Abstract
Background/Objectives: A significant breakthrough in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment has occurred with the introduction of targeted therapies and immunotherapy. However, not all patients treated with these therapies would respond to treatment, and patients who respond to treatment would acquire resistance at some time point. This is why we need new biomarkers that can predict response to therapy. The aim of this study was to investigate whether soluble programmed cell death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) could be a predictive biomarker in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-positive NSCLC. Materials and Methods: Blood samples from 35 patients with EGFR-mutated (EGFRmut) adenocarcinoma who achieved disease control with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR TKI) therapy were collected for sPD-L1 analysis. We analyzed sPD-L1 concentrations in 30 healthy middle-aged subjects, as a control population, to determine the reference range. Adenocarcinoma patients were divided into two groups, i.e., a group with low sPD-L1 (≤182.5 ng/L) and a group with high sPD-L1 (>182.5 ng/L). Results: We found that progression-free survival (PFS) was 18 months, 95% CI (11.1–24.9), for patients with low sPD-L1 and 25 months, 95% CI (8.3–41.7), for patients with high sPD-L1. There was no statistically significant difference in PFS between the groups (p = 0.100). Overall survival (OS) was 34.4 months, 95% CI (26.6–42.2), for patients with low sPD-L1 and 84.1 months, 95% CI (50.6–117.6), for patients with high sPD-L1; there was also no statistically significant difference between the groups (p = 0.114). Conclusion: In our study, we found that patients with high sPD-L1 had numerically better PFS and OS, but this has no statistical significance. Further studies with a larger number of patients are needed to evaluate the role of sPD-L1 as a predictive biomarker in patients with EGFRmut NSCLC.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide [1,2]. Despite significant advances in treatment, non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains an incurable disease for the majority of patients [1]. For a long time, chemotherapy was the standard of care for patients with the advanced stage of the disease. For these patients, the five-year overall survival (OS) was less than 5% [2]. A big step was made with the introduction of targeted therapies and immunotherapy.
The activation of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway leads to the exhaustion of T-cells and continuous tumor growth [1]. Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibodies have demonstrated impressive results in the treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC without targetable mutations [1]. However, a significant proportion of patients experienced disease progression shortly after starting immunotherapy even after biomarker selection [3], such as PD-L1. Some studies have shown that the upregulation of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway was associated with resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)–tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy [1,4,5,6]. It was also reported that high levels of membrane PD-L1 were correlated with primary resistance and a poor response to EGFR TKIs [1,4,5,6]. One of them found that PD-L1 expression was increased in patients who acquired resistance to EGFR TKIs [4], whereas several others have reported a correlation between high PD-L1 expression and primary resistance and poor response to EGFR TKIs [5,6].
It was found that PD-L1 exists as a membrane-bound, soluble form [7] and in exosomes [8]. No correlation was found between membrane PD-L1 and the soluble form, and it has been acknowledged that the tumor microenvironment and nonmalignant cells may generate soluble programmed cell death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) as well [9]. It could be found on the surface of the various cells, and in addition, sPD-L1 can be released from PD-L1-positive tumor cells or immune cells [10]. sPD-L1 can be detected not only in patients with carcinomas, but also in other diseases and in the healthy population with the highest levels in adults between 51 and 70 years [7,9]. It can also be found in the plasma and in other liquids such as pleural effusion in lung cancer patients, but also in the supernatant of mPD-L1-positive malignant cell lines, and it is a product of mPD-L1 cleavage [7]. Also, it was shown that besides the proteolytic process of mPD-L1/exoPL-L1, sPD-L1 can arise from the translation of alternatively spliced PD-L1 mRNA. Different variants of sPD-L1 can arise, which are structurally and functionally variable. It was speculated that two variants, PD-L1v1 and PD-L1v4 mRNA, were more expressed in cancer cells than in normal tissue [11,12].
Sagawa et al. [13] in their research found that the secretion of PD-L1v4 resisted anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy compared to wild-type PD-L1, which was explained as a decoy effect. They concluded that the decoy effect of PD-L1 splicing variants may be one of the mechanisms of treatment resistance.
