Common Denominator of MASLD and Some Non-Communicable Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
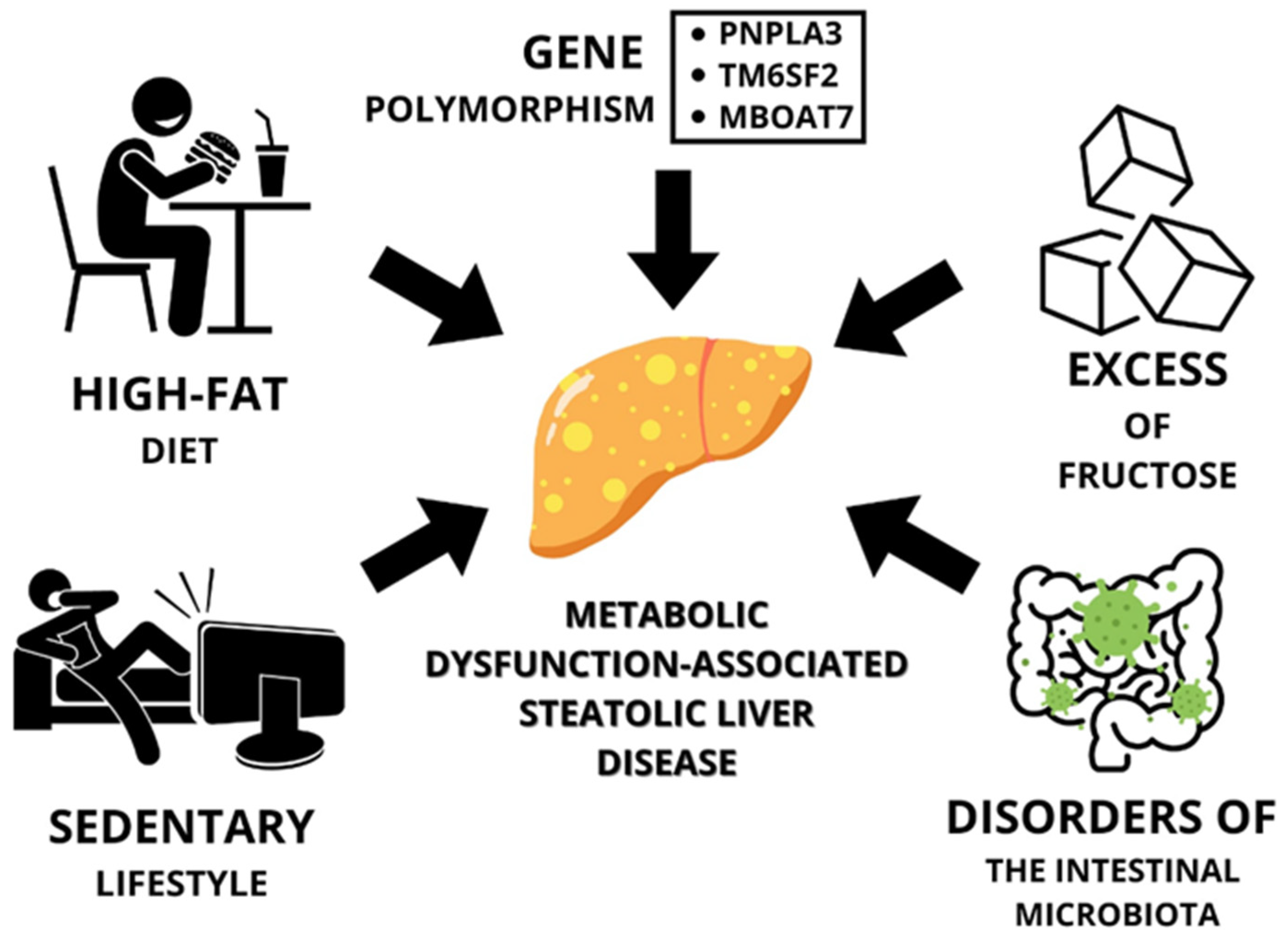
2. Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
2.1. Lifestyle
2.1.1. High-Fat Diet
2.1.2. A Diet High in Fructose
2.1.3. Sedentary Lifestyle
2.2. Gut Microbiota Disorders vs. MASLD
3. Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
3.1. High Supply of Fats and Carbohydrates in the Diet
3.2. Genetic Factors
4. Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic-Related Steatohepatitis
4.1. Risk Factors
4.1.1. Chronic Inflammation
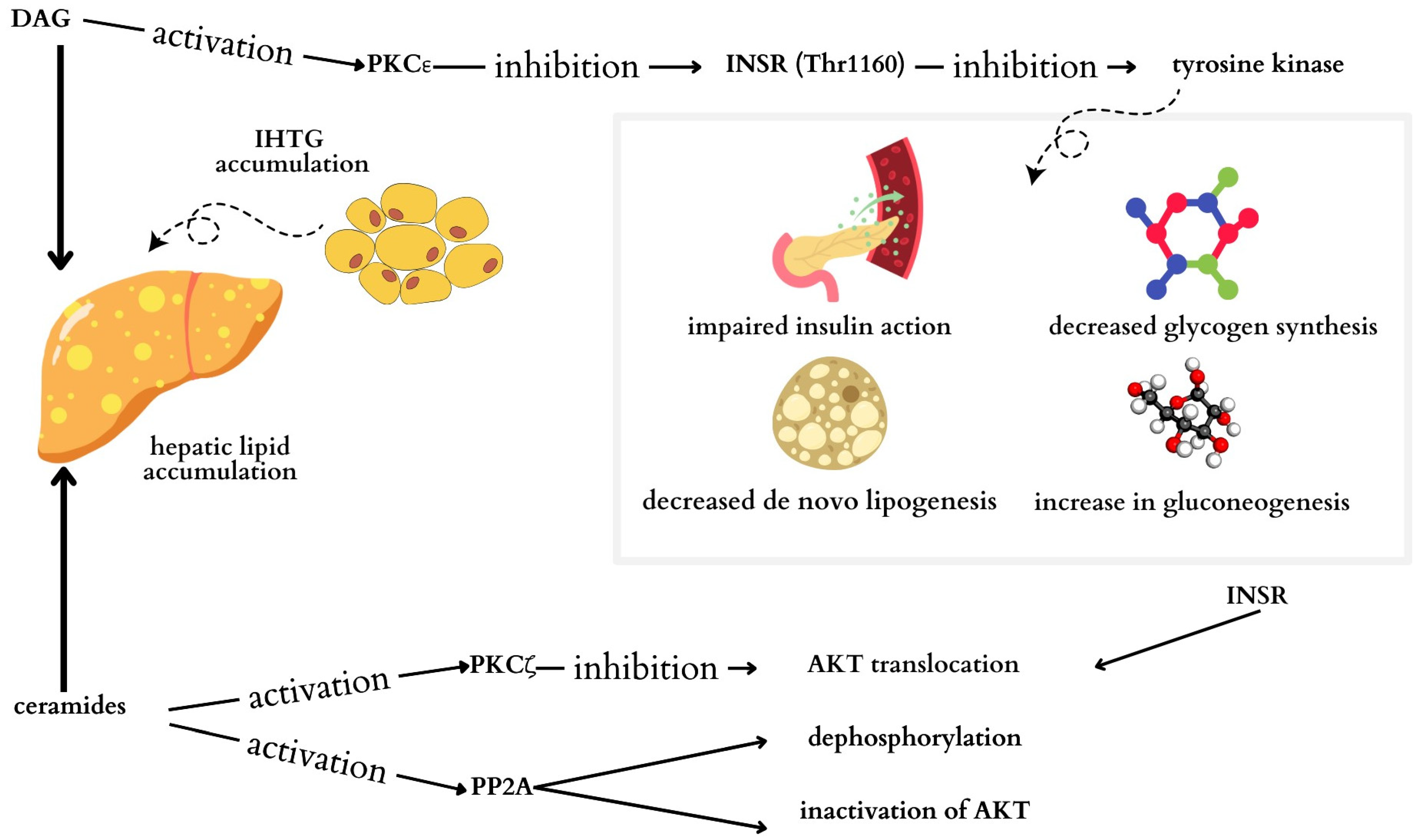
4.1.2. Insulin Resistance
4.1.3. Abnormal Lipid Profile
4.2. Complications Associated with Cardiovascular Disease
4.2.1. MASLD and Hypertension
4.2.2. MASLD and Structural Abnormalities of the Heart
4.2.3. MASLD and Cardiac Arrhythmias
4.2.4. Ischemic Stroke
4.3. Pharmacological Therapeutic Strategies
| Drug/Group of Drugs | Mechanism of Action in MASLD | Mechanism of Action in CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Statins [67] | Reduces cholesterol synthesis and liver triglyceride levels | Anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative, anticoagulant, antioxidant |
| Vitamin E [67,72] | Reduces steatosis and hepatitis | No evidence of reducing cardiovascular risk. May increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke and heart failure. |
| Ursodeoxycholic acid [72,89] | Improves hepatocyte secretory function and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine activity. Reduces aminotransferase activity and inhibits hepatic steatosis. | No evidence of CVD risk reduction |
| Hypotensive drug angiotensin II receptor antagonists [89] | Inhibition of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), which leads to activation of PPAR-γ, resulting in better control of adipose tissue proliferation and adipokine production | Inhibition of the RAAS lowering blood pressure |
| Hypoglycemic drugs [90] | Reduces insulin resistance and improves plasma lipid levels | Reduces oxidative stress, stimulates lipolysis, improves mitochondrial function, suppresses apoptosis, and alters the renin-angiotensin system |
5. Liver Cancer and Metabolic-Related Steatohepatitis
5.1. Genetic Factors
5.2. Gut Microbiota
5.3. Adipose Tissue and Associated Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
5.4. Diet
5.5. Other Factors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| apoB | apolipoprotein B |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ChREBP | carbohydrate response element-binding protein |
| CLD | chronic liver disease |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| DAG | diacylglycerol |
| DCA | deoxycholic acid |
| DNL | de novo lipogenesis |
| DSS | dextran sulfate sodium |
| EF | ejection fraction |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| FAS | fatty acid synthesis |
| FLI | fatty liver index |
| GGTP | gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HMGCoA | reductase 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase |
| HOMA-IR | insulin resistance index |
| HPCs | liver progenitor cells |
| IHTG | intrahepatic triglycerides |
| IKK | inhibitor κB kinase |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| INSR | insulin receptor |
| IR | insulin resistance |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LCD | low-calorie diet |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| LV | left ventricular |
| MAFLD | metabolic-associated fatty liver disease |
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-B |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PKCζ | protein kinase C-ζ |
| Pklr | l-type pyruvate kinase |
| PNPLA3 | patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 |
| PPAR-α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α |
