Beneficial Effects of Tianeptine on Hippocampus-Dependent Long-Term Memory and Stress-Induced Alterations of Brain Structure and Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Stress, Neuroplasticity and Symptoms of Depression
3. Tianeptine Prevents Stress-Induced Alterations of Neuroplasticity
4. Stress and Synaptic Plasticity: Stabilization by Tianeptine
5. Tianeptine Protects Memory from Stress and Enhances Learning and Memory
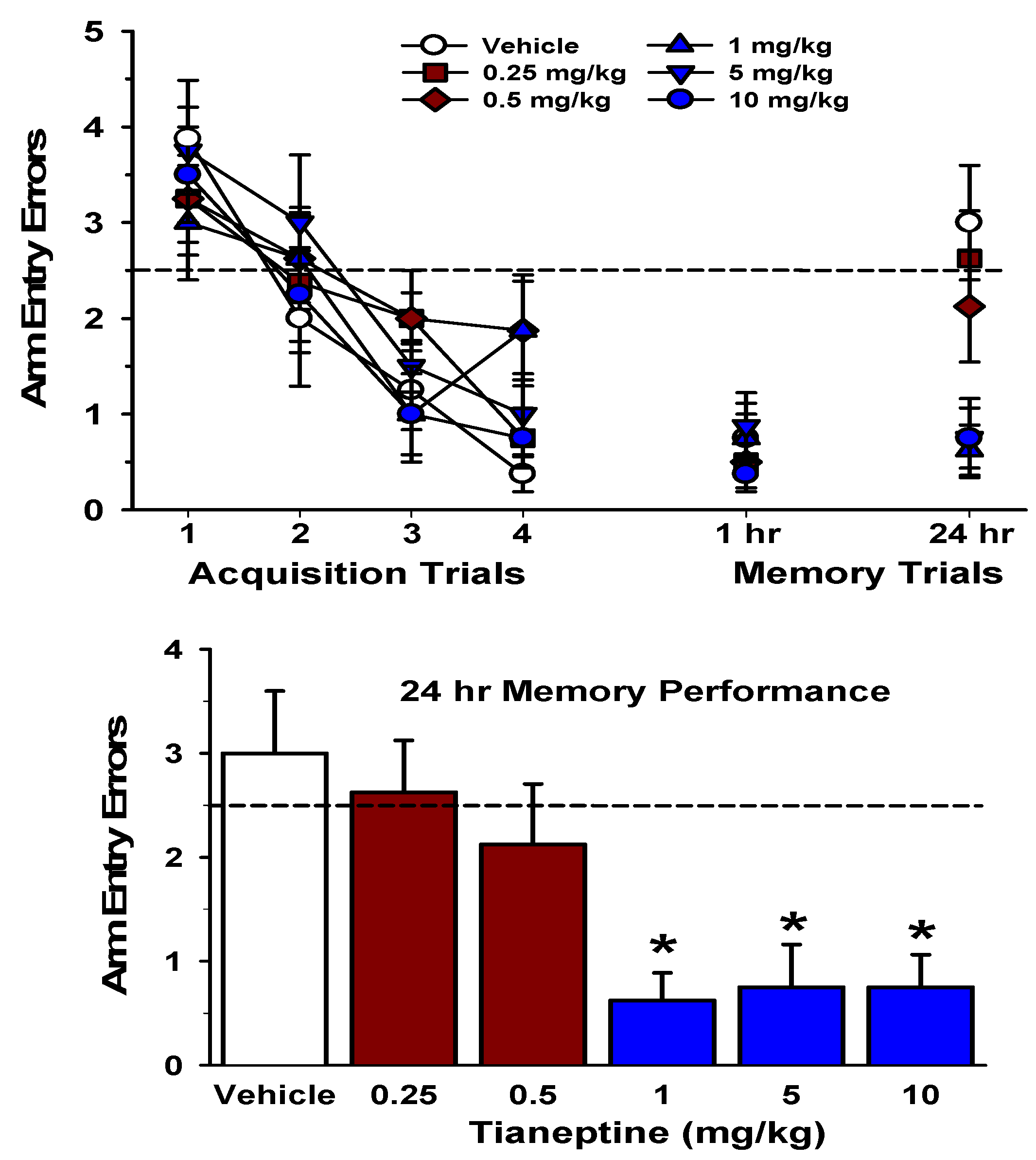
6. Mechanisms Underlying Tianeptine’s Procognitive and Anti-Stress Effects
7. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Druss, B.G.; Rask, K.; Katon, W.J. Major depression, depression treatment and quality of primary medical care. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2008, 30, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, M.; Blazer, D.G. Depression in long-term care. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2008, 9, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Morilak, D.A.; Frazer, A. Antidepressants and brain monoaminergic systems: a dimensional approach to understanding their behavioural effects in depression and anxiety disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 7, 193–218. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, B.; Byford, S.; Knapp, M. Evidence of cost-effective treatments for depression: a systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2005, 84, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, M.; Linda, F.K.; Ramesh, S. Role of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in psychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Svenningsson, P.; Bateup, H.; Qi, H.; Takamiya, K.; Huganir, R.L.; Spedding, M.; Roth, B.L.; McEwen, B.S.; Greengard, P. Involvement of AMPA receptor phosphorylation in antidepressant actions with special reference to tianeptine. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 3509–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Racagni, G.; Popoli, M. The pharmacological properties of antidepressants. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 25, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Racagni, G.; Popoli, M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the long-term action of antidepressants. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 10, 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, O.; Nestler, E.J. New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 137–151. [Google Scholar]
- Maoz, H. Failure of first SSRI for depression--what is the next step? Isr. J. Psychiatry Relat. Sci. 2007, 44, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papakostas, G.I.; Fava, M.; Thase, M.E. Treatment of SSRI-resistant depression: a meta-analysis comparing within- versus across-class switches. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Brink, C.B.; Harvey, B.H.; Brand, L. Tianeptine: a novel atypical antidepressant that may provide new insights into the biomolecular basis of depression. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2006, 1, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kucia, K.; Malecki, A.; Gabryel, B.; Trzeciak, H.I. Effect of antidepressants on the phospholipase A(2) activity in plasma membranes of the rat brain cortex. Polish J. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pitra, P.; Tokarski, K.; Grzegorzewska, M.; Hess, G. Effects of repetitive administration of tianeptine, zinc hydroaspartate and electroconvulsive shock on the reactivity of 5-HT (7) receptors in rat hippocampus. Pharmacol. Rep. 2007, 59, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Uzbay, T.I. Tianeptine: potential influences on neuroplasticity and novel pharmacological effects. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 915–924. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S.; Chattarji, S.; Diamond, D.M.; Jay, T.M.; Reagan, L.P.; Svenningsson, P.; Fuchs, E. The neurobiological properties of tianeptine (Stablon): from monoamine hypothesis to glutamatergic modulation. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, D.M.; Campbell, A.; Park, C.R.; Vouimba, R.M. Preclinical research on stress, memory, and the brain in the development of pharmacotherapy for depression. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 14 (Suppl. 5), S491–S495. [Google Scholar]
- Atmaca, M.; Kuloglu, M.; Tezcan, E.; Buyukbayram, A. Switching to tianeptine in patients with antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2003, 18, 277–280. [Google Scholar]
- Bonierbale, M.; Lancon, C.; Tignol, J. The ELIXIR study: evaluation of sexual dysfunction in 4557 depressed patients in France. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2003, 19, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Brion, S.; Audrain, S.; De Bodinat, C. Major depressive episodes in patients over 70 years of age. Evaluation of the efficiency and acceptability of tianeptine and mianserin. Presse Med. 1996, 25, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Szadoczky, E.; Furedi, J. Efficacy and acceptability of tianeptine and sertraline in the acute treatment phase of depression. Enceph.-Re. De Psychiatr. Clin. Biol. Ther. 2002, 28, 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Invernizzi, G.; Aguglia, E.; Bertolino, A.; Casacchia, M.; Ciani, N.; Marchesi, G.F.; Nardini, M.; Rapisarda, V. The efficacy and safety of tianeptine in the treatment of depressive disorder: results of a controlled double-blind multicentre study vs. amitriptyline. Neuropsychobiology 1994, 30, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hindmarch, I. Expanding the horizons of depression: beyond the monoamine hypothesis. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2001, 16, 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- Pacher, P.; Kecskemeti, V. Trends in the development of new antidepressants. Is there a light at the end of the tunnel? Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 925–943. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, J.; Toga, A.W.; Hojatkashani, C.; Thompson, P.; Costafreda, S.G.; Cleare, A.J.; Williams, S.C.; Bullmore, E.T.; Scott, J.L.; Mitterschiffthaler, M.T.; et al. Subregional hippocampal deformations in major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.D.; Vythilingam, M.; Vermetten, E.; Anderson, G.; Newcomer, J.W.; Charney, D.S. Effects of glucocorticoids on declarative memory function in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 55, 811–815. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, S.; Macqueen, G. The role of the hippocampus in the pathophysiology of major depression. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004, 29, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Esch, T.; Stefano, G.B.; Fricchione, G.L.; Benson, H. The role of stress in neurodegenerative diseases and mental disorders. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2002, 23, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Pittenger, C.; Duman, R.S. Stress, depression, and neuroplasticity: a convergence of mechanism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 88–109. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S.; Olie, J.P. Neurobiology of mood, anxiety, and emotions as revealed by studies of a unique antidepressant: tianeptine. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 525–537. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, E.; Czeh, B.; Kole, M.H.; Michaelis, T.; Lucassen, P.J. Alterations of neuroplasticity in depression: the hippocampus and beyond. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 14 (Suppl. 5), S481–S490. [Google Scholar]
- Sheline, Y.I. 3D MRI studies of neuroanatomic changes in unipolar major depression: the role of stress and medical comorbidity. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 48, 791–800. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, S.; McEwen, B.S. Neurobiological and clinical effects of the antidepressant tianeptine. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, L.R.; Stark, C.E.; Clark, R.E. The medial temporal lobe. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 279–306. [Google Scholar]
- Eichenbaum, H. Hippocampus: cognitive processes and neural representations that underlie declarative memory. Neuron 2004, 44, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, N.J.; Squire, L.R.; Clark, R.E. Spatial memory, recognition memory, and the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14515–14520. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, N.J.; Squire, L.R.; Clark, R.E. Reversible hippocampal lesions disrupt water maze performance during both recent and remote memory tests. Learn. Mem. 2006, 13, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kaut, K.P.; Bunsey, M.D. The effects of lesions to the rat hippocampus or rhinal cortex on olfactory and spatial memory: retrograde and anterograde findings. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2001, 1, 270–286. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I. Distributed encoding and retrieval of spatial memory in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7535–7542. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, S.N.; Cole, C.; Ryan, J.D. Relational memory for object identity and spatial location inrats with lesions of perirhinal cortex, amygdala and hippocampus. Brain Res. Bull. 2005, 65, 501–512. [Google Scholar]
- Winocur, G.; Moscovitch, M.; Caruana, D.A.; Binns, M.A. Retrograde amnesia in rats with lesions to the hippocampus on a test of spatial memory. Neuropsychologia 2005, 43, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld, R.S.; Ranganath, C. Prefrontal cortex and long-term memory encoding: an integrative review of findings from neuropsychology and neuroimaging. Neuroscientist 2007, 13, 280–291. [Google Scholar]
- Pare, D.; Quirk, G.J.; LeDoux, J.E. New vistas on amygdala networks in conditioned fear. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Phelps, E.A.; LeDoux, J.E. Contributions of the amygdala to emotion processing: from animal models to human behavior. Neuron 2005, 48, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- LeDoux, J.E. Emotional memory: in search of systems and synapses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 702, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kanner, A.M. Structural MRI changes of the brain in depression. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2004, 35, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Maletic, V.; Robinson, M.; Oakes, T.; Iyengar, S.; Ball, S.G.; Russell, J. Neurobiology of depression: an integrated view of key findings. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2007, 61, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar]
- Vasic, N.; Walter, H.; Hose, A.; Wolf, R.C. Gray matter reduction associated with psychopathology and cognitive dysfunction in unipolar depression: A voxel-based morphometry study. J. Affect. Disord. 2008, 109, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Sharma, V.K.; Das, S.; Goswami, U.; Gandhi, A. Neuro-cognitive functions in patients of major depression. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 51, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ebmeier, K.; Rose, E.; Steele, D. Cognitive impairment and fMRI in major depression. Neurotox. Res. 2006, 10, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Drevets, W.C. Neuroimaging studies of mood disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 48, 813–829. [Google Scholar]
- Frodl, T.; Meisenzahl, E.; Zetzsche, T.; Bottlender, R.; Born, C.; Groll, C.; Jager, M.; Leinsinger, G.; Hahn, K.; Moller, H.J. Enlargement of the amygdala in patients with a first episode of major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 51, 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- Siegle, G.J.; Carter, C.S.; Thase, M.E. Use of FMRI to predict recovery from unipolar depression with cognitive behavior therapy. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 735–738. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff, C.B.; Vale, W.W. The neurobiology of depression: inroads to treatment and new drug discovery. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66 (Suppl. 7), 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kendler, K.S.; Karkowski, L.M.; Prescott, C.A. Causal relationship between stressful life events and the onset of major depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 837–841. [Google Scholar]
