Application of the TaqMan ARMS-PCR Approach for Genotyping Drug-Induced Hearing Loss Using Dried Blood Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction and Preparation of the Real Sample
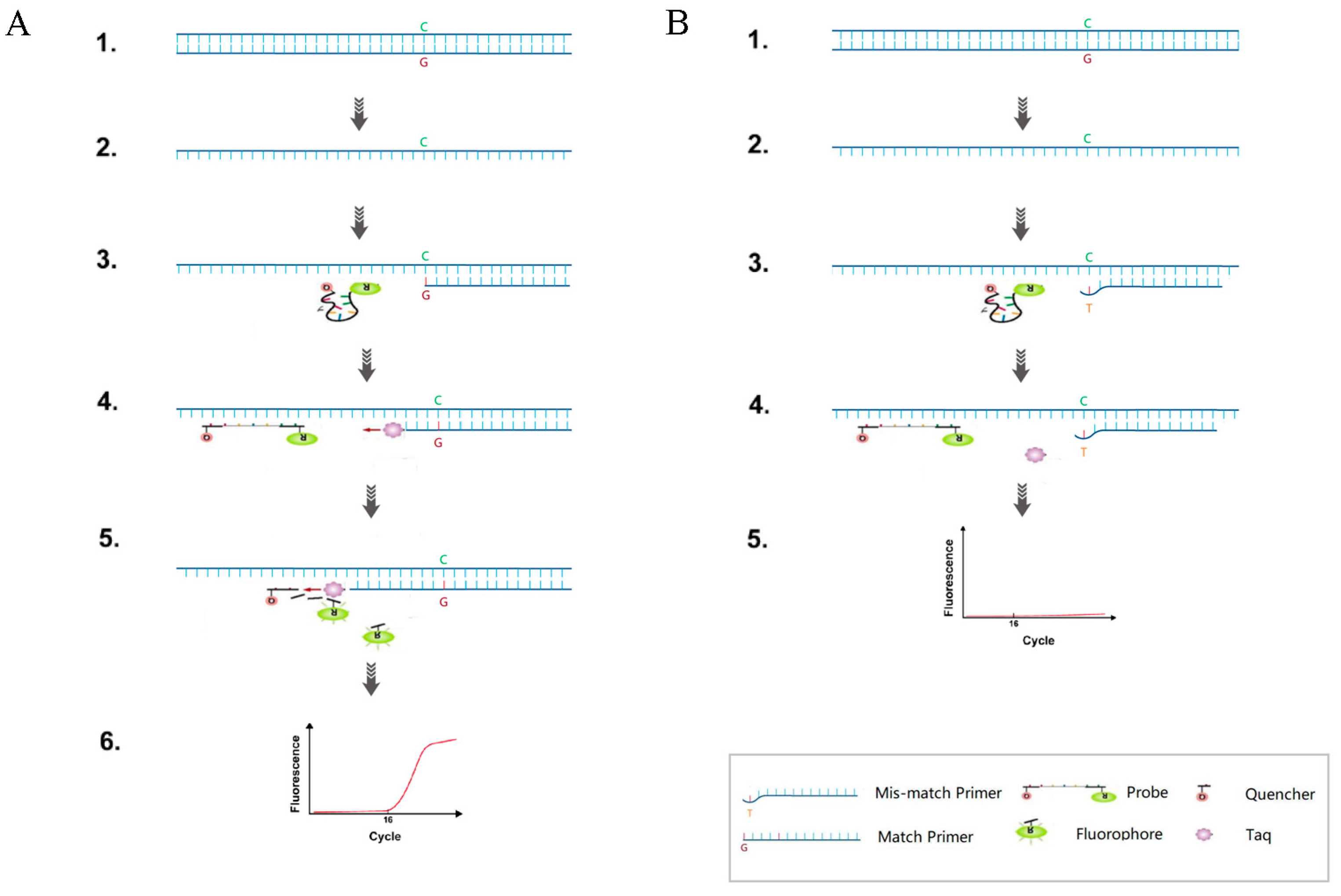
2.2. Primer and Probe Design and TaqMan-ARMS-PCR Detection
2.3. TaqMan-ARMS-PCR Reaction
2.4. Analysis of the Sensitivity, Specificity, and Repeatability
2.5. The Detection Limit of Plasmid and Real Samples
2.6. Genotyping Validation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
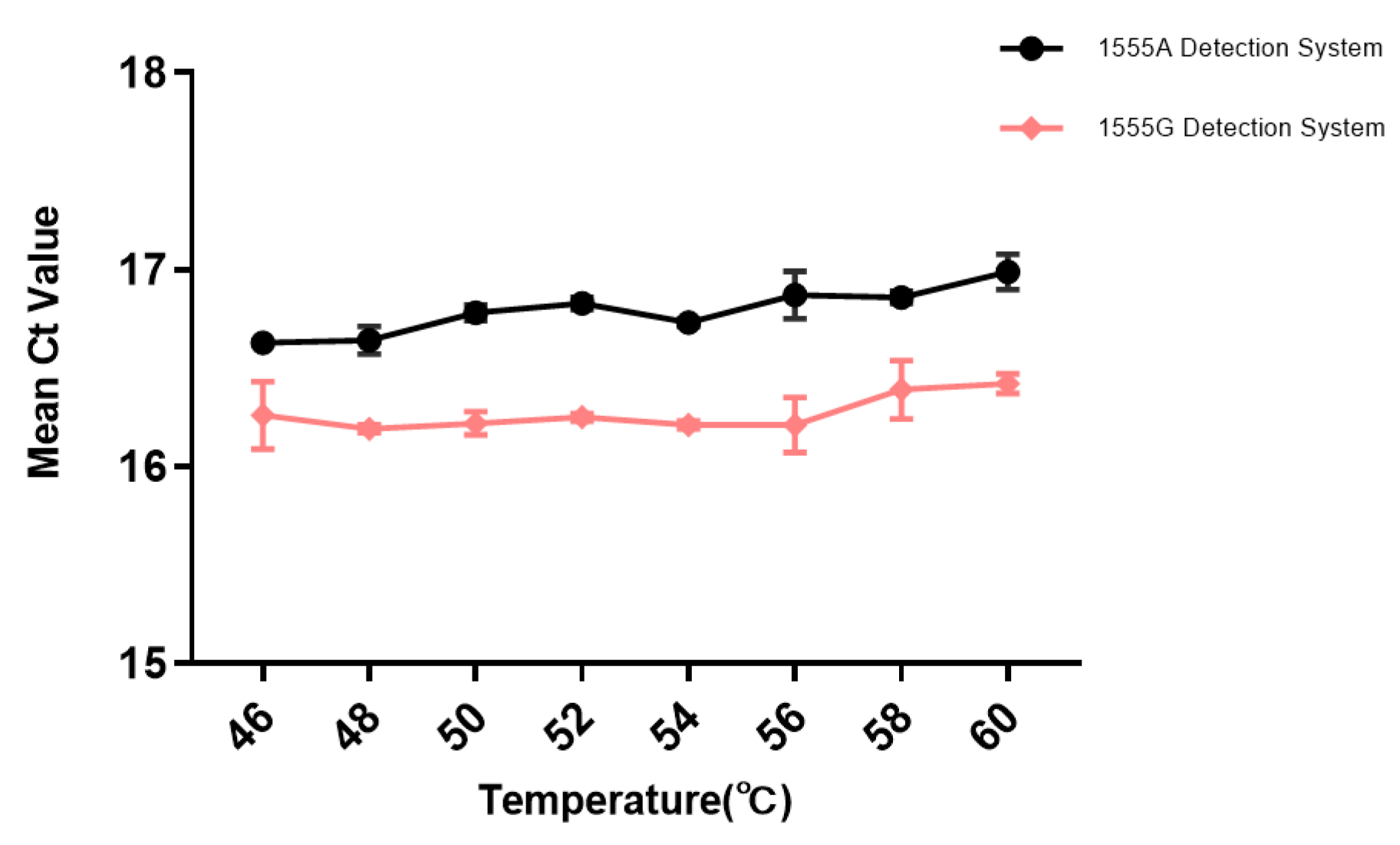
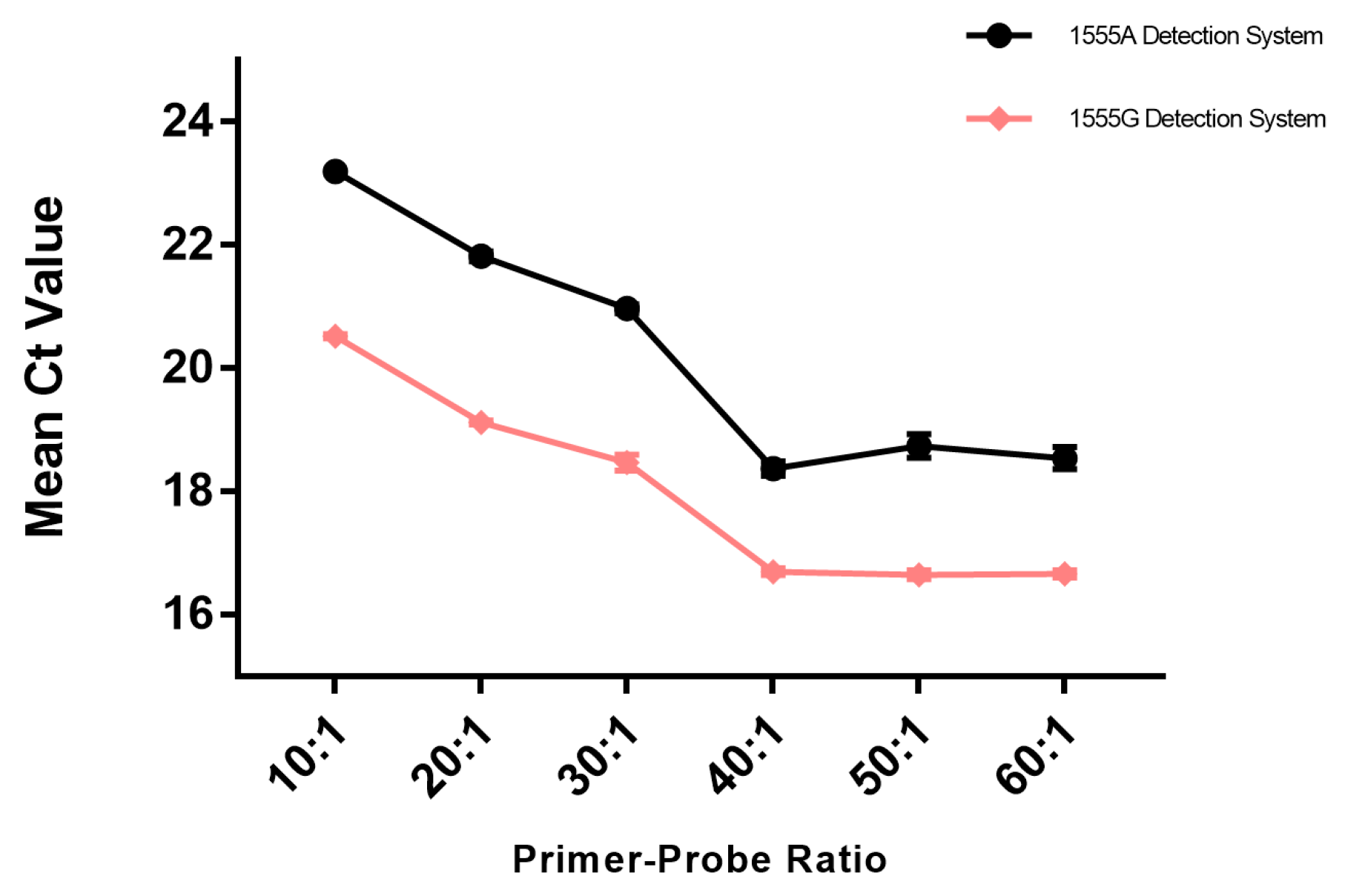
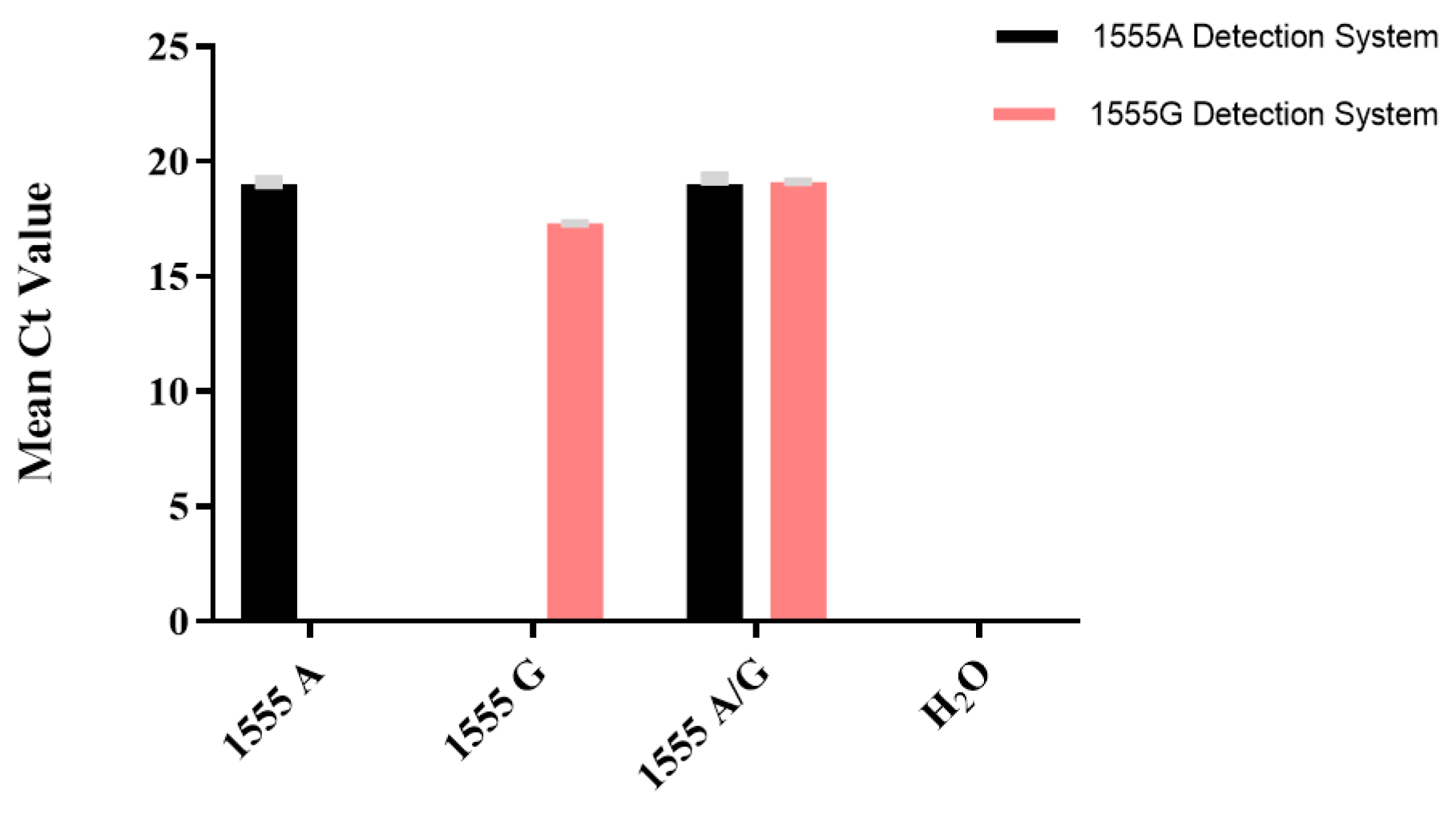
3.1. Optimization of TaqMan-ARMS-PCR
3.2. Performance of the Analysis
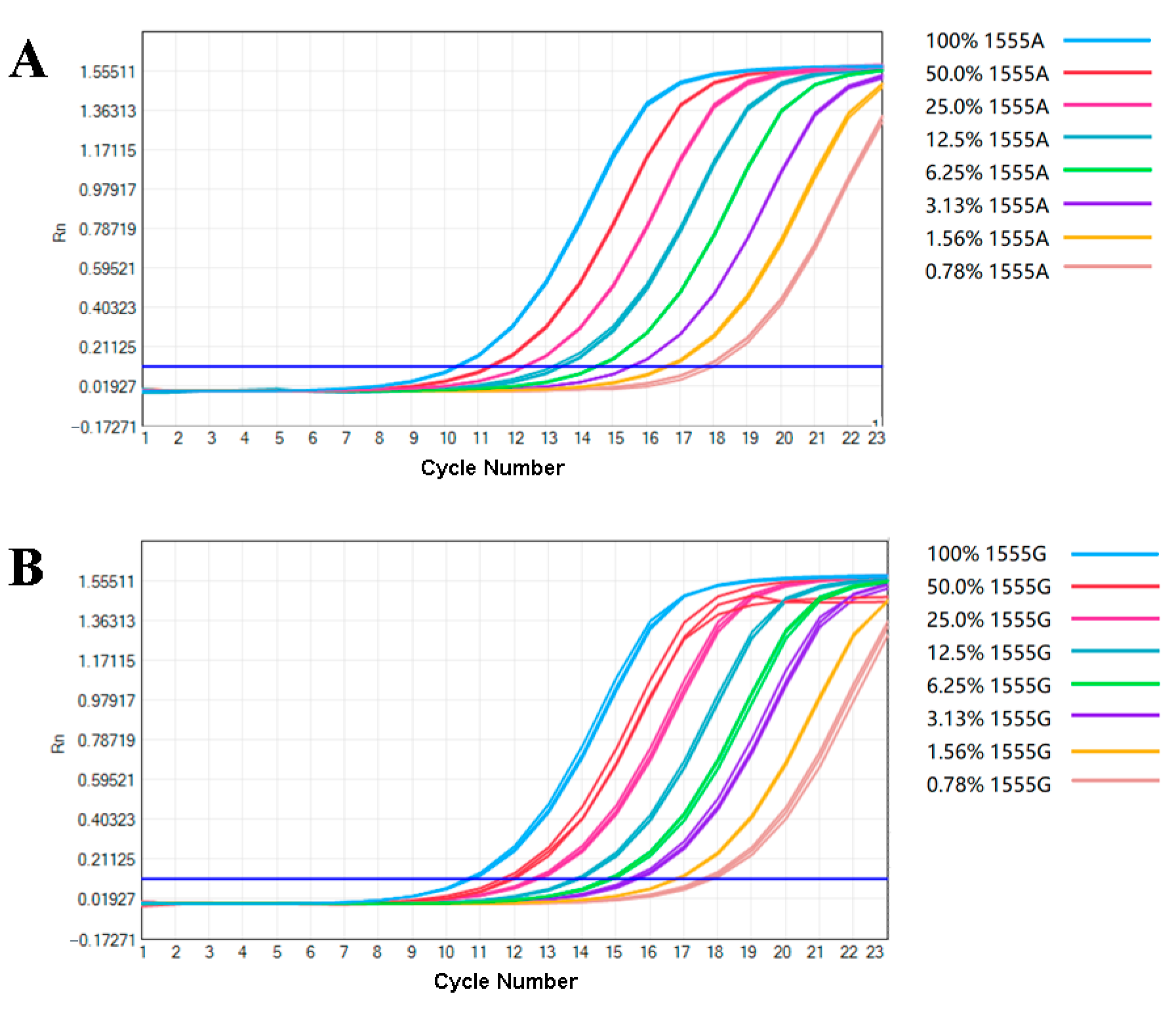
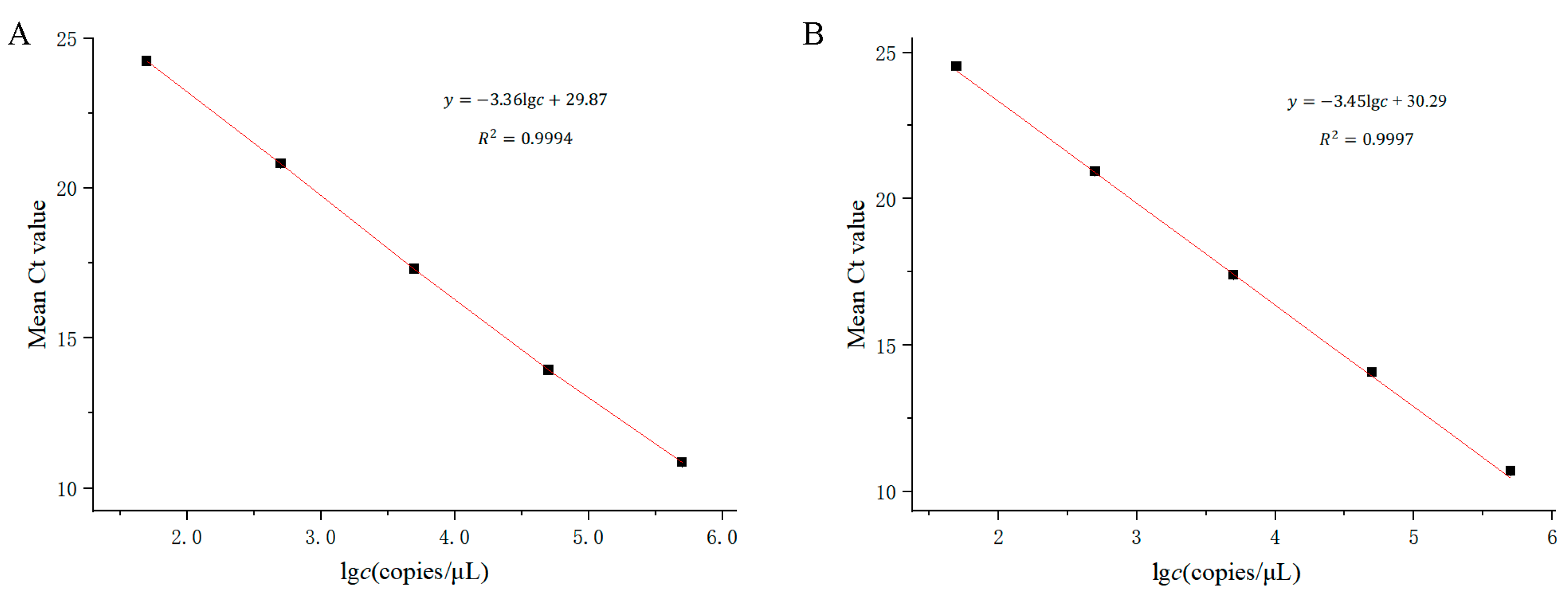
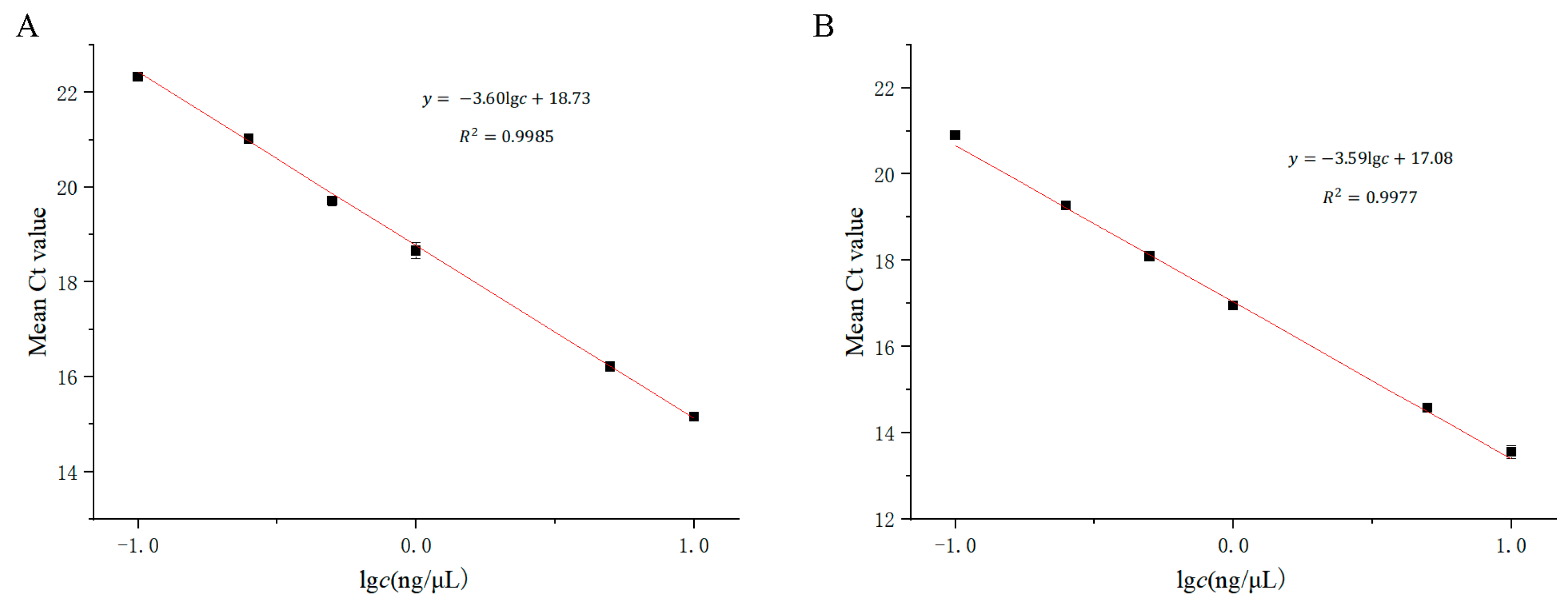
3.3. Performance of the Detection Limit of Plasmid and Real Samples
3.4. Performance of the TaqMan-ARMS-PCR Assay for Clinical Samples Compared with Sanger Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chadha, S.; Kamenov, K.; Cieza, A. The world report on hearing, 2021. Bull. World Health Organ. 2021, 99, 242A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Shim, Y.J.; Han, J.-H.; Song, J.-J.; Koo, J.-W.; Oh, S.H.; Lee, S.; Oh, D.-Y.; Choi, B.Y. The molecular etiology of deafness and auditory performance in the postlingually deafened cochlear implantees. