Abstract
Hearing loss is a health crisis that affects more than 60 million Americans. Currently, sodium thiosulfate is the only drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to counter hearing loss. Sirtuins were proposed as therapeutic targets in the search for new compounds or drugs to prevent or cure age-, noise-, or drug-induced hearing loss. Sirtuins are proteins involved in metabolic regulation with the potential to ameliorate sensorineural hearing loss. The mammalian sirtuin family includes seven members, SIRT1-7. This paper is a literature review on the sirtuins and their protective roles in sensorineural hearing loss. Literature search on the NCBI PubMed database and NUsearch included the keywords ‘sirtuin’ and ‘hearing’. Studies on sirtuins without relevance to hearing and studies on hearing without relevance to sirtuins were excluded. Only primary research articles with data on sirtuin expression and physiologic auditory tests were considered. The literature review identified 183 records on sirtuins and hearing. After removing duplicates, eighty-one records remained. After screening for eligibility criteria, there were forty-eight primary research articles with statistically significant data relevant to sirtuins and hearing. Overall, SIRT1 (n = 29) was the most studied sirtuin paralog. Over the last two decades, research on sirtuins and hearing has largely focused on age-, noise-, and drug-induced hearing loss. Past and current studies highlight the role of sirtuins as a mediator of redox homeostasis. However, more studies need to be conducted on the involvement of SIRT2 and SIRT4-7 in hearing protection.
1. Introduction
Sirtuins are a highly conserved family of proteins across species. Silent information regulator 2 (Sir2), the first sirtuin identified, was described as an anti-aging factor in yeasts [1]. Sir2 is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent histone deacetylase (HDAC) which can affect transcription in telomeres [1]. There are seven sirtuin paralogs in mammals, SIRT1-7 [2]. All mammalian sirtuins are NAD+-dependent HDAC with varying affinity for NAD+ [2,3]. They differ from the classical HDACs, HDAC1-10, which are Zn2+-dependent HDACs [4]. Under normal physiological conditions, NAD+ is important for sirtuin function and possibly a rate-limiting co-substrate [5]. NAD+ increases due to stresses such as exercise, which also acutely upregulates sirtuins [6,7]. Due to the requirement of NAD+, the functions of sirtuins have been studied in the background of cellular energy and metabolism [8].
In mammals, NAD+ is mostly recycled from nicotinamide (NAM) but can also be produced de-novo from tryptophan and niacin [9]. NAD+ can gain an electron to become NADH [9]. Only 10% of NAD+ is phosphorylated into NADP+, and NADP+ can be reduced to NADPH via catalysis by nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) [9]. The NADPH/NADP+ ratio is higher in the mitochondria compared to the cytosol and the nucleus [10]. This may be because NNT is a mitochondrial enzyme in the inner mitochondrial membrane [11]. NADPH is converted into NADP+ via glutathione (GSH) and this reduction allows the conversion of H2O2 into H2O and O2 in a redox reaction, decreasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) loads [12]. The NADPH/NADP+ ratio can acutely decrease due to oxidative stresses such as H2O2 and superoxide [13]. Overall, the NADPH/NADP+ ratio can indicate if the antioxidant defense is being maintained, and the deficiency in NAD+, the precursor to NADPH, can be an indication of oxidative stress in diseases such as cancers [14]. On the contrary, NAD+ boosting molecules such as niacin may help to remove excessive ROS and may ameliorate age-related diseases [15,16].
SIRT1 (mammalian Sir2) affects cell division, microtubule organization, metabolism, and transcription for many physiological processes [17]. Having an NAD binding domain, SIRT1 maintains the NADH/NAD+ ratio by consuming NAD+ [18]. Once SIRT1 binds NAD+, it can activate an anti-ROS pathway by deacetylating lysine residues of SOD2 [19]. SIRT1 can inhibit NF-kB, decreasing inflammatory cytokines and, subsequently, ROS [20]. SIRT2 is ubiquitously found in mammalian cells and it is an ADP-ribosyl transferase utilizing NAD+, which contributes to redox homeostasis [21]. SIRT2 is known to deacetylate FOXO3a, and deacetylated FOXO3a shows antioxidant properties, while acetylated FOXO3a can induce apoptosis via caspase-3 [22]. SIRT3 is expressed in the mitochondria during oxidative stress, affecting the oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain and regulating ROS [23]. SIRT3 activates isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2), a producer of mitochondrial NADPH, which activates the GSH-mediated antioxidant pathway [23]. SIRT3 also activates SOD2 and FOXO3A by deacetylation, decreasing ROS [24]. In the background of ROS and apoptosis, the role of SIRT4 has been elusive, but a recent study showed that the expressions in GSH and SOD2 decreased in Sirt4−/− mice, suggesting that SIRT4 could be involved in activating antioxidants [25]. Like SIRT3, SIRT5 is also expressed in the mitochondria, where it activates IDH2 and mediates an anti-ROS pathway via NADPH and GSH [26]. However, SIRT3 and SIRT5 activate IDH2 differently (lysine deacetylation and desuccinylation, respectively) [24,26]. SIRT6 is known to stabilize and increase the expression of NRF2, which is known to respond to oxidative stress [27]. NAD+ inducers such as luteolin can act as SIRT6 activators [28]. The study on SIRT7 as an anti-ROS agent has been lacking, but a recent study showed that SIRT7 expression increased in response to treating human granulosa-lutein (hGL) cells with celastrol, a natural product with antioxidant properties [29].
Hearing loss in humans can be a sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), resulting from cochlear damage from noise (NIHL, noise-induced hearing loss), drugs (DIHL, drug-induced hearing loss), cancer, age (ARHL, age-related hearing loss), and genetic defects [30]. Conductive hearing loss can arise due to damage in the outer and middle ear, which could be due to allergies and ear infections. One of the earliest works studying the effect of SIRT1 on ARHL included a 2014 study on ubiquinol-10 supplementation and progressive hearing threshold shifts in C57BL/6 mice [31,32]. Someya et al. have shown in C57BL/6 mouse models that SIRT3 protects against ARHL [33,34,35]. SIRT3 could exert its effect under calorie restriction and act via deacetylating IDH2 [33]. There needs to be further studies on the other members of sirtuins (SIRT2, 4, 5, 6, and 7) to establish their roles in hearing loss and protection. It is also important to establish causality between sirtuin dysregulation and hearing loss.
There has been no review investigating sirtuins in the mechanism of hearing protection. This literature review will cover the basic principles linking sirtuins and hearing loss, categorize all peer-reviewed studies published until now, and summarize potential applications of sirtuins in ameliorating hearing loss. This review will conclude by summarizing which sirtuins are protective of hearing loss and where the research should go next.
2. Selection of Studies
2.1. Literature Review Eligibility Criteria
The literature review aimed to collect data on the roles of sirtuins in SNHL. In May 2024, an initial literature review was conducted, using the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) PubMed search (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 1 May 2024). Publication date was set between 2001 and 2024. To study how sirtuins could modify hearing loss, the search terms were (sirtuin) AND (hearing), which indicated that studies must contain both words ‘sirtuin’ and ‘hearing’. Similar phrases such as sirtuin 1, hearing loss, and noise-induced hearing loss were included in the search terms. Next, a similar literature search was conducted using NUsearch, a library search tool provided by Northwestern University. The search conditions were any field, containing words ‘sirtuin’ AND ‘hearing’ in titles and abstracts, and published between 2001 and 2024. Last, ClinicalTrials.gov was checked for any ongoing clinical trials involving sirtuins in hearing loss.
The literature review further screened for in vitro and in vivo studies of cell cultures, explant cultures, animal models, and clinical studies. All eligible studies had to show links between sirtuin expression and hearing using molecular and physiological lab techniques. Therefore, studies that investigated sirtuins without consideration for hearing loss were excluded, and studies that investigated hearing loss without sirtuins as molecular targets were also excluded. Often, the search found papers that only mentioned sirtuins and hearing in the introduction and did not further discuss. Such papers were excluded. Writings without primary data, such as reviews, were excluded.
2.2. Identifying Bias and Heterogeneus Results
Risk of errors and bias were investigated in the studies found through the literature review. First, almost all C57BL/6 mice intrinsically develop hearing loss due to Cdh23753A mutation starting from an early age of 2 months and develop severe hearing loss at 9 months [36,37]. In contrast, CBA/CaJ mice maintain hearing until 24 months [38,39]. Therefore, the literature search scrutinized studies using C57BL/6 mice or inbred mice to see whether the Cdh23753A mutation could have inadvertently affected their results. One study did not use the correct controls in their Chapter 3.1 [40]. The study was supposed to compare the mice with the vehicle treatment and mice with the drug treatment, but this was not shown. Instead, conclusions were drawn by comparing the mice with no treatment and mice with the drug treatment, showing significant differences in hearing [40]. One study stated that the sirtuin expression was upregulated due to noise and sirtuin expression was inhibited by a SIRT2 inhibitor, AK-7 [41]. While the study did not show sirtuin expressions experimentally, the authors argued that AK-7 treatment decreased SIRT2 expression, subsequently decreasing sirtuin expression. There were conflicting results among studies [32,42]. In such cases, possible causes were determined by evaluating different effect measurements and different animal characteristics, and the heterogenous results were further explored in later chapters.
2.3. Effect Measures in Selected Papers
Sirtuin expression was typically measured using quantitative PCR (qPCR) and the unit was the relative mRNA level of sirtuins against a reference mRNA level (e.g., beta-actin). To normalize expression levels in western blots, sirtuin expression was measured using internal controls such as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Immunostaining using conjugated antibodies/primary + secondary antibodies was typically used to visualize the localization of sirtuins in the cochlea. Immunostaining of sirtuins was often run simultaneously with myosin-VIIa to visualize hair cells, anti-CtBP2 + GluR2 to visualize synapses, and Hoechst/DAPI to visualize DNA, although each study used different staining reagents and techniques.
Auditory brainstem responses (ABRs) to pure tone stimuli at sound levels between 20 and 90 dB SPL were typically recorded as an auditory measurement in animal studies. Thresholds were determined from the recordings as the sound level for a visual response. Likewise, the delay and the amplitude of wave I were determined from the recordings. Distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAEs), a measure of cochlear nonlinearity, were determined by the level of the cubic distortion product in dB SPL. Outer hair cell function is likely the dominant source for the nonlinearity in the cochlea, and a change in DPOAEs indicates a change in outer hair cell function [43].
Not all studies were considered equal in terms of certainty. More certainty was given to studies that included statistically significant expression of sirtuins, auditory testing results, and immunostaining. It was also more confident to suggest that the expression of sirtuins was causal to hearing protection if the study included sirtuin knock-out models to establish the causality of sirtuins in hearing protection.
