Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI)-Based Theranostics
Abstract
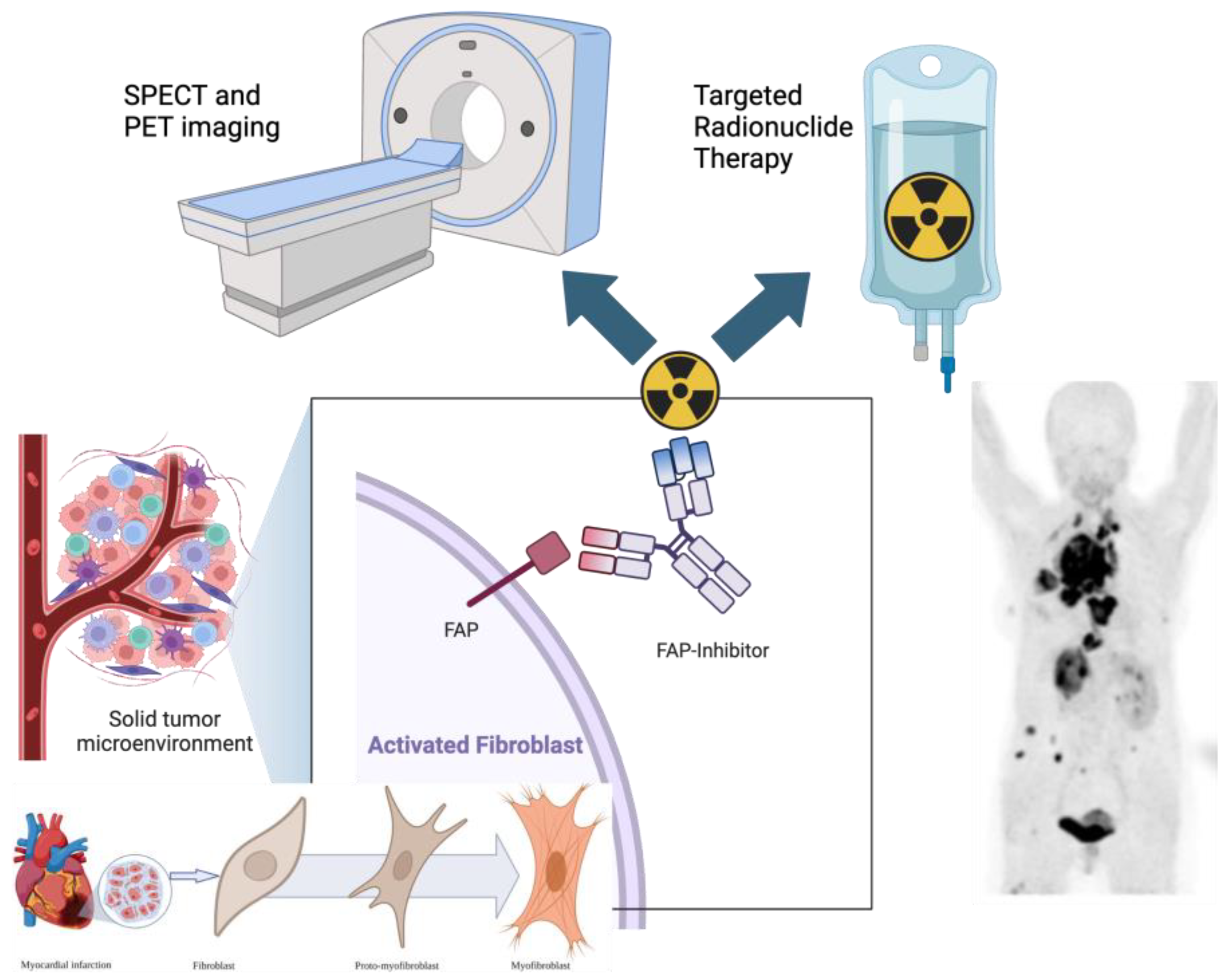
1. Introduction to FAPI Theranostics
FAPI-Based Radioligands
2. Fibroblast Activation Protein in Cancer Imaging
3. The Potential Role of FAPI PET Imaging in Specific Cancers
3.1. CNS Malignancies
3.2. Head and Neck Cancer
3.3. Thyroid Cancer
3.4. Breast Cancer
3.5. Limitations and Clinical Considerations of FAPI PET in Breast Cancer
3.6. Clinical Relevance and Theranostic Potential
3.7. Lung Cancer
3.8. Esophageal Cancer
3.9. Gastric Cancer
3.10. Pancreatic Cancer
3.11. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.12. Colorectal Cancer
3.13. FAPI PET/CT in Gynecological Malignancies
3.14. FAPI PET/CT in Soft-Tissue Sarcomas and Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs)
3.15. FAPI PET/CT in Genitourinary Malignancies
4. Summary of the Role of FAP-Based Imaging in Oncology
5. FAPI PET in Cardiovascular Disease
5.1. Myocardial Infarction
5.2. Myocardial Diseases
5.3. Atherosclerosis
5.4. Other Cardiovascular Conditions
6. Summary of the Potential Role of FAP-Based Imaging in Cardiovascular Disease
7. The Role of FAPI PET Imaging in Inflammatory and Infectious Conditions
7.1. Role in Inflammation Imaging
7.2. Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases (IMIDs)
7.3. Systemic Vasculitis
7.4. Inflammatory Arthritis
7.5. Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) and Fibrosis Imaging
7.6. Role in Infection Imaging
7.7. Tuberculosis (TB)
7.8. Post-COVID-19 Lung Changes
7.9. Aspergillosis and Other Fungal Infections
7.10. Periprosthetic Joint Infections (PJI)
8. Summary of the Potential Role of FAP-Based Imaging in Infection- and Inflammation Imaging
9. Discussion and Recommendations Regarding the Imaging Role of FAPI-Based PET
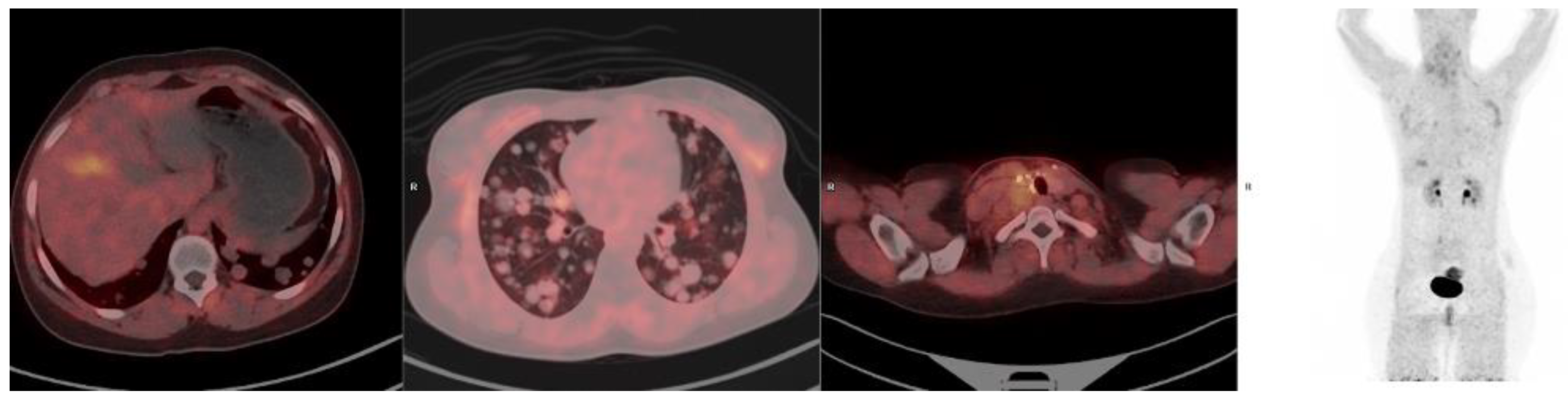
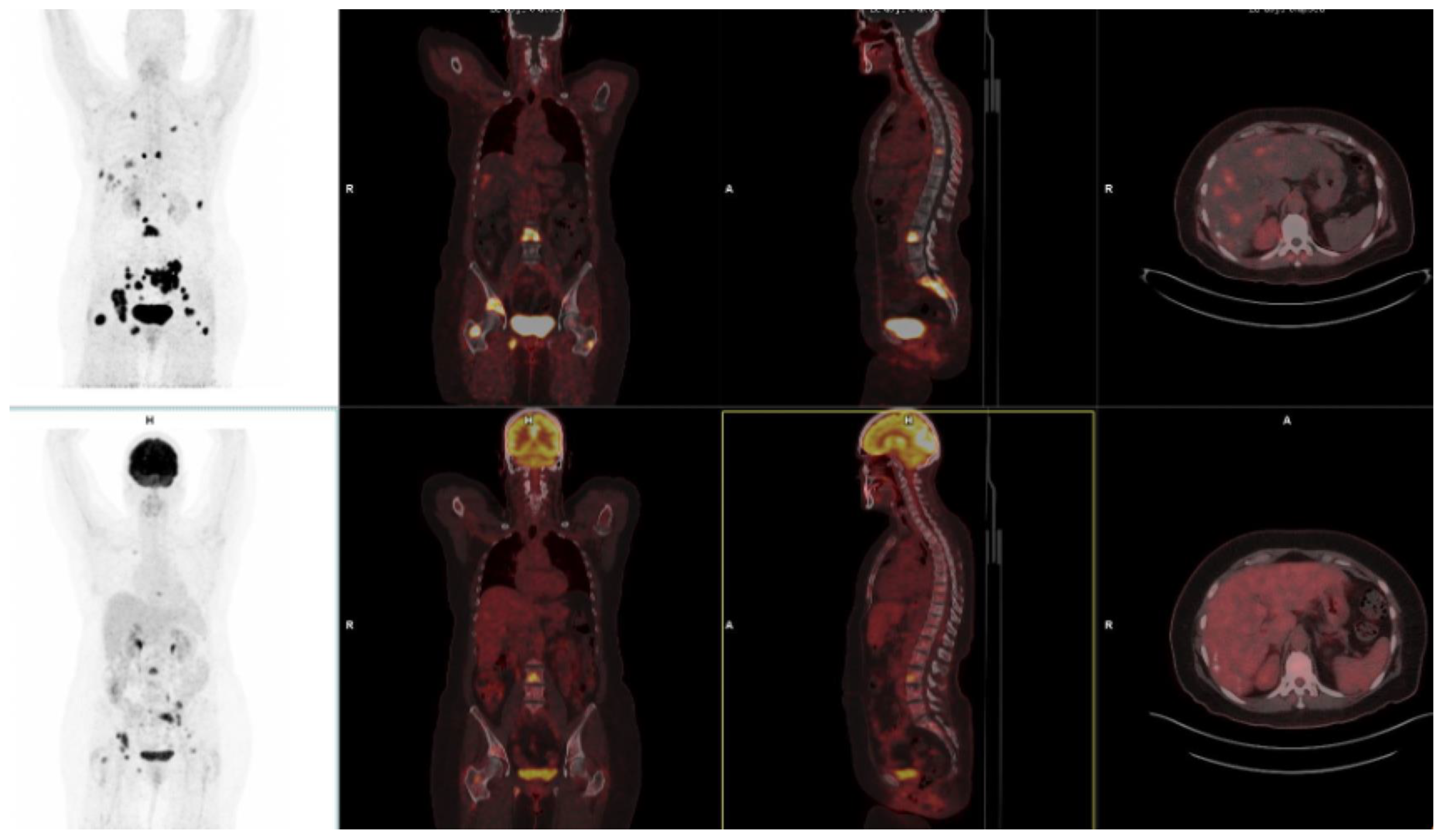
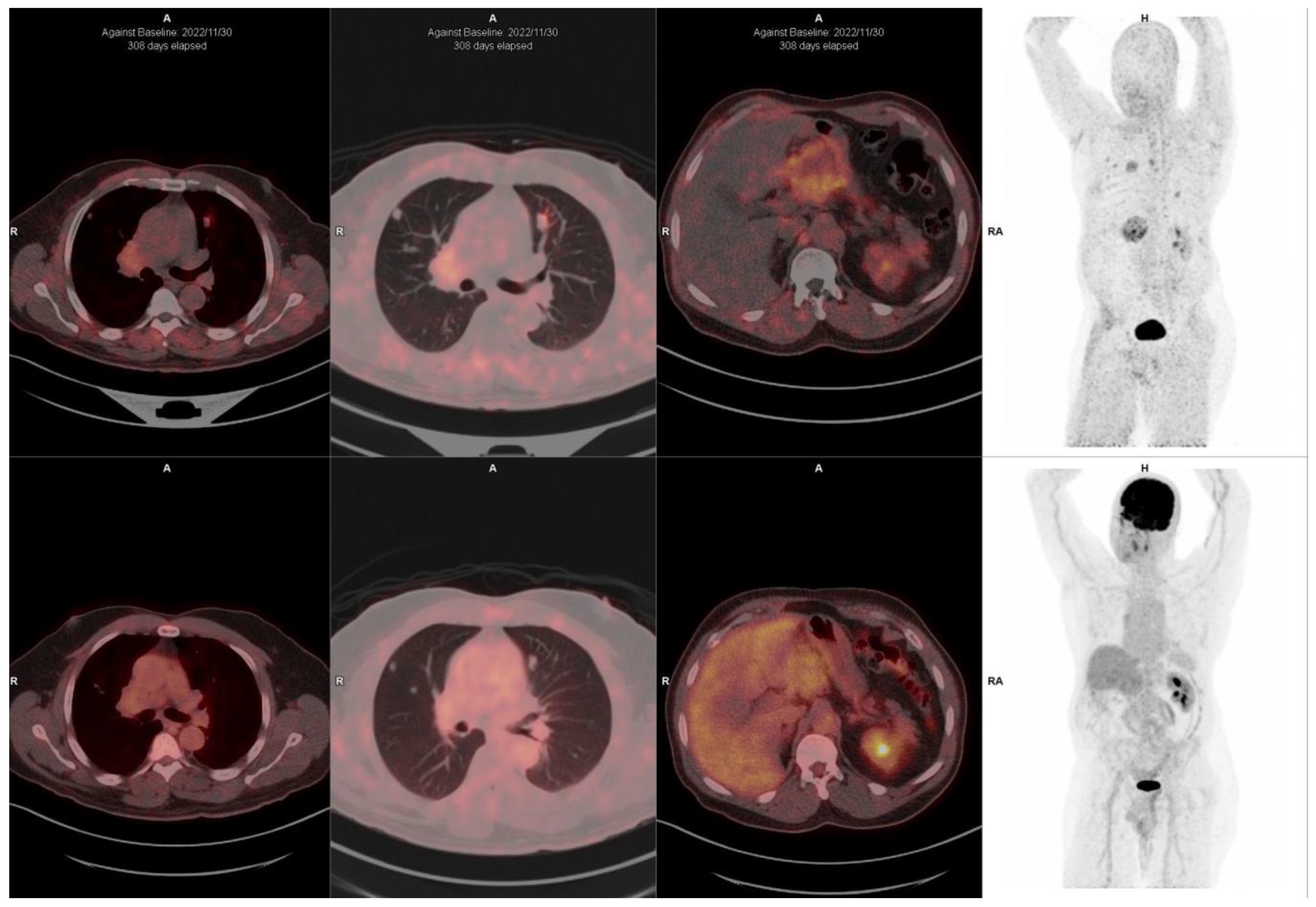
10. FAPI-Based Theranostic Approaches
| Author | Year of Publication | Country | Tracer | Population | Cancers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baum et al. [123] | 2022 | Germany | 177Lu-FAP-2286; 68Ga-FAPI-2286; 68Ga-FAPI-04 | 11 patients | 5 pancreas; 4 breast; 1 rectum; 1 ovary. |
| Ferdinandus et al. [124] | 2022 | Germany | 90Y-FAPI-46; 68Ga-FAPI-46 | 9 patients | 3 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; 4 sarcomas, 1 chordoma, 1 neuroendocrine tumor |
| Lindner et al. [34] | 2020 | Germany | 99mTc-FAP-34; 68Ga-FAPI-46; 90Y-FAPI-46 | 2 patients | 1 pancreas; 1 ovarian |
| Lindner et al. [41] | 2018 | Germany | 90Y-FAPI-04; 68Ga-FAPI-04 | 2 patients | 2 breast |
| Ballal et al. [30] | 2021 | India | 177Lu-DOTA.SA.FAPI; 177Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPI)2 68Ga-DOTA.SA.FAP | 10 patients | 5 thyroid; 4 breast; 1 paraganglioma |
| Ballal et al. [125] | 2022 | India | 68Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPI; 177Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPI)2 | 15 patients | 15 thyroid cancers |
| Assadi et al. [126] | 2021 | Iran | 177Lu-FAPI-46; 68Ga-FAPI-46 | 21 patients | 2 ovarian cancer; 2 sarcomas, 3 colon cancer; 5 breast cancer; 2 pancreatic cancer; 2 prostate cancer; 1 cervical cancer; 1 lung cancer; 1 cholangiocarcinoma; 1 thyroid |
| Kuyumcu et al. [127] | 2021 | Turkey | 177Lu-DOTA-FAPI-04; 68Ga-FAPI-04 | 4 patients | 1 breast; 1 thymic carcinoma, 1 thyroid cancer, 1 ovarian cancer |
11. Challenges and Limitations in FAPI Therapeutic Approaches
12. The Potential Role of FAPI PET-Based Theranostic Approaches
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balkwill, F.R.; Capasso, M.; Hagemann, T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Complexity and opportunities EMT: A naturally occurring transdifferentiation program. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busek, P.; Mateu, R.; Zubal, M.; Kotackova, L.; Sedo, A. Targeting fibroblast activation protein in cancer—Prospects and caveats. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 1933–1968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baghban, R.; Roshangar, L.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Seidi, K.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Jaymand, M.; Kolahian, S.; Javaheri, T.; Zare, P. Tumor microenvironment complexity and therapeutic implications at a glance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Flechsig, P.; Lindner, T.; Abderrahim, L.; Altmann, A.; Mier, W.; Adeberg, S.; Rathke, H.; Röhrich, M.; Winter, H.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Tracer uptake in 28 different kinds of cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; Lindner, T.; Marschalek, M.M.; Loktev, A.; Lehnert, W.; Debus, J.; Jäger, D.; Flechsig, P.; Altmann, A.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Biodistribution and preliminary dosimetry estimate of 2 DOTA-containing FAP-targeting agents in patients with various cancers. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loktev, A.; Lindner, T.; Mier, W.; Debus, J.; Altmann, A.; Jäger, D.