Identification of Active Markers of Chinese Formula Yupingfeng San by Network Pharmacology and HPLC-Q-TOF–MS/MS Analysis in Experimental Allergic Rhinitis Models of Mice and Isolated Basophilic Leukemia Cell Line RBL-2H3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimization of Chromatography Conditions
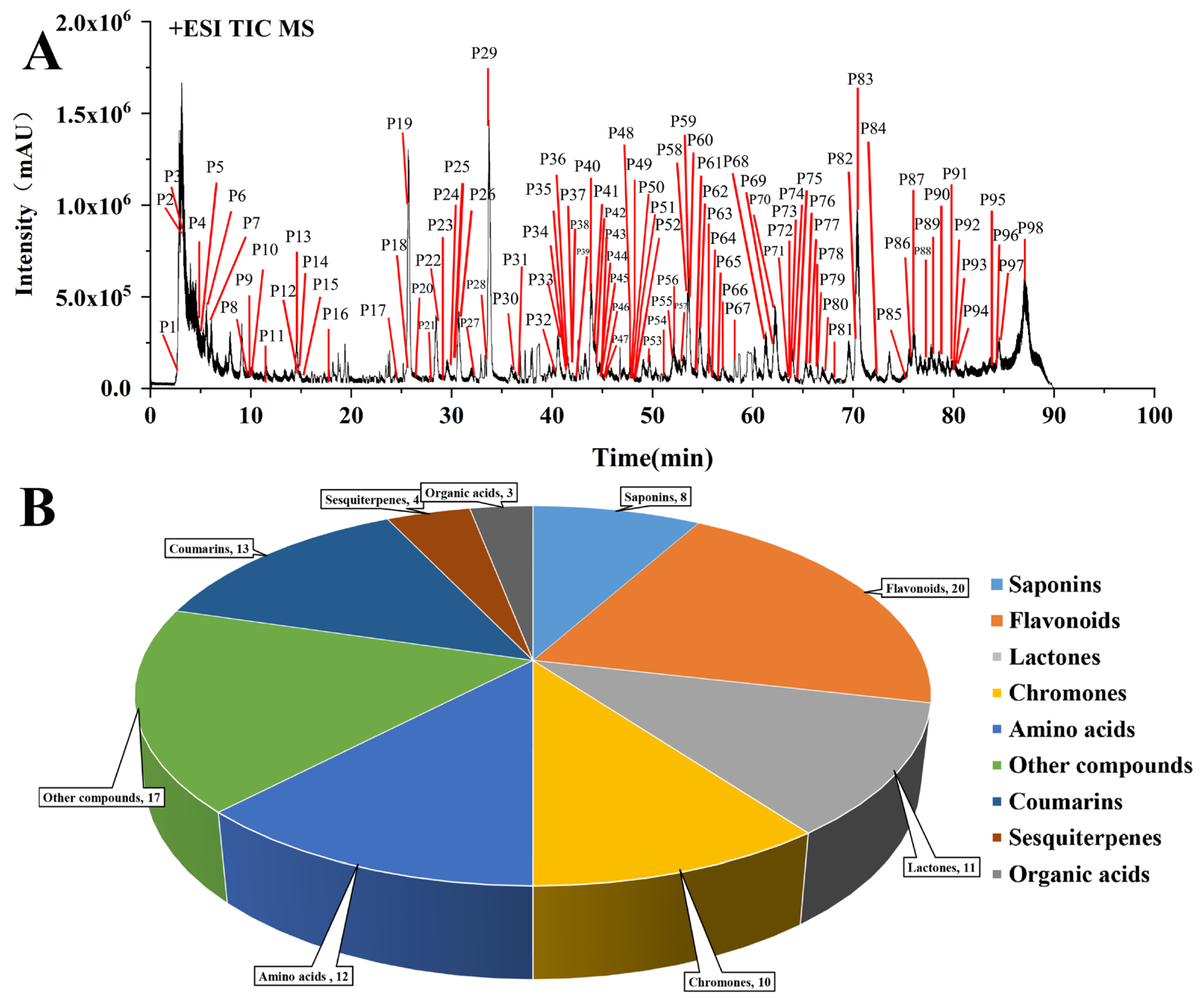
2.2. Chemical Profile of YPFS
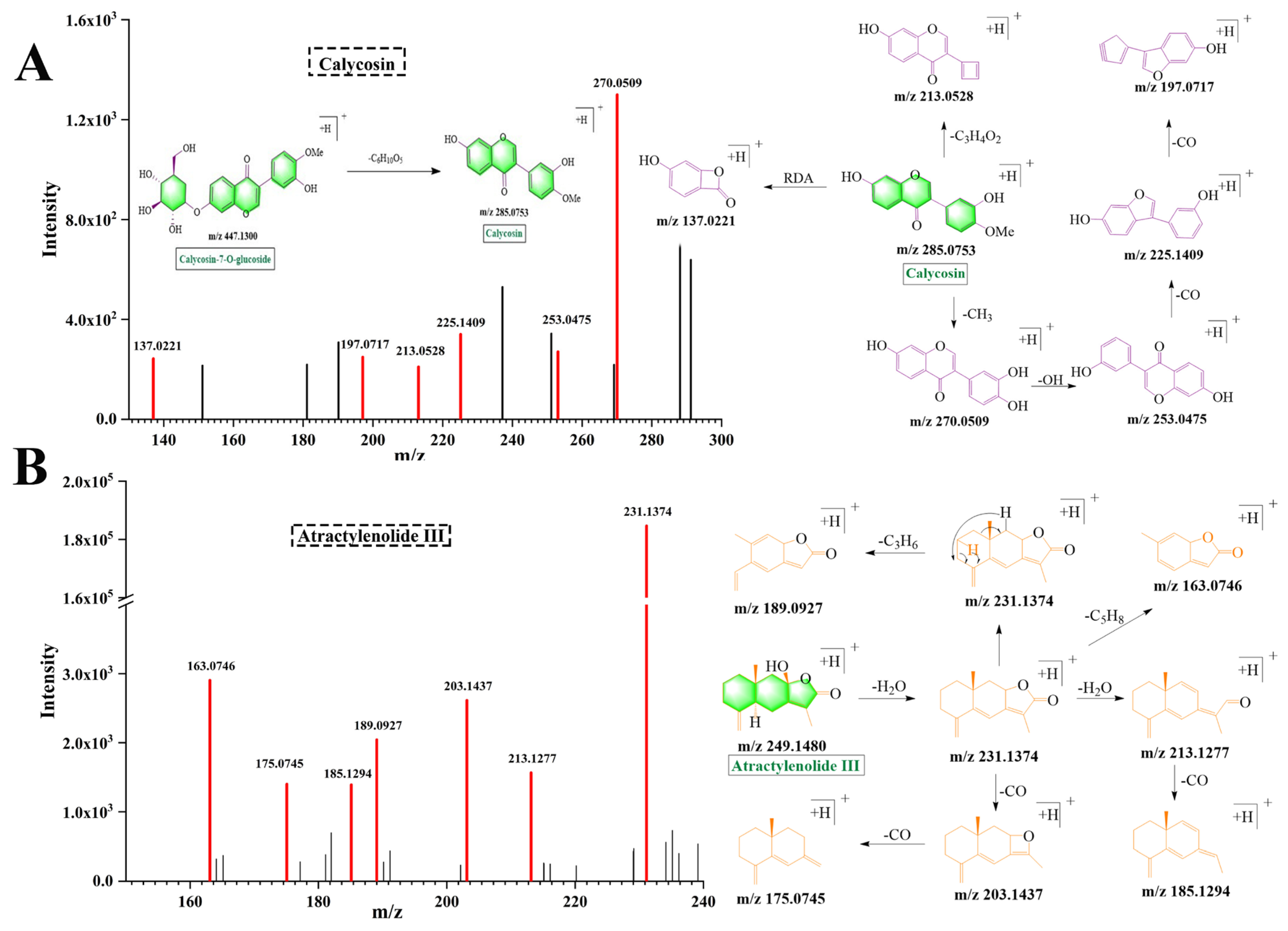
2.3. Characterization of Compounds
2.3.1. Flavonoids
2.3.2. Lactones
2.3.3. Coumarins
2.3.4. Chromones
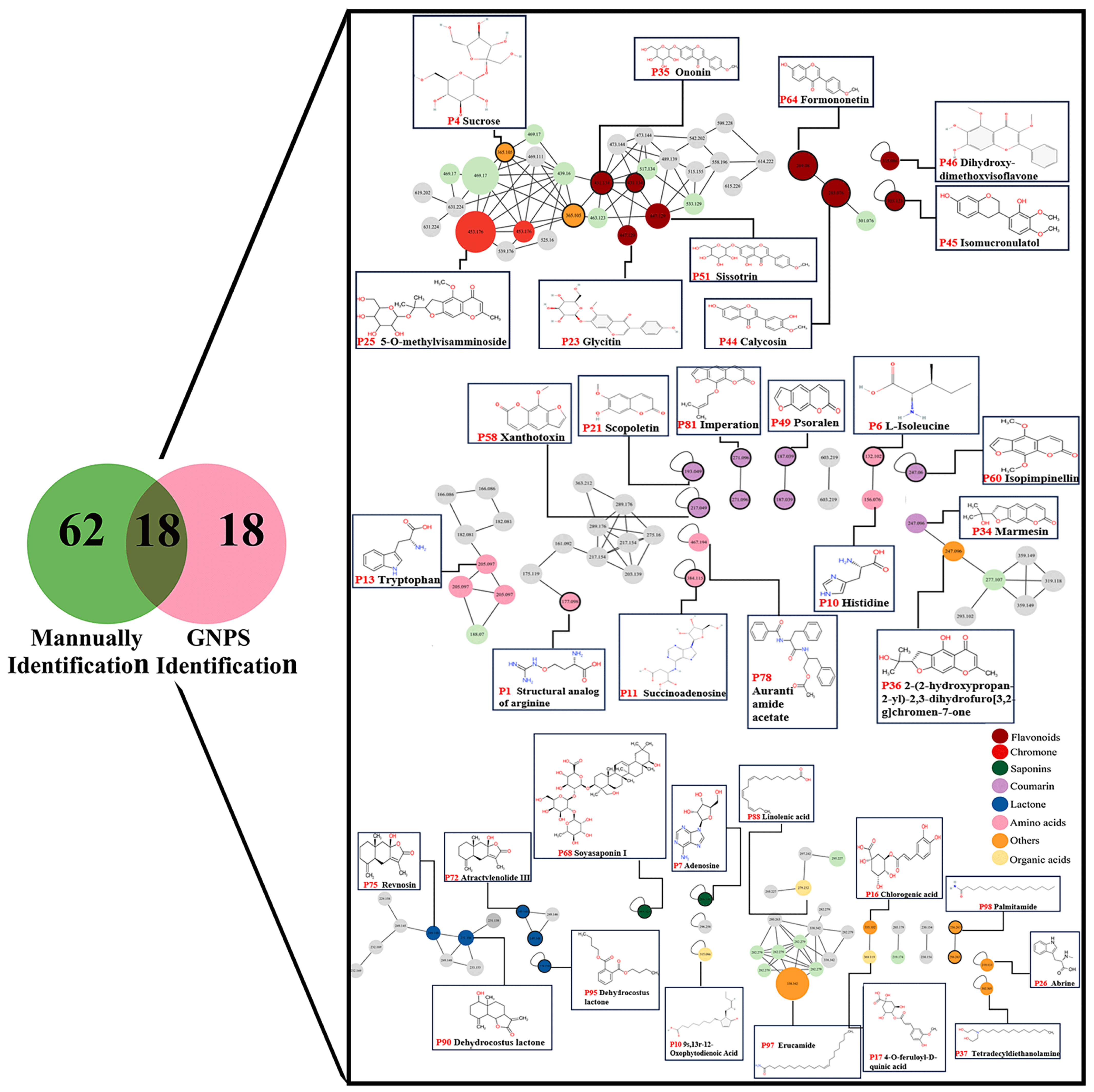
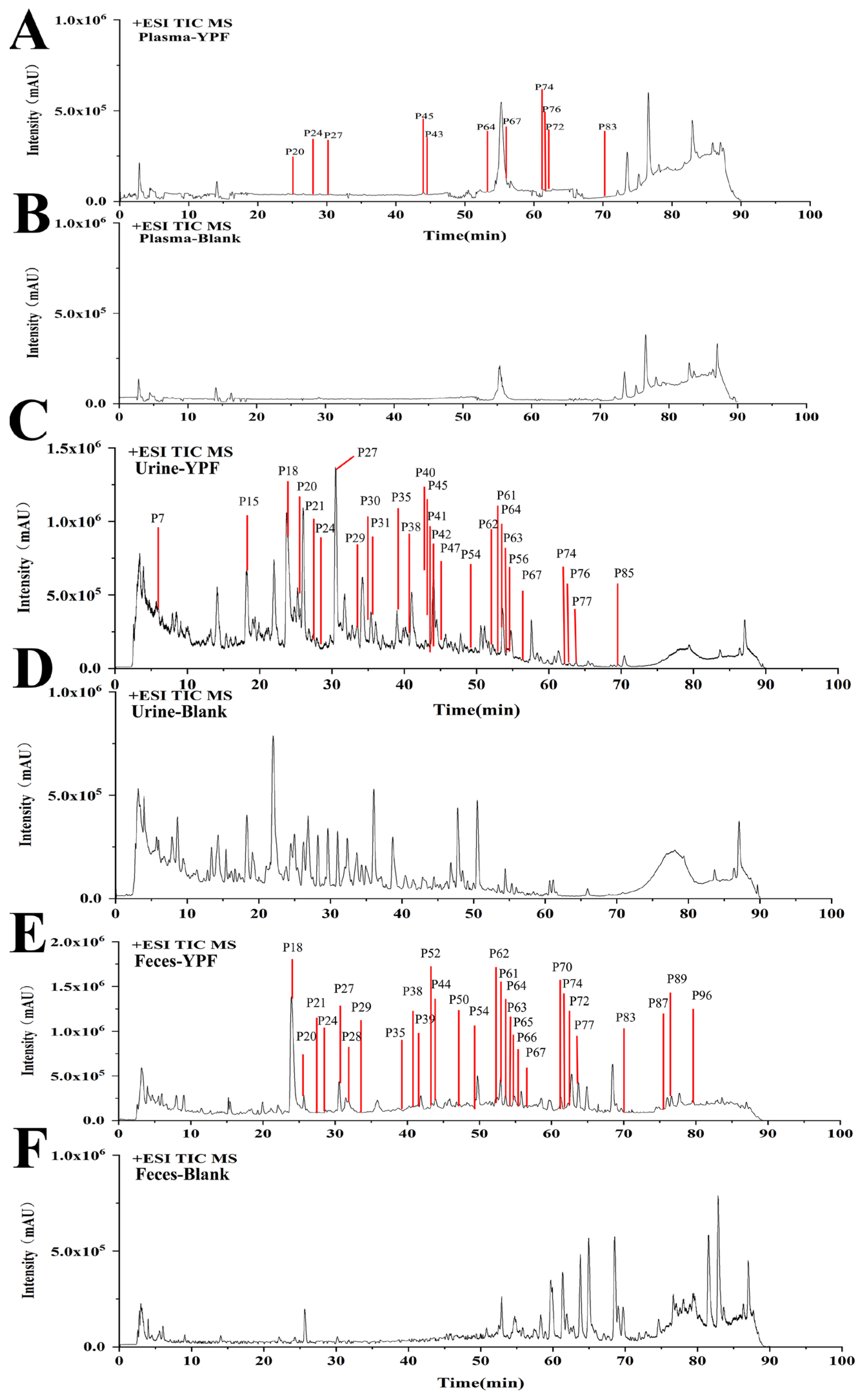
2.4. Identification of YPFS Prototype Components In Vivo
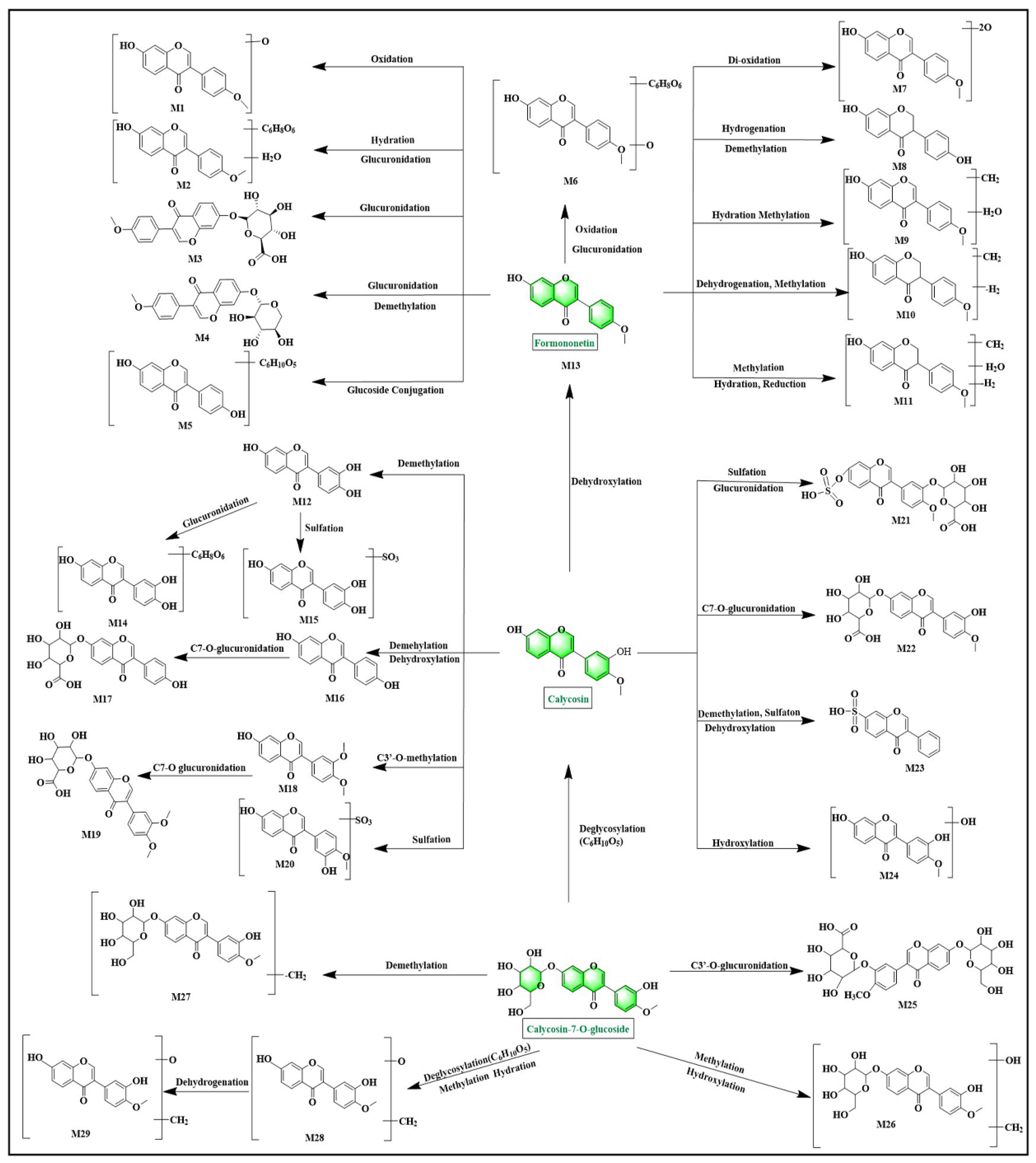
2.5. Identification of YPFS Metabolites in Vivo
2.5.1. Flavonoid Metabolites
2.5.2. Saponins Metabolites
2.5.3. Lactones Metabolites
2.5.4. Chromone and Coumarin Metabolites
2.6. Metabolic Types
2.7. Network Pharmacology
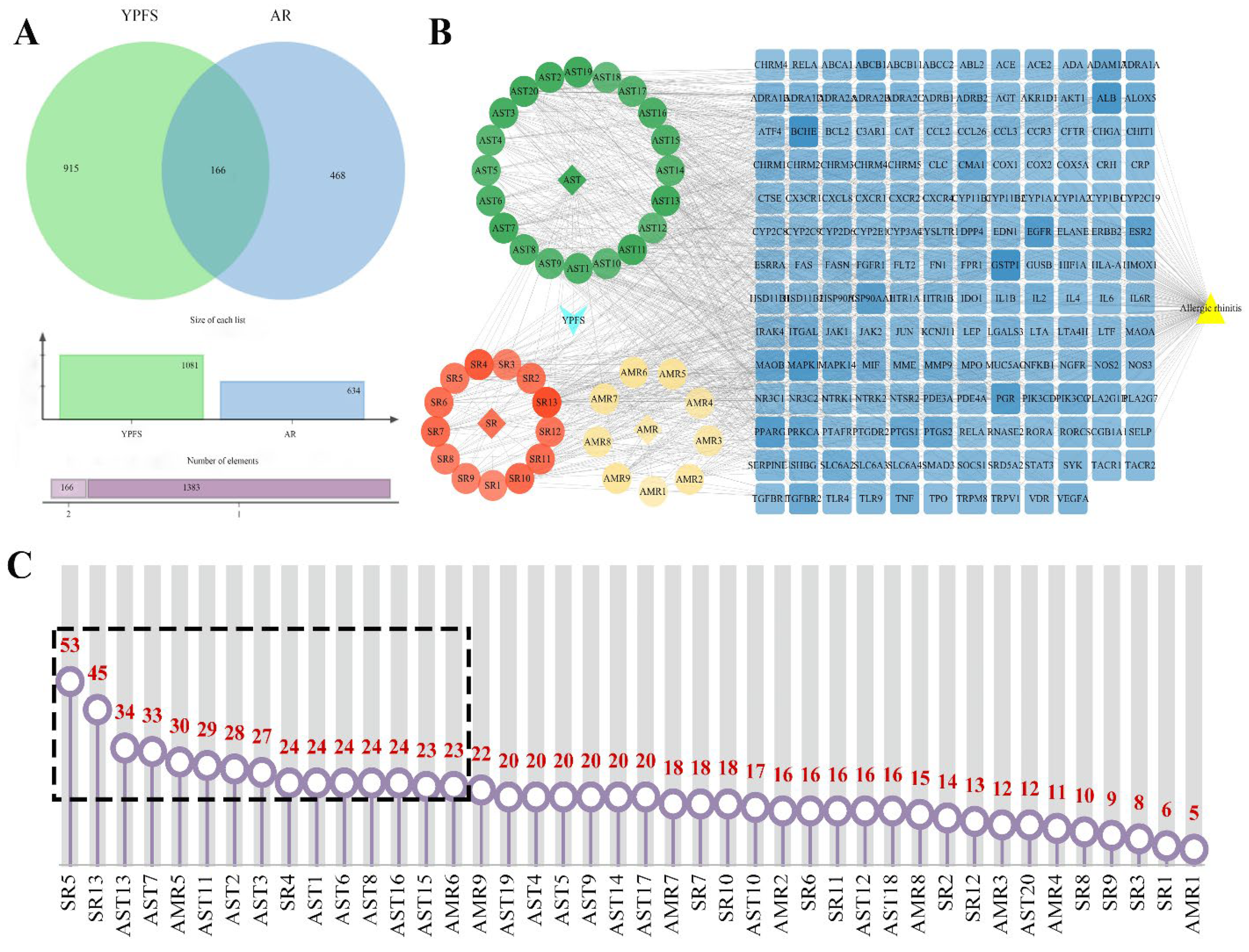
2.7.1. Construction of YPFS Composition-Targets-AR Networks and Screening of the Key Components
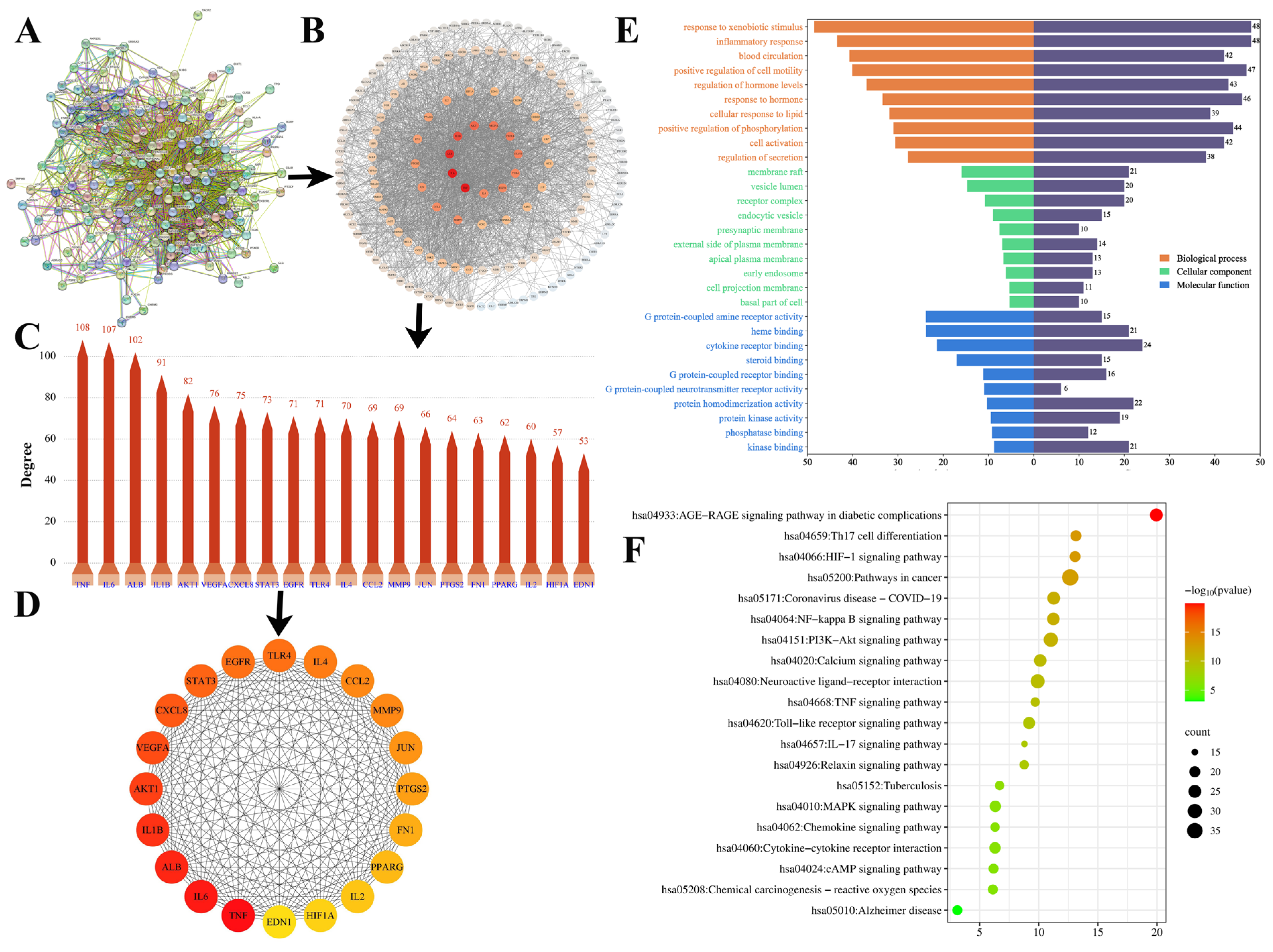
2.7.2. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Analysis and Screening of the Key Targets
2.7.3. GO and KEGG Analysis
2.8. Molecular Docking
2.9. Validating the Anti-AR Activity of Active Components (Vitro)
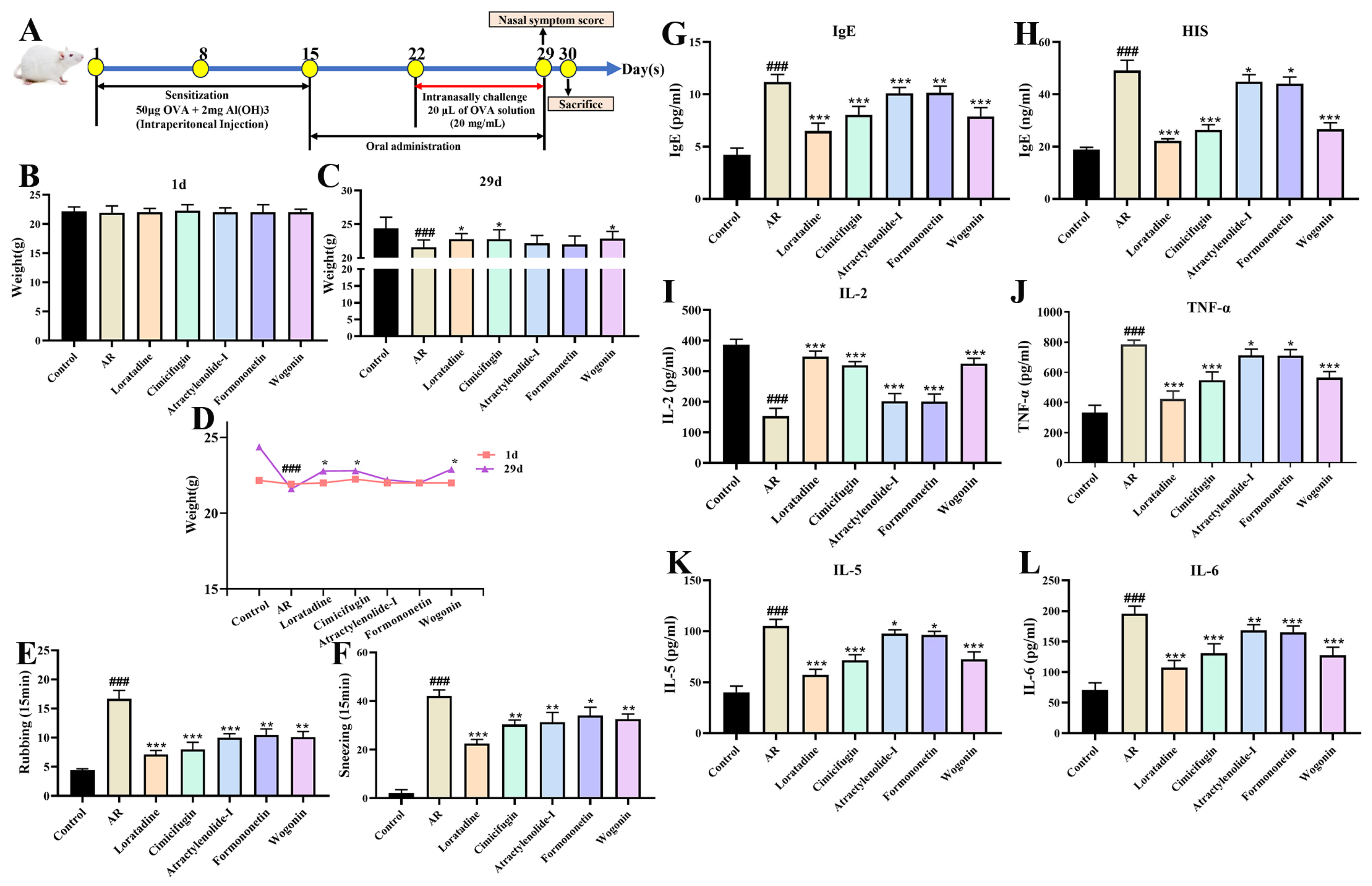
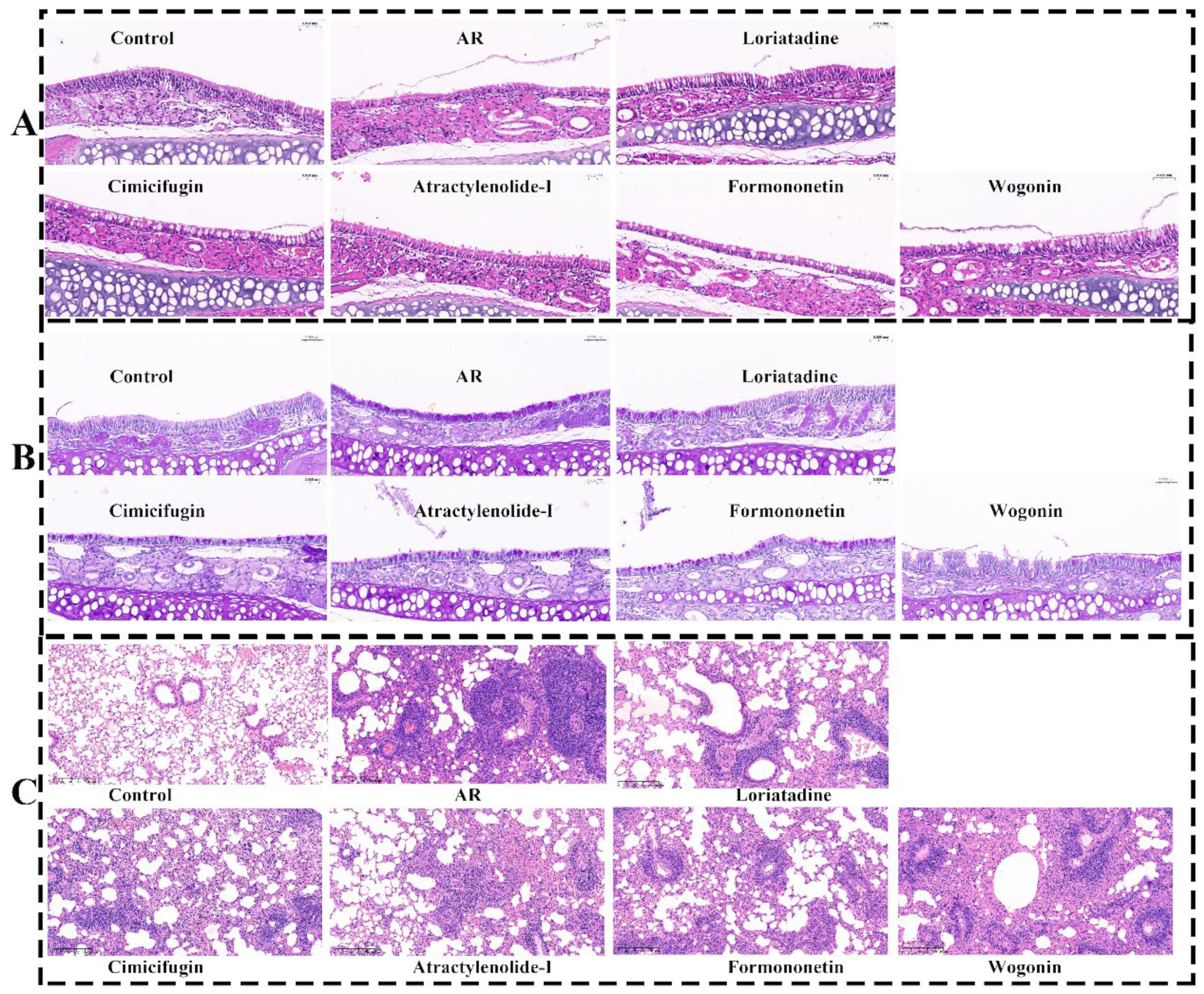
2.10. Validating the Anti-AR Activity of Active Components (Vivo)
2.10.1. Active Components Improve Nasal Symptom Score and Serum Indicators
2.10.2. Active Components Improve Pathological State of Nasal Mucosa and Lung
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Instrument
4.2. Extraction of YPFS
4.3. Animal Experiments
4.4. Sample Pretreatment
4.5. HPLC and MS Condition
4.5.1. Optimized Detection Conditions
4.5.2. Conditions of Chromatography and Methodological Study
4.5.3. Conditions of Mass Spectrometry
4.6. Molecular Networks
4.7. Network Pharmacology
4.7.1. Screening of Prototype Compounds Targets and Disease Targets
4.7.2. Compound–Target–Disease Network Construction and Screening of Key Components
4.7.3. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network and Screening of Key Targets