However, it has been proven that sPD-L1 holds its biological activity, and it is able to specifically bind to the PD-1 receptor in peripheral blood, thus activating the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway [10]. It could be the way how sPD-L1 achieves a systematic immunosuppressive effect.
The exosomes are membrane-bound vesicles, which can be found in blood, urine, and other body fluids [8]. They are secreted by tumor cells under oxidative stress [8]. It was confirmed that tumor cells can release exosomes carrying PD-1, PD-L1, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) [8].
It was found that EGFR mutations were directly associated with PD-L1 upregulation in NSCLC patients, which could lead to increased risk of tumor immune escape [1,14]. There is evidence that activated STAT3 (signaling transducer and activator of transcription 3) binds to the PD-L1 promoter and, in that way, promotes the transcription of PD-L1 [1,14]. It was shown that the EGFR signaling pathway was involved in the activation of the IL-6/Janus kinase (JAK)/STAT3 pathway [1,14,15]. This could imply that EGFR signaling could regulate PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway. EGFR activation has been found to upregulate PD-L1 through p-ERK1/2/p-c-Jun [16].
There is large heterogeneity among studies that have explored the role of soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) as a prognostic and/or predictive biomarker [8,10,17]. Different tests have been used to detect sPD-L1, but there is no consensus on the range of positive results.
The purpose of this pilot study is to investigate whether sPD-L1 could potentially be a predictive biomarker in patients with EGFR-mutated (EGFRmut) lung adenocarcinoma treated with EGFR TKIs based on a comparison of sPD-L1 blood levels and clinical outcomes. Since the samples are obtained from peripheral blood, it is suggested that it might be a valuable source of material for monitoring responses to therapy and further treatment decisions, as liquid biopsy is non-invasive, easy to perform, and can be repeated at any time point.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Data Collection
Patients with EGFRmut advanced lung adenocarcinoma who were treated at the Clinic for Pulmonology, University Clinical Center of Serbia, from February 2012 until January 2017 were enrolled in this study. All patients were treated with first-line EGFR TKIs: gefitinib, erlotinib, and afatinib. Data on sex, age, smoking status [i.e., non-smokers, ex-smokers (patients who stopped smoking one year before treatment), and smokers], stage of disease, response to therapy (ORR), time to disease progression (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were collected. Response to therapy included complete response, partial response, stable disease, and progression of disease.
A responder is defined as a patient who had a complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) for at least 4 weeks during treatment (confirmed response). Disease control is defined as response—as defined above—or stable disease (SD) for at least 6 weeks. PFS is defined as the time from the start of the therapy until disease progression or death, whichever occurs first. OS is defined as the time from the start of the therapy until death.
The source material used in this study was peripheral blood because liquid biopsy is non-invasive, easy to perform, and can be repeated during the treatment. Blood samples were collected from 35 of the patients for sPD-L1 analysis, who achieved disease control with EGFR TKI therapy (these patients had started EGFR TKIs and achieved disease control) and who were alive at the moment the analysis was performed. We also analyzed sPD-L1 concentrations in 30 healthy middle-aged subjects to determine reference ranges for sPD-L1 in the healthy population. Reference limits for the healthy middle-aged population have been calculated by a nonparametric method as 2.5th and 97.5th percentile values [18]. This is the usual method for reference boundary determination for parameters with non-normal distribution, such as PD-L1 [15].
2.2. Sample Collection
Blood samples were collected into lithium heparin tubes (BD Diagnostics, Wokingham, UK). Samples were diluted 1:2, and the total volume of the samples used was 100 μL (0.1 mL) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. Plasma was isolated by centrifugation at 1000× g RCF for 15 min and stored at −80 °C until analysis. We used the DuoSet ELISA system (R&D Systems Europe, Ltd., Abingdon, UK) for PD-L1 (B7-H1/CD274) determination in plasma as a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) specific to the human B7-H1T.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The results are presented as counts (%), means ± standard deviation, or median (25th–75th percentile) depending on data type and distribution. Groups were compared using the nonparametric Pearson Chi-square test. Kaplan–Meier curves with a log-rank tests were used to assess survival and group differences regarding survival. All p-values less than 0.05 were considered significant. All data were analyzed using SPSS 29.0 (IBM Corp. Released 2023. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0. Armonk, NY, USA: IBM Corp.) and R 3.4.2. (R Core Team (2017). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/, accessed on 2 December 2024).
