Recombinant Destabilase from Hirudo medicinalis Is Able to Dissolve Human Blood Clots In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recombinant Destabilase Isolation
2.2. Isopeptidase Assay
2.3. Coagulation Tests
2.4. Blood Clot Preparation
- Thromboembolism;
- Acute thrombosis against the background of atherosclerotic artery stenosis, including hemorrhage into an atherosclerotic plaque;
- Progression of previously existing subclinical arterial thrombosis.
2.5. Thrombolysis by Destabilase and Streptokinase
2.6. Blood Clot Destabilization
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
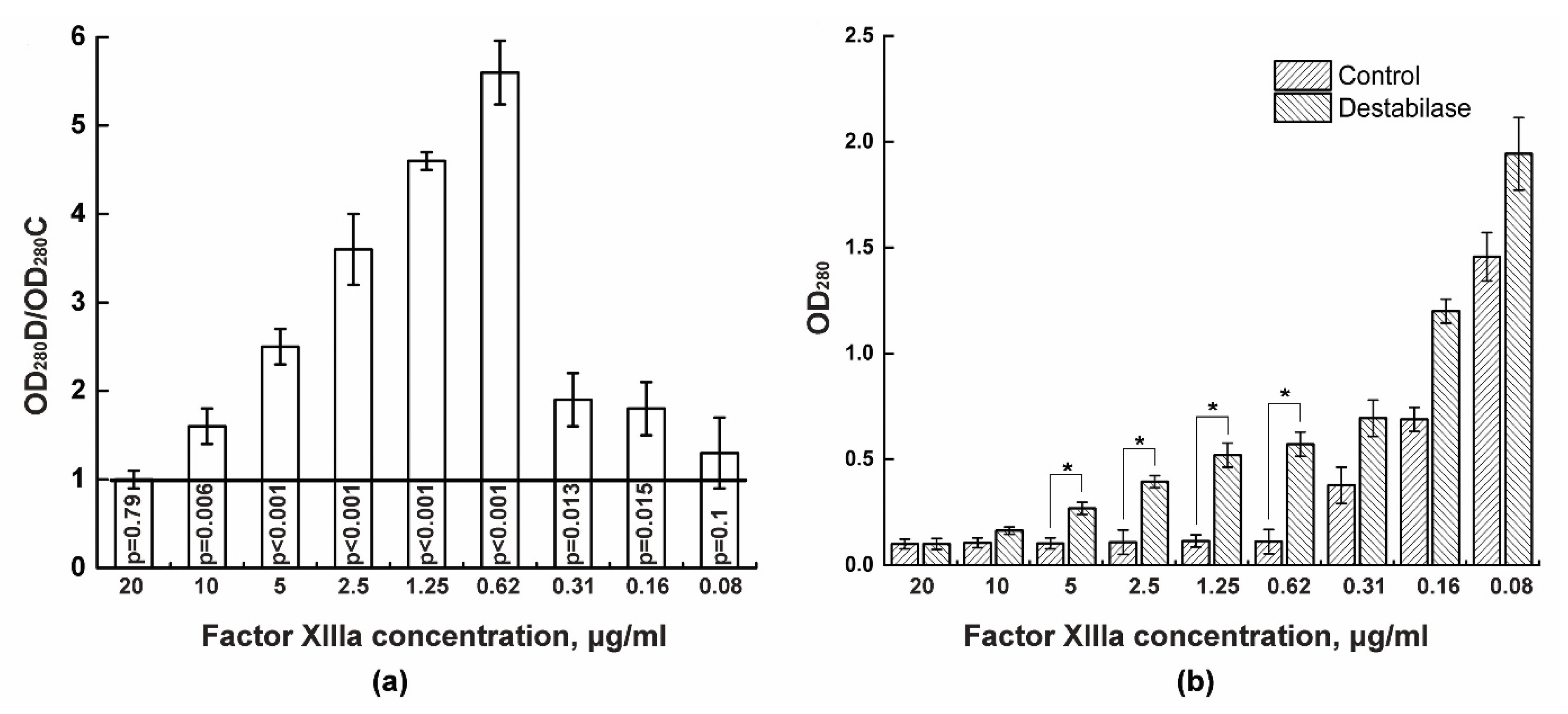
3.1. Isopeptidase Assay
3.2. Coagulation Tests
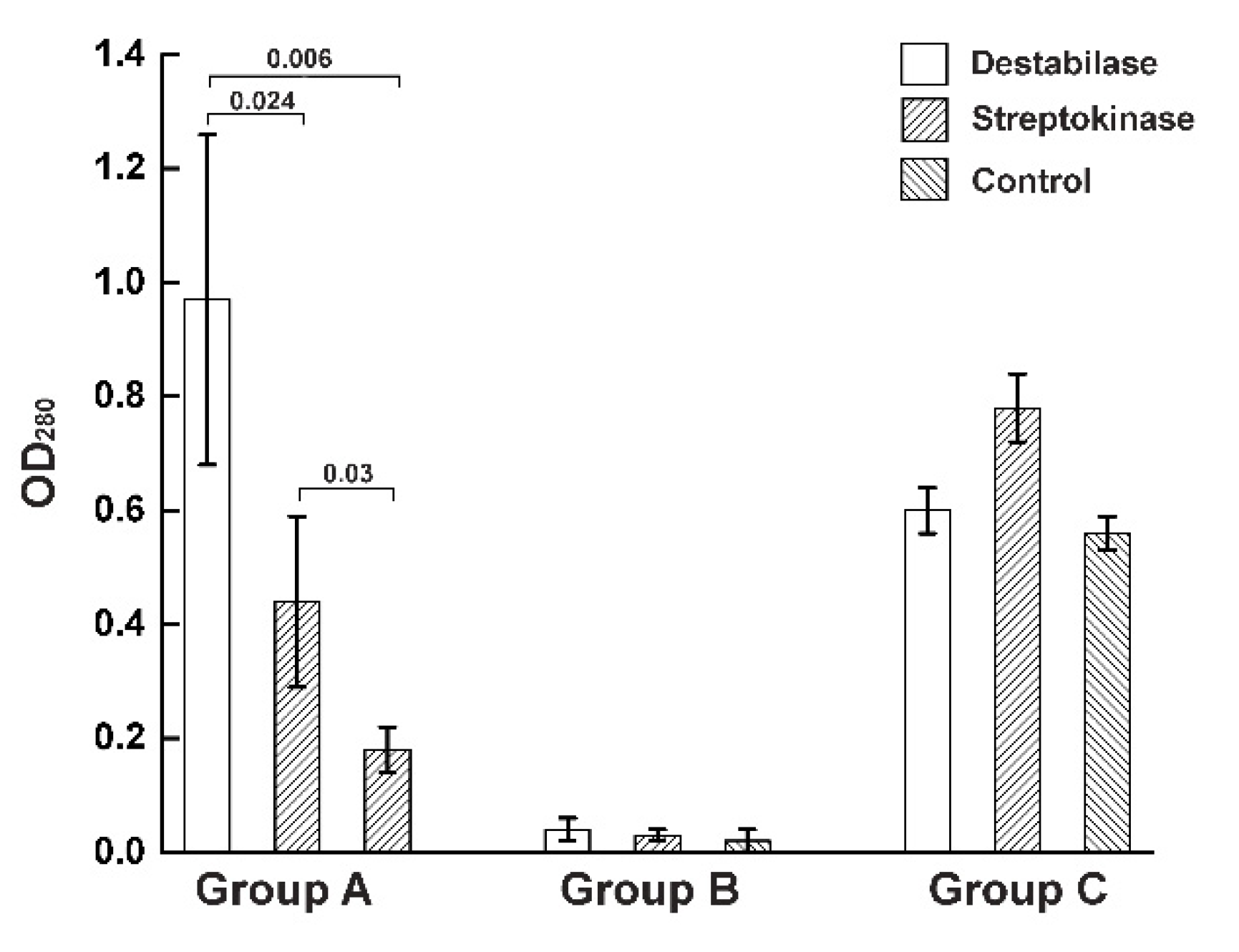
3.3. Thrombolysis by Destabilase or Streptokinase
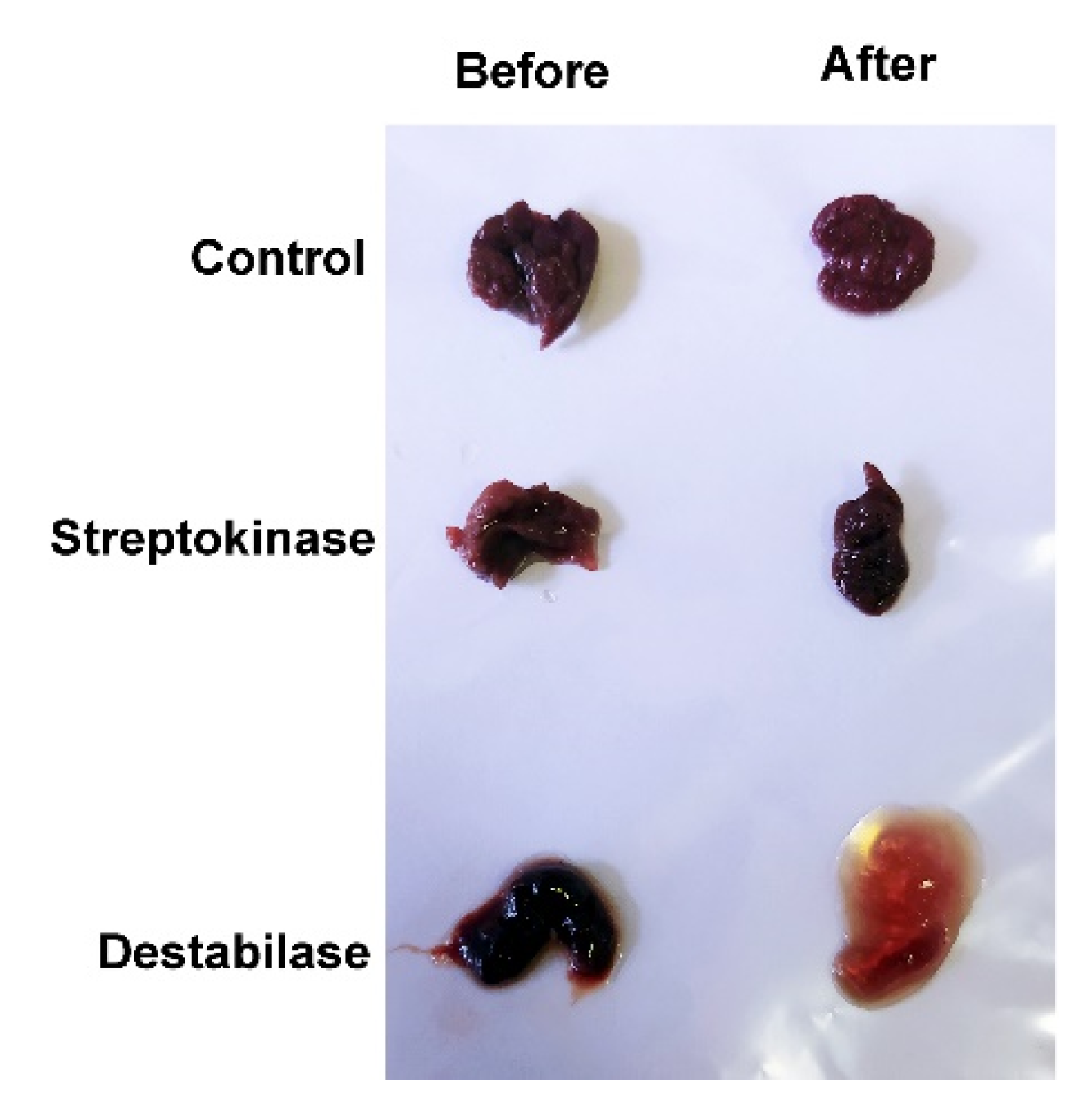
3.4. Blood Clot Destabilization
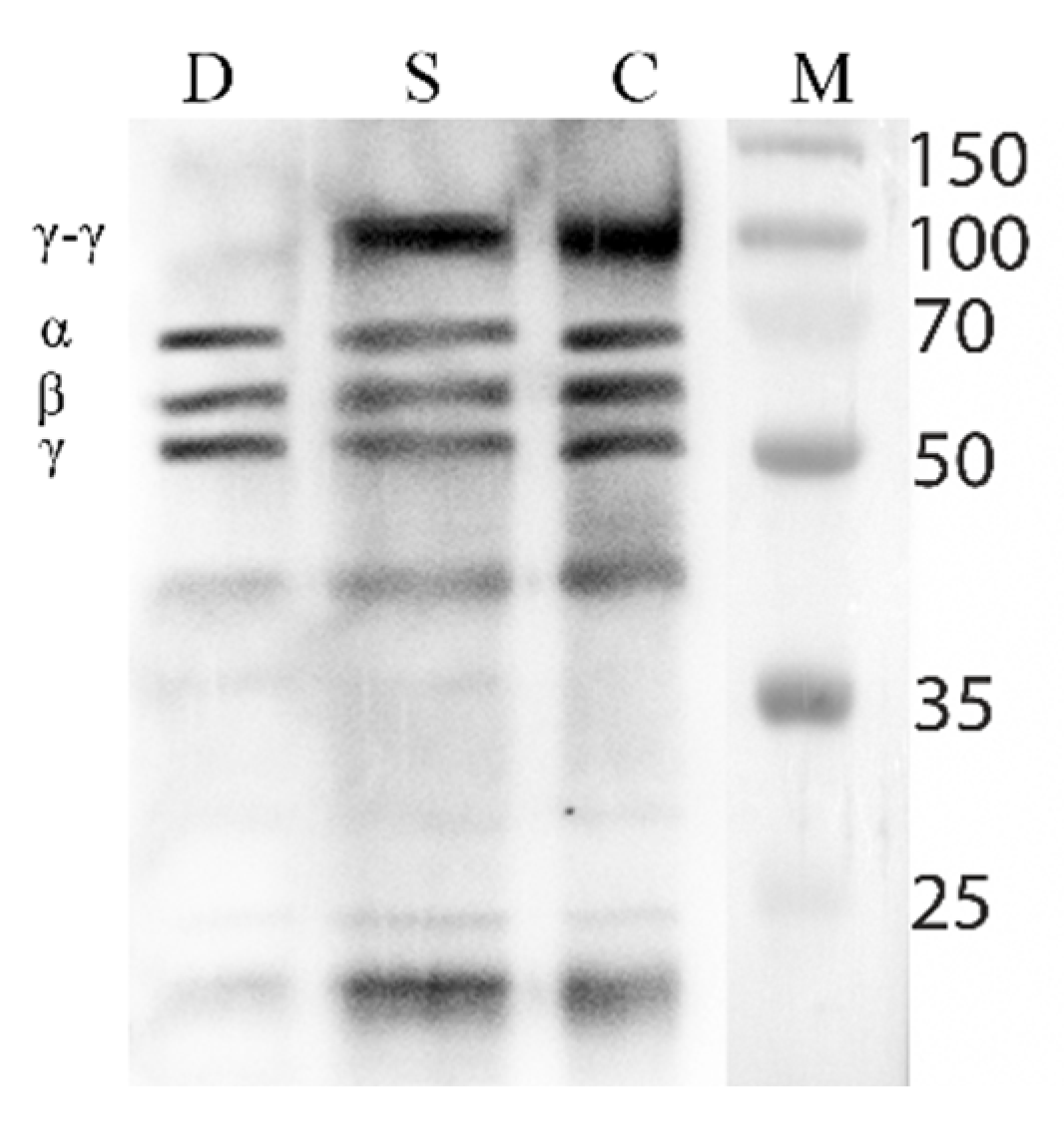
3.5. Fibrinolytic Activity of the Destabilase
4. Discussion
- Fresh clots—dark, easily detached from the vessel wall and fragmented when pressed with fingers;
- Aged clots—light, fixed to the vessel wall, dense, fragmented only with a sharp instrument;
- Aged embolus—a denser and lighter fragment of an aged intracardiac clot (its presence was confirmed by transesophageal ultrasound in the postoperative period),
- Atherosclerotic plaque—located subintimal, heterogeneous, can be calcified.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Age-Sex Specific All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality for 240 Causes of Death, 1990-2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Karp Leaf, R.S.; Dzik, W.H.; Carlson, J.C.T.; Fogerty, A.E.; Waheed, A.; Goodarzi, K.; Bendapudi, P.K.; Bornikova, L.; Gupta, S.; et al. COVID-19 