Adenosine Monophosphate as a Metabolic Adjuvant Enhances Antibiotic Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Exogenous AMP Promotes Gentamicin Killing of Gentamicin-Resistant S. aureus
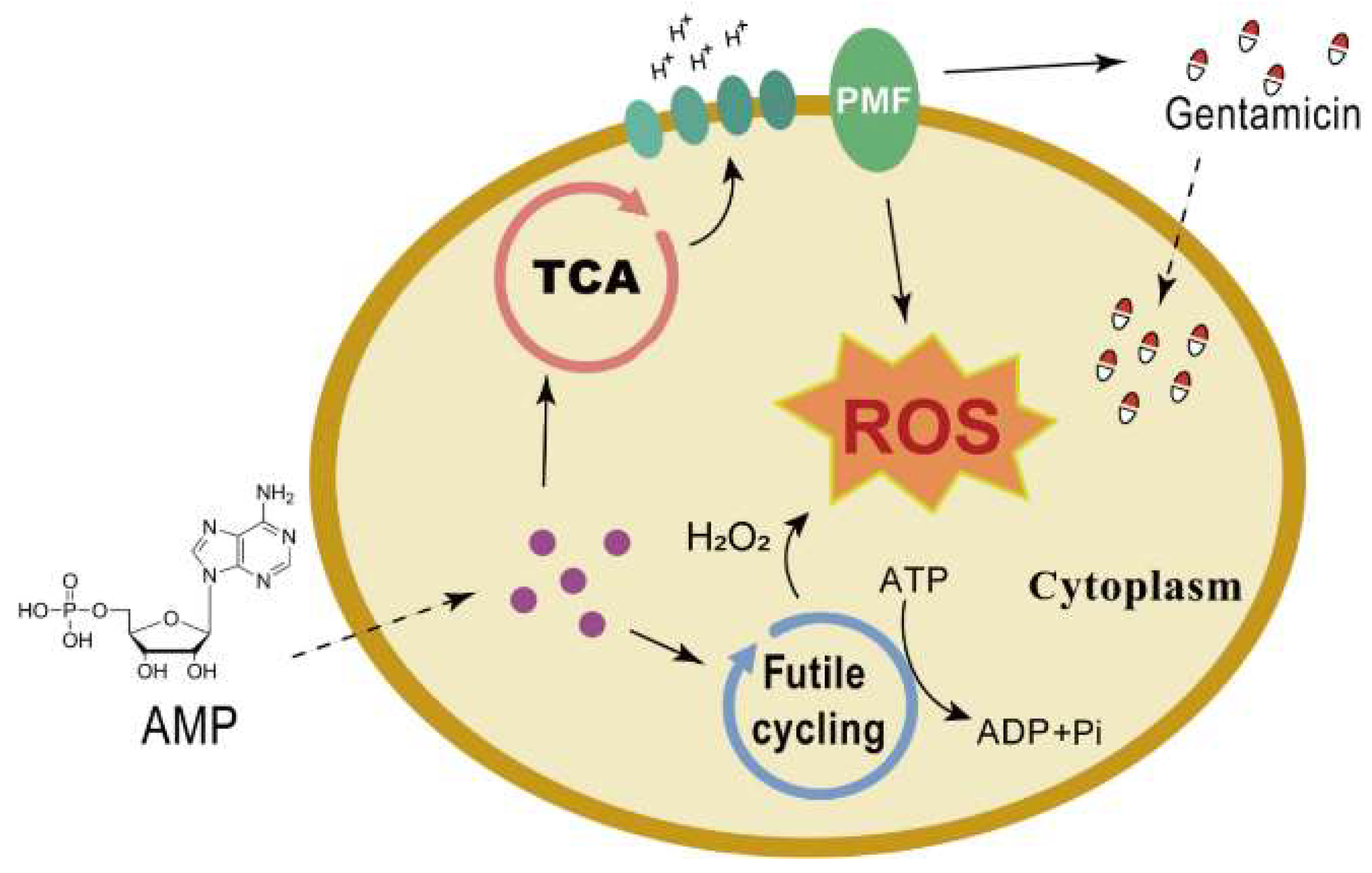
2.2. AMP Enhances Proton Motive Force via the TCA Cycle to Increase Antibiotic Uptake
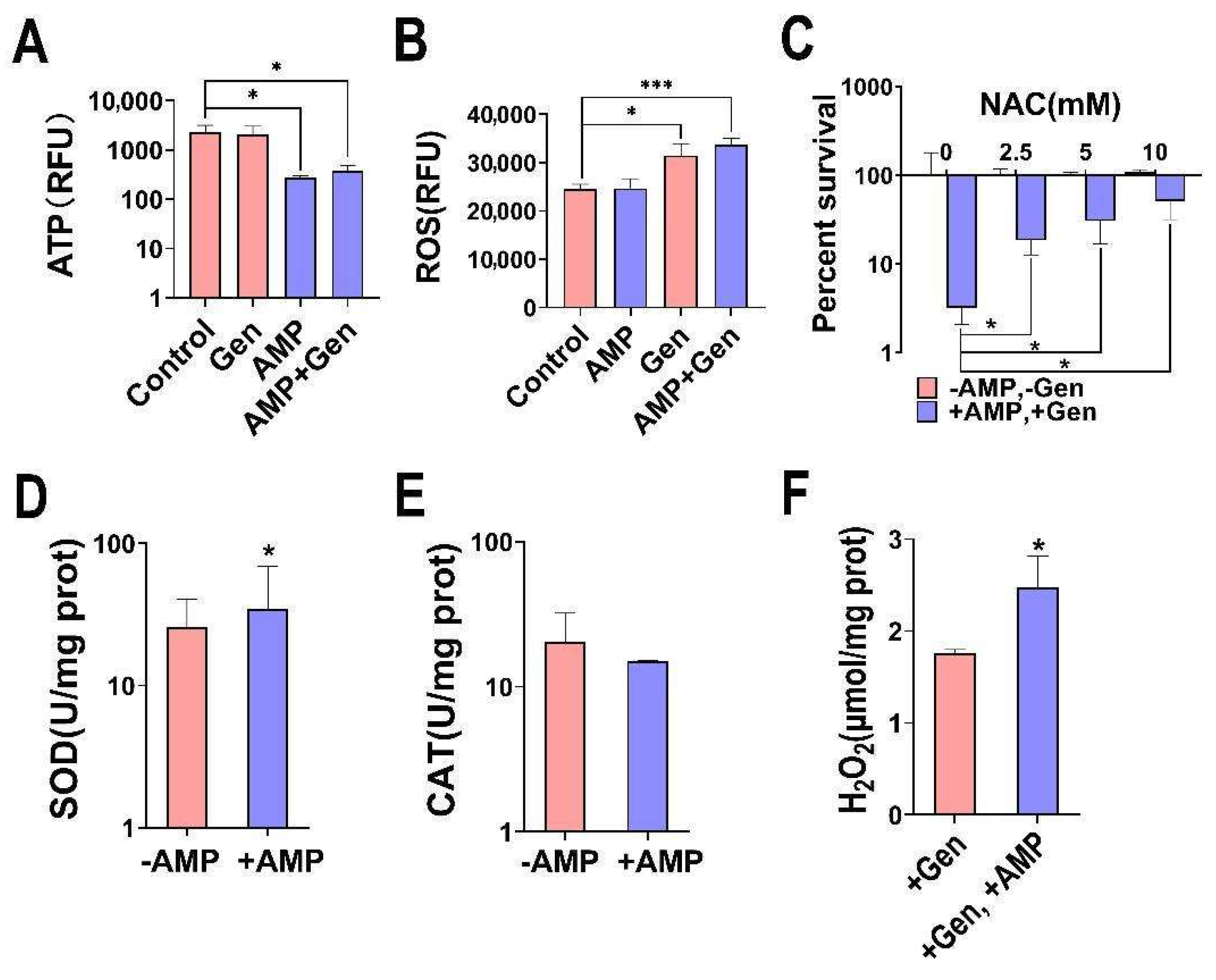
2.3. AMP Induces Bacterial Oxidative Stress for a Synergistic Bactericidal Effect
2.4. The Synergistic Effect of AMP Is Extensive
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
4.2. Antibiotic Bactericidal Assays
4.3. ΔpH and Δψ Measurement
4.4. ROS Measurement
4.5. ATP Measurement
4.6. H2O2 Measurement
4.7. SOD Activity Measurement
4.8. Catalase Activity Measurement
4.9. Determination of MIC
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nardulli, P.; Ballini, A.; Zamparella, M.; De Vito, D. The role of stakeholders’ understandings in emerging antimicrobial resistance: A one health approach. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.-W.-K.; Millar, B.-C.; Moore, J.-E. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.-X.; Lu, P.; Chen, Y.-B.; Shen, P.; Zheng, B.; Ji, J.-R.; Ying, C.-Q.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Xiao, Y.-H. ESKAPE in China: Epidemiology and characteristics of antibiotic resistance. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2317915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekema, D.-J.; Pfaller, M.-A.; Shortridge, D.; Zervos, M.; Jones, R.-N. Twenty-year trends in antimicrobial susceptibilities among Staphylococcus aureus from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance program. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, S47–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Loubet, P.; Pouget, C.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Molle, V. Staphylococcus aureus toxins: An update on their pathogenic properties and potential treatments. Toxins 2021, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.-R.; Claeys, K.-C.; Barber, K.-E.; Rybak, M.-J. High-dose daptomycin therapy for staphylococcal endocarditis and when to apply it. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2014, 16, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Mairpady Shambat, S.; Brugger, S.-D.; Zinkernagel, A.-S. Antibiotic resistance and persistence-implications for human health and treatment perspectives. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e51034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendel, A.-F.; Otchwemah, R.; Layer-Nicolaou, F.; Mattner, F.; Tellez-Castillo, C.-J.; Skov, R.; Oberländer, H.; Werner, G.; Strommenger, B. Investigating a possible link between antiseptic treatment and the increased occurrence of daptomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 1334.e1–1334.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, M.; Frees, D.; Ingmer, H. Antibiotic resistance and the MRSA problem. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnet, S.; Blanchard, J.-S. Molecular insights into aminoglycoside action and resistance. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 477–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad Hendri, N.-A.; Nor Amdan, N.-A.; Dounis, S.-O.; Sulaiman Najib, N.; Louis, S.