3. Results
A total of 105 EGFRmut advanced adenocarcinoma patients were enrolled in this study. Blood samples were collected from 35 of them for sPD-L1 analysis, who achieved disease control and who were still alive at the time the blood was collected.
Reference limits for the healthy middle-aged population were calculated by a nonparametric method as 2.5th and 97.5th percentile values15: sPD-L1: 31.0–182.5 ng/L.
The mean sPD-L1 value for the EGFRmut adenocarcinoma group of patients was 155.74 ng/L, and 28.6% of the patients had sPD-L1 levels above the upper limit for healthy controls.
Therefore, adenocarcinoma patients were divided into two groups depending on the sPD-L1 level, i.e., a group with low sPD-L1 (≤182.5 ng/L) and a group with high sPD-L1 (>182.5 ng/L).
The main demographic and baseline characteristics of these two groups of patients are presented in Table 1. There are no statistically significant differences between the groups (Chi-square test).

Table 1.
Comparative view of demographic characteristics for groups of patients with low and high sPD-L1.
All patients were treated with first-line EGFR TKIs (Gefitinib, Erlotinib, or Afatinib; 33, 1, 1, respectively).
Disease control was achieved in all patients in both groups. A total of 48% of patients in the group with low sPD-L1 and 30% in the group with high sPD-L1 were responders. There were no statistically significant differences between the groups regarding their response to EGFR TKIs (Chi-square test, p = 0.206) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Response to EGFR TKIs by group (p = 0.206).
Progression-free survival was 18 months, 95% CI (11.1–24.9), for patients with low sPD-L1 and 25 months, 95% CI (8.3–41.7), for patients with high sPD-L1. There was no statistically significant difference in PFS between these groups (p = 0.100). Figure 1 shows the Kaplan–Meier curves of PFS in patients with low and high sPD-L1.
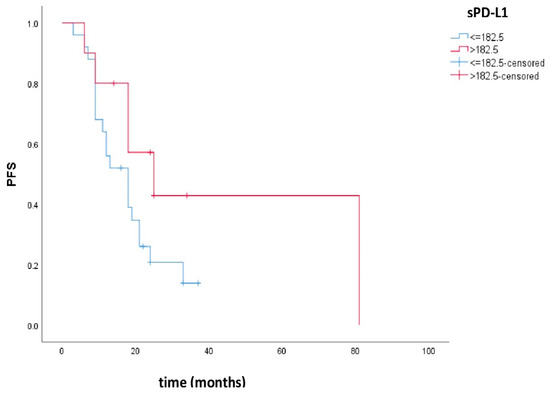
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier curves of PFS in patients with low and high sPD-L1. Patients with high sPD-L1 levels had better PFS compared to patients with low sPD-L1, but there was no statistical significance (p = 0.100).
Overall survival was 34.4 months, 95% CI (26.6–42.2), in the group of patients with low sPD-L1 and 84.1 months, 95% CI (50.6–117.6), in the group with high sPD-L1. There was no statistically significant difference in OS between these groups (p = 0.114). Figure 2 shows the Kaplan–Meier curves of OS in patients with low and high sPD-L1.
