Abstract
The skin barrier is essential for maintaining the body’s internal homeostasis, protecting against harmful external substances, and regulating water and electrolyte balance. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers notable advantages in restoring skin barrier function due to its diverse components, targets, and pathways. Recent studies have demonstrated that active ingredients in TCM can safely and effectively repair damaged skin barriers, reinstating their proper functions. This review article provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanisms underlying skin barrier damage and explores how the bioactive constituents of TCM contribute to skin barrier repair, thereby offering a theoretical framework to inform clinical practices.
1. Introduction
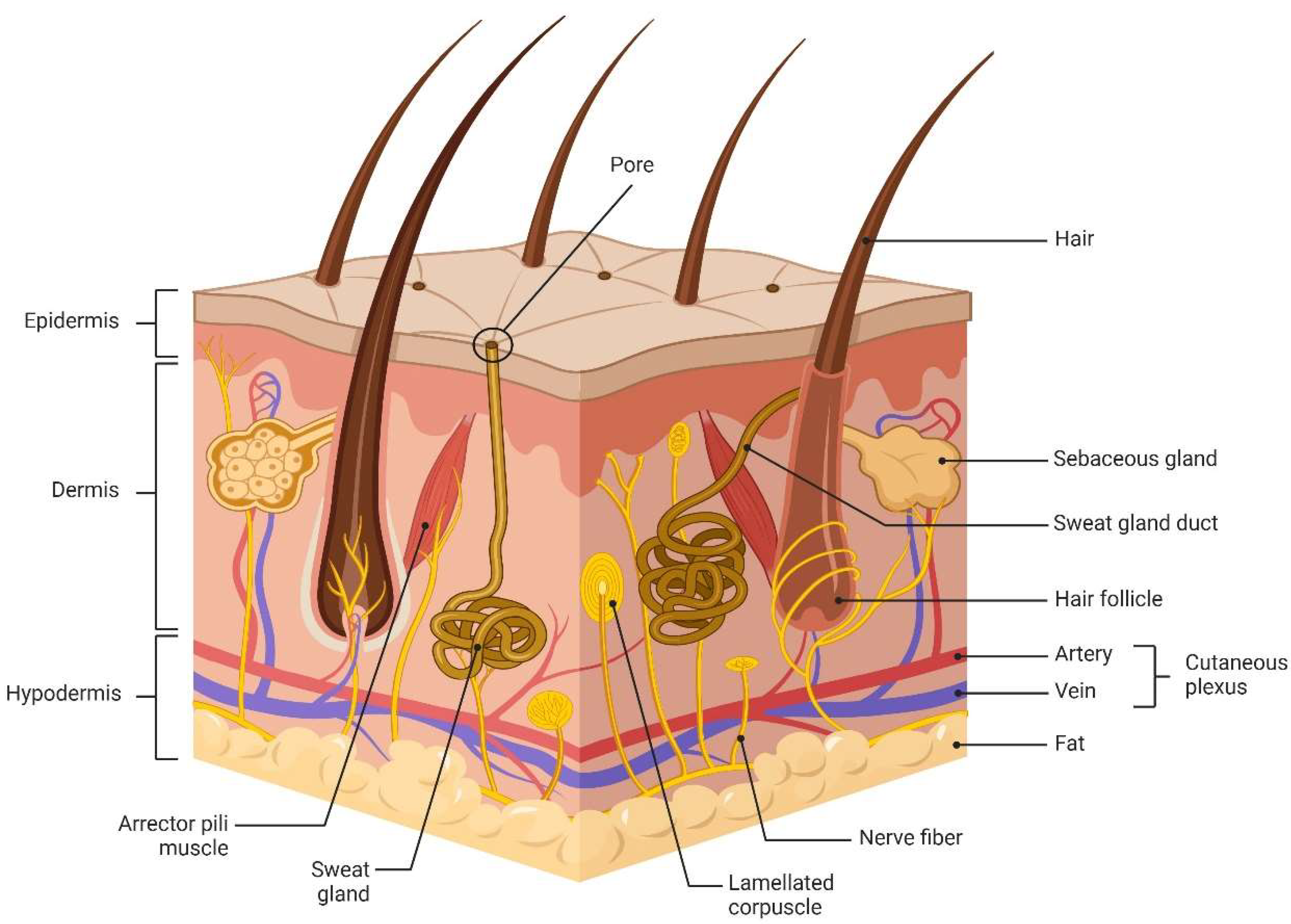
The skin, being the largest organ in the human body, serves various functions, including acting as a barrier. It is composed of the epidermis, the dermis, and subcutaneous tissue, and it contains accessory organs (sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles), blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves and muscles, regulating temperature and providing immunity [1]. One of these functions, the skin barrier, is of utmost importance. Serving as the primary defense mechanism of the body, the skin effectively shields against damage caused by external chemical, physical, mechanical, biological, and other factors, while also preventing water and nutrient loss [2]. Figure 1 illustrates the skin’s structure.
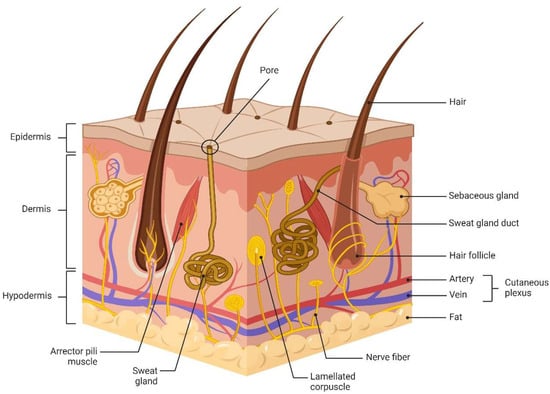
Figure 1.
Skin structure.
Impaired skin barrier function can result in the infiltration of harmful environmental substances into the body, including pathogenic bacteria, allergens, toxins, and irritants, potentially triggering systemic allergic reactions. The prevalence of impaired skin barrier function is on the rise due to shifts in environmental conditions and lifestyle factors, leading to various skin issues such as flushing, papules, scales, itching, and stinging [3]. Many diseases, including eczema, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, acne, and chloasma, are associated with compromised skin barrier function [4]. Within the European dermatology patient population, male patients make up 48.98%, with female patients slightly outnumbering males at 51.02%. Research indicates that 43.35% of patients have experienced at least one skin disease in the past 12 months. The most prevalent types of skin disease include fungal skin infections, acne, and atopic dermatitis [5].
The treatment of skin diseases in recent years has involved the use of steroids, antihistamines, emollients, and immunomodulators. However, prolonged use of steroids can result in various adverse effects. Prolonged use of steroids can lead to thinning and weakening of the skin, resulting in wrinkles, purple lines, and ecchymoses. Additionally, it may cause hair to become finer and even result in hair loss. Chronic steroid use suppresses immune system function, which increases the risk of skin infections [6]. Furthermore, long-term steroid use may create dependency, and discontinuation can trigger rebound dermatitis [7]. Modern medicine has made significant progress in treating skin diseases through various methods, but different treatments can sometimes have side effects. For example, immunotherapy modulates the immune system to alleviate symptoms or prevent disease progression and has shown remarkable efficacy in treating conditions like melanoma and psoriasis. However, this method can also hyperactivate the immune system, leading to attacks on healthy cells and causing side effects such as fatigue, rashes, and intestinal problems [8]. Isotretinoin has been effective in treating severe acne, but it comes with side effects that should not be overlooked, including potential fetal malformations, dry skin and lips, nosebleeds, and photosensitivity [9]. Additionally, when topical treatments are ineffective, phototherapy is a viable option for controlling symptoms, although it may cause premature skin aging, pigment changes, and an increased risk of skin cancer with long-term use; hence, it is generally not recommended for children [10].
Research has demonstrated that traditional Chinese medicine is both safe and efficacious in the treatment of skin diseases. It has been shown to alleviate itching, decrease skin inflammation, enhance quality of life, reduce reliance on steroids and antibiotics, and prevent recurrence [11].
In order to comprehensively review the mechanism and state-of-the art of traditional Chinese medicine in repairing the skin barrier, a systematic search was conducted on major scientific databases, including Medline, PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Scopus, from 1 January 2013 to 31 November 2023. Manual searches were also conducted to find relevant articles. The literature search process aimed to cover a wide range of studies detailing the mechanisms and therapeutic potential of various TCMs. The specific keywords, ‘skin barrier’ and ‘mechanism of action’, along with their related synonyms and terms, were employed in the search. The criteria for selecting studies in this review were predetermined, and all peer-reviewed research articles, review papers, and clinical trial reports published in English were included. Articles that are not directly related to the pharmacological effects of traditional Chinese medicine and those focused solely on chemical synthesis without involving biological effects were excluded. A total of 149 articles were selected to review in this research.
2. Physiological Properties and Functions of Skin Barrier
The skin has a distinct network of immune functions that specialize in recognizing, processing, and presenting antigens. Functionally, the skin barrier can be categorized into four levels, namely the physical barrier, chemical barrier, microbial barrier, and immune barrier. These levels are interconnected and collaborate closely to uphold the skin’s health and defense mechanisms.
Hydrophobic lipids play a crucial role as the skin’s physical barrier, constructing a framework to secure mature keratinocytes. The lipid envelope comprises ceramides, fatty acids, and cholesterol, which interact within the matrix [12]. The alteration of the arrangement and structure of this lipid framework may lead to elevated transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and increased allergen infiltration [13]. Tight junctions (TJs) are integral in forming the side walls of cells, maintaining high solute concentrations between layers to restrict the transport of solutes and TEWL. They also play a crucial role in responding to barrier disruption, with their expression influenced by toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling. Increased TLR signaling can help prevent the entry of external antigens, microorganisms, and other substances into the skin, while also regulating substance transport, proliferation, and differentiation of epidermal cells, as well as lipid secretion [14]. Collectively, these structures and functions serve as the skin’s primary defense mechanism.
The chemical layer of the skin barrier consists of lipids, natural moisturizing factors (NMFs), and compounds that help maintain an acidic pH. These elements are crucial for keeping the skin barrier adequately hydrated, preventing dysbiosis, and optimizing pH for enzyme functions associated with keratinization, desquamation, and lipid synthesis [15]. Lipids in the stratum corneum (SC) protect the skin against TEWL, UV radiation, oxidation, and pathogens. Additionally, lipids also participate in various biological processes, such as biochemical signaling pathways, skin barrier repair, deactivating Staphylococcus spp., and shaping skin microbiota. However, lipids also interact with other Gram-positive bacteria to strengthen the physical barrier of the skin, acting as an extracellular ‘mortar’ within the SC [16].
The acid mantle plays a critical role in maintaining the skin’s physiological pH (in the range of 4 to 6), which is essential for homeostasis, fostering antimicrobial conditions, ensuring barrier integrity, and facilitating recovery [17]. Additionally, skin regeneration, desquamation, and lipid metabolism are closely related to skin pH. Proteases such as kallikrein-related peptidase (KLK) and cathepsin mediate skin desquamation by breaking down connections between keratinocytes in the SC [18]. Skin pH affects protease activity and lipid metabolism, thereby influencing the structure of the lipid bilayer in the SC. Ceramide precursors, such as glucosylceramide and sphingomyelin, are initially stored in lamellar bodies found within the stratum granulosum (SG) of the skin [19]. These precursor molecules undergo enzymatic modifications at the junctions between the SG and SC. Specifically, enzymes like β-glucocerebrosidase and acid sphingomyelinase catalyze these modifications to convert the precursors into ceramides. The ceramides are essential components of the intercellular lipids in the outermost layer of the skin [20]. Another important molecule in the skin is profilaggrin, which is primarily composed of L-histidine. The proteolysis of profilaggrin, releasing a significant amount of L-histidine, contributes to the formation of natural moisturizing factors (NMFs) in the SC [21]. Other than L-histidine, NMFs consist of a variety of components essential for maintaining skin hydration and barrier function, including pyrrolidone carboxylic acid, uric acid, lactic acid, urea, citrate, and various sugars. These compounds are naturally present in the skin or can be applied through skincare products like moisturizers to support the skin’s barrier function, maintain hydration and promote overall skin health [22].
Upon analysis of the microbial layer, researchers have discovered a diverse microbiota consisting of symbiotic microorganisms and bacteria that inhabit the outer surface of the dermis [23]. Commensal microorganisms interact with the chemical and immune layers of the skin barrier through signaling mechanisms with host keratinocytes. This interaction prompts the production of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), such as human beta-defensins (hBDs) and cathelicidins, which are crucial for inhibiting microbial growth on the skin’s surface [15]. Some human beta-defensins, like hBD-1, are constitutively expressed. On the other hand, defensins like hBD-2, hBD-3, and hBD-4 are induced and increased in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines and specific inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis [15]. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are produced by microorganisms like Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus hominis, demonstrating bactericidal properties against the pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus [24]. AMPs play a role in bridging innate and adaptive immune responses by promoting the migration of innate inflammatory cells, enhancing dendritic cells and T cells during infections, and potentially influencing antibody class switching [15]. AMPs may help strengthen the skin barrier by upregulating the proteins that constitute TJs. The presence of commensal microorganisms in the epidermis limits the space and nutrients available for potentially harmful microorganisms. Staphylococcus epidermidis, a healthy commensal organism, plays a role in upregulating TJs proteins and maintaining physical barriers, highlighting the interconnectedness of functional skin layers [25].
In the immune layer of the skin, immune cells play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the skin barrier. They recognize factors that can disrupt the barrier, communicate with commensal microorganisms, and activate immune pathways. The presence and recruitment of both innate and adaptive cell types ensures that they work together to establish the skin’s immune barrier [26]. Innate immune cells in the skin constantly monitor the external environment using pattern recognition receptors and selectively respond to factors that can breach the barrier. This includes epidermal Langerhans cells (LCs) and dermal dendritic cells (DCs), which play essential roles in detecting and responding to potential threats to the skin barrier. Resident T cells and keratinocytes possess the ability to initiate signaling pathways in response to damage to the skin barrier. Crucial interactions occur between the immune and microbial components of the skin barrier, which work together to maintain a healthy balance, prevent dysbiosis, and promote innate and adaptive immune responses. This interaction also serves to control the growth of commensal microorganisms, ultimately protecting against potentially harmful pathogens, such as Staphylococcus aureus. This regulation ensures that these microbial populations do not proliferate to levels that could provoke inflammation [27]. Keratinocytes play a crucial role in maintaining epidermal populations of immune cells through cytokine signaling. Resident memory T cells (Trm) are sustained by cytokinds such as IL-7, IL-15, and TGF-β, while LCs receive support from stimulating factor 1 ligand and TGF-B. Macrophages, on the other hand, rely on IL-34 for their maintenance. Additionally, keratinocytes possesses numerous pattern recognition receptors that can detect both pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) associated with microbial invasion and mechanical stress. This recognition leads to the activation of second messenger pathways such as NF-κB or MAPK, the expression of pro-inflammatory genes, the secretion of cytokines, and the initiation of cell-mediated inflammatory reactions [27].
The skin barrier plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health and overall body defense by preventing moisture loss, resisting harmful external substances, providing physical protection, supporting immune defense, facilitating sensation, and regulating temperature. Understanding the structural and physiological properties of the skin barrier is essential for effectively protecting and repairing it. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and employing scientifically backed skincare practices, individuals can maintain the integrity of their skin barrier, thereby enhancing overall skin health and ensuring that it remains resilient and functional in its protective role.