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lei, W.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Huang, M. Detecting mitochondrial mutations associated with aminoglycoside ototoxicity by noninvasive prenatal testing. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zha, S.; Lu, N.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, W.; Zha, J. Carrier frequencies of hearing loss variants in newborns of China: A meta-analysis. J. Evid. Based Med. 2019, 12, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Kasai, S.; Goto, S.; Nishio, S.Y.; Sawada, K.; Tokuda, I.; Itoh, K.; Usami, S.I.; Matsubara, A. Prevalence of the mitochondrial 1555 A>G and 1494 C>T mutations in a community-dwelling population in Japan. Hum. Genome Var. 2020, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thy, M.; Timsit, J.F.; de Montmollin, E. Aminoglycosides for the Treatment of Severe Infection Due to Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagur, P.; Ghosh, M.; Patra, A. Chapter 5—Aminoglycoside antibiotics. In Medicinal Chemistry of Chemotherapeutic Agents; Acharya, P.C., Kurosu, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 135–155. [Google Scholar]
- Dillard, L.K.; Martinez, R.X.; Perez, L.L.; Fullerton, A.M.; Chadha, S.; McMahon, C.M. Prevalence of aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss in drug-resistant tuberculosis patients: A systematic review. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, H.O.; Al-Shuhaib, M.B.S. Exploring the Potential and Limitations of PCR-RFLP and PCR-SSCP for SNP Detection: A Review. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Jin, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhai, W.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Cheng, W.; Cai, B.; Qiang, R.; et al. Unexpected DMD Gene Mutations Detected by CMA and CNV-seq in amniotic Fluid and Aborted Fetus Samples. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, K.C.; Ozel, A.B.; Halvorsen, M.; Jacobi, P.M.; Golden, K.; Underwood, M.; Germain, M.; Tregouet, D.-A.; Reitsma, P.H.; Kearon, C.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies rare variants in STAB2 associated with venous thromboembolic disease. Blood 2020, 136, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimekalai, R.; Suresh, G.; Govinda Kurup, H.; Athiappan, S.; Kandalam, M. Role of NGS and SNP genotyping methods in sugarcane improvement programs. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Li, X.; Mai, L.; Wang, R.; Tang, S.; Hu, L. Visual single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) detection for ALDH2 genotyping based on multiplex ligation probe amplification (MLPA) and lateral flow assay. Microchem. J. 2023, 194, 109329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-Z.; Li, j.; Cui, J.