Enhanced Topical Delivery of Methotrexate via Transferosome-Loaded Microneedle Array Patch: Formulation, Optimization, and In Vitro–In Vivo Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
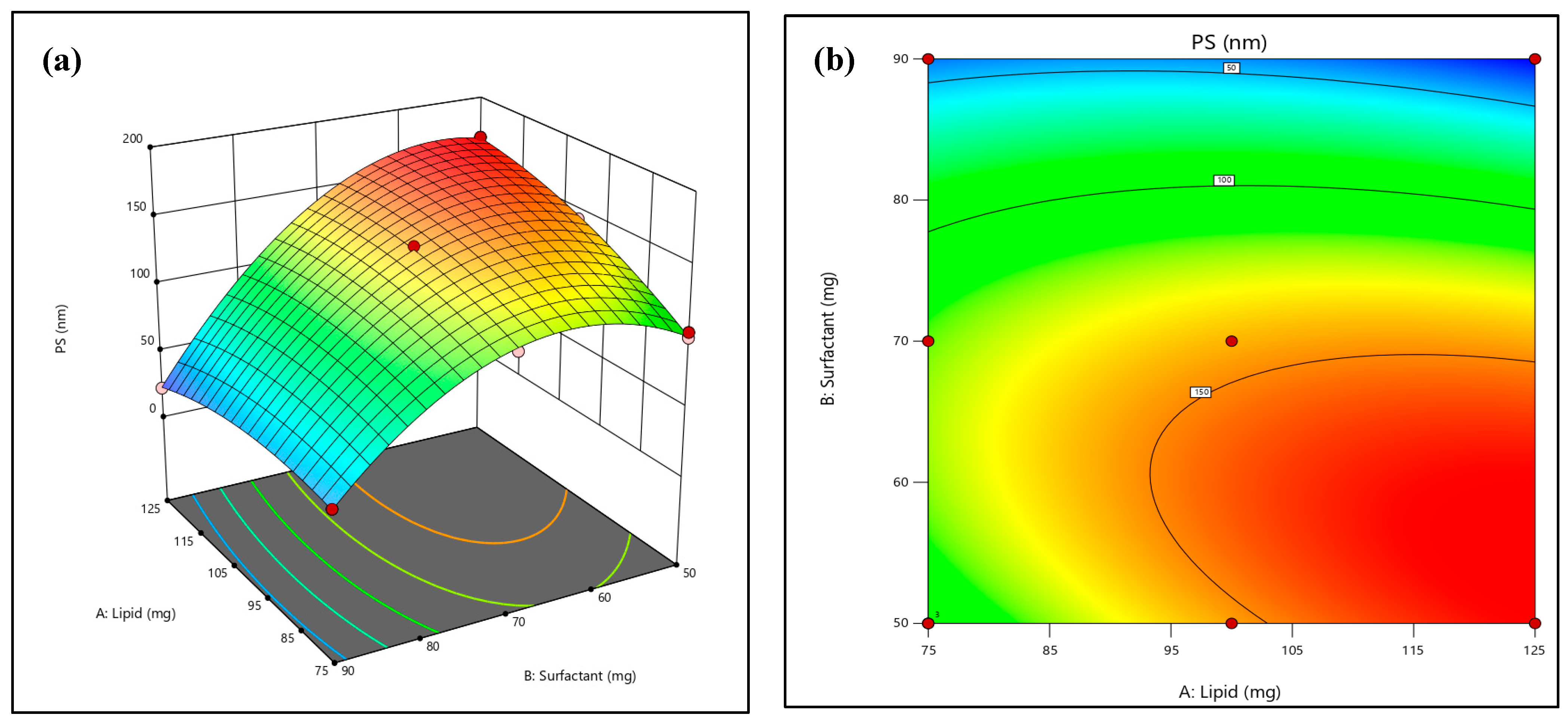
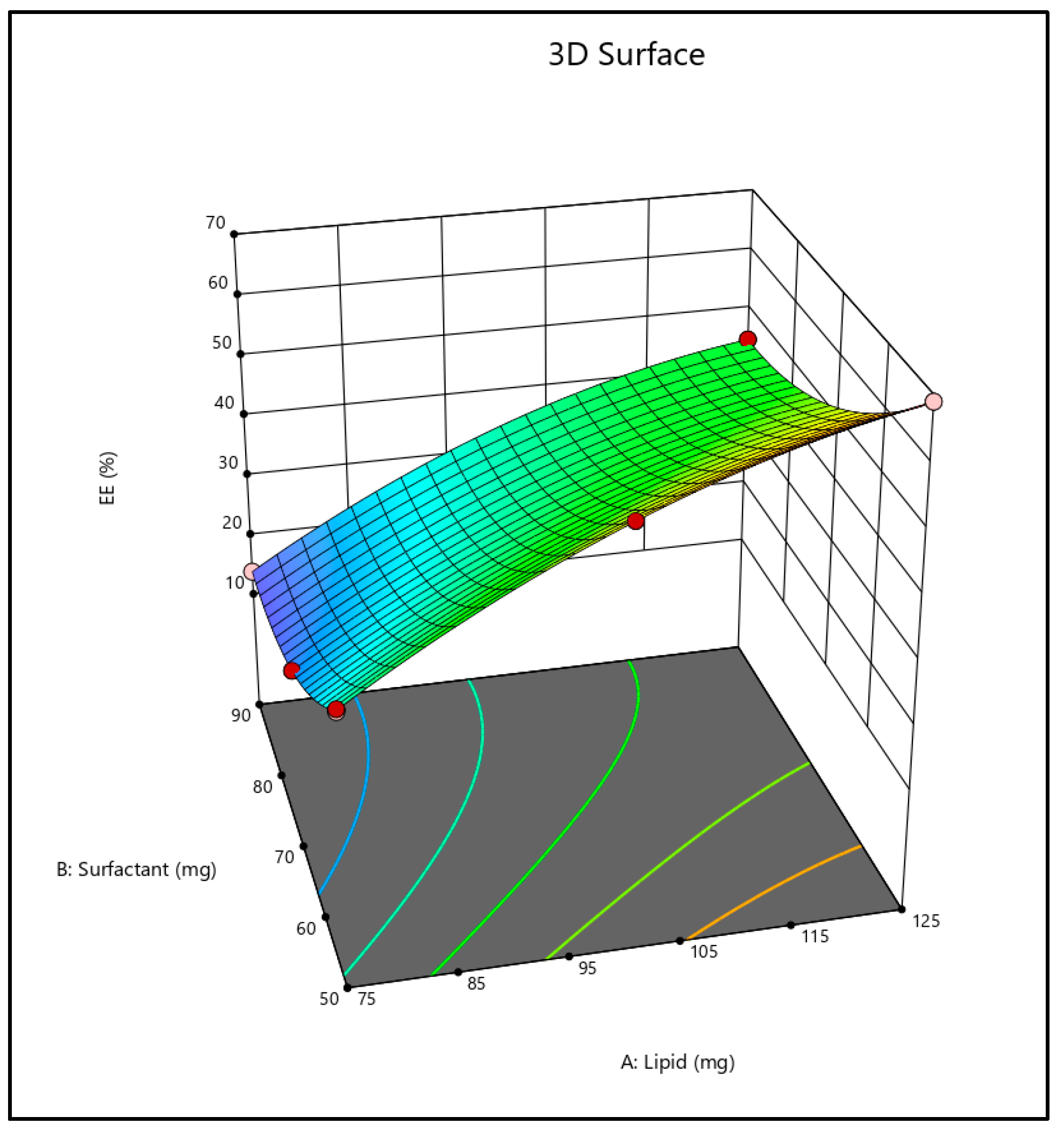
2.1. Optimization of Formulation Using 32 Full Factorial Design
2.2. Effect on the Vesicles Size
2.3. Effect on Entrapment Efficiency
2.4. Optimization of Formulation
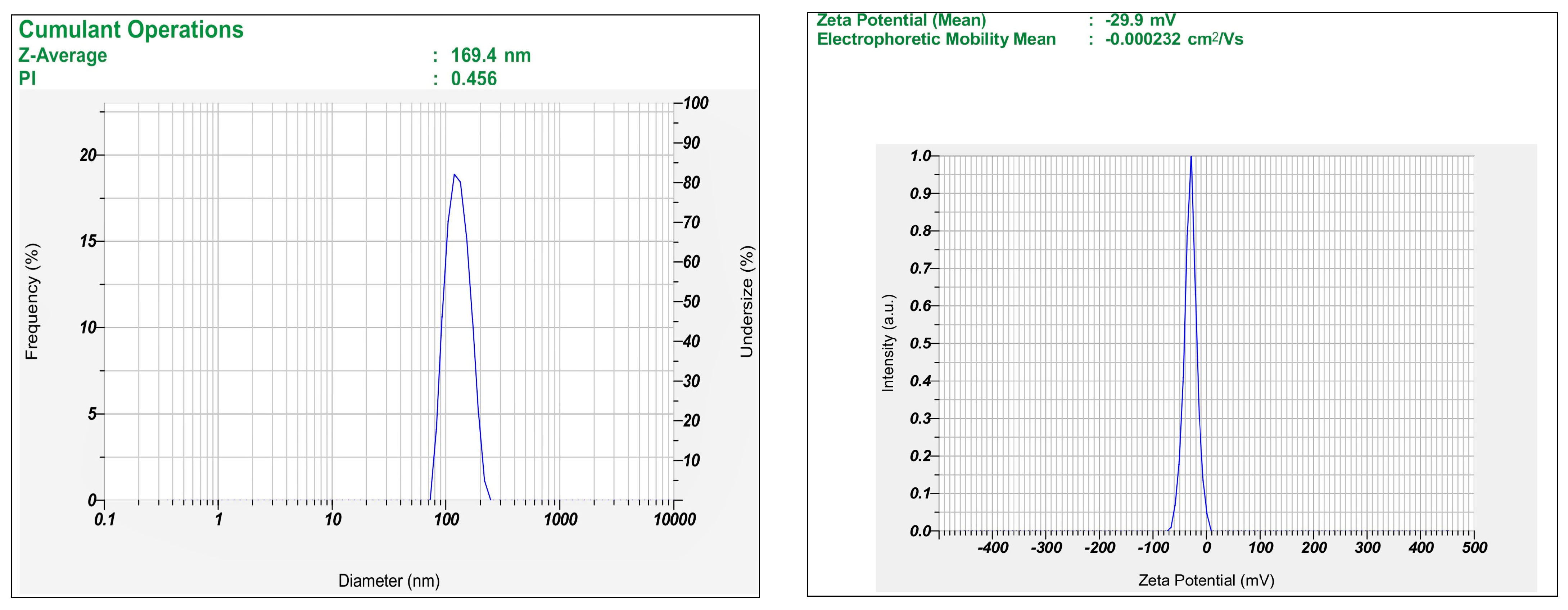
2.5. Characterization of MTX-Loaded Transferosomes
2.5.1. Percentage Entrapment Efficiency
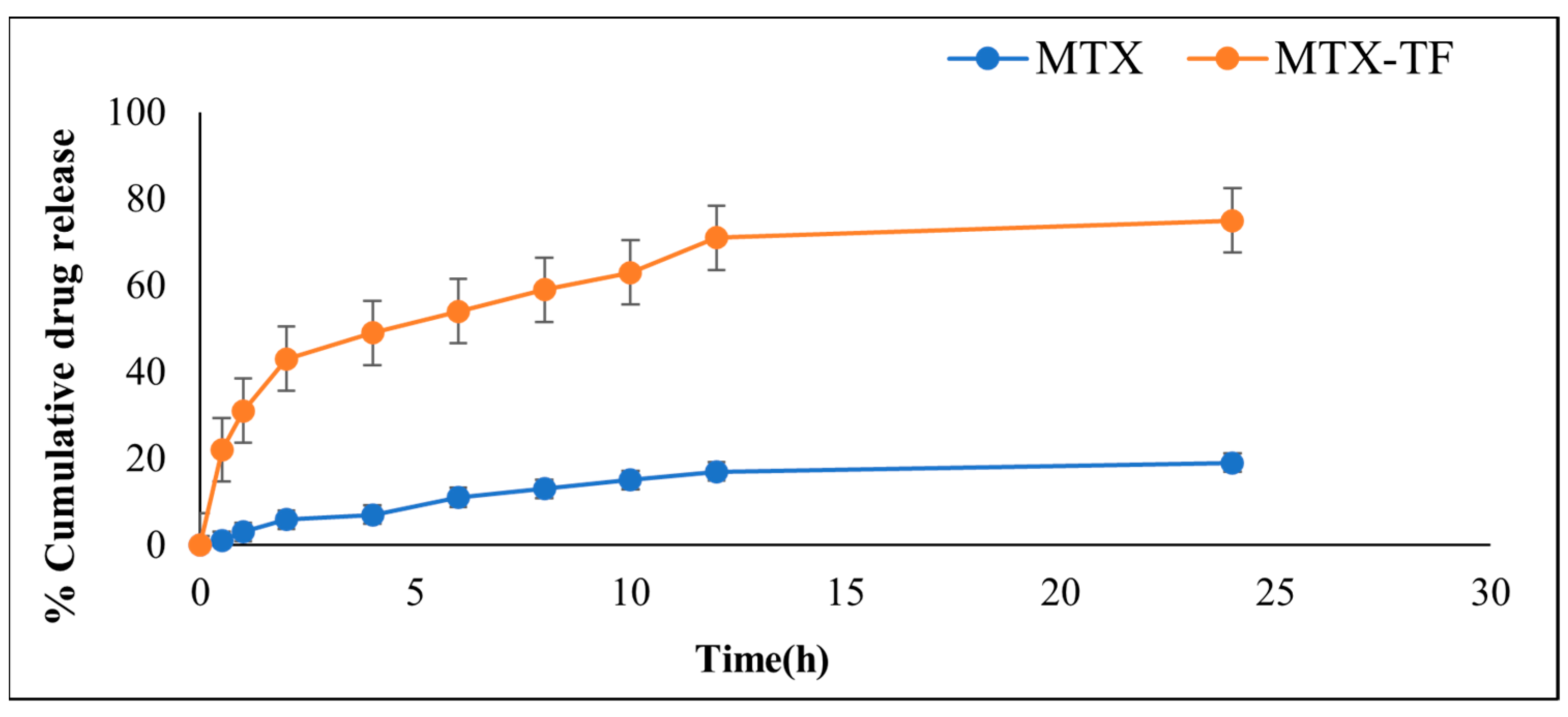
2.5.2. In Vitro Drug Release
2.5.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
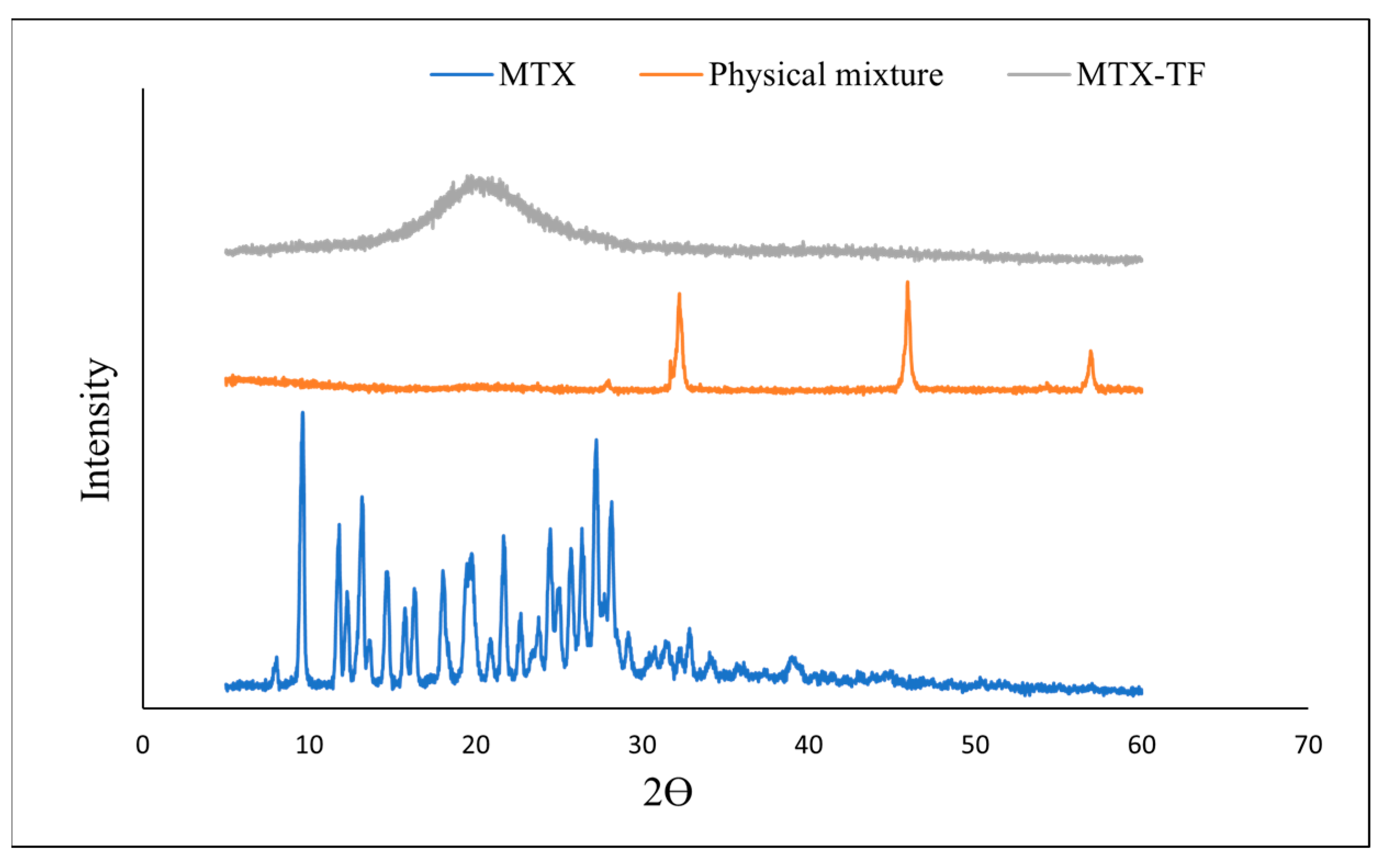
2.5.4. X-Ray Diffraction
2.5.5. Physical Stability Studies
2.6. Fabrication and Morphological Characterization of MTX-MNs and MTX-TF-MNs
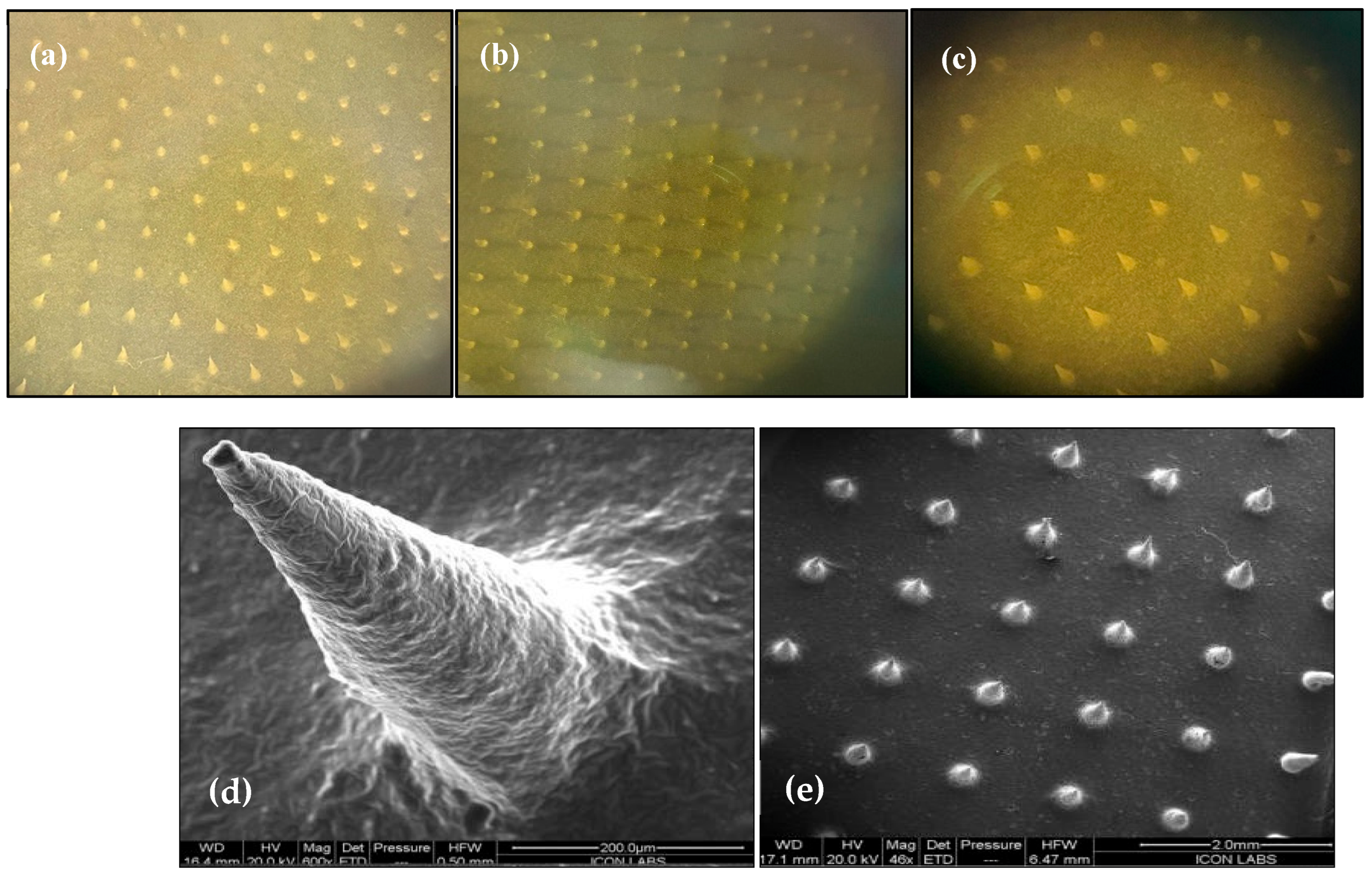
2.6.1. Characterization of Microneedle Array Patch
2.6.2. Drug Content Determination
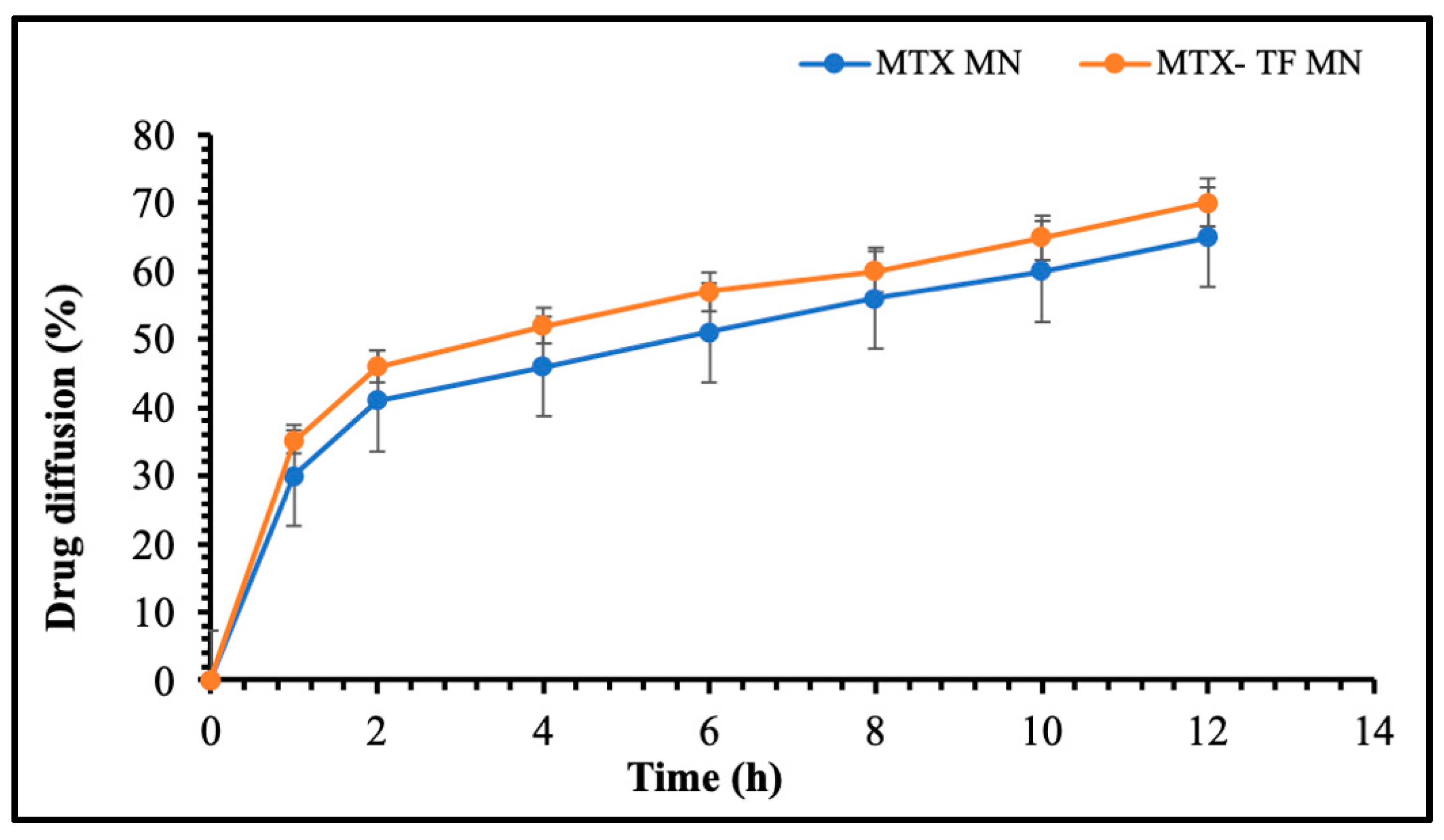
2.6.3. In Vitro Release Study of MTX-MN and MTX-TF-MN
2.6.4. Ex Vivo Permeation Study
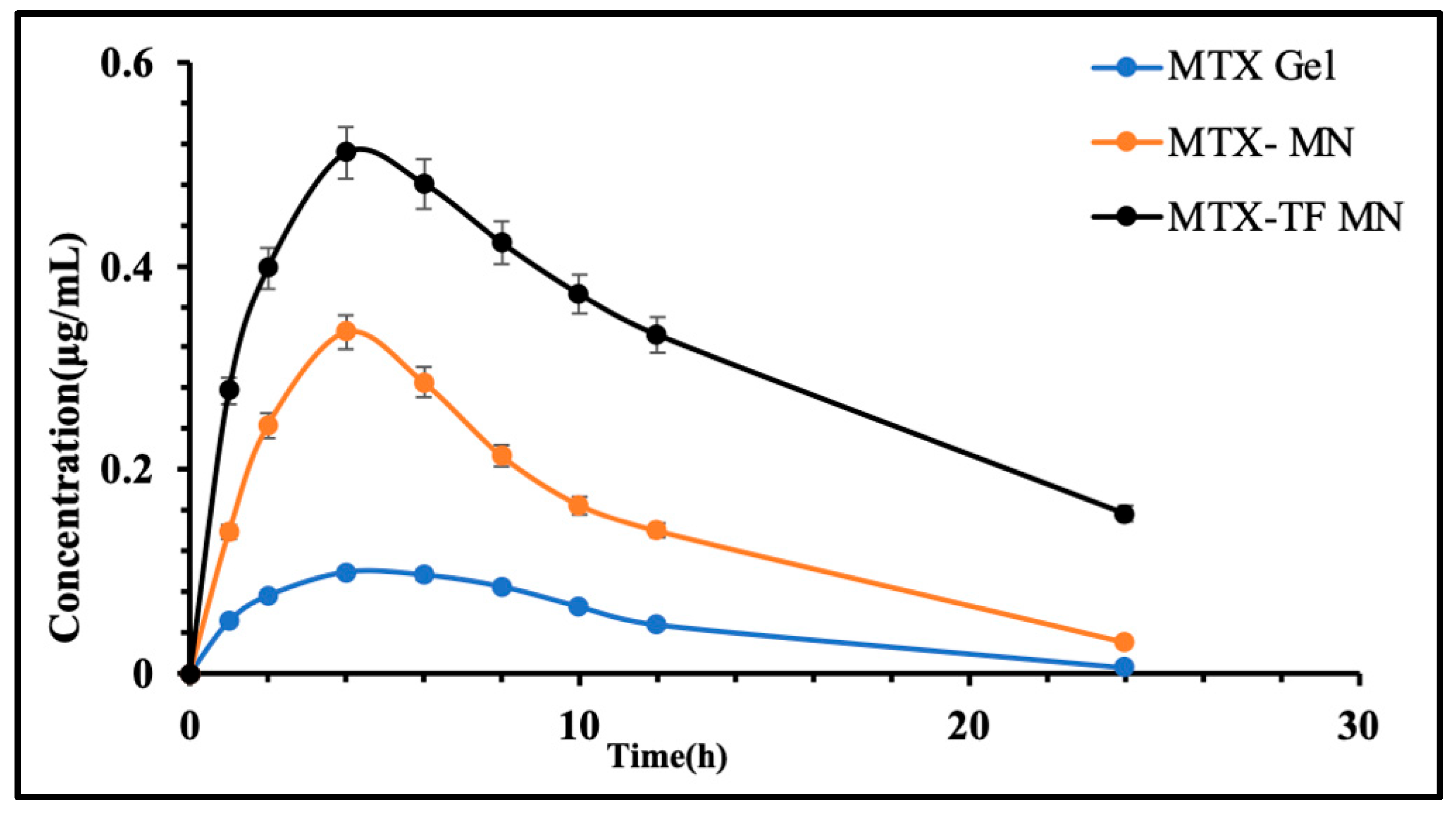
2.6.5. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Assessment
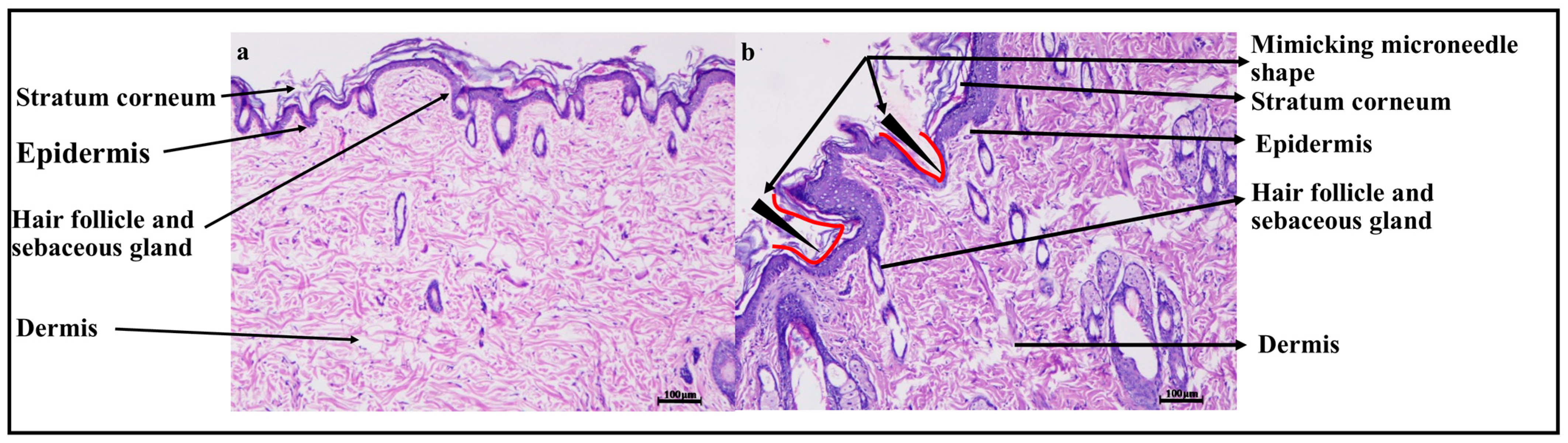
2.6.6. Histopathology Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Method
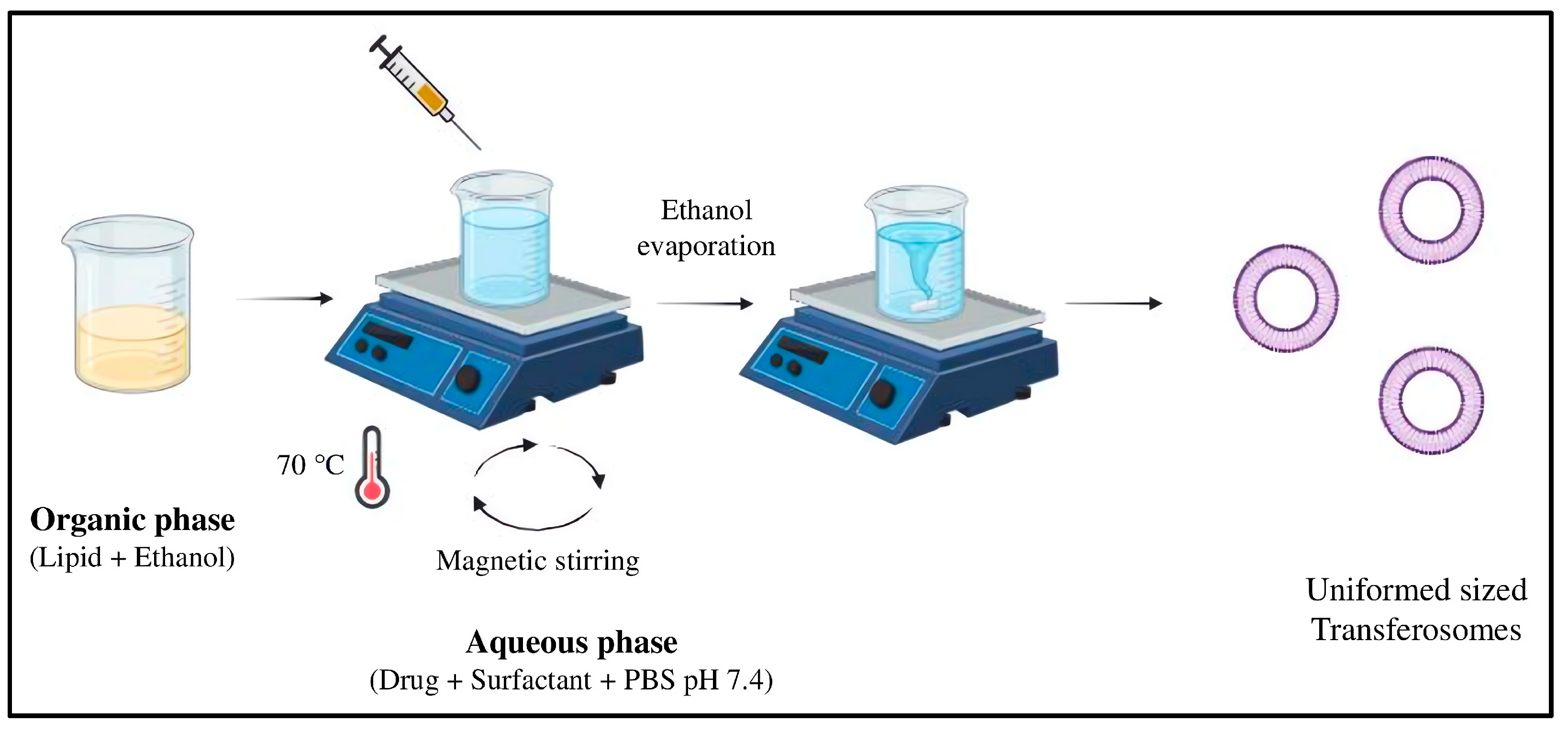
3.2.1. Preparation and Characterization of MTX-Loaded Transferosomes
3.2.2. Experiment Design for Optimization
3.2.3. Optimization of the Formulation
3.2.4. Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential Analysis of Fabricated Vesicles
3.2.5. HPLC Analysis of Methotrexate
3.2.6. Entrapment Efficiency
3.2.7. In Vitro Drug Release
3.2.8. Morphological Characterization of Transferosomes
3.2.9. X-Ray Diffraction