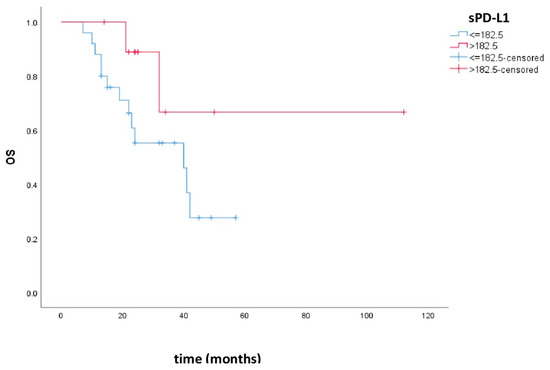
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curves of OS in patients with low and high sPD-L1. Patients with high sPD-L1 levels had better OS compared to patients with low sPD-L1, but there was no statistical significance (p = 0.114).
4. Discussion
The majority of lung cancer studies have shown that patients with elevated sPD-L1 had worse treatment and overall survival outcomes. We conducted this study in patients with EGFRmut lung adenocarcinoma who achieved disease control in order to investigate whether this finding also applies to this group of patients. Considering that there is no consensus on the reference range for sPD-L1, we have also investigated which group of patients in other studies had elevated values.
The mean sPD-L1 value for our group of patients was 155.74 ng/L, and 28.6% of patients had sPD-L1 levels above the upper limit for healthy controls. A possible explanation could be the fact that the majority of our patients achieved disease control, and another reason could be the small number of patients.
In a study by Li et al. [8], there was no significant difference between levels of sPD-L1 in 48 patients with NSCLC and healthy controls. This might be due to the fact that the majority of patients (i.e., 76.5% of them) were at stage I-IIIa and almost 86% did not have distant metastases [8]. They also found that patients with stage II/III/IV had significantly higher levels of sPD-L1 than patients with stage I, but there were no significant differences between the groups [8].
However, in two other studies, it was reported that levels of sPD-L1 were higher in patients with lung cancer than in healthy controls [2,3,17]. However, these studies included patients with advanced NSCLC [2,3,17], and in the previously mentioned study, the majority of patients were at stage I-IIIa [8].
The PFS in our study was 18 months, 95% CI (11.1–24.9), for patients with low sPD-L1 and 25 months, 95% CI (8.3–41.7), for patients with high sPD-L1. There was no statistically significant difference in the PFS between these groups (p = 0.100). This could be due to the small number of patients.
The OS was 34.4 months, 95% CI (26.6–42.2), for patients with low sPD-L1 and 84.1 months, 95% CI (50.6–117.6), for patients with high sPD-L1, but there was no statistical significance between the groups (p = 0.114). This could also be due to the small number of patients.
A possible explanation for these results, since all our patients achieved disease control, could be the reactivation of T-cells, which led to the initiation of immune response, thus killing the tumor cells and leading to the consequent release of sPD-L1. Another possible explanation for our results could be the presence of co-mutations. As already known, the most common co-mutation in EGFR-mutated NSCLC is tumor protein p53 (TP53). It has been proven that patients with EGFRmut NSCLC who also have TP53-positive mutation have worse prognosis than EGFRmut patients who have TP53 wild-type tumors. Besides this co-mutation, the other most frequent co-mutations include retinoblastoma 1 (RB1), CTNNB1, and phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PIK3)CA. PIK3CA and CTNNB1 are more frequent in patients with advanced stages of disease, while TP53 and RB1 are equally found in patients with early and advanced stages of disease [19].
Jiao et al. [20] conducted a study that investigated the correlation between TP53 and EGFR in patients with metastatic NSCLC. They found that the presence of TP53 was a negative prognostic factor for OS. The rate of TP53 was higher in the EGFRmut group of patients than in the EGFR wild-type (EGFRwt) group [20]. Patients with EGFRwt NSCLC and TP53 wild-type had the best prognosis. The same results were shown in patients with exon 19/21 and the TP53 wild-type [20].
As mentioned previously, most of the studies have shown that patients with high sPD-L1 have worse treatment outcomes, regardless of the type of therapy applied.
The results of a meta-analysis conducted by Wei et al. have shown that patients with solid cancers and high levels of sPD-L1 had a shorter OS than those with low levels of sPD-L1 [10].
