Ginsenoside RK1 Induces Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through an FSP1-Dependent Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
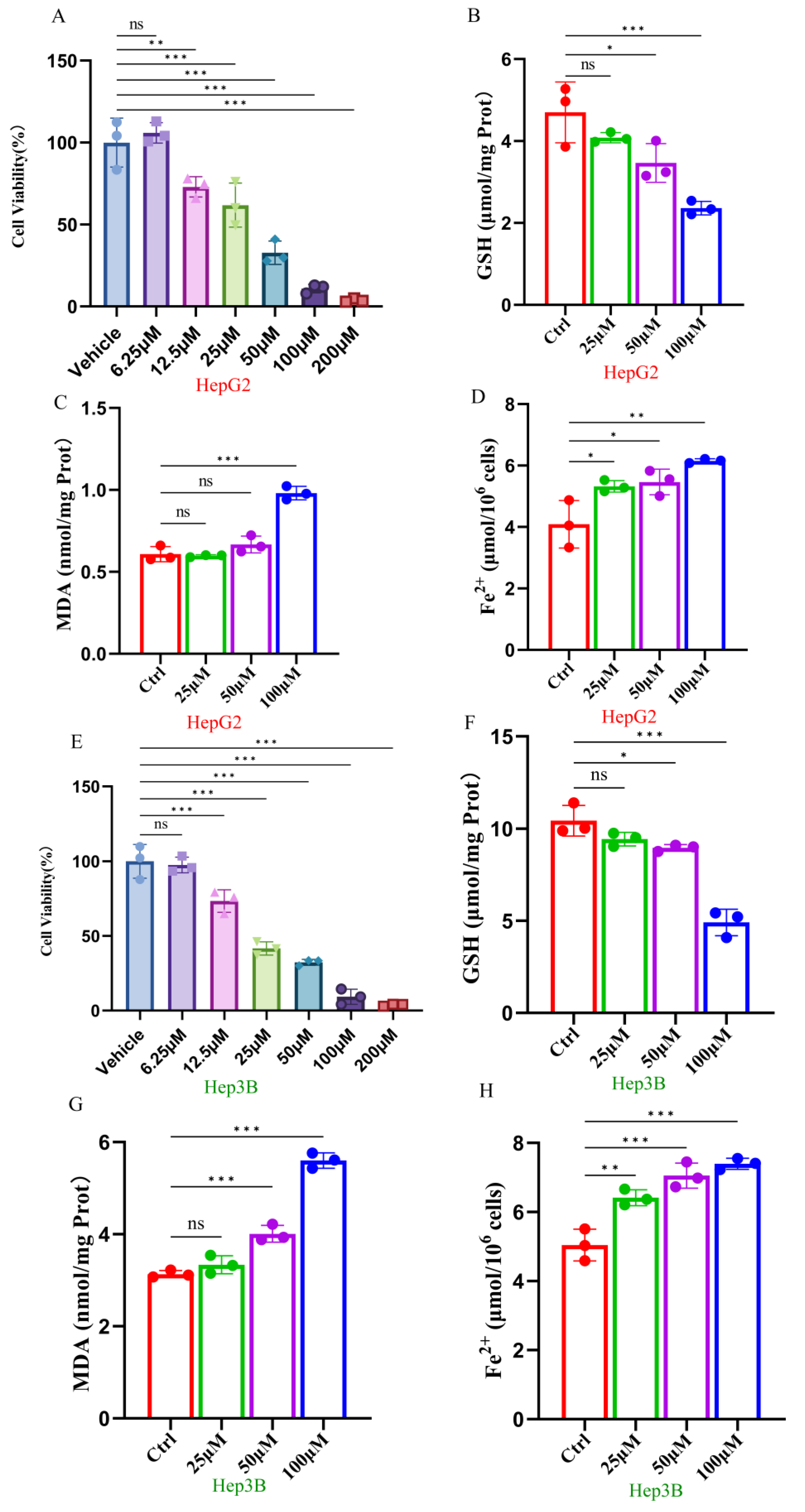
2.1. Ginsenoside RK1 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Viability by Mediating Ferroptosis
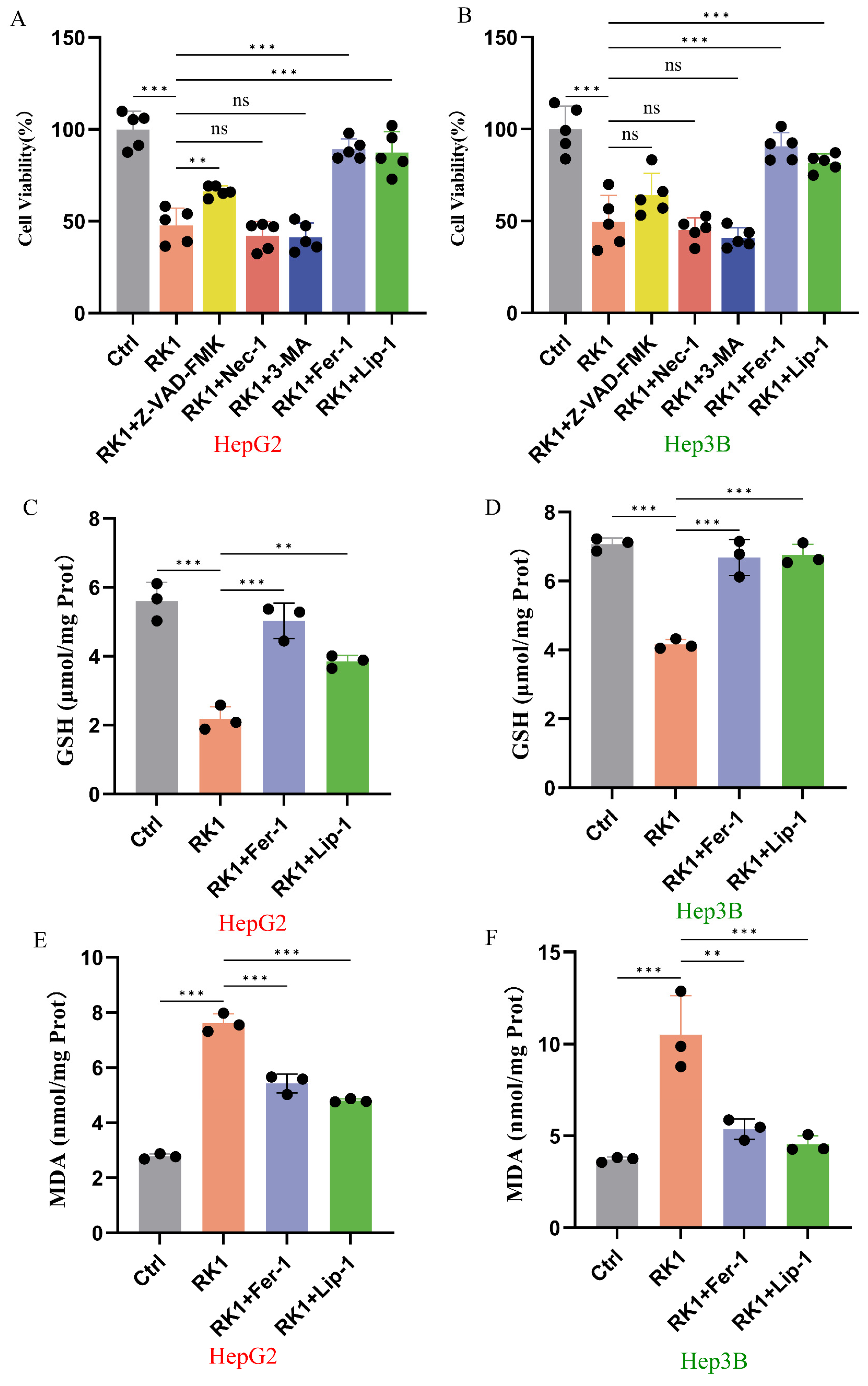
2.2. Effect of Ferroptosis Inhibitors Fer-1 and Lip-1 on the Activity of Ginsenoside RK1
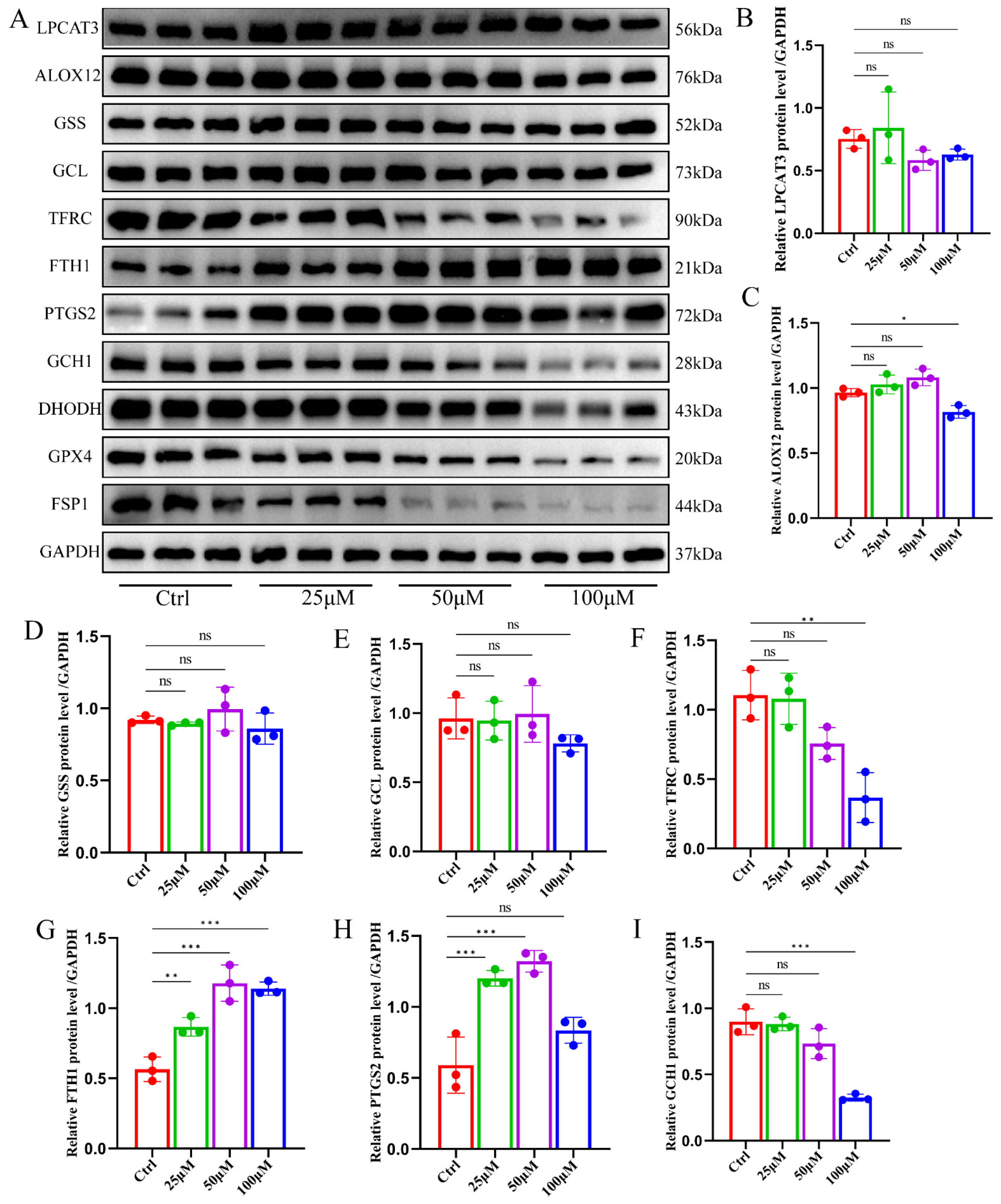
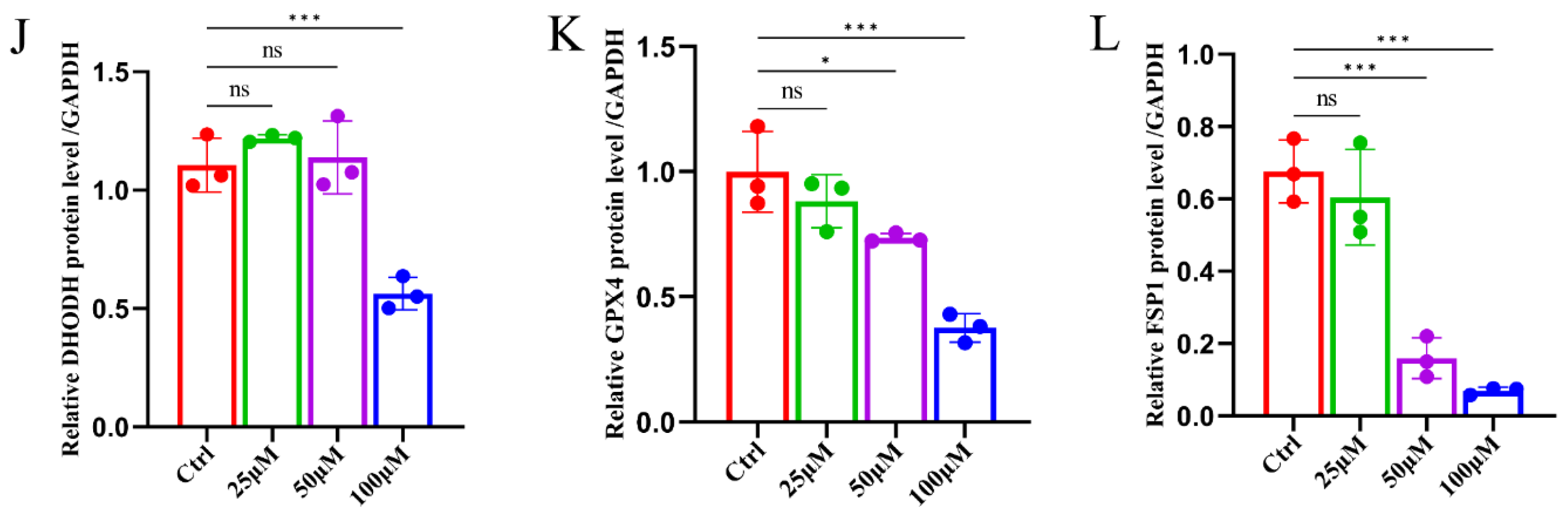
2.3. Ginsenoside RK1 Induces Ferroptosis by Inhibiting the Ferroptosis Defense System
2.4. Ginsenoside RK1 Promotes Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Down-Regulating FSP1
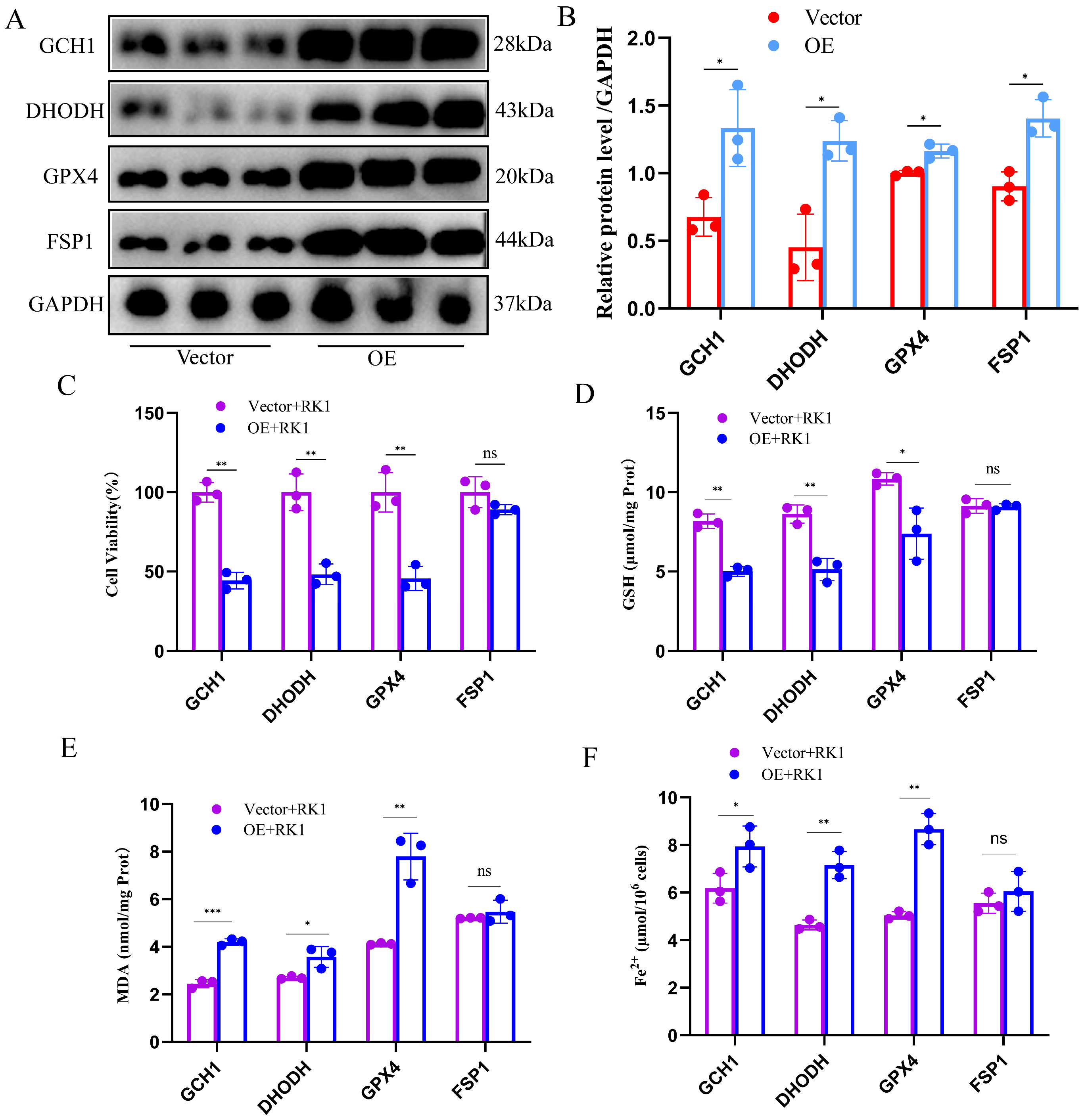
2.5. Overexpression of FSP1 Alleviated Ginsenoside RK1-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Death
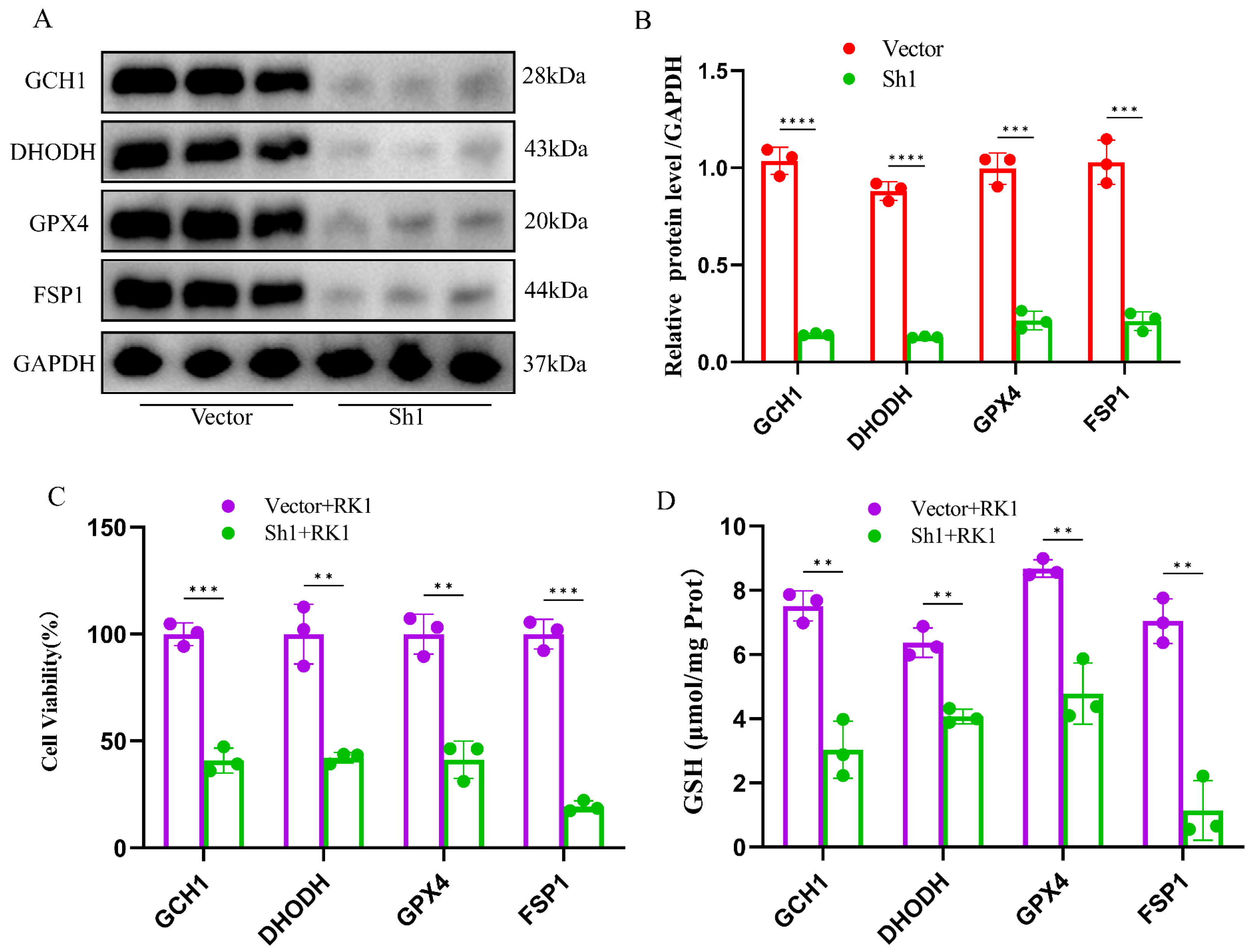
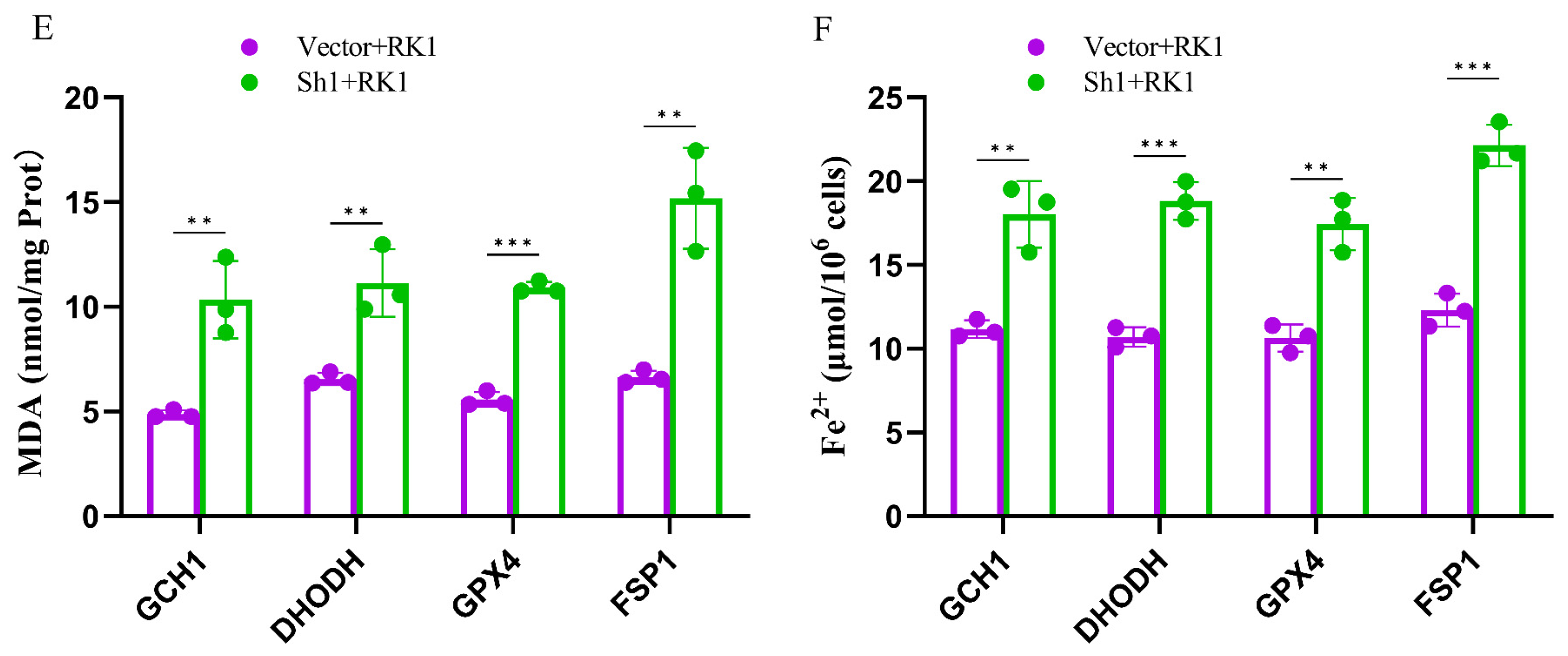
2.6. Silencing FSP1 Exacerbated Ginsenoside RK1-Induced Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Main Instruments
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. CCK8 Experiment
4.6. GSH, Malondialdehyde (MDA) Assay
4.7. Western Blot Detection of Corresponding Protein Expression Levels
4.8. RT-qPCR Detection of Corresponding mRNA Expression Level