- Nestler, E.J.; Gould, E.; Manji, H. Preclinical models: status of basic research in depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 52, 503–528. [Google Scholar]
- Anisman, H.; Matheson, K. Stress, depression, and anhedonia: caveats concerning animal models. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 525–546. [Google Scholar]
- Gambarana, C.; Scheggi, S.; Tagliamonte, A.; Tolu, P.; De Montis, M.G. Animal models for the study of antidepressant activity. Brain Res. Brain Res. Protoc. 2001, 7, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, R.; Borsini, F. Animal models of depression in drug discovery: A historical perspective. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 84, 436–452. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, C.D.; Magarinos, A.M.; LeDoux, J.E.; McEwen, B.S. Repeated restraint stress facilitates fear conditioning independently of causing hippocampal CA3 dendritic atrophy. Behav. Neurosci. 1999, 113, 902–913. [Google Scholar]
- Kole, M.H.; Costoli, T.; Koolhaas, J.M.; Fuchs, E. Bidirectional shift in the cornu ammonis 3 pyramidal dendritic organization following brief stress. Neuroscience 2004, 125, 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, K.G.; Buckelew, S.K.; Staffiso-Sandoz, G.; Gaffga, S.; Carpenter, W.; Fisher, J.; Kinsley, C.H. Activity-stress induces atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons in male rats. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 65, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Magarinos, A.M.; McEwen, B.S. Stress-induced atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3c neurons: comparison of stressors. Neuroscience 1995, 69, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Magarinos, A.M.; McEwen, B.S.; Flugge, G.; Fuchs, E. Chronic psychosocial stress causes apical dendritic atrophy of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons in subordinate tree shrews. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 3534–3540. [Google Scholar]
- McKittrick, C.R.; Magarinos, A.M.; Blanchard, D.C.; Blanchard, R.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Sakai, R.R. Chronic social stress reduces dendritic arbors in CA3 of hippocampus and decreases binding to serotonin transporter sites. Synapse 2000, 36, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, A.; Mitra, R.; Shankaranarayana Rao, B.S.; Chattarji, S. Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6810–6818. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Gould, E.; McEwen, B.S. Stress induces atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. Brain Res. 1992, 588, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Cerqueira, J.J.; Mailliet, F.; Almeida, O.F.; Jay, T.M.; Sousa, N. The prefrontal cortex as a key target of the maladaptive response to stress. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2781–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.C.; Wellman, C.L. Chronic stress alters dendritic morphology in rat medial prefrontal cortex. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 60, 236–248. [Google Scholar]
- Radley, J.J.; Rocher, A.B.; Miller, M.; Janssen, W.G.; Liston, C.; Hof, P.R.; McEwen, B.S.; Morrison, J.H. Repeated stress induces dendritic spine loss in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Liston, C.; Miller, M.M.; Goldwater, D.S.; Radley, J.J.; Rocher, A.B.; Hof, P.R.; Morrison, J.H.; McEwen, B.S. Stress-induced alterations in prefrontal cortical dendritic morphology predict selective impairments in perceptual attentional set-shifting. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7870–7874. [Google Scholar]
- Radley, J.J.; Rocher, A.B.; Janssen, W.G.; Hof, P.R.; McEwen, B.S.; Morrison, J.H. Reversibility of apical dendritic retraction in the rat medial prefrontal cortex following repeated stress. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 196, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Bloss, E.B.; Janssen, W.G.; McEwen, B.S.; Morrison, J.H. Interactive effects of stress and aging on structural plasticity in the prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6726–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, A.; Jadhav, S.; Chattarji, S. Prolonged behavioral stress enhances synaptic connectivity in the basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 2006, 143, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Zoladz, P.R.; Conrad, C.D.; Fleshner, M.; Diamond, D.M. Acute episodes of predator exposure in conjunction with chronic social instability as an animal model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Stress 2008, 11, 259–281. [Google Scholar]
- Sunanda; Rao, B.S.S.; Raju, T.R. Chronic restraint stress impairs acquisition and retention of spatial memory task in rats. Curr. Sci. 2000, 79, 1581–1584. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, N.; Lukoyanov, N.V.; Madeira, M.D.; Almeida, O.F.; Paula-Barbosa, M.M. Reorganization of the morphology of hippocampal neurites and synapses after stress-induced damage correlates with behavioral improvement. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Diamond, D.M. Chronic psychosocial stress impairs learning and memory and increases sensitivity to yohimbine in adult rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 994–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Luine, V.; Villegas, M.; Martinez, C.; McEwen, B.S. Repeated stress causes reversible impairments of spatial memory performance. Brain Res. 1994, 639, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Krugers, H.J.; Douma, B.R.K.; Andringa, G.; Bohus, B.; Korf, J.; Luiten, P.G.M. Exposure to chronic psychosocial stress and corticosterone in the rat: Effects on spatial discrimination learning and hippocampal protein kinase C gamma immunoreactivity. Hippocampus 1997, 7, 427–436. [Google Scholar]
