Expression of G2019S LRRK2 in Rat Primary Astrocytes Mediates Neurotoxicity and Alters the Dopamine Synthesis Pathway in N27 Cells via Astrocytic Proinflammatory Cytokines and Neurotrophic Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Rat Primary Astrocyte Isolation, Culture, and Transfection
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Isolation of mRNA and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
2.5. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.6. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. N27 Cell Culture and Treatment with the CM of rASTROs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
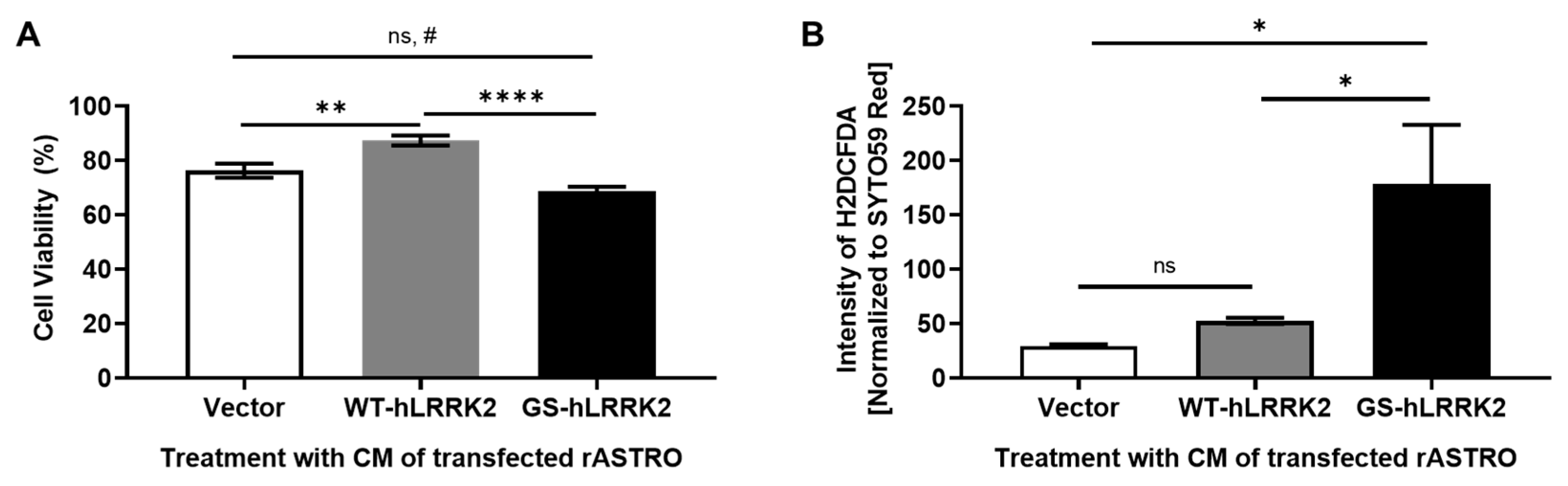
3.1. G2019S LRRK2 Expression-derived Cytotoxicity in rASTROs
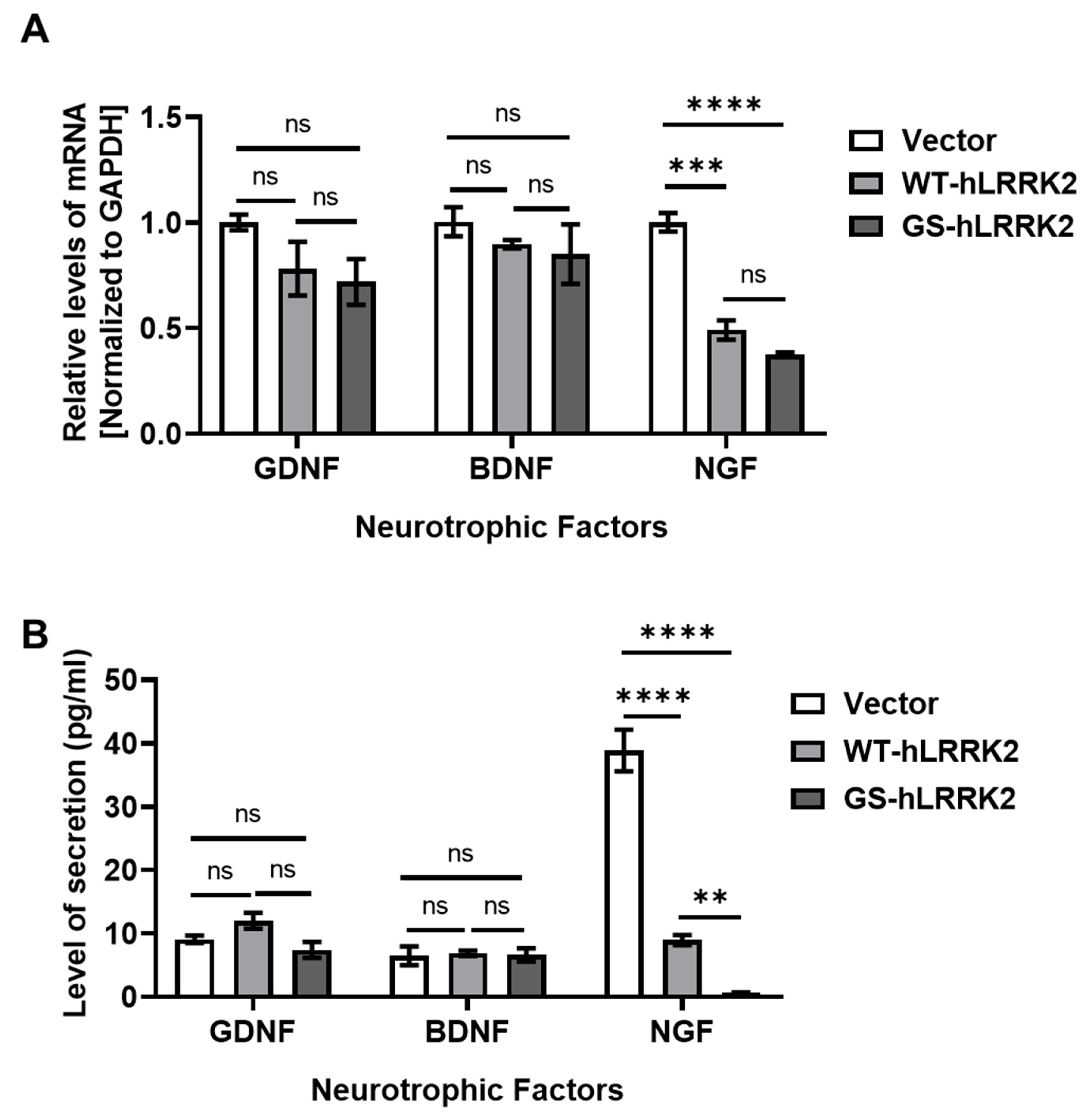
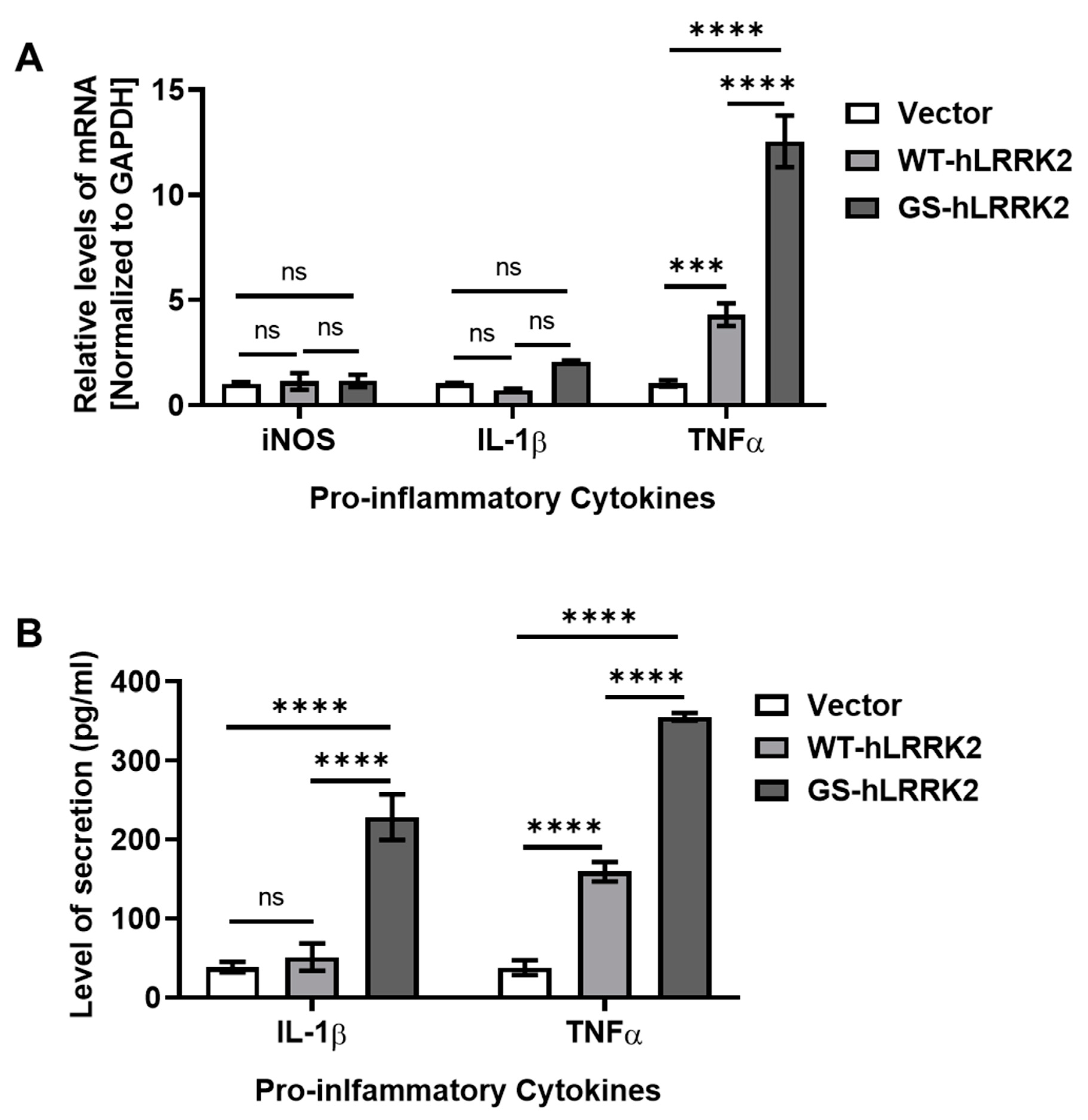
3.2. Alterations in Neurotrophic Factors and Proinflammatory Cytokines due to G2019S LRRK2 Expression in rASTROs
3.3. Astrogliosis in G2019S LRRK2-Expressing rASTROs
3.4. G2019S LRRK2-Expressing rASTROs Promote Neurotoxicity and the Dopamine Synthesis Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawal, O.; Ulloa Severino, F.P.; Eroglu, C. The role of astrocyte structural plasticity in regulating neural circuit function and behavior. Glia 2022, 70, 1467–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heithoff, B.P.; George, K.K.; Phares, A.N.; Zuidhoek, I.A.; Munoz-Ballester, C.; Robel, S. Astrocytes are necessary for blood-brain barrier maintenance in the adult mouse brain. Glia 2021, 69, 436–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Catalan, N.A.; Doe, C.Q.; Ackerman, S.D. The role of astrocyte-mediated plasticity in neural circuit development and function. Neural. Dev. 2021, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, E.; Lengacher, S.; Dias, S.; Magistretti, P.J.; Finsterwald, C. Astrocytes as Key Regulators of Brain Energy Metabolism: New Therapeutic Perspectives. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 825816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Swanson, R.A. Astrocytes and Brain Injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requie, L.M.; Gómez-Gonzalo, M.; Speggiorin, M.; Managò, F.; Melone, M.; Congiu, M.; Chiavegato, A.; Lia, A.; Zonta, M.; Losi, G.; et al. Astrocytes mediate long-lasting synaptic regulation of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.; Gharagozloo, M.; Simard, C.; Gris, D. Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and Release. Cells 2019, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekanaviciute, E.; Buckwalter, M.S. Astrocytes: Integrative Regulators of Neuroinflammation in Stroke and Other Neurological Diseases. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnerbauer, M.; Rothhammer, V. Protective Functions of Reactive Astrocytes Following Central Nervous System Insult. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 573256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.R.; Lee, B.D. Pathological Functions of LRRK2 in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Gonzalez, P.; Mato, S.; Chara, J.C.; Verkhratsky, A.; Matute, C.; Cavaliere, F. Astrocytic atrophy as a pathological feature of Parkinson’s disease with LRRK2 mutation. npj Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.H.; Nam, D.; Seo, M.K.; Park, S.W.; Seol, W.; Son, I. LRRK2 Kinase Inhibitor Rejuvenates Oxidative Stress-Induced Cellular Senescence in Neuronal Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 9969842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Kim, B.; Byun, J.-W.; Baik, S.H.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Mook-Jung, I.; Song, W.K.; Shin, J.-H.; Seo, H.; et al. LRRK2 G2019S mutation attenuates microglial motility by inhibiting focal adhesion kinase. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, I.; Bubacco, L.; Greggio, E. LRRK2 and neuroinflammation: Partners in crime in Parkinson’s disease? J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, B.; Caridade-Silva, R.; Soares-Guedes, C.; Martins-Macedo, J.; Gomes, E.D.; Monteiro, S.; Teixeira, F.G. Neuroinflammation and Parkinson’s Disease-From Neurodegeneration to Therapeutic Opportunities. Cells 2022, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutti, V.; Carini, G.; Filippini, A.; Castrezzati, S.; Giugno, L.; Gennarelli, M.; Russo, I. LRRK2 Kinase Inhibition Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Cytotoxicity in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease-Related Neuroinflammation. Cells 2023, 12, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.H.; Lee, H.; Son, I.; Seol, W. G2019s LRRK2 promotes mitochondrial fission and increases TNFα-mediated neuroinflammation responses. Anim. Cells Syst. 2019, 23, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.H.; Kim, H.; Nam, D.; Heo, J.; Son, I. Nuclear α-Synuclein-Derived Cytotoxic Effect via Altered Ribosomal RNA Processing in Primary Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselet, E.; Callebert, J.; Parain, K.; Joubert, C.; Hunot, S.; Hartmann, A.; Jacque, C.; Perez-Diaz, F.; Cohen-Salmon, C.; Launay, J.M.; et al. Role of TNF-alpha receptors in mice intoxicated with the parkinsonian toxin MPTP. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 177, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spampinato, S.F.; Bortolotto, V.; Canonico, P.L.; Sortino, M.A.; Grilli, M. Astrocyte-Derived Paracrine Signals: Relevance for Neurogenic Niche Regulation and Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, F.; Quintana, F.J. The Role of Astrocytes in CNS Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipp, F.; Bittner, S.; Schafer, D.P. Cytokines as emerging regulators of central nervous system synapses. Immunity 2023, 56, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becher, B.; Spath, S.; Goverman, J. Cytokine networks in neuroinflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizang-Ginsberg, E.; Ziff, E.B. Nerve growth factor regulates tyrosine hydroxylase gene transcription through a nucleoprotein complex that contains c-Fos. Genes Dev. 1990, 4, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.K.; Shukla, S.; Seth, K.; Agrawal, A.K. Nerve growth factor increases survival of dopaminergic graft, rescue nigral dopaminergic neurons and restores functional deficits in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 398, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.H.; Nam, D.; Seo, M.; Park, S.W.; Seol, W.; Son, I. LRRK2 Inhibition Mitigates the Neuroinflammation Caused by TLR2-Specific α-Synuclein and Alleviates Neuroinflammation-Derived Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss. Cells 2022, 11, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, J.-h.; Kim, H.; Park, S.M.; Joe, E.-h.; Jou, I. Parkinson’s disease-associated LRRK2-G2019S mutant acts through regulation of SERCA activity to control ER stress in astrocytes. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, S.T.; Vecchio, L.M.; Bergeron, Y.; Hossain, M.M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Bermejo, M.K.; Kile, B.; Sotnikova, T.D.; Siesser, W.B.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; et al. Increased expression of the dopamine transporter leads to loss of dopamine neurons, oxidative stress and l-DOPA reversible motor deficits. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 74, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Chen, S.; Le, W.D. The role of Nurr1 in the development of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 77, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felger, J.C.; Treadway, M.T. Inflammation Effects on Motivation and Motor Activity: Role of Dopamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 216–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, S.B.; Zigmond, M.J.; Hastings, T.G. Modification of Dopamine Transporter Function: Effect of Reactive Oxygen Species and Dopamine. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.-J.; Kim, D.-K.; Kim, C.; Mante, M.; Adame, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Ulusoy, A.; Klinkenberg, M.; Jeong, G.R.; Bae, J.R.; et al. LRRK2 kinase regulates α-synuclein propagation via RAB35 phosphorylation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desplats, P.; Lee, H.