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Barthe, P.; Roumestand, C.; et al. A tumor imaging method targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jacobson, F.L.; Van den Abbeele, A.D. Importance of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT for detection of cancer. Radiology 2022, 303, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, P.; Igerc, I.; Beyer, T.; Reinprecht, P.; Hausegger, K. Advantages and limitations of FDG PET in the follow-up of breast cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2004, 31 (Suppl. 1), S125–S134. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, S.; Scholtens, A.M.; Gormsen, L.C. Patient preparation and patient-related challenges with FDG-PET/CT in infectious and inflammatory disease. PET Clin. 2020, 15, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Novruzov, E.; Schmitt, D.; Cardinale, J.; Watabe, T.; Choyke, P.L.; Alavi, A.; Haberkorn, U.; Giesel, F.L. Clinical applications of fibroblast activation protein inhibitor positron emission tomography (FAPI-PET). NPJ Imaging 2024, 2, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, C.; Denlinger, N.; Yang, Y. Recent advances and challenges in cancer immunotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, A.A.; Weiner, L.M. The role of fibroblast activation protein in health and malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rettig, W.J.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Beresford, H.R.; Oettgen, H.F.; Melamed, M.R.; Old, L.J. Cell-surface glycoproteins of human sarcomas: Differential expression in normal and malignant tissues and cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 3110–3114. [Google Scholar]
- Chandekar, K.R.; Prashanth, A.; Vinjamuri, S.; Kumar, R. FAPI PET/CT Imaging-An Updated Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Moon, E.S.; Kramer, V.S.; Roesch, F.; Kumari, S.; Tripathi, M.; ArunRaj, S.T.; Sarswat, S.; Bal, C. Biodistribution, Pharmacokinetics, Dosimetry of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi, and the Head-to-Head Comparison with [18F]F-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Various Cancers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1915–1931. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Ruan, D.; Pang, Y.; Hao, B.; Dai, Y.; Wu, X.; Guo, W.; Fan, C.; Wu, J.; et al. Usefulness of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in patients presenting with inconclusive [18F]FDG PET/CT findings. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Peng, D.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, L. The potential utility of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 as a novel broad-spectrum oncological and non-oncological imaging agent-comparison with [18F]FDG. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawski, S.E.; Lai, J.H.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sudmeier, J.L.; Sanford, D.G.; et al. Identification of selective and potent inhibitors of fibroblast activation protein and prolyl oligopeptidase. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3467–3677. [Google Scholar]
- Linz, C.; Brands, R.C.; Kertels, O.; Dierks, A.; Brumberg, J.; Gerhard-Hartmann, E.; Hartmann, S.; Schirbel, A.; Serfling, S.; Zhi, Y.; et al. Targeting fibroblast activation protein in newly diagnosed squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: Initial experience and comparison to [18F]FDG PET/CT and MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3951–3960. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Pang, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhao, L.; Fan, C.; Ke, J.; Guo, P.; Hao, B.; Fu, H.; Xie, C.; et al. Imaging fibroblast activation protein in liver cancer: A single-center post hoc retrospective analysis to compare [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT versus MRI and [18F]-FDG PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1604–1617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sollini, M.; Kirienko, M.; Gelardi, F.; Fiz, F.; Gozzi, N.; Chiti, A. State-of-the-art of FAPI-PET imaging: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 4396–4414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roustaei, H.; Kiamanesh, Z.; Askari, E.; Sadeghi, R.; Aryana, K.; Treglia, G. Could fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-specific radioligands be considered as pan-tumor agents? Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2022, 2022, 3948873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gege, Z.; Xueju, W.; Bin, J. Head-to-head comparison of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT and FDG PET/CT for the detection of peritoneal metastases: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2023, 220, 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhong, H.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Pang, H. [68Ga]Ga-FAPI PET for the evaluation of digestive system tumors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesel, F.L.; Adeberg, S.; Syed, M.; Lindner, T.; Jiménez-Franco, L.D.; Mavriopoulou, E.; Staudinger, F.; Tonndorf-Martini, E.; Regnery, S.; Rieken, S.; et al. FAPI-74 PET/CT using either 18F-AlF or cold-kit 68Ga labeling: Biodistribution, radiation dosimetry, and tumor delineation in lung cancer patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, T.