- Bodnoff, S.R.; Humphreys, A.G.; Lehman, J.C.; Diamond, D.M.; Rose, G.M.; Meaney, M.J. Enduring effects of chronic corticosterone treatment on spatial learning, synaptic plasticity, and hippocampal neuropathology in young and mid-aged rats. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandi, C.; Merino, J.J.; Cordero, M.I.; Touyarot, K.; Venero, C. Effects of chronic stress on contextual fear conditioning and the hippocampal expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule, its polysialylation, and L1. Neuroscience 2001, 102, 329–339. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, A.; Pillai, A.G.; Chattarji, S. Recovery after chronic stress fails to reverse amygdaloid neuronal hypertrophy and enhanced anxiety-like behavior. Neuroscience 2004, 128, 667–673. [Google Scholar]
- Bloss, E.B.; Janssen, W.G.; McEwen, B.S.; Morrison, J.H. Interactive effects of stress and aging on structural plasticity in the prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6726–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Magarinos, A.M.; Orchinik, M.; McEwen, B.S. Morphological changes in the hippocampal CA3 region induced by non-invasive glucocorticoid administration: a paradox. Brain Res. 1998, 809, 314–318. [Google Scholar]
- Woolley, C.S.; Gould, E.; McEwen, B.S. Exposure to excess glucocorticoids alters dendritic morphology of adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Brain Res. 1990, 531, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wellman, C.L. Dendritic reorganization in pyramidal neurons in medial prefrontal cortex after chronic corticosterone administration. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 49, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Magarinos, A.M.; McEwen, B.S. Stress-induced atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3c neurons: involvement of glucocorticoid secretion and excitatory amino acid receptors. Neuroscience 1995, 69, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Gould, E.; Cameron, H.A.; Daniels, D.C.; McEwen, B.S. Phenytoin prevents stress- and corticosterone-induced atrophy of CA3 pyramidal neurons. Hippocampus 1992, 2, 431–435. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, C.F.; Nemeroff, C.B. Hypercortisolemia and depression. Psychosom. Med. 2005, 67 (Suppl. 1), S26–S28. [Google Scholar]
- Pariante, C.M.; Miller, A.H. Glucocorticoid receptors in major depression: relevance to pathophysiology and treatment. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 49, 391–404. [Google Scholar]
- Kendell, S.F.; Krystal, J.H.; Sanacora, G. GABA and glutamate systems as therapeutic targets in depression and mood disorders. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets. 2005, 9, 153–168. [Google Scholar]
- Krystal, J.H.; Sanacora, G.; Blumberg, H.; Anand, A.; Charney, D.S.; Marek, G.; Epperson, C.N.; Goddard, A.; Mason, G.F. Glutamate and GABA systems as targets for novel antidepressant and mood-stabilizing treatments. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7 (Suppl. 1), S71–S80. [Google Scholar]
- Sanacora, G.; Gueorguieva, R.; Epperson, C.N.; Wu, Y.T.; Appel, M.; Rothman, D.L.; Krystal, J.H.; Mason, G.F. Subtype-specific alterations of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate in patients with major depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 705–713. [Google Scholar]
- Czeh, B.; Michaelis, T.; Watanabe, T.; Frahm, J.; de Biurrun, G.; Van Kampen, M.; Bartolomucci, A.; Fuchs, E. Stress-induced changes in cerebral metabolites, hippocampal volume, and cell proliferation are prevented by antidepressant treatment with tianeptine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12796–12801. [Google Scholar]
- Magarinos, A.M.; Deslandes, A.; McEwen, B.S. Effects of antidepressants and benzodiazepine treatments on the dendritic structure of CA3 pyramidal neurons after chronic stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 371, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Gould, E.; Daniels, D.C.; Cameron, H.; McEwen, B.S. Tianeptine attenuates stress-induced morphological changes in the hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 222, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, A.G.; Munoz, C.; Chattarji, S. The antidepressant tianeptine prevents the dendritic hypertrophy in the amygdala and increase in anxiety induced by chronic stress in the rat. Soc. Neurosci. Abst. 2004, 34, 762.1. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, C.D.; Galea, L.A.M.; Kuroda, Y.; McEwen, B.S. Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y maze, and this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment. Behav. Neurosci. 1996, 110, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Zoladz, P.R.; Halonen, J.; Munoz, C.; Diamond, D.M. Daily tianeptine treatment initiated after stress onset blocks the effects of chronic psychosocial stress on physiology and behavior in an animal model of PTSD. Soc. Neuro. Sci. Abst. 2007, 37, 171.17. [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt, N.S.; Sullivan, G.M.; McEwen, B.S.; Gorman, J.M.; LeDoux, J.E. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram increases fear after acute treatment but reduces fear with chronic treatment: A comparison with tianeptine. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 55, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Ehninger, D.; Kempermann, G. Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 331, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, E.; Beylin, A.; Tanapat, P.; Reeves, A.; Shors, T.J. Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Shors, T.J.; Miesegaes, G.; Beylin, A.; Zhao, M.; Rydel, T.; Gould, E. Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 2001, 410, 372–376. [Google Scholar]