-J.; Bae, E.-J.; Patrick, C.; Rockenstein, E.; Crews, L.; Spencer, B.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.-J. Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of α-synuclein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13010–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Ho, D.-H.; Suk, J.-E.; You, S.; Michael, S.; Kang, J.; Joong Lee, S.; Masliah, E.; Hwang, D.; Lee, H.-J.; et al. Neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Suk, J.-E.; Patrick, C.; Bae, E.-J.; Cho, J.-H.; Rho, S.; Hwang, D.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.-J. Direct Transfer of α-Synuclein from Neuron to Astroglia Causes Inflammatory Responses in Synucleinopathies *. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9262–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.-J.; Zhang, J.-B.; Liu, J.-Y.; Zhao, F.-L.; Yao, X.-Y.; Tang, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.-R.; Cheng, X.-Y.; Hu, L.-F.; Wang, F.; et al. LRRK2 G2019S promotes astrocytic inflammation induced by oligomeric α-synuclein through NF-κB pathway. iScience 2023, 26, 108130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Human LRRK2 | CTTCTGAGATGAGTTTTTGTTCCTCGAC | |
| Myc taq | GAGTCATGATGACAGCACAGC | |
| BDNF | Forward | GTTCGGCATTGCGAGTTCCAG |
| Reverse | TTGAGCACGTGATCGAAGAGC | |
| GDNF | Forward | GACTCCAATATGCCCGAAGA |
| Reverse | TAGCCCAAACCCAAGTCAGT | |
| NGF | Forward | ACCTCTTCGGACACTCTGGA |
| Reverse | GTCCGTGGCTGTGGTCTTAT | |
| TNFα | Forward | ACTGAACTTCGGGGTGATTG |
| Reverse | GCTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGAC | |
| TGFβ | Forward | GCAACAACGCAATCTATGAC |
| Reverse | CCTGTATTCCGTCTCCTT | |
| IL-1β | Forward | CCAGGATGAGGACCCAAGCA |
| Reverse | TCCCGACCATTGCTGTTTCC | |
| iNOS (NOS2) | Forward | CACCTTGGAGTTCACCCAGT |
| Reverse | ACCACTCGTACTTGGGATGC | |
| TH | Forward | TTCCCCATGTTCAACGGACC |
| Reverse | GCGAGCACAGTAATCACCTTC | |
| DAT | Forward | GGAAGCTGGTCAGCCCCTGCT |
| Reverse | GAATTGGCGCACCTCCCCTCTG | |
| NURR1 | Forward | CTACGCTTAGCATACAGGTC |
| Reverse | TTCCTTGAGCCCGTGTCT | |
| GAPDH | Forward | CAAGTTCAACGGCACAGTCAAG |
| Reverse | ACATACTCAGCACCAGCATCAC | |
| Antibody | Company | Catalog Number | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| PARP (poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase) | Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA | 9542S | 1/1000 |
| NGF | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA | Sc-518166 | 1/200 |
| TNFα | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-52746 | 1/200 |
| β-actin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-47778 | 1/3000 |