3. Literature Review
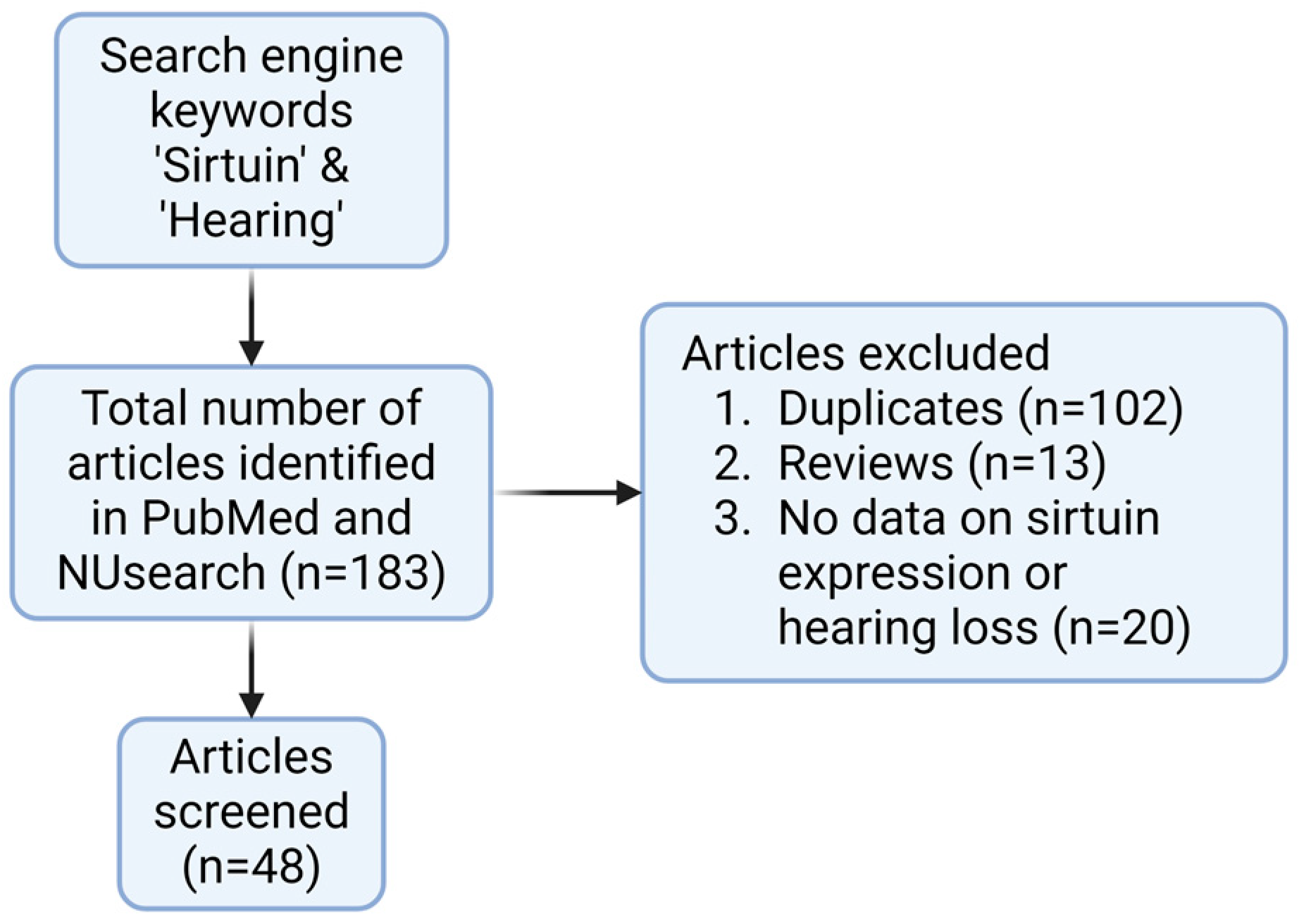
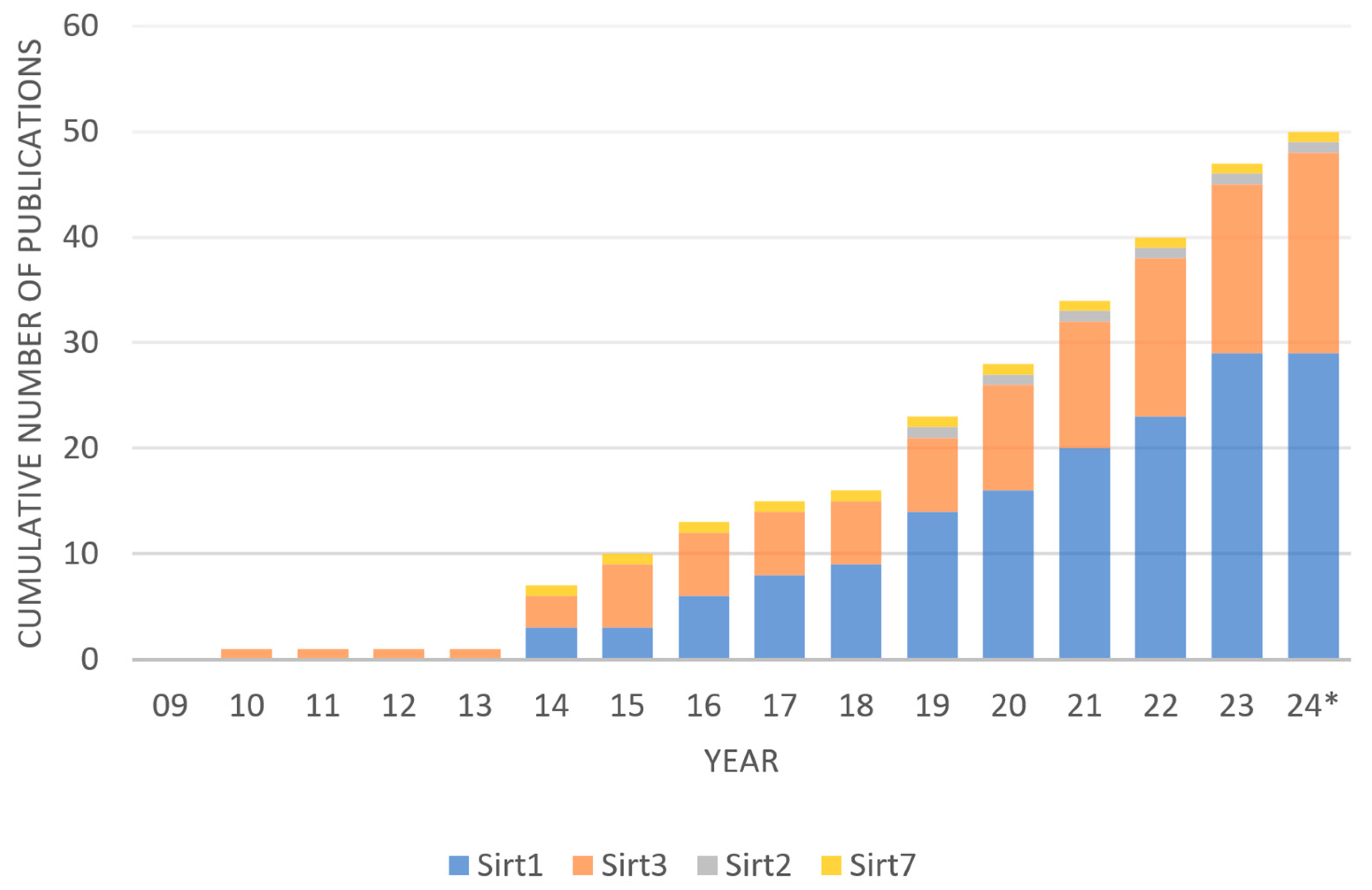
NCBI PubMed search identified 81 records and NUsearch identified 102 records, resulting in 183 records in total (Figure 1). Duplicates within NCBI PubMed (n = 0) and duplicates within NUsearch (n = 24) were removed. Next, duplicates between NCBI PubMed and NUsearch were removed (n = 78), resulting in 81 records. Next, ineligible studies were screened. Reviews (n = 13) were excluded. Studies without primary data on hearing loss and sirtuin expression (n = 20) were excluded. Forty-eight records remained eligible for downstream discussion. SIRT1 (n = 29) and SIRT3 (n = 19) have been the most studied sirtuins, while SIRT2 (n = 1) and SIRT7 (n = 1) were rarely studied in connection to hearing loss (Figure 2). SIRT3 was the first sirtuin linked to hearing loss. Some publications had significant results in both SIRT1 and SIRT3 concerning hearing loss. The shortlisted studies from the literature review (n = 48) have been categorized by study type (cells, explant, and animals), treatment (small molecule drug, plant extract, and sirtuin inhibitor etc.), relevance (ABR threshold shifts and sirtuin expression etc.), and year of publication (2010–2024) (Table 1). From the shortlisted literature review papers, experimental drug candidates used in each study were categorized by the types of hearing loss they investigated (Table 2). Fourteen drugs were involved in ARHL or cellular senescence. Seven drugs were used to ameliorate noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). Eleven drugs were investigated for their use in drug-induced hearing loss (DIHL). One drug was studied for early-onset hearing loss (EOHL). Two drugs were studied for hearing loss occurring in Ménière’s disease and one drug was studied for hearing loss occurring in diabetes type 2. All studies found investigated SNHL, including ARHL/induced cellular senescence (n = 25), NIHL (n = 9), DIHL (n = 11), hearing loss in Ménière’s disease (n = 2), and diabetes-associated hearing loss (n = 1). No study reported that sirtuins were involved in conductive hearing loss, auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder, or congenital deafness. In addition, no studies investigated sirtuins in connection to GJB2 mutations and other non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss. It indicates that sirtuins most likely ameliorate cochlear damage in the inner ear, and sirtuin dysregulation can be triggered by aging and environmental factors.
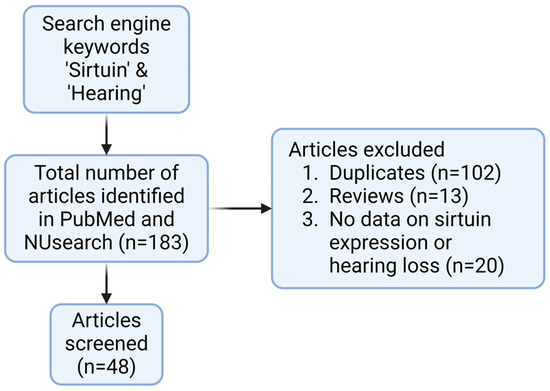
Figure 1.
Flow diagram representing the screening process for articles investigating sirtuins in hearing loss. Created with BioRender.com.
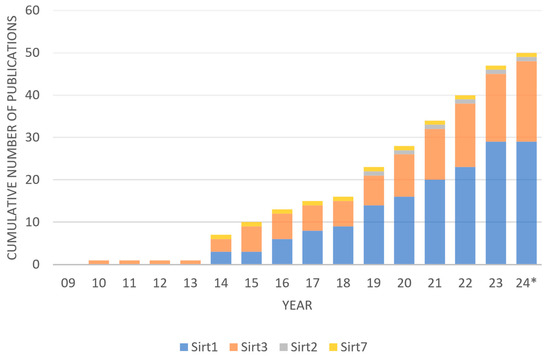
Figure 2.
Sirtuin and hearing loss research over time by the number of publications in each sirtuin paralog * Up to May 2024.

Table 1.