4.7.4. GO and KEGG
4.8. Dockings
4.9. Validating the Anti-AR Activity of Active Components In Vitro
4.10. Validating the Anti-AR Activity of Active Components In Vivo
4.11. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bousquet, J.; Anto, J.M.; Bachert, C.; Baiardini, I.; Bosnic-Anticevich, S.; Walter Canonica, G.; Melén, E.; Palomares, O.; Scadding, G.K.; Togias, A.; et al. Allergic rhinitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, J.; Fu, Q.; He, S.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Tan, G.; Tao, Z.; Wang, D.; Wen, W.; et al. Chinese Society of Allergy Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 300–353. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, V.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Ebisawa, M.; El-Gamal, Y.; Fernandez Rivas, M.; Fineman, S.; Geller, M.; Gonzalez-Estrada, A.; Greenberger, P.A.; Sanchez Borges, M.; et al. World Allergy Organization Anaphylaxis Guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lan, F.; Zhang, L. Advances and highlights in allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 3383–3389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Wei, W.; Yao, C.; Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Guo, D.-A. Advances in the chemical constituents, pharmacological properties and clinical applications of TCM formula Yupingfeng San. Fitoterapia 2023, 164, 105385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Wang, M.; Tian, Y.; Qi, J.; Qiu, Z. Systematic analysis and identification of the absorption and metabolic components of Zengye decoction in type 2 diabetic rats by HPLC-ESI-Q-TOF–MS/MS. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Feng, W.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xin, Z.-H.; Li, M.; Xin, L.; Gong, Y.-D. Effects and mechanism of Chinese medicine Jiawei Yupingfeng in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 19, 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Nikles, S.; Monschein, M.; Zou, H.