Ding et al. [21] conducted a meta-analysis, and they also concluded that higher levels of sPD-L1 were associated with worse OS. Statistical significance was also observed in subgroup analysis stratified by cancer type (hematological neoplasms or non-hematological neoplasms), sample size (more or less than 100), cut-off value of sPD-L1 (more or less than 6.51 ng/mL), and ethnicity (Asian or European) [21].
Jin et al. [22] investigated the role of sPD-L1 in patients with small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). They found significantly higher levels of sPD-L1 in SCLC patients than in healthy controls. Also, higher levels of sPD-L1 have been found in patients who had no response to chemotherapy and in patients who died within the 12 months of the follow-up period [22].
In a study conducted by Jovanovic et al. [23], 47% of EGFRmut adenocarcinoma patients had high sPD-L1, i.e., all patients who were PD-L1-positive (these patients had advanced disease), 43% of patients with EGFRwt NSCLC, 64% of patients with squamous cell carcinoma, and 31% of patients with SCLC. Patients with higher sPD-L1 levels had shorter overall survival compared with patients with lower sPD-L1 levels, but without statistical significance. Also, higher sPD-L1 levels have been observed in patients with more advanced stages of disease [23].
There were 15 patients with EGFRmut adenocarcinoma who were included in this study [23]. These patients had lower baseline sPD-L1 levels than patients with EGFRwt NSCLC: 134.4 ng/L vs. 161.4 ng/L, respectively [23]. This difference was not statistically significant, and in our study, the mean sPD-L1 level was 155.74 ng/L. Our result was closer to that of the EGFRwt group of patients. A possible reason for such discrepancies could be the fact that we collected samples from patients who achieved disease control, whereas in the study by Jovanovic [23], the samples were collected at baseline.
Okuma et al. [2] found results similar to those of the majority of published papers. Patients with advanced lung cancer and high sPD-L1 had worse prognoses compared to patients with low sPD-L1 levels [2,3]. No correlation was noted among sPD-L1 levels and age, sex, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS), histological subtypes, mutational status, stage of disease, smoking status, and previous history of radiotherapy [2,3]. In this study, there were 19 EGFRmut patients and 3 patients with ALK rearrangements [2]. The authors found higher levels of sPD-L1 in these patients than in EGFRwt- and ALK-negative patients, but this difference was not statistically significant [2]. They did not investigate the correlation between the outcomes of EGFR TKI-treated patients and levels of sPD-L1. However, this study was conducted before the immunotherapy had been introduced; therefore, those patients were treated with chemotherapy. Most of the patients were chemotherapy-naïve (67.7%), and the levels of sPD-L1 were similar with the levels of sPD-L1 in the group of previously treated patients [2].
Jia et al. [1] investigated whether sPD-L1 could predict responses to EGFR TKIs in patients with EGFRmut lung adenocarcinoma. They found that patients with high pre-treatment or on-treatment sPD-L1 levels had decreased ORR compared with patients with low sPD-L1 [1]. There were no differences in the treatment response between patients with or without a reduction in sPD-L1 levels [1]. They also found that patients with high baseline sPD-L1 levels and that patients with high on-treatment sPD-L1 levels had shortened PFS, but this difference was not statistically significant [1]. The median PFS for the whole group was 12.5 months, but patients with lower pre-treatment levels of sPD-L1 had statistically superior PFS (16.1 months) compared to patients with higher pre-treatment sPD-L1 levels (9.9 months) [1]. Patients with higher on-treatment levels of sPD-L1 also had shorter PFS, but there was no statistical significance [1]. They did not investigate the association between sPD-L1 and overall survival. No association was observed between sPD-L1 levels and T790M status at the time of progression [1]. Other clinical characteristics such as gender, age, ECOG PS score, tumor stage, smoking status, EGFR status, and type of EGFR TKI received were not associated with the therapeutic response [1].