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Kleist, C.; Krämer, S.; Mier, W.; Cardinale, J.; Kauczor, H.U.; Jäger, D.; et al. 18F-labeled tracers targeting fibroblast activation protein. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2021, 6, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus, P.; Gierse, F.; Burg, M.C.; Büther, F.; Asmus, I.; Dorten, P.; Cufe, J.; Roll, W.; Neri, D.; Cazzamalli, S.; et al. Translational imaging of the fibroblast activation protein (FAP) using the new ligand, [68Ga]Ga-OncoFAP-DOTAGA. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Millul, J.; Bassi, G.; Mock, J.; Elsayed, A.; Pellegrino, C.; Zana, A.; Dakhel Plaza, S.; Nadal, L.; Gloger, A.; Schmidt, E.; et al. An ultra-high-affinity small organic ligand of fibroblast activation protein for tumor-targeting applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101852118. [Google Scholar]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Moon, E.S.; Kramer, V.S.; Roesch, F.; Kumari, S.; Bal, C. First-In-Human Results on the Biodistribution, Pharmacokinetics, and Dosimetry of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [177Lu]Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pang, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, F.; Xu, W.; Meng, T.; Shang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Y.; Wu, H.; et al. Comparison of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI and [18F]FDG uptake in patients with gastric signet-ring-cell carcinoma: A multicenter retrospective study. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrich, M.; Naumann, P.; Giesel, F.L.; Choyke, P.L.; Staudinger, F.; Wefers, A.; Liew, D.P.; Kratochwil, C.; Rathke, H.; Liermann, J.; et al. Impact of 68Ga-FAPIPET/CT imaging on the therapeutic management of primary and recurrent pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.P.; Novruzov, E.; Zhao, T.; Greifenstein, L.; Jakobsson, V.; Perrone, E.; Mishra, A.; Eismant, A.; Ghai, K.; Klein, O.; et al. Radiomolecular theranostics with fibroblast-activation-protein inhibitors and peptides. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 54, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, T.; Altmann, A.; Krämer, S.; Kleist, C.; Loktev, A.; Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.; Mier, W.; Marme, F.; Debus, J.; et al. Design and Development of 99mTc-Labeled FAPI Tracers for SPECT Imaging and 188Re Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Haberkorn, U.; Giesel, F.L. 68Ga- or 18F-FAPI PET/CT—What it can and cannot. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 7877–7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamson, E.J.; Keane, F.M.; Tholen, S.; Schilling, O.; Gorrell, M.D. Understanding fibroblast activation protein (FAP): Substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, E. Turning foes to friends: Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Alhaskawi, A.; Wang, Z.; Lai, J.; Yao, C.; Liu, Z.; Ezzi, S.H.A.; Kota, V.G.; Abdulla, M.H.A.H.; et al. The Superiority of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT Versus FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Various Malignancies. Cancers 2023, 15, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopci, E.; Fanti, S. Non-FDG PET/CT. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020, 216, 669–718. [Google Scholar]
- Wass, G.; Clifford, K.; Subramaniam, R.M. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Accuracy of FAPI PET/CT in Oncologic Studies: Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, T.; Loktev, A.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Debus, J.; Jäger, D.; Mier, W.; Haberkorn, U. Development of quinoline-based theranostic ligands for the targeting of fibroblast activation protein. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watabe, T.; Liu, Y.; Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Shirakami, Y.; Lindner, T.; Ooe, K.; Toyoshima, A.; Nagata, K.; Shimosegawa, E.; Haberkorn, U.; et al. Theranostics Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein in the Tumor Stroma: 64Cu- and 225Ac-Labeled FAPI-04 in Pancreatic Cancer Xenograft Mouse Models. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loktev, A.; Lindner, T.; Burger, E.M.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Debus, J.; Marmé, F.; Jäger, D.; Mier, W.; et al. Development of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Targeted Radiotracers with Improved Tumor Retention. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Rathke, H.; Fink, R.; Dendl, K.; Debus, J.; Mier, W.; Jäger, D.; Lindner, T.; Haberkorn, U. [153Sm]Samarium-labeled FAPI-46 radioligand therapy in a patient with lung metastases of a sarcoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3011–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, C.; Gai, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, X. The 99mTc-labeled FAPI peptide probes exhibit excellent targeting specificity and sensitivity to FAP in SPECT/CT imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65 (Suppl. 2), 242429. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, H.; Cao, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z. [68Ga] Ga-FAPI PET/CT in brain tumors: Comparison with [18F]F-FDG PET/CT. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1436009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Chen, M.; Fu, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Zuo, C.; Guan, Y.; Xu, H. Heterogeneity of fibroblast activation protein expression in the microenvironment of an intracranial tumor cohort: Head-to-head comparison of gallium-68 FAP inhibitor-04 (68Ga-FAPi-04) and fluoride-18 fluoroethyl-L-tyrosine (18F-FET) in positron emission tomography-computed tomography imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 4450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Pang, Y.; Fu, K.; Shang, Q.; Wu, H.; Sun, L.; Lin, Q.; Chen, H. Fibroblast activation protein-based theranostics in cancer research: A state-of-the-art review. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, L.; Teliti, M.; Chytiris, S.; Sparano, C.; Coperchini, F.; Villani, L.; Calì, B.; Petrone, L.; Magri, F.; Trimboli, P.; et al. The American Thyroid Association risk classification of papillary thyroid cancer according to presurgery cytology. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2024, 190, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmo, P.; Alongi, P.; Baratto, L.; Conte, M.; Abenavoli, E.M.; Buschiazzo, A.; Celesti, G.; Dondi, F.; Filice, R.; Gorica, J.; et al. FAPi-based agents in thyroid cancer: A new step towards diagnosis and therapy? A systematic review of the literature. Cancers 2024, 16, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Satapathy, S.; Roesch, F.; Chandekar, K.R.; Martin, M.; Shakir, M.; Agarwal, S.; Rastogi, S.; Moon, E.S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in Radioiodine-Resistant Follicular Cell-Derived Thyroid Cancers Treated with [177Lu]Lu-DOTAGA.FAPi Dimer Therapy. Thyroid 2025, 32, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourbakhsh, S.; Salehi, Y.; Farzanehfar, S.; Ghaletaki, R.; Kashi, M.B.; Abbasi, M. FAPI PET/CT provides higher uptake and better target to back ground in recurrent and metastatic tumors of patients with Iodine refractory papillary thyroid cancer compared with FDG PET CT. Nuklearmedizin 2024, 63, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Zhang, C. Progress in the application of radiolabeled FAPI in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2024, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiong, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, B.; Zhang, C. Comparison of the diagnostic value of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in breast cancer: A systematic review. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2024, 12, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elboga, U.; Sahin, E.; Kus, T.; Cayirli, Y.B.; Aktas, G.; Uzun, E.; Cinkir, H.Y.; Teker, F.; Sever, O.N.; Aytekin, A.; et al. Superiority of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT scan in detecting additional lesions compared to 18FDG PET/CT scan in breast cancer. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2021, 35, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, W.; Meng, T.; Fan, C.; Fu, H.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, L.; Huang, J.; Mi, Y.; et al. FAP-targeted PET/CT imaging in patients with breast cancer from a prospective bi-center study: Insights into diagnosis and clinic management. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, S.; Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Wu, K.; Kong, L.; Xue, J.; Chen, X.; Miao, W.; Zhu, Y. 68Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor PET/CT for the early and late prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients: A prospective study. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novruzov, E.; Mori, Y.; Alavi, A.; Giesel, F.L. The impact of FAP imaging in lung cancer and beyond: A new chapter. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 1946–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Huang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhong, H.; Han, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, P. Performance of [18F] FDG PET/CT versus FAPI PET/CT for lung cancer assessment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.C.; Bai, L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ji, B. Diagnostic performance of FAPI PET/CT for the detection of lymph node metastases in lung cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Acad. Radiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.; Ke, M.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Yin, W.; He, J.; et al. [18F] FAPI adds value to [18F] FDG PET/CT for diagnosing lymph node metastases in stage I-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective study. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Pang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Hu, S.; Lin, L.E.; Fu, L.; Sun, L.; Wu, H.; et al. 68Ga-fibroblast activation protein inhibitor PET/CT on gross tumour volume delineation for radiotherapy planning of oesophageal cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 158, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, X.; You, Z.