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; Fan, D.; Lu, A.; Yu, K.; Isaac, G.; Bauer, R. Metabolic profiling of the traditional Chinese medicine formulation Yu Ping Feng San for the identification of constituents relevant for effects on expression of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β and IL-4 in U937 cells. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yue, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, C.; Wu, T. Method for rapidly discovering active components in Yupingfeng granules by UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 55, e4627. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Liang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, J. A Comparative Study of Serum Pharmacochemistry of Kai-Xin-San in Normal and AD Rats Using UPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ma, C.; Shi, W.; Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Lou, Y.; Fan, G. A Systematic Study of Yiqi Qubai Standard Decoction for Treating Vitiligo Based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Combined with Chemometrics, Molecular Docking, and Cellular and Zebrafish Assays. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Liang, Q.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z. Pseudoephedrine alleviates atopic dermatitis-like inflammatory responses in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ju, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Ding, L.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L. A complementary chromatographic strategy for integrated components characterization of Imperatae Rhizoma based on convergence and liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry and molecular network. J. Chromatogr. 2022, 1678, 463342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Y. The chemical composition analysis of Yixin Tongmai Granules using UHPLC-MS/MS and exploration of its potential mechanism in treatment of coronary artery disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Medicine 2025, 104, e41620. [Google Scholar]
