Searching for Novel HDAC6/Hsp90 Dual Inhibitors with Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity: In Silico Screening and In Vitro Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
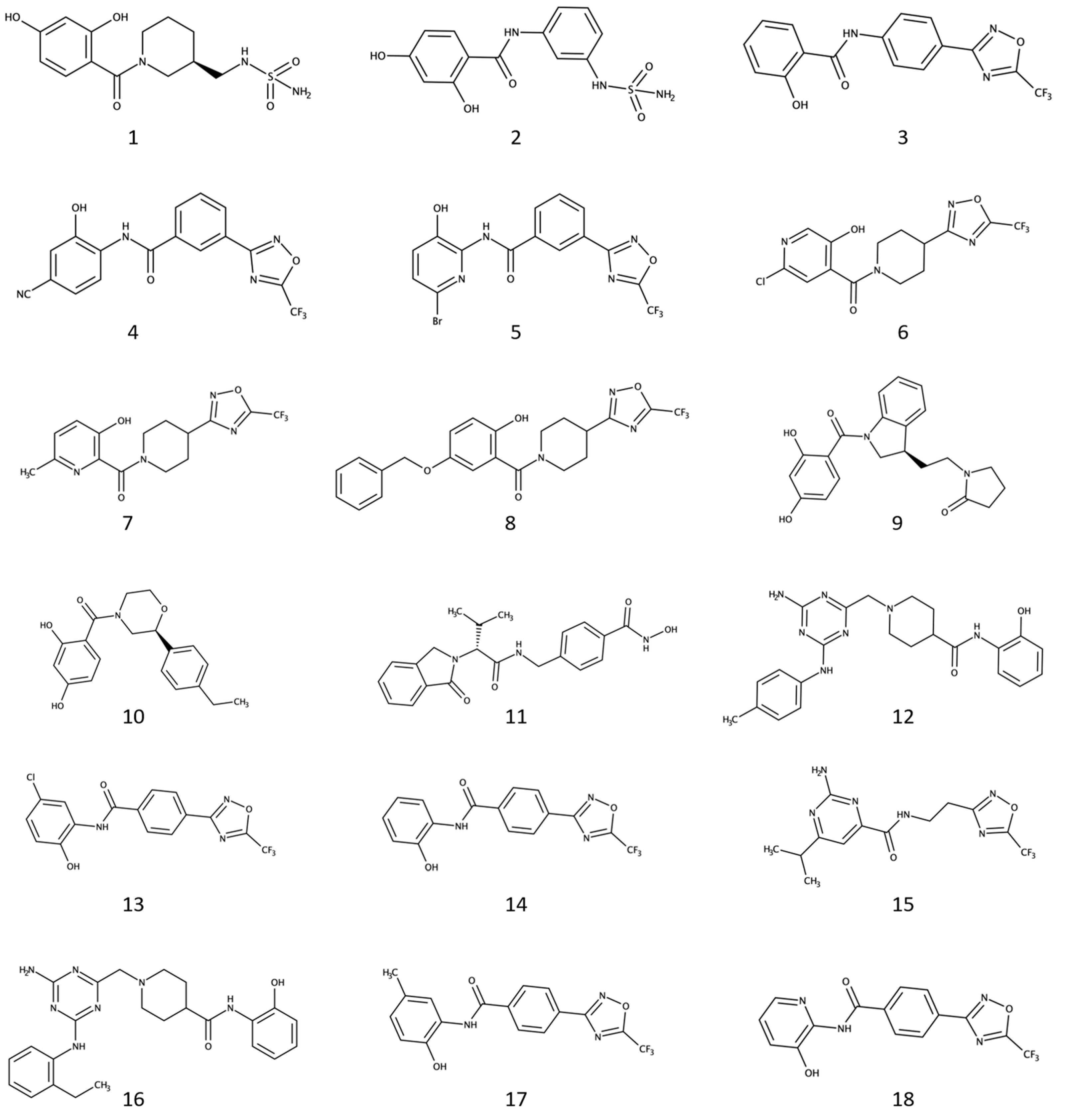
2.1. Virtual Screening and Selection of Commercially-Available Dual Inhibitor Candidates
2.2. Four Selected Ligands Inhibit HDAC6 and Decrease Viability of Human PCA Cells
2.3. HDAC6-Targeting in LNCaP and PC-3 Cells
2.4. Binding Mode of the Four Discovered Hit Compounds into HDAC6 and Their Optimization for Dual Inhibitory Activity
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Molecular Modeling
4.1.1. Preparation of HDAC6 and Hsp90 ChEMBL Ligands
4.1.2. Protein Data Bank (PDB, www.rcsb.org/, Accessed on 1 April 2020)
4.1.3. The ZINC Database Preparation
4.1.4. Two-Dimensional Ligand-Based Similarity Screening
4.1.5. Structure-Based Screening
4.2. Experimental Methods
4.2.1. Fluorimetric HDAC6 Assay
4.2.2. Hsp90 Assay
4.2.3. Cell Lines
4.2.4. Cell Viability Assays
4.2.5. Protein Extraction and Immunoblotting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, T.C.S.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Ganesan, A. Thirty Years of HDAC Inhibitors: 2020 Insight and Hindsight. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12460–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; He, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Mo, F.; Yang, S.; Han, J.; Wei, X. Targeting Epigenetic Regulators for Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruijter, A.J.M.D.; Gennip, A.H.V.; Caron, H.N.; Kemp, S.; Kuilenburg, A.B.P.V. Histone Deacetylases (HDACs): Characterization of the Classical HDAC Family. Biochem. J. 2003, 370, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micelli, C.; Rastelli, G. Histone Deacetylases: Structural Determinants of Inhibitor Selectivity. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Dong, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors in Cancer: A Patent Review (2017-Present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Li, Z.; Zhuo, X.-T.; Hui, Z.; Xie, T.; Ye, X.-Y. Novel Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Inhibitors: A Patent Review (2016–2019). Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindisi, M.; Saraswati, A.P.; Brogi, S.; Gemma, S.; Butini, S.; Campiani, G. Old but Gold: Tracking the New Guise of Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Enzyme as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Rare Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallavalle, S.; Pisano, C.; Zunino, F. Development and Therapeutic Impact of HDAC6-Selective Inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shin, D.; Kwon, S.H. Histone Deacetylase 6 Plays a Role as a Distinct Regulator of Diverse Cellular Processes. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 775–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, D.; Tan, Y. Role of HDAC6 and Its Selective Inhibitors in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 719390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Xie, F.; Qin, P.; Liu, Y.; Niu, H.; Sun, J.; Xue, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. Recent Development of Selective Inhibitors Targeting the HDAC6 as Anti-Cancer Drugs: Structure, Function and Design. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 138, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moi, D.; Citarella, A.; Bonanni, D.; Pinzi, L.; Passarella, D.; Silvani, A.; Giannini, C.; Rastelli, G. Synthesis of Potent and Selective HDAC6 Inhibitors Led to Unexpected Opening of a Quinazoline Ring. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11548–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halsall, J.A.; Turner, B.M. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: An Evolutionarily Ancient Resistance Response May Explain Their Limited Success. BioEssays 2016, 38, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citarella, A.; Moi, D.; Pinzi, L.; Bonanni, D.; Rastelli, G. Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives: From Synthetic Strategies to Medicinal Chemistry Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21843–21849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanni, D.; Citarella, A.; Moi, D.; Pinzi, L.; Bergamini, E.; Rastelli, G. Dual Targeting Strategies on Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90). Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 1474–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-X.; Wan, R.-Z.; Liu, Z.-P. Recent Advances in the Discovery of Potent and Selective HDAC6 Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, Y.; Christianson, D.W. Histone Deacetylase 6 Structure and Molecular Basis of Catalysis and Inhibition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarev, A.D.; Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Schiöth, H.B. Recent Developments of HDAC Inhibitors: Emerging Indications and Novel Molecules. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4577–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottamal, M.; Zheng, S.; Huang, T.; Wang, G. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Clinical Studies as Templates for New Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3898–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverría, P.C.; Bernthaler, A.; Dupuis, P.; Mayer, B.; Picard, D. An Interaction Network Predicted from Public Data as a Discovery Tool: Application to the Hsp90 Molecular Chaperone Machine. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, T.; Rios, Z.; Mei, Q.; Lin, X.; Cao, S. Heat Shock Proteins and Cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 226–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schopf, F.H.; Biebl, M.M.; Buchner, J. The HSP90 Chaperone Machinery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pick, E.; Kluger, Y.; Giltnane, J.M.; Moeder, C.; Camp, R.L.; Rimm, D.L.; Kluger, H.M. High HSP90 Expression Is Associated with Decreased Survival in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2932–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciocca, D.R.; Calderwood, S.K. Heat Shock Proteins in Cancer: Diagnostic, Prognostic, Predictive, and Treatment Implications. Cell Stress Chaperones 2005, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neckers, L.; Workman, P. Hsp90 Molecular Chaperone Inhibitors: Are We There Yet? Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.W.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Heat Shock Proteins: Agents of Cancer Development and Therapeutic Targets in Anti-Cancer Therapy. Cells 2019, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, R.C.; Vieusseux, J.L.; Lang, B.J.; Nguyen, C.H.; Kouspou, M.M.; Britt, K.L.; Price, J.T. Histone Deacetylase Activity Mediates Acquired Resistance towards Structurally Diverse HSP90 Inhibitors. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgobba, M.; Rastelli, G. Structure-Based and in Silico Design of Hsp90 Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepel, J.; Mollapour, M.; Giaccone, G.; Neckers, L. Targeting the Dynamic HSP90 Complex in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, L.; Foschi, F.; Christodoulou, M.S.; Passarella, D.; Rastelli, G. Design and Synthesis of Hsp90 Inhibitors with B-Raf and PDHK1 Multi-Target Activity. ChemistryOpen 2021, 10, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anighoro, A.; Pinzi, L.; Marverti, G.; Bajorath, J.; Rastelli, G. Heat Shock Protein 90 and Serine/Threonine Kinase B-Raf Inhibitors Have Overlapping Chemical Space. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31069–31074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, L.; Benedetti, R.; Altucci, L.; Rastelli, G. Design of Dual Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 6 and Heat Shock Protein 90. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11473–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, O.H.; Mahboobi, S.; Sellmer, A. Drugging the HDAC6-HSP90 Interplay in Malignant Cells. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, J.J.; Murphy, P.J.M.; Gaillard, S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.-T.; Nicchitta, C.V.; Yoshida, M.; Toft, D.O.; Pratt, W.B.; Yao, T.