Novel Anti-Enterovirus A71 Compounds Discovered by Repositioning Antivirals from the Open-Source MMV Pandemic Response Box
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
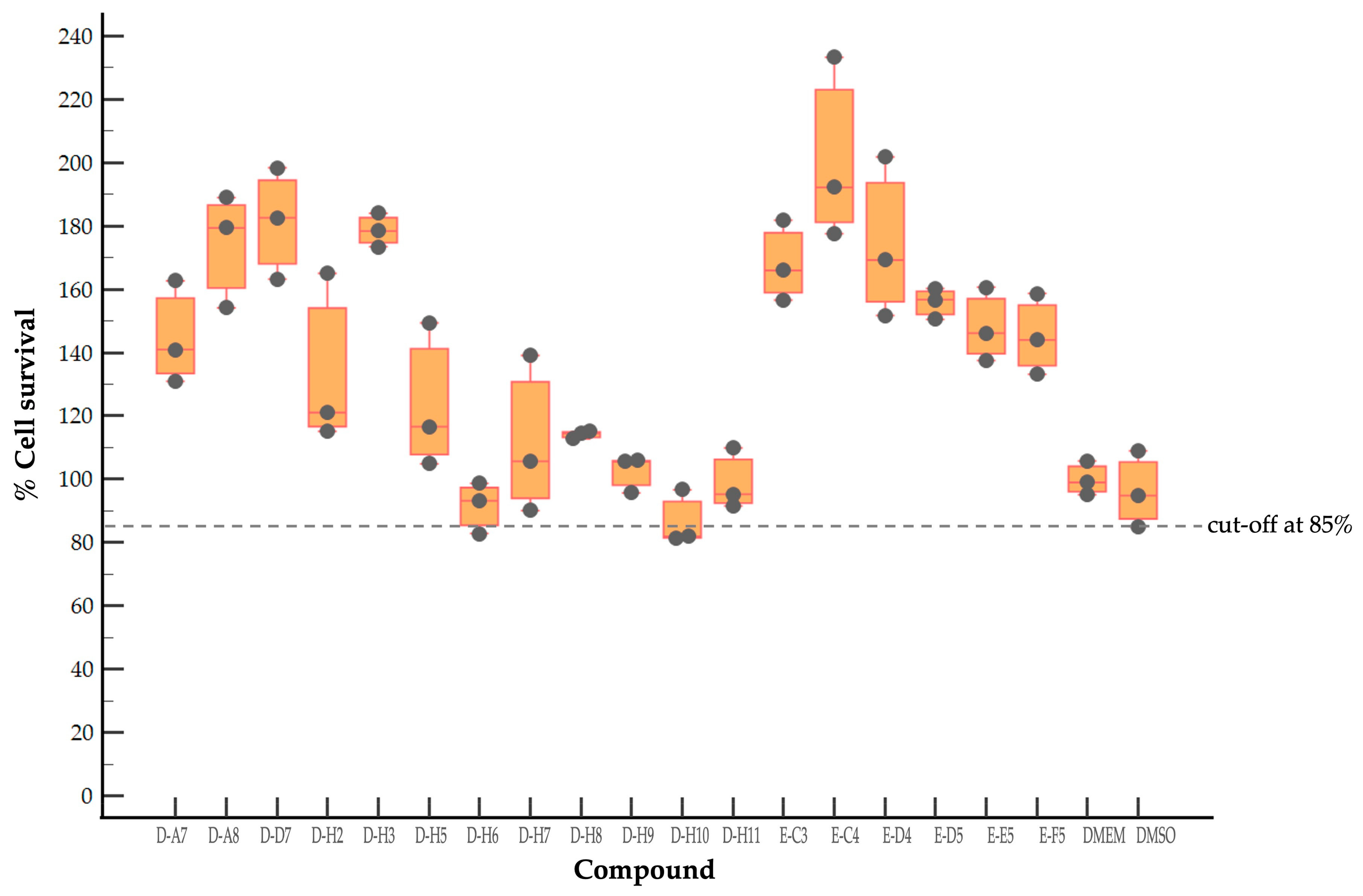
2.1. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Antiviral Compounds of the MMV Pandemic Response Box
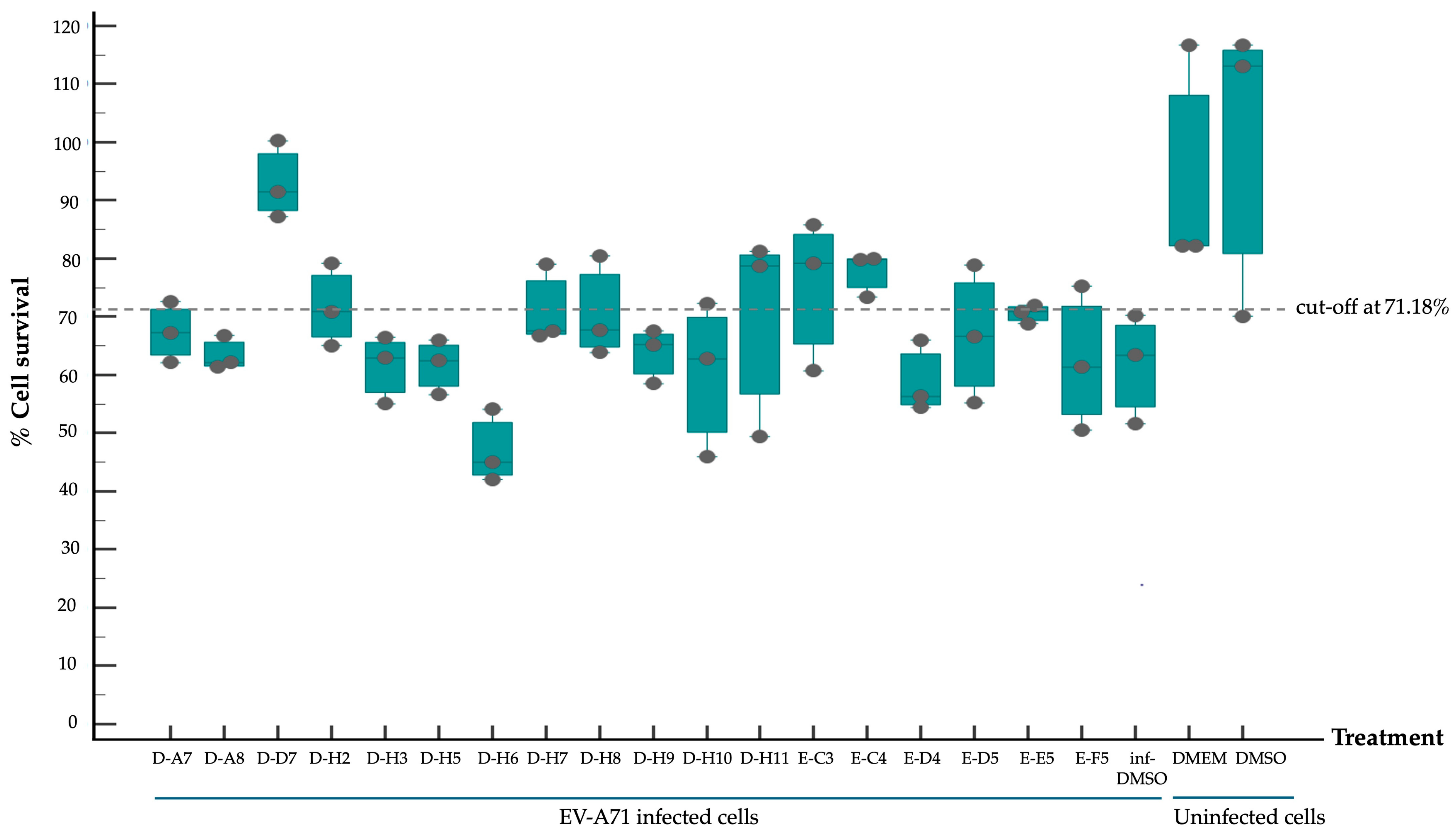
2.2. Screening of Compounds with Potential Anti-EV-A71 Activity
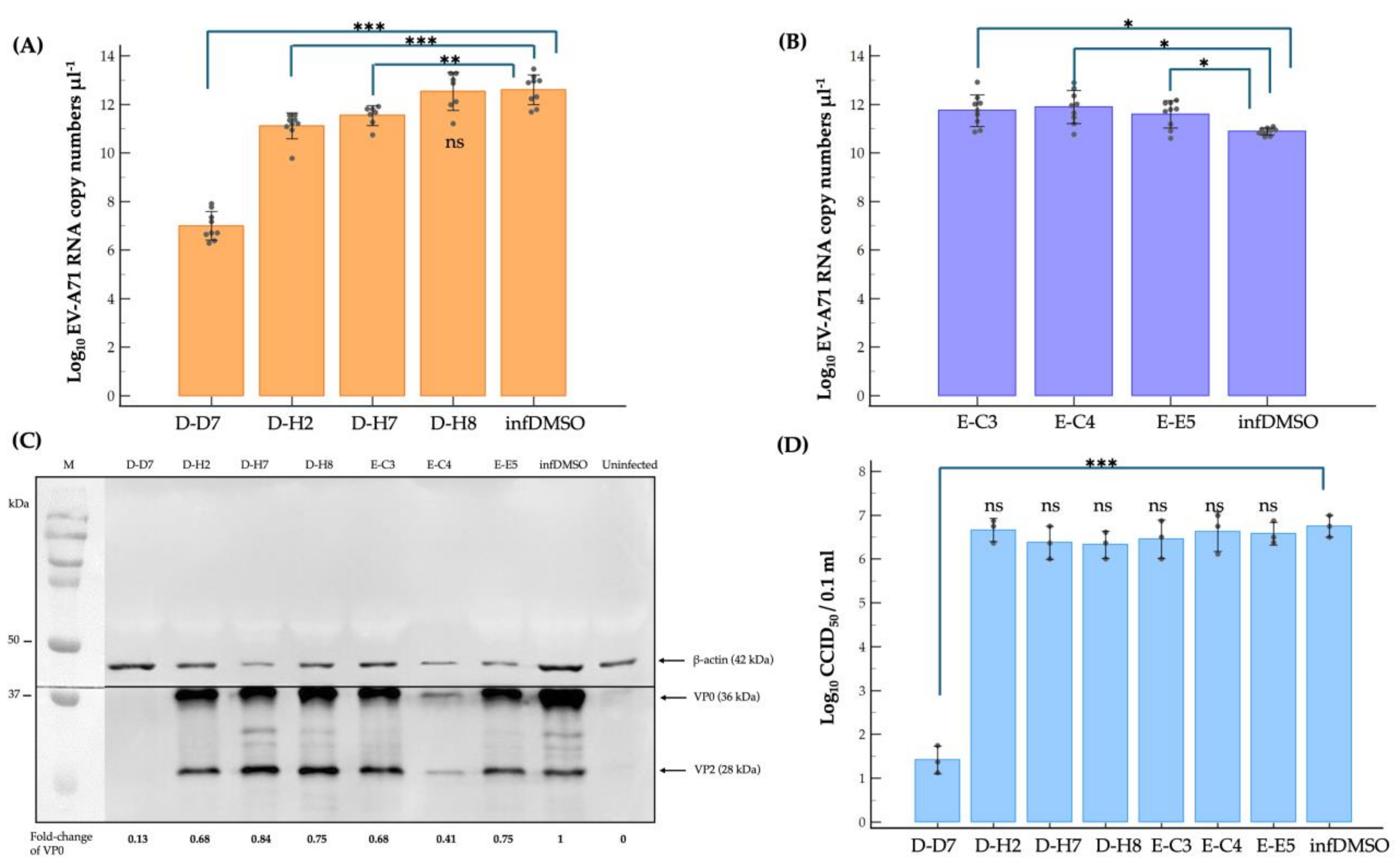
2.3. Dissecting Mechanism of Inhibitory Effect of the Hit Compounds on EV-A71 Replication
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Virus
4.2. Compound Preparation of the Pandemic Response Box
4.3. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
4.4. Virus Reduction Assays
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, L.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Gau, S.S.; Lu, C.Y.; Hsia, S.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, L.M.; Lin, T.Y. Enterovirus A71 Neurologic Complications and Long-term Sequelae. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, W.M.; Badaruddin, H.; La, H.; Chen, M.I.; Cook, A.R. Severity and Burden of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in Asia: A Modelling Study. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.C.; Wong, K.T. Understanding Enterovirus 71 Neuropathogenesis and Its Impact on Other Neurotropic Enteroviruses. Brain Pathol. 2015, 25, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Control of Enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.D.; Li, P.Q.; Huang, Y.G.; Li, W.; Ma, L.Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, N.; Lu, J.M.; Chen, W.Q.; Liu, G.M.; et al. Factors Associated with Fatal Outcome of Children with Enterovirus A71 Infection: A Case Series. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puenpa, J.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. The History of Enterovirus A71 Outbreaks and Molecular Epidemiology in The Asia-Pacific Region. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Jit, M.; Wu, J.T.; Yang, J.; Leung, K.; Liao, Q.; Yu, H. Economic Costs and Health-related Quality of Life for Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Patients in China. PLoS ONE 2017, 2, e0184266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Ren, M.; Nie, T.; Cui, J.; Chang, Z.; Li, Z. Basic Reproduction Number of Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16 and A6: Evidence From Outbreaks of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in China between 2011 and 2018. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e2552–e2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, L.; Mo, Z.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Mao, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. An Inactivated Enterovirus 71 Vaccine in Healthy Children. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Meng, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liu, P.; Shi, N.; Tao, H.; et al. 2-Year Efficacy, Immunogenicity, and Safety of Vigoo Enterovirus 71 Vaccine in Healthy Chinese Children: A Randomized Open-Label Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Xu, W.; Xia, J.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, L.; Mao, Q.; Wu, J.; et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Immunogenicity of An Enterovirus 71 Vaccine in China. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, M. Enterovirus A71 Antivirals: Past, Present, and Future. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1542–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Pang, Z.; Fan, H.; Tong, Y. Advances in Anti-EV-A71 Drug Development Research. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 56, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercorelli, B.; Palù, G.; Loregian, A. Drug Repurposing for Viral Infectious Diseases: How Far Are We? Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, T. Strategy, Progress, and Challenges of Drug Repurposing for Efficient Antiviral Discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 660710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samby, K.; Besson, D.; Dutta, A.; Patra, B.; Doy, A.; Glossop, P.; Mills, J.; Whitlock, G.; van Huijsduijnen, R.H.; Monaco, A.; et al. The Pandemic Response Box—Accelerating Drug Discovery Efforts after Disease Outbreaks. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, R.; Zhou, M.; Shek, R.; Wilson, J.W.; Tillery, L.; Craig, J.K.; Salukhe, I.A.; Hickson, S.E.; Kumar, N.; James, R.M.; et al. High-throughput Screening of the ReFRAME, Pandemic Box, and COVID Box Drug Repurposing Libraries against SARS-CoV-2 Nsp15 Endoribonuclease to Identify Small-molecule Inhibitors of Viral Activity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.S.; de Godoy, A.S.; Santos, I.A.; Noske, G.D.; de Oliveira, K.I.Z.; Gawriljuk, V.O.; Gomes Jardim, A.C.; Oliva, G. Discovery of an Imidazonaphthyridine and a Riminophenazine as Potent Anti-Zika Virus Agents Through a Replicon-based High-throughput Screening. Virus Res. 2021, 299, 198388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.N.; Song, Z.G.; Jiang, T.; Shi, B.S.; Hu, Y.W.; Yuan, Z.H. Rupintrivir is a Promising Candidate for Treating Severe Cases of Enterovirus-71 Infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janissen, R.; Woodman, A.; Shengjuler, D.; Vallet, T.; Lee, K.M.; Kuijpers, L.; Moustafa, I.M.; Fitzgerald, F.; Huang, P.N.; Perkins, A.L.; et al. Induced Intra- and Intermolecular Template Switching as a Therapeutic Mechanism against RNA Viruses. Mol. Cell. 2021, 81, 4467–4480.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandemic Response Box Supporting Information. Available online: https://www.mmv.org/mmv-open/pandemic-response-box/pandemic-response-box-supporting-information (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- 2D Structure Image of CID 6478675 (2-Pyridone-Containing Peptidomimetics). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6478675 (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- 2D Structure Image of CID 71481097 (Selinexor). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/71481097 (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- 2D Structure Image of CID 5271819 (T-1106). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5271819 (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- 2D Structure Image of CID 2782 (Clemizole). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2782 (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Dragovich, P.S.; Prins, T.J.; Zhou, R.; Johnson, T.O.; Hua, Y.; Luu, H.T.; Sakata, S.K.; Brown, E.L.; Maldonado, F.C.; Tuntland, T.; et al. Structure-based Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Irreversible Human Rhinovirus 3C Protease Inhibitors. 