Exploration of Ultrasound-Enhanced Transdermal Delivery Efficiency and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rutin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vitro Diffusion of Porcine Skin
2.2. In Vitro Diffusion of Nude Mouse Skin
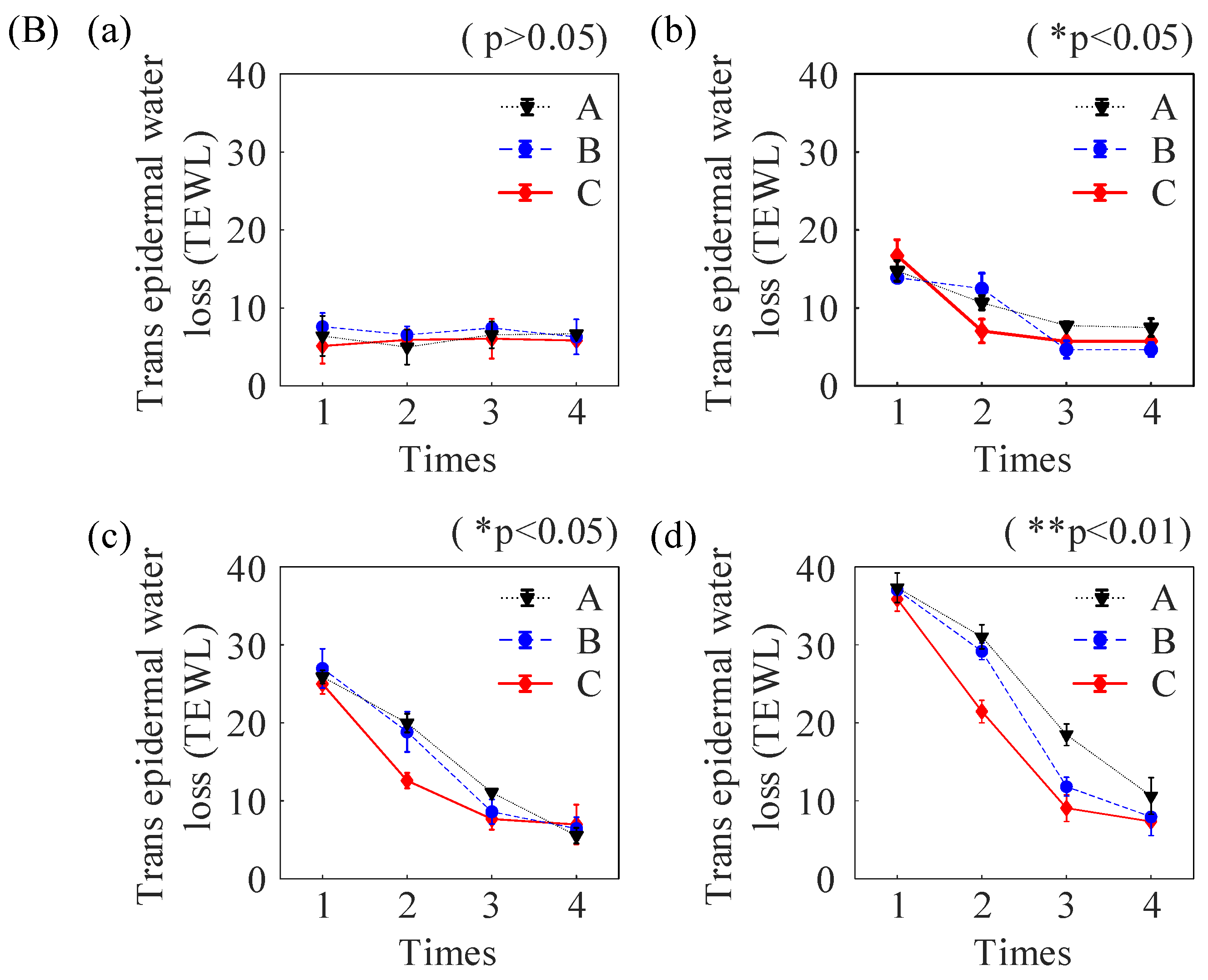
2.3. In Vivo Experiments in Nude Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Instruments
4.3. Skin Sample Preparation
4.4. In Vitro Release Studies
4.5. Animal Treatments
4.6. HPLC and Analytical Methods
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calabro, M.L.; Tommasini, S.; Donato, P.; Stancanelli, R.; Raneri, D.; Catania, S.; Costa, C.; Villari, V.; Ficarra, P.; Ficarra, R. The Rutin/β-Cyclodextrin Interactions in Fully Aqueous Solution: Spectroscopic Studies and Biological Assays. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 36, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Semwal, R.; Joshi, S.K.; Semwal, R.B.; Semwal, D.K. Health Benefits and Limitations of Rutin-A Natural Flavonoid with High Nutraceutical Value. Phytochem. Lett. 2021, 46, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A.K. The Pharmacological Potential of Rutin. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.; Khan, F.; Qari, H.A.; Oves, M. Rutin (Bioflavonoid) as Cell Signaling Pathway Modulator: Prospects in Treatment and Chemoprevention. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șerban, G.; Pop, I.A.; Horvath, T.; Bota, S. The Isolation and Identification of Rutin from Pharmaceutical Products. Analele Univ. Din Oradea Fasc. Ecotoxicologie Zooteh. Și Tehnol. De Ind. Aliment. 