The Role of RASSF1C in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
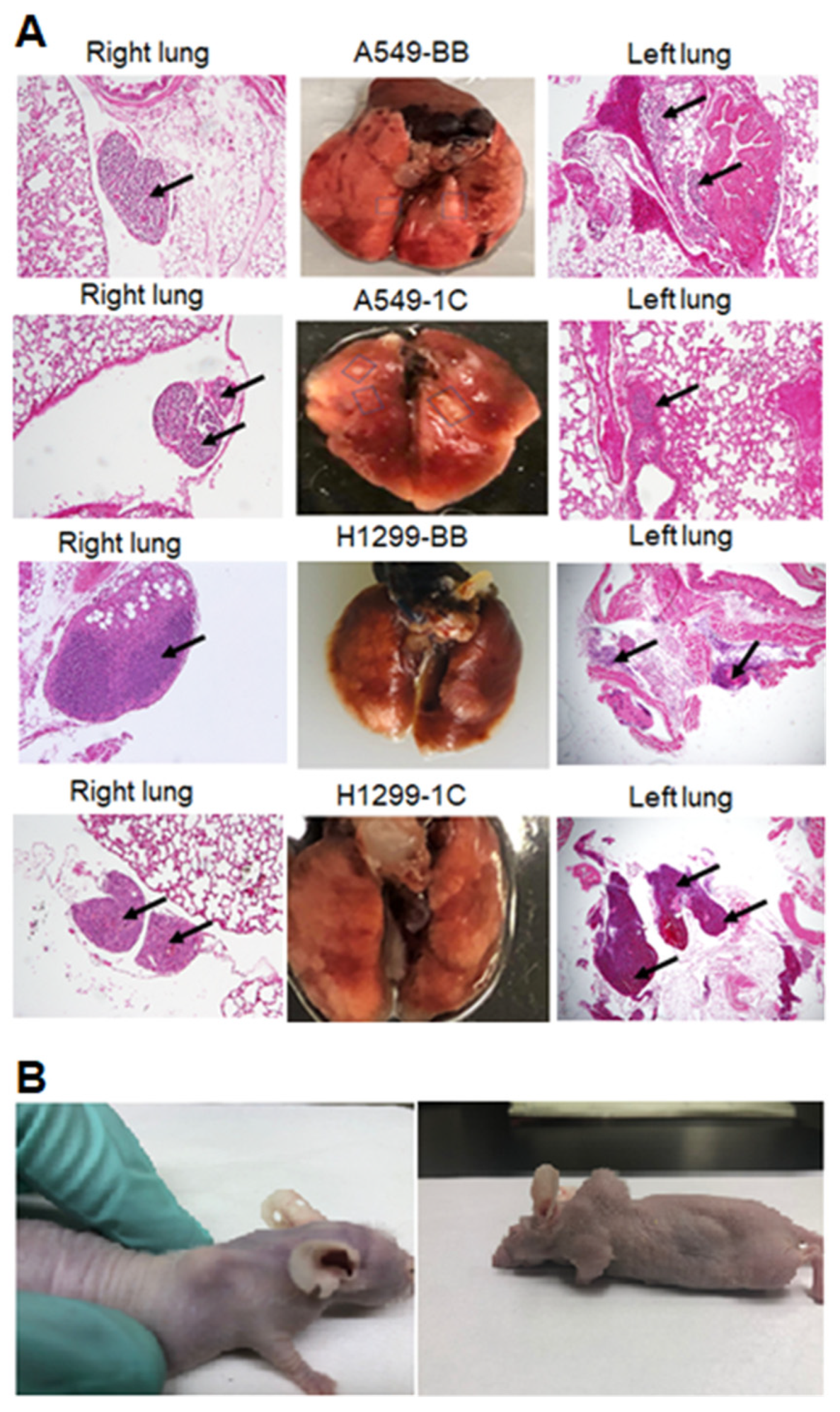
2.2. Lung Metastasis Model
2.3. Subcutaneous Animal Model
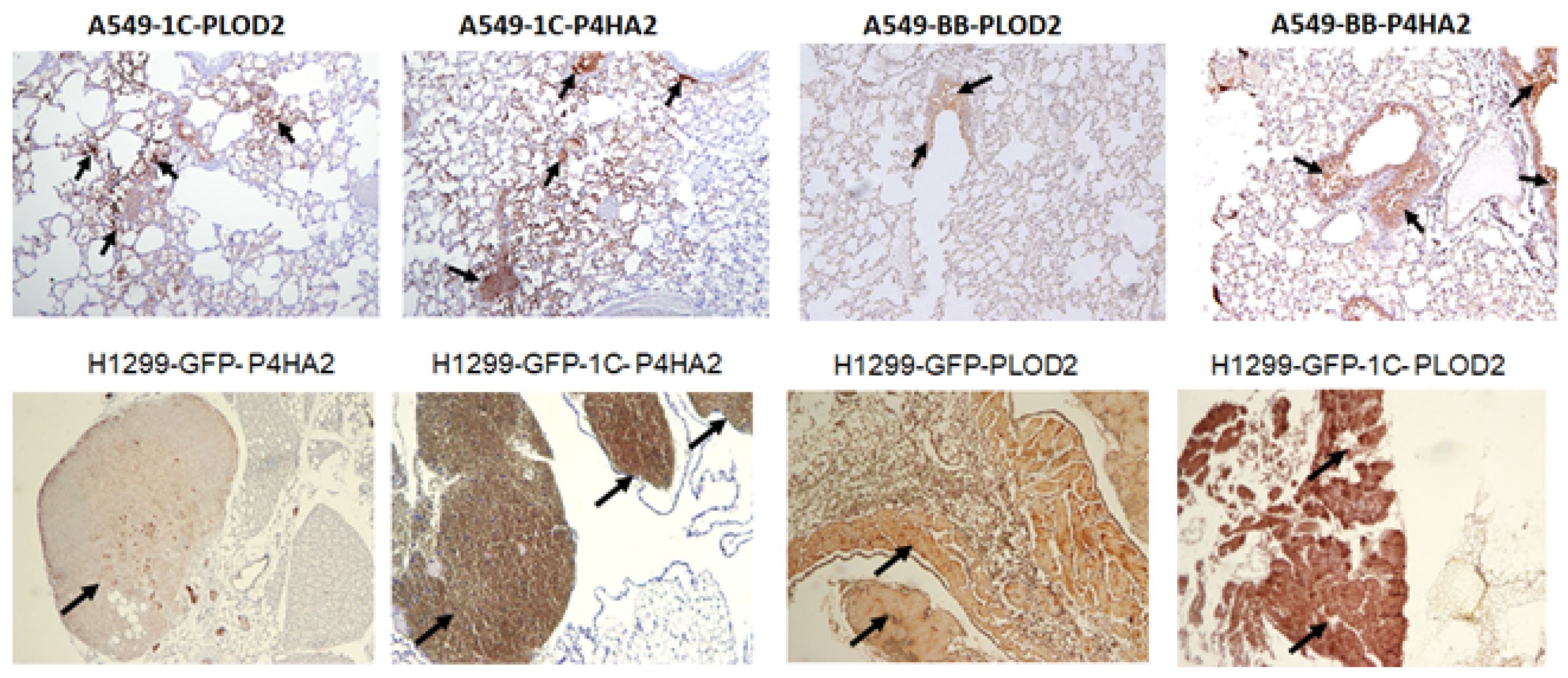
2.4. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. RT-PCR Analysis
2.6. Cell Migration Assay
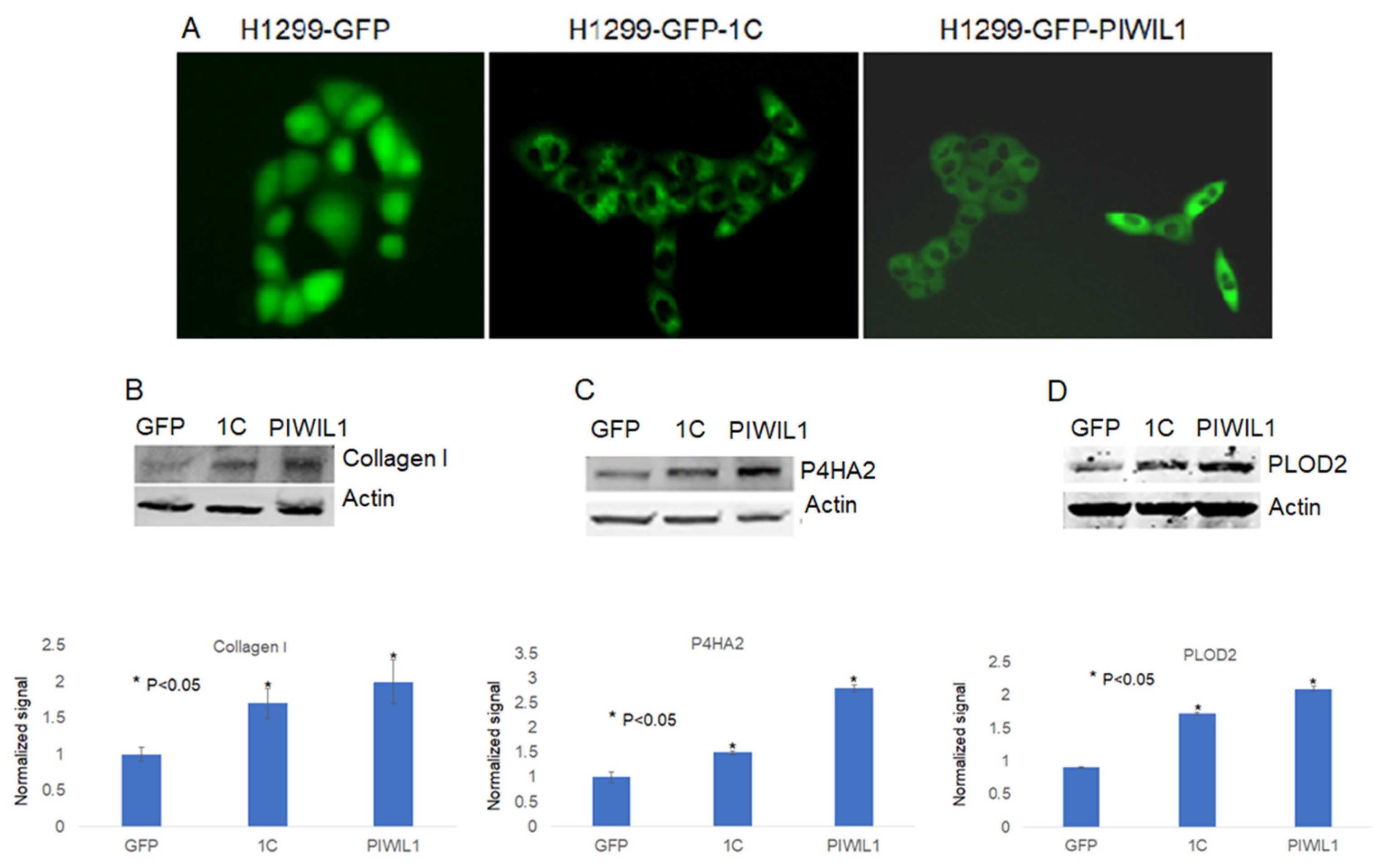
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
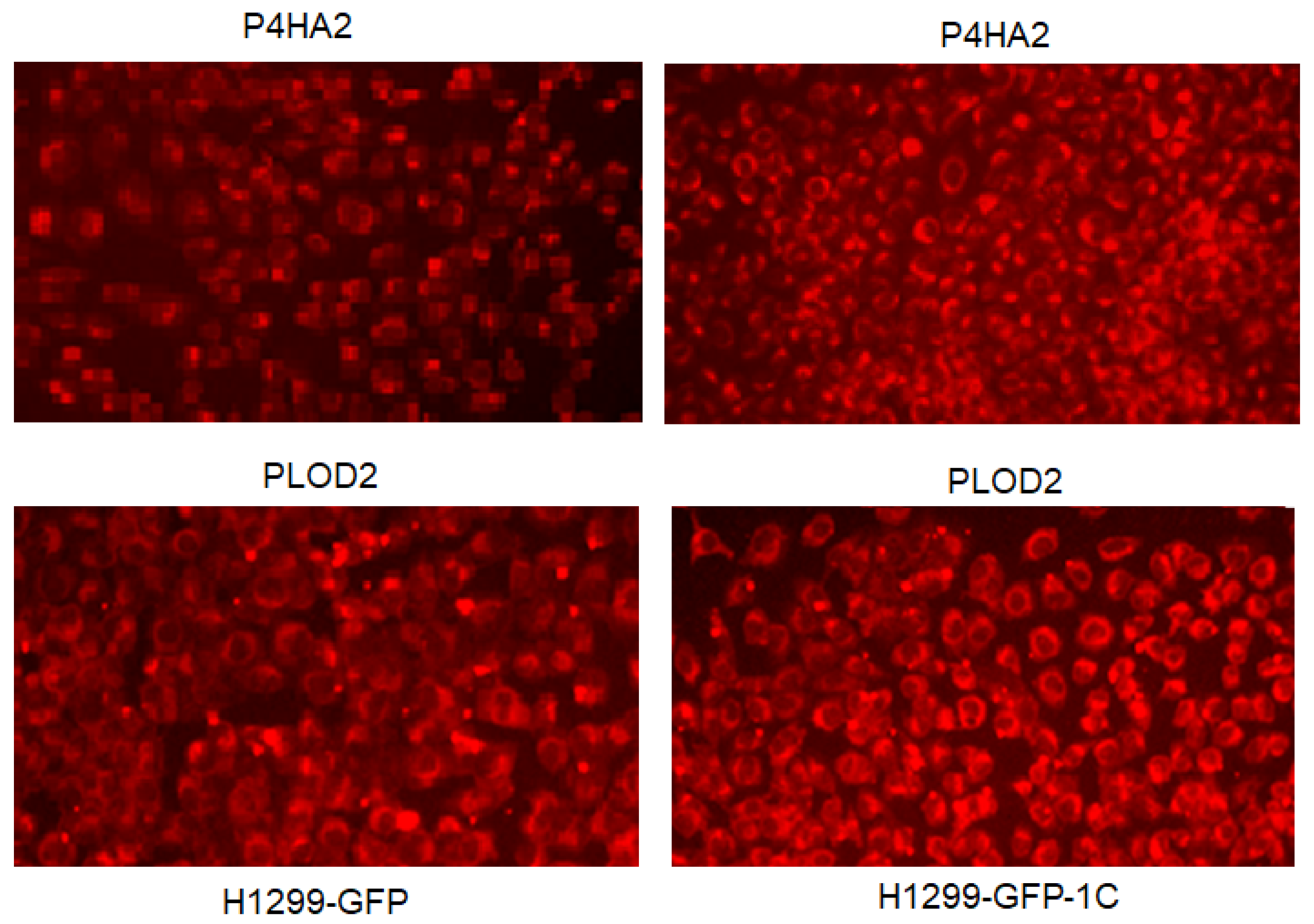
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
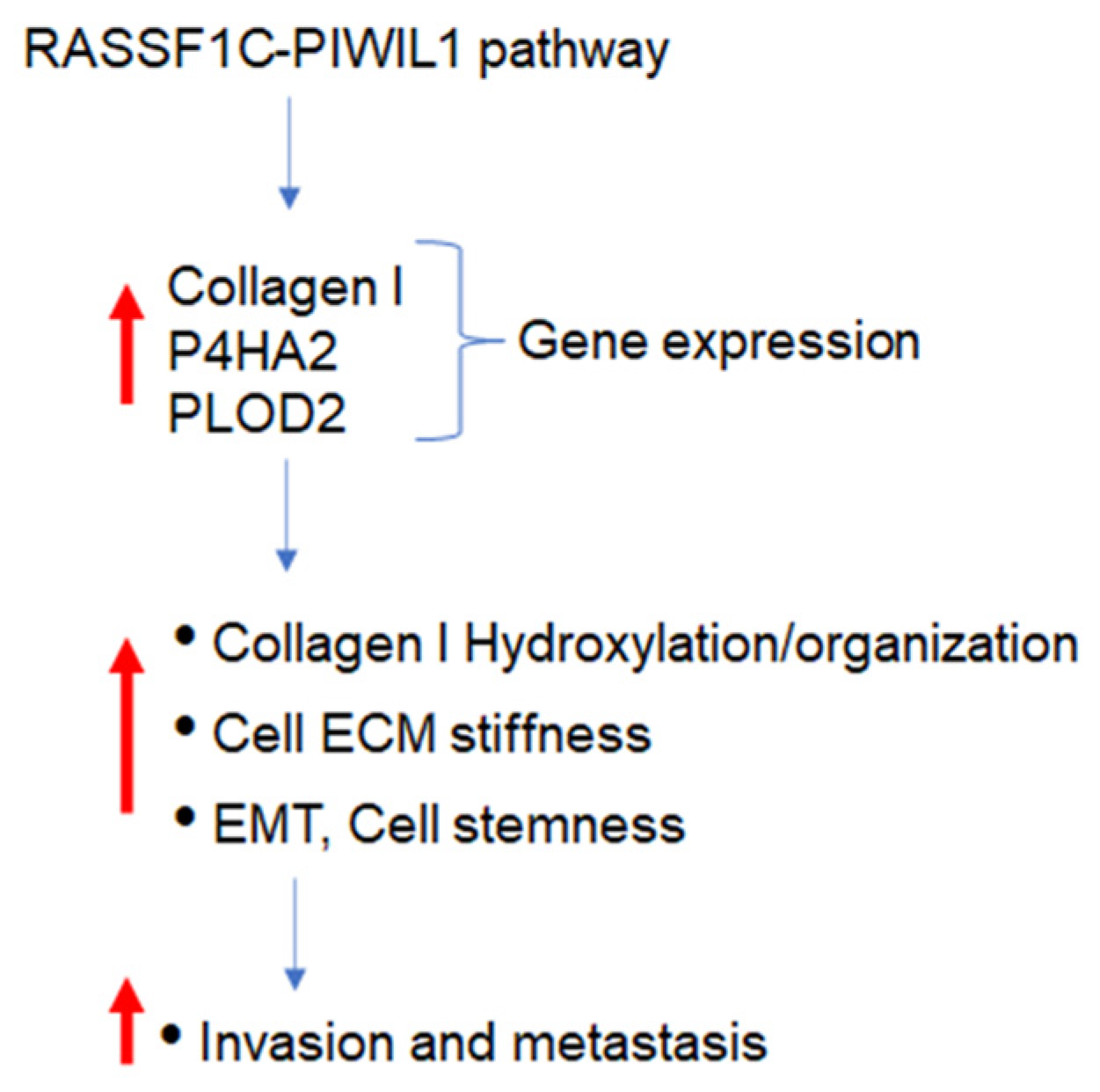
3.1. RASSF1C Overexpression Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Metastasis In Vivo
3.2. RASSF1C Overexpression Up-Regulates P4HA2 and PLOD2 Gene Expression In Vitro
3.3. RASSF1C Overexpression Up-Regulates P4HA2 and PLOD2 Gene Expression In Vivo
3.4. PIWIL1 Promotes piRNAs Attenuate Lung Cancer Cell Invasion/Migration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Miller, K.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, A.R.; Miake-Lye, I.M.; Beroes, J.M.; Shekelle, P.G. Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systemic Review of Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness; VA-ESP project #05-226. Bookshelf ID: NBK153078; National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Herbst, R.S.; Heymach, J.V.; Lipman, S.M. Molecular