8. Pharmacological Optimization of Orally Bioavailable 2-Pyridone-containing Peptidomimetics. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4572–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podar, K.; Shah, J.; Chari, A.; Richardson, P.G.; Jagannath, S. Selinexor for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einav, S.; Sobol, H.D.; Gehrig, E.; Glenn, J.S. The Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS4B RNA Binding Inhibitor Clemizole is Highly Synergistic with HCV Protease Inhibitors. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2D Structure Image of CID 24780598 (Danirixin). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/24780598 (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- 2D Structure Image of CID 1455 (Pocapavir). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/1455 (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- 2D Structure Image of CID 65015 (Plerixafor). Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/65015 (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Madan, A.; Chen, S.; Yates, P.; Washburn, M.L.; Roberts, G.; Peat, A.J.; Tao, Y.; Parry, M.F.; Barnum, O.; McClain, M.T.; et al. Co-administered With Standard-of-Care Antiviral (Oseltamivir): A Phase 2b, Global, Randomized Study of Adults Hospitalized with Influenza. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanko, K.; Sun, L.; Froeyen, M.; Leyssen, P.; Delang, L.; Mirabelli, C.; Neyts, J. Comparative Analysis of the Molecular Mechanism of Resistance to Vapendavir across a Panel of Picornavirus Species. Antivir. Res. 2021, 195, 105177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPersio, J.F.; Uy, G.L.; Yasothan, U.; Kirkpatrick, P. Plerixafor. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Polio Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/68762/1/WHO_IVB_04.10.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Dragovich, P.S.; Prins, T.J.; Zhou, R.; Brown, E.L.; Maldonado, F.C.; Fuhrman, S.A.; Zalman, L.S.; Tuntland, T.; Lee, C.A.; Patick, A.K.; et al. Structure-based Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Irreversible Human Rhinovirus 3C Protease Inhibitors. 6. Structure-activity Studies of Orally Bioavailable, 2-Pyridone-containing Peptidomimetics. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1607–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, J.; Fan, T.; Qin, B.; Guo, L.; Lei, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Jin, Q. Crystal Structure of Human Enterovirus 71 3C Protease. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, X.; Jin, Q.; He, B.; Wang, J. Cleavage of The Adaptor Protein TRIF by Enterovirus 71 3C Inhibits Antiviral Responses Mediated by Toll-like Receptor 3. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8811–8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, T.; Murray, J.; Walker, C.J.; Chang, H.; Tamir, S.; Hou, B.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.G.; Tripp, R.A.; Landesman, Y. Selinexor, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export, Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Protects The Respiratory System In Vivo. Antivir. Res. 2021, 192, 105115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanpan, K.; Srimanote, P.; Tongtawe, P.; Khantisitthiporn, O.; Supasorn, O.; Rattanakomol, P.; Thanongsaksrikul, J. Transcriptome of Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells in Response to 2B Protein of Enterovirus-A71. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Ganter, B.; Meier, C. Improving Properties of The Nucleobase Analogs T-705/T-1105 As Potential Antiviral. Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 2021, 57, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Torres, S.; Myers, A.L.; Klatte, J.M.; Rhoden, E.E.; Oberste, M.S.; Collett, M.S.; McCulloh, R.J. First Use of Investigational Antiviral Drug Pocapavir (v-073) for Treating Neonatal Enteroviral Sepsis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, S.; Thakkar, R.; Fong, K.T.; Ng, J.; Bearden, D.R.; Mishra, N.; Thakur, K.T.; Riley, C.S. Compassionate-use Pocapavir and Immunoglobulin Therapy for Treatment of Rituximab-associated Enterovirus Meningoencephalitis. J. Neurovirol. 2022, 28, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copelyn, J.; Hincks, J.R.; Wilmshurst, J.M.; Petersen, W.; Howard, W.; Jallow, S.; Moonsamy, S.; Seakamela, L.; Suchard, M.; Collett, M.S.; et al. Clearance of Immunodeficiency-associated Vaccine-derived Poliovirus Infection with Pocapavir. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catching, A.; Te Yeh, M.; Bianco, S.; Capponi, S.; Andino, R. A Tradeoff Between Enterovirus A71 Particle Stability and Cell Entry. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Chang, C.L.; Wang, P.S.; Tsai, Y.; Liu, H.S. Enterovirus 71-induced Autophagy Detected In Vitro and In Vivo Promotes Viral Replication. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspar, B.; Cocchiara, P.; Melet, A.; Van Emelen, K.; Van der Aa, A.; Milligan, G.; Herbeuval, J.P. CXCR4 as a Novel Target in Immunology: Moving Away from Typical Antagonists. Future Drug Discov. 2022, 4, FDD77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Bauer, M.; Press, A.T. The Immunological Function of CXCR2 in The Liver During Sepsis. J. Inflamm. 2022, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, K.N.; Peterson, K.L.; Schneider, P.A.; Meng, X.W.; Dai, H.; Hess, A.D.; Smith, B.D.; Rodriguez-Ramirez, C.; Karp, J.E.; Kaufmann, S.H.; et al. CXCR4 Chemokine Receptor Signaling Induces Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via Regulation of The Bcl-2 Family Members Bcl-XL, Noxa, and Bak. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 22899–22914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y. Activation of PI3K/Akt Pathway Limits JNK-mediated Apoptosis during EV71 Infection. Virus Res. 2014, 192, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanongsaksrikul, J.; Srimanote, P.; Tongtawe, P.; Glab-Ampai, K.; Malik, A.A.; Supasorn, O.; Chiawwit, P.; Poovorawan, Y.; Chaicumpa, W. Identification and Production of Mouse ScFv to Specific Epitope of Enterovirus-71 Virion Protein-2 (VP2). Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B Colorimetric Assay for Cytotoxicity Screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanakomol, P.; Srimanote, P.; Tongtawe, P.; Khantisitthiporn, O.; Supasorn, O.; Thanongsaksrikul, J. Host Neuronal PRSS3 Interacts with Enterovirus A71 3A Protein and Its Role in Viral Replication. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound (MMV ID) [21] | ChEMBL ID | Trivial Name | Formula | Structure [22,23,24,25] | Mode of Action |
| D-D7 (MMV1782112) | CHEMBL 141816 | 2-pyridone-containing peptidomimetics | C25H31N5O7 | 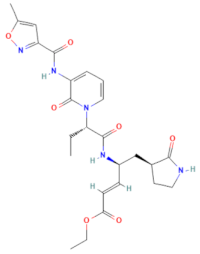 | Polyprotein processing inhibitor of human rhinovirus 3C protease [26] |