3. Skin-Related Diseases
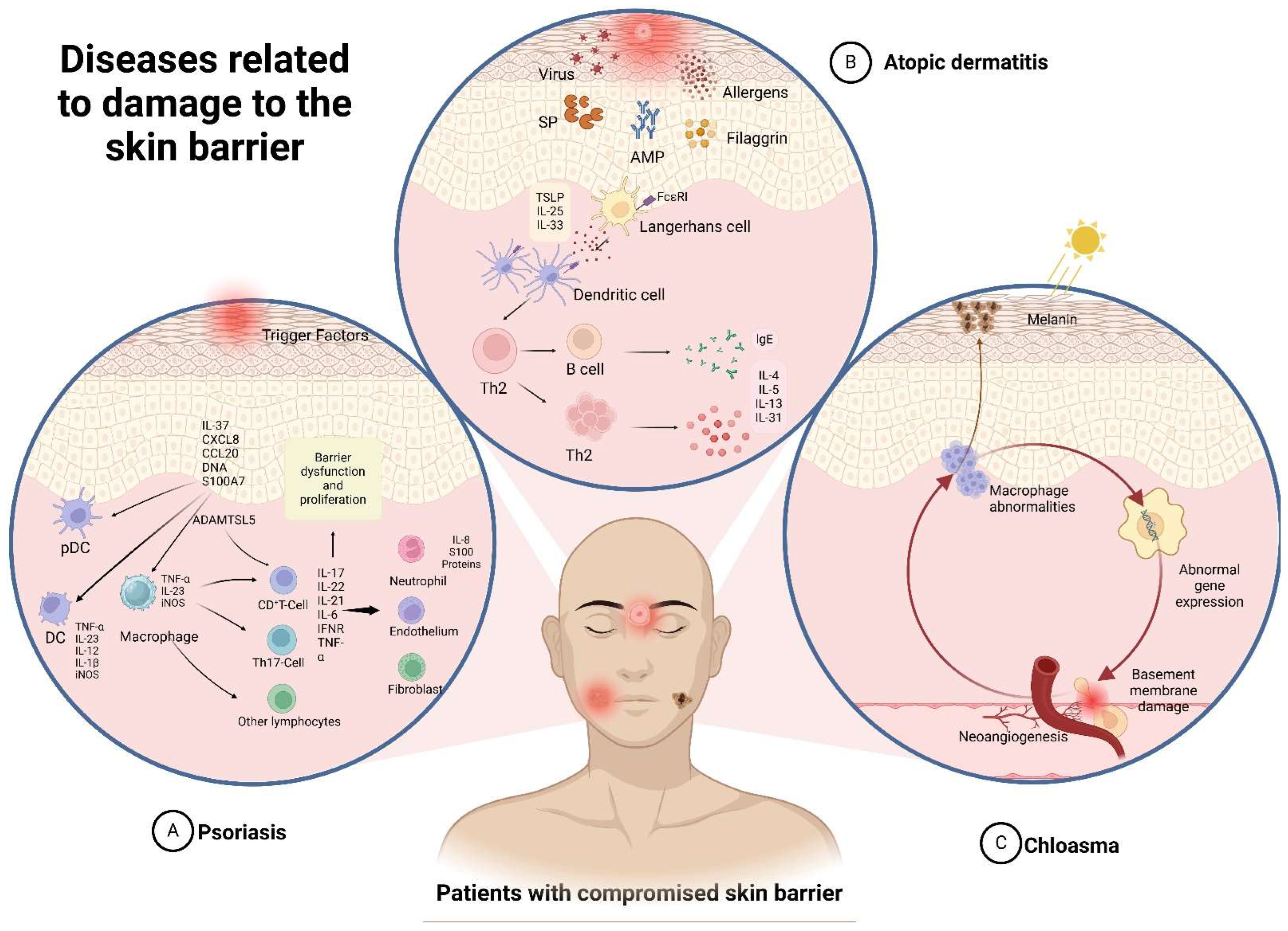
Impairment of the skin barrier’s function can lead to various common skin diseases, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and acne, and may also trigger urticaria and skin cancer. Clinical management typically involves the use of topical steroids, oral antihistamines, or topical moisturizers. However, these skin conditions often recur due to inadequate treatment, repeated allergen exposure, and chronic urticaria inflammation. The following subsection discusses the pathogenesis of several common skin diseases and their typical clinical treatments. Figure 2 illustrates the skin’s pathogenic mechanism.
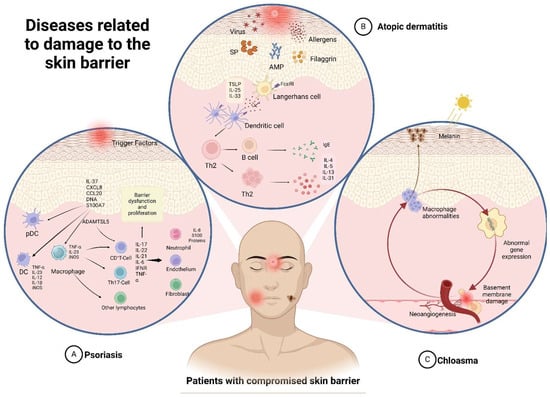
Figure 2.
Skin pathogenic mechanism.
3.1. Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by eczema, lichenoid lesions, and severe itching. Its pathogenesis is primarily associated with skin barrier dysfunction and immune dysregulation. AD is often associated with asthma, allergies, rhinitis, and other atopic diseases [28]. AD can affect approximately 12% of children and 7.2% of adults, with a higher prevalence observed among young children. Around 60% of children develop the disease before the age of 1, and 90% before the age of 5. The affected areas vary with age, and symptoms include changes in the skin and severe itching, significantly impacting the patient’s quality of life. Research has established a connection between the incidence of AD and keratinocytes, which are influenced by numerous factors. Additional studies have demonstrated that mutations in genes responsible for encoding proteins such as filaggrin and claudin-1 within keratinocytes contribute to the structural fragility of the SC and the increased permeability of TJs. This increased permeability facilitates antigen infiltration, activates dendritic cell (DCs), and triggers the release of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). These processes ultimately stimulate a type II adaptive immune response targeting the epidermis. Key cytokines involved in exacerbating barrier dysfunction include IL-4 and IL-13, which suppress filaggrin expression and interfere with TJs. Additionally, IL-4-activated B cells contribute to the production of IgE antibodies against both foreign and self-antigens. TSLP and IgE can trigger itching, perpetuating the disruption of the skin barrier [29]. This breakdown in the skin barrier can result in reduced levels of filaggrin, ceramide, and antimicrobial peptides. Additionally, there can be an increase in serine proteases and serum IgE levels, ultimately leading to immune dysfunction [30].
The prevalence of AD is increasing annually [31]. Various medications, including corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, antihistamines, and systemic immunosuppressants, are used for clinical treatment, but these drugs have their limitations. Topical corticosteroids (TCS) and calcineurin inhibitors (TCI) are the primary local treatments for AD and are extensively used in clinical practice. However, prolonged use of TCS on large areas of skin can lead to adverse local and systemic reactions (reference). Abrupt discontinuation of these medications can result in adverse effects, such as sleep disturbances, severe itching, skin pain, and discomfort, due to the complex interactions involving inflammatory cells and cytokines, which can compromise skin integrity [32].
3.2. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin disease characterized by chronic inflammatory signaling and the excessive proliferation of keratinocytes. It is characterized by thickening of the epidermis, the abnormal proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes, and infiltration of inflammatory cells into the skin layers. Psoriasis is characterized by erythema and papules, as well as round patches with silvery white scales as clinical symptoms. Although the exact cause is still unclear, most researchers believe that the abnormal proliferation and apoptosis of keratinocytes are among the main factors contributing to skin damage in this disease. Triggering factors can be classified into internal and external causes [33]. The pathogenesis of psoriasis involves both internal and external factors. Internal causes include genetic predisposition, immune dysregulation, environmental influences, and oxidative stress. External factors primarily involve damage to keratinocytes due to mild trauma, infections, sunburn, systemic medications, stress, physical injury, air pollution, and biological agents.
Psoriasis can occur at any age, but it is common in the elderly. The pathogenesis includes the overexpression of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and the activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), triggered by damaged keratinocytes. Proteins include LL37, β-defensin, and S100 proteins, which are released from damaged cells and contribute to the autoimmune response seen in psoriasis These substances form complexes that activate pDCs to produce type I interferon (IFN), thereby promoting the development of psoriatic plaques. Type I IFN signaling can further enhance the phenotypic maturation of myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) and participate in the differentiation and function of Th1 and Th17 cells. Additionally, pro-inflammatory dendritic cells release IL-23, which stimulates T cells to produce IL-17. This cascade activates epidermal keratinocytes to release pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, CXCL1, and CCL20, exacerbating the onset and progression of psoriasis symptoms [34].
Currently, there is a lack of reliable clinical diagnostic methods for psoriasis. Typically, doctors use the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) to assess the severity of the disease and determine suitable treatment options. While there is no definitive cure for psoriasis, treatment options vary from topical creams for mild cases to a combination of phototherapy and systemic medications for moderate-to-severe cases. However, these treatments have their limitations and may lead to side effects such as itching, flushing, and high blood pressure with prolonged use [35].
3.3. Chloasma
Chloasma is an acquired pigmented skin disease primarily influenced by factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, thyroid dysfunction, and so on. These factors lead to abnormal gene expression in exposed skin areas, impacting melanin metabolism, oxidative stress, skin barrier function, and the composition of neural factors [36]. Chloasma is common in young and middle-aged Asian women. It manifests as bilaterally symmetrical brown spots of varying shades, significantly affecting appearance and increasing psychological stress for patients. Further research has found that the formation of chloasma involves several factors, including excessive melanin production, an increased number of melanocytes and mast cells, abnormal gene regulation, neovascularization, and damage to the basement membrane. Ultraviolet (UV) rays play a significant role in promoting melanin production in the skin. Studies have shown that melanin production is regulated through various signal transduction pathways. Examples include Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/Akt, cAMP/PKA, and SCF/c-kit-mediated signaling pathways. UV irradiation leads to the expression of several melanocyte-specific genes and stimulates the release of key factors involved in melanin synthesis. This results in a significant increase in melanocyte-specific gene expression, thereby causing melanin synthesis. Melanin is significantly increased in the affected skin layers, which may be caused by abnormal cell–cell interactions. Furthermore, the pathogenesis of chloasma is known to be associated with inflammatory mediators, oxidative stress, neuroactive molecules, and sebocytes [37].
Because of its complex pathogenesis, chloasma treatment is difficult and can easily lead to recurrence, seriously affecting the patient’s life quality. Effective management of chloasma requires long-term treatment, and current treatment methods include the topical application of various substances, chemical peels, and laser therapy. Traditional treatment methods primarily involve laser elimination or the regeneration of fibroblasts to improve the skin environment. However, studies have shown that laser treatment can easily cause recurrence and damage facial collagen, leading to patient dissatisfaction [38] Topical drug options for chloasma include hydroquinone, retinoic acid, and glucocorticoids, among others. However, these treatments can be painful and have side effects, making them difficult for patients to tolerate. Consequently, there is an urgent need for new drug treatments that can improve the physiological and psychological conditions of patients with chloasma.
3.4. Other Related Diseases
Eczema is a common allergic inflammatory skin disease, mainly characterized by skin itching, scales, erythema, and exudation [39]. Approximately 20% of children and 1–3% of adults worldwide suffer from eczema [40]. In recent years, the incidence of eczema has been increasing, with complex and diverse causes. The condition is persistent and prone to recurrence. Severe cases can cause intense itching or cracking pain, significantly impacting patients’ daily life, work, and physical and mental health. The pathogenesis of eczema involves genetic and environmental factors, with immune cells and cytokines, such as TH2 (IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IL-31), TH17 (IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22, and IL-26), and TH9 cells, playing crucial roles in the disease’s development [41]. In terms of treatment, modern medicine utilizes topical glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors, glucocorticoids, antihistamines, immunosuppressants, and other drugs to manage eczema. Topical corticosteroids are often the first choices. However, long-term use can lead to drug resistance and poor patient compliance, necessitating combined systemic therapy. Abrupt discontinuation of steroids may cause adverse reactions, so treatment should be administered with caution [42].
Acne is a chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting the pilosebaceous glands. Its primary clinical features include various lesions on the face, chest and back, such as comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, cysts and scars. The condition typically manifests during adolescence and can persist for years. Symptoms often improve or resolve after adolescence, with non-inflammatory or inflammatory acne commonly appearing on the face, neck, trunk, and back [43]. Acne activates innate immunity via the expression of protease activated receptors (PARs), tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α and toll-like receptors (TLRs), and the production of interferon (INF) γ, interleukins (IL-8, IL12, IL-1), TNF, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) by keratinocytes, resulting in the hyperkeratinization of the pilosebaceous unit [44]. Current medical treatments for acne primarily involve topical benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, or retinoic acid, as well as oral medications like minocycline and zinc sulfate. While these treatments can achieve certain clinical effects, prolonged use may lead to the development of drug-resistant strains of bacteria, such as increased levels of Propionibacterium acnes, elevated blood lipid levels, and other side effects. Acne is also prone to recurrence if not promptly and effectively treated, potentially leading to scarring and psychological issues that impact patients’ life quality [45].
Mast cells are the primary effector cells in urticaria. These cells are widely distributed in the skin, mucosa, and other areas of the body, and they have high-affinity immunoglobulin E (IgE) receptors. Mast-cell degranulation leads to the rapid release of various inflammatory mediators, such as histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins, which, in turn, cause vasodilation and leakage of plasma in and below the skin. There is also a more delayed (4–8 h) secretion of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 4 and 5) that potentially leads to further inflammatory responses and longer-lasting lesions [46].
DNA damage serves as a critical link in the development of skin cancer. When the skin barrier is compromised, carcinogens are more likely to penetrate skin cells and directly impact the cell’s DNA. This interaction can trigger mutations in the genetic material of the cells, leading to a loss of control over the normal processes of cell growth and differentiation [47]. Research indicates that exposure to harmful external substances and carcinogens can elicit an inflammatory response in the skin. Prolonged chronic inflammation may result in abnormal cell proliferation and an imbalance in apoptosis, thereby heightening the risk of skin cancer [48]. Additionally, research has demonstrated that the immune system is crucial in eliminating abnormal cells and preventing tumor development. When the skin barrier is compromised, the functionality of immune cells may be impaired, allowing abnormal cells to evade detection by the immune system, thereby increasing the risk of skin cancer [49]. In summary, damage to the skin barrier makes it easier for carcinogens to enter the skin, and increases the risk of skin cancer through multiple mechanisms such as causing DNA damage, promoting chronic inflammation, and weakening immune function. Therefore, maintaining the integrity and health of the skin barrier is of vital importance in preventing the occurrence of skin cancer.
4. The Mechanism and Targets of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Restoring Skin Barrier
In recent years, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has assumed a crucial role in treating skin diseases. It is noted for its significant therapeutic effects and minimal side effects, positioning it as an alternative therapy for managing and controlling various skin conditions. There is a growing demand for natural plant-based products, further boosting TCM’s popularity in dermatological treatments. Recent studies have demonstrated that the bioactive components of TCM effectively repair the skin barrier. These findings not only establish a theoretical basis for, but also highlight the practical value of using TCM in clinical treatments for skin diseases.