-W.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Bian, W.-Y.; Kan, F.-G.; Zhao, F.; Chang, T.-M.; Zhao, G.-A.; et al. Analysis of Gene Mutations in Geographically Related Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Henan Province, China, Using the Reverse Dot Blot Hybridization. Int. J. Integr. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 01–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Gale, R.E.; Shakoori, A.R. Detection of FLT3/TKD and IDH1 Mutations in Pakistani Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients by Denaturing HPLC. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedon, M.N.; Jackson, L.; Harrison, J.W.; Ruth, K.S.; Tyrrell, J.; Hattersley, A.T.; Wright, C.F. Use of SNP chips to detect rare pathogenic variants: Retrospective, population based diagnostic evaluation. BMJ 2021, 372, n214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Gong, J.; Zhai, Z.; He, L.; Meng, F.; Xiao, D. A multisite SNP genotyping and macrolide susceptibility gene method for Mycoplasma pneumoniae based on MALDI-TOF MS. iScience 2021, 24, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klafke, G.M.; Miller, R.J.; Tidwell, J.P.; Thomas, D.B.; Sanchez, D.; Feria Arroyo, T.P.; Pérez de León, A.A. High-resolution melt (HRM) analysis for detection of SNPs associated with pyrethroid resistance in the southern cattle fever tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2019, 9, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najd-Hassan-Bonab, L.; Hedayati, M.; Shahzadeh Fazeli, S.A.; Daneshpour, M.S. An optimized method for PCR-based genotyping to detect human APOE polymorphisms. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.-H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, M.B.; Shin, Y.-W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-W. Molecular marker analysis of Cynanchum wilfordii and C. auriculatum using the simple ARMS-PCR method with mismatched primers. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 11, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.H.R.; Pashapour, S.; Farhadi, M.; Zabihi, A. Human papillomavirus infection and its relationship with common polymorphism of HLA gene by PCR method. Gene Rep. 2023, 31, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Xia, X.; Deng, R.; Gao, H.; Dong, Y. Sensitive Detection of a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism in Foodborne Pathogens Using CRISPR/Cas12a-Signaling ARMS-PCR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8451–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Qiu, L.; Sheng, A.-Z.; Wan, X.-Y.; Cheng, D.-Y.; Huang, J. Quantitative detection method of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei using TaqMan probe real-time PCR. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 151, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalchuk, S.N.; Arkhipova, A.L. Development of TaqMan PCR assay for genotyping SNP rs211250281 of the bovine agpat6 gene. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 3250–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cario, R.; Kura, A.; Suraci, S.; Magi, A.; Volta, A.; Marcucci, R.; Gori, A.M.; Pepe, G.; Giusti, B.; Sticchi, E. Sanger Validation of High-Throughput Sequencing in Genetic Diagnosis: Still the Best Practice? Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 592588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossley, B.M.; Bai, J.; Glaser, A.; Maes, R.; Porter, E.; Killian, M.L.; Clement, T.; Toohey-Kurth, K. Guidelines for Sanger sequencing and molecular assay monitoring. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akuta, N.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Detection of TERT promoter mutation in serum cell-free DNA using wild-type blocking PCR combined with Sanger sequencing in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 3604–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-H.; Yang, C.-J. De novo exon 18 G724S point mutation may be sensitive to Gefitinib. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 918–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wei, H.; Rong, Z.; Wang, S. Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR combined with dual-color fluorescent lateral flow assay for the discrimination of SARS-CoV-2 and its mutations with a handheld wireless reader. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewi, A.L.; Paramita, D.K.; Fachiroh, J. Development of Tetra-primer Amplification Refractory Mutation System (ARMS) PCR for Detection of CHRNA3 rs8040868. Indones. Biomed. J. 2021, 13, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Dalhaimer, P.; Zhao, L. Tetra-Primer Amplification-Refractory Mutation System (ARMS)-PCR for Genotyping Mouse Leptin Gene Mutation. Animals 2022, 12, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Conc. (Copies/μL) | Intra-Day (n = 10) | Inter-Day (n = 15) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (Copies/μL) | CV (%) | Mean ± SD (Copies/μL) | CV (%) | ||
| Wild-type detection for 1555A plasmid | A-50000 | 14.19 ± 0.05 | 0.34% | 14.17 ± 0.48 | 3.36% |
| A-5000 | 17.47 ± 0.08 | 0.48% | 17.51 ± 0.47 | 2.67% | |
| A-500 | 21.13 ± 0.10 | 0.47% | 21.21 ± 0.38 | 1.79% | |
| Mutant-type detection for 1555G plasmid | G-50000 | 14.28 ± 0.04 | 0.26% | 14.28 ± 0.22 | 1.53% |
| G-5000 | 17.49 ± 0.40 | 2.30% | 17.63 ± 0.29 | 1.64% | |
| G-500 | 21.65 ± 0.57 | 2.63% | 21.27 ± 0.09 | 0.41% | |
| Sanger Sequencing | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1555AA | 1555AG | 1555GG | |||
| TaqMan-ARMS-PCR | 1555AA | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 1555AG | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | |
| 1555GG | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | |
| Total | 100 | 6 | 7 | 113 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Ding, M. Application of the TaqMan ARMS-PCR Approach for Genotyping Drug-Induced Hearing Loss Using Dried Blood Samples. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 5454-5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060326
Tan J, Zhang X, Wei X, Ding M. Application of the TaqMan ARMS-PCR Approach for Genotyping Drug-Induced Hearing Loss Using Dried Blood Samples. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(6):5454-5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060326
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Jiefeng, Xiaoqing Zhang, Xue Wei, and Min Ding. 2024. "Application of the TaqMan ARMS-PCR Approach for Genotyping Drug-Induced Hearing Loss Using Dried Blood Samples" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 6: 5454-5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060326
APA StyleTan, J., Zhang, X., Wei, X., & Ding, M. (2024). Application of the TaqMan ARMS-PCR Approach for Genotyping Drug-Induced Hearing Loss Using Dried Blood Samples. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(6), 5454-5466. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060326