- Dranovsky, A.; Hen, R. Hippocampal neurogenesis: regulation by stress and antidepressants. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, R.S. Depression: a case of neuronal life and death? Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 56, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henn, F.A.; Vollmayr, B. Neurogenesis and depression: etiology or epiphenomenon? Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 56, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, B.L.; Praag, H.; Gage, F.H. Adult brain neurogenesis and psychiatry: a novel theory of depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2000, 5, 262–269. [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky, R.M. Is impaired neurogenesis relevant to the affective symptoms of depression? Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 56, 137–139. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, E.; Tanapat, P. Stress and hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 46, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Heine, V.M.; Maslam, S.; Zareno, J.; Joels, M.; Lucassen, P.J. Suppressed proliferation and apoptotic changes in the rat dentate gyrus after acute and chronic stress are reversible. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Heine, V.M.; Zareno, J.; Maslam, S.; Joels, M.; Lucassen, P.J. Chronic stress in the adult dentate gyrus reduces cell proliferation near the vasculature and VEGF and Flk-1 protein expression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1304–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, K.; Nacher, J.; Hof, P.R.; McEwen, B.S. Repeated restraint stress suppresses neurogenesis and induces biphasic PSA-NCAM expression in the adult rat dentate gyrus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 879–886. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbrock, H.; Koros, E.; Bloching, A.; Podhorna, J.; Borsini, F. Effect of chronic intermittent restraint stress on hippocampal expression of marker proteins for synaptic plasticity and progenitor cell proliferation in rats. Brain Res. 2005, 1040, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.D.; Duman, R.S. The role of neurotrophic factors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis, antidepressant treatments and animal models of depressive-like behavior. Behav. Pharmacol. 2007, 18, 391–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lucassen, P.J.; Vollmann-Honsdorf, G.K.; Gleisberg, M.; Czeh, B.; de Kloet, E.R.; Fuchs, E. Chronic psychosocial stress differentially affects apoptosis in hippocampal subregions and cortex of the adult tree shrew. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 14, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Young, D. Predatory stress induces hippocampal cell death by apoptosis in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 421, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lucassen, P.J.; Fuchs, E.; Czeh, B. Antidepressant treatment with tianeptine reduces apoptosis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and temporal cortex. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 55, 789–796. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.A.; Makino, S.; Kvetnansky, R.; Post, R.M. Effects of stress on neurotrophic factor expression in the rat brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 771, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.A.; Makino, S.; Kvetnansky, R.; Post, R.M. Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Ueyama, T.; Kawai, Y.; Nemoto, K.; Sekimoto, M.; Tone, S.; Senba, E. Immobilization stress reduced the expression of neurotrophins and their receptors in the rat brain. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 28, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Alfonso, J.; Frick, L.R.; Silberman, D.M.; Palumbo, M.L.; Genaro, A.M.; Frasch, A.C. Regulation of hippocampal gene expression is conserved in two species subjected to different stressors and antidepressant treatments. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Barrientos, R.M.; Sprunger, D.B.; Campeau, S.; Higgins, E.A.; Watkins, L.R.; Rudy, J.W.; Maier, S.F. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA downregulation produced by social isolation is blocked by intrahippocampal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Neuroscience 2003, 121, 847–853. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlovsky, N.; Matar, M.A.; Kaplan, Z.; Kotler, M.; Zohar, J.; Cohen, H. Long-term down-regulation of BDNF mRNA in rat hippocampal CA1 subregion correlates with PTSD-like behavioural stress response. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 10, 741–758. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, S.; Imbe, H.; Morikawa, Y.; Kubo, C.; Senba, E. Chronic stress, as well as acute stress, reduces BDNF mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus but less robustly. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, J.M.; Lumley, L.A.; Medina, W.; Robison, C.L.; Chang, W.E.; Alagappan, A.; Bah, M.J.; Dawood, M.Y.; Shah, J.D.; Mark, B.; et al. Acute social defeat reduces neurotrophin expression in brain cortical and subcortical areas in mice. Brain Res. 2004, 1025, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmusson, A.M.; Shi, L.; Duman, R. Downregulation of BDNF mRNA in the hippocampal dentate gyrus after re-exposure to cues previously associated with footshock. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 27, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Roceri, M.; Cirulli, F.; Pessina, C.; Peretto, P.; Racagni, G.; Riva, M.A. Postnatal repeated maternal deprivation produces age-dependent changes of brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in selected rat brain regions. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 55, 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- Roceri, M.; Hendriks, W.; Racagni, G.; Ellenbroek, B.A.; Riva, M.A. Early maternal deprivation reduces the expression of BDNF and NMDA receptor subunits in rat hippocampus. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7, 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Scaccianoce, S.; Del Bianco, P.; Caricasole, A.; Nicoletti, F.; Catalani, A. Relationship between learning, stress and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuroscience 2003, 121, 825–828. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, E.; Hashimoto, K.; Okamura, N.; Koike, K.; Komatsu, N.; Kumakiri, C.; Nakazato, M.; Watanabe, H.; Shinoda, N.; Okada, S.; et al. Alterations of serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depressed patients with or without antidepressants. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Karege, F.; Perret, G.; Bondolfi, G.; Schwald, M.; Bertschy, G.; Aubry, J.M. Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in major depressed patients. Psychiatry Res. 2002, 109, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Aydemir, C.; Yalcin, E.S.; Aksaray, S.; Kisa, C.; Yildirim, S.G.; Uzbay, T.; Goka, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) changes in the serum of depressed women. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 30, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Reagan, L.P.; Hendry, R.M.; Reznikov, L.R.; Piroli, G.G.; Wood, G.E.; McEwen, B.S.; Grillo, C.A. Tianeptine increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the rat amygdala. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 565, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Castren, E. Neurotrophic effects of antidepressant drugs. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Dowlatshahi, D.; MacQueen, G.M.; Wang, J.F.; Young, L.T. Increased hippocampal BDNF immunoreactivity in subjects treated with antidepressant medication. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Reznikov, L.R.; Grillo, C.A.; Piroli, G.G.; Pasumarthi, R.K.; Reagan, L.P.; Fadel, J. Acute stress-mediated increases in extracellular glutamate levels in the rat amygdala: differential effects of antidepressant treatment. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S. Mood disorders and allostatic load. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, C.R. LTP forms 1, 2 and 3: different mechanisms for the "long" in long-term potentiation. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Song, E.Y.; Kosten, T.A. Stress effects in the hippocampus: synaptic plasticity and memory. Stress 2006, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, D.M.; Park, C.R.; Woodson, J.C. Stress generates emotional memories and retrograde amnesia by inducing an endogenous form of hippocampal LTP. Hippocampus 2004, 14, 281–291. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, D.M.; Park, C.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Woodson, J.C. Competitive interactions between endogenous LTD and LTP in the hippocampus underlie the storage of emotional memories and stress-induced amnesia. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 1006–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, D.M.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Halonen, J.; Zoladz, P.R. The temporal dynamics model of emotional memory processing: a synthesis on the neurobiological basis of stress-induced amnesia, flashbulb and traumatic memories, and the Yerkes-Dodson Law. Neural Plast. 2007, 60803. [Google Scholar]
- Korz, V.; Frey, J.U. Stress-related modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats: Involvement of adrenal steroid receptors. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7281–7287. [Google Scholar]
- Mailliet, F.; Qi, H.; Rocher, C.; Spedding, M.; Svenningsson, P.; Jay, T.M. Protection of stress-induced impairment of hippocampal/prefrontal LTP through blockade of glucocorticoid receptors: implication of MEK signaling. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 211, 593–596. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S. Corticosteroids and hippocampal plasticity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 746, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Foy, M.R.; Thompson, R.F. Behavioral stress modifies hippocampal plasticity through N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4750–4753. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S. Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Popoli, M.; Gennarelli, M.; Racagni, G. Modulation of synaptic plasticity by stress and antidepressants. Bipolar Disord. 2002, 4, 166–182. [Google Scholar]
- Akirav, I.; Richter-Levin, G. Mechanisms of amygdala modulation of hippocampal plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9912–9921. [Google Scholar]
- Akirav, I.; Richter-Levin, G. Biphasic modulation of hippocampal plasticity by behavioral stress and basolateral amygdala stimulation in the rat. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10530–10535. [Google Scholar]
- Jay, T.M.; Rocher, C.; Hotte, M.; Naudon, L.; Gurden, H.; Spedding, M. Plasticity at hippocampal to prefrontal cortex synapses is impaired by loss of dopamine and stress: Importance for psychiatric diseases. Neurotox. Res. 2004, 6, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Rocher, C.; Spedding, M.; Munoz, C.; Jay, T.M. Acute stress-induced changes in hippocampal/prefrontal circuits in rats: effects of antidepressants. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Shakesby, A.C.; Anwyl, R.; Rowan, M.J. Overcoming the effects of stress on synaptic plasticity in the intact hippocampus: rapid actions of serotonergic and antidepressant agents. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 3638–3644. [Google Scholar]
- Vouimba, R.M.; Munoz, C.; Diamond, D.M. Differential effects of predator stress and the antidepressant tianeptine on physiological plasticity in the hippocampus and basolateral amygdala. Stress 2006, 9, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Mailliet, F.; Spedding, M.; Rocher, C.; Zhang, X.; Delagrange, P.; McEwen, B.; Jay, T.M.; Svenningsson, P. Antidepressants reverse the attenuation of the neurotrophic MEK/MAPK cascade in frontal cortex by elevated platform stress; reversal of effects on LTP is associated with GluA1 phosphorylation. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Diamond, D.M. The stressed hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 453–462. [Google Scholar]