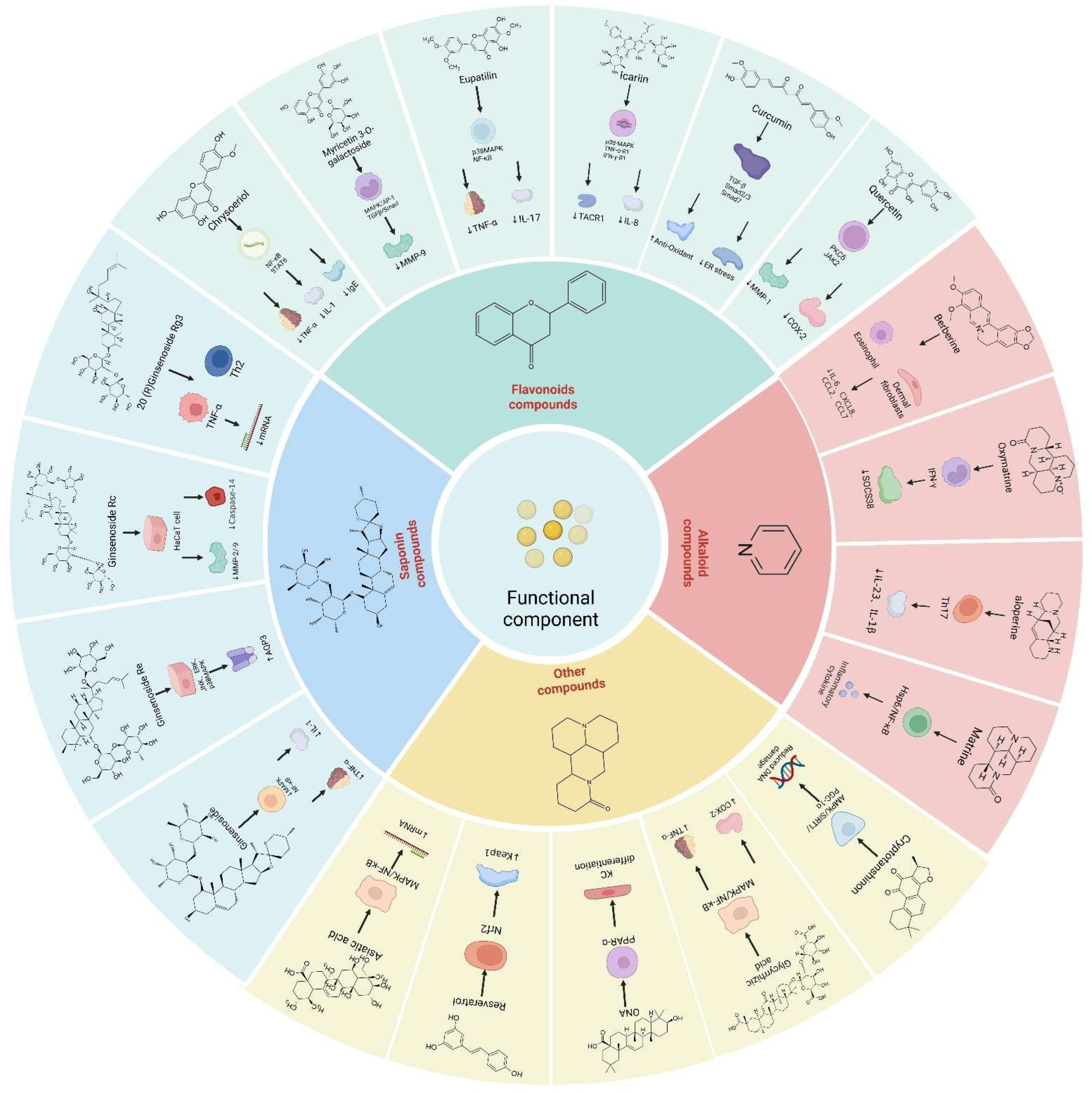
The mechanism of action of the bioactive constituents (functional factors [50]) of TCM in repairing the skin barrier is intricate and involves multiple signaling pathways. External stimuli can activate several signaling pathways, including the p38 protein kinase, NF-κB, MAPK, Keap1-Nrf2-ARE, Nrf2/ARE, and TRPV1 [51]. The activation of these pathways triggers a cascade of biological reactions, such as caspase-3 activation, oxidative stress, the abnormal expression of MMPs, inflammatory responses, DNA damage, autophagy, and excessive melanin synthesis. The bioactive constituents of TCM can enhance skin barrier function and promote repair by modulating these mechanisms. Figure 3 shows the mechanisms of action of functional factors.
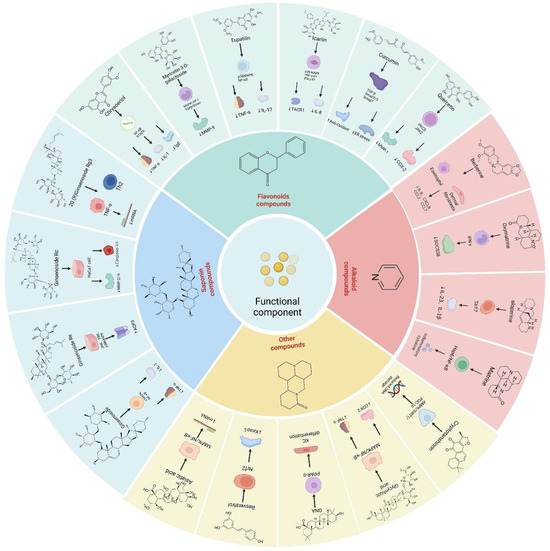
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of action of functional factors.
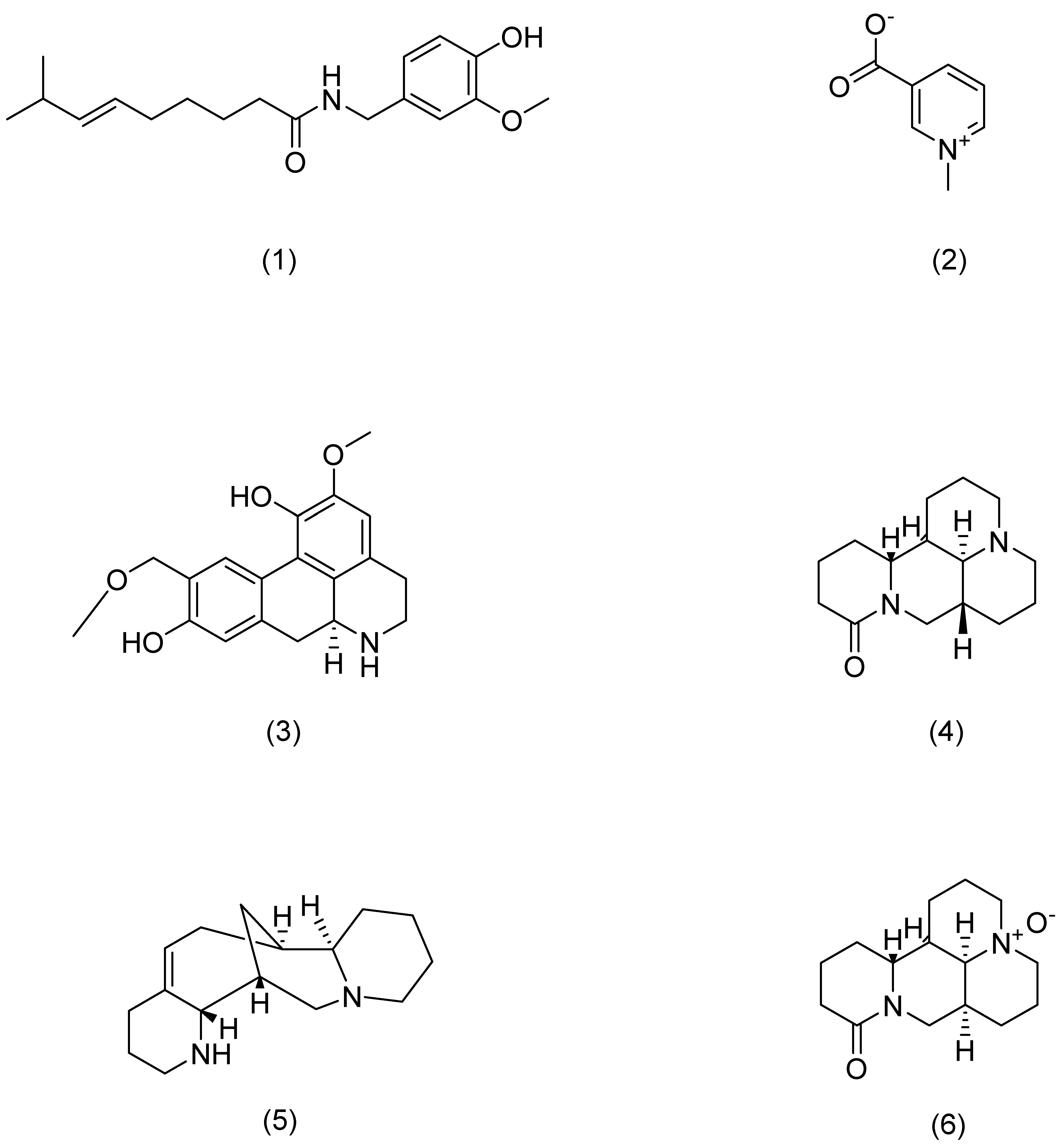
4.1. Ginsenoside
Ginsenosides, extracted from the roots, stems, and leaves of ginseng, are recognized as pharmacologically active compounds that contribute significantly to skin barrier repair. They exhibit various beneficial properties, including immune enhancement, metabolic boosting, anti-tumor effects, fatigue reduction, and anti-aging properties [52]. Ginsenosides are widely utilized for their protective and therapeutic effects on various systems, including the cardiovascular, nervous, immune, and endocrine systems. Additionally, studies have highlighted their diverse biological functions, such as anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties [53].
Further research has demonstrated that ginsenosides have significant effects on the treatment of AD. Kim et al. showed that ginsenoside Rh2 and Rg3 can reduce the increase in TNF-α and IL-4 mRNA expression induced by TNCB, exerting anti-inflammatory effects and inhibiting TNF-α mRNA expression in vivo, thus effectively treating AD in mice [54]. Additionally, Kee et al. conducted a study using mouse models of anaphylactic shock and AD-like skin lesions to evaluate the anti-allergic effects of Korean red ginseng. Their findings indicated that the aqueous extract of Korean red ginseng was effective in reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting the release of TNF-α [55].
Sohn et al. conducted an experiment using DNCB to induce AD-like skin lesions in Balb/c mice, monitoring their scratching behavior and measuring the levels of IL-4, IL-10, serum IgE, and splenocytes through reverse-transcription methods. They utilized various techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, and ELISA to assess Korean red ginseng’s effects on DNCB-induced MAPKs and Ikaros. The study demonstrated that topical Korean red ginseng administration significantly improved AD symptoms and reduced scratching behaviors in mice. The Korean red ginseng exhibited notable effects in the mouse model of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) induced by DNcB. Specifically, in these AD-like mice, the topical application of RG led to significant improvements in the skin lesions associated with the condition. Furthermore, RG also resulted in a reduction of cytokines activated by Th2 cells, including IL-4 and IL-10, along with a decrease in serum IgE levels. The anti-atopic effects of RG appear to be primarily mediated through the modulation of specific signaling pathways. In particular, RG seems to inhibit the MAPK signaling cascades, which encompass ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK. Concurrently, RG activates CK2α, which in turn plays a role in further reducing the transcriptional activity of Ikaros. This inhibition of Ikaros by RG seems to contribute to a downregulation of IL-4 and IL-10 expression in splenocytes [56].
Numerous studies on skin anti-aging demonstrate that ginsenosides play a crucial role in effectively treating skin barrier damage induced by ultraviolet radiation. Oh et al. conducted a detailed study investigating the skin-protecting effects of ginsenoside Rc against UVB-induced damage using HaCaT cells. Their research highlighted ginsenoside Rc’s potential in counteracting photoaging and preserving skin barrier function. The results indicated that ginsenoside Rc effectively inhibited the increase in ROS production and MMP-2/-9 levels in UVB-exposed HaCaT keratinocytes. Additionally, the ginsenoside Rc maintained GSH content and SOD activity; GSH and SOD are crucial antioxidants in skin cells. Moreover, the ginsenoside Rc promoted caspase-14 activity and prevented the downregulation of filaggrin expression, thereby supporting its role in protecting against UVB-induced skin damage and aging [57].
Oh et al. assessed the skin anti-photoaging properties of ginsenoside Rb1 in human dermal HaCaT keratinocytes. Their findings demonstrate that ginsenoside Rb1 boosts the antioxidant capacity of keratinocytes by neutralizing ROS and decreasing MMP-2 levels. These effects contribute to the anti-aging benefits of ginsenoside Rb 1, highlighting its potential in protecting skin cells against photoaging [58].
Li et al. employed the UVB-irradiated BALB/c hairless mouse model to assess the efficacy of ginsenoside in preserving skin epidermal thickness and reducing TEWL. They also investigated the impact of ginsenoside on filaggrin (FLG) degradation, skin barrier function as indicated by involucrin (IVL) protein levels, claudin-1 (Cldn-1) expression, aquaporin 3 (AQP3) levels, and MAPK phosphorylation. The findings indicated that the ginsenoside enhanced epidermal barrier function after damage by UVB and reinstated the levels of protein expression and distribution for FLG, IVL, Cldn-1, and AQP3 in the epidermis. Additional research revealed that ginsenoside suppressed JNK in HaCaT cells irradiated with UVB, as well as ERK phosphorylation and the p38MAPK pathway, resulting in the increased expression of IVL and AQP3 [51].
In a study by Liu et al., the potential of ginsenoside C-Mx in protecting human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) from UVB-induced damage was explored. The findings indicated that the ginsenoside C-Mx demonstrated the ability to mitigate the intracellular expression of ROS, MMP-1, and IL-6 induced by UVB while promoting the secretion of TGF-β and type I procollagen. Additionally, the ginsenoside C-Mx was able to counteract the UVB-induced decrease in type I procollagen by modulating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Furthermore, it was observed that the ginsenoside C-Mx inhibited the activation of the MMP inducer AP-1 transcription factor. This compound also displayed significant antioxidant properties by enhancing the nuclear accumulation of Nrf2, resulting in the increased expression of cytoprotective antioxidants like HO-1 and NQO-1 [59].
Overall, the study revealed that ginsenoside C-Mx holds promise as a protective agent against UVB-induced damage in human dermal fibroblasts. Its ability to regulate key pathways, such as TGF-β/Smad signaling, and inhibit the activation of MMP inducer AP-1 transcription factor demonstrates its potential in restoring cellular health and promoting collagen production. Additionally, the antioxidant capacity of ginsenoside C-Mx, as evidenced by its impact on the expression of cytoprotective antioxidants, further highlights its beneficial effects in combating oxidative stress and maintaining cellular integrity. This comprehensive protective mechanism underscores the therapeutic potential of ginsenoside C-Mx in skin-care and anti-aging applications.