-R. Ultrastructural and morphological studies on variables affecting Escherichia coli with selected commercial antibiotics. Cell Surf. 2024, 11, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jospe-Kaufman, M.; Siomin, L.; Fridman, M. The relationship between the structure and toxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Jo, J.-W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ko, K.-S.; Lee, W.-S. Polymyxin B nonapeptide potentiates the eradication of Gram-negative bacterial persisters. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0368723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saifi, S.; Ashraf, A.; Hasan, G.-M.; Shamsi, A.; Hassan, M.-I. Insights into the preventive actions of natural compounds against Klebsiella pneumoniae infections and drug resistance. Fitoterapia 2024, 173, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.-Y.; Pan, Z.-Y.; Liao, X.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Guo, J.; Pang, R.; Chen, X.-H.; Ye, G.-Z.; Su, Y.-B. Uracil restores susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to aminoglycosides through metabolic reprogramming. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1133685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-B.; Peng, B.; Li, H.; Cheng, Z.-X.; Zhang, T.-T.; Zhu, J.-X.; Li, D.; Li, M.-Y.; Ye, J.-Z.; Du, C.-C.; et al. Pyruvate cycle increases aminoglycoside efficacy and provides respiratory energy in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1578–E1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.-K.; Su, Y.-B.; Ye, H.-Q.; Dai, Z.-Y.; Yi, H.; Yang, K.-X.; Zhang, T.-T.; Chen, Z.-G. Glucose-potentiated amikacin killing of cefoperazone/sulbactam resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 800442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Li, X.; Xie, C.-L.; Chen, P.; Luo, W.; Lin, C.-X.; Wang, Q.; Shu, D.-M.; Luo, C.-L.; Qu, H.; et al. Fructose-enabled killing of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enteritidis by gentamicin: Insight from reprogramming metabolomics. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.-Y.; Pan, Z.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Guo, J.; Liao, X.; Pang, R.; Xu, Q.-Q.; Ye, G.-Z.; Su, Y.-B. L-glutamine sensitizes Gram-positive-resistant bacteria to gentamicin killing. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0161923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Li, H.; Peng, X.-X. Functional metabolomics: From biomarker discovery to metabolome reprogramming. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Li, H.; Peng, X.-X. Call for next-generation drugs that remove the uptake barrier to combat antibiotic resistance. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.-Y.; Fan, L.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Guo, J.; Dong, X.-S.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Su, Y.-B. Quantitative proteomics reveals reduction in central carbon and energy metabolisms contributes to gentamicin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Proteom. 2023, 277, 104849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mates, S.-M.; Eisenberg, E.-S.; Mandel, L.-J.; Patel, L.; Kaback, H.-R.; Miller, M.-H. Membrane potential and gentamicin uptake in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 6693–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taber, H.