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y. Role of 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the initial staging of Esophageal Cancer. Nuklearmedizin 2023, 62, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ristau, J.; Giesel, F.L.; Haefner, M.F.; Staudinger, F.; Lindner, T.; Merkel, A.; Schlittenhardt, J.; Kratochwil, C.; Choyke, P.L.; Herfarth, K.; et al. Impact of primary staging with fibroblast activation protein specific enzyme inhibitor (FAPI)-PET/CT on radio-oncologic treatment planning of patients with esophageal cancer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Wegen, S.; Claus, K.; Linde, P.; Rosenbrock, J.; Trommer, M.; Zander, T.; Tuchscherer, A.; Bruns, C.; Schlößer, H.A.; Schröder, W.; et al. Impact of FAPI-46/dual-tracer PET/CT imaging on radiotherapeutic management in esophageal cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, A.A.; Flamen, P. FAP-targeted PET imaging in gastrointestinal malignancies: A comprehensive review. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Li, B.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, Y. Head-to-head comparison of [18F] FDG PET and [68Ga] Ga-FAPI-04 PET in the diagnosis of gastric and pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2024, 12, 513–526. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Huang, C.; Li, D. Head-to-head comparison of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in the detection of cancer recurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 2779. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; Cai, J. The Role of FAPI PET Imaging in Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-analysis Compared with 18F-FDG PET. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 32, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Liu, M.; Shu, Q.; Chen, X.; Cai, L. Performance of fibroblast activating protein inhibitor PET imaging for pancreatic neoplasms assessment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 7804–7812. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Singhal, T.; Parida, G.K.; Rahman, A.; Agrawal, K. Diagnostic performance of FAPI PET/CT vs. 18F-FDG PET/CT in evaluation of liver tumors: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther. 2024, 33, 77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manuppella, F.; Pisano, G.; Taralli, S.; Caldarella, C.; Calcagni, M.L. Diagnostic performances of PET/CT using fibroblast activation protein inhibitors in patients with primary and metastatic liver tumors: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z. Head-to-head comparison of the diagnostic performance between 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 3166–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, M.; Zhu, H.; Wu, A.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X. Diagnostic value of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 in patients with colorectal cancer in comparison with [18F]F-FDG PET/CT. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1087792. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Hao, P.; Peng, R. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI PET CT/MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in metastatic lesions of gynecological cancers: A systematic review and head-to-head meta-analysis. Acta Radiol. 2024, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendl, K.; Koerber, S.A.; Finck, R.; Mokoala, K.M.; Staudinger, F.; Schillings, L.; Heger, U.; Röhrich, M.; Kratochwil, C.; Sathekge, M.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI-PET/CT in patients with various gynecological malignancies. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 4089–4100. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Q.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L. Head-to-head comparison of 18F-FDG and 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT for radiological evaluation of cervical cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 48, 928–932. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, S.; Yan, W.; Luo, Z.; Song, S. Head-to-head evaluation of [18F]FDG and [6Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in recurrent soft tissue sarcoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wen, F.; Lin, F.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Predictive performance of [18F]F-fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI)-42 positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in evaluating response of recurrent or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Complementary or alternative to [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT? Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 5333. [Google Scholar]