In summary, ginsenosides can exert their skin-protecting properties by inhibiting multiple signaling pathways, such as JNK, ERK phosphorylation, p38MAPK, and NF-κB. By modulating these pathways, ginsenoside contributes to the improvement and repair of the skin barrier. This provides new directions for treating various skin diseases, offering potential therapeutic benefits in enhancing skin health and mitigating damage. Table 1 lists the ginsenosides’ mechanisms of action.

Table 1.
Ginsenosides’ mechanisms of action.
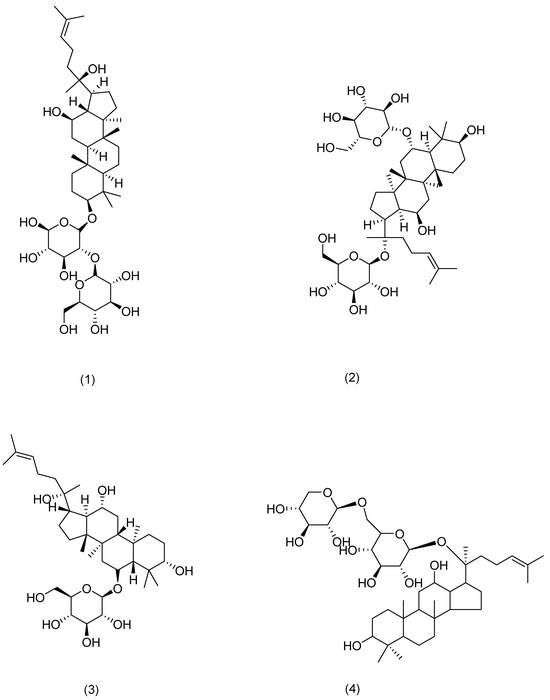
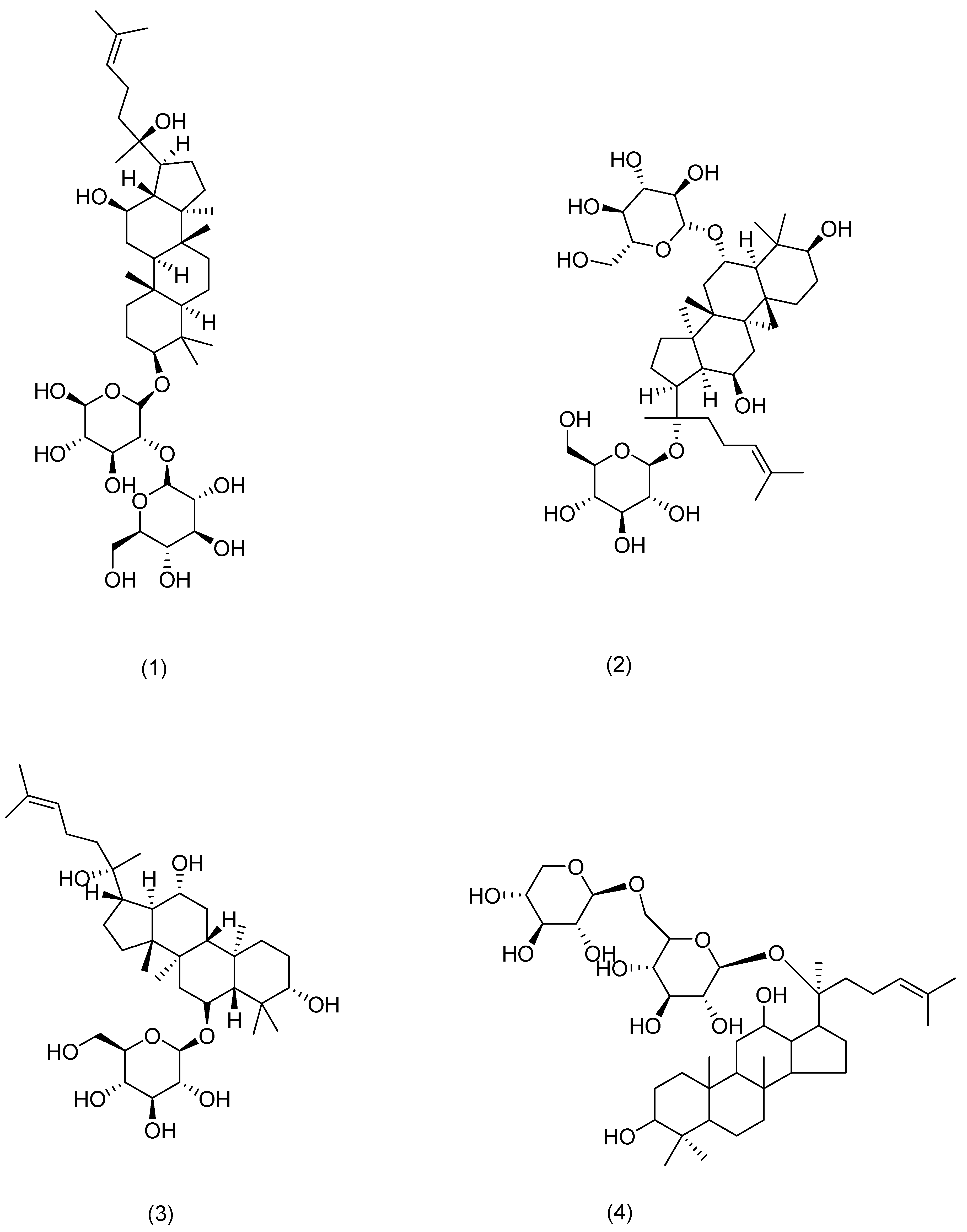
Figure 4.
Structural formula of ginsenosides.
4.2. Flavonoids
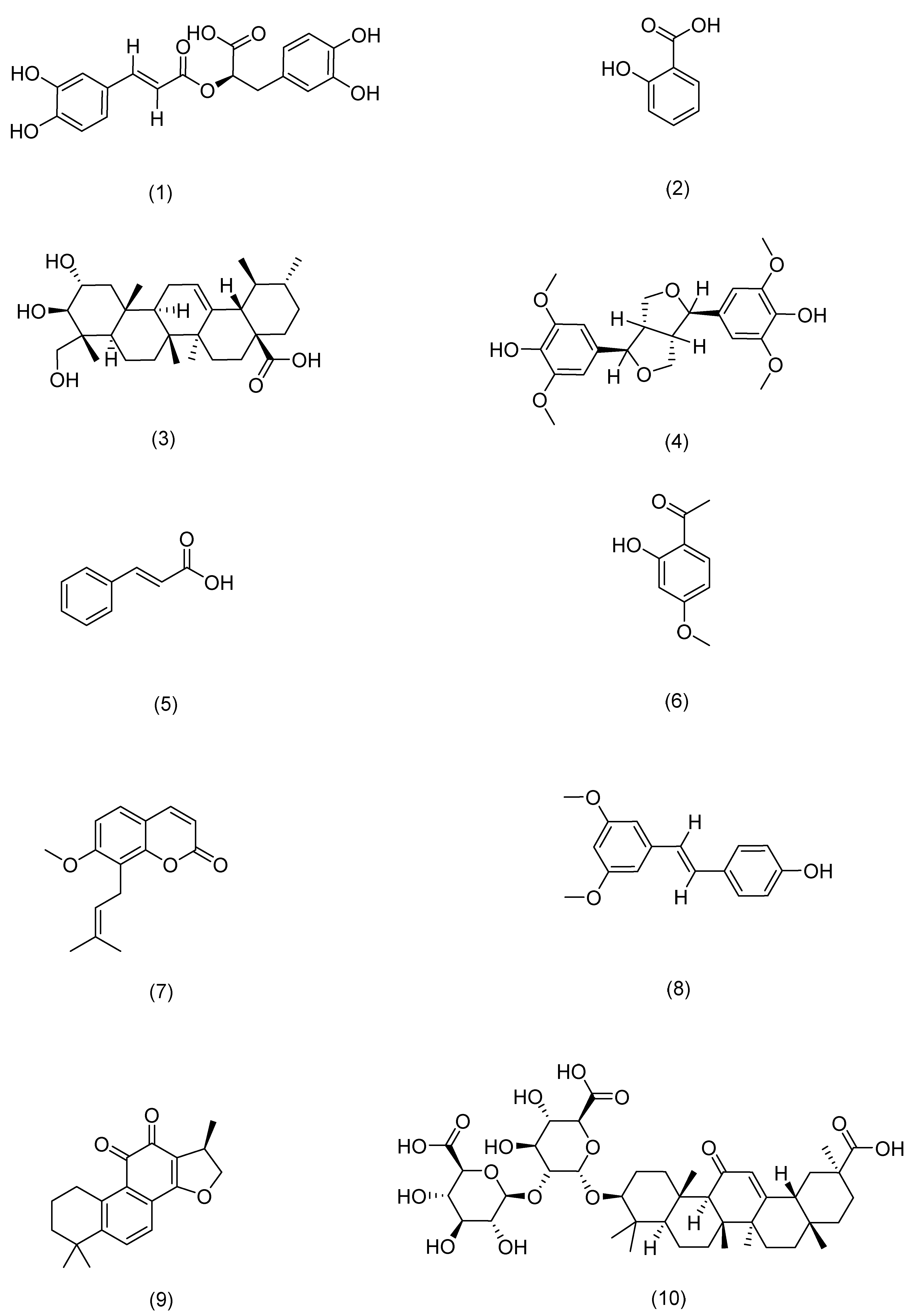
Natural flavonoids are commonly found in plants as either O-glycosides or C-glycosides. Research indicates that these compounds are crucial for various biological functions and offer numerous health benefits, such as reducing inflammation, combating oxidative stress, preventing mutations, inhibiting cancer growth, and fighting off bacteria. They have the capacity to shield cell membranes, reduce cholesterol levels, combat atherosclerosis and cancer, alleviate spasms, and function as antioxidants, inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase, and agents for photoprotection [64]. These multifaceted properties underscore the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in promoting overall health and preventing a wide range of diseases.
Flavonoids exhibit targeted effects in repairing the skin barrier. Studies have found that aureiodictyin reduces the protein levels of phosphorylated p65 (Ser536), phosphorylated STAT3 (Tyr705), inducible iNOS, COX-2, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the swollen ears of mice. In vitro experiments also demonstrated its ability to decrease the production of NO and prostaglandin E2 by cells, inhibit the phosphorylation of κB (Ser32), p65 (Ser536), and Janus kinase 2 (Tyr1007/1008), reduce the nuclear localization of p50, p65, and STAT3, and lower the mRNA levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1, IL-3β, and TNF-α, which are transcriptionally regulated by NF-κB and STAT6 in cell models [65].
Sangaraju et al. studied the effect of galangin (GAL) on IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation. The GAL significantly reduced the IMQ-induced PASI score, as well as skin and ear thickness, hematological markers, and nitrite levels. It also regulated the protein levels of pro-inflammatory mediators COX-2 and iNOS, the NF-κB pathway, and pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-17, IL-23, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the skin. Additionally, compared to the IMQ group, the GAL restored the levels of antioxidant markers such as SOD, CAT, GST, GSH, GR, and Vit-C, the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, and the protein Nrf2/HO-1 in the skin [66].
Flavonoids demonstrate therapeutic effects on various skin diseases. Luteolin 7-O-glucoside has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory effects in AD [67]. Research indicated that luteolin 7-O-glucoside reduces serum IgE and IL-4 levels, increases skin hydration, and exhibits strong anti-atopic dermatitis activity. Bai et al. investigated the effects of isoflavins from mugwort leaves on psoriasis using HaCaT cells and an IMQ-induced mouse model. In vitro experiments revealed that isoflavins inhibited the p38-MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, thereby reducing the excessive proliferation of HaCaT cells stimulated by LPS. In vivo studies showed that isozoranthin reduced TNF-α, IL-6, IL-23, and IL-17 levels in the sera of mice, effectively alleviating IMQ-induced psoriasis in mice [68]. Liu et al. utilized IMQ or TNF-α to induce psoriasis-like models in mice or HaCaT cells to study the effects of cimiculin. The results demonstrated that cimiculin reduced epidermal hyperplsia, PASI scores, ear thickness, and histological psoriasis-like lesions in mice. Cimiculin also lowered levels of GSH, SOD, and CAT. Mechanistically, cimiculin inhibited the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-17A, and IL-22. It achieved this by inhibiting the phosphorylation of NF-κB (IκB and p65) and MAPK (JNK, ERK and p38) signaling pathways activated by IMQ. Additionally, cimiculin induced the downregulation of ICAM-1 and inhibited inflammatory factors in TNF-α-treated cells [69].
Xiong H et al. used a TNF-α-induced HaCaT cell inflammation model and an IMQ-induced psoriasis animal model to study the effects of glycyrrhizic acid (GL) on the skin. In vitro experiments showed that the GL reduced the level of ICAM-1 in TNF-α-stimulated HaCaT cells, inhibited monocyte adhesion to keratinocytes, suppressed the phosphorylation of p65 after IκB degradation, and blocked ERK and the phosphorylation of p38-MAPK. In vivo experiments demonstrated that GL delayed the onset of psoriasis in mice, thereby reducing ICAM-1 expression in epidermal tissue [70].
Kong et al. studied how icariin inhibited the inflammatory response induced by TNF-α/IFN-γ through the p38-MAPK signaling pathway in human keratinocytes. The results showed that icariin inhibited the production of IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and MCP-1 induced by TNF-α/IFN-γ. Additionally, icariin reduced IL-8 and IL-1β in HaCaT cells, as well as the expression of ICAM-1 and TACR1 genes, indicating that icariin mediated these effects by inhibiting the p38-MAPK signaling pathway and regulating TNF-α-R1 and IFN-γ-R1 signals [71]. Table 2 lists flavonoids’ mechanisms of action.

Table 2.
Flavonoids’ mechanisms of action.