2016, 15, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.K.; Kim, S.-H. Rutin Suppresses Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, S.-N.; Kim, K.; Joo, D.H.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S.B.; Kim, M.J. Biological Effects of Rutin on Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Odetti, P.R.; Borgoglio, A.; Pascale, A.D.; Rolandi, R.; Adezati, L. Prevention of Diabetes-Increased Aging Effect on Rat Collagen-Linked Fluorescence by Aminoguanidine and Rutin. Diabetes 1990, 39, 796–801. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Ali, A.; Ali, J.; Sahni, J.K.; Baboota, S. Rutin: Therapeutic Potential and Recent Advances in Drug Delivery. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.K.; Kalita, B. Design and Evaluation of Phyto-Phospholipid Complexes (Phytosomes) of Rutin for Transdermal Application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 4, 051–057. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ni, W.; Aisha, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, M. A Rutin Nanocrystal Gel as an Effective Dermal Delivery System for Enhanced Anti-Photoaging Application. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajbafvala, A.; Salabat, A. Microemulsion and Microemulsion Gel Formulation for Transdermal Delivery of Rutin: Optimization, in-Vitro/Ex-Vivo Evaluation and SPF Determination. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kwon, M.; Choi, H.E.; Kim, K.S. Recent Advances in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man-li, Y.; Ming-yue, Z.; Xue-qing, H.U.; Feng, C.; Cong-fen, H.E.; Yan, J.I.A. Progress in Research of Skin Permeability of Cosmetics Evaluation Method and Enhancement Technology. China Surfactant Deterg. Cosmet. 2020, 50, 793. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhi, R.M.; Sobhi, A.M. A Single-blinded Comparative Study between the Use of Glycolic Acid 70% Peel and the Use of Topical Nanosome Vitamin C Iontophoresis in the Treatment of Melasma. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2012, 11, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Jin, Q.; Zhi, J.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, J.; Pi, L.; Nan, M.; Jin, Z.; Jin, C. Mussel Adhesive Protein Treatment Delivered by Microneedling for Sensitive Skin: A Clinical Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, A.-H.; Chung, H.-Y.; Chen, W.-S.; Yeh, M.-K. Efficacy of Combined Ultrasound-and-Microbubbles-Mediated Diclofenac Gel Delivery to Enhance Transdermal Permeation in Adjuvant-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Rat. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, Y.; Xing, R.; Xu, B.; Guoliang, D.; Wang, P. Effect of Ultrasound-Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery Efficiency of Nanoparticles and Brucine. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3273816. [Google Scholar]