- Ortolan, N.; Urso, L.; Zamberlan, I.; Filippi, L.; Buffi, N.M.; Cittanti, C.; Uccelli, L.; Bartolomei, M.; Evangelista, L. Is there a role for FAPI PET in urological cancers? Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 28, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagens, M.J.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; Wondergem, M.; Boellaard, T.N.; Sanguedolce, F.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Bex, A.; Vis, A.N.; van der Poel, H.G.; Mertens, L.S.; et al. A Systematic Review on the Diagnostic Value of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor PET/CT in Genitourinary Cancers. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Fibrotic disease and the TH1/TH2 paradigm. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nagaraju, C.K.; Dries, E.; Popovic, N.; Singh, A.A.; Haemers, P.; Roderick, H.L.; Claus, P.; Sipido, K.R.; Driesen, R.B. Global fibroblast activation throughout the left ventricle but localized fibrosis after myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganath, K.; Craig, N.; Barton, A.; Joshi, S.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Erba, P.A.; Glaudemans, A.W.; Saraste, A.; Bucerius, J.; Lubberink, M.; et al. Cardiovascular PET imaging of fibroblast activation: A review of the current literature. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2024, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewton, N.; Liu, C.Y.; Croisille, P.; Bluemke, D.; Lima, J.A.C. Assessment of Myocardial Fibrosis with Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 891–903. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.K.; Noguera-Ortega, E.; Xiao, Z.; Todd, L.; Scholler, J.; Song, D.; Liousia, M.; Lohith, K.; Xu, K.; Edwards, K.J.; et al. Monitoring Therapeutic Response to Anti-FAP CAR T Cells Using [18F]AlF-FAPI-74. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5330–5342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lyu, Z.; Han, W.; Zhao, H.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhao, C.; Tian, L.; et al. A clinical study on relationship between visualization of cardiac fibroblast activation protein activity by Al18F-NOTA-FAPI-04 positron emission tomography and cardiovascular disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 921724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Serfling, S.E.; Leistner, D.M.; Speer, T.; Werner, R.A. FAPI-PET in Cardiovascular Disease. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 54, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Takawale, A.; Lee, J.; Kassiri, Z. Cardiac fibroblasts, fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodelling in heart disease. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2012, 5, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmanns, J.; Hoffmann, D.; Habbaba, Y.; Schmitto, J.D.; Sedding, D.; Fraccarollo, D.; Galuppo, P.; Bauersachs, J. Fibroblast activation protein alpha expression identifies activated fibroblasts after myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 87, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Varasteh, Z.; Mohanta, S.; Robu, S.; Braeuer, M.; Li, Y.; Omidvari, N.; Topping, G.; Sun, T.; Nekolla, S.G.; Richter, A.; et al. Molecular Imaging of Fibroblast Activity After Myocardial Infarction Using a 68Ga-Labeled Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor, FAPI-04. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Diekmann, J.; Koenig, T.; Thackeray, J.T.; Derlin, T.; Czerner, C.; Neuser, J.; Ross, T.L.; Schäfer, A.; Tillmanns, J.; Bauersachs, J.; et al. Cardiac Fibroblast Activation in Patients Early After Acute Myocardial Infarction: Integration with MR Tissue Characterization and Subsequent Functional Outcome. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xie, B.; Wang, J.; Xi, X.Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, B.X.; Li, L.; Hua, C.; Zhao, S.; Su, P.; Chen, M.; et al. Fibroblast activation protein imaging in reperfused ST-elevation myocardial infarction: Comparison with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, C.; Du, X. [18F]AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET imaging of fibroblast activation protein in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63 (Suppl. 2), 3330. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Zhang, X.; He, S.; Gai, Y.; Qin, C.; Hu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bai, P.; Wang, J.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET visualize heart failure: From mechanism to clinic. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 475–485. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Xu, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.F.; Zhao, S. Early detection of anthracyclineinduced cardiotoxicity using [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 51, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, M.; Xi, X.Y.; Chen, B.X.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, B.; Dong, Z.; et al. Myocardial Activity at 18FFAPI PET/CT and Risk for Sudden Cardiac Death in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Radiology 2022, 306, e221052. [Google Scholar]