4.9. Plasmid Transfection
4.10. Statistical Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zheng, R.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Chen, R.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; He, J. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2024, 4, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Glandorff, C.; Sun, M. Ferroptosis: A new hunter of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zang, X.; Zhai, Y.Z. The Emerging Role of Ferroptosis in Liver Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 801365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, S.; Yin, P.; Mi, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Bi, Y. Ginsenoside Rk1 inhibits HeLa cell proliferation through an endoplasmic reticulum signaling pathway. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, L.; Wan, S.; Li, Y.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk1 Prevents UVB Irradiation-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Response, and Collagen Degradation via the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15804–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Sun, J.; Xiong, L.; Li, A.; Li, L.; Wu, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, G.; Zhao, X. Ginsenoside RK1 improves cognitive impairments and pathological changes in Alzheimer’s disease via stimulation of the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 122, 155168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qu, L.; Bai, X.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Liu, H.; Fu, R.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk1 induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 186, 114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.M.; Lee, J.; Im, W.T.; Chun, S. Ginsenoside Rk1 Induces Apoptosis in Neuroblastoma Cells Through Loss of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Activation of Caspases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Stockwell, B.R. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Glandorff, C.; Sun, M. Exploring the mystery of tumor metabolism: Warburg effect and mitochondrial metabolism fighting side by side. Cell. Signal. 2024, 120, 111239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Patel, D.N.; Welsch, M.; Skouta, R.; Lee, E.D.; Hayano, M.; Thomas, A.G.; Gleason, C.E.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Slusher, B.S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. eLife 2014, 3, e02523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yin, H.; Qu, L.; Ma, X.; Fu, R.