- Brennen, C.E. Cavitation and Bubble Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Seah, B.C.-Q.; Teo, B.M. Recent Advances in Ultrasound-Based Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7749–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, C.C.J.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. An Investigation of the Role of Cavitation in Low-Frequency Ultrasound-Mediated Transdermal Drug Transport. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Low-Frequency Sonophoresis. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Ultrasound-Mediated Transdermal Protein Delivery. Science 1995, 269, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, B.E.; Hart, D.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. Ultrasound-Mediated Transdermal Drug Delivery: Mechanisms, Scope, and Emerging Trends. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 330–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ita, K. Recent Progress in Transdermal Sonophoresis. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shah, A.; Amiri, N.; Marcus, C.; Nayeem, M.O.G.; Bhayadia, A.K.; Karami, A.; Dagdeviren, C. A Conformable Ultrasound Patch for Cavitation-Enhanced Transdermal Cosmeceutical Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, A.-H.; Ma, W.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Yeh, M.-K. Penetration Depth, Concentration and Efficiency of Transdermal α-Arbutin Delivery after Ultrasound Treatment with Albumin-Shelled Microbubbles in Mice. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia Filho, A.L.M.; Villaverde, A.B.; Munin, E.; Aimbire, F.; Albertini, R. Comparative Study of the Topical Application of Aloe Vera Gel, Therapeutic Ultrasound and Phonophoresis on the Tissue Repair in Collagenase-Induced Rat Tendinitis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Lim, G.