All-time studies linking sirtuins and hearing loss listed chronologically.

Table 2.
Drugs investigated in relation to different types of hearing loss.
4. Discussion
4.1. SIRT1 in ARHL
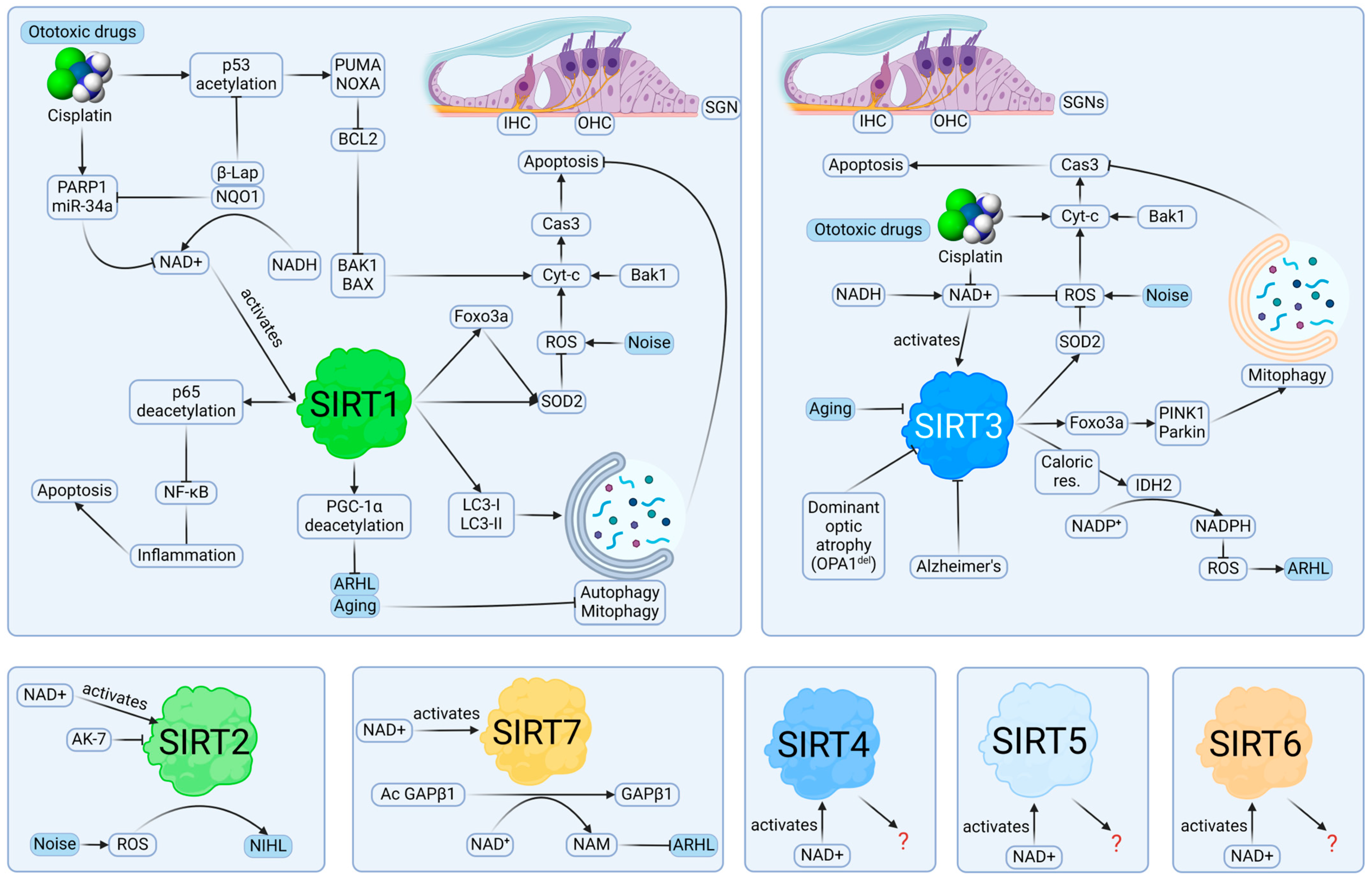
Of 48 studies, SIRT1 has been investigated in 29 studies. This popularity could be due to its verified role in extending life and delaying aging [86,87]. SIRT1 is a ubiquitous protein in the mammalian cochleae; it has been identified in inner hair cells (IHCs), OHCs, supporting cells (SCs), SV, and spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) [32]. It has been suggested that SIRT1 expression in a mouse cochlea could decrease due to noise exposure, cell senescence, and ototoxic drugs, which will be discussed in later chapters (Figure 3) [51,53,56].
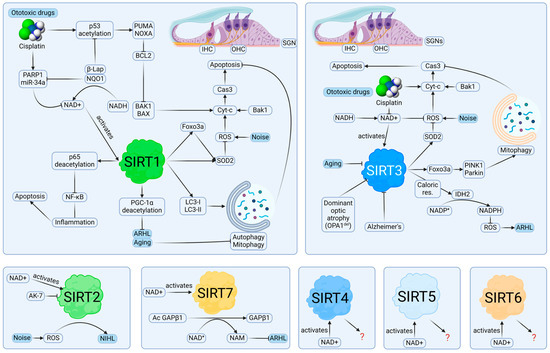
Figure 3.
Potential roles of sirtuins in hearing loss. SIRT1 and SIRT3 can modulate ROS in the pathologies leading to hearing loss, evidenced by studies in cell cultures and animal models. The major mechanism is the inhibition of intrinsic apoptosis pathway in IHCs, OHCs, and SGNs. Autophagy and mitophagy, which are triggered by pathways involving SIRT1 and SIRT3, can keep the cells under the threshold of caspase-3 activity sufficient for triggering apoptosis, providing protective roles. Inhibition of SIRT2 may be beneficial in NIHL. It is unclear if SIRT4, SIRT5, and SIRT6 are involved in hearing loss or hearing protection. Created with BioRender.com.
Xiong et al. studied the role of SIRT1 in ARHL in 2014 using C57BL/6 mice and ABR measurements [32]. It was reported that old mice (12–16 months old, n = 37) showed elevated ABR thresholds compared to young mice (1–2 months old, n = 44) at 4, 8, 16, and 32 kHz (p < 0.01). The old mice showed ~90% loss of OHC and ~50% loss of IHC. qPCR showed that Sirt1 mRNA expression was ~2 times higher in old mice (n = 20) than young mice (n = 12), and this was replicated in antibody staining which showed a reduction of SIRT1 expression in old mice. The old and young mice did not differ in the endocochlear potential (EP) measurement. However, whether SIRT1 dysregulation was a causal factor in hearing loss was unclear.
In Sirt1 KO mice (Sirt1+/−), SIRT1 deficiency delayed ARHL at 8, 16, and 32 kHz (p < 0.05) [42]. This was in contrast to the notion that SIRT1 can activate an anti-ROS pathway by activating SOD2 [18]. In the same study, 12-month-old Sirt1+/+ mice showed increases in hearing thresholds compared to 3-month-old Sirt1+/+ mice, while 12-month-old Sirt1+/− mice did not show increases in hearing thresholds, showing that SIRT1 insufficiency protected against ARHL. There was no sign of loss of the SGNs and SCs in old Sirt1+/− mice, compared to old Sirt1+/+ mice. This study tested that all mice used in the experiment had cadherin 23 mutation (Cdh23753A/753A), which is expected in C57BL/6J and causes ARHL. There was an expression of forkhead box O3 (FOXO3a) in SCs, such as Claudius and Deiters’ cells. FOXO3A is a transcriptional factor that could give rise to superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), which can reduce ROS, while SIRT1 can also activate SOD2 directly [51] (Figure 3). Overall, this result contrasted with the original theory that SIRT1 is a potent antioxidant and a part of the anti-apoptotic pathway, as seen in Xiong et al. [32].
However, all later studies indicated that SIRT1 expression is linked to hearing protection in ARHL [31,49,61,71,72,73,78]. Compared to mice younger than 2 months, mice older than 12 months showed decreased levels of SIRT1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) (p < 0.05) [78]. In HEI-OC1 cells, SIRT1 overexpression reduced apoptosis induced by H2O2, and increased PGC-1α expression (p < 0.05) [78]. This showed that SIRT1 is involved in an anti-apoptotic pathway and PGC-1α could be involved in the process of ARHL, although it was not shown whether SIRT1 overexpression would exert the same effects in vivo. In vivo protection against ARHL by SIRT1 overexpression was demonstrated using resveratrol in a separate study [73].
SAMP1/sku mice, originating from the senescence-accelerated mouse prone 1 (SAMP1) mouse strain, is a mouse strain displaying accelerated senility [88,89]. SIRT1 (p < 0.01) and SIRT3 (p < 0.01) expression increased in 7-month-old SAMP1/sku mice that had been given a Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) supplement since they were 1 month old [31]. In addition, CoQ10 also reduced hearing thresholds at 32 kHz when the mice were 7 (p < 0.05) and 13 months (p < 0.05) old. This study suggested that CoQ10 may help PGC-1α deacetylation, which is mediated by SIRT1 activation, and CoQ10 supplement may help counter ARHL in aging mice.
In 10-month-old C57BL/6 mice, the resveratrol supplement reduced ABR threshold elevations at 8, 16, and 32 kHz by 10–20 dB (p < 0.001) [73]. The same study showed that increased SIRT1 expression was associated with increased PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and Parkin expression in HEI-OC1 cells under the stress of ursodeoxycholic acid, showing that SIRT1 may trigger mitophagy under oxidative stress. A similar study demonstrated that compared to 2-month-old mice, 12-month-old mice showed lower expressions of autophagy markers (LC3-II and p62) (p < 0.001), while small interfering RNA (siRNA)-induced reduction of SIRT1 resulted in cell deaths in HEI-OC1 (p < 0.05) [72]. These studies suggest that SIRT1 boosts cell survival via mitophagy and autophagy. Another study showed that β-Lapachone, an anti-cancer drug, could restore SIRT1 (p < 0.05) and SIRT3 (p < 0.05) expression to the control level in 24-month-old mice, while β-Lapachone also decreased p53 expression (p < 0.05) [71]. Decreased p53 expression could indicate a reduction in p53-dependent apoptosis via pro-apoptotic transcription factors such as PUMA, NOXA, BID, and BAD [90]. In a more recent study, luteolin was used as a protective agent in HEI-OC1 cells treated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) [61]. It reported that luteolin-induced SIRT1 expression reduced p53 (p < 0.05) as well as p21 expression (p < 0.05). While a reduced p53 expression can suggest an anti-apoptotic effect of luteolin-induced SIRT1, p21 may negatively regulate p53-dependent apoptosis [91,92]. In HEI-OC1 cells, N6-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit (METTL3) KO increased SIRT1 expression (p < 0.05) and decreased apoptotic signals (p < 0.05) [49]. The apoptotic signal was captured using flow cytometry during which Annexin V was used to detect apoptotic cells. However, Annexin V may bind to any cells that lost plasma membrane integrity (e.g., necrotic cells), so it may not fully represent p53-dependent apoptosis [93]. Increased SIRT1 expression did not affect METTL3 expression, indicating that SIRT1 is in a downstream signaling pathway.