- Zoladz, P.R.; Diamond, D.M. Linear and non-linear dose-response functions reveal a hormetic relationship between stress and learning. Dose Response 2008, 7, 132–148. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Zoladz, P.R.; Munoz, C.; Fleshner, M.; Diamond, D.M. Pre-training administration of tianeptine, but not propranolol, protects hippocampus-dependent memory from being impaired by predator stress. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zoladz, P.R.; Park, C.R.; Munoz, C.; Fleshner, M.; Diamond, D.M. Tianeptine: an antidepressant with memory-protective properties. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffard, R.; Mocaer, E.; Poignant, J.C.; Micheau, J.; Marighetto, A.; Meunier, M.; Beracochea, D. Effects of tianeptine on spontaneous alternation, simple and concurrent spatial discrimination learning and on alcohol-induced alternation deficits in mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 1991, 2, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Meneses, A. Tianeptine: 5-HT uptake sites and 5-HT1-7 receptors modulate memory formation in an autoshaping Pavlovian/instrumental task. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2002, 26, 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zoladz, P.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Schaefer, D.; Danysz, W.; Diamond, D.M. Enhancement of long-term spatial memory in adult rats by the noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists, memantine and neramexane. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 298–306. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.R.; Zoladz, P.R.; Conrad, C.D.; Fleshner, M.; Diamond, D.M. Acute predator stress impairs the consolidation and retrieval of hippocampus-dependent memory in male and female rats. Learn. Mem. 2008, 15, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Conboy, L.; Tanrikut, C.; Zoladz, P.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Sandi, C.; Diamond, D.M. The antidepressant agomelatine blocks the adverse effects of stress on memory and enables spatial learning to rapidly increase neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) expression in the hippocampus of rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zoladz, P.R.; Woodson, J.C.; Haynes, V.F.; Diamond, D.M. Activation of a remote (1-year old) emotional memory interferes with the retrieval of a newly formed hippocampus-dependent memory in rats. Stress 2010, 13, 36–52. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, D.M.; Park, C.R.; Heman, K.L.; Rose, G.M. Exposing rats to a predator impairs spatial working memory in the radial arm water maze. Hippocampus 1999, 9, 542–552. [Google Scholar]
- Sandi, C.; Woodson, J.C.; Haynes, V.F.; Park, C.R.; Touyarot, K.; Lopez-Fernandez, M.A.; Venero, C.; Diamond, D.M. Acute stress-induced impairment of spatial memory is associated with decreased expression of neural cell adhesion molecule in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 856–864. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, D.M.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Woodson, J.C.; Conrad, C.D.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Mervis, R.F. Influence of predator stress on the consolidation versus retrieval of long-term spatial memory and hippocampal spinogenesis. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Woodson, J.C.; Smith, T.P.; Fleshner, M.; Diamond, D.M. Permissive influence of stress in the expression of a U-shaped relationship between serum corticosterone levels and spatial memory errors in rats. Dose Response 2006, 4, 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Musazzi, L.; Milanese, M.; Farisello, P.; Zappettini, S.; Tardito, D.; Barbiero, V.S.; Bonifacino, T.; Mallei, A.; Baldelli, P.; Racagni, G.; et al. Acute stress increases depolarization-evoked glutamate release in the rat prefrontal/frontal cortex: the dampening action of antidepressants. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riedel, G.; Platt, B.; Micheau, J. Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 140, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bagley, J.; Moghaddam, B. Temporal dynamics of glutamate efflux in the prefrontal cortex and in the hippocampus following repeated stress: effects of pretreatment with saline or diazepam. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lowy, M.T.; Gault, L.; Yamamoto, B.K. Adrenalectomy attenuates stress-induced elevations in extracellular glutamate concentrations in the hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Lowy, M.T.; Wittenberg, L.; Yamamoto, B.K. Effect of acute stress on hippocampal glutamate levels and spectrin proteolysis in young and aged rats. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, B. Stress preferentially increases extraneuronal levels of excitatory amino acids in the prefrontal cortex: comparison to hippocampus and basal ganglia. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Hsu, K.S. Behavioral stress enhances hippocampal CA1 long-term depression through the blockade of the glutamate uptake. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 4288–4293. [Google Scholar]
- Bartanusz, V.; Aubry, J.M.; Pagliusi, S.; Jezova, D.; Baffi, J.; Kiss, J.Z. Stress-induced changes in messenger RNA levels of N-methyl-D-aspartate and AMPA receptor subunits in selected regions of the rat hippocampus and hypothalamus. Neuroscience 1995, 66, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Krugers, H.J.; Koolhaas, J.M.; Bohus, B.; Korf, J. A single social stress-experience alters glutamate receptor-binding in rat hippocampal CA3 area. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 154, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, B.S.; Magarinos, A.M.; Reagan, L.P. Structural plasticity and tianeptine: cellular and molecular targets. Eur. Psychiatry 2002, 17, S318–S330. [Google Scholar]
- Joels, M.; Velzing, E.; Nair, S.; Verkuyl, J.M.; Karst, H. Acute stress increases calcium current amplitude in rat hippocampus: temporal changes in physiology and gene expression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Kole, M.H.; Swan, L.; Fuchs, E. The antidepressant tianeptine persistently modulates glutamate receptor currents of the hippocampal CA3 commissural associational synapse in chronically stressed rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 807–816. [Google Scholar]
- Krugers, H.J.; Alfarez, D.N.; Karst, H.; Parashkouhi, K.; van Gemert, N.; Joels, M. Corticosterone shifts different forms of synaptic potentiation in opposite directions. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 697–703. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, B.J.; Goodnick, P.J. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of affective disorders--III. Tolerability, safety and pharmacoeconomics. J. Psychopharmacol. 1998, 12, S55–S87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Moon, B.H.; Lee, K.J.; Kang, S.W.; Lee, M.S.; Choi, S.H.; Chun, B.G.; Shin, K.H. Effects of repeated tianeptine treatment on CRF mRNA expression in non-stressed and chronic mild stress-exposed rats. Neuropharmacology 2006, 50, 824–833. [Google Scholar]