- Puls, M.; Beuthner, B.E.; Topci, R.; Vogelgesang, A.; Bleckmann, A.; Sitte, M.; Lange, T.; Backhaus, S.J.; Schuster, A.; Seidler, T.; et al. Impact of myocardial fibrosis on left ventricular remodelling, recovery, and outcome after transcatheter aortic valve implantation in different haemodynamic subtypes of severe aortic stenosis. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann, J.; Neuser, J.; Röhrich, M.; Derlin, T.; Zwadlo, C.; Koenig, T.; Weiberg, D.; Jäckle, F.; Kempf, T.; Ross, T.L.; et al. Molecular Imaging of Myocardial Fibroblast Activation in Patients with Advanced Aortic Stenosis Before Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Pilot Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Monslow, J.; Todd, L.; Chojnowski, J.E.; Govindaraju, P.K.; Assoian, R.K.; Puré, E. Fibroblast activation protein regulates lesion burden and the fibroinflammatory response in Apoe-deficient mice in a sexually dimorphic manner. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1118–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Dendl, K.; Koerber, S.A.; Finck, R.; Mokoala, K.M.; Staudinger, F.; Schillings, L.; Heger, U.; Röhrich, M.; Kratochwil, C.; Sathekge, M. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 727–744. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmala, A.; Serfling, S.E.; Michalski, K.; Lindner, T.; Schirbel, A.; Higuchi, T.; Hartrampf, P.E.; Derlin, T.; Buck, A.K.; Weich, A.; et al. Molecular imaging of arterial fibroblast activation protein: Association with calcified plaque burden and cardiovascular risk factors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Ning, J.; Li, J.; Lai, Z.; Shi, X.; Xing, H.; Hacker, M.; Liu, B.; Huo, L.; Li, X. Feasibility of In Vivo Imaging of Fibroblast Activation Protein in Human Arterial Walls. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT Versus 18F-FDG PET/CT for the Evaluation of Disease Activity in Takayasu Arteritis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Park, C.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.S. Serial 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT After Treatment of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 48, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lartey, D.A.; Schilder, L.A.; Zwezerijnen, G.J.C.; D’haens, G.R.A.M.; Grootjans, J.; Löwenberg, M. FAPi PET/CT Imaging to Identify Fibrosis in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Chen, H.; Hou, P.; Cheng, L.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Lv, J.; Ke, M.; Wu, X.; Lei, Y.; et al. Comparison of [18F]FAPI-42 and [18F]FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of systemic vasculitis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 52, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidkonz, C.; Kuwert, T.; Götz, T.I.; Ramming, A.; Atzinger, A. Recent advances in nuclear medicine and their role in inflammatory arthritis: Focus on the emerging role of FAPI PET/CT. Skelet. Radiol. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, M.; Kim, G.H.; Rerkpichaisuth, V.; Teng, P.Y.; Armstrong, W.R.; Carlucci, G.; Dahlbom, M.; Abtin, F.; Lari, S.M.; Fishbein, G.A.; et al. Correlation of FAPI PET uptake with immunohistochemistry in explanted lungs from patients with advanced interstitial lung disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Wu, X.; Pang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, H. [18F]FDG and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the evaluation of tuberculous lesions. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 651–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gong, W.; Yang, X.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y. Increased FAPI activity in pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 48, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sviridenko, A.; Boehm, A.; di Santo, G.; Uprimny, C.; Nilica, B.; Fritz, J.; Giesel, F.L.; Haberkorn, U.; Sahanic, S.; Decristoforo, C.; et al. Enhancing Clinical Diagnosis for Patients with Persistent Pulmonary Abnormalities After COVID-19 Infection: The Potential Benefit of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musameh, K.; O’Brien, S.; Mehboob, R.; Butler, T.; Cunningham, Z.; Buckley, C.; Atzinger, A.; Kuwert, T.; Mitchell, P.; Donnelly, S.C. Evaluation of fibroblast activation protein-specific PET/CT in a patient with post-COVID pneumonitis. Respirol. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e01446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullik, Y.; Wessendorf, T.E.; Theegarten, D.; Winantea, J.; Hautzel, H.; Opitz, M. Aspergillus fumigatus: Is Dual-Tracer 18FDG/68Ga-FAPI PET/CT Capable of Distinguishing Fungal Infection and Unspecific Inflammation from Recurrent Lung Cancer? Clin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 49, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qi, E.; Hao, L.; et al. Diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 for periprosthetic hip joint infection. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentestuen, M.; Al-Obaydi, N.; Zacho, H.D. FAPI-avid nonmalignant PET/CT findings: An expedited systematic review. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 53, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, D.; Rizzo, A.; Slart, R.H.; Hess, S.; Noriega-Álvarez, E.; Wakfie-Corieh, C.G.; Leccisotti, L.; Glaudemans, A.W.; Gheysens, O.; Treglia, G. The Role of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor Positron Emission Tomography in Inflammatory and Infectious Diseases: An Updated Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoven, A.F.v.D.; Keijsers, R.G.M.; Lam, M.G.E.H.