More recently, there has been an increased focus on the effect of microRNA (miRNA) and SIRT1. Currently, 16 miRNAs are known to affect SIRT1 expression [94]. It was reported that H19 overexpression could upregulate SIRT1 expression by suppressing miR-653-5p (p < 0.05) [58]. H19 is a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and its expression is typically reduced in aged mice [58]. Old mice displayed an increase in miR-29B expression (p < 0.05) and a decrease in SIRT1 expression (p < 0.05), while miR-34a inhibition restored SIRT1 expression to the control level (p < 0.05) [78]. Therefore, it is likely that the miRNA activity is an upstream process in the inner ear, controlling SIRT1 expression.
There were also reports of natural products such as cocoa polyphenol extract, which could increase SIRT1 and SIRT3 expression in HEI-OC1, OC-k3, and conditionally immortalized stria vascularis (SV-k1) cells under H2O2-induced oxidative stress [50].
4.2. SIRT1 in NIHL
The first electrophysiological evidence showing SIRT1 involvement in NIHL was in 2017 [76]. A resveratrol dietary supplement was used in mice to ameliorate SIRT1 reduction, which was caused by noise exposure [76]. Ginsenoside RD, a natural product, reduced noise-induced temporary threshold shift at 2, 4, and 8 kHz in mice [52,68]. The expression of BAX was elevated, and Bcl2 decreased after the noise exposure (p < 0.001). Pre-treatment with ginsenoside RD restored the SIRT1 expression to the original level (p < 0.001), while expression of BAX was reduced and B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2) expression increased. Given that BAX is known to be pro-apoptotic and BCL2 is known to inhibit the release of cytochrome-c [95], it can be suggested that ginsenoside RD attenuates NIHL by inhibiting the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. However, the study lacked the understanding of causality between SIRT1 expression and hair cell apoptosis; the study needed a method to see if ginsenoside RD would exert the same otoprotection when Sirt1 was knocked out. Apelin-13 was another otoprotective molecule that could ameliorate SIRT1 expression in mice exposed to noise (p < 0.001) [65]. In a TUNEL assay, fewer apoptotic cells were seen in Apelin-13-treated mice than untreated mice after noise exposure. However, this otoprotection was not verified by ABRs or DPOAEs.
In guinea pigs, noise exposure caused NIHL, which was characterized by decreases in IHC ribbon synapse density between IHCs and SGNs, without the deaths of hair cells [57]. The number of presynaptic ribbons per IHC decreased 1 day, 1 week, and 1 month post-noise exposure (p < 0.01), but resveratrol-treated mice showed protection against ribbon synapse loss (p < 0.01). SIRT1 expression decreased by ~10 folds in SGNs (p < 0.01) and ~2 folds in OC (p < 0.01) 1 day after noise exposure, while SIRT1 expression in SV did not change. In addition, SOD2 activity decreased in response to noise exposure (p < 0.01) and increased in response to resveratrol (p < 0.01). Overall, the study gave evidence of SIRT1-mediated protection against oxidative stress in NIHL at presynaptic ribbons.
One study showed that the expressions of SIRT1 and caspase-3 were upregulated in noise-exposed rats by approximately 0.5 folds (p < 0.05) [53]. This study was unique, as it indicated noise-induced apoptosis via SIRT1 expression, as opposed to other studies that stated that SIRT1 expression decreased after noise exposure and SIRT1 activates antioxidant pathways [57].
4.3. SIRT1 in DIHL
Platinum drugs and aminoglycosides have been the main drugs to be investigated in DIHL research. One of the first studies linking cisplatin and hearing loss was conducted in 2014 in which cisplatin decreased SIRT1 expression (p < 0.05) in HEI-OC1 cells [85]. In the same study, in NADH dehydrogenase quinone 1 (NQO1) KO mice, in which NAD+ metabolism is impaired, cisplatin treatment caused hearing loss at 4, 8, 16, and 32 kHz [85]. β-lapachone, known to elevate NQO1 expression, restored the hearing thresholds to pre-cisplatin treatment levels in WT mice but not in Nqo1−/− mice. This suggested that consumption of NAD+ by SIRT1 may be crucial in protection against cisplatin-induced hearing loss. In a similar setting using cisplatin-treated mice, Dunnione (NAD+ inducer via NQO1) restored SIRT1 expression to the original level (p < 0.05), but not in Nqo1−/− mice [79].
There has been an ongoing debate about whether SRT1720, a synthetic small molecule capable of inducing SIRT1, can be used against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. SRT1720 was used in HEI-OC1 cells, zebrafish lateral line hair cells, and C57BL/6 mice treated with cisplatin [74]. In HEI-OC1 cells, cisplatin increased SIRT1 expression (p < 0.01), which contrasted with what was found previously [74,85]. At the same time, cisplatin also increased LC3-11 (p < 0.05) but decreased p62 expression (p < 0.05), while SRT1720 exacerbated these effects. This suggested that SIRT1720 may activate autophagy through SIRT1 expression. In mice, SRT1720 reduced cisplatin-induced hearing loss at 4, 8, 16, and 32 kHz (p < 0.01) and ameliorated hair cell deaths [74]. In a study unrelated to hearing loss, SRT1720 increased the mean lifespan of mice by 8.8% [96]. One study found that SRT1720 did not activate SIRT1 directly, and that there may be many intermediaries involved [97]. SRT2104, a more recent version of SRT1720, has gone through clinical trials for type 2 diabetes (NCT00933062, NCT00937872, NCT00938275, and NCT01031108), but its effect on hearing loss has not yet been investigated [98].
Thymoquinone is a natural product and an antioxidant, and it was found that thymoquinone supplement in 9-month-old C57BL/6J mice, compared to 2-month-old mice, increased SIRT1 (p < 0.001) and decreased Bak1 expression (p < 0.001) [40]. The increase in SIRT1 and decrease in Bak1 expressions show that thymoquinone increased antioxidant activity and downregulated the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. Electron micrographs showed that thymoquinone protected the structure of stereocilia [40]. It was stated that ABR measurements showed significant threshold shifts at 8, 16, and 22 kHz in thymoquinone-treated mice compared to untreated mice, but the differences were small (~3 dB), and the experiments were not well controlled. In addition, the study did not provide evidence on whether thymoquinone-induced SIRT1 expression and reduced apoptosis were dependent or independent events.
4.4. SIRT3 in ARHL
In 2010, Someya et al. reported that SIRT3 could give protection against ARHL using C57BL/6 mouse models [33,34]. The study backcrossed C57BL/6J Sirt3+/− mice four times, resulting in ~94% congenic mice of the genotypes Sirt3+/+, Sirt3+/−, and Sirt3−/−. Furthermore, 2-month-old and 12-month-old mice were referred to as young and old mice, respectively. Caloric restriction, a 25% reduction from the original, ameliorated ARHL at 8, 16, and 32 kHz (p < 0.05) in WTs. However, there was no significant change in hearing thresholds in Sirt3−/− mice. This showed that SIRT3 is vital for hearing protection under caloric restriction. In addition, Sirt3 increased IDH2 activity in the inner ear (p < 0.05) of Sirt3+/+ mice, but not in Sirt3−/− mice. This showed that SIRT3 could alleviate oxidative stress by increasing IDH2 activity and upregulating NADH under caloric restriction. There was a question over the role Cdh23753A played in ARHL of the C57BL/6J mice and how other strains would respond to caloric restriction.
Another study in cochlear cultures showed that H2O2 induced a loss of synapses and hair cells (p < 0.01) and reduced the expression of FOXO3a and SOD2 (p < 0.05) [59]. In addition, inhibition of SIRT3 exacerbated hair cell deaths, as seen in a TUNEL staining. Interestingly, 0.5 mM H2O2 increased SIRT3 expression, but 1 mM H2O2 decreased SIRT3 expression. This suggested that SIRT3 activity can increase in response to oxidative stress, but its capacity is limited and can become overwhelmed. A similar result was observed in a more recent study, which showed that SIRT3 overexpression in H2O2-treated cells could increase IDH2 expression and activate FOXO3a and SOD2. Moreover, using a TUNEL study, it was shown that SIRT3 overexpression could reduce apoptosis [54]. Western blots confirmed that the apoptosis was caused via caspase 3 [54].
Cytidine monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (Cmah) KO mice showed hearing loss in old ages, and a microarray analysis using Expression BeadChip showed decreases of expressions in SIRT3, SIRT4, SIRT5, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 subunit alpha (Hif1α), FOXO3a, and SOD2 expression [80]. Given that HIF1α, FOXO3a, and SOD2 are downstream regulators of SIRT3, it is possible that knocking out Cmah resulted in a dysregulated SIRT3 expression and antioxidant activity. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis showed enrichment in oxidative phosphorylation from the microarray data. In addition, decreased expressions were observed in SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5, which are known to be expressed in the mitochondria under stress conditions [99]. Taken together, Cmah KO mice seemed to show mitochondrial dysregulation. This study was a rare case in which a microarray chip was used to study sirtuins and hearing loss. However, it investigated whole cochlear tissues, not single cells, and lacked auditory tests such as ABR and DPOAE in animal models.
Optic atrophy type 1 (Opa1) is a gene known for optic atrophy, in which 11 out of 19 known mutations are also associated with SNHL at various ages, from childhood to 30 years old [100]. One study found that senescent hair cells (induced by D-gal) showed increased OPA1 acetylation and decreased SIRT3 expression [46]. Kaempferol, an activator of SIRT3, increased SIRT3 expression, decreased SOD2 acetylation, decreased OPA1 acetylation, and overall increased the viability of D-gal-treated cells. The study also showed that the Sirt3 KO genotype caused hearing loss at 5, 6, 8, 11.3, 16, 22, and 32 kHz (p < 0.05) in 6-month-old mice, although there was no evidence that OPA1 acetylation/deacetylation was involved in the hearing loss. Therefore, in vivo evidence that Opa1 mutations could cause hearing loss via SIRT3 is still missing. A more recent study used Opa1delTTAG mice, and it showed that Opa1+/− caused hearing loss at 12 months of age (but not 1 and 6 months) in mice at 2~32 kHz (p < 0.01). Interestingly, 1-month-old Opa1+/− mice had the highest beclin1 and SIRT3 expressions (p < 0.001) compared to 6- and 12-month-old mice. This showed that Opa1delTTAG+/− mutant mice initially showed upregulated autophagy. Conversely, Parkin was most upregulated in 12-month-old Opa1+/− mice compared to 12-month-old Opa1+/+ mice. This showed that mitophagy could be upregulated in older Opa1+/− mice. There was no conclusive evidence that SIRT3 was involved in autophagy and mitophagy, but SIRT3 may have been involved in FOXO3a and PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy, which could have prevented caspase-3-driven apoptosis.