3.2.10. Physical Stability Studies
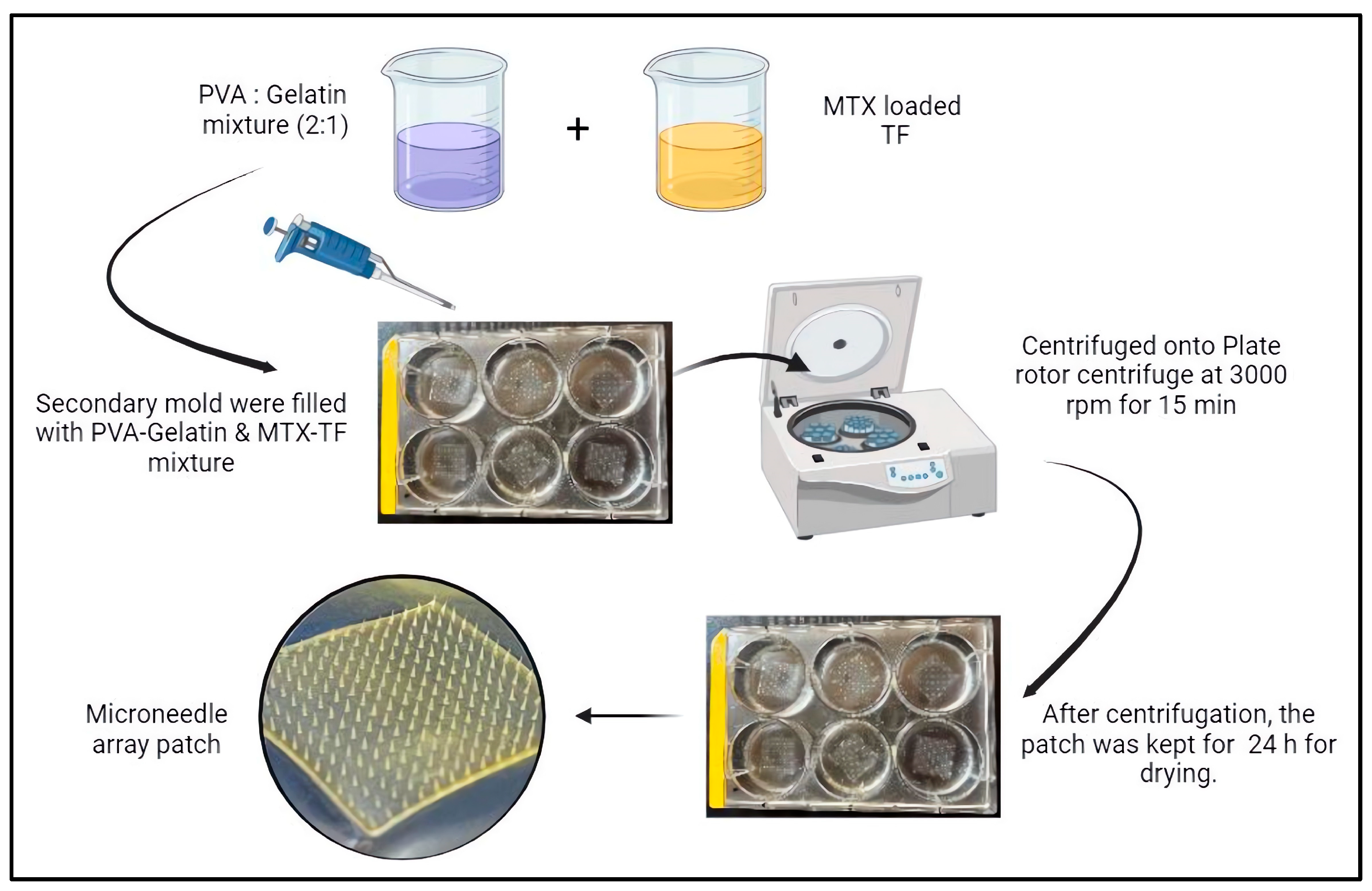
3.3. Fabrication of Microneedle Array Patch
3.4. Morphological Characterization of MTX-TF-Loaded MNs
3.4.1. Optical Microscopy and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.4.2. Determination of MTX Content in MTX-MNs and MTX-TF-MNs
3.4.3. In Vitro Release Assay for MTX-MN and MTXTF-MN
3.4.4. Ex Vivo Permeation
3.4.5. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Assessment
3.4.6. Histopathology Study
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brajac; Franjo, G. History of Psoriasis. In Psoriasis; Jose, O.D., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tampa, M. Brief history of psoriasis. Transylv. Rev. 2018, 27 (Suppl. 2), 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Nestle, F.O.; Conrad, C. Mechanisms of psoriasis. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2004, 1, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basko-Plluska, J.L.; Petronic-Rosic, V. Psoriasis: Epidemiology, natural history, and differential diagnosis. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2012, 2, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette, R.; Pinter, A.; Ferris, L.K.; Gerdes, S.; Rich, P.; Vender, R.; Miller, M.; Shen, Y.-K.; Kannan, A.; Li, S. An Oral Interleukin-23–Receptor Antagonist Peptide for Plaque Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontong, J.C.; Singh, S.; Siriyong, T.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Transferosomes stabilized hydrogel incorporated rhodomyrtone-rich extract from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf fortified with phosphatidylcholine for the management of skin and soft-tissue infections. Biotechnol. Lett. 2024, 46, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Das, P.; Arora, G. Systematic review and recommendations to combine newer therapies with conventional therapy in psoriatic disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 696597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.R.; Yang, H.S.; Song, I.