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Verburg, F.A.; Vogel, W.V.; Lavalaye, J. Current research topics in FAPI theranostics: A bibliometric analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Gharapapagh, E.; Dabiri, S.; Heidari, P.; Aghanejad, A. Theranostics in targeting fibroblast activation protein bearing cells: Progress and challenges. Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudicella, R.; Spataro, A.; Crocè, L.; Giacoppo, G.; Romano, D.; Davì, V.; Lopes, M.; Librando, M.; Nicocia, A.; Rappazzo, A.; et al. Preliminary findings of the role of FAPi in prostate cancer theranostics. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, T.; Weber, W.A.; Eiber, M. Future of theranostics: An outlook on precision oncology in nuclear medicine. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60 (Suppl. 2), 13S–19S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sidrak, M.M.A.; De Feo, M.S.; Corica, F.; Gorica, J.; Conte, M.; Filippi, L.; Schillaci, O.; De Vincentis, G.; Frantellizzi, V. Fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI)-based theranostics—Where we are at and where we are heading: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.P.; Schuchardt, C.; Singh, A.; Chantadisai, M.; Robiller, F.C.; Zhang, J.; Mueller, D.; Eismant, A.; Almaguel, F.; Zboralski, D.; et al. Feasibility, Biodistribution, and Preliminary Dosimetry in Peptide-Targeted Radionuclide Therapy of Diverse Adenocarcinomas Using 177Lu-FAP-2286: First-in-Humans Results. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferdinandus, J.; Costa, P.F.; Kessler, L.; Weber, M.; Hirmas, N.; Kostbade, K.; Bauer, S.; Schuler, M.; Ahrens, M.; Schildhaus, H.U.; et al. Initial Clinical Experience with 90Y-FAPI-46 Radioligand Therapy for Advanced-Stage Solid Tumors: A Case Series of 9 Patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Moon, E.S.; Roesch, F.; Kumari, S.; Agarwal, S.; Tripathi, M.; Sahoo, R.K.; Mangu, B.S.; Tupalli, A.; et al. Novel Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor-Based Targeted Theranostics for Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients: A Pilot Study. Thyroid 2022, 32, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Assadi, M.; Rekabpour, S.J.; Jafari, E.; Divband, G.; Nikkholgh, B.; Amini, H.; Kamali, H.; Ebrahimi, S.; Shakibazad, N.; Jokar, N.; et al. Feasibility and Therapeutic Potential of 177Lu-Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor-46 for Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Cancers: A Preliminary Study. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, e523–e530. [Google Scholar]
- Kuyumcu, S.; Kovan, B.; Sanli, Y.; Buyukkaya, F.; Has Simsek, D.; Özkan, Z.G.; Isik, E.G.; Ekenel, M.; Turkmen, C. Safety of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Targeted Radionuclide Therapy by a Low-Dose Dosimetric Approach Using 177Lu-FAPI04. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 641–646. [Google Scholar]

| FAP Ligand | Diagnostic Isotope | Therapeutic Isotope | Reference | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAP-02 | 68Ga | Lindner et al. [41] | Early small-molecule FAP tracer | |
| FAP-04 | 68Ga | 90Y, 225Ac | Lindner et al. [41], Watabe et al. [42] | First clinical applied small-molecule FAP tracer |
| FAP-34 | 99mTc | 188Re | Lindner et al. [34] | Applied for diagnostic scintigraphy and SPECT, theranostic application |
| Tc99m FAPI | 99mTc | Wang et al. [45] | Applied for diagnostic scintigraphy and SPECT | |
| FAP-46 | 68Ga | 90Y, 153Sm | Loktev et al. [43], Kratochwil et al. [44] | Applied for diagnostic, potential theranostic application |
| FAP-74 | 68Ga, 18F | Giesel et al. [26], Lindner et al. [27] | Applied for diagnostic PET with 18F, potential application with 68Ga | |
| OncoFAP-DOTAGA | 68Ga | Backhaus et al. [28], Millul et al. [29] | Applied for diagnostic PET, considered for theranostic application | |
| DOTA.SA.FAPI | 68Ga | Ballal et al. [30] | Applied for diagnostic PET | |
| Boron pro-alanine-FAPI | 68Ga | Poplawski et al. [19] | Applied for diagnostic PET | |
| DOTAGA. (SA.FAPI)2 | 68Ga | 177Lu | Ballal et al. [30] | Applied for diagnostic PET, theranostic application |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serumula, W.; Pillay, V.; Hadebe, B.; Vorster, M. Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI)-Based Theranostics. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040522
Serumula W, Pillay V, Hadebe B, Vorster M. Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI)-Based Theranostics. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040522
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerumula, William, Venesen Pillay, Bawinile Hadebe, and Mariza Vorster. 2025. "Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI)-Based Theranostics" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040522
APA StyleSerumula, W., Pillay, V., Hadebe, B., & Vorster, M. (2025). Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI)-Based Theranostics. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040522