-S.; Kim, N.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.-C. Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery by Sonophoresis and Simultaneous Application of Sonophoresis and Iontophoresis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskos, K.V.; Guy, R.H. Assessment of Skin Barrier Function Using Transepidermal Water Loss: Effect of Age. Pharm. Res. 1989, 6, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S. Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Low-Frequency Sonophoresis. In BioMEMS and Biomedical Nanotechnology; Ferrari, M., Desai, T., Bhatia, S., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 223–236. ISBN 978-0-387-25565-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, Q.; Lei, L.; Hu, B. Low-Frequency Low Energy Ultrasound Combined with Microbubbles Induces Distinct Apoptosis of A7r5 Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 3282–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.A.; Tadros, M.I.; Mohamed, M.I.; Nageeb El-Helaly, S. Low-Frequency versus High-Frequency Ultrasound-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Agomelatine-Loaded Invasomes: Development, Optimization and in-Vivo Pharmacokinetic Assessment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8893–8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, S.; Kaur, C.D.; Gupta, A.; Verma, N. Skin Targeting Approaches in Cosmetics. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2019, 53, 577–594. [Google Scholar]
- Brucks, R.; Nanavaty, M.; Jung, D.; Siegel, F. The Effect of Ultrasound on the in Vitro Penetration ofIbuprofen Through Human Epidermis. Pharm. Res. 1989, 06, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, E. Drug Delivery across the Skin. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2002, 2, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S.; Farrell, J.; Tang, H.; Terahara, T.; Kost, J.; Langer, R. Determination of Threshold Energy Dose for Ultrasound-Induced Transdermal Drug Transport. J. Control. Release 2000, 63, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, U.; Kaiser, M.; Toll, R.; Mangelsdorf, S.; Audring, H.; Otberg, N.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Porcine Ear Skin: An in Vitro Model for Human Skin. Skin. Res. Technol. 2007, 13, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Qin, F.H.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, X. Enhancing Percutaneous Permeability of Sinomenine Hydrochloride Using Dual-Frequency Sonophoresis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintov, A.C.; Botner, S. Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Microemulsion and Aqueous Systems: Influence of Skin Storage Conditions on the in Vitro Permeability of Diclofenac from Aqueous Vehicle Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 311, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Acute Skin Barrier Disruption with Repeated Tape Stripping: An in Vivo Model for Damage Skin Barrier. Skin. Res. Technol. 2013, 19, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-C.; Shen, L.-C.; Sheu, H.-M.; Lu, C.