| D-H2 (MMV1593517) | CHEMBL 3545185 | Selinexor | C17H11F6N7O |  | Nuclear export protein inhibitor of CRM1 or XPO1 [27] |
| D-H7 (MMV1782104) | CHEMBL 261459 | T-1106 | C10H13N3O6 | 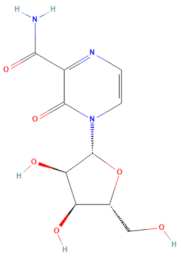 | RNA polymerase inhibitor of EV-A71 [20] |
| D-H8 (MMV002015) | CHEMBL 1407943 | Clemizole | C19H20ClN3 | 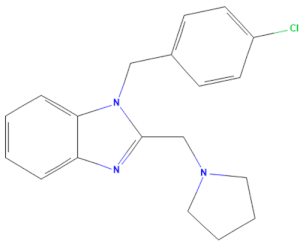 | NS4B protease inhibitor of HCV [28] |
| Compound (MMV ID) [21] | ChEMBL ID | Trivial Name | Formula | Structure [29,30,31] | Mode of Action |
| E-C3 (MMV1581034) | CHEMBL 3039531 | Danirixin | C19H21ClFN3O4S |  | Reversible antagonist of CXCR2 chemokine receptor [32] |
| E-C4 (MMV1580485) | CHEMBL 1235858 | Pocapavir | C21H17Cl3O3 | 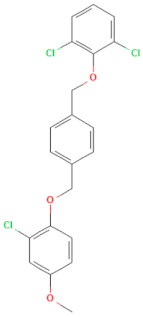 | Viral capsid inhibitor of enteroviruses [33] |
| E-E5 (MMV1580502) | CHEMBL 18442 | Plerixafor | C28H54N8 | 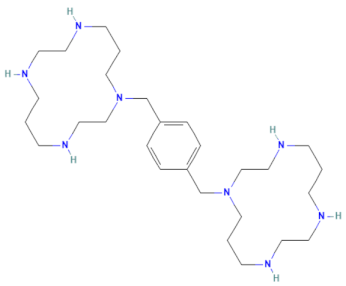 | CXCR4 chemokine receptor antagonists [34] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lochaiyakun, N.; Srimanote, P.; Khantisitthiporn, O.; Thanongsaksrikul, J. Novel Anti-Enterovirus A71 Compounds Discovered by Repositioning Antivirals from the Open-Source MMV Pandemic Response Box. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060785
Lochaiyakun N, Srimanote P, Khantisitthiporn O, Thanongsaksrikul J. Novel Anti-Enterovirus A71 Compounds Discovered by Repositioning Antivirals from the Open-Source MMV Pandemic Response Box. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(6):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060785
Chicago/Turabian StyleLochaiyakun, Nattinee, Potjanee Srimanote, Onruedee Khantisitthiporn, and Jeeraphong Thanongsaksrikul. 2024. "Novel Anti-Enterovirus A71 Compounds Discovered by Repositioning Antivirals from the Open-Source MMV Pandemic Response Box" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 6: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060785
APA StyleLochaiyakun, N., Srimanote, P., Khantisitthiporn, O., & Thanongsaksrikul, J. (2024). Novel Anti-Enterovirus A71 Compounds Discovered by Repositioning Antivirals from the Open-Source MMV Pandemic Response Box. Pharmaceuticals, 17(6), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060785