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk1 regulates glutamine metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibition of the ERK/c-Myc pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3793–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Fu, R.; Ma, P.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk1 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma by calcium signaling pathway. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25107–25118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yang, J.; Qu, L.; Deng, X.; Duan, Z.; Fu, R.; Liang, L.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk1 induces apoptosis and downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by targeting the NF-κB pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Yang, X.R.; Chung, W.Y.; Dennison, A.R.; Zhou, J. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Pan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, J.; Cai, X. The microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. eBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louandre, C.; Marcq, I.; Bouhlal, H.; Lachaier, E.; Godin, C.; Saidak, Z.; Francois, C.; Chatelain, D.; Debuysscher, V.; Barbare, J.C.; et al. The retinoblastoma (Rb) protein regulates ferroptosis induced by sorafenib in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Jiang, Z.M.; Ma, X.F.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Li, L.L.; Wu, W.H.; Wang, T. Saikosaponin-d Inhibits the Hepatoma Cells and Enhances Chemosensitivity through SENP5-Dependent Inhibition of Gli1 SUMOylation Under Hypoxia. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Dang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Effects of saikosaponin-d on syndecan-2, matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 in rats with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 32, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayano, M.; Yang, W.S.; Corn, C.K.; Pagano, N.C.; Stockwell, B.R. Loss of cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS) induces the transsulfuration pathway and inhibits ferroptosis induced by cystine deprivation. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Chung, S.W. ROS-mediated autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, S.; Freitas, F.P.; Shah, R.; Aldrovandi, M.; da Silva, M.C.; Ingold, I.; Goya Grocin, A.; Xavier da Silva, T.N.; Panzilius, E.; Scheel, C.H.; et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2019, 575, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, G.; Yan, Y.; Lee, H.; Koppula, P.; Wu, S.; Zhuang, L.; Fang, B.; et al. DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nature 2021, 593, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Min, J. DHODH tangoing with GPX4 on the ferroptotic stage. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, V.A.N.; Bezjian, C.T.; Pfeiffer, S.; Ringelstetter, L.; Muller, C.; Zandkarimi, F.; Merl-Pham, J.; Bao, X.; Anastasov, N.; Kossl, J.; et al. GTP Cyclohydrolase 1/Tetrahydrobiopterin Counteract Ferroptosis through Lipid Remodeling. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Ferrington, D.A.; Kannan, R. Glutathione Metabolism and the Novel Role of Mitochondrial GSH in Retinal Degeneration. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascon, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhai, E.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Cai, S.; Chen, J. m6A-mediated regulation of PBX1-GCH1 axis promotes gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by elevating tetrahydrobiopterin levels. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.K.; Dyberg, C.; Embaie, B.T.; Alchahin, A.; Milosevic, J.; Ding, J.; Otte, J.; Tummler, C.; Hed Myrberg, I.; Westerhout, E.M.; et al. DHODH is an independent prognostic marker and potent therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e153836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersuker, K.; Hendricks, J.M.; Li, Z.; Magtanong, L.; Ford, B.; Tang, P.H.; Roberts, M.A.; Tong, B.; Maimone, T.J.; Zoncu, R.; et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, F.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Mo, Y.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, M.; Qi, L.; Chen, J.; et al. AIFM2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis through activation of SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling. Oncogenesis 2023, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier da Silva, T.N.; Schulte, C.; Alves, A.N.; Maric, H.M.; Friedmann Angeli, J.P. Molecular characterization of AIFM2/FSP1 inhibition by iFSP1-like molecules. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, M.; Xiao, C.; Hu, X.; Vanneste, S.; Dong, J.; Le, J. A conserved but plant-specific CDK-mediated regulation of DNA replication protein A2 in the precise control of stomatal terminal division. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18126–18131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′~3′) | Product Length/bp |
|---|---|---|
| FSP1 | F:GCGTGCCCTCTGGAGAAG R:TCGTCGGGTCCTTCTTTACT | 303 |
| GCH1 | F:CGAGCTGAACCTCCCTAACC R:CACACCCAACATTGTGCTGG | 508 |
| DHODH | F:GGAAGTGAGAGTTCTGGGCC R:CACACTGGCAATGTCCTCCT | 577 |
| GPX4 | F:GCCAGGGAGTAACGAAGAGA R:CAGCCGTTCTTGTCGATGAG | 198 |
| GAPDH | F:CCAGAACATCATCCCTGCCT R:CCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTG | 185 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, M. Ginsenoside RK1 Induces Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through an FSP1-Dependent Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070871
Jiang Y, Yu Y, Pan Z, Wang Z, Sun M. Ginsenoside RK1 Induces Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through an FSP1-Dependent Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070871
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yulang, Yongxin Yu, Ziyang Pan, Ziyuan Wang, and Mingyu Sun. 2024. "Ginsenoside RK1 Induces Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through an FSP1-Dependent Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070871
APA StyleJiang, Y., Yu, Y., Pan, Z., Wang, Z., & Sun, M. (2024). Ginsenoside RK1 Induces Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through an FSP1-Dependent Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070871