| Vimentin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-6260 | 1/5000 |
| GFAP (gial fibrillary acidic protein) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-33673 | 1/5000 |
| TH (tyrosine hydroxylase) | Cell Signaling Technology | 2792S | 1/1000 |
| DAT (dopamine transporter) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-14002 | 1/1000 |
| NURR1/NR4A2 (nuclear receptor-related 1/nuclear receptor 4A2) | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA | 10975-2-ap | 1/1000 |
| GAPDH (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-32233 | 1/5000 |
| Anti-LRRK2/Dardarin, NeuroMab clone N241A/34 Pure IgG | UC Davis/NIH NeuroMab Facility | 75-253 | 1/100 |
| Peroxidase-conjugated AffiniPure goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) | Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories Inc., West Grove, PA, USA | 115-035-003 | 1/5000 |
| Peroxidase-conjugated AffiniPure goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) | Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories Inc. | 111-035-144 | 1/5000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, D.H.; Kim, H.; Nam, D.; Seo, M.K.; Park, S.W.; Son, I. Expression of G2019S LRRK2 in Rat Primary Astrocytes Mediates Neurotoxicity and Alters the Dopamine Synthesis Pathway in N27 Cells via Astrocytic Proinflammatory Cytokines and Neurotrophic Factors. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4324-4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050263
Ho DH, Kim H, Nam D, Seo MK, Park SW, Son I. Expression of G2019S LRRK2 in Rat Primary Astrocytes Mediates Neurotoxicity and Alters the Dopamine Synthesis Pathway in N27 Cells via Astrocytic Proinflammatory Cytokines and Neurotrophic Factors. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(5):4324-4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050263
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Dong Hwan, Hyejung Kim, Daleum Nam, Mi Kyoung Seo, Sung Woo Park, and Ilhong Son. 2024. "Expression of G2019S LRRK2 in Rat Primary Astrocytes Mediates Neurotoxicity and Alters the Dopamine Synthesis Pathway in N27 Cells via Astrocytic Proinflammatory Cytokines and Neurotrophic Factors" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 5: 4324-4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050263
APA StyleHo, D. H., Kim, H., Nam, D., Seo, M. K., Park, S. W., & Son, I. (2024). Expression of G2019S LRRK2 in Rat Primary Astrocytes Mediates Neurotoxicity and Alters the Dopamine Synthesis Pathway in N27 Cells via Astrocytic Proinflammatory Cytokines and Neurotrophic Factors. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(5), 4324-4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050263