There have been discussions over the relationship between Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and hearing loss [101,102]. However, no research has shown that hearing loss occurring in AD could involve dysregulation of sirtuins until recently. The model 3xTgAD is a widely used AD mouse model, while 3xTgAD/Polβ+/− shows a decreased Polβ expression which causes deficient base excision repair and neuronal deaths, more closely mirroring AD occurring in humans [103]. Compared to wild type mice, 3xTgAD/Polβ+/− mice showed hearing loss at 16–32 kHz in ABR (p < 0.01) and 16 kHz in DPOAE (p < 0.001) with a decreased NAD+ level in the cochlea (p < 0.01). In addition, 3xTgAD/Polβ+/− mice showed a reduction in phosphoglycerate mutase 2 (PGAM2), SIRT3, and ac-SOD2 in the cochlea [44]. Given the reduction of NAD+, SIRT3, and SOD2 activation, there was an indication that redox homeostasis was impaired in the murine AD model.
4.5. SIRT3 in NIHL
NIHL was first investigated in conjunction with hearing loss in WldS Tg+/− Sirt3−/− mice [83]. WldS Tg+/− Sirt3−/− mice showed an overexpression of NAD+ while SIRT3 expression was abolished [83]. It was demonstrated that WldS Tg+/− mice were protected from hearing loss by noise at 8, 16, and 32 kHz, but Sirt3 KO prevented the protection [83]. NR (NAD+ precursor) supplement further protected against NIHL at 8, 16, and 32 kHz, but the Sirt3−/− genotype abolished the protection [83]. NR also prevented neurite degeneration, which suggested that NR may drive antioxidant response, as neurites are typically vulnerable to ROS [104]. This suggested that SIRT3 is an upstream regulator of NAD+-dependent antioxidant activity in NIHL. However, the role of SIRT3 in NIHL is disputed, as one study showed that knocking out SIRT3 did not affect recovery from temporary threshold shift or synaptic loss [69]. The study suggested that Sirt3−/− mice may have EOHL before noise exposure, but there was no clear evidence. Another study showed that the Sirt3−/− genotype caused EOHL in 6-, 8-, and 12-week-old mice [66]. Confocal imaging showed that the Sirt3−/− genotype caused irregular morphology of synapses in the IHCs, indicating that SIRT3 deficiency may have caused synaptopathy, an early sign of neuronal death.
Drug delivery with small biomaterials near or through the round window membrane is an important research topic in hearing loss. It has several advantages over other drug delivery methods such as injections via IV, middle ear tympanic membrane, round window membrane, and semicircular canal [105,106,107,108]. Systemic delivery using IV injections does not always reach the targets due to the blood labyrinth barrier (BLB), while intratympanic injections often cannot penetrate the round window membrane. An experimental drug, SODZIF-8, was created by embedding SOD2 and ZIF-8 (a drug delivery structure with biocompatibility and low toxicity) [55,109]. SODZIF-8 was injected in rats through the round window membrane one day before noise exposure [55]. SODZIF-8 injection reduced cochlear ROS and apoptosis, while SIRT3 and SOD2 expression increased. ABR measurements showed that SODZIF-8 reduced NIHL from day 1 after noise exposure until day 28, at frequencies between 4 and 32 kHz (p < 0.05). The effect of SODZIF-8 may not be limited to NIHL, as its benefit was also shown in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury [110].
4.6. SIRT3 in DIHL
Adjudin temporarily weakens the cell adhesion between Sertoli and germ cells, and it is being researched for male contraceptives [111]. Adjudin was associated with protection against DIHL via pathways involving SIRT3 [81]. Rat cochlear explant cultures were treated with gentamicin, and the adjudin-treated group showed an increased SIRT3 expression (p < 0.05) and a reduction in ROS production compared to the group without adjudin treatment [81]. ABR showed a 5 to 10 dB threshold difference in gentamicin-treated mice, which were pre-treated with adjudin, compared to no pre-treatment (p < 0.001). Antibody staining showed the protection of OHCs in the mouse group with adjudin pre-treatment. However, a 5 to 10 dB threshold shift may not be substantial enough to warrant a future clinical trial. In another study, gentamicin treatment in HEI-OC1 cells and cochlear explants reduced SIRT3 expression [67]. Dihydromyricetin is an antioxidant known to function via PGC-1α [67,112]. Dihydromyricetin also reduced gentamicin-induced apoptosis in HEI-OC1 cells (p < 0.01). Interestingly, PGC-1α was found to be an upstream regulator of SIRT3 expression, as SIRT3 inhibition did not affect PGC-1α, but PGC-1α inhibition resulted in a reduction of both PGC-1α and SIRT3. This was opposed to SIRT1, an upstream regulator known to deacetylate PGC-1α in hearing protection [31].
Honokiol is a natural product being investigated for DIHL [66]. Honokiol is a bark isolate, like paclitaxel [113]. In mice treated with cisplatin, 1-h pre-treatment with honokiol protected hearing which was assessed by ABR, DPOAE, and immunohistochemistry counts [66]. SIRT3 expression was observed in HNK-treated mice and the protein was concentrated in OHCs, showing that honokiol may exert its antioxidant effect through SIRT3 [66]. Interestingly, honokiol treatment reduced HeLa and HCT116 cell counts by ~50%, and accelerated deaths in cells treated with cisplatin [66]. This suggested that honokiol, like sodium thiosulfate, may be a candidate as an otoprotective agent during cancer treatment. In addition, it displayed a synergistic effect with cisplatin against cancer cells, and the synergy between honokiol and anti-cancer drugs has already been observed in the past [114,115]. Honokiol has been previously known as an inducer of p53-dependent apoptosis, an inducer of both apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells, and more recently, an inducer of paraptosis, a mode of non-apoptotic cancer cell death via mitochondrial and cytoplasmic swelling [116,117,118]. There needs to be a future study into why honokiol kills cancer cells, but not OHCs, as reported in the study by Tan et al. [66].
Paraquat is a known ototoxic chemical that works through ROS, causing apoptosis of IHC and OHCs [119]. In rats, both Sirt3+/− and Sirt3−/− mice cochleae showed hair cell loss without significant differences [63]. It suggests that SIRT3 expression does not confer protection against every ROS-generating drug, or that SIRT3-mediated otoprotection alone is not always sufficient in DIHL.
4.7. SIRT2 in Hearing Loss
Currently, there is little evidence to suggest that SIRT2 responds to oxidative stresses in the cochlea [50,66]. One study showed that IP injection of AK-7 (a SIRT2 inhibitor) 1 day before noise exposure resulted in IHC protection (p < 0.01) and ameliorated threshold shifts at 8, 16, 24, 32 kHz 1~14 days post-noise exposure (p < 0.05) [41]. Western blots using HEI-OC1 cells showed that SIRT2 expression increased in response to menadione, an ROS generator. However, the study did not show direct evidence that SIRT2 expression was modified in response to noise, nor if SIRT2 inhibition was causal to hearing protection. AK-7 reportedly inhibited SIRT2 in neurodegenerative mouse models in the past, but it is unknown if SIRT2 could be inhibited in the cochlea, although AK-7 is reportedly BLB-permeable [120,121]. Overall, inhibiting SIRT2 may be beneficial for treating hearing loss, contrary to SIRT1 and SIRT3.
RNA sequencing typically analyzes RNA expressions from mixed cells. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) gives information on individual cells. This allows the study of genome-wide gene expression by cell types such as OHCs, IHCs, and SCs [122]. Compared to microarray chips which investigate only a set number of genes, scRNAseq can detect a higher percentage of genes [80]. One available database, the Mouse Cochlea Aging Atlas (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/aging/single-cell_marker?project=Mouse_Cochlea, accessed on 1 May 2024), compiled the list of mRNAs which were sequenced by a 2023 scRNAseq project on ARHL [123]. The Atlas comparing old (15-month-old) and young (2-month-old) C57BL/6J mice showed SIRT2 logFC of 1.13 (FDR adj p = 5.23 × 10−263) in Deiters’ cells/outer pillar cells and logFC of 1.66 (FDR adj p = 2.54 × 10−71) in oligodendrocytes of the cochlear nerves. SIRT2 upregulation in aging mice was consistent with a previous study which showed that SIRT2 increased under oxidative stress in HEI-OC1 cells [41]. However, RNAseq did not capture the expression of the other sirtuin paralogs (SIRT1 and SIRT3-7). The rest of the cell types such as hair cells, SGNs, intermediate cells, and Reissner’s membrane cells also lacked data on the expressions of sirtuins. Genes involved in hearing loss, Sod2, Pink1, and Idh2, were searched in the sequencing results, but failed to be sequenced in any cell type. There could be several reasons; scRNAseq could be affected by low read depth (low coverage) and low-quality RNA samples (low RIN), and the lengths of transcripts could cause enrichment bias. Therefore, it would not be possible to read the entire genome equally, and some sirtuins may not have been mapped in the Mouse Cochlea Aging Atlas. One solution would be targeting relevant genes only by using custom panels of genes and increasing their read depth [124]. For example, 125 genes are currently associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss [125], and it would be promising to design a panel using the SureSelect Target Enrichment System to target the 125 genes.
4.8. SIRT7 in Hearing Loss
SIRT7 has been rarely studied in connection to hearing loss [84]. SIRT7 is unique among sirtuins in that it is mostly expressed in the nucleolus and activates RNA polymerase I via deacetylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) [126,127]. One study showed that SIRT7 was involved in the deacetylation of GA binding protein β1 (GABPβ1), an important transcription factor for mitochondrial genes [84]. Sirt7−/− mice displayed ARHL at 33–34 weeks compared to 8–9 weeks at 5, 8, 10, 15, and 30 kHz. Sirt7+/+ mice also showed the same hearing loss at 30 kHz, but not at 5, 8, 10, and 15 kHz. This showed that hearing loss observed in Sirt7−/− mice could just have been due to aging. C57BL/6J mice used in this experiment likely harbored Cdh23753A mutation causing ARHL, but it was not genotyped. In the same study using HEK293T cells, overexpression of SIRT7 decreased the level of ac-GABPβ1, while SIRT1 and SIRT6 did not, in western blot assays. Overall, SIRT7 deficiency seen in Sirt7−/− mice suggested that it may accelerate ARHL through mitochondrial dysregulation, but there should be further studies with mice strains which maintain normal hearing over the lifespan.
4.9. SIRT4, SIRT5, and SIRT6
Little evidence suggests that SIRT4, SIRT5, and SIRT6 could be involved in hearing loss. Only one study so far suggests their involvements in hearing loss, albeit without evidence of auditory tests [128]. The study in ARHL showed the distribution of SIRT1-7 in young (8 weeks old) and old (22-month-old) CBA/J mice using quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) [128]. SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT4, SIRT5, SIRT6, and SIRT7 showed an increase in expression in vestibular end organs (utricle, saccule, and crista ampullae) of old mice (p < 0.05). SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT4, SIRT6, and SIRT7 showed decreased expression in vestibular ganglions. SIRT1, SIRT3, and SIRT5 showed decreased expression in cochleae (OC, lateral walls, and SGNs).