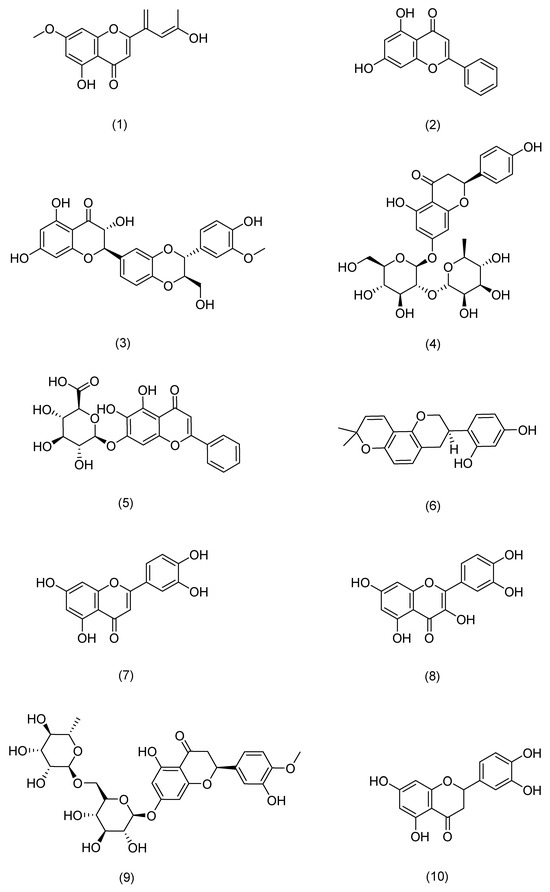
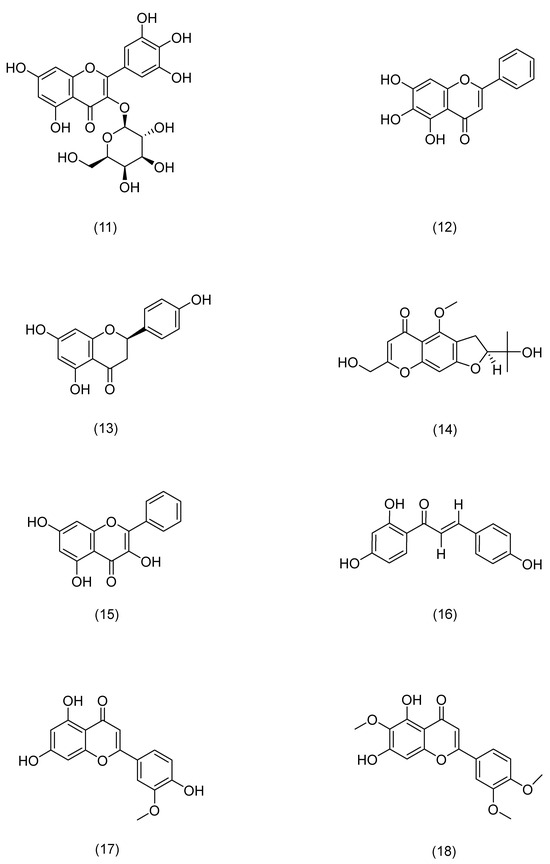
Figure 5.
Structural formula of flavonoids.
4.3. Alkaloid
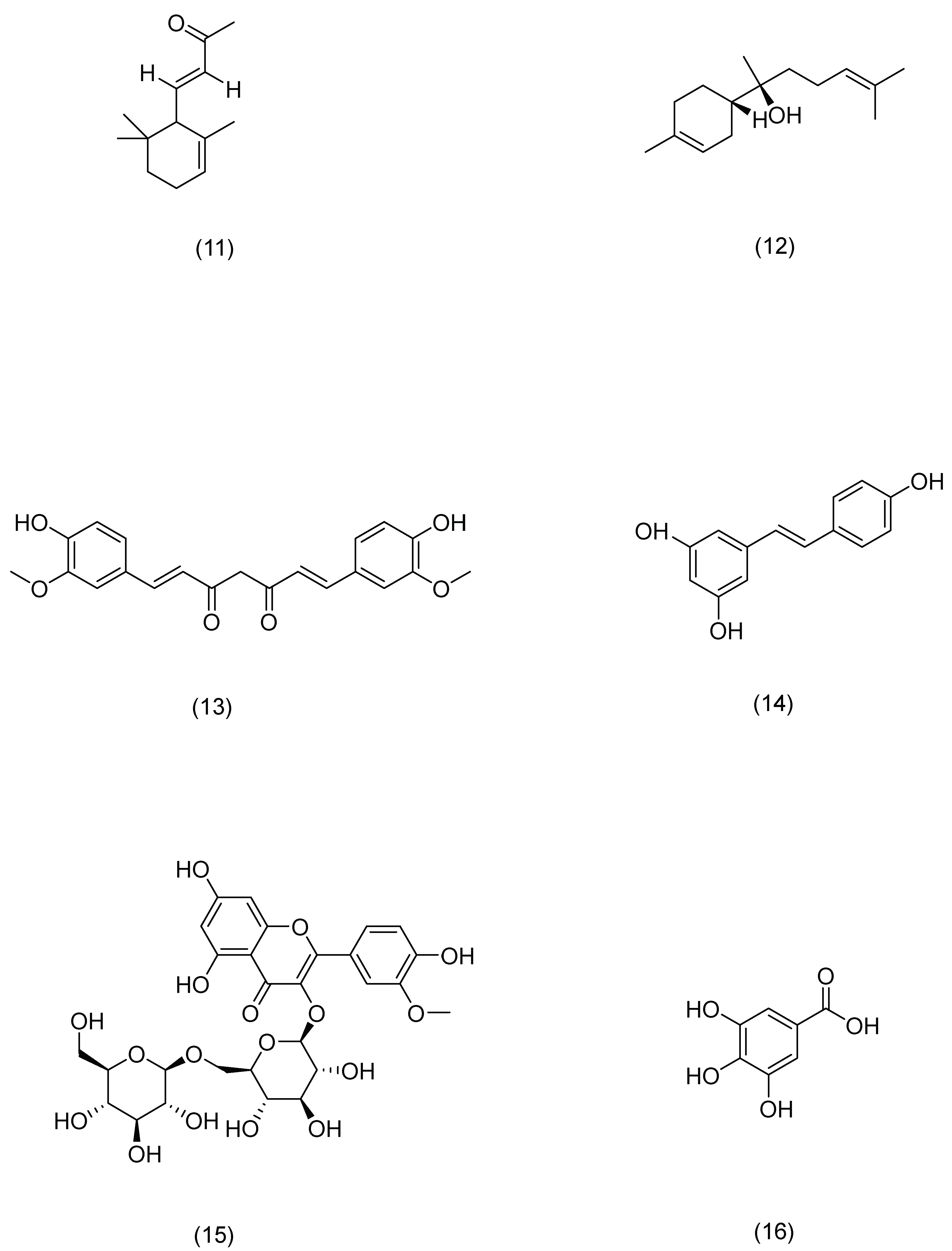
In traditional Chinese medicine, alkaloids constitute a category of naturally occurring organic chemicals commonly found in a variety of Chinese herbal remedies. They possess complex structures and exhibit a wide array of biological activities, including anti-tumor, anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, analgesic, and immune regulatory effects. Alkaloids are employed in medicine as local anesthetics, stimulants, analgesics, anticancer drugs, antihypertensive agents, and antiarrhythmic medications [86].
Studies have demonstrated significant the therapeutic effects of traditional Chinse medicine alkaloids on skin-related diseases. Gao et al. used TNF-α and IFN-γ to stimulate HaCaT cells and treated them with oxymatrine. The results showed that the oxymatrine sensitized the HaCaT cells to the IFN-γ pathway and repaired the skin barrier by activating p1, JNK, and Akt, while downregulating MDC, ICAM-1, and SOCS1 [87]. Chan et al. investigated the pathological changes in psoriasis-like inflammation induced by the transdermal delivery of capsaicin. The authors used an imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like mouse model to evaluate the therapeutic effect of the topical application of capsaicin. The results demonstrated that capsaicin administration inhibited the imiquimod-induced activation of IL-23/IL-17 pathways. Psoriasis-like erythematous appearance and microscopic features were significantly reduced, along with a notable decrease in the tissue gene expression of core psoriasis cytokines, such as IL-23, IL-17A, IL-22, TNF-α, and IL-6, after the capsaicin treatment [88].
Huang et al. explored the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of matrine on AD. The results showed that matrine reduces the expression of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) and decreases the levels of Th2 cytokines in ear tissue and serum. Additionally, it inhibits the Hsp6/NF-κB signaling axis in HaCaT cells, thereby suppressing the secretion of inflammatory cytokines. These findings suggest that matrine can modulate Th2/Th90 inflammatory responses and potentially alleviate skin-related diseases [89].
Tsang et al. investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of berberine in AD-like skin inflammation. The authors found that berberine effectively inhibits the release of IL-6 in eosinophil culture and eosinophil–dermal fibroblast co-culture, as well as the release of CXCL8, CCL2, and CCL7. This action helps to improve allergic inflammation and mitigate the activation state of eosinophils [90].
Norisoboldine, an isoquinoline alkaloid from Wuyao, was investigated for its impact on NFAT activation and its potential in treating AD. The study utilized a luciferase gene assay, K562-luc cells, and Western blotting to examine NFAT dephosphorylation in K562-luc and Jurkat cells. Additionally, real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR was employed to detect IL-2 expression in Jurkat cells. The results indicated that norisoboldine inhibited IL-2 expression in Jurkat cells induced by PMA plus ionomycin, and reduced mRNA levels of INF-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, and IL-6 in mouse ears [91].
Zhou et al. investigated the therapeutic effect of squamine on psoriasis using flow cytometry, Western blot analysis, and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR for analysis. The findings revealed that the squamine not only inhibited Th17 differentiation, but also suppressed dendritic cell activation, thereby reducing the expression and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-23 and IL-1β [92].
Alkaloid compounds have demonstrated extensive potential in repairing the skin barrier. They achieve this by inhibiting various proteins and inflammatory factors through mechanisms such as IFN-γ pathway inhibition, Hsp6/NF-κB signaling suppression, the modulation of Th2 and Th17 differentiation, and reductions in inflammatory factor mRNA expression. Notably, alkaloids inhibit IL-23, IL-1β, and IL-6, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, promoting cell proliferation and differentiation, and enhancing skin barrier function. These compounds hold promise for treating damaged skin barriers. Future research should delve deeper into their specific molecular mechanisms and explore their clinical applications to offer more treatment options for skin barrier dysfunction. Table 3 summarizes alkaloids’ mechanisms of action.

Table 3.
Alkaloids’ mechanisms of action.
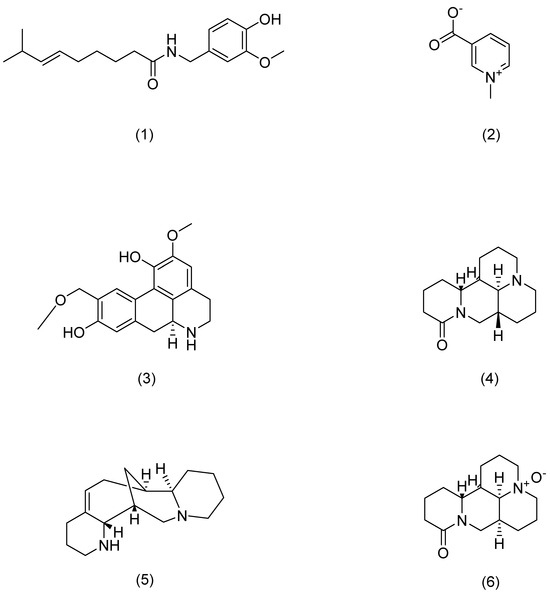
Figure 6.
Structural formula of alkaloids.
4.4. Carbohydrates
Polysaccharides are polar complex macromolecular compounds composed of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds, with a degree of polymerization exceeding 10. Polysaccharide drugs possess intricate molecular structures, perform diverse biological functions, and interact with multiple molecular targets [94]. Consequently, they play crucial roles in Chinese herbal medicine, in which various polysaccharides exhibit activities such as anti-tumor, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-radiation, anti-viral, hypolipidemic, and immunomodulatory effects [95]. As a result, polysaccharides have garnered significant attention in both scientific research and traditional medicine practices.
Carbohydrate compounds play a significant role in repairing the skin barrier. Li et al. studied the effects of ginseng oligosaccharide extract (GSO), demonstrating its ability to reduce UVB-induced epidermal thickening and water loss. Additionally, GSO improved levels of FLG, IVL, and AQP3 proteins. Further investigation revealed that mRNA and related proteins associated with desquamation, such as SPINK5, KLK5, KLK7, and DSG1, returned to normal levels [96].
Li et al. investigated the photoprotective effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide (LBP) on UVB-induced photodamage in HaCaT cells. The findings indicated that LBP reduced cell viability, ROS production, and mitigated DNA damage. Moreover, LBP inhibited p38 MAPK activation, reversed caspase-3 activation, and suppressed MMP-9 expression. LBP promoted Nrf2 nuclear translocation and increased the expression of Nrf2-dependent ARE target genes [97].
Chen et al. explored the effects and mechanisms of astragalus polysaccharide (APS) in improving imiquimod-induced psoriasis in mice. The authors measured inflammatory factor secretion using ELISA and skin macrophage infiltration by flow cytometry to assess the APS’s impact on psoriasis. The results demonstrated that high-dose APS significantly reduced skin-tissue macrophage infiltration. APS improved psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice by inhibiting skin macrophage infiltration and reducing serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 [98].
Yuan et al. utilized BALB/c female mice as animal models and nerve growth factor (NFG)-activated PC12 cells as cutaneous nerve cell models to investigate the repairing effects of aloe polysaccharide (AP) on UVB-damaged nerve cells. The authors employed an MTT assay for cell viability analysis, TUNEL and annexin-V/PI staining for cell apoptosis detection, flow cytometry (FCM) for cell-cycle analysis, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity assessment, and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR plus Western blotting for detecting levels of Bax, Bcl-2, Caspase-3, Cyclin D1, Keap1, Nrf2, GCLC, and GSTP1 expression. The results demonstrated that AP inhibited cell apoptosis, enhanced cell viability, and improved antioxidant capacity in UVB-damaged never cells. Furthermore, AP upregulated the expression levels of Keap1, Nrf2, GCLC, and GSTP1, indicating the activation of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. These findings suggest that AP not only repairs UVB-induced damage in nerve cells, but also ameliorates UVB-induced damage in NFG-activated skin nerve cells through the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway [99].
In summary, polysaccharides exhibit potential in repairing skin barrier damage by enhancing cellular functions and modulating signaling pathways such as Keap1/Nrf2/ARE and MAPK. This capability extends to improving skin diseases associated with barrier dysfunction, laying a foundation for future research in this area of dermatology. Table 4 summarizes carbohydrates’ mechanisms of action.

Table 4.
Carbohydrates’ mechanisms of action.
4.5. Other Compounds
Other compounds, such as coumarins, phenolic acids, and pentacyclic triterpenoids, also play a role in repairing the skin barrier.
The effects of gallic acid following topical skin application were investigated by monitoring transepidermal water loss, erythema index, and protein expression [100]. The study’s results indicated that the expression levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), interleukin-6, and matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) were significantly inhibited in skin treated with gallic acid. This effect effectively reduces skin dryness, thickness, and wrinkle formation by negatively regulating the secretion of MMP-1 while positively regulating the expression of elastin, type I procollagen, and transforming growth factor-β1. After exploring the protective effects and potential mechanisms of GA on psoriasis-like skin diseases in vitro and in vivo [101], the results showed that GA can significantly reduce the mRNA and protein expression levels of psoriasis-related keratin 16 and keratin 17. In addition, GA significantly improved the skin lesion area and severity scores of psoriasis-like mice, while also significantly reducing epidermal hyperplasia in the mice. The study also found that GA inhibited Nrf2 activity in the process of targeting keratin 16 and keratin 17. The study investigated the effect of GA on the inflammatory response induced by DNCB. The experiments involved measuring the thicknesses of mouse ears and conducting histopathological examinations. Additionally, changes in serum levels of IgE and TNF-α were analyzed to elucidate the mechanism of action of GA. The mRNA expression levels of TNF-α, IL-4, IFN-γ, and IL-17 were assessed to understand the impact of GA on lymph nodes. The study also examined the influence of GA on regulatory T cells (Treg) and TH17 cells. The results demonstrated that the GA significantly reduced the thicknesses of the mouse ears. Compared to the model group, the serum IgE and TNF-α levels were markedly lower in the GA group. Furthermore, the lymph node weight, as well as the TNF-α levels in the lymph nodes of the mice treated with the GA, showed significant reductions. The expression of IL-4, IFN-γ, and IL-17 mRNA was also significantly decreased. In comparison to the model group, the expressions of IL-4, IL-5, IL-17, and IL-23 were reduced, while the expressions of IL-10 and TGF-β were significantly increased. The analysis of the Th17 cell signature genes revealed that the ROR-γt expression was significantly lower in the GA group, whereas the SOCS3 expression was elevated. These findings suggest that GA exerts a therapeutic effect on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis (AD) inflammation [102].