- Malca-Garcia, G.R.; Zagal, D.; Graham, J.; Nikolić, D.; Friesen, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Dynamics of the isoflavone metabolome of traditional preparations of Trifolium pratense L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Anand, S.K.; Tiwari, K.N.; Mishra, S.K.; Kakkar, P. Phytochemical profiling and cytotoxic evaluation of Premna serratifolia L. against human liver cancer cell line. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, P. A novel and comprehensive strategy for quality control in complex Chinese medicine formula using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS and UHPLC-MS/MS combined with network pharmacology analysis: Take Tangshen formula as an example. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1183, 122889. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Xiao, S.; Cao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Y. Improvement of glucolipid metabolism and oxidative stress via modulating PI3K/Akt pathway in insulin resistance HepG2 cells by chickpea flavonoids. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101630. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Wu, M.; Shu, L.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y. A practical method for rapid discrimination of constituents in Psoraleae Fructus by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS. J. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 58, e4966. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Cheng, C.; Au, R.; Tong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Fang, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Qin-Yu-Qing-Chang decoction reshapes colonic metabolism by activating PPAR-γ signaling to inhibit facultative anaerobes against DSS-induced colitis. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Yao, Z.; Qin, Z.; Liu, L.; Song, X.; Dai, Y.; Kiyohara, H.; Yamada, H.; Yao, X. In vivo metabolic profiles of Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang, a famous traditional Chinese medicine prescription, in rats by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 171, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y. Metabolite Identification of Huangqi Jianzhong Tang in Rat Urine and Feces after Oral Administration Based on UHPLC-Q-Exactive-MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2023, 61, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, C.; Cui, X.; Pei, X.; Li, A.; Qin, X.; Du, C.; Du, H. Metabolic profile and underlying antioxidant improvement of Ziziphi Spinosae Folium by human intestinal bacteria. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126651. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Hu, K.; Li, D.; Guo, H.; Sun, L.; Xie, Z. Microbial-Transferred Metabolites and Improvement of Biological Activities of Green Tea Catechins by Human Gut Microbiota. Foods 2024, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Liao, C.; Liang, F.; Tian, L. Safety and onset time of modified Yupingfeng nasal spray versus mometasone furoate nasal spray on house dust mites-induced moderate to severe allergic rhinitis: A prospective, multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel-group clinical trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 344, 119574. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Qiu, S. Tolerogenic dendritic cells and TLR4/IRAK4/NF-κB signaling pathway in allergic rhinitis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1276512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, L.; Yu, D.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y. Three Artemisia pollens trigger the onset of allergic rhinitis via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim Soltani, Z.; Badripour, A.; Haddadi, N.S.; Elahi, M.; Kazemi, K.; Afshari, K.; Dehpour, A.R. Allergic rhinitis in BALB/c mice is associated with behavioral and hippocampus changes and neuroinflammation via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108725. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Xu, O.; Wang, J.; Shan, C.; Ren, X. Luteolin ameliorates inflammation and Th1/Th2 imbalance via regulating the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in allergic rhinitis rats. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, B.; Ma, X.; Jiang, R. Daphnetin Mitigates Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis in Mice by Regulating Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-kB Signaling. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2022, 37, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, Y. Action Mechanism of Yupingfeng Capsule for Combined Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma Syndrome via the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Pathway. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 85, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, Y.; Pan, R.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Yu-Ping-Feng-San alleviates inflammation in atopic dermatitis mice by TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 329, 118092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, G.; Hong, M. Cimifugin suppresses allergic inflammation by reducing epithelial derived initiative key factors via regulating tight junctions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Liu, X.; Song, Z.; Song, F.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification reveal the mechanism of the traditional Chinese medicine YU-Pingfeng San alleviating allergic rhinitis inflammatory responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 934130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.A.; Jung, J.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Kang, G.; Kim, S.T. Anti-inflammatory effect of wogonin on allergic responses in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in the mouse. Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 9, 2152656718764145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Sun, S.; Zuo, T.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Zheng, J.; Hong, M. Sanfeng Tongqiao Dripping Pills alleviate House Dust Mite-induced allergic rhinitis in mice by inhibiting Th2 differentiation and repairing the nasal epithelial barrier. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Integrative analysis of network pharmacology and proteomics to identify key targets of Tuomin-Zhiti-Decoction for allergic rhinitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, A. Formononetin ameliorates IL-13-induced inflammation and mucus formation in human nasal epithelial cells by activating the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Tao, W.; Ma, J.; Lin, S.-C. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Study of Yupingfeng Powder in the Treatment of Allergic Diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Chen, H.; Long, J.; Song, J.; Xie, L.; Li, X. Atractylenolides (I, II, and III): A review of their pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2021, 44, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, D.; Liu, W.; Xie, J.; Lu, Z.; Yang, H.; Yan, H.; Wang, L.; Che, C. Therapeutic effect of Atractylenolide I on Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis by affecting MyD88/NF-κB pathway and IL-1β, IL-10 expression. Cytokine 2023, 162, 156112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhi, W.; Liu, F.; He, Z.; Wang, X.; Niu, X. Atractylenolide I restores HO-1 expression and inhibits Ox-LDL-induced VSMCs proliferation, migration and inflammatory responses in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 353, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, B.; Liang, X.; Liu, C.; Xia, T.; Xie, Y.; Deng, X.; Tan, X. Higenamine alleviates allergic rhinitis by activating AKT1 and suppressing the EGFR/JAK2/c-JUN signaling. Phytomedicine 2021, 86, 153565. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nguyen, T.; Piao, C.H.; Fan, Y.J.; Shin, D.-U.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, H.-J.; Song, C.H.; Shin, H.S.; Chai, O.H. Anti-allergic rhinitis activity of α-lipoic acid via balancing Th17/Treg expression and enhancing Nrf2/HO-1 pathway signaling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.H.; Du, N.N.; Qiao, Y.J.; Zhang, G.X.; Yao, G.D.; Huang, X.X.; Song, S.J. Rapid isolation of cytotoxic daphnane diterpenoids from Daphne altaica Pall. using MS-DIAL. Fitoterapia 2025, 181, 106385. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Su, Q.; Shi, Y. Molecular mechanism of IgE-mediated FcεRI activation. Nature 2025, 637, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Q.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Yue, T.; Long, F. Adenosine cyclic phosphate with ultrasonic-assisted pectinase extraction alleviated allergic reactions in RBL-2H3 through inhibiting the influx of intracellular Ca2+. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 832–841. [Google Scholar]
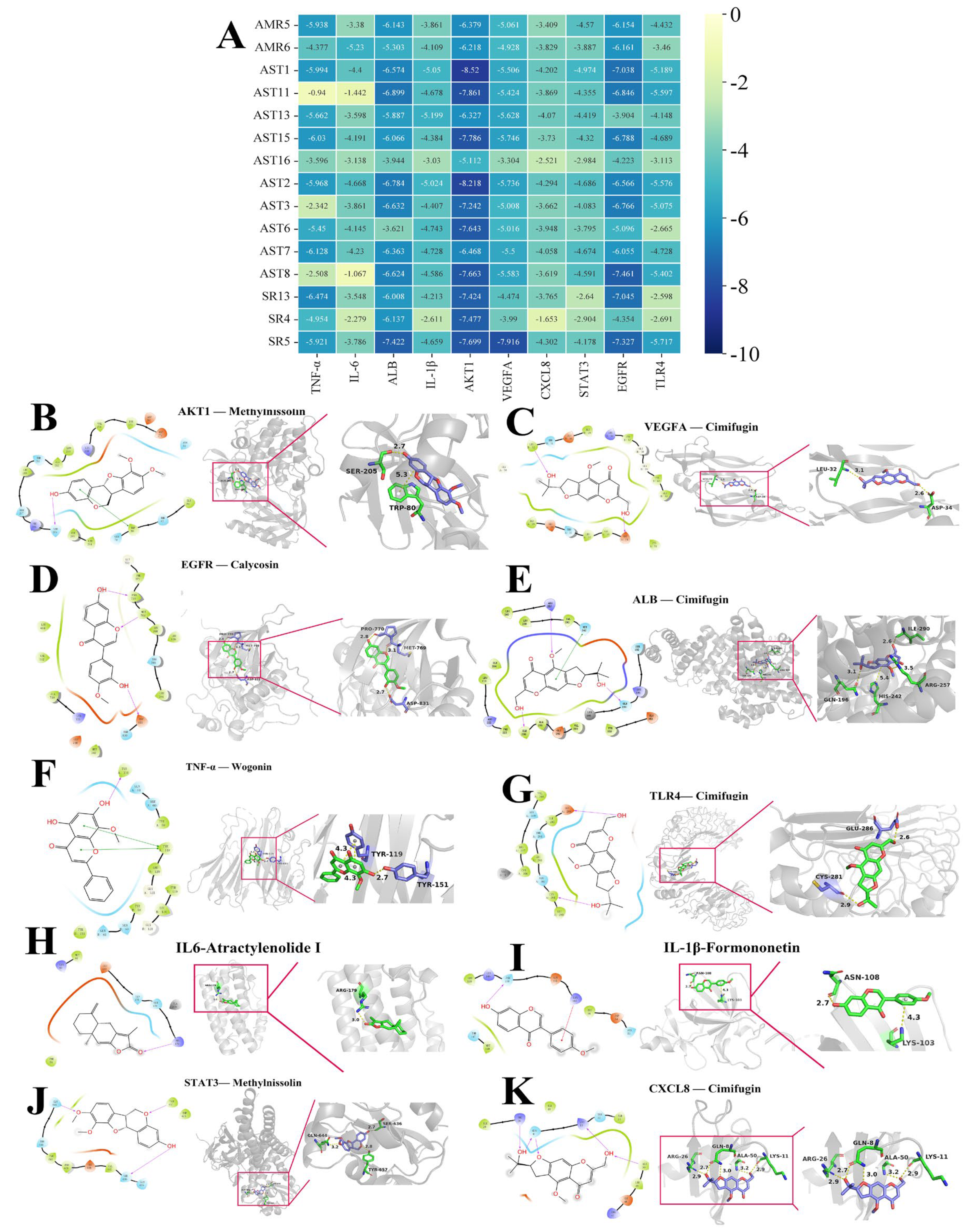