-S.; Choi, H.-G.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, D.W. Alternative Methotrexate Oral Formulation: Enhanced Aqueous Solubility, Bioavailability, Photostability, and Permeability. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzún, P.; Gallardo-Toledo, E.; Morales, J.; Arriagada, F. Transfersomes as alternative topical nanodosage forms for the treatment of skin disorders. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 2465–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, C.; Bharadia, P. In-vitro and ex-vivo evaluation of transfersomal gel of methotrexate. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 59, e22643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadarani, B.; Majumdar, A.; Kamble, P.; Paradkar, S.; Mathur, A.; Sachdev, S.; Chaudhari, P.; Mohanty, B. AB0079 Transdermal delivery of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: Are we deep enough? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Supaweera, N.; Nwabor, O.F.; Yusakul, G.; Chaichompoo, W.; Suksamrarn, A.; Panpipat, W.; Chunglok, W. Polymeric scaffold integrated with nanovesicle-entrapped curcuminoids for enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Nanomedicine 2024, 19, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohite, P.; Puri, A.; Munde, S.; Ade, N.; Kumar, A.; Jantrawut, P.; Singh, S.; Chittasupho, C. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles in the Management of Dermal Disorders Through a Non-Invasive Process: A Review. Gels 2024, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y. Microneedles: A potential strategy in transdermal delivery and application in the management of psoriasis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 14040–14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Malviya, R.; Alam, A.; Sagar, S. Advances in microneedle-based approaches for skin diseases: A comprehensive review of therapeutic applications and future perspectives. Anti-Infect. Agents 2024, 22, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Gupta, R.; Vanshita, n. Microneedle technology: An insight into recent advancements and future trends in drug and vaccine delivery. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2021, 19, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.S.; Nawaz, A.; Asmari, M.; Uddin, J.; Ullah, H.; Ahmad, S. Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehshahri, A.; Kumar, A.; Madamsetty, V.S.; Uzieliene, I.; Tavakol, S.; Azedi, F.; Fekri, H.S.; Zarrabi, A.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Thakur, V.K. New Horizons in Hydrogels for Methotrexate Delivery. Gels 2021, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmana, M.; Arifin, M.A.B.; Mahmood, S. A Review on Transfersomes: Promising Carrier for Transdermal Drug Delivery. In Proceedings of the 6th National Conference for Postgraduate Research (NCON-PGR 2022), Virtual, 15 November 2022; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, J.; Jani, H.; Patel, Y.; Mohite, P.; Puri, A.; Chidrawar, V.R.; Datta, D.; Bandi, S.P.; Ranch, K.; Singh, S. Polyol-modified deformable liposomes fortified contact lenses for improved ocular permeability. Nanomedicine 2025, 20, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Supaweera, N.; Nwabor, O.F.; Chaichompoo, W.; Suksamrarn, A.; Chittasupho, C.; Chunglok, W. Poly (vinyl alcohol)-gelatin-sericin copolymerized film fortified with