki, M.; Ameshima, S.; Tsuchida, T.; Tsujikawa, T.; Kiyono, Y.; Okazawa, H.; et al. Prognostic Value of Dual-Time-Point 18F-FDG PET for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquelin, V.; Mekinian, A.; Brillet, P.Y.; Nunes, H.; Fain, O.; Valeyre, D.; Soussan, M. FDG-PET/CT in the prediction of pulmonary function improvement in nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. A Pilot Study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 2200–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, A.M.; Win, T.; Screaton, N.J.; Berovic, M.; Endozo, R.; Booth, H.; Kayani, I.; Menezes, L.J.; Dickson, J.C.; Ell, P.J. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and diffuse parenchymal lung disease: Implications from initial experience with 18F-FDG PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, H.H.; Soo Hoo, G.W.; Khonsary, S.A.; Mandelkern, M.; Brown, C.V.; Santiago, S.M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evaluation with positron emission tomography. Respiration 2006, 73, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desogere, P.; Tapias, L.F.; Rietz, T.A.; Rotile, N.; Blasi, F.; Day, H.; Elliott, J.; Fuchs, B.C.; Lanuti, M.; Caravan, P. Optimization of a Collagen-Targeted PET Probe for Molecular Imaging of Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desogere, P.; Tapias, L.F.; Hariri, L.P.; Rotile, N.J.; Rietz, T.A.; Probst, C.K.; Blasi, F.; Day, H.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Weinreb, P.; et al. Type I collagen-targeted PET probe for pulmonary fibrosis detection and staging in preclinical models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaf4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schniering, J.; Benesova, M.; Brunner, M.; Haller, S.; Cohrs, S.; Frauenfelder, T.; Vrugt, B.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Schibli, R.; Distler, O.; et al. Visualisation of interstitial lung disease by molecular imaging of integrin alphavbeta3 and somatostatin receptor 2. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, J.; Goirand, F.; Bouchard, A.; Frenay, J.; Moreau, M.; Mothes, C.; Oudot, A.; Helbling, A.; Guillemin, M.; Bonniaud, P.; et al. [(18)F]FMISO PET/CT imaging of hypoxia as a non-invasive biomarker of disease progression and therapy efficacy in a preclinical model of pulmonary fibrosis: Comparison with the [(18)F]FDG PET/CT approach. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3058–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniering, J.; Guo, L.; Brunner, M.; Schibli, R.; Ye, S.; Distler, O.; Behe, M.; Maurer, B. Evaluation of (99m)Tc-rhAnnexin V-128 SPECT/CT as a diagnostic tool for early stages of interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Nie, D.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Su, S.; Sun, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, X.; Tang, G. Apoptotic PET Imaging of Rat Pulmonary Fibrosis with Small-Molecule Radiotracer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schniering, J.; Benesova, M.; Brunner, M.; Haller, S.; Cohrs, S.; Frauenfelder, T.; Vrugt, B.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Schibli, R.; Distler, O.; et al. (18)F-AzaFol for Detection of Folate Receptor-beta Positive Macrophages in Experimental Interstitial Lung Disease-A Proof-of-Concept Study. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkova, A.; Busek, P.; Sedo, A.; Konvalinka, J. Molecular recognition of fibroblast activation protein for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamson, E.J.; Keane, F.M.; Tholen, S.; Schilling, O.; Gorrell, M.D. Understanding fibroblast activation protein (FAP): Substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varasteh, Z.; Mohanta, S.; Robu, S.; Braeuer, M.; Li, Y.; Omidvari, N.; Topping, G.; Sun, T.; Nekolla, S.G.; Richter, A.; et al. Molecular Imaging of Fibroblast Activity After Myocardial Infarction Using a (68)Ga-Labeled Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor, FAPI-04. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xing, H.; Yang, X.; Li, F.; Yao, S.; Congwei, J.; Zhao, H.; Hacker, M.; Huo, L.; Li, X. Comparison of PET imaging of activated fibroblasts and (18)F-FDG for diagnosis of primary hepatic tumours: A prospective pilot study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Luo, W.; Liu, H.; Lv, T.; Wang, J.; Qin, J.; Ou, S.; Chen, Y. Value of [(68)Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 imaging in the diagnosis of renal fibrosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3493–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidkonz, C.; Rauber, S.; Atzinger, A.; Agarwal, R.; Gotz, T.I.; Soare, A.; Cordes, M.; Prante, O.; Bergmann, C.; Kleyer, A.; et al. Disentangling inflammatory from fibrotic disease activity by fibroblast activation protein imaging. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Wang, P.; Su, X.H.; Lu, Y.Q. Assessment of pulmonary fibrosis induced by paraquat using Al18F-NODA-FAPI-04 PET/CT. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 18, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, P.S.; Zukas, A.; Chandan, V.; Katzenstein, A.L.; Puré, E. Fibroblast activation protein: A serine protease expressed at the remodeling interface in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Human. Pathol. 2006, 37, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.H.; Zhu, Q.; Li, H.H.; Ra, H.J.; Majumdar, S.; Gulick, D.L.; Jerome, J.A.; Madsen, D.H.; Christofidou-Solomidou, M.; Speicher, D.W.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) Accelerates Collagen Degradation and Clearance from Lungs in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8070–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Fang, Q.; Fu, Z.; Li, J.; Lai, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Peng, X.; Hu, K.; Nie, X.