and coagulation: Bleeding and thrombotic manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Blood 2020, 136, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimenko, A.V. Thrombolysis with plasminogen activators: Use and research of serine proteinases, promise and actuality. Biomed. Khim. 2014, 60, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madonov, P.G.; Kinsht, D.N.; Ershov, K.I.; Shilova, M.A.; Solov’ev, O.N. Experience with clinical administration of new drug Thrombovasim(R) in vascular surgery. Angiol. Sosud. Khir. 2015, 21, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nedaeinia, R.; Faraji, H.; Javanmard, S.H.; Ferns, G.A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Goli, M.; Mashkani, B.; Nedaeinia, M.; Haghighi, M.H.H.; Ranjbar, M. Bacterial staphylokinase as a promising third-generation drug in the treatment for vascular occlusion. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 819–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Koh, C.Y. Metalloproteases Affecting Blood Coagulation, Fibrinolysis and Platelet Aggregation from Snake Venoms: Definition and Nomenclature of Interaction Sites. Toxins 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostic, T.; Perisic, Z.; Milic, D.; Apostolovic, S.; Martinovic, S.S.; Bozinovic, N.; Mitov, V.; Vidanovic, M. Coronary flow and hemorrhagic complications after alteplase and streptokinase administration in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2009, 66, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Uhrig, D.; Fowler, S.; DeLaney, M.C.; Alexandrov, A.V. Intravenous Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Does Not Impact Mortality in Acute Ischemic Stroke at Any Time Point up to 6 Months: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. CNS Drugs 2015, 29, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medcalf, R.L. Desmoteplase: Discovery, Insights and Opportunities for Ischaemic Stroke. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillermin, A.; Yan, D.J.; Perrier, A.; Marti, C. Safety and Efficacy of Tenecteplase versus Alteplase in Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warach, S.J.; Dula, A.N.; Milling, T.J.J. Tenecteplase Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansueto, G.; Costa, D.; Capasso, E.; Varavallo, F.; Brunitto, G.; Caserta, R.; Esposito, S.; Niola, M.; Sardu, C.; Marfella, R.; et al. The Dating of Thrombus Organization in Cases of Pulmonary Embolism: An Autopsy Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamasa, K.; Watanabe, I.; Cercek, B.; Yano, J.; Fishbein, M.C.; Ganz, W. Selective Decrease in Lysis of Old Thrombi after Rapid Administration of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1989, 14, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stafford, J.L. The Fibrinolytic Mechanism in Haemostasis: A Review. J. Clin. Pathol. 1964, 17, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenberg, C.S.; Birckbichler, P.J.; Rice, R.H. Transglutaminases: Multifunctional Cross-Linking Enzymes That Stabilize Tissues. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1991, 5, 3071–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivard, A.; Lin, L.; Parsonsb, M.W. Review of Stroke Thrombolytics. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Streiff, M.B.; Agnelli, G.; Connors, J.M.; Crowther, M.; Eichinger, S.; Lopes, R.; McBane, R.D.; Moll, S.; Ansell, J. Guidance for the Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 41, 32–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasternack, R.; Büchold, C.; Jähnig, R.; Pelzer, C.; Sommer, M.; Heil, A.; Florian, P.; Nowak, G.; Gerlach, U.; Hils, M. Novel Inhibitor ZED3197 as Potential Drug Candidate in Anticoagulation Targeting Coagulation FXIIIa (F13a). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bäuml, C.A.; Schmitz, T.; Paul George, A.A.; Sudarsanam, M.; Hardes, K.; Steinmetzer, T.; Holle, L.A.; Wolberg, A.S.; Pötzsch, B.; Oldenburg, J.; et al. Coagulation Factor XIIIa Inhibitor Tridegin: On the Role of Disulfide Bonds for Folding, Stability, and Function. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3513–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, T.; Bäuml, C.A.; Imhof, D. Inhibitors of blood coagulation factor XIII. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 605, 113708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Kohler, H.P. New Developments in the Area of Factor XIII. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chérifi, F.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Bioactive Molecules Derived from Snake Venoms with Therapeutic Potential for the Treatment of Thrombo-Cardiovascular Disorders Associated with COVID-19. Protein J. 2021, 40, 799–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W. Snake Venoms in Diagnostic Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oršolić, N. Bee Venom in Cancer Therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarev, V.N.; Shkarupeta, M.M.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Levitskii, S.A.; Titova, G.A.; Akopian, T.A.; Govorun, V.M. Recombinant Plasmid Constructs Expressing Gene for Antimicrobial Peptide Melittin for the Therapy of Mycoplasma and Chlamydia Infections. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 144, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.-G. Hirudin in Renal Insufficiency. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 28, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Barkley, T.W.J. Medicinal Leech Therapy: New Life for an Ancient Treatment. Nursing 2015, 45, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskova, I.P.; Nikonov, G.I. Destabilase: An Enzyme of Medicinal Leech Salivary Gland Secretion Hydrolyzes the Isopeptide Bonds in Stabilized Fibrin. Biokhimiia 1985, 50, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Callewaert, L.; Michiels, C.W. Lysozymes in the Animal Kingdom. J. Biosci. 2010, 35, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavalova, L.L.; Artamonova, I.I.; Berezhnoy, S.N.; Tagaev, A.A.; Baskova, I.P.; Andersen, J.; Roepstorff, P.; Egorov, T.A. Multiple Forms of Medicinal Leech Destabilase-Lysozyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 306, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalova, L.; Lukyanov, S.; Baskova, I.; Snezhkov, E.; Akopov, S.; Berezhnoy, S.; Bogdanova, E.; Barsova, E.; Sverdlov, E.D. Genes from the Medicinal Leech (Hirudo Medicinalis) Coding for Unusual Enzymes That Specifically Cleave Endo-Epsilon (Gamma-Glu)-Lys Isopeptide Bonds and Help to Dissolve Blood Clots. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1996, 253, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdyumov, A.S.; Manuvera, V.A.; Baskova, I.P.; Lazarev, V.N. A Comparison of the Enzymatic Properties of Three Recombinant Isoforms of Thrombolytic and Antibacterial Protein--Destabilase-Lysozyme from Medicinal Leech. BMC Biochem. 