In the same study, SIRT3 was the least expressed sirtuin in all tissues, in young and old mice, suggesting that SIRT3 expression may be stress-dependent [128]. In addition, SIRT3 did not show much change between young and old mice. SIRT2 and SIRT4 expression showed a very similar, almost equal expression in vestibular ganglions, cochleae, and acoustic nerves. SIRT5 showed a slight decrease in expression in the cochlea of aging mice, and this showed that SIRT5 may have similar roles to SIRT3, which is associated with ARHL. This is supported by past studies showing that IDH2 is a common substrate of SIRT3 and SIRT5, albeit with different modes of binding [47,129]. SIRT6 was sparsely expressed in various inner ear tissues and did not differ much in young and old mice [128]. SIRT7 was the most expressed sirtuin in the cochlea, although there was no difference in young and old mice. This study would have benefitted from physiological auditory tests, SIRT KO mouse models, and inhibiting transcription factors upstream and downstream of sirtuins to ascertain the causality between sirtuin expressions and hearing. In addition, a whole-genome analysis could have been an effective tool to verify the roles of sirtuins and hearing [80].
5. Summary
Sirtuins are a family of NAD+-dependent deacetylases working through activating key enzymes for stress resistance pathways, and are the key regulators of the intrinsic anti-ROS systems. With seven highly conserved members (SIRT1-7) which differ in catalytic activities and subcellular locations (in cytoplasm: SIRT1 and SIRT2; in mitochondria: SIRT3-5; and in nucleus: SIRT1, 2, 6, 7), sirtuins govern cellular processes including homeostasis, responses to stress, DNA damage repairing, inflammation, and apoptosis. Since the indication of SIRT3 involvement in ARHL in calorie-restricted mice in 2010, there has been an increase in research in SIRT1 and SIRT3 in relation to hearing protection. Recently, there have been probes into other sirtuins such as SIRT7, studied in 2014, and SIRT2, studied in 2019. It is expected that more roles of sirtuins will be found in future studies.
SIRT1 acts in an anti-inflammatory pathway via NF-κB, resulting in an anti-apoptosis response. In ARHL, SIRT1 can act via LC3-I and LC3-II to increase autophagy and mitophagy, keeping cells less sensitive to apoptosis and allowing them to overcome death. SIRT1 can also act via activating FOXO3a and SOD2 to keep redox in balance against extra ROS which can be caused by noise exposure. SIRT1-mediated redox homeostasis is important, as ROS can activate caspase-3-mediated apoptosis and hair cell death and neuronal death in the cochlea. Aging and AD negatively regulate the expression of SIRT1 and SIRT3 in the cochlea, while specific mouse models such as OPA1del also show aberrant SIRT3 expression. Unlike SIRT1, SIRT3 seems dependent on oxidative stresses for it to be expressed. One example is caloric restriction, which can activate IDH2 and ensure the redox balance by maintaining the oxidized-to-reduced-NAD (NAD+/NADH) ratio, keeping ROS in check over time, and delaying ARHL. SIRT3 and SIRT1 share specific regulatory proteins, such as SOD2 and FOXO3A, showing that they are both capable of diffusing superoxide and preventing caspase-3-mediated apoptosis. In addition, certain stresses such as noise and ototoxic drugs initially increase SIRT1 and SIRT3 concentrations, but the concentrations sharply decrease afterward. Similarly, SIRT1 and SIRT3 were linked to ARHL, NIHL, and DIHL. However, there are several differences. One difference is that only SIRT3 affects cisplatin-induced hearing loss. The role of SIRT1 in cisplatin-induced hearing loss is still to be confirmed. In addition, flavonoids and natural products increase the expression of SIRT3, but not SIRT1. This suggests that SIRT3 is the primary inhibitor of ROS caused by ototoxic drugs. Another important difference is that the Sirt1−/− mouse genotype is more punishing than the Sirt3−/− mouse genotype. Most of the mice missing SIRT1 (Sirt1−/−) die before birth, while mice missing SIRT3 (Sirt3−/−) survive. Studies investigating intrinsic hearing loss in SIRT3−/− are limited. It implies that SIRT3 as an antioxidant mediator is required but not essential. SIRT7 is special in that it is expressed in the nucleolus, but mediates the expression of mitochondrial proteins. Like Sirt1−/− mice, C57BL/6 Sirt7−/− mice show ARHL, possibly via mitochondrial dysregulation. However, the fact that Sirt7+/+ mice also lose hearing casts doubt over the result, and it is suggested that another study is to be conducted in the future with mice strains which can maintain normal hearing over the lifespan. SIRT2, the odd one out, seems to ameliorate NIHL when inhibited. However, there is doubt over the effectiveness of the SIRT2 inhibitor (AK-7) and it is hoped that a more effective SIRT2 inhibitor will be found in the future. A study involving Sirt2−/− mice would be a good follow-up study to show evidence that SIRT2 is required to control noise-induced ROS. SIRT4, SIRT5, and SIRT6 lacked any evidence of involvement in hearing loss, but their expressions were slightly altered in an ARHL model of mice in various tissue types of an ARHL model of mice. The lack of studies found in SIRT4-6 is a major limitation of this review, as it is unclear if SIRT4-6 are indeed unrelated to the mechanisms of hearing loss, or if SIRT4-6 simply lack the research volumes. A whole-genome assay such as scRNAseq and SureSelect Target Enrichment System would be beneficial in discovering the roles of SIRT4-6 and other transcriptional regulators involved in hearing loss.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.T.; Methodology, C.K.; Validation, C.K., X.T. and C.-P.R.; Writing, C.K.; Funding acquisition, X.T.; Supervision, X.T. and C.-P.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by NIH with grant number R01-DC019434 (X.T.). This research was also funded by Hearing Health Foundation (X.T.) and American Hearing Research Foundation (X.T.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would also like to express our gratitude to the reviewers for taking their time and effort.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
ABR (auditory brainstem response); AD (Alzheimer’s disease); ARHL (age-related hearing loss); Bcl2 (B-cell lymphoma 2); BLB (blood labyrinth barrier); C2-4B (C2 calcium-dependent domain-containing protein 4B); Cas3 (caspase-3); CDH23 (cadherin 23); CDK9 (cyclin-dependent kinase 9); Cmah (cytidine monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase); CoQ10 (coenzyme Q10); D-gal (D-galactose); DIHL (drug-induced hearing loss); DPOAE (distortion product otoacoustic emissions); ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay); EOHL (early-onset hearing loss); EP (endocochlear potential); FDA (food and drug administration); FOXO3a (forkhead box O3); GAPDH (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase); GABPβ1 (GA binding protein β1); H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide); HCT16 (human colorectal carcinoma 16); HDAC (histone deacetylase); HEI-OC1 (House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1); HEK293T (human embroynic kidney 293T); Hif1α (HIF1A hypoxia-inducible factor 1 subunit alpha); IDH2 (isocitrate dehydrogenase 2); IHC (inner hair cell); KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes); KO (knock-out); lncRNA (long non-coding RNA); METTL3 (N6-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit); miRNA (microRNA); NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide); NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information); NIHHL (noise-induced hidden hearing loss); NIHL (noise-induced hearing loss); NNT (nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase); NQO1 (NADH dehydrogenase quinone 1); NR (nicotinamide riboside); NRH (dihydronicotinamide riboside); OC (Organ of Corti); OHC (outer hair cell); OPA1 (Optic atrophy type 1); PGAM2 (phosphoglycerate mutase 2); PGC-1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha); PINK1 (PTEN-induced kinase 1); qPCR (quantitative PCR); ROS (reactive oxygen species); RT-qPCR (quantitative reverse transcription PCR); SC (supporting cell); scRNAseq (single cell RNAseq); SGN (spiral ganglion neuron); Sir2 (silent information regulator 2); siRNA (small interfering RNA); SIRT1-7 (sirtuin 1-7); SNHL (sensorineural hearing loss); SOD2 (superoxide dismutase 2); SV (stria vascularis); SV-k1 (conditionally immortalized stria vascularis cell line).
References
- Imai, S.; Armstrong, C.M.; Kaeberlein, M.; Guarente, L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature 2000, 403, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.J.; Zhang, T.N.; Chen, H.H.; Yu, X.F.; Lv, J.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, J.Q.; Wei, Y.F.; et al. The sirtuin family in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilopoulos, A.; Fritz, K.S.; Petersen, D.R.; Gius, D. The human sirtuin family: Evolutionary divergences and functions. Hum. Genom. 2011, 5, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.J.; Christianson, D.W. Structure, mechanism, and inhibition of the zinc-dependent histone deacetylases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 59, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantó, C.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Pirinen, E.; Youn, D.Y.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Cen, Y.; Fernandez-Marcos, P.J.; Yamamoto, H.; Andreux, P.A.; Cettour-Rose, P.; et al. The NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Su, L.; Bu, T.; Zhang, Y. Exercise training upregulates intracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase expression in humans: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1287421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.G.; Matchett, K.B.; Davison, G.W. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the SIRT1 response to exercise. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, A.S.; Andersen, C.; Daoud, M.; Anderson, K.A.; Laursen, J.S.; Chakladar, S.; Huynh, F.K.; Colaço, A.R.; Backos, D.S.; Fristrup, P.; et al. Investigating the Sensitivity of NAD+-dependent Sirtuin Deacylation Activities to NADH. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7128–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.; Huber, P.E.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Shen, G.; Zou, B. NAD+ metabolism: Pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallin, O.; Reymond, L.; Gondrand, C.; Raith, F.; Koch, B.; Johnsson, K. Semisynthetic biosensors for mapping cellular concentrations of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides. eLife 2018, 7, e32638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.N.S.; Shen, X.; Pardue, S.; Krzywanski, D.M. Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) regulates mitochondrial ROS and endothelial dysfunction in response to angiotensin II. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, R.S.; Handy, D.E.; Loscalzo, J. NAD(H) and NADP(H) Redox Couples and Cellular Energy Metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Dong, W.; Stephanopoulos, G.N.; Sikes, H.D. Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway and glucose anaplerosis support maintenance of mitochondrial NADPH pool under mitochondrial oxidative stress. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2020, 5, e10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ying, W. NAD+ Deficiency Is a Common Central Pathological Factor of a Number of Diseases and Aging: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajman, L.; Chwalek, K.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The In Vivo Evidence. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Gao, L.; Liao, N.; Xu, X.; Yu, W.; Hong, W. Association between niacin and mortality among patients with cancer in the NHANES retrospective cohort. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Gil, N.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Chun, K.H.; Fang, G.; Kim, J.; Cho, H.; Jang, C.Y.; Cha, H.J. Sirt1 Regulates Microtubule Dynamics through Negative Regulation of Plk1 in Mitosis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Chhabra, G.; Ndiaye, M.A.; Garcia-Peterson, L.M.; Mack, N.J.; Ahmad, N. The Role of Sirtuins in Antioxidant and Redox Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, S.; Chen, Z.; Dai, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, K.S. SIRT1/3 Activation by Resveratrol Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury in a Septic Rat Model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7296092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, F.; Hoberg, J.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Keller, M.D.; Jones, D.R.; Frye, R.A.; Mayo, M.W. Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Embo J. 2004, 23, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michan, S.; Sinclair, D. Sirtuins in mammals: Insights into their biological function. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; Wu, M.; Jia, L.; Guo, J. Role of FOXO3a Transcription Factor in the Regulation of Liver Oxidative Injury. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Dittenhafer-Reed, K.E.; Denu, J.M. SIRT3 protein deacetylates isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) and regulates mitochondrial redox status. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14078–14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Qiu, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Han, L.; Ge, J.; et al. Sirt3-dependent deacetylation of SOD2 plays a protective role against oxidative stress in oocytes from diabetic mice. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, H.; Mei, C.; Cui, M.; He, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Sirtuin4 alleviates severe acute pancreatitis by regulating HIF-1α/HO-1 mediated ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, F.; Sun, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Guan, K.L.; et al. SIRT5 promotes IDH2 desuccinylation and G6PD deglutarylation to enhance cellular antioxidant defense. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ren, S.; Li, Z.; Hao, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D. Sirt6 mediates antioxidative functions by increasing Nrf2 abundance. Exp. Cell Res. 2023, 422, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Lee, W.; Yun, J.M. Luteolin and fisetin suppress oxidative stress by modulating sirtuins and forkhead box O3a expression under in vitro diabetic conditions. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Ramírez, R.; González-Fernández, R.; Hernández, J.; Martín-Vasallo, P.; Palumbo, A.; Ávila, J. Celastrol and Melatonin Modify SIRT1, SIRT6 and SIRT7 Gene Expression and Improve the Response of Human Granulosa-Lutein Cells to Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L.L.; Tucci, D.L. Hearing Loss in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Sawashita, J.; Kubo, H.; Nishio, S.Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Suzuki, N.; Yoshimura, H.; Tsuruoka, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Ubiquinol-10 supplementation activates mitochondria functions to decelerate senescence in senescence-accelerated mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 2606–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Dai, M.; Ou, Y.; Pang, J.; Yang, H.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; et al. SIRT1 expression in the cochlea and auditory cortex of a mouse model of age-related hearing loss. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 51, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Someya, S.; Yu, W.; Hallows, W.C.; Xu, J.; Vann, J.M.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Tanokura, M.; Denu, J.M.; Prolla, T.A. Sirt3 mediates reduction of oxidative damage and prevention of age-related hearing loss under caloric restriction. Cell 2010, 143, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Someya, S.; Yamasoba, T.; Weindruch, R.; Prolla, T.A.; Tanokura, M. Caloric restriction suppresses apoptotic cell death in the mammalian cochlea and leads to prevention of presbycusis. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, R.J.; Price, J.M.; Henry, K.R. Dietary restriction and presbyacusis: Periods of restriction and auditory threshold losses in the CBA/J mouse. Audiology 1988, 27, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikkawa, Y.; Seki, Y.; Okumura, K.; Ohshiba, Y.; Miyasaka, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Ozaki, M.; Matsuoka, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Yonekawa, H. Advantages of a mouse model for human hearing impairment. Exp. Anim. 2012, 61, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erway, L.C.; Shiau, Y.W.; Davis, R.R.; Krieg, E.F. Genetics of age-related hearing loss in mice. III. Susceptibility of inbred and F1 hybrid strains to noise-induced hearing loss. Hear. Res. 1996, 93, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keithley, E.M.; Canto, C.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Fischel-Ghodsian, N.; Johnson, K.R. Age-related hearing loss and the ahl locus in mice. Hear. Res. 2004, 188, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, G.; Lu, J.; Gao, Y.G.; Song, L.; Li, G.L.; Wu, H. Cellular Differences in the Cochlea of CBA and B6 Mice May Underlie Their Difference in Susceptibility to Hearing Loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, S.A.; Mostafa, F.; Alnamshan, M.M.; Elshewemi, S.S.; Sorour, J.M. Thymoquinone ameliorates age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6J mice by modulating Sirt1 activity and Bak1 expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Ding, H. The SIRT2 inhibitor AK-7 decreases cochlear cell apoptosis and attenuates noise-induced hearing loss. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Linser, P.; Park, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; White, K.; Vann, J.M.; Ding, D.; Prolla, T.A.; Someya, S. Sirt1 deficiency protects cochlear cells and delays the early onset of age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6 mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 43, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowling, T.; Wen, H.; Meenderink, S.W.F.; Dong, W.; Meaud, J. Intracochlear distortion products are broadly generated by outer hair cells but their contributions to otoacoustic emissions are spatially restricted. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Sahbaz, B.D.; Pekhale, K.; Chu, X.; Okur, M.N.; Grati, M.; Isgrig, K.; Chien, W.; Chrysostomou, E.; Sullivan, L.; et al. Early-Onset Hearing Loss in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease and Increased DNA Damage in the Cochlea. Aging Biol. 2024, 1, 20240025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affortit, C.; Coyat, C.; Saidia, A.R.; Ceccato, J.C.; Charif, M.; Sarzi, E.; Flamant, F.; Guyot, R.; Cazevieille, C.; Puel, J.L.; et al. The human OPA1(delTTAG) mutation induces adult onset and progressive auditory neuropathy in mice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Pan, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, R.; Zou, T.; Guo, D.; Shen, Y.; Ji, P.; Huang, W.; Wen, Q.; et al. Excessive processing and acetylation of OPA1 aggravate age-related hearing loss via the dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Jia, S.; Deng, H.; Tang, J.; Sun, X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; et al. Dual modifying of MAVS at lysine 7 by SIRT3-catalyzed deacetylation and SIRT5-catalyzed desuccinylation orchestrates antiviral innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2314201121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, R.D.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Ontario, M.; Cammilleri, G.; Pantano, L.; Scuto, M.; Tomasello, M.; Spanò, S.; Salinaro, A.T.; et al. Redox Modulation of Meniere Disease by Coriolus Versicolor Treatment, a Nutritional Mushroom Approach with Neuroprotective Potential. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Ming, R.; Wei, J.; Du, P.; Li, X.; Zong, S.; Xiao, H. METTL3 Reduces Oxidative Stress-induced Apoptosis in Presbycusis by Regulating the N6-methyladenosine Level of SIRT1 mRNA. Neuroscience 2023, 521, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Chacón, L.D.M.; Yanes-Díaz, J.; de Lucas, B.; Riestra-Ayora, J.I.; Madrid-García, R.; Sanz-Fernández, R.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, C. Cocoa Polyphenol Extract Inhibits Cellular Senescence via Modulation of SIRT1 and SIRT3 in Auditory Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, Z.; Gong, S.; Du, Z. Adenovirus-mediated SIRT1 protects cochlear strial marginal cells in a D-gal-induced senescent model in vitro. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Liu, Y.H.; Ji, S.F.; Xue, X.M.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, M.; Chang, Y.M.; Wang, X.C. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rd on military aviation noise-induced cochlear hair cell damage in guinea pigs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 23965–23981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Jeon, J.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.Y. Differential Expression of miRNAs and Their Predicted Target Pathways in Cochlear Nucleus Following Chronic Noise Exposure in Rats. Cells 2022, 11, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Liang, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Du, Z.; Gong, S. SIRT3-mediated deacetylation protects inner hair cell synapses in a H(2)O(2)-induced oxidative stress model in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 418, 113280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Han, C.; Geng, F.; Zhang, S.; Qu, Y.; Tang, W. Superoxide dismutase@zeolite Imidazolate Framework-8 Attenuates Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 885113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Mao, S.; Shi, H.; Yu, D.; Chen, Z.; Su, K.; Xing, Y.; Dong, H.; et al. A reduced form of nicotinamide riboside protects the cochlea against aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity by SIRT1 activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Li, C.C.; Chen, X.M.; Huang, L.G.; Zhang, M.; Ruan, B.; Wang, X.C. Involvement of the SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway in Noise-Induced Hidden Hearing Loss. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 798395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Shu, T.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, M.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y. LncRNA H19 inhibits oxidative stress injury of cochlear hair cells by regulating miR-653-5p/SIRT1 axis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2022, 54, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Z.; He, L.; Liang, W.; Liu, K.; Gong, S. ROS-Induced Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mediated by Inhibition of SIRT3 in Cultured Cochlear Cells. Neural Plast. 2022, 2022, 5567174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Yeo, S.G.; Kim, Y.J. Environmental enrichment modulates silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) activity to attenuate central presbycusis in a rat model of normal aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 155, 111552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.Z.; Li, B.S.; Gao, S.S.; Seo, J.H.; Choi, B.M. Luteolin inhibits H2O2-induced cellular senescence via modulation of SIRT1 and p53. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 25, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Xiong, H.; Pang, J.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Liang, Z.; Huang, X.; He, F.; Jian, B.; He, W.; et al. Modulation of NAD(+) biosynthesis activates SIRT1 and resists cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 349, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Prolla, T.; Someya, S.; Manohar, S.; Salvi, R. Roles of Bak and Sirt3 in Paraquat-Induced Cochlear Hair Cell Damage. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, T. Protective Effects of N1-Methylnicotinamide Against High-Fat Diet- and Age-Induced Hearing Loss via Moderate Overexpression of Sirtuin 1 Protein. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 634868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshsirat, S.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Peyvandi, A.A.; Heidari, F.; Peyvandi, M.; Simani, L.; Niknazar, S. Apelin-13 prevents apoptosis in the cochlear tissue of noise-exposed rat via Sirt-1 regulation. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 114, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Agarwal, A.; Lim, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; O′Brien, J.; Tran, E.; Zheng, J.; Gius, D.; et al. Systemic application of honokiol prevents cisplatin ototoxicity without compromising its antitumor effect. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4416–4434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Dong, Y.; Ma, X. Dihydromyricetin Protects Against Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity via PGC-1α/SIRT3 Signaling in vitro. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Ji, S.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Xue, X.M.; Xu, J.; Gu, Z.H.; Deng, S.L.; Liu, C.D.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y.M.; et al. Ginsenoside Rd Ameliorates Auditory Cortex Injury Associated with Military Aviation Noise-Induced Hearing Loss by Activating SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Shah, L.; Dang, N.; Tan, X.; Almudevar, A.; White, P.M. SIRT3 promotes auditory function in young adult FVB/nJ mice but is dispensable for hearing recovery after noise exposure. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuto, M.; Di Mauro, P.; Ontario, M.L.; Amato, C.; Modafferi, S.; Ciavardelli, D.; Trovato Salinaro, A.; Maiolino, L.; Calabrese, V. Nutritional Mushroom Treatment in Meniere’s Disease with Coriolus versicolor: A Rationale for Therapeutic Intervention in Neuroinflammation and Antineurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Cao, W.; Oh, G.S.; Lee, S.; Shen, A.; Khadka, D.; Lee, S.B.; Sharma, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Choe, S.K.; et al. Augmentation of cellular NAD+ by NQO1 enzymatic action improves age-related hearing impairment. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Xiong, H.; Ou, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Lai, L.; Ye, Y.; Su, Z.; Lin, H.; et al. SIRT1 protects cochlear hair cell and delays age-related hearing loss via autophagy. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 80, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Chen, S.; Lai, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; Pang, J.; Su, Z.; Lin, H.; Zheng, Y. Modulation of miR-34a/SIRT1 signaling protects cochlear hair cells against oxidative stress and delays age-related hearing loss through coordinated regulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 79, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhan, T.; Cheng, G.; Jia, H.; Ye, Y.; Su, Z.; Chen, H.; Lin, H.; Lai, L.; et al. Sirtuin 1 and Autophagy Attenuate Cisplatin-Induced Hair Cell Death in the Mouse Cochlea and Zebrafish Lateral Line. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Rhee, J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.H. The Protective Effect of Egb 761 Against 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Hearing Loss: The Role of Sirtuin 1. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 11, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Ou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Pang, J.; Lai, L.; Zheng, Y. Resveratrol Promotes Recovery of Hearing following Intense Noise Exposure by Enhancing Cochlear SIRT1 Activity. Audiol. Neurootol. 2017, 22, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Shen, J.; Li, D.; Ming, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Lai, J.; Shi, M.; Ji, Q.; Xing, Y. MiR-34a contributes to diabetes-related cochlear hair cell apoptosis via SIRT1/HIF-1α signaling. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 246, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Wei, L.; Zha, D.J.; Qiu, J.H.; Chen, F.Q.; Qiao, L.; Qiu, Y. miR-29b overexpression induces cochlear hair cell apoptosis through the regulation of SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling: Implications for age-related hearing loss. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Pandit, A.; Oh, G.S.; Shen, A.; Lee, S.B.; Khadka, D.; Lee, S.; Shim, H.; Yang, S.H.; Cho, E.Y.; et al. Dunnione ameliorates cisplatin ototoxicity through modulation of NAD+ metabolism. Hear. Res. 2016, 333, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.N.; Park, W.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Gurunathan, S.; Kim, J.H. Oxidative stress and ROS metabolism via down-regulation of sirtuin 3 expression in Cmah-null mice affect hearing loss. Aging 2015, 7, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Xia, L.; Shao, J.; Yin, S.; Cheng, C.Y.; Xia, W.; Gao, W.Q. Adjudin protects rodent cochlear hair cells against gentamicin ototoxicity via the SIRT3-ROS pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Pang, J.; Yang, H.; Dai, M.; Liu, Y.; Ou, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Activation of miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 signaling contributes to cochlear hair cell apoptosis: Implications for age-related hearing loss. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.D.; Maqsood, S.; Huang, J.Y.; Pan, Y.; Harkcom, W.; Li, W.; Sauve, A.; Verdin, E.; Jaffrey, S.R. Activation of SIRT3 by the NAD⁺ precursor nicotinamide riboside protects from noise-induced hearing loss. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Jo, Y.S.; Lo Sasso, G.; Stein, S.; Zhang, H.; Perino, A.; Lee, J.U.; Zeviani, M.; Romand, R.; Hottiger, M.O.; et al. A SIRT7-dependent acetylation switch of GABPβ1 controls mitochondrial function. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Oh, G.S.; Shen, A.; Lee, S.B.; Choe, S.K.; Kwon, K.B.; Lee, S.; Seo, K.S.; Kwak, T.H.; Park, R.; et al. Augmentation of NAD+ by NQO1 attenuates cisplatin-mediated hearing impairment. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Liang, W. SIRT1 and SIRT6: The role in aging-related diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, M.; Ge, Y.; Wang, X. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 187, 111215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuki, A.; Maeda, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Kamimura, R.; Masuyama, T.; Suzuki, S. SAMP1/Sku as a murine model for tubulointerstitial nephritis: A study using unilateral ureteral obstruction. Exp. Anim. 2005, 54, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aoyama, Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Yoshimoto, T.; Niimi, K.; Takahashi, E.; Itakura, C. Impaired motor function in senescence-accelerated mouse prone 1 (SAMP1). Brain Res. 2013, 1515, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Zhou, X. The ARTS of p53-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 14, mjac074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartel, A.L.; Tyner, A.L. The role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 639–649. [Google Scholar]
- Engeland, K. Cell cycle regulation: p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, L.C.; Marfell, B.J.; Scott, A.P.; Waterhouse, N.J. Quantitation of Apoptosis and Necrosis by Annexin V Binding, Propidium Iodide Uptake, and Flow Cytometry. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 2016, prot087288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakuchi, M. MicroRNA Regulation of SIRT1. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulsoom, B.; Shamsi, T.S.; Afsar, N.A.; Memon, Z.; Ahmed, N.; Hasnain, S.N. Bax, Bcl-2, and Bax/Bcl-2 as prognostic markers in acute myeloid leukemia: Are we ready for Bcl-2-directed therapy? Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.J.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Mercken, E.M.; Palacios, H.H.; Ward, T.M.; Abulwerdi, G.; Minor, R.K.; Vlasuk, G.P.; Ellis, J.L.; Sinclair, D.A.; et al. The SIRT1 activator SRT1720 extends lifespan and improves health of mice fed a standard diet. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacholec, M.; Bleasdale, J.E.; Chrunyk, B.; Cunningham, D.; Flynn, D.; Garofalo, R.S.; Griffith, D.; Griffor, M.; Loulakis, P.; Pabst, B.; et al. SRT1720, SRT2183, SRT1460, and resveratrol are not direct activators of SIRT1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8340–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baksi, A.; Kraydashenko, O.; Zalevkaya, A.; Stets, R.; Elliott, P.; Haddad, J.; Hoffmann, E.; Vlasuk, G.P.; Jacobson, E.W. A phase II, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multi-dose study of SRT2104, a SIRT1 activator, in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, J.M.; Andrabi, S.A. SIRT3 Regulation Under Cellular Stress: Making Sense of the Ups and Downs. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leruez, S.; Milea, D.; Defoort-Dhellemmes, S.; Colin, E.; Crochet, M.; Procaccio, V.; Ferré, M.; Lamblin, J.; Drouin, V.; Vincent-Delorme, C.; et al. Sensorineural hearing loss in OPA1-linked disorders. Brain 2013, 136, e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehramiz, M.; Porter, T.; O‘Brien, E.K.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; Laws, S.M. A Potential Role for Sirtuin-1 in Alzheimer’s Disease: Reviewing the Biological and Environmental Evidence. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2023, 7, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla, R.; Donmez, G. The role of sirtuins in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, P.; Misiak, M.; Wang, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Leandro, G.S.; Liu, D.; Tian, J.; Baptiste, B.A.; Cong, W.N.; Brenerman, B.M.; et al. DNA polymerase β deficiency leads to neurodegeneration and exacerbates Alzheimer disease phenotypes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K. Reactive oxygen species induce neurite degeneration before induction of cell death. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2016, 59, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.E.; Carpena, N.T.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, S.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Chung, W.H. Round-window delivery of lithium chloride regenerates cochlear synapses damaged by noise-induced excitotoxic trauma via inhibition of the NMDA receptor in the rat. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Lim, Y.; Knowles, J.; Kim, H.W. Auditory disorders and future therapies with delivery systems. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, 2041731418808455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Shi, F.; Yu, D.; Wu, H. A single dose of dexamethasone encapsulated in polyethylene glycol-coated polylactic acid nanoparticles attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss following round window membrane administration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3567–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, X.; Wang, R.; Xu, L.; Ma, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Z. Advancements in the studies of novel nanomaterials for inner ear drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Q. Synthesis and modification of ZIF-8 and its application in drug delivery and tumor therapy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37600–37620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Bi, L.; Liu, H.; Ding, X. SOD mineralized zeolitic imidazole framework-8 for the treatment of chemotherapy-related acute kidney injury. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 229, 113447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, K.W.; Mruk, D.D.; Lie, P.P.; Lui, W.Y.; Cheng, C.Y. Adjudin, a potential male contraceptive, exerts its effects locally in the seminiferous epithelium of mammalian testes. Reproduction 2011, 141, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Mao, Y.; Ding, L.; Zeng, X.A. Dihydromyricetin: A review on identification and quantification methods, biological activities, chemical stability, metabolism and approaches to enhance its bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Mao, J.W.; Tan, X.L. Research progress on the source, production, and anti-cancer mechanisms of paclitaxel. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Q.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.M.; Chen, C.G.; Long, W.G.; Jiang, Q.; Li, J. Synergistic killing effect of paclitaxel and honokiol in non-small cell lung cancer cells through paraptosis induction. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Beitler, J.J.; Wang, H.; Lee, M.J.; Huang, W.; Koenig, L.; Nannapaneni, S.; Amin, A.R.; Bonner, M.; Shin, H.J.; et al. Honokiol enhances paclitaxel efficacy in multi-drug resistant human cancer model through the induction of apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battle, T.E.; Arbiser, J.; Frank, D.A. The natural product honokiol induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells. Blood 2005, 106, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Fang, X.; Shen, S. Honokiol induces apoptosis and autophagy via the ROS/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Huang, M.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, P.; Huang, M.Q.; Lu, J.J. Paraptosis: A non-classical paradigm of cell death for cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicotera, T.M.; Ding, D.; McFadden, S.L.; Salvemini, D.; Salvi, R. Paraquat-induced hair cell damage and protection with the superoxide dismutase mimetic m40403. Audiol. Neurootol. 2004, 9, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wales, P.; Quinti, L.; Zuo, F.; Moniot, S.; Herisson, F.; Rauf, N.A.; Wang, H.; Silverman, R.B.; Ayata, C.; et al. The sirtuin-2 inhibitor AK7 is neuroprotective in models of Parkinson’s disease but not amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and cerebral ischemia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, V.; Quinti, L.; Kim, J.; Vollor, L.; Narayanan, K.L.; Edgerly, C.; Cipicchio, P.M.; Lauver, M.A.; Choi, S.H.; Silverman, R.B.; et al. The sirtuin 2 inhibitor AK-7 is neuroprotective in Huntington’s disease mouse models. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzano, R.; Gwilliam, K.; Rose, K.; Milon, B.; Matern, M.S. Cell Type-Specific Expression Analysis of the Inner Ear: A Technical Report. Laryngoscope 2021, 131 (Suppl. 5), S1–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhang, W.; Ren, J.; Ma, S.; Sun, S.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Ji, Z.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic atlas of mouse cochlear aging. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisi, A.; Palaniappan, S.; Maccarrone, M. Advanced Omics Techniques for Understanding Cochlear Genome, Epigenome, and Transcriptome in Health and Disease. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, A.E.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Schaefer, A.M.; Smith, R.J.H. Genetic Hearing Loss Overview. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, E.; Voit, R.; Liszt, G.; Magin, C.; Grummt, I.; Guarente, L. Mammalian Sir2 homolog SIRT7 is an activator of RNA polymerase I transcription. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, M.F.; Chen, S.; Poetz, F.; Schnölzer, M.; Voit, R.; Grummt, I. SIRT7-dependent deacetylation of CDK9 activates RNA polymerase II transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takumida, M.; Takumida, H.; Katagiri, Y.; Anniko, M. Localization of sirtuins (SIRT1-7) in the aged mouse inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016, 136, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, H.L.; Xu, J.; Tan, J.; Fu, L.N.; Wang, J.L.; Zou, T.H.; Sun, D.F.; Gao, Q.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; et al. Sirtuin5 contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis by enhancing glutaminolysis in a deglutarylation-dependent manner. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).