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) Expression in Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 207, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, T.; Screaton, N.J.; Porter, J.C.; Ganeshan, B.; Maher, T.M.; Fraioli, F.; Endozo, R.; Shortman, R.I.; Hurrell, L.; Holman, B.F.; et al. Pulmonary (18)F-FDG uptake helps refine current risk stratification in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobashi, T.; Kubo, T.; Nakamoto, Y.; Handa, T.; Koyasu, S.; Ishimori, T.; Mishima, M.; Togashi, K. 18F-FDG Uptake in Less Affected Lung Field Provides Prognostic Stratification in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondue, B.; Castiaux, A.; Van Simaeys, G.; Mathey, C.; Sherer, F.; Egrise, D.; Lacroix, S.; Huaux, F.; Doumont, G.; Goldman, S. Absence of early metabolic response assessed by 18F-FDG PET/CT after initiation of antifibrotic drugs in IPF patients. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrich, M.; Leitz, D.; Glatting, F.M.; Wefers, A.K.; Weinheimer, O.; Flechsig, P.; Kahn, N.; Mall, M.A.; Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein-Specific PET/CT Imaging in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases and Lung Cancer: A Translational Exploratory Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, C.; Distler, J.; Treutlein, C.; Tascilar, K.; Schmidkonz, C.J.T.L.R. 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET-CT for molecular assessment of fibroblast activation and risk evaluation in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: A single-centre, pilot study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2022, 12, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscitti, F.; Ravanetti, F.; Essers, J.; Ridwan, Y.; Belenkov, S.; Vos, W.; Ferreira, F.; KleinJan, A.; van Heijningen, P.; Van Holsbeke, C.; et al. Longitudinal assessment of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by Micro-CT correlates with histological evaluation in mice. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2017, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, F.; Ravanetti, F.; Donofrio, G.; Ridwan, Y.; van Heijningen, P.; Essers, J.; Villetti, G.; Cacchioli, A.; Vos, W.; Stellari, F.F. A Multimodal Imaging Approach Based on Micro-CT and Fluorescence Molecular Tomography for Longitudinal Assessment of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 134, e56443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondue, B.; Sherer, F.; Van Simaeys, G.; Doumont, G.; Egrise, D.; Yakoub, Y.; Huaux, F.; Parmentier, M.; Rorive, S.; Sauvage, S.; et al. PET/CT with 18F-FDG- and 18F-FBEM-labeled leukocytes for metabolic activity and leukocyte recruitment monitoring in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamchaoui, K.; Makhloufi, Y.; Saumon, G. Glucose transporter gene expression in freshly isolated and cultured rat pneumocytes. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2002, 175, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, W.E.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Zoia, O.; Stathopoulos, G.T.; Han, W.; Plieth, D.; Loyd, J.E.; Neilson, E.G.; Blackwell, T.S. Characterization of fibroblast-specific protein 1 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, B.J.; Ryter, S.W.; Rosas, I.O. Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 515–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-de la Mora, D.A.; Sanchez-Roque, C.; Montoya-Buelna, M.; Sanchez-Enriquez, S.; Lucano-Landeros, S.; Macias-Barragan, J.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Role and New Insights of Pirfenidone in Fibrotic Diseases. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwapiszewska, G.; Gungl, A.; Wilhelm, J.; Marsh, L.M.; Thekkekara Puthenparampil, H.; Sinn, K.; Didiasova, M.; Klepetko, W.; Kosanovic, D.; Schermuly, R.T.; et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals the complexity of pirfenidone effects in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, B.B.; Hogaboam, C.M. Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L152–L160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.; Ask, K.; Warburton, D.; Gauldie, J.; Kolb, M. The bleomycin animal model: A useful tool to investigate treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, H.; Song, X.; Lv, X.; Shao, F.; Long, Y.; Song, Y.; Song, W.; Qiao, P.; Gai, Y.; Jiang, D.; et al. [68Ga]FAPI PET for Imaging and Treatment Monitoring in a Preclinical Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Comparison to [18F]FDG PET and CT. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060726
Ji H, Song X, Lv X, Shao F, Long Y, Song Y, Song W, Qiao P, Gai Y, Jiang D, et al. [68Ga]FAPI PET for Imaging and Treatment Monitoring in a Preclinical Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Comparison to [18F]FDG PET and CT. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(6):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060726
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Hao, Xiangming Song, Xiaoying Lv, Fuqiang Shao, Yu Long, Yangmeihui Song, Wenyu Song, Pengxin Qiao, Yongkang Gai, Dawei Jiang, and et al. 2024. "[68Ga]FAPI PET for Imaging and Treatment Monitoring in a Preclinical Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Comparison to [18F]FDG PET and CT" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 6: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060726
APA StyleJi, H., Song, X., Lv, X., Shao, F., Long, Y., Song, Y., Song, W., Qiao, P., Gai, Y., Jiang, D., & Lan, X. (2024). [68Ga]FAPI PET for Imaging and Treatment Monitoring in a Preclinical Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Comparison to [18F]FDG PET and CT. Pharmaceuticals, 17(6), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060726