-W.; Mueller, J.-P.; Miller, P.-F.; Arrow, A.-S. Bacterial uptake of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Microbiol. Rev. 1987, 51, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeaux, D.; Chauhan, A.; Létoffé, S.; Fischer, F.; de Reuse, H.; Beloin, C.; Ghigo, J.-M. pH-mediated potentiation of aminoglycosides kills bacterial persisters and eradicates in vivo biofilms. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, A.; Seregina, T.; Nagornykh, M.; Luhachack, L.-G.; Korolkova, N.; Lopes, L.-E.; Kotova, V.; Zavilgelsky, G.; Shakulov, R.; Shatalin, K.; et al. Mechanism of H2S-mediated protection against oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6022–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.-F.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chen, J.-J.; Peng, X.-X.; Chen, Z.-G.; Li, H. Synergy of alanine and gentamicin to reduce nitric oxide for elevating killing efficacy to antibiotic-resistant Vibrio alginolyticus. Virulence 2021, 12, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolfsen, K.-J.; Brynildsen, M.-P. Futile cycling increases sensitivity toward oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Metab. Eng. 2015, 29, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-Y.; Deng, S.-Y.; Zhang, M.-H.; Geng, Z.-M.; Sun, C.; Bian, H.-A.; Xu, W.-M.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Liu, F.; Wu, H.-H. The effect of adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP) on tenderness, microstructure and chemical-physical index of duck breast meat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaby, A.-R.; Wright, J.-V. Nutritional therapy in medical practice. In Proceedings of the Nutritional Therapy in Medical Practice Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–28 October 1996; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, J.-E.; Korman, N.-J.; Bickers, D.-R.; Millikan, L.E. Topical capsaicin treatment of chronic postherpetic neuralgia. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1989, 21, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-W.; Wu, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Munang’andu, H.-M.; Peng, B. Fructose promotes ampicillin killing of antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus agalactiae. Virulence 2023, 14, 2180938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.-L.; Chen, Z.-G.; Yang, T.-C.; Jiang, M.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.-X.; Yang, M.-J.; Zhu, J.-X.; Zhang, T.-T.; Li, H.; et al. Glutamine promotes antibiotic uptake to kill multidrug-resistant uropathogenic bacteria. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj0716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, S.-F.; Xiang, J.; Chen, Y.-T.; Peng, X.-X.; Li, H.; Peng, B. Exogenous pyruvate promotes gentamicin uptake to kill antibiotic-resistant Vibrio alginolyticus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Feng, D.-Y.; Zhou, J.-X.; Wu, W.-B.; Zheng, W.-Z.; Gan, W.-L.; Jiang, M.; Li, H.; Peng, X.-X.; Zhang, T.-T. Metabolomics method in understanding and sensitizing carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii to meropenem. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.-R.; Brynildsen, M.-P.; Collins, J.