-C. Tape Stripping and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Treatment Increase the Molecular Weight Cutoff of Polyethylene Glycol Penetration across Murine Skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2003, 295, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
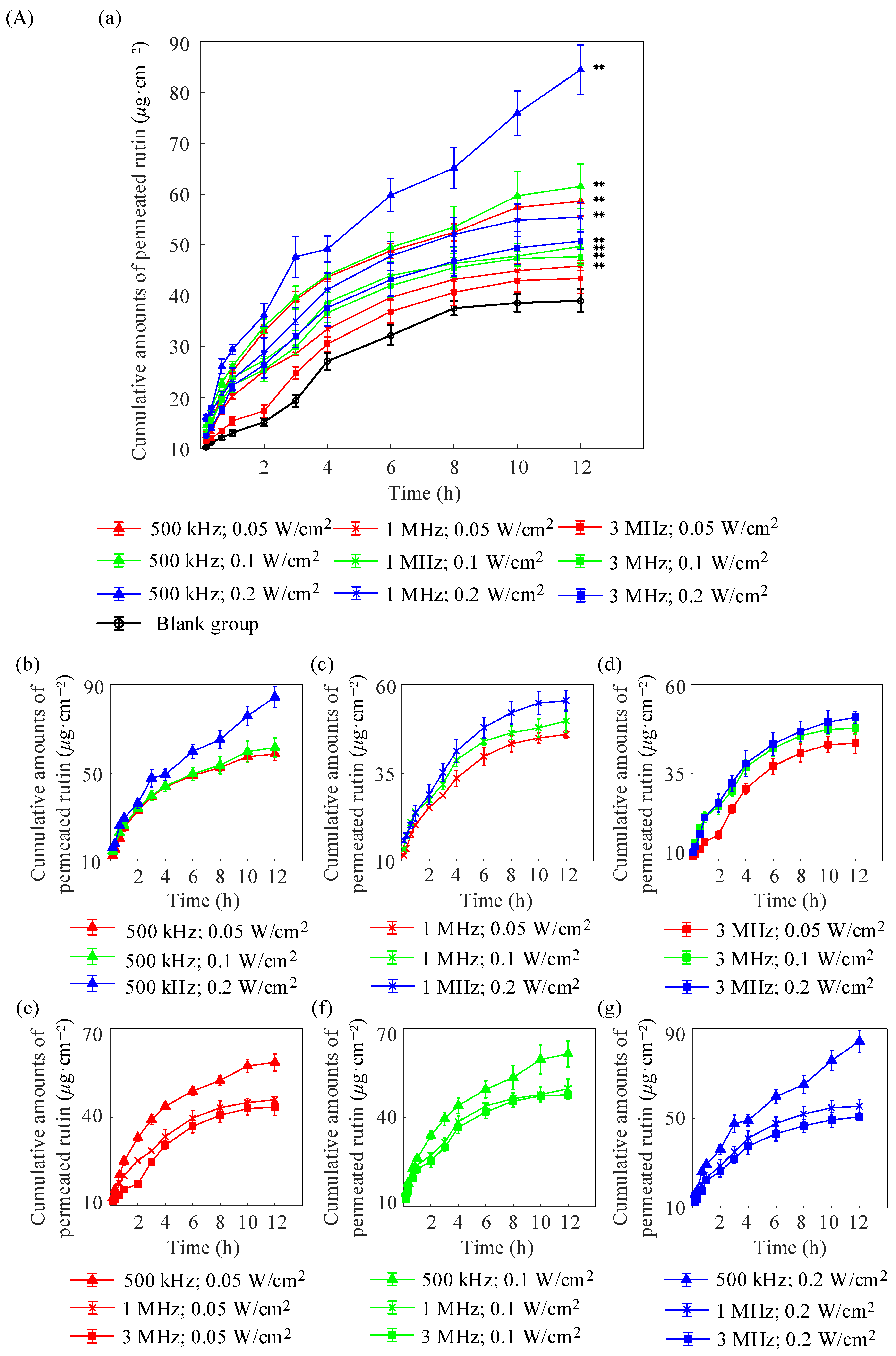
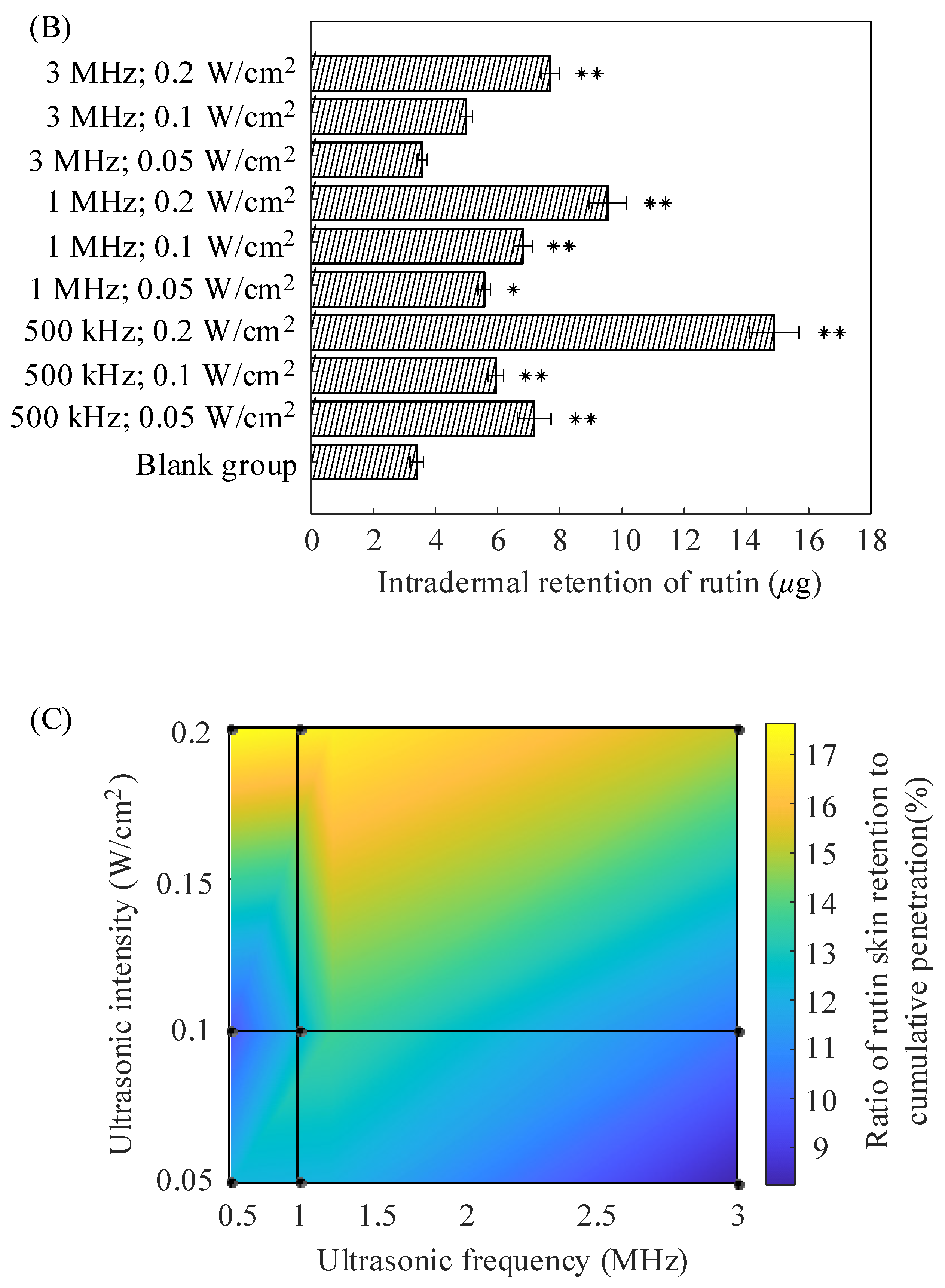
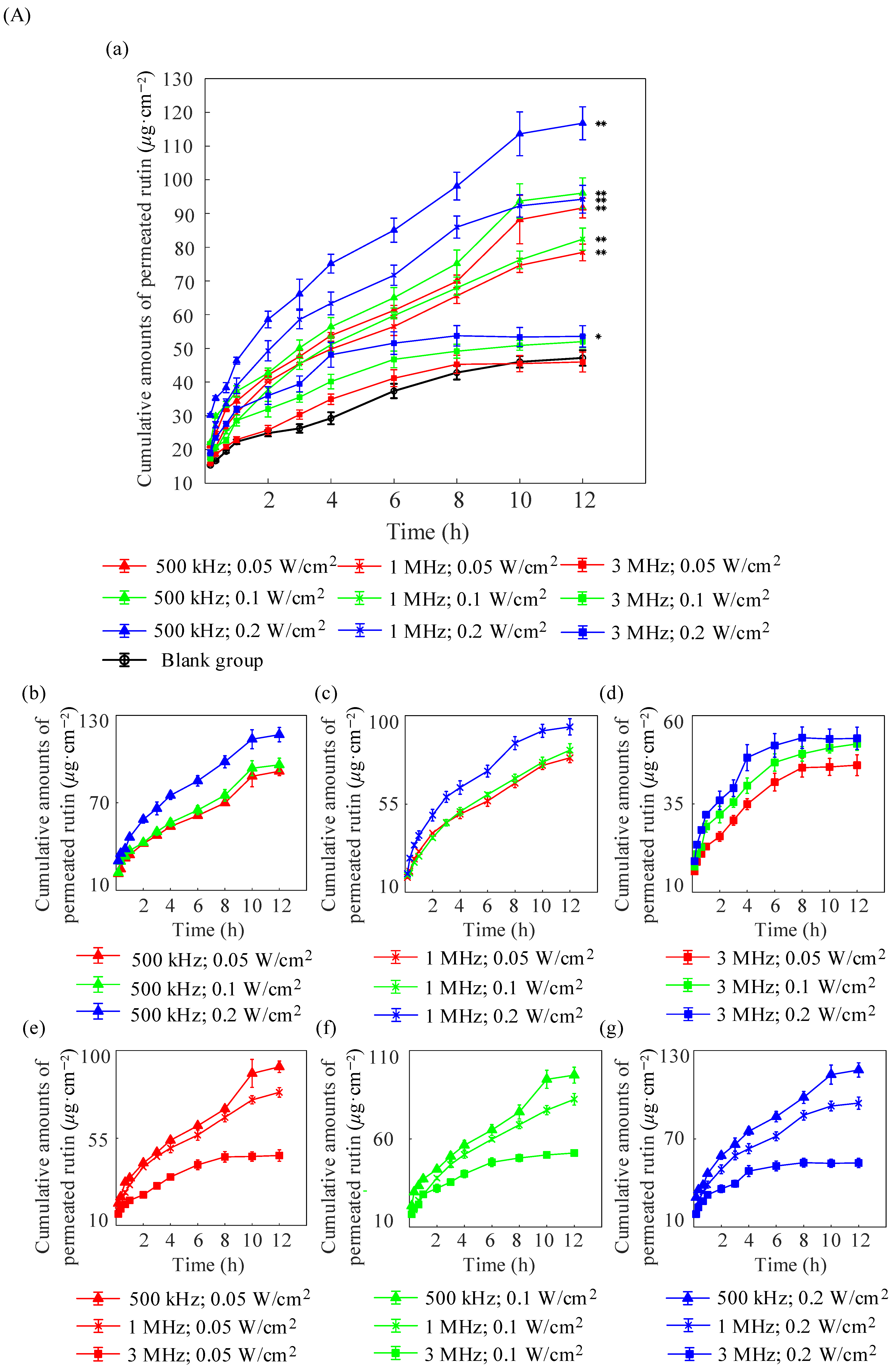
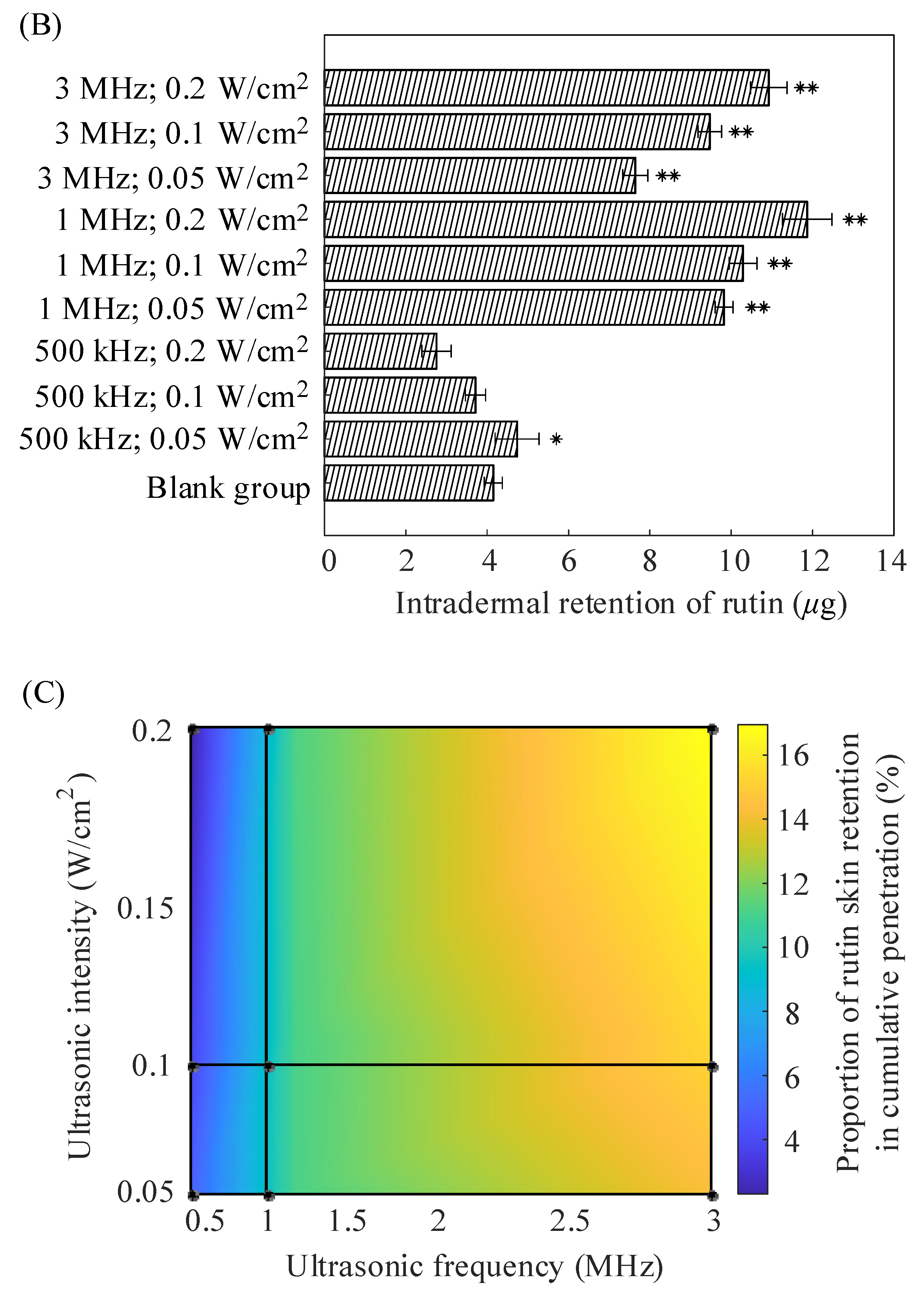
| Formulations | (μg/cm2) | (μg/cm2/h) | (cm/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank group | 39.025 ± 1.211 | 2.396 ± 0.068 | 0.12 ± 0.003 |
| 500 kHz; 0.05 W/cm2 | 58.597 ± 1.892 | 3.842 ± 0.99 | 0.192 ± 0.005 |
| 500 kHz; 0.1 W/cm2 | 61.542 ± 1.814 | 3.924 ± 0.109 | 0.196 ± 0.006 |
| 500 kHz; 0.2 W/cm2 | 84.454 ± 1.718 | 5.695 ± 0.068 | 0.285 ± 0.004 |
| 1 MHz; 0.05 W/cm2 | 45.903 ± 0.963 | 2.853 ± 0.03 | 0.143 ± 0.002 |
| 1 MHz; 0.1 W/cm2 | 49.738 ± 1.831 | 3.03 ± 0.111 | 0.151 ± 0.006 |
| 1 MHz; 0.2 W/cm2 | 55.459 ± 1.129 | 3.307 ± 0.044 | 0.165 ± 0.002 |
| 3 MHz; 0.05 W/cm2 | 43.401 ± 1.737 | 2.664 ± 0.112 | 0.133 ± 0.008 |
| 3 MHz; 0.1 W/cm2 | 47.714 ± 1.282 | 2.942 ± 0.065 | 0.147 ± 0.005 |
| 3 MHz; 0.2 W/cm2 | 50.758 ± 1.683 | 3.185 ± 0.107 | 0.159 ± 0.006 |
| Formulations | (μg/cm2) | (μg/cm2/h) | (cm/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank group | 47.161 ± 1.522 | 3.93 ± 0.104 | 0.197 ± 0.004 |
| 500 kHz; 0.05 W/cm2 | 91.636 ± 1.714 | 7.636 ± 0.117 | 0.382 ± 0.005 |
| 500 kHz; 0.1 W/cm2 | 96.056 ± 2.131 | 8.005 ± 0.145 | 0.4 ± 0.006 |
| 500 kHz; 0.2 W/cm2 | 116.787 ± 2.215 | 9.732 ± 0.151 | 0.487 ± 0.006 |