Oleanolic acid, a common pentacyclic triterpenoid found widely in plants in its free acid form, exhibits various pharmacological activities, including hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties [103]. Studies have indicated that oleanolic acid and its derivatives can enhance the recovery of the mouse epidermal permeability barrier. For instance, experiments involving tape-stripped mouse skin assessed parameters such as TEWL, hydration levels, and morphological changes using electron microscopy. The findings revealed improvements in TWEL stability, the increased presence of secretions and lamellar bodies, and the notable formation of lipid bilayers. Moreover, in HaCaT cells treated with ursolic acid (UA) and oleanolic acid (ONA), protein expression levels of PPAR-α, involucrin, loricrin, and filaggrin were significantly enhanced, be twofold and threefold, respectively, indicating that these compounds promote epidermal keratinocyte differentiation and contribute to skin barrier function recovery through the PPAR-α pathway [104].
Tsang et al. explored the anti-inflammatory effects of gallic acid and chlorogenic acid in AD-like skin inflammation. The experiments demonstrated that these compounds effectively inhibit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 in IL-31- and IL-33-treated eosinophil–dermal fibroblast co-cultures, as well as the release of chemokines CCL7 and CXCL8 [90].
In a study conducted by Kim et al., the therapeutic effects and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Terminalia chebula extract, a traditional Chinese medicine, were investigated in an in vivo AD mouse model. The findings revealed that the extract decreased serum levels of IgE, histamine, and inflammation-related mediators, such as MDC, TARC, RANTES, and TSLP. Additionally, the extract strongly inhibited the expression of inflammatory chemokines RANTES and MDC in HaCaT cells stimulated with IFN-γ/TNF-α. This inhibition was associated with the suppression of phosphorylated STAT1/3 and NK-κB subunits, as well as the nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Furthermore, the extract effectively suppressed the transcription of IFNγ, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 in IFNγ/TNF-α-stimulated HaCaT cells, demonstrating its potential for treating AD [105].
Similarly, Song et al. studied the therapeutic effect of galangal extract on AD mice. The results showed that the extract inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory factors such as MDC, RANTES, IP-10, and I-TAC in HaCaT cells stimulated by IFN-γ and TNF-α. It also inhibited the phosphorylation of MAPK, NF-κB, and STAT1. These findings suggest that these Chinese herbal extracts may have significant anti-inflammatory and therapeutic effects on AD [106].
Ming et al. pointed out that the inhibitory effect of Daqing leaf extract extends to AD mice and HaCaT cells at a mechanistic level. Their findings indicate that the extract reduces the expression levels of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase proteins. Moreover, it hinders the translocation of p65 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, ultimately leading to the decreased mRNA expression of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-13 in skin tissues affected by disease. Furthermore, in HaCaT cells, the extract demonstrated the ability to impede the regulation of activated T cells and the production of TARC, MDC, MCP-1, and MIP-3a [107]. Han et al. discovered that extracts from Artemisia annua (AWE) significantly impacted a mouse model of DNCB-induced AD. The findings indicated that the AWE alleviated AD symptoms in the mice and suppressed the mRNA and protein expressions of IgE, IL-4, IL-6, IL-13, IL-17, TNF-α, and TSLP. Moreover, the AWE treatment also reduced the phosphorylation levels of p38 MAPK and NFκB in the ear tissues of the AD mice [108].
To summarize, the repair of the damaged skin barrier is facilitated by coumarins, phenolic acids, and pentacyclic triterpenoids through the activation of signaling pathways such as ITK, PLC-γ1, NF-κB, and MAPK. These compounds have significant effects, providing a basis and new ideas for their future clinical application in skin diseases. Table 5 lists the compounds’ mechanisms of action.

Table 5.
Compounds’ mechanisms of action.
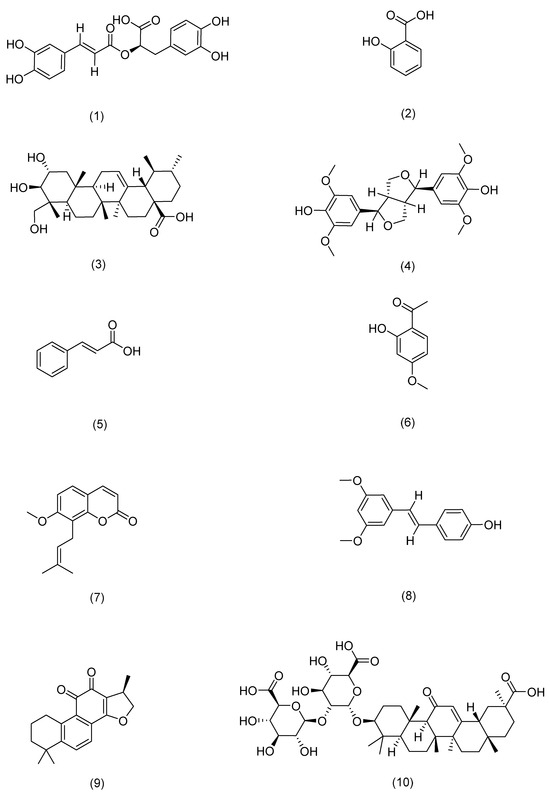
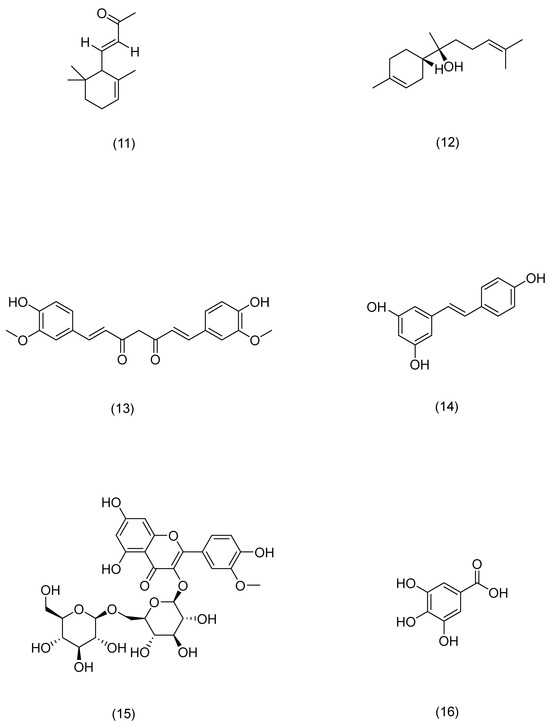
Figure 7.
Structural formula of aother.
5. State-of-the-Art Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine
With the advancement of modern pharmacology and clinical trials, increasing numbers of studies have reported the application of active ingredients and preparations from traditional Chinese medicine in repairing the skin barrier. Researchers have begun to develop traditional Chinese medicines with skin barrier functions to treat skin diseases such as psoriasis, AD, and acne. Therefore, traditional Chinese medicine has great development potential for repairing the skin barrier, providing broad prospects for its application in the treatment of skin diseases.
Kim et al. conducted an 8-week open, non-comparative clinical study using red ginseng extract to treat patients with AD. The research results showed that red ginseng extract has significant therapeutic effects on patients with AD. It can significantly reduce eczema area and severity index scores, improve itching and sleep disturbance, and reduce the use of topical medications [124]. Lee et al. conducted an 18-week clinical trial on AD patients using red ginseng extract and verified the clinical efficacy of the extract through the SCORAD index, as well as TEWL, DI, SI, and the skin-surface moisture rate. All the indicators improved after 16 weeks, showing that the extract could improve skin barrier function and reduce serum IgE levels without specific side effects. These findings suggest that the extract may have potentially beneficial effects in improving disease severity and skin barrier function, and in alleviating itching and sleep disturbance [125].
Kim et al. studied AD-like skin lesions in an NC/Nga mouse model induced using DNFB. The results showed that Uncaria could inhibit the development of AD in this model by reducing the production of IFN-γ [126]. Theoharides et al. treated four patients with AD and psoriasis with tetramethoxyluteolin. All the patients experienced improvements in their skin conditions, demonstrating the potential role of this ingredient in improving different skin conditions [127].
Lee et al. extracted an alkaloid-rich component, INM-A, from Indigo Naturalis and analyzed its chemical characteristics and anti-psoriasis activity to determine its in vitro mechanism and in vivo efficacy for psoriasis treatment. The results showed that INM-A can significantly improve the skin condition of mice with psoriasis, reduce the levels of IL-17A, and inhibit polarized Th17 cells. Additionally, INM-A targets IL-17A, which can inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress caused by OXPHOS in skin cells [128].
Shi et al. studied the therapeutic effect of oxymatrine on patients with severe plaque psoriasis. The authors stained skin tissue with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), Ki-67, and Bcl-2, and identified cells using terminal deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUTP nick labeling (TUNEL). The results showed that oxymatrine regulated mitosis, inhibited the overexpression of PCNA and Ki-67 in skin lesions, and promoted the recovery of apoptotic Bcl-2 expression, thereby improving psoriasis skin lesions [129]. Zhou et al. conducted a clinical trial of p-oxymatrine in the treatment of patients with relapsed severe plaque psoriasis. The findings indicated that the oxymatrine treatment effectively reduced the recurrence rate compared to the acitretin group and resulted in a significant decrease in adverse reactions, indicating that the oxymatrine treatment effectively improved severe plaque psoriasis [130].
The bioactive constituents of traditional Chinese medicine have shown broad potential in restoring the skin barrier, achieving protection and repair through various mechanistic targets. Future research should further explore the specific molecular mechanisms and clinical application potential of these bioactive constituents to provide more options for treating skin barrier dysfunction. Table 6 summarizes the pharmacological effects and applications

Table 6.
Pharmacological effects and applications.
6. Summary and Outlook
Human skin is often considered the primary defense mechanism and barrier against various infections affecting the body. Maintaining healthy skin is crucial for overall well-being, and it is achievable through a combination of modern allopathic and natural remedies. Common skin conditions like AD, psoriasis, eczema, acne, and chloasma pose significant healthcare challenges. Plant and animal extracts have proven effective in treating skin infections.
With the advancement of science and technology, the clinical demand for traditional Chinese medicine has significantly increased. As a vital component of traditional medicine, traditional Chinese medicine has amassed extensive experience in the treatment of skin diseases. Numerous traditional Chinese medicines exhibit anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anti-allergic properties, effectively alleviating the symptoms of skin conditions and enhancing overall skin health. Consequently, natural herbal remedies for skin diseases have emerged as crucial elements in the management of skin infections. Traditional Chinese medicine extracts have made substantial contributions to human healthcare. Certain extracts and compound preparations derived from traditional Chinese medicine, such as berberine, coix seed, and angelica dahurica, have demonstrated their efficacy in treating skin diseases through clinical trials. These traditional remedies are applicable in the treatment of common skin disorders, including eczema, psoriasis, acne, and urticaria. Additionally, traditional Chinese medicine possesses several unique advantages in addressing skin diseases. Primarily, it emphasizes holistic conditioning, which can enhance both the internal and the external environments of the human body, thereby boosting immunity and reducing the incidence and recurrence of skin diseases. Furthermore, traditional Chinese medicine is characterized by its diversity, allowing for personalized treatment approaches tailored to individuals’ constitutions and conditions, ultimately improving therapeutic outcomes.
Recent years have seen significant advancements in research into the functional elements in traditional Chinese medicine, with an increasing number of components showing potential in preventing and treating skin ailments. These factors, which are integral to traditional medicine, are gaining recognition in modern medical practice. Future studies should focus on understanding the mechanisms of action of these functional components and confirming their efficacy through clinical trials. This will promote the utilization and advancement of traditional Chinese medicine in treating skin diseases.