| RAAS | renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| SCD-1 | stearoyl CoA-desaturase-1 |
| SGLT2 | sodium-glucose transporter 2 |
| SNP | nucleotide polymorphism |
| SOCS | suppressor of cytokine signaling |
| Srebp1c | factor binding sterol regulatory element 1 |
| SREBP-1c | sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes |
| TERT | telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TG | triglycerides |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TM6SF2 | transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| UDCA | ursodeoxycholic acid |
| VLKCD | very low-calorie ketogenic diet |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Eslam, M.; Sarin, S.K.; Wong, V.W.; Fan, J.G.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ahn, S.H.; Zheng, M.H.; Shiha, G.; Yilmaz, Y.; Gani, R.; et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 889–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A. Evaluation of obesity. Who are the obese? Postgrad. Med. 2003, 114, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayoral, L.P.; Andrade, G.M.; Mayoral, E.P.; Huerta, T.H.; Canseco, S.P.; Rodal Canales, F.J.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Cruz, M.M.; Pérez Santiago, A.D.; Alpuche, J.J.; et al. Obesity subtypes, related biomarkers & heterogeneity. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, J.T.; Marsche, G. Obesity-Related Changes in High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, M.; Kułaga, Z. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and primary hypertension. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Xia, M.F.; Bian, H.; Gao, X. NAFLD and Diabetes: Two Sides of the Same Coin? Rationale for Gene-Based Personalized NAFLD Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S. Fibrotic Burden Determines Cardiovascular Risk among Subjects with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gut Liver 2022, 16, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Ye, J.; Xu, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Updated mechanisms of MASLD pathogenesis. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Honda, Y.; Imajo, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Kessoku, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nogami, A.; Higurashi, T.; Kato, S.; et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with fatty liver disease as defined from the metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease point of view: A retrospective nationwide claims database study in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.X.; Schwabe, R.F. The gut microbiome and liver cancer: Mechanisms and clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, J.; Chan, K.E.; Wong, Z.Y.; Tan, C.; Tan, B.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Tang, A.S.P.; Tay, P.; Xiao, J.; et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.K.; Chuah, K.H.; Rajaram, R.B.; Lim, L.L.; Ratnasingam, J.; Vethakkan, S.R. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Mantovani, A.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of the association between NAFLD and metabolically healthy or metabolically unhealthy obesity. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, H.; Gao, X. Insights into contribution of genetic variants towards the susceptibility of MAFLD revealed by the NMR-based lipoprotein profiling. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meroni, M.; Longo, M.; Rustichelli, A.; Dongiovanni, P. Nutrition and Genetics in NAFLD: The Perfect Binomium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tan, H.; Wan, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, X. PPAR-γ signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 245, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trépo, E.; Valenti, L. Update on NAFLD genetics: From new variants to the clinic. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevzorova, Y.A.; Cubero, F.J. Obesity under the moonlight of c-MYC. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1293218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flessa, C.M.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Kyrou, I.; Leca, B.M.; Lianou, M.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kaltsas, G.; Kassi, E.; Randeva, H.S. Genetic and Diet-Induced Animal Models for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez, K.T.; Enos, R.T.; Bader, J.E.; Sougiannis, A.T.; Carson, M.S.; Chatzistamou, I.; Carson, J.A.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Murphy, E.A. Prolonged high-fat-diet feeding promotes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alters gut microbiota in mice. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbie, L.J.; Burgess, J.; Hamid, A.; Nevitt, S.J.; Hydes, T.J.; Alam, U.; Cuthbertson, D.J. Effect of a Low-Calorie Dietary Intervention on Liver Health and Body Weight in Adults with Metabolic-Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Overweight/Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nucci, S.; Bonfiglio, C.; Donvito, R.; Di Chito, M.; Cerabino, N.; Rinaldi, R.; Sila, A.; Shahini, E.; Giannuzzi, V.; Pesole, P.L.; et al. Effects of an Eight Week Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) on White Blood Cell and Platelet Counts in Relation to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in Subjects with Overweight and Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Bae, H.; Song, W.S.; Jang, C. Dietary Fructose and Fructose-Induced Pathologies. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 42, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.; Mu, W.; Roncal, C.; Cheng, K.Y.; Johnson, R.J.; Scarpace, P.J. Fructose-induced leptin resistance exacerbates weight gain in response to subsequent high-fat feeding. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1370–R1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.; Tümer, N.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, K.Y.; Scarpace, P.J. Prevention and reversal of diet-induced leptin resistance with a sugar-free diet despite high fat content. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel, P.; López-Sánchez, P.; Ramos-Tovar, E. Fructose and the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegatheesan, P.; De Bandt, J.P. Fructose and NAFLD: The Multifaceted Aspects of Fructose Metabolism. Nutrients 2017, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Horst, K.W.; Serlie, M.J. Fructose Consumption, Lipogenesis, and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiStefano, J.K. Fructose-mediated effects on gene expression and epigenetic mechanisms associated with NAFLD pathogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, G.; Datz, C.; Reiberger, T.; Trauner, M. Diet and exercise in NAFLD/NASH: Beyond the obvious. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2249–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.Q.; Bai, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, G.Y.; Fang, C.W.; Wang, F.; Qin, X.J. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, N.I.; Zhang, X.; Balakrishnan, M.; Daniel, C.R.; Hwang, J.P.; McNeill, L.H.; Thrift, A.P. Physical activity and diet quality in relation to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in a representative sample of U.S. adults using NHANES 2017–2018. Prev. Med. 2022, 154, 106903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.; Zou, J.; Ran, W.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, H.; Guo, J. Advancements in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1087260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolites in NAFLD Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Coker, O.O.; Chu, E.S.; Fu, K.; Lau, H.C.