2015, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manuvera, V.A.; Kurdyumov, A.S.; Filonova, K.A.; Lazarev, V.N. Generation of Recombinant Destabilase-Lysozyme from Medicinal Leeches in Three Different Expression Systems. Protein Expr. Purif. 2015, 116, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskova, I.P.; Zavalova, L.L. Polyfunctionality of destabilase, a lysozyme from a medicinal leech. Bioorg. Khim. 2008, 34, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskova, I.P.; Kalabushev, S.N.; Akhaev, D.N.; Bobrovsky, P.A.; Manuvera, V.A.; Lazarev, V.N. Role of Isopeptidolysis in the Process of Thrombolysis. Thromb. Res. 2018, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorgalaleh, A.; Tabibian, S.; Assadollahi, V.; Shamsizadeh, M.; Zareban, I.; Soori, S.; Daneshi, M. Comparison of 2 Methods of Clot Solubility Testing in Detection of Factor XIII Deficiency. Lab. Med. 2016, 47, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jennings, I.; Kitchen, S.; Woods, T.A.L.; Preston, F.E. Problems Relating to the Laboratory Diagnosis of Factor XIII Deficiency: A UK NEQAS Study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 2603–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyshelesky, A.; Iakobishvili, Z.; Matz, I.; Golovchiner, G.; Vaturi, M.; Siegel, R.J.; Birnbaum, Y. There Is Synergism between High-Intensity, Low-Frequency Ultrasound and Streptokinase but Not with Eptifibatide, Heparin, and Aspirin. Differential Effects on Fresh and Aged Blood Clots. An In Vitro Study. Thromb. Res. 2001, 103, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teknomo, K. Online Hierarchial Clustering Calculator. Available online: https://people.revoledu.com/kardi/tutorial/Clustering/Online-Hierarchical-Clustering.html (accessed on 16 March 2020).