Zhang et al. [24] conducted a study that included 72 patients with EGFRmut NSCLC and also 31 patients with EGFR wild-type NSCLC as a control group. They found lower levels of sPD-L1 in the EGFRmut group of patients compared to the control group [7,24]. Patients with EGFRmut adenocarcinoma were divided into two groups depending on response after two months of EGFR TKI therapy: the disease progression group and the disease control group. The results showed lower levels of sPD-L1 after EGFR TKIs and significantly higher sPD-L1 levels in the disease progression group compared to the disease control group [7,24].
In another study, Zhang et al. [17] found that patients with low levels of sPD-L1 had longer OS. The same results were found in the EGFRmut group of patients (24 of 73 patients), but there was no statistical significance [3,9,17]. This study was also conducted before the immunotherapy era.
Zhao et al. [25] investigated the levels of sPD-L1 in patients treated with radiotherapy (RT) or concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy. They reported that lower levels of baseline sPD-L1 were correlated with longer OS in NSCLC patients treated with RT only [3,25]. Also, sPD-L1 levels were significantly lower at week 2 and week 4 when compared to baseline before RT, but not after RT [3,25]. sPD-L1 levels recovered to the baseline after RT, which may be explained by an increase in inflammation [25]. In the group of patients treated with concurrent chemotherapy and RT, OS was not significantly different between those with low and high baseline sPD-L1 [25]. A subgroup of patients treated with a high dose of RT and having low baseline sPD-L1 levels had the longest survival [25].
Levels of sPD-L1 were also investigated in patients treated with immunotherapy.
Okuma et al. [26] included 39 patients with NSCLC who were treated with nivolumab in a second-line setting or beyond. Plasma samples were collected at baseline. Patients with high sPD-L1 levels had shorter OS and shorter PFS compared to patients with low sPD-L1 levels [26]. The ORR was higher in the group with low sPD-L1 levels compared to the group with high sPD-L1 levels [26].
Another study conducted by Costantini et al. [27] included 43 patients with advanced NSCLC (EGFRwt- and ALK-negative) treated with nivolumab in their second-line treatment or beyond. Samples were collected upon initial diagnosis, before the initiation of nivolumab and again after two months of therapy. There was no difference in sPD-L1 levels collected upon the initial diagnosis and before the initiation of nivolumab between responders and non-responders to nivolumab [27]. However, after two months of nivolumab, sPD-L1 levels were significantly higher in non-responders [27]. An increase in sPD-L1 levels after two months of treatment was associated with lower overall response rates compared to patients who had decreased or stable sPD-L1 levels [27]. They also found that high sPD-L1 levels were correlated with shorter PFS and OS [27].
Bonomi et al. [28] conducted a study with 20 patients with NSCLC and ECOG PS 2. Patients were divided into two groups. One group of patients was treated with pembrolizumab monotherapy, and the other group of patients was treated with combination therapy: pembrolizumab plus carboplatin/paclitaxel. Blood samples were collected at baseline, at week 4, and at week 7. They found that patients with disease progression had higher baseline levels of sPD-L1 compared with patients who had a response to therapy, but this was not statistically significant [28]. No significant changes in levels of sPD-L1 were observed [28].
Dronca et al. [29] reported on 60 NSCLC and melanoma patients who were treated with anti-PD-1 therapy. They found that patients with high baseline sPD-L1 levels had no response to therapy, and they also found increased levels of sPD-L1 after the first tumor assessment in patients who did not have a response to therapy [29].
Wang and He [30] conducted a meta-analysis to identify the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of sPD-L1 in patients with NSCLC. Eleven studies were included in the analysis. They found that high levels of sPD-L1 were correlated with worse OS and PFS [30]. Correlation was not found between levels of sPD-L1 and age, sex, smoking status, ECOG PS, or EGFR mutation status [30].
Zhu and Song [31] found in their research that patients with lung cancer who were treatment-naïve had significantly higher sPD-L1 levels compared to healthy individuals and patients with benign tumors. They also found a positive correlation between poor ECOG PS and the later stage of the disease [31]. sPD-L1 levels were higher in EGFRmut patients compared to EGFRwt patients [31]. This difference was not statistically significant, but there were a small number of patients included in the analysis: 18 EGFRmut and 12 EGFRwt [31]. Also, a correlation was not found between PFS and sPD-L1 levels [31].