vesicle-entrapped demethoxycurcumin/bisdemethoxycurcumin for improved stability, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and skin tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 129071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnam, S.; Jindal, A.B.; Paul, A.T. Quality by design-based optimization of teriflunomide and quercetin combinational topical transferosomes for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Gulbake, A.; Jain, A.; Shilpi, S.; Hurkat, P.; Jain, S.K. Dual drug delivery using “smart” liposomes for triggered release of anticancer agents. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Cao, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ma, T.; Wang, Q. High efficacy combined microneedles array with methotrexate nanocrystals for effective anti-rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 2397–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.M.; Salem, H.F.; Abdelmohsen, H.F.; Attia, S.K. Preparation and clinical evaluation of nano-transferosomes for treatment of erectile dysfunction. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2431–2447. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, A.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Khire, A.; Jaiswal, S.; Banerjee, R. Levonorgestrel Microneedle Array Patch for Sustained Release Contraception: Formulation, Optimization and In Vivo Characterization. Molecules 2022, 27, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shaibani, A.J.N.; Ghareeb, M.M. Formulation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of olanzapine nanoparticles dissolving microneedles for transdermal delivery. Pharmacia 2024, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Wu, J.C.; von Meerwall, E.D. Mathematical Modeling and Experimental Characterization of Polymer Dissolution. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 5626–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbary, A.A.; AbouGhaly, M.H.H. Design and optimization of topical methotrexate loaded niosomes for enhanced management of psoriasis: Application of Box–Behnken design, in-vitro evaluation and in-vivo skin deposition study. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadarani, B.; Majumdar, A.; Paradkar, S.; Mathur, A.; Sachdev, S.; Mohanty, B.; Chaudhari, P. Enhanced skin permeation of Methotrexate from penetration enhancer containing vesicles: In vitro optimization and in vivo evaluation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Pahal, S.; Badnikar, K.; Nayak, M.M.; Subramanyam, D.N.; Vemula, P.K.; Krishnan, U.M. Methotrexate delivering microneedle patches for improved therapeutic efficacy in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 642, 123184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adin, S.N.; Gupta, I.; Aqil, M.; Mujeeb, M.; Najmi, A.K. Nanotransethosomal dual-drug loaded gel of methotrexate and mangiferin as a potent synergistic intervention for rheumatoid arthritis via transdermal delivery. J. Drug Target. 2024, 33, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasibi, F.; Nasirpour, A.; Varshosaz, J.; García-Manrique, P.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Gutiérrez, G.; Matos, M. Formulation and Characterization of Taxifolin-Loaded Lipid Nanovesicles (Liposomes, Niosomes, and Transfersomes) for Beverage Fortification. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, S.; Krishna, K.; Shirin, V.A.; Sankar, R.; Pramod, K.; Gangadharappa, H. Drug delivery systems for the treatment of psoriasis: Current status and prospects. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Geng, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Advanced nanocarrier-and microneedle-based transdermal drug delivery strategies for skin diseases treatment. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Meng, S. Site-specific drug delivery in the skin for the localized treatment of skin diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, N.; Madni, A.; Balasubramanian, V.; Rehman, M.; Correia, A.; Kashif, P.M.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Santos, H.A. Development and optimization of methotrexate-loaded lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ou, R.; Guan, S.; Ye, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, J. A novel drug delivery gel of terbinafine hydrochloride with high penetration for external use. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.R.; Bashir, S.; Khan, D.H.; Shahzadi, I.; Rashid, S.A.; Khan, M.H.; Abdullah, Z.; Mahmood, A.; Sarfraz, M. Optimization and validation of an analytical method for the estimation of methotrexate in rabbit plasma. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 35, 267–272. [Google Scholar]


| Batch | Y1 Vesicle Size (nm) | Y2 Entrapment Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | 169.4 ± 4.4 | 69.22 ± 1.48 |
| B2 | 22.1 ± 3.9 | 45.14 ± 0.74 |
| B3 | 40.1 ± 4.9 | 13.92 ± 2.58 |
| B4 | 100.4± 0.1 | 33.85 ± 1.86 |
| B5 | 116.8 ± 3.2 | 17.91 ± 0.37 |
| B6 | 99.8 ± 2.1 | 33.94 ± 0.61 |
| B7 | 145.9± 0.5 | 39.52 ± 1.34 |
| B8 | 103.7 ± 1.6 | 33.47 ± 3.48 |
| B9 | 143.7 ± 1.4 | 56.42 ± 0.51 |
| Parameters | Plasma | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MTX Marketed Gel | MTX-MN | MTX-TF-MN | |
| Tmax (h) | 2.5 ± 0.0 | 3.1 ± 0.15 | 3.4 ± 0.17 |
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 0.25 ± 0.16 | 0.47 ± 0.27 | 0.50 ± 0.41 |
| AUC0–t (μg/mL·h) | 2.25 ± 0.51 | 4.94 ± 0.27 | 7.68 ± 0.24 |