- Baskova, I.P.; Nikonov, G.I. Destabilase, the Novel Epsilon-(Gamma-Glu)-Lys Isopeptidase with Thrombolytic Activity. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1991, 2, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalova, L.L.; Lazarev, V.N.; Levitsky, S.A.; Yudina, T.G.; Baskova, I.P. Destabilase-Lysozyme of Medicinal Leech. Multifunctionality of Recombinant Protein. Biochemistry 2010, 75, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.R.; Houng, A.K.; Reed, G.L. Catalytic Life of Activated Factor XIII in Thrombi. Implications for Fibrinolytic Resistance and Thrombus Aging. Circulation 2000, 102, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katona, E.; Penzes, K.; Molnar, E.; Muszbek, L. Measurement of Factor XIII Activity in Plasma. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiruvenkatarajan, V.; Pruett, A.; Adhikary, S. Das Coagulation Testing in the Perioperative Period. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, M.J.; Murthy, M.S.; Peterson, E.J. Bleeding Risk with Systemic Thrombolytic Therapy for Pulmonary Embolism: Scope of the Problem. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2015, 6, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omraninava, A.; Hashemian, A.M.; Masoumi, B. Effective Factors in Door-to-Needle Time for Streptokinase Administration in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction Admitted to the Emergency Department. Trauma Mon. 2016, 21, e19676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, S.D.; Granger, C.B.; Pieper, K.S.; Lee, K.L.; Gore, J.M.; Simoons, M.; Armstrong, P.W.; Topol, E.J.; Califf, R.M. Incidence and Predictors of Bleeding after Contemporary Thrombolytic Therapy for Myocardial Infarction. The Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries (GUSTO) I Investigators. Circulation 1997, 95, 2508–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slivka, A.; Pulsinelli, W. Hemorrhagic Complications of Thrombolytic Therapy in Experimental Stroke. Stroke 1987, 18, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ringleb, P.A.; Schellinger, P.D.; Schranz, C.; Hacke, W. Thrombolytic Therapy within 3 to 6 Hours after Onset of Ischemic Stroke: Useful or Harmful? Stroke 2002, 33, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalanuria, A.A.; Nyquist, P.; Ling, G. The Prevention and Regression of Atherosclerotic Plaques: Emerging Treatments. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2012, 8, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naderi, M.; Dorgalaleh, A.; Tabibian, S.; Alizadeh, S.; Eshghi, P.; Solaimani, G. Current Understanding in Diagnosis and Management of Factor XIII Deficiency. Iran. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 3, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Martinuzzo, M.; Barrera, L.; Altuna, D.; Bana, F.T.; Bieti, J.; Amigo, Q.; D’Adamo, M.; Lopez, M.S.; Oyhamburu, J.; Otaso, J.C. Effects of Factor XIII Deficiency on Thromboelastography. Thromboelastography with Calcium and Streptokinase Addition Is More Sensitive than Solubility Tests. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 8, e2016037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swieringa, F.; Spronk, H.M.H.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; van der Meijden, P.E.J. Integrating Platelet and Coagulation Activation in Fibrin Clot Formation. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskova, I.P.; Aguejouf, O.M.; Azougagh-Oualane, F.; Zavalova, L.L.; Basanova, A.V.; Doutremepuich, C. Arterial Antithrombotic Effect of Piyavit, the Novel Pharmacological Preparation from the Medicinal Leech, and of Its Components, Prostanoids and Enzyme Destabilase. Thromb. Res. 1995, 77, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.W.; Teoh, H.; Verma, S. Endothelial Cell Control of Thrombosis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2015, 15, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, B.A.; Arocha-Piñango, C.L.; Gil San Juan, A. Degradation of Human Factor XIII by Lonomin V, a Purified Fraction of Lonomia Achelous Caterpillar Venom. Thromb. Res. 1997, 87, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskova, I.P.; Zavalova, L.L.; Kuzina, E.V. Endo-epsilon-(gamma-Glu)Lys-isopeptidolysis as a sign of highly-specific proteolysis. Bioorg. Khim. 1994, 20, 492–497. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | Age | Characteristics | Diagnosis | Comorbidity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 63 | An aged clot fragment from the right femoral artery | ASVD. Aortic, iliac, left femoral, and popliteal arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the right femoral and popliteal arteries. | IHD, old myocardial infarction |
| T2 | 63 | A fresh right femoral arterial clot fragment * | ASVD. Aortic, iliac, left femoral, and popliteal arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the right femoral and popliteal arteries. | IHD, old myocardial infarction |
| T3 | 68 | A fresh right femoral arterial clot fragment * | ASVD of the femoral, popliteal, and tibial arteries. Right femoral artery thrombosis | IHD, HT |
| T4 | 76 | A mixed thromboembolism from the left brachial artery (old embolus and fresh continued clot) * | Left brachial artery thrombosis | IHD, Permanent A-fib, HT |
| T5 | 74 | An aged right popliteal clot fragment | ASVD. Aortic, iliac, femoral, tibial, and left popliteal arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the right popliteal artery | IHD, chronic cholecystitis, chronic pancreatitis, chronic bronchitis. |
| T6 | 75 | An aged femoral arterial clot fragment from the proximal part of the left femoral artery, intimately associated with the atherosclerotic plaque | ASVD. Aortic, iliac, popliteal, tibial, and right femoral arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the left femoral artery. | IHD, megaloblastic anemia, chronic gastritis, hip, and knee osteoarthritis |
| T7 | 75 | An aged femoral arterial clot fragment from the distal part of the left femoral artery, intimately associated with the atherosclerotic plaque | ASVD. Aortic, iliac, popliteal, tibial, and right femoral arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the left femoral artery. | IHD, megaloblastic anemia, chronic gastritis, hip, and knee osteoarthritis |
| T8 | 65 | The fresh blood clot fragment up to 8 cm long in the right tibial vein, floating in the popliteal vein. During surgical treatment for an open fracture, thrombectomy was performed * | Open comminuted fractures of the tibia and fibula with displacement. Floating clot of the right tibial and popliteal veins. | Post-traumatic bleeding, HT |
| T9 | 74 | An aged left femoral arterial clot fragment | ASVD. Iliac, right femoral, and popliteal arteries, right posterior tibial artery stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the left femoral and popliteal arteries. | HT |
| T10 | 70 | Fragment of an organized aged clot fragment from the right brachial artery | Thromboembolism of the right brachial artery | IHD, Permanent A-fib |
| T11 | 78 | A fresh left femoral arterial clot fragment * | ASVD. Aortic, iliac, right femoral, and popliteal arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the left femoral and popliteal arteries | IHD, HT, Right kidney cyst. |
| T12 | 72 | A fresh right femoral arterial clot fragment * | ASVD. Tibial and left popliteal arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the right popliteal and femoral arteries. | IHD, COPD |
| T13 | 72 | An aged right popliteal clot fragment | ASVD. Tibial and left popliteal arteries stenosis with thrombotic occlusion of the right popliteal and femoral arteries. | IHD, COPD |
| T14 | 66 | The apex fragment of the floating part of the left femoral vein clot ** | Occlusive thrombosis of the tibial and popliteal veins, floating thrombosis of the left femoral veins. | Injury: partial rupture of the Achilles tendon, IHD, HT, chronic cholecystitis, chronic pancreatitis. |
| T15 | 68 | The fragment of fresh clot from the right brachial artery * | Thromboembolism of the right brachial artery | IHD, permanent A-fib, HT, chronic gastritis, chronic duodenitis, postcholecystectomy syndrome |
| Test Name: | APTT | TT | PT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Destabilase | 35 ± 2.3 | 20.2 ± 1.2 | 11.3 ± 0.8 |
| Control | 34.3 ± 1.5 | 19.5 ± 1.4 | 10.8 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bobrovsky, P.; Manuvera, V.; Baskova, I.; Nemirova, S.; Medvedev, A.; Lazarev, V. Recombinant Destabilase from Hirudo medicinalis Is Able to Dissolve Human Blood Clots In Vitro. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 2068-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030143
Bobrovsky P, Manuvera V, Baskova I, Nemirova S, Medvedev A, Lazarev V. Recombinant Destabilase from Hirudo medicinalis Is Able to Dissolve Human Blood Clots In Vitro. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2021; 43(3):2068-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030143
Chicago/Turabian StyleBobrovsky, Pavel, Valentin Manuvera, Izolda Baskova, Svetlana Nemirova, Alexandr Medvedev, and Vassili Lazarev. 2021. "Recombinant Destabilase from Hirudo medicinalis Is Able to Dissolve Human Blood Clots In Vitro" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 43, no. 3: 2068-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030143
APA StyleBobrovsky, P., Manuvera, V., Baskova, I., Nemirova, S., Medvedev, A., & Lazarev, V. (2021). Recombinant Destabilase from Hirudo medicinalis Is Able to Dissolve Human Blood Clots In Vitro. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 43(3), 2068-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb43030143