Although most of these studies showed worse prognosis or treatment resistance in patients with increased sPD-L1 levels, there are a few studies with results similar to ours. A study conducted by Tiako Meyo et al. [32] investigated the predictive value of biomarkers in advanced NSCLC, including sPD-L1. They included 87 patients, who were divided into two groups: patients treated with nivolumab (51 of them) and a control group of patients with EGFRmut NSCLC (36 of them). Patients treated with nivolumab were older, and 96% of them were former or active smokers, while patients in the EGFRmut group were non-smokers in almost 70% of cases [32]. In the nivolumab group, 52.9% of the patients had a positive sPD-L1 level, while all the patients in the EGFRmut group had a positive sPD-L1 level. The mean sPD-L1 level was higher in the EGFRmut group [32]. Positive levels of sPD-L1 in the nivolumab group were correlated with shorter PFS [32]. However, such correlation was not found in the EGFRmut group of patients [32]. Interestingly, after two cycles of nivolumab, patients with increased or stable levels of sPD-1 had longer PFS and OS [32]. The reduction in levels of sPD-L1 after two cycles of nivolumab was associated with worse outcomes in a univariate analysis, but these results have not been confirmed in a multivariate analysis [32].
Zheng et al. [33] found that patients with advanced gastric cancer and higher levels of sPD-L1 had better prognoses, similarly to our study. Vecchiarelli et al. [34] investigated whether sPD-L1 testing is feasible, whether its levels are changed after therapy, and also whether the baseline levels of sPD-L1 are correlated with the outcomes of treatment. They included 56 patients with advanced NSCLC, and there were 11 patients with EGFRmut NSCLC who were treated with EGFR TKIs. Only three patients were treated with immunotherapy. They observed that patients tretaed with cehmotherapy had a significant increase in median sPD-L1 after 3 months of treatment. But patients tretaed with TKIs and immunotherapy did not have significant changes in median sPD-L1 levels [34]. No significant differences in ORR, PFS, and OS were observed between patients with high and low sPD-L1 levels [34]. These differences were found neither in the group of patients treated with chemotherapy nor in the group of patients treated with TKIs and immunotherapy [34].
Sorensen et al. [35] showed in 38 EGFRmut NSCLC patients treated with erlotinib that the levels of sPD-1 were higher at the time of disease progression than at baseline. Interestingly, they also found that patients with an increase in sPD-1 level during erlotinib therapy had statistically significant longer PFS and OS, compared to patients with decreasing or undetectable sPD-1 [35]. They did not find this correlation between sPD-1 levels and the emergence of a T790M mutation [35].
Another study showed improved PFS and OS for NSCLC patients with a stable level of sPD-1 or an increase in sPD-1 after treatment with two cycles of nivolumab [36]. The underlying mechanism for increased levels of sPD-1 after certain modalities of treatment (radiotherapy, anti-EGFR therapy, and anti-PD-1 immunotherapy) may be the reactivation of tumor-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes [36]. These cells make up the primary source of sPD-1 in circulation [36]. Reactivation can result at least partly from increased antigen presentation by APCs, upregulation of HLA-I on tumor cells, and alleviating T-cells’ inhibition after treatments such as radiotherapy, EGFR TKIs, and anti-PD-1 immunotherapy [33]. A similar mechanism of action could be at the basis of the action of sPD-L1.
A comparative view of different studies with cut-off values used for sPD-L1 is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparative view of different studies and cut-off values used for sPD-L1.
The limitations of our study are the small number of patients and the different reference values for sPD-L1 compared to other studies. We included 35 patients who achieved disease control, because they were alive at the moment the analysis was performed. Our study bring inconsistent data relative to sPD-L1 as a predictive biomarker, at first in patients treated with chemotherapy but now also in patients treated with TKIs and immunotherapies. The major limitation of sPD-L1 as a biomarker in the context of clinics, besides the inconsistent data, is the absence of standardization of sPD-L1 measurement, as several ELISA kits and different thresholds were used in the studys. Thus, it is impossible to make a comparison of the results and to make a conclusion about the reference range. It is necessary to perform another study with a larger number of patients. Furthermore, it would be interesting to see the impact on the results if the samples were also collected at baseline and if patients who did not have a response to treatment were included in the analysis.