| 1 MHz; 0.05 W/cm2 | 78.471 ± 1.568 | 6.539 ± 0.107 | 0.327 ± 0.004 |
| 1 MHz; 0.1 W/cm2 | 82.411 ± 1.812 | 6.868 ± 0.123 | 0.343 ± 0.005 |
| 1 MHz; 0.2 W/cm2 | 94.249 ± 2.033 | 7.854 ± 0.138 | 0.393 ± 0.006 |
| 3 MHz; 0.05 W/cm2 | 45.960 ± 1.719 | 3.83 ± 0.117 | 0.192 ± 0.005 |
| 3 MHz; 0.1 W/cm2 | 51.987 ± 1.364 | 4.332 ± 0.093 | 0.217 ± 0.004 |
| 3 MHz; 0.2 W/cm2 | 53.569 ± 1.777 | 4.464 ± 0.121 | 0.223 ± 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Q.; He, B.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. Exploration of Ultrasound-Enhanced Transdermal Delivery Efficiency and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rutin. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040464
Yue Q, He B, Guo Z, Zhang N, Zhang M, Zhang Y. Exploration of Ultrasound-Enhanced Transdermal Delivery Efficiency and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rutin. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040464
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Qing, Bingbing He, Zhenyu Guo, Ningtao Zhang, Mei Zhang, and Yufeng Zhang. 2025. "Exploration of Ultrasound-Enhanced Transdermal Delivery Efficiency and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rutin" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040464
APA StyleYue, Q., He, B., Guo, Z., Zhang, N., Zhang, M., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Exploration of Ultrasound-Enhanced Transdermal Delivery Efficiency and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rutin. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040464