Origins of Cancer: Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dammann, R.; Takahashi, T.; Pfeifer, G.P. The CpG island of the novel tumor suppressor gene RASSF1A is intensely methylated in primary small cell lung carcinomas. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3563–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dammann, R.; Li, C.; Yoon, J.H.; Chin, P.L.; Bates, S.; Pfeifer, G.P. Epigenetic inactivation of a RAS association domain family protein from the lung tumor suppressor locus 3p21.3. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbee, D.G.; Forgacs, E.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Shivakumar, L.; Fong, K.; Gao, B.; Randle, D.; Kondo, M.; Virmani, A.; Bader, S.; et al. Epigenetic Inactivation of RASSF1A in Lung and Breast Cancers and Malignant Phenotype Suppression. Gynecol. Oncol. 2001, 93, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agathanggelou, A.; Honorio, S.; Macartney, D.P.; Martinez, A.; Dallol, A.; Rader, J.; Fullwood, P.; Chauhan, A.; Walker, R.; A Shaw, J.; et al. Methylation associated inactivation of RASSF1A from region 3p21.3 in lung, breast and ovarian tumours. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agathanggelou, A.; Bièche, I.; Ahmed-Choudhury, J.; Nicke, B.; Dammann, R.; Baksh, S.; Gao, B.; Minna, J.D.; Downward, J.; Maher, E.R.; et al. Identification of novel gene expression targets for the Ras association domain family 1 (RASSF1A) tumor suppressor gene in non-small cell lung cancer and neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, M.; El-Kalla, M.; Baksh, S. RASSF1 Polymorphisms in Cancer. Mol. Biol. Int. 2012, 2012, 365213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaar, Y.G.; Minera, M.G.; Hatran, L.K.; Strong, D.D.; Mohan, S.; Reeves, M.E. Ras association domain family 1C protein stimulates human lung cancer cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L1185–L1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, M.E.; Baldwin, M.L.; Aragon, R.; Baldwin, S.; Chen, S.-T.; Li, X.; Mohan, S.; Amaar, Y.G. RASSF1C modulates the expression of a stem cell renewal gene, PIWIL1. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, M.E.; Firek, M.; Chen, S.T.; Amaar, Y. The RASSF1 gene and the opposing effects of the RASSF1A and RASSF1C isoforms on cell proliferation and apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Int. 2013, 2013, 145096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, M.E.; Aragon, R.J.; Alfakhouri, M.; Chen, S.-T.; Lowen, N.; Mohan, S.; Amaar, Y.G. Ras-Association Domain Family 1C Protein Enhances Breast Tumor Growth in Vivo. Cancer Growth Metastasis 2012, 5, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, M.E.; Firek, M.; Chen, S.