-P. HDAC6 Regulates Hsp90 Acetylation and Chaperone-Dependent Activation of Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, J.J.; Cohen, T.J.; Yao, T.-P. Chaperoning Steroid Hormone Signaling via Reversible Acetylation. Nucl. Recept. Signal 2005, 3, e004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, P.J.M.; Morishima, Y.; Kovacs, J.J.; Yao, T.-P.; Pratt, W.B. Regulation of the Dynamics of Hsp90 Action on the Glucocorticoid Receptor by Acetylation/Deacetylation of the Chaperone. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33792–33799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anighoro, A.; Bajorath, J.; Rastelli, G. Polypharmacology: Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7874–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcook, M.A.; Sramkoski, R.M.; Fujioka, H.; Daneshgari, F.; Almasan, A.; Shukla, S.; Nanavaty, R.R.; Gupta, S. Combination Simvastatin and Metformin Induces G1-Phase Cell Cycle Arrest and Ripk1- and Ripk3-Dependent Necrosis in C4-2B Osseous Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Fiskus, W.; Yang, Y.; Lee, P.; Joshi, R.; Fernandez, P.; Mandawat, A.; Atadja, P.; Bradner, J.E.; Bhalla, K. HDAC6 Inhibition Enhances 17-AAG—Mediated Abrogation of Hsp90 Chaperone Function in Human Leukemia Cells. Blood 2008, 112, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, J.; Wang, Y.; Dar, J.A.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Nelson, J.B.; Wang, Z. HDAC6 Regulates Androgen Receptor Hypersensitivity and Nuclear Localization via Modulating Hsp90 Acetylation in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, I.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Cheng, J.-J.; Nepali, K.; Chuang, K.-H.; Liou, J.-P. Rational Design of Synthetically Tractable HDAC6/HSP90 Dual Inhibitors to Destroy Immune-Suppressive Tumor Microenvironment. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 46, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warr, W.A.; Nicklaus, M.C.; Nicolaou, C.A.; Rarey, M. Exploration of Ultralarge Compound Collections for Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 2021–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Wang, S.; Balius, T.E.; Singh, I.; Levit, A.; Moroz, Y.S.; O’Meara, M.J.; Che, T.; Algaa, E.; Tolmachova, K.; et al. Ultra-Large Library Docking for Discovering New Chemotypes. Nature 2019, 566, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastelli, G.; Pinzi, L. Computational Polypharmacology Comes of Age. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, T.; Irwin, J.J. ZINC 15—Ligand Discovery for Everyone. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, W. Zinc Binding Groups for Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magwenyane, A.M.; Mhlongo, N.N.; Lawal, M.M.; Amoako, D.G.; Somboro, A.M.; Sosibo, S.C.; Shunmugam, L.; Khan, R.B.; Kumalo, H.M. Understanding the Hsp90 N-Terminal Dynamics: Structural and Molecular Insights into the Therapeutic Activities of Anticancer Inhibitors Radicicol (RD) and Radicicol Derivative (NVP-YUA922). Molecules 2020, 25, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, N.J.; Shen, S.; Barinka, C.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Christianson, D.W. Molecular Basis for the Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6 by a Mercaptoacetamide Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moi, D.; Bonanni, D.; Belluti, S.; Linciano, P.; Citarella, A.; Franchini, S.; Sorbi, C.; Imbriano, C.; Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G. Discovery of Potent Pyrrolo-Pyrimidine and Purine HDAC Inhibitors for the Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 260, 115730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasial, S.; Hu, Y.; Vogt, M.; Bajorath, J. Activity-Relevant Similarity Values for Fingerprints and Implications for Similarity Searching. F1000Research 2016, 5, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.; Hahn, M. Extended-Connectivity Fingerprints. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2020-1: QikProp, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA. 2020. Available online: https://www.schrodinger.com/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Horoszewicz, J.S.; Leong, S.S.; Kawinski, E.; Karr, J.P.; Rosenthal, H.; Chu, T.M.; Mirand, E.A.; Murphy, G.P. LNCaP Model of Human Prostatic Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Namekawa, T.; Ikeda, K.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Inoue, S. Application of Prostate Cancer Models for Preclinical Study: Advantages and Limitations of Cell Lines, Patient-Derived Xenografts, and Three-Dimensional Culture of Patient-Derived Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Svoboda, M.; Zhang, G.; Cavasin, M.A.; Motlova, L.; McKinsey, T.A.; Eubanks, J.H.; Bařinka, C.; Kozikowski, A.P. Structural and in Vivo Characterization of Tubastatin A, a Widely Used Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbins, C.E.; Russo, A.A.; Schneider, C.; Rosen, N.; Hartl, F.U.; Pavletich, N.P. Crystal Structure of an Hsp90-Geldanamycin Complex: Targeting of a Protein Chaperone by an Antitumor Agent. Cell 1997, 89, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, N.J.; Mahendran, A.; Breslow, R.; Christianson, D.W. Unusual Zinc-Binding Mode of HDAC6-Selective Hydroxamate Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13459–13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, N.J.; Osko, J.D.; Diedrich, D.; Kurz, T.; Hooker, J.M.; Hansen, F.K.; Christianson, D.W. Histone Deacetylase 6-Selective Inhibitors and the Influence of Capping Groups on Hydroxamate-Zinc Denticity. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8054–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymock, B.W.; Barril, X.; Brough, P.A.; Cansfield, J.E.; Massey, A.; McDonald, E.; Hubbard, R.E.; Surgenor, A.; Roughley, S.D.; Webb, P.; et al. Novel, Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Molecular Chaperone Hsp90 Discovered through Structure-Based Design. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4212–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CHEMBL1201862 Document Report Card. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/document_report_card/CHEMBL1201862/ (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- George, P.; Bali, P.; Annavarapu, S.; Scuto, A.; Fiskus, W.; Guo, F.; Sigua, C.; Sondarva, G.; Moscinski, L.; Atadja, P.; et al. Combination of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor LBH589 and the Hsp90 Inhibitor 17-AAG Is Highly Active against Human CML-BC Cells and AML Cells with Activating Mutation of FLT-3. Blood 2005, 105, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL Database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945–D954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2020-1: LigPrep, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA. 2020. Available online: https://www.schrodinger.com/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Hawkins, P.C.D.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer Generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and Validation Using High Quality Structures from the Protein Databank and Cambridge Structural Database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMEGA 3.0.1.2: OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM, USA. Available online: http://www.eyesopen.com (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- OpenEye Python Toolkits 2020.1.0, OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM, USA. 2020. Available online: http://www.eyesopen.com (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Schrödinger Release 2020-1: Maestro, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA. 2020. Available online: https://www.schrodinger.com/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Wright, L.; Barril, X.; Dymock, B.; Sheridan, L.; Surgenor, A.; Beswick, M.; Drysdale, M.; Collier, A.; Massey, A.; Davies, N.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationships in Purine-Based Inhibitor Binding to HSP90 Isoforms. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brough, P.A.; Barril, X.; Beswick, M.; Dymock, B.W.; Drysdale, M.J.; Wright, L.; Grant, K.; Massey, A.; Surgenor, A.; Workman, P. 3-(5-Chloro-2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-Pyrazole-4-Carboxamides as Inhibitors of the Hsp90 Molecular Chaperone. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5197–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, F.; Carrez, C.; Pilorge, F.; Dupuy, A.; Parent, A.; Bertin, L.; Thompson, F.; Ferrari, P.; Fassy, F.; Lamberton, A.; et al. Tricyclic Series of Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) Inhibitors Part I: Discovery of Tricyclic Imidazo[4,5-c]Pyridines as Potent Inhibitors of the Hsp90 Molecular Chaperone. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7206–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brough, P.A.; Aherne, W.; Barril, X.; Borgognoni, J.; Boxall, K.; Cansfield, J.E.; Cheung, K.-M.J.; Collins, I.; Davies, N.G.M.; Drysdale, M.J.; et al. 4,5-Diarylisoxazole Hsp90 Chaperone Inhibitors: Potential Therapeutic Agents for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 196–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W. Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Domain of an HSP90 in the Presence of an the Inhibitor. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/3TUH (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Bussenius, J.; Blazey, C.M.; Aay, N.; Anand, N.K.; Arcalas, A.; Baik, T.; Bowles, O.J.; Buhr, C.A.; Costanzo, S.; Curtis, J.K.; et al. Discovery of XL888: A Novel Tropane-Derived Small Molecule Inhibitor of HSP90. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5396–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.N.; Stuckey, J.A. Structure of Heat Shock Protein 90 Bound to CS312. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4YKW (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Madhavi Sastry, G.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and Ligand Preparation: Parameters, Protocols, and Influence on Virtual Screening Enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Grant, G.H.; Graham Richards, W. Dynamics of Conserved Waters in Human Hsp90: Implications for Drug Design. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2008, 5, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, R.; Barril, X.; Dymock, B.W.; Grant, K.; Northfield, C.J.; Robertson, A.G.S.; Surgenor, A.; Wayne, J.; Wright, L.; James, K.; et al. A Fluorescence Polarization Assay for Inhibitors of Hsp90. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 350, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compound ID | HDAC6 IC50 (μM) | LNCaP GI50 (μM) | PC-3 GI50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 17 | 9.5 ± 0.7 | 9.5 ± 0.5 |
| 8 | 6.5 | 51.6 ± 3.7 | 51.8 ± 0.6 |
| 11 | 0.005 | 41.3 ± 8.7 | 13.9 ± 2.9 |
| 18 | 2.7 | >75 | 21 ± 5.4 |
| Tubastatin-A | 0.007 | 5.9 ± 1.5 | 11.1 ± 1.6 |
| Geldanamycin | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | |
| SAHA | 0.014 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinzi, L.; Belluti, S.; Piccinini, I.; Imbriano, C.; Rastelli, G. Searching for Novel HDAC6/Hsp90 Dual Inhibitors with Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity: In Silico Screening and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081072
Pinzi L, Belluti S, Piccinini I, Imbriano C, Rastelli G. Searching for Novel HDAC6/Hsp90 Dual Inhibitors with Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity: In Silico Screening and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(8):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081072
Chicago/Turabian StylePinzi, Luca, Silvia Belluti, Isabella Piccinini, Carol Imbriano, and Giulio Rastelli. 2024. "Searching for Novel HDAC6/Hsp90 Dual Inhibitors with Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity: In Silico Screening and In Vitro Evaluation" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 8: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081072
APA StylePinzi, L., Belluti, S., Piccinini, I., Imbriano, C., & Rastelli, G. (2024). Searching for Novel HDAC6/Hsp90 Dual Inhibitors with Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity: In Silico Screening and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals, 17(8), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081072