| AUC0–∞ (μg/mL·h) | 2.27 ± 0.17 | 5.15 ± 0.21 | 10.26 ± 0.11 |
| Independent Variables | Levels | ||
| Low (−1) | Medium (0) | High (+1) | |
| X1 lipid concentration (mg/mL) | 75 | 100 | 125 |
| X2 surfactant concentration (mg/mL) | 50 | 70 | 90 |
| Dependent Variables | |||
| Y1 | Vesicle size (nm) | Lower | |
| Y2 | EE (%) | Highest | |
| Batch | LS-90 (X1) | Tw-80 (X2) |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | 125 | 50 |
| B2 | 125 | 90 |
| B3 | 75 | 90 |
| B4 | 75 | 50 |
| B5 | 75 | 70 |
| B6 | 75 | 50 |
| B7 | 100 | 70 |
| B8 | 75 | 50 |
| B9 | 100 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinde, S.; Singh, A.K.; Chidrawar, V.R.; Rajput, A.; Singh, S. Enhanced Topical Delivery of Methotrexate via Transferosome-Loaded Microneedle Array Patch: Formulation, Optimization, and In Vitro–In Vivo Assessment. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040594
Shinde S, Singh AK, Chidrawar VR, Rajput A, Singh S. Enhanced Topical Delivery of Methotrexate via Transferosome-Loaded Microneedle Array Patch: Formulation, Optimization, and In Vitro–In Vivo Assessment. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040594
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinde, Snehal, Anil Kumar Singh, Vijay R. Chidrawar, Amarjitsing Rajput, and Sudarshan Singh. 2025. "Enhanced Topical Delivery of Methotrexate via Transferosome-Loaded Microneedle Array Patch: Formulation, Optimization, and In Vitro–In Vivo Assessment" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040594
APA StyleShinde, S., Singh, A. K., Chidrawar, V. R., Rajput, A., & Singh, S. (2025). Enhanced Topical Delivery of Methotrexate via Transferosome-Loaded Microneedle Array Patch: Formulation, Optimization, and In Vitro–In Vivo Assessment. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040594