5. Conclusions
In our study, we found that patients with high sPD-L1 had numerically better PFS and OS, but there was no statistical significance; however, this is not in concordance with the results of the majority of previous studies.
Further studies with a larger study population are needed for better understanding the potential role of sPD-L1 as a predictive non-invasive biomarker in EGFRmut NSCLC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.Ć.K. and D.J.; methodology, V.Ć.K., D.J., J.K.S. and I.S.; software, I.S.; validation, V.Ć.K. and D.J.; formal analysis, V.Ć.K., D.J., N.S., M.G., A.K., D.R., M.R.M., B.Š., N.Č., K.L., M.S. and I.S.; investigation, V.Ć.K., J.K.S., N.S., M.G., A.K., D.R., M.R.M., B.Š., N.Č., K.L. and M.S.; resources, V.Ć.K., J.K.S., N.S., M.G., D.R., B.Š., N.Č., K.L. and M.S.; data curation, V.Ć.K., D.J., J.K.S. and A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, V.Ć.K. and D.J.; writing—review and editing, V.Ć.K. and D.J.; supervision, V.Ć.K. and D.J.; project administration, V.Ć.K. and D.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and it was approved by the Ethics Committee of School of Medicine Belgrade University of 06.06.2017 (No. 61206-2300/2-17).
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects gave their informed consent for participation in this study before any procedure was performed.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author (who will accurately indicate the status of the data).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Ren, S.; Su, C.; Gao, G.; Li, W.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.; Zhou, C. Soluble PD-L1 as a Predictor of the Response to EGFR-TKIs in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients With EGFR Mutations. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuma, Y.; Hosomi, Y.; Nakahara, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Sagawa, Y.; Homma, S. High plasma levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 are prognostic for reduced survival in advanced lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 104, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, A.; Takam Kamga, P.; Dumenil, C.; Chinet, T.; Emile, J.F.; Giroux Leprieur, E. Plasma Biomarkers and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: New Tools for Better Patient Selection? Cancers 2019, 11, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.J.; Kim, D.W.; Koh, J.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Jeon, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Change in PD-L1 Expression After Acquiring Resistance to Gefitinib in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, 263–270.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Tseng, J.S.; Chen, K.C.; Ku, W.H.; Su, K.Y.; Chen, J.J.W.; Chen, H.W.; Yu, S.L.; Yang, T.Y.; et al. High PD-L1 expression correlates with primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in treatment naïve advanced EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Dong, Z.Y.; Xie, Z.; Yan, L.X.; Li, Y.F.; Su, J.; Liu, S.Y.; Yin, K.; Chen, R.L.; Huang, S.M.; et al. Strong Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression Predicts Poor Response and De Novo Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Among NSCLC Patients With EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Hejleh, T.; Furqan, M.; Ballas, Z.; Clamon, G. The clinical significance of soluble PD-1 and PD-L1 in lung cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 143, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhi, C.; Liang, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Lv, T.; Shen, Q.; Song, Y.; Lin, D.; et al. Clinical significance of PD-L1 expression in serum-derived exosomes in NSCLC patients. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lang, J. Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1: Predictive and prognostic significance in cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97671–97682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. Prognostic significance of circulating soluble programmed death ligand-1 in patients with solid tumors: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.V.; Maansson, C.T.; Daugaard, T.F.; Andresen, B.S.; Sorensen, B.S.; Nielsen, A.L. Trans-Regulation of Alternative PD-L1 mRNA Processing by CDK12 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, C.; Thuru, X.; Quesnel, B. Soluble Programmed Death Ligand-1 (sPD-L1): A Pool of