Effect of Aqueous Extract of Phenolic Compounds Obtained from Red Wine in Experimental Model of Colitis in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Induction of Experimental Colitis
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Preparation and Characterization of Phenolic Compound Extract
2.6. Monitoring of Clinical Signs
2.7. Biological Markers
2.8. Analysis of the Inflammatory Response
2.9. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Phenolic Compounds Extract
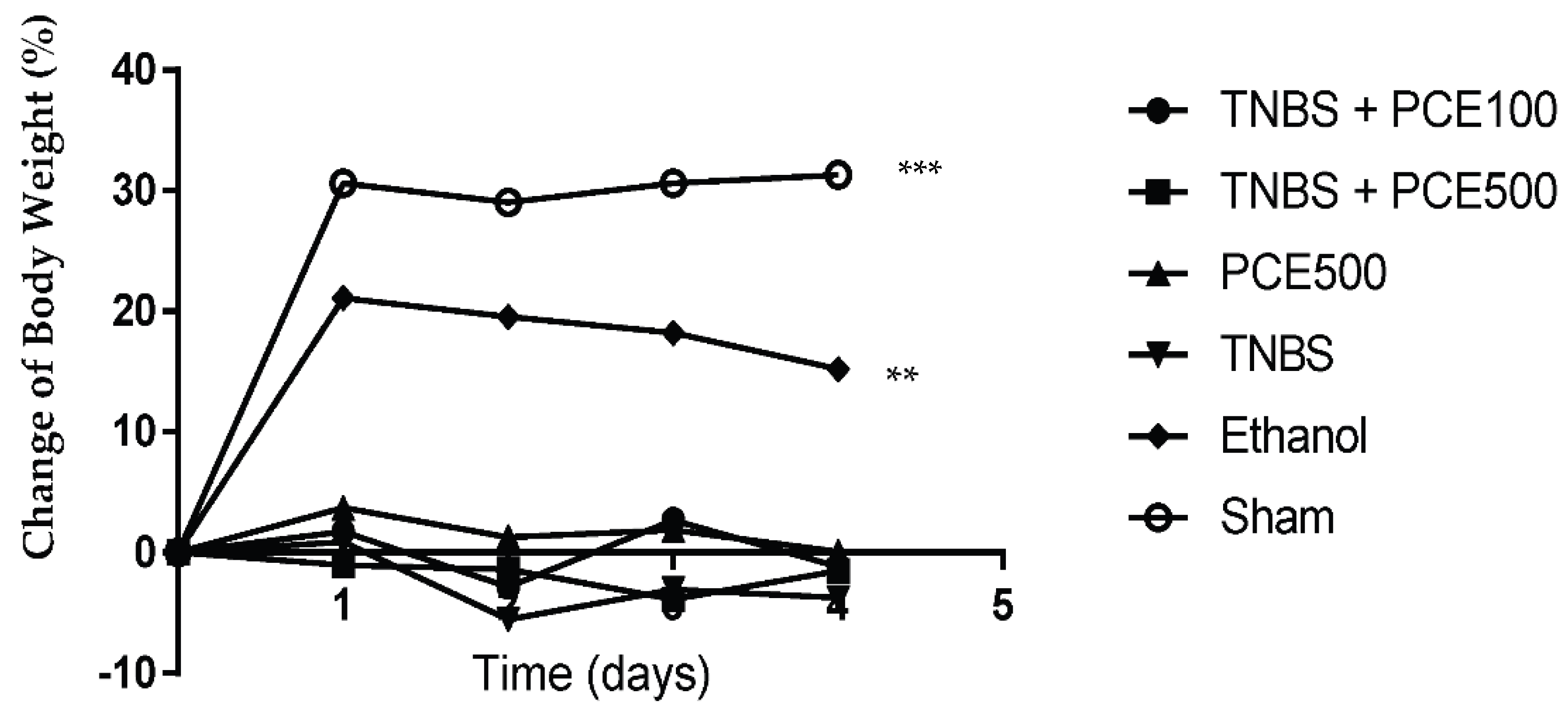
3.2. Manifestation of Clinical Signs
3.3. Biological Markers
3.3.1. Colon Length
3.3.2. Fecal Hemoglobin
3.3.3. Alkaline Phosphatase
3.3.4. Renal Function
3.3.5. Hepatic Function
3.4. Analysis of the Inflammatory Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Sodagari, H.R.; Farzaei, M.H.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Mahmoudi, M.; Rezaei, N. Dietary anthocyanins as a complementary medicinal approach for management of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussenna, A.; Goncalves-Mendes, N.; Joubert-Zakeyh, J.; Pereira, B.; Fraisse, D.; Vasson, M.-P.; Texier, O.; Felgines, C. Impact of basal diet on dextran sodium sulphate (DSS)-induced colitis in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, T.; Kim, D.; Lim, B. Natural Products as a Source of Anti-Inflammatory Agents Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Molecules 2013, 18, 7253–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geier, M.; Butler, R.; Howarth, G. Inflammatory bowel disease: Current insights into pathogenesis and new therapeutic options; probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gionchetti, P.; Rizzello, F.; Annese, V.; Armuzzi, A.; Biancone, L.; Castiglione, F.; Comberlato, M.; Cottone, M.; Danese, S.; Daperno, M.; et al. Use of corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs in inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical practice guidelines of the Italian Group for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, K.; Roggenbuck, D.; Laass, M.W. Diagnosis and classification of ulcerative colitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.; Langner, C.; Driessen, A.; Ensari, A.; Geboes, K.; Mantzaris, G.; Villanacci, V.; Becheanu, G.; Nunes, P.B.; Cathomas, G.; et al. European consensus on the histopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatab, S.; Sepanlou, S.G.; Ikuta, K.; Vahedi, H.; Bisignano, C.; Safiri, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Nixon, M.R.; Abdoli, A.; Abolhassani, H.; et al. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyams, J.S. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1994, 19, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves de Almeida, A.C.; De-Faria, F.M.; Dunder, R.J.; Manzo, L.P.B.; Souza-Brito, A.R.M.; Luiz-Ferreira, A. Recent Trends in Pharmacological Activity of Alkaloids in Animal Colitis: Potential Use for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 8528210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, A.; Biancheri, P.; Allan, P.; Corazza, G.R.; Di Sabatino, A. Innate and adaptive immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisni, E.; Valerii, M.C.; De Fazio, L.; Cavazza, E.; Borsetti, F.; Sgromo, A.; Candela, M.; Centanni, M.; Rizello, F.; Strillacci, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 Silencing for the Treatment of Colitis: A Combined In Vivo Strategy Based on RNA Interference and Engineered Escherichia Coli. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, C.; Ferreira, E.; Freitas, V.; Almeida, L.; Barbosa, R.M.; Laranjinha, J. Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of red wine extract: Unveiling the mechanisms in colonic epithelial cells. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Fernandes, F.; Pinto-Carnide, O.; Valentão, P.; Falco, V.; Martín, J.P.; Ortiz, J.M.; Arroyo-García, R.; Andrade, P.B.; Castro, I. Identification of Vitis vinifera L. grape berry skin color mutants and polyphenolic profile. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraige, K.; Pereira-Filho, E.R.; Carrilho, E. Fingerprinting of anthocyanins from grapes produced in Brazil using HPLC–DAD–MS and exploratory analysis by principal component analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, L.; Cuervo, A.; Salazar, N.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Gueimonde, M.; González, S. The relationship between phenolic compounds from diet and microbiota: Impact on human health. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2424–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.H.; Lai, C.S.; Ho, C.T. Anti-inflammatory activity of natural dietary flavonoids. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Boto-Ordóñez, M.; Murri, M.; Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Estruch, R.; Cardona Diaz, F.; Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Tinahones, F.J. Influence of red wine polyphenols and ethanol on the gut microbiota ecology and biochemical biomarkers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas, M.; Cueva, C.; Muñoz-González, I.; Jiménez-Girón, A.; Sánchez-Patán, F.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Bartolomé, B. Studies on Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Wine Polyphenols: From Isolated Cultures to Omic Approaches. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrdoljak, J.; Kumric, M.; Kurir, T.T.; Males, I.; Martinovic, D.; Vilovic, M.; Bozic, J. Effects of Wine Components in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, F.; Deiana, M.; Guina, T.; Gamba, P.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Poli, G. Wine consumption and intestinal redox homeostasis. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, V.; Rocha, J.; Alves, P.; Mota-Filipe, H.; Sepodes, B.; Pinto, R. Thiadiazolidinone-8 Ameliorates Inflammation Associated with Experimental Colitis in Mice. Pharmacology 2018, 101, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, V.; Rocha, J.; Mota-Filipe, H.; Sepodes, B.; Pinto, R. Hemin reduces inflammation associated with TNBS-induced colitis. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, V.; Rocha, J.; Alves, P.; Mota-Filipe, H.; Sepodes, B.; Pinto, R.M.A. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Erythropoietin in the TNBS-induced Colitis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 120, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice-Evans, C.; Miller, N.; Paganga, G. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.A.; Bolling, B.W. A review of the efficacy of dietary polyphenols in experimental models of inflammatory bowel diseases. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1773–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, I. Usefulness of fecal lactoferrin and hemoglobin in diagnosis of colorectal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalingam, N.A.; Kao, J.Y.; Young, V.B. Microbial ecology of the murine gut associated with the development of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.S.; Rajmane, A.R.; Adil, M.; Kandhare, A.D.; Ghosh, P.; Bodhankar, S.L. Naringin ameliorates acetic acid induced colitis through modulation of endogenous oxido-nitrosative balance and DNA damage in rats. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 28, 132–145. [Google Scholar]
- Giovinazzo, G.; Grieco, F. Functional Properties of Grape and Wine Polyphenols. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antuono, I.; Garbetta, A.; Linsalata, V.; Minervini, F.; Cardinali, A. Polyphenols from artichoke heads (Cynara cardunculus (L.) subsp. scolymus Hayek): In Vitro bio-accessibility, intestinal uptake and bioavailability. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C. Extraction, identification, fractionation and isolation of phenolic compounds in plants with hepatoprotective effects. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1068–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mateus, V.; Estarreja, J.; Silva, I.; Gonçalves, F.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Pinto, R. Effect of Aqueous Extract of Phenolic Compounds Obtained from Red Wine in Experimental Model of Colitis in Mice. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 2745-2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44060188
Mateus V, Estarreja J, Silva I, Gonçalves F, Teixeira-Lemos E, Pinto R. Effect of Aqueous Extract of Phenolic Compounds Obtained from Red Wine in Experimental Model of Colitis in Mice. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(6):2745-2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44060188
Chicago/Turabian StyleMateus, Vanessa, João Estarreja, Inês Silva, Fernando Gonçalves, Edite Teixeira-Lemos, and Rui Pinto. 2022. "Effect of Aqueous Extract of Phenolic Compounds Obtained from Red Wine in Experimental Model of Colitis in Mice" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 6: 2745-2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44060188
APA StyleMateus, V., Estarreja, J., Silva, I., Gonçalves, F., Teixeira-Lemos, E., & Pinto, R. (2022). Effect of Aqueous Extract of Phenolic Compounds Obtained from Red Wine in Experimental Model of Colitis in Mice. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(6), 2745-2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44060188