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Chan, A.W.H.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Dietary cholesterol drives fatty liver-associated liver cancer by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gut 2021, 70, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-liver axis: Pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Gut Microbiota-Derived Components and Metabolites in the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Yu, C.H.; Li, X.J.; Yao, J.M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Yoon, S.H.; Yu, W.Y. Gut dysbiosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 997018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, H.; Long, X.; Ni, Y.; Qian, L.; Nychas, E.; Siliceo, S.L.; Pohl, D.; Hanhineva, K.; Liu, Y.; Xu, A.; et al. Risk assessment with gut microbiome and metabolite markers in NAFLD development. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabk0855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Lin, A.; Kong, M.; Yao, X.; Yin, M.; Xia, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Intestinal microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.; Schnabl, B. Microbiota and Fatty Liver Disease-the Known, the Unknown, and the Future. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, P.; Cai, X.; Yu, X.; Gong, L. Markers of insulin resistance associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-diabetic population. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, S.; Jacobs, S.; Kröger, J.; Stefan, N.; Fritsche, A.; Weikert, C.; Boeing, H.; Schulze, M.B.; Kröger, J. Association between the Fatty Liver Index and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the EPIC-Potsdam Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Tsuboya, T.; Tsuji, K.; Dohke, M.; Maguchi, H. Independent Association Between Improvement of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Reduced Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzica, C.M.; Sfarti, C.; Trifan, A.; Zenovia, S.; Cuciureanu, T.; Nastasa, R.; Huiban, L.; Cojocariu, C.; Singeap, A.M.; Girleanu, I.; et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Bidirectional Relationship. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 28, 6638306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Costea, C.F.; Ciocoiu, M.; Lacatusu, C.M.; Maranduca, M.A.; Ouatu, A.; Floria, M. The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 31, 3920196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Baker, R.D.; Bhatia, T.; Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1969–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolowska, E.; Blachnio-Zabielska, A. The Role of Ceramides in Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumashiro, N.; Erion, D.M.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; Beddow, S.A.; Chu, X.; Still, C.D.; Gerhard, G.S.; Han, X.; Dziura, J.; et al. Cellular mechanism of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16381–16385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Zhou, Y.; Sädevirta, S.; Leivonen, M.; Arola, J.; Orešič, M.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Hepatic ceramides dissociate steatosis and insulin resistance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Roles of Diacylglycerols and Ceramides in Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghanem, L.; Zhang, X.; Jaiswal, R.; Seyoum, B.; Mallisho, A.; Msallaty, Z.; Yi, Z. Effect of Insulin and Pioglitazone on Protein Phosphatase 2A Interaction Partners in Primary Human Skeletal Muscle Cells Derived from Obese Insulin-Resistant Participants. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 42763–42773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armandi, A.; Rosso, C.; Caviglia, G.P.; Bugianesi, E. Insulin Resistance across the Spectrum of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Metabolites 2021, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titchenell, P.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Birnbaum, M.J. Unraveling the Regulation of Hepatic Metabolism by Insulin. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Skeletal muscle inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Kawada, N.; Japan Study Group of NAFLD (JSG-NAFLD). The Role of Insulin Resistance and Diabetes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Stender, S.; Pietrelli, A.; Mancina, R.M.; Cespiati, A.; Petta, S.; Pelusi, S.; Pingitore, P.; Badiali, S.; Maggioni, M.; et al. Causal relationship of hepatic fat with liver damage and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 283, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccatonda, A.; Andreetto, L.; D’Ardes, D.; Cocco, G.; Rossi, I.; Vicari, S.; Schiavone, C.; Cipollone, F.; Guagnano, M.T. From NAFLD to MAFLD: Definition, Pathophysiological Basis and Cardiovascular Implications. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Csermely, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Corey, K.E.; Simon, T.G.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellinger, J.L.; Pencina, K.M.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Seshadri, S.; Fox, C.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Speliotes, E.K. Hepatic steatosis and cardiovascular disease outcomes: An analysis of the Framingham Heart Study. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 470–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badmus, O.O.; Hinds, T.D., Jr.; Stec, D.E. Mechanisms Linking Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) to Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Cuevas, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Pathophysiological Molecular Mechanisms of Obesity: A Link between MAFLD and NASH with Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postic, C.; Girard, J. Contribution of de novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: Lessons from genetically engineered mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripodi, A.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Primignani, M.; Chantarangkul, V.; Clerici, M.; Mannucci, P.M.; Peyvandi, F.; Bertelli, C.; Valenti, L.; Fargion, S. Procoagulant imbalance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platek, A.E.; Szymanska, A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease as a cardiovascular risk factor. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 9, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorczyca-Głowacka, I.; Wełnicki, M.; Mamcarz, A.; Filipiak, K.J.; Wożakowska-Kapłon, B.; Barylski, M.; Szymański, F.M.; Kasprzak, J.D.; Tomasiewcz, K. The expert opinion of the Working Group on Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy of the Polish Cardiac Society. Kardiol. Pol. 2023, 81, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabravolski, S.A.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Baig, M.S.; Popkova, T.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Mitochondrial Lipid Homeostasis at the Crossroads of Liver and Heart Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bini, S.; D’Erasmo, L.; Di Costanzo, A.; Minicocci, I.; Pecce, V.; Arca, M. The Interplay between Angiopoietin-Like Proteins and Adipose Tissue: Another Piece of the Relationship between Adiposopathy and Cardiometabolic Diseases? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnagarin, R.; Tan, K.; Adams, L.; Matthews, V.B.; Kiuchi, M.G.; Marisol Lugo Gavidia, L.; Lambert, G.W.; Lambert, E.A.; Herat, L.Y.; Schlaich, M.P. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)-A Condition Associated with Heightened Sympathetic Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wider, M.D. Metabolic syndrome and the hepatorenal reflex. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2016, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S.; Argano, C.; Colomba, D.; Cammà, C.; Di Marco, V.; Cabibi, D.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Marchesini, G.; Pinto, A.; Licata, G.; et al. Epicardial fat, cardiac geometry and cardiac function in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Association with the severity of liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, E.P.; Dhindsa, D.S.; Lee, S.K.; Sandesara, P.B.; Chalasani, N.P.; Sperling, L.S. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Heart: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, F.; Qin, J.J.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, M.M.; Sun, T.; Huang, X.; Deng, K.Q.; Zuo, X.; Yao, D.; et al. The prevalence of MAFLD and its association with atrial fibrillation in a nationwide health check-up population in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1007171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.G.; Ju, S.Y.; Mei, Y.Z.; Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Zheng, A.J.; Ding, Y.B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies on the potential association between NAFLD/MAFLD and risk of incident atrial fibrillation. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, R.; Fargion, S.; Fracanzani, A.L. Brain involvement in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canillas, L.; Soriano-Varela, A.; Rodríguez-Campello, A.; Giralt-Steinhauer, E.; Cuadrado-Godia, E.; Broquetas, T. High prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with a first episode of acute ischemic stroke. Impact on disability and death. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1003878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duell, P.B.; Welty, F.K.; Miller, M.; Chait, A.; Hammond, G.; Ahmad, Z.; Cohen, D.E.; Horton, J.D.; Pressman, G.S.; Toth, P.P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Risk: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, e168–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caussy, C.; Aubin, A.; Loomba, R. The Relationship Between Type 2 Diabetes, NAFLD, and Cardiovascular Risk. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2021, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsakos, T.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Bakasis, A.D.; Kyrou, I.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Randeva, H.S.; Kassi, E. SGLT-2 Inhibitors in NAFLD: Expanding Their Role beyond Diabetes and Cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Verma, S. Mechanisms of cardiovascular benefits of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: A state-of-the-art review. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapaksha, I.G.; Gunarathne, L.S.; Asadi, K.; Laybutt, R.; Andrikopoulous, S.; Alexander, I.E.; Watt, M.J.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 Therapy Improves Liver Fibrosis and Glycemic Control in Diabetic Mice with Fatty Liver. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1056–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milic, S.; Mikolasevic, I.; Krznaric-Zrnic, I.; Stanic, M.; Poropat, G.; Stimac, D.; Vlahovic-Palcevski, V.; Orlic, L. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Emerging targeted therapies to optimize treatment options. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 4835–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Dalbeni, A. Treatments for NAFLD: State of Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelotti, G.A.; Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. NAFLD, NASH and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.; Poklepovic, A.; Moyneur, E.; Barghout, V. Population-based risk factors and resource utilization for HCC: US perspective. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Otgonsuren, M.; Henry, L.; Venkatesan, C.; Mishra, A.; Erario, M.; Hunt, S. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the United States from 2004 to 2009. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stine, J.G.; Wentworth, B.J.; Zimmet, A.; Rinella, M.E.; Loomba, R.; Caldwell, S.H.; Argo, C.K. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis without cirrhosis compared to other liver diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertle, J.; Dechêne, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Penndorf, V.; Herzer, K.; Kaiser, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Gerken, G.; Syn, W.K.; Canbay, A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progresses to hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of apparent cirrhosis. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 15, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Romeo, S.; Valenti, L. Hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver: Role of environmental and genetic factors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12945–12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapito, D.H.; Mencin, A.; Gwak, G.Y.; Pradere, J.P.; Jang, M.K.; Mederacke, I.; Caviglia, J.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Adeyemi, A.; Bataller, R.; et al. Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gäbele, E.; Dostert, K.; Hofmann, C.; Wiest, R.; Schölmerich, J.; Hellerbrand, C.; Obermeier, F. DSS induced colitis increases portal LPS levels and enhances hepatic inflammation and fibrogenesis in experimental NASH. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiwa, K.; Ishigami, M.; Ishizu, Y.; Kuzuya, T.; Honda, T.; Hayashi, K.; Hirooka, Y.; Katano, Y.; Goto, H. DSS colitis promotes tumorigenesis and fibrogenesis in a choline-deficient high-fat diet-induced NASH mouse model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.K.; Kim, S.J.; Rah, S.H.; Kang, J.I.; Jung, H.E.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, J.O.; Park, B.S.; Yoon, T.Y.; et al. Reconstruction of LPS Transfer Cascade Reveals Structural Determinants within LBP, CD14, and TLR4-MD2 for Efficient LPS Recognition and Transfer. Immunity 2017, 46, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.X.; Yan, H.X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wu, H.P.; Dong, W.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Zou, S.S.; et al. Endotoxin accumulation prevents carcinogen-induced apoptosis and promotes liver tumorigenesis in rodents. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.Y.; Han, Z.P.; Sun, K.; Zhang, S.S.; Hou, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Gao, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Q.D.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma induced by lipopolysaccharide. BMC Med. 2012, 31, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.M.; Schwacha, H.; Steinbrückner, B.; Brinkmann, F.E.; Ditzen, A.K.; Aponte, J.J.; Pelz, K.; Berger, D.; Kist, M.; Blum, H.E. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in human cirrhosis is associated with systemic endotoxemia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, A.; Kowalewski, M.P. Molecular Mechanisms of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Induced Inflammation in an Immortalized Ovine Luteal Endothelial Cell Line (OLENDO). Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, H.; Chen, P.; Xie, H.; Tao, Y. Demystifying the manipulation of host immunity, metabolism, and extraintestinal tumors by the gut microbiome. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Loo, T.; Atarashi, K.; Kanda, H.; Sato, S.; Oyadomari, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Oshima, K.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M.; et al. Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer through senescence secretome. Nature 2013, 499, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleij, A.; Hechenbleikner, E.M.; Goodwin, A.C.; Badani, R.; Stein, E.M.; Lazarev, M.G.; Ellis, B.; Carroll, K.C.; Albesiano, E.; Wick, E.C.; et al. The Bacteroides fragilis toxin gene is prevalent in the colon mucosa of colorectal cancer patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marengo, A.; Rosso, C.; Bugianesi, E. Liver Cancer: Connections with Obesity, Fatty Liver, and Cirrhosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A.; Chiang, D.Y.; Newell, P.; Peix, J.; Thung, S.; Alsinet, C.; Tovar, V.; Roayaie, S.; Minguez, B.; Sole, M.; et al. Pivotal role of mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1972–1983.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanni, E.; Bugianesi, E. Obesity and liver cancer. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, M.B.; Lavine, J.E. Dietary fructose in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 57, 5525–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Mapakshi, S.; Natarajan, Y.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Richardson, P.A.; Li, L.; Desiderio, R.; Thrift, A.P.; Asch, S.M.; et al. Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1828–1837.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, J.; Jaques, B.; Chattopadyhay, D.; Lochan, R.; Graham, J.; Das, D.; Aslam, T.; Patanwala, I.; Gaggar, S.; Cole, M.; et al. Hepatocellular cancer: The impact of obesity, type 2 diabetes and a multidisciplinary team. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Fontana, R.J.; Fu, S.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Su, G.L.; Lok, A.S. Alcohol, tobacco and obesity are synergistic risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Obesity [15,16,18,19,21,26,28,32,37] | Type 2 Diabetes [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62] | Cardiovascular Disease [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] | Hepatocellular Carcinoma [38,96,97,98,106,110,111,112,113,114] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common factors | Genetic factors:
| Chronic inflammation:
| Chronic inflammation: increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines; increase in the
| Genetic factors:
High leptin levels; Low adiponectin levels. Lifestyle:
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferenc, K.; Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S.; Sokal-Dembowska, A.; Stasik, K.; Filip, R. Common Denominator of MASLD and Some Non-Communicable Diseases. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 6690-6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070399
Ferenc K, Jarmakiewicz-Czaja S, Sokal-Dembowska A, Stasik K, Filip R. Common Denominator of MASLD and Some Non-Communicable Diseases. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(7):6690-6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070399
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerenc, Katarzyna, Sara Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, Aneta Sokal-Dembowska, Katarzyna Stasik, and Rafał Filip. 2024. "Common Denominator of MASLD and Some Non-Communicable Diseases" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 7: 6690-6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070399
APA StyleFerenc, K., Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S., Sokal-Dembowska, A., Stasik, K., & Filip, R. (2024). Common Denominator of MASLD and Some Non-Communicable Diseases. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(7), 6690-6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070399