-J. Metabolite-enabled eradication of bacterial persisters by aminoglycosides. Nature 2011, 473, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Acker, H.; Coenye, T. The role of reactive oxygen species in antibiotic-mediated killing of bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswin, H.-P.; Haddrell, A.-E.; Hughes, C.; Otero-Fernandez, M.; Thomas, R.-J.; Reid, J.-P. Oxidative stress contributes to bacterial airborne loss of viability. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0334722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górniak, I.; Bartoszewski, R.; Króliczewski, J. Comprehensive review of antimicrobial activities of plant flavonoids. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.-A.; Oliva, M.-A.; Martinez, C.-A.; Cambraia, J. Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2003, 49, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.-Q.; Yang, Z.-J.; Yang, Y.-G.; Jiang, L.-W.; Hu, L.-F. CsCAT3, a catalase gene from Cucumis sativus, confers resistance to a variety of stresses to Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 31, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Lin, J.-H.; Liu, L.; Ye, J.-Z.; Su, Y.-B. Promoting effect of Fe3+ on gentamicin resistance in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 625, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izallalen, M.; Mahadevan, R.; Burgard, A.; Postier, B.; Didonato, R., Jr.; Sun, J.; Schilling, C.-H.; Lovley, D.R. Geobacter sulfurreducens strain engineered for increased rates of respiration. Metab. Eng. 2008, 10, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitzenberg, D.-A.; Lee, J.-S.; Mills, K.-B.; Kim, J.-S.; Liu, L.; Vázquez-Torres, V.; Colgan, S.-P.; Kao, D.-J. Adenosine awakens metabolism to enhance growth-independent killing of tolerant and persister bacteria across multiple classes of antibiotics. mBio 2022, 13, e00480-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, M.; Xu, D.; Peng, X.-X.; Li, H. Reduced redox-dependent mechanism and glucosemediated reversal in gentamicin-resistant Vibrio alginolyticus. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 4724–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, T.-S.; Wu, J.-H.; Chen, X.-W.; Chen, Z.-G.; Zheng, J.; Peng, B. Exogenous glycine promotes oxidation of glutathione and restores sensitivity of bacterial pathogens to serum-induced cell death. Redox Biol. 2022, 58, 102512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M100-Ed33; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 1–382.



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Maituersong, Z.; Wang, T.; Su, Y. Adenosine Monophosphate as a Metabolic Adjuvant Enhances Antibiotic Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070933
Zhang W, Wu Z, Maituersong Z, Wang T, Su Y. Adenosine Monophosphate as a Metabolic Adjuvant Enhances Antibiotic Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070933
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenxuan, Zhenyi Wu, Zulifukeer Maituersong, Ting Wang, and Yubin Su. 2024. "Adenosine Monophosphate as a Metabolic Adjuvant Enhances Antibiotic Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070933
APA StyleZhang, W., Wu, Z., Maituersong, Z., Wang, T., & Su, Y. (2024). Adenosine Monophosphate as a Metabolic Adjuvant Enhances Antibiotic Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070933