- Holsboer, F. The rationale for corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor (CRH-R) antagonists to treat depression and anxiety. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1999, 33, 181–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kasckow, J.W.; Baker, D.; Geracioti, T.D., Jr. Corticotropin-releasing hormone in depression and post-traumatic stress disorder. Peptides 2001, 22, 845–851. [Google Scholar]
- Strohle, A.; Holsboer, F. Stress responsive neurohormones in depression and anxiety. Pharmacopsychiatry 2003, 36 (Suppl. 3), S207–S214. [Google Scholar]
- Reagan, L.P.; Rosell, D.R.; Wood, G.E.; Spedding, M.; Munoz, C.; Rothstein, J.; McEwen, B.S. Chronic restraint stress up-regulates GLT-1 mRNA and protein expression in the rat hippocampus: reversal by tianeptine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, V.R.; Finkbeiner, S. NMDA and AMPA receptors: old channels, new tricks. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Svenningsson, P.; Tzavara, E.T.; Witkin, J.M.; Fienberg, A.A.; Nomikos, G.G.; Greengard, P. Involvement of striatal and extrastriatal DARPP-32 in biochemical and behavioral effects of fluoxetine (Prozac). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3182–3187. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Suzuki, K.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Blumenthal, R.; Chen, Z.; Falke, C.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Manji, H.K. The anticonvulsants lamotrigine, riluzole, and valproate differentially regulate AMPA receptor membrane localization: relationship to clinical effects in mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 793–802. [Google Scholar]
- Barria, A.; Muller, D.; Derkach, V.; Griffith, L.C.; Soderling, T.R. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science 1997, 276, 2042–2045. [Google Scholar]
- Roche, K.W.; O'Brien, R.J.; Mammen, A.L.; Bernhardt, J.; Huganir, R.L. Characterization of multiple phosphorylation sites on the AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit. Neuron 1996, 16, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Uzbay, T.; Kayir, H.; Celik, T.; Yuksel, N. Acute and chronic tianeptine treatments attenuate ethanol withdrawal syndrome in rats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 30, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Ceyhan, M.; Kayir, H.; Uzbay, I.T. Investigation of the effects of tianeptine and fluoxetine on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in rats. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2005, 39, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Uzbay, T.I.; Kayir, H.; Ceyhan, M. Effects of tianeptine on onset time of pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in mice: possible role of adenosine A1 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Florio, C.; Prezioso, A.; Papaioannou, A.; Vertua, R. Adenosine A1 receptors modulate anxiety in CD1 mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1998, 136, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, N.; Kemp, N.; Adeyemo, O.; Buchanan, P.; Stone, T.W. Anxiolytic activity of adenosine receptor activation in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Prediger, R.D.; Batista, L.C.; Takahashi, R.N. Adenosine A1 receptors modulate the anxiolytic-like effect of ethanol in the elevated plus-maze in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 499, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Prediger, R.D.; da Silva, G.E.; Batista, L.C.; Bittencourt, A.L.; Takahashi, R.N. Activation of adenosine A1 receptors reduces anxiety-like behavior during acute ethanol withdrawal (hangover) in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar]
- File, S.E.; Andrews, N.; al Farhan, M. Anxiogenic responses of rats on withdrawal from chronic ethanol treatment: effects of tianeptine. Alcohol Alcohol. 1993, 28, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- File, S.E.; Mabbutt, P.S. Effects of tianeptine in animal-models of anxiety and on learning and memory. Drug Dev. Res. 1991, 23, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Defrance, R.; Marey, C.; Kamoun, A. Antidepressant and anxiolytic activities of tianeptine: an overview of clinical trials. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1988, 11 (Suppl. 2), S74–S82. [Google Scholar]
- Wilde, M.I.; Benfield, P. Tianeptine. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in depression and coexisting anxiety and depression. Drugs 1995, 49, 411–439. [Google Scholar]
- Guelfi, J.D.; Pichot, P.; Dreyfus, J.F. Efficacy of tianeptine in anxious-depressed patients: results of a controlled multicenter trial versus amitriptyline. Neuropsychobiology 1989, 22, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Onder, E.; Tural, U.; Aker, T. A comparative study of fluoxetine, moclobemide, and tianeptine in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder following an earthquake. Eur. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zoladz, P.R.; Muñoz, C.; Diamond, D.M. Beneficial Effects of Tianeptine on Hippocampus-Dependent Long-Term Memory and Stress-Induced Alterations of Brain Structure and Function. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 3143-3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103143
Zoladz PR, Muñoz C, Diamond DM. Beneficial Effects of Tianeptine on Hippocampus-Dependent Long-Term Memory and Stress-Induced Alterations of Brain Structure and Function. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(10):3143-3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103143
Chicago/Turabian StyleZoladz, Phillip R., Carmen Muñoz, and David M. Diamond. 2010. "Beneficial Effects of Tianeptine on Hippocampus-Dependent Long-Term Memory and Stress-Induced Alterations of Brain Structure and Function" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 10: 3143-3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103143
APA StyleZoladz, P. R., Muñoz, C., & Diamond, D. M. (2010). Beneficial Effects of Tianeptine on Hippocampus-Dependent Long-Term Memory and Stress-Induced Alterations of Brain Structure and Function. Pharmaceuticals, 3(10), 3143-3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103143