-T.; Amaar, Y.G. Evidence that RASSF1C Stimulation of Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation Depends on IGFBP-5 and PIWIL1 Expression Levels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, M.E.; Baldwin, S.W.; Baldwin, M.L.; Chen, S.-T.; Moretz, J.M.; Aragon, R.J.; Li, X.; Strong, D.D.; Mohan, S.; Amaar, Y.G. Ras-association domain family 1C protein promotes breast cancer cell migration and attenuates apoptosis. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reeves, M.E.; Firek, M.; Jliedi, A.; Amaar, Y.G. Identification and characterization of RASSF1C piRNA target genes in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34268–34282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaar, Y.G.; Reeves, M.E. RASSF1C regulates miR-33a and EMT marker gene expression in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amaar, Y.G.; Reeves, M.E. The impact of the RASSF1C and PIWIL1 on DNA methylation: The identification of GMIP as a tumor suppressor. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 4082–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.M. Orthotopic Mouse Models of Tumor Metastasis Expressing Fluorescent Reporters Produce Imageable Circulating Tumor Cells. Cancer Microenviron. 2014, 7, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altorki, N.K.; Markowitz, G.J.; Gao, D.; Port, J.L.; Saxena, A.; Stiles, B.; McGraw, T.; Mittal, V. The lung microenvironment: An important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.; Wei, T.; Meng, H.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J. Role of the dynamic tumor microenvironment in controversies regarding immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR mutations. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, A.; Tousif, S.; Wang, Y.; Hough, K.; Khan, S.; Strenkowski, J.; Chacko, B.K.; Darley-Usmar, V.M.; Deshane, J.S. Lung Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization. Cells 2020, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.L.; Pernemalm, M.; Crosbie, P.A.; Whetton, A.D. The role of the tumor-microenvironment in lung cancer-metastasis and its relationship to potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankova, D.; Jiang, Y.; Chatzifrangkeskou, M.; Vendrell, I.; Buzzelli, J.; Ryan, A.; Brown, C.; O’Neill, E. RASSF1A controls tissue stiffness and cancer stem-like cells in lung adenocarcinoma. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆CT method. Methods 2021, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Huang, Y.; Wei, X.; Yu, X.; Feng, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, M.; Shi, X.; et al. PLOD2 regulated by transcription factor FOXA1 promotes metastasis in NSCLC. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gjaltema, R.A.; de Rond, S.; Rots, M.G.; Bank, R.A. Procollagen Lysyl Hydroxylase 2 Expression Is Regulated by an Alternative Downstream Transforming Growth Factor β-1 Activation Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28465–28476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilkes, D.M.; Bajpai, S.; Chaturvedi, P.; Wirtz, D.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible Factor 1 (HIF-1) Promotes Extracellular Matrix Remodeling under Hypoxic Conditions by Inducing P4HA1, P4HA2, and PLOD2 Expression in Fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10819–10829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Aniello, C.; Cermola, F.; Palamidessi, A.; Wanderlingh, L.G.; Gagliardi, M.; Migliaccio, A.; Varrone, F.; Casalino, L.; Matarazzo, M.R.; De Cesare, D.; et al. Collagen Prolyl Hydroxylation–Dependent Metabolic Perturbation Governs Epigenetic Remodeling and Mesenchymal Transition in Pluripotent and Cancer Cells. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 3235–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Konno, Y.; Ihira, K.; Xu, D.; Kobayashi, N.; Yue, J.; Watari, H. Critical Roles of PIWIL1 in Human Tumors: Expression, Functions, Mechanisms, and Potential Clinical Implications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 656993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Gene | Fold Change T47D-1C H1299-1C | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| P4HA2 | 3.7 2 | <0.01 |
| PLOD2 | 1.6 1.3 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaar, Y.G.; Reeves, M.E. The Role of RASSF1C in the Tumor Microenvironment. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 1113-1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020074
Amaar YG, Reeves ME. The Role of RASSF1C in the Tumor Microenvironment. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(2):1113-1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020074
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaar, Yousef G., and Mark E. Reeves. 2023. "The Role of RASSF1C in the Tumor Microenvironment" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 2: 1113-1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020074
APA StyleAmaar, Y. G., & Reeves, M. E. (2023). The Role of RASSF1C in the Tumor Microenvironment. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(2), 1113-1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020074