| Compound | Protein-PDBID | Affinity KJ/Mol | Site (xyz) | Bonding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methylnissolin (AST1) | AKT1-3O96 | −8.52 | (8.59, −7.1, 13.14) | SER, TRP |
| Cimifugin (SR5) | VEGFA-1MKK | −7.916 | (5, 0, 16) | LEU, ASP |
| Calycosin (AST8) | EGFR-1M17 | −7.461 | (21.29, 0.54, 52.36) | MET, PRO, ASP |
| Cimifugin (SR5) | ALB-2BX8 | −7.422 | (5.46, −10.15, 7.28) | ILE, ARG, GLN, HIS |
| Wogonin (SR13) | TNF-α-2AZ5 | −6.474 | (−19.82, 74.94, 33.46) | TYR |
| Cimifugin (SR5) | TLR4-2Z63 | −5.717 | (−0.1, −53.56, 13.23) | GLU, CYS |
| Atractylenolide I (AMR6) | IL6-1ALU | −5.23 | (0, 5, 0) | ARG |
| Formononetin (AST13) | IL-1β-6Y8M | −5.199 | (6.95, 25.46, −9.28) | LYS, ASN |
| Methylnissolin (AST1) | STAT3-6NJS | −4.974 | (13.24, 56.43, 0.24) | SER, GLN, TYR |
| Cimifugin (SR5) | CXCL8-1ICW | −4.302 | (−6, 29, 30) | ARG, GLN, ALA, LYS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Qi, J. Identification of Active Markers of Chinese Formula Yupingfeng San by Network Pharmacology and HPLC-Q-TOF–MS/MS Analysis in Experimental Allergic Rhinitis Models of Mice and Isolated Basophilic Leukemia Cell Line RBL-2H3. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040540
Li X, Zhao C, Qi J. Identification of Active Markers of Chinese Formula Yupingfeng San by Network Pharmacology and HPLC-Q-TOF–MS/MS Analysis in Experimental Allergic Rhinitis Models of Mice and Isolated Basophilic Leukemia Cell Line RBL-2H3. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040540
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinqi, Caining Zhao, and Jin Qi. 2025. "Identification of Active Markers of Chinese Formula Yupingfeng San by Network Pharmacology and HPLC-Q-TOF–MS/MS Analysis in Experimental Allergic Rhinitis Models of Mice and Isolated Basophilic Leukemia Cell Line RBL-2H3" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040540
APA StyleLi, X., Zhao, C., & Qi, J. (2025). Identification of Active Markers of Chinese Formula Yupingfeng San by Network Pharmacology and HPLC-Q-TOF–MS/MS Analysis in Experimental Allergic Rhinitis Models of Mice and Isolated Basophilic Leukemia Cell Line RBL-2H3. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040540