Funding
This review was supported by the Guangxi Science and Technology Major Program Grant (No.GUIKEAA23023035); National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Youth Qihuang Scholars Support Project (No. 2022256); Guangxi Youth Qihuang Scholars Support Project (No. 202213); and Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Guipai Xinglin Top Talent Funding Project (No. 2022C013).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine | IL-13 | interleukin-13 |
| TEWL | transepidermal water loss | TCS | topical corticosteroids |
| TJs | tight junctions | TCI | calcineurin inhibitors |
| TLR | toll-like receptor | pDCs | plasmacytoid dendritic cells |
| NMFs | natural moisturizing factors | IFN | interferon |
| SC | stratum corneum | mDCs | myeloid dendritic cells |
| UV | ultraviolet | IL-17 | interleukin-17 |
| KLK | kallikrein-related peptidase | IL-1 | interleukin-1 |
| SG | stratum granulosum | IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| AMPs | antimicrobial peptides | CXCL1 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 |
| hBDs | human beta-defensins | CCL20 | chemokine ligand 20 |
| LCs | langerhans cells | PASI | Psoriasis Area and Severity Index |
| DCs | dermal dendritic cells | TH2 | T helper cell 2 |
| IL-7 | interleukin-7 | TH17 | T helper cell 17 |
| IL-15 | interleukin-15 | TH9 | T helper cell 9 |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor b | TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL-34 | interleukin-34 | TNCB | 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns | DNCB | 1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene |
| DAMPs | damage-associated molecular patterns | CK2α | casein kinase 2 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-B | GSH | glutathione, reduced |
| AD | atopic dermatitis | BALB/c | laboratory-bred strain |
| TSLP | thymic stromal lymphopoietin | IVL | involucrin |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E | AQP3 | aquaporin 3 |
| IL-4 | interleukin-4 | ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay | COX-7 | cyclooxygenase-7 |
| HaCaT | human keratinocyte cells | COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| UVB | ultraviolet B | GAL | galangin |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase | GST | glutathione S-transferase |
| FLG | filaggrin | GR | glutathione reductase |
| Cldn-1 | claudin-1 | LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| NHDF | human dermal fibroblasts | GL | glycyrrhizic acid |
| AP-1 | activator protein-1 | MCP-1 | monocyte chemotactic protein-1 |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase-1-IN-1 | TLR | toll-like receptors |
| NQO-1 | NAD (P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 | SOCS1 | suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide sythase | PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species | SPINK5 | serine protease inhibitor Kazal type-5 |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β | KLK7 | kallikrein-related peptidase 7 |
| IMQ | imiquimod | LBP | lycium barbarum polysaccharide |
| CAT | catalase | APS | astragalus polysaccharide |
| GSH | glutathione, reduced | AP | aloe polysaccharide |
| Vit-C | vitamin C | FCM | flow cytometry |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 | Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ | GSTP1 | glutathione S-transferase Pi |
| TACR1 | tachykinin receptor 1 | UA | ursolic acid |
| UVA | ultraviolet A | SREBP-1 | sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 |
| PKCδ | protein kinase C-δ | RANTES | recombinant human C-C motif chemokine 5 |
| CD177 | CD177 Molecule | IP-10 | recombinant human C-X-C motif chemokine 10 |
| MDC | monodansylcadaverine | MIP-3a | macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 |
| NFAT | nuclear factor of activated T cells | PI3K | phosphatidylin-ositol-3-kinase |
| PMA | phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate | SIRT1 | silent information regulator family protein 1 |
| GSO | ginseng oligosaccharide | HBD-2 | human β-defensin-2 |
| KLK5 | kallikrein-related peptidase 5 | SCORAD | SCORing Atopic Dermatitis |
| DSG1 | desmoglein 1 | INM-A | Indigo Naturalis |
| NFG | nerve growth factor | PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
| MTT | thiazolyl blue | TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick labeling |
| PI | propidium iodide | PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor γ coactivator lalpha |
| Bax | BCL2-associated X | OXPHOS | oxidative phosphorylation |
| GCLC | glutamate cysteine ligase catalysis | Ki-67 | large (395 kDa) nuclear protein |
| NFG | nerve growth factor | ITK | interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase |
| ONA | oleanolic acid | CD4(+) | cluster of differentiation 4 receptors |
| TARC | thymic and activating regulatory chemokine | MCP-1 | monocyte chemotactic protein-1 |
References
- Harris-Tryon, T.A.; Grice, E.A. Microbiota and maintenance of skin barrier function. Science 2022, 376, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.S.; Chae, Y.J.; Choi, J.W.; Chang, J.E. Potential Therapeutic Approaches through Modulating the Autophagy Process for Skin Barrier Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yosipovitch, G.; Misery, L.; Proksch, E.; Metz, M.; Ständer, S.; Schmelz, M. Skin Barrier Damage and Itch: Review of Mechanisms, Topical Management and Future Directions. Acta Derm. -Venereol. 2019, 99, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.F.; Zhou, Y.C.; Yang, L.T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.J.; Qiu, S.Q.; Cheng, B.H.; Zeng, X.H. Involvement and repair of epithelial barrier dysfunction in allergic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1348272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.A.; Paul, C.; Nijsten, T.; Gisondi, P.; Salavastru, C.; Taieb, C.; Trakatelli, M.; Puig, L.; Stratigos, A. Prevalence of most common skin diseases in Europe: A population-based study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2022, 36, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grennan, D.; Wang, S. Steroid Side Effects. JAMA 2019, 322, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, W.C.; Sumita, J.M.; Rodrigues, A.G.; Liuson, D.; Tanaka, E. Rebound phenomenon to systemic corticosteroid in atopic dermatitis. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2005, 33, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E.J.; Reijers, S.J.M.; Van Akkooi, A.C.J.; Van Houdt, W.J.; Hayes, A.J. Isolated limb perfusion for locally advanced melanoma in the immunotherapy era. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paichitrojjana, A.; Paichitrojjana, A. Oral Isotretinoin and Its Uses in Dermatology: A Review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 2573–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, E.; Geisler, A.N.; Nguyen, J.; Kohli, I.; Hamzavi, I.; Lim, H.W.; Jagdeo, J. Visible light. Part I: Properties and cutaneous effects of visible light. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, J.; Li, H.; Chen, D.; Mo, X. The formulae and biologically active ingredients of Chinese herbal medicines for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahle, F.F.; Gebre-Mariam, T.; Dobner, B.; Wohlrab, J.; Neubert, R.H. Skin diseases associated with the depletion of stratum corneum lipids and stratum corneum lipid substitution therapy. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 28, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strugar, T.L.; Kuo, A.; Seité, S.; Lin, M.; Lio, P. Connecting the Dots: From Skin Barrier Dysfunction to Allergic Sensitization, and the Role of Moisturizers in Repairing the Skin Barrier. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2019, 18, 581. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar, J.; Chandan, N.; Lio, P.; Shi, V. The Skin Barrier and Moisturization: Function, Disruption, and Mechanisms of Repair. Skin. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2023, 36, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiatsurayanon, C.; Ogawa, H.; Niyonsaba, F. The Role of Host Defense Peptide Human β-defensins in the Maintenance of Skin Barriers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Gan, Y.; He, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, C. The mechanism of skin lipids influencing skin status. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Yosipovitch, G. Skin pH: From basic science to basic skin care. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, K.A.; Lee, T.R.; Lee, A.Y. Complementary effect of hydroquinone and retinoic acid on corneocyte desquamation with their combination use. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 87, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boer, D.E.C.; van Smeden, J.; Al-Khakany, H.; Melnik, E.; van Dijk, R.; Absalah, S.; Vreeken, R.J.; Haenen, C.C.P.; Lavrijsen, A.P.M.; Overkleeft, H.S.; et al. Skin of atopic dermatitis patients shows disturbed β-glucocerebrosidase and acid sphingomyelinase activity that relates to changes in stratum corneum lipid composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Smeden, J.; Bouwstra, J.A. Stratum Corneum Lipids: Their Role for the Skin Barrier Function in Healthy Subjects and Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2016, 49, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, N.K. l-Histidine Supplementation in Adults and Young Children with Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema). J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2576s–2579s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spada, F.; Barnes, T.M.; Greive, K.A. Skin hydration is significantly increased by a cream formulated to mimic the skin’s own natural moisturizing systems. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 11, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A.; Segre, J.A. The skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, P.M.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Immunologic, microbial, and epithelial interactions in atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäsler, K.; Bergmann, S.; Heisig, M.; Naegel, A.; Zorn-Kruppa, M.; Brandner, J.M. The role of tight junctions in skin barrier function and dermal absorption. J. Control Release 2016, 242, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyerich, S.; Eyerich, K.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Biedermann, T. Cutaneous Barriers and Skin Immunity: Differentiating A Connected Network. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Naik, S.; Nagao, K. Choreographing Immunity in the Skin Epithelial Barrier. Immunity 2019, 50, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M. Regulation of Filaggrin, Loricrin, and Involucrin by IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, AHR, and NRF2: Pathogenic Implications in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M.; Chiba, T.; Tsuji, G.; Ulzii, D.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Kadono, T. Atopic dermatitis: Immune deviation, barrier dysfunction, IgE autoreactivity and new therapies. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, L.C.; Billi, A.C.; Ward, N.L.; Harms, P.W.; Zeng, C.; Maverakis, E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Cytokinocytes: The diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguniewicz, M.; Leung, D.Y. Atopic dermatitis: A disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sum, C.H.; Ching, J.; Zhang, H.; Loo, S.; Lo, C.W.; Lai, M.K.; Cheong, P.K.; Yu, C.L.; Lin, Z.X. Integrated Chinese and western medicine interventions for atopic dermatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabat, R.; Philipp, S.; Höflich, C.; Kreutzer, S.; Wallace, E.; Asadullah, K.; Volk, H.D.; Sterry, W.; Wolk, K. Immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainichi, T.; Kitoh, A.; Otsuka, A.; Nakajima, S.; Nomura, T.; Kaplan, D.H.; Kabashima, K. The epithelial immune microenvironment (EIME) in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhawaga, O.Y.; Ellety, M.M.; Mofty, S.O.; Ghanem, M.S.; Mohamed, A.O. Review of natural compounds for potential psoriasis treatment. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.B.; Lambert, C.; Lotti, T.M.; Hercogová, J.; Sintim-Damoa, A.; Schwartz, R.A. Melasma. G. Ital. Di Dermatol. E Venereol. Organo Uff. Soc. Ital. Di Dermatol. E Sifilogr. 2012, 147, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chen, Q.; Xia, Y. New Mechanistic Insights of Melasma. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piętowska, Z.; Nowicka, D.; Szepietowski, J.C. Understanding Melasma—How Can Pharmacology and Cosmetology Procedures and Prevention Help to Achieve Optimal Treatment Results? A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenholz, I.; Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Lee, Y.A. The genetics of the skin barrier in eczema and other allergic disorders. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Timm, K.; Kühl, A.A.; Heine, G.; Worm, M. Impact of systemic alitretinoin treatment on skin barrier gene and protein expression in patients with chronic hand eczema. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.Z.; Geliebter, J.; Tiwari, R.; Li, X.M. Traditional Chinese medicine for food allergy and eczema. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, A.; Christen-Zäch, S.; Taieb, A.; Paul, C.; Thyssen, J.P.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Vestergaard, C.; Seneschal, J.; Werfel, T.; Cork, M.J.; et al. ETFAD/EADV Eczema task force 2020 position paper on diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults and children. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2020, 34, 2717–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Xie, H.; Cheng, L.; Li, J. Clinical characteristics and epidermal barrier function of papulopustular rosacea: A comparison study with acne vulgaris. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dréno, B.; Bettoli, V.; Araviiskaia, E.; Sanchez Viera, M.; Bouloc, A. The influence of exposome on acne. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2018, 32, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Zaid, N.A.; Sekar, M.; Bonam, S.R.; Gan, S.H.; Lum, P.T.; Begum, M.Y.; Mat Rani, N.N.I.; Vaijanathappa, J.; Wu, Y.S.; Subramaniyan, V.; et al. Promising Natural Products in New Drug Design, Development, and Therapy for Skin Disorders: An Overview of Scientific Evidence and Understanding Their Mechanism of Action. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 23–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, D.P.; Bressler, R.B. Urticaria and angioedema. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1992, 76, 805–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, H.J.H. DNA Damage, Aging, and Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapp, V.; Álvarez-Abril, B.; Leuzzi, G.; Kroemer, G.; Ciccia, A.; Galluzzi, L. The DNA Damage Response and Inflammation in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1521–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaria, R.N.; Postow, M.; Burton, E.M.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Ross, M.I.; Torres-Cabala, C.; Glitza, I.C.; Duan, F.; Milton, D.R.; Busam, K.; et al. Neoadjuvant relatlimab and nivolumab in resectable melanoma. Nature 2022, 611, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Zou, Y.; Xiang, W.; Lu, N. Evaluation of the Composite Skin Patch Loaded with Bioactive Functional Factors Derived from Multicellular Spheres of EMSCs for Regeneration of Full-thickness Skin Defects in Rats. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 19, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, R.; Wang, M.; Zhai, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Sun, L.; Zhao, D. Ginsenosides repair UVB-induced skin barrier damage in BALB/c hairless mice and HaCaT keratinocytes. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, D. Insights into Recent Studies on Biotransformation and Pharmacological Activities of Ginsenoside Rd. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, N.R.; Ko, S.G.; Moon, P.D.; Park, H.J. Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates skin disorders via down-regulation of MDM2/HIF1α signaling pathway. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, B.K.; Yoon, S.K.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Park, Y.M. Effects of topically applied Korean red ginseng and its genuine constituents on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, J.Y.; Jeon, Y.D.; Kim, D.S.; Han, Y.H.; Park, J.; Youn, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Ahn, K.S.; Um, J.Y.; Hong, S.H. Korean Red Ginseng improves atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions by suppressing expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in vivo and in vitro. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, E.H.; Jang, S.A.; Lee, C.H.; Jang, K.H.; Kang, S.C.; Park, H.J.; Pyo, S. Effects of korean red ginseng extract for the treatment of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Lim, H.W.; Park, K.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Yoon, J.Y.; Kim, K.; Lim, C.J. Ginsenoside Rc protects against UVB-induced photooxidative damage in epidermal keratinocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Kim, K.; Lim, C.J. Protective properties of ginsenoside Rb1 against UV-B radiation-induced oxidative stress in human dermal keratinocytes. Die Pharm. 2015, 70, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Hwang, E.; Park, B.; Ngo, H.T.T.; Xiao, Y.K.; Yi, T.H. Ginsenoside C-Mx Isolated from Notoginseng Stem-leaf Ginsenosides Attenuates Ultraviolet B-mediated Photoaging in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Huang, T.H.; Yeh, K.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Shen, S.C.; Liou, C.J. Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorates allergic airway inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.J.; Choi, W.Y.; Jung, H.J. Stereoselective skin anti-photoaging properties of ginsenoside Rg3 in UV-B-irradiated keratinocytes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; He, Q.; Chen, W.; Long, J.; Zhang, B. Ginsenoside Rg1 abolish imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis in BALB/c mice via downregulating NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.K.; Choo, M.K.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Ginsenoside Rh1 possesses antiallergic and anti-inflammatory activities. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 133, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.H.; Ha, S.E.; Park, M.Y.; Bhosale, P.B.; Abusaliya, A.; Park, K.I.; Heo, J.D.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, G.S. Flavones: Six Selected Flavones and Their Related Signaling Pathways That Induce Apoptosis in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Bai, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Fu, X.Q.; Zhu, P.L.; Li, J.K.; Chou, J.Y.; Yin, C.L.; Wang, Y.P.; et al. Chrysoeriol ameliorates TPA-induced acute skin inflammation in mice and inhibits NF-κB and STAT3 pathways. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2020, 68, 153173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaraju, R.; Alavala, S.; Nalban, N.; Jerald, M.K.; Sistla, R. Galangin ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in BALB/c mice via down regulating NF-κB and activation of Nrf2 signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.G.; Park, N.J.; Jegal, J.; Choi, S.; Lee, S.W.; Yi, L.W.; Kim, S.N.; Yang, M.H. Stellera chamaejasme and Its Main Compound Luteolin 7-O-Glucoside Alleviates Skin Lesions in Oxazolone- and 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Stimulated Murine Models of Atopic Dermatitis. Planta Medica 2019, 85, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Cheng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, F.; Sun, T.; Hao, J. Eupatilin inhibits keratinocyte proliferation and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice via the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2023, 45, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, B.; Tu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Cimifugin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation via NF-κB/MAPK pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Xu, Y.; Tan, G.; Han, Y.; Tang, Z.; Xu, W.; Zeng, F.; Guo, Q. Glycyrrhizin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice and inhibits TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 expression via NF-κB/MAPK in HaCaT cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 35, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Xu, F.; Pang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J. Icariin inhibits TNF-α/IFN-γ induced inflammatory response via inhibition of the substance P and p38-MAPK signaling pathway in human keratinocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.Y.; Park, N.J.; Jo, B.G.; Paik, J.H.; Choi, S.; Kim, S.N.; Yang, M.H. 7-O-Methylluteolin Suppresses the 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway and Atopic Dermatitis-like Lesions. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Wu, N.L.; Pu, C.M.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Chang, D.C.; Hung, C.F. Chrysin alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation and reduces the release of CCL20 and antimicrobial peptides. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, A.; Zdarilová, A.; Walterová, D.; Vostálová, J. Flavonolignans from Silybum marianum moderate UVA-induced oxidative damage to HaCaT keratinocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 48, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, D.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Dang, Y.; Ye, X. Naringin protects ultraviolet B-induced skin damage by regulating p38 MAPK signal pathway. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 82, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, M.A.; Yang, K.; Jani, A.; Abed, R.A.; Taufique, A.K.; Dosunmu, T.G.; Yusuf, N. Protective Effect of Baicalin Against TLR4-mediated UVA-induced Skin Inflammation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Ai, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, B.; Tang, M.; Zhang, L.; He, T. Glabridin Liposome Ameliorating UVB-Induced Erythema and Lethery Skin by Suppressing Inflammatory Cytokine Production. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendrisch, F.; Esser, P.R.; Schempp, C.M.; Wölfle, U. Luteolin as a modulator of skin aging and inflammation. BioFactors 2021, 47, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.J.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.; Lim, T.G.; Byun, S. Quercetin Directly Targets JAK2 and PKCδ and Prevents UV-Induced Photoaging in Human Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Im, A.R.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, J.D.; Chae, S. The flavonoid hesperidin exerts anti-photoaging effect by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 expression via mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.F.; Liu, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Chang, L.; Karisma, V.W.; Weixu; Diao, Q.; Xue, M.; Tang, X.; et al. Eriodictyol protects skin cells from UVA irradiation-induced photodamage by inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2022, 226, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Karadeniz, F.; Lee, J.I.; Park, S.Y.; Seo, Y.; Kong, C.S. Anticatabolic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Myricetin 3-O-β-d-Galactopyranoside in UVA-Irradiated Dermal Cells via Repression of MAPK/AP-1 and Activation of TGFβ/Smad. Molecules 2020, 25, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.F.; Ma, K.H.; Chang, Y.J.; Lo, L.C.; Jhap, T.Y.; Su, Y.H.; Liu, P.S.; Chueh, S.H. Baicalein inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 1 expression via activation of TRPV1-Ca-ERK pathway in ultraviolet B-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.K.; Ha, S.J.; Jung, C.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, M.H.; Mottamal, M.; Bode, A.M.; Lee, K.W.; et al. Naringenin targets ERK2 and suppresses UVB-induced photoaging. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Mo, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, D.; Yan, F. Inhibitory effects of isoliquiritin on an atopic dermatitis model through the CD177/JAK2/STAT pathway in vitro and in vivo. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, A.H.; Xu, H.Y.; Yan, G.L.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.J. Natural alkaloids: Basic aspects, biological roles, and future perspectives. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.J.; Ding, P.J.; Yang, L.L.; He, X.F.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, D.M.; Tian, Y.X.; Zhang, H.M. Oxymatrine Sensitizes the HaCaT Cells to the IFN-γ Pathway and Downregulates MDC, ICAM-1, and SOCS1 by Activating p38, JNK, and Akt. Inflammation 2018, 41, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.C.; Lee, M.S.; Huang, W.C.; Chang, W.Y.; Krueger, J.G.; Tsai, T.F. Capsaicin attenuates imiquimod-induced epidermal hyperplasia and cutaneous inflammation in a murine model of psoriasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Hu, F.; Yang, Z.B.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, R.; Yan, Y.N.; Wang, H.Z.; Wang, C. Matrine regulates Th1/Th2 inflammatory responses by inhibiting the Hsp90/NF-κB signaling axis to alleviate atopic dermatitis. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.S.; Jiao, D.; Chan, B.C.; Hon, K.L.; Leung, P.C.; Lau, C.B.; Wong, E.C.; Cheng, L.; Chan, C.K.; Lam, C.W.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Pentaherbs Formula, Berberine, Gallic Acid and Chlorogenic Acid in Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Inflammation. Molecules 2016, 21, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, W.; Lin, G.; Liu, G.; Deng, W.; Zhai, C.; Bian, C.; He, G.; Hu, Z. Norisoboldine, an alkaloid from Radix linderae, inhibits NFAT activation and attenuates 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced dermatitis in mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 38, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.F.; Wang, F.X.; Sun, F.; Liu, X.; Rong, S.J.; Luo, J.H.; Yue, T.T.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C.L.; Lu, W.Y.; et al. Aloperine Ameliorates IMQ-Induced Psoriasis by Attenuating Th17 Differentiation and Facilitating Their Conversion to Treg. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 778755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, A.N.; Malik, A.T.; Naikoo, H.S.; Raghu, R.S.; S, A.T. Trigonelline, a naturally occurring alkaloidal agent protects ultraviolet-B (UV-B) irradiation induced apoptotic cell death in human skin fibroblasts via attenuation of oxidative stress, restoration of cellular calcium homeostasis and prevention of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 202, 111720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. The structures and biological functions of polysaccharides from traditional Chinese herbs. Progress. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 163, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kan, J.; Jin, C. Isolation, structural characterization and bioactivities of naturally occurring polysaccharide-polyphenolic conjugates from medicinal plants-A reivew. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, R.; Jing, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Sun, L.; Zhao, D. Protective effect of oligosaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer against UVB-induced skin barrier damage in BALB/c hairless mice and human keratinocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.; Peng, L.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, E.; Liang, B.; Li, R.; Zhu, H. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects human keratinocytes against UVB-induced photo-damage. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.X.; Zheng, S.; Guo, C.Y.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on imiquimod-induced psoriasiform dermatitis in mice and its mechanisms. Chin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 38, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Duan, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, M. Aloe polysaccharide protects skin cells from UVB irradiation through Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signal pathway. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Sun, Z.W.; Yi, T.H. Gallic acid regulates skin photoaging in UVB-exposed fibroblast and hairless mice. Phytother. Res. PTR 2014, 28, 1778–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Han, L.; Lu, C. Gallic acid inhibits the expression of keratin 16 and keratin 17 through Nrf2 in psoriasis-like skin disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Zhou, X. Gallic Acid Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Inflammation Through Immune Regulation in a Mouse Model. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollier, J.; Goossens, A. Oleanolic acid. Phytochemistry 2012, 77, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.W.; Hong, S.P.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, B.; Bak, H.; Ryoo, H.C.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, S.K. Simultaneous effect of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid on epidermal permeability barrier function and epidermal keratinocyte differentiation via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha. J. Dermatol. 2007, 34, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Song, H.K.; Park, S.H.; Jang, S.; Park, K.S.; Song, K.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, T. Terminalia chebula Retz. extract ameliorates the symptoms of atopic dermatitis by regulating anti-inflammatory factors in vivo and suppressing STAT1/3 and NF-ĸB signaling in vitro. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 104, 154318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.K.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, S.; Kim, T. Alpinia officinarum water extract inhibits the atopic dermatitis-like responses in NC/Nga mice by regulation of inflammatory chemokine production. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, W.K.; Yang, J.H.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-Atopic Effect of Isatidis Folium Water Extract in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced HaCaT Cells and DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Mouse Model. Molecules 2023, 28, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wang, G.; Han, X.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Chou, G.; Yang, L.; Wu, X. Artemisia annua water extract attenuates DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis by restraining Th2 cell mediated inflammatory responses in BALB/c mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 291, 115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, N.; Liang, B.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, E.; Peng, L.; Deng, H.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H. Pterostilbene protects against UVB-induced photo-damage through a phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent Nrf2/ARE pathway in human keratinocytes. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 22, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Liu, R.; Jing, R.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Fu, M.; Ye, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, W.; et al. Cryptotanshinone protects skin cells from ultraviolet radiation-induced photoaging via its antioxidant effect and by reducing mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibiting apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1036013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrukh, M.R.; Nissar, U.A.; Kaiser, P.J.; Afnan, Q.; Sharma, P.R.; Bhushan, S.; Tasduq, S.A. Glycyrrhizic acid (GA) inhibits reactive oxygen Species mediated photodamage by blocking ER stress and MAPK pathway in UV-B irradiated human skin fibroblasts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 148, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Fu, M.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Feng, B.; Li, E.; Nishijima, Y.; Sun, Z.; Hu, Z. α-ionone promotes keratinocyte functions and accelerates epidermal barrier recovery. Ann. Transl. Med. 2023, 11, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wu, H.; Sun, L.; Cheng, K.; Lv, Z.; Chen, K.; Qian, F.; Li, Y. (-)-α-Bisabolol Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis by Inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB Signaling in Mast Cell. Molecules 2022, 27, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Taha, A.; Xu, C. Protective effect of curcumin against ultraviolet A irradiation-induced photoaging in human dermal fibroblasts. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7227–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chan, F.; Sun, H.; Yan, J.; Fan, D.; Zhao, D.; An, J.; Zhou, D. Resveratrol protects human keratinocytes HaCaT cells from UVA-induced oxidative stress damage by downregulating Keap1 expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ke, J.; Wu, X.; Yan, Y. Astragaloside prevents UV-induced keratinocyte injury by regulating TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, C.W.; Cho, S.H. The Beneficial Effect of Korean Red Ginseng Extract on Atopic Dermatitis Patients: An 8 Weeks Open, Noncomparative Clinical Study. Ann. Dermatol. 2018, 30, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.G.; Son, S.W. Efficacy of korean red ginseng in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Jung, J.A.; Kim, T.H.; Seo, S.W.; Jung, S.K.; Park, C.S. Oral administration of Uncariae rhynchophylla inhibits the development of DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions via IFN-gamma down-regulation in NC/Nga mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Stewart, J.M.; Tsilioni, I. Tolerability and benefit of a tetramethoxyluteolin-containing skin lotion. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2017, 30, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Wang, C.M.; Song, Y.C.; Liu, C.T.; Chu, M.Y.; Yen, H.R. An alkaloid-rich phytopharmaceutical prepared from Qing Dai against IL-17A-induced psoriasis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.J.; Zhou, H.; Ma, A.L.; Wang, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, N.; Song, H.B.; Bo, K.P.; Ma, W. Oxymatrine therapy inhibited epidermal cell proliferation and apoptosis in severe plaque psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.J.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.G.; Xia, L.; Song, H.B.; Bo, K.P.; Ma, W. Efficacy of oxymatrine for treatment and relapse suppression of severe plaque psoriasis: Results from a single-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, G.D.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.S.; Jin, Y.H.; Park, Y.S.; Park, C.S. Rosmarinic acid attenuates 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Cong, T.; Wen, X.; Li, X.; Du, D.; He, G.; Jiang, X. Salicylic acid treats acne vulgaris by suppressing AMPK/SREBP1 pathway in sebocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, G.H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, E.K.; Chung, K.H.; Lee, K.J.; An, J.H. Immunomodulatory and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Asiatic Acid in a DNCB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Animal Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Joo, Y.H.; Karadeniz, F.; Ko, J.; Kong, C.S. Syringaresinol Inhibits UVA-Induced MMP-1 Expression by Suppression of MAPK/AP-1 Signaling in HaCaT Keratinocytes and Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.C.; Korivi, M.; Lin, F.Y.; Li, M.L.; Lin, R.W.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, H.L. Trans-cinnamic acid attenuates UVA-induced photoaging through inhibition of AP-1 activation and induction of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant genes in human skin fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Du, J.; Hwang, E.; Yi, T.H. Paeonol extracted from Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. ameliorated UVB-induced skin photoaging via DLD/Nrf2/ARE and MAPK/AP-1 pathway. Phytother. Res. PTR 2018, 32, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hong, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y. Effects of osthole on skin barrier and chronic pruritus in mice with specific dermatitis. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2021, 43, 3489–3492. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Wang, L.Q.; Yuan, B.C.; Liu, Y. The Pharmacological Activities of Licorice. Planta Medica 2015, 81, 1654–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Hu, M.; Zang, X.; Liu, Q.; Du, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Du, Z.; Xiang, Z. Luteolin attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice via suppression of inflammation response. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaid, M.; Haas, P.; Beuerle, T.; Scholl, S.; Beerhues, L. Hyperforin production in Hypericum perforatum root cultures. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 222, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Lin, N.; Wu, Y. Hyperforin Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Murine Skin Inflammation by Modulating IL-17A-Producing γδ T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 635076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tang, H.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Q.; Li, X. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. (Lamiaceae): A review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1353–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.W.; Lin, T.Y.; Yang, P.M.; Fang, J.Y.; Li, W.T.; Pan, T.L. Therapeutic efficacy of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi against psoriasis-like lesions via regulating the responses of keratinocyte and macrophage. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.A.; Shabaan, A.A.; May, M.; Ali, Y.M. Topical application of indigo-plant leaves extract enhances healing of skin lesion in an excision wound model in rats. J. Appl. Biomed. 2022, 20, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.J.; Di, T.T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.X.; Meng, Y.J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Li, P.; Zhao, J.X. Indirubin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice by inhibiting inflammatory responses mediated by IL-17A-producing γδ T cells. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 101, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Qin, S.; Han, J.; Meng, J.; Liang, A. A review of the ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Fructus Gardeniae (Zhi-zi). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 289, 114984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Di, T.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, N.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Paeonol ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice by inhibiting the maturation and activation of dendritic cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.; Hao, H.; Ijaz, M.; Raza, A. Pharmacological Effects of Houttuynia cordata Thunb (H. cordata): A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Han, L. Quercetin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via the NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 48, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.D.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.L.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, H.X.; Qi, R.Q.; Chen, H.D.; Gao, X.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin in a mouse model of MC903-induced atopic dermatitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelsen, A.B. The traditional uses, chemical constituents and biological activities of Plantago major L. A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 71, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, D.; Gruber, M.; Woehs, F.; Prinz, S.; Etzlstorfer, B.; Prucker, C.; Fuzzati, N.; Kopp, B.; Moeslinger, T. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthesis by Cimicifuga racemosa (Actaea racemosa, black cohosh) extracts in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, C.Z.; Mohammadi, S.; Sawadogo, W.R.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, C.S. Pharmacological Effects of Ginseng: Multiple Constituents and Multiple Actions on Humans. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 1085–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, K.; Tao, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Kou, S.; Gu, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; et al. A Review of Flavonoids from Cassia Species and their Biological Activity. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.H.; Kim, I.H.; Seo, J.J. In vitro activity of kaempferol isolated from the Impatiens balsamina alone and in combination with erythromycin or clindamycin against Propionibacterium acnes. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Fenugreek Cultivation with Emphasis on Historical Aspects and its uses in Traditional Medicine and Modern Pharmaceutical Science. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, G.D.; Ahn, H.J.; Cho, J.J.; Park, Y.S.; Park, C.S. The inhibitory effect of naringenin on atopic dermatitis induced by DNFB in NC/Nga mice. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Song, X. Green Tea (Camellia sinensis): A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Molecules 2022, 27, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Kwon, H.H.; Min, S.U.; Thiboutot, D.M.; Suh, D.H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves acne in humans by modulating intracellular molecular targets and inhibiting P. acnes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takooree, H.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Venugopala, K.N.; Jeewon, R.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F. A systematic review on black pepper (Piper nigrum L.): From folk uses to pharmacological applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, S210–s243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, A.; Fatemeh, K.; Leila, N.; Mona, P.; Mohammad, Z.; Mozafar, K. Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of the Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.): An overview of the new finding. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 41, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.F.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.A.; Zhu, H.L. A Review: The Anti-inflammatory, Anticancer and Antibacterial Properties of Four Kinds of Licorice Flavonoids Isolated from Licorice. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 1997–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Magdy Beshbishy, A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Prasad Devkota, H. Traditional Uses, Bioactive Chemical Constituents, and Pharmacological and Toxicological Activities of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. (Fabaceae). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkhaus, B.; Lindner, M.; Schuppan, D.; Hahn, E.G. Chemical, pharmacological and clinical profile of the East Asian medical plant Centella asiatica. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2000, 7, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, W.; Tao, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Gao, L.; Yin, L.; Ye, Y. Comparison of Chemical Compositions and Antioxidant Activities for the Immature Fruits of Citrus changshan-huyou Y.B. Chang and Citrus aurantium L. Molecules 2023, 28, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Song, K.M.; Jung, C.H. Diosmin restores the skin barrier by targeting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in atopic dermatitis. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2021, 81, 153418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Yan, L.; Yuan, Z.; Long-Bo, Z.; Da-Hui, L.; Xian-Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Li-Ping, K. Research progress on chemical constituents from Artemisiae argyi Folium and their pharmacological activities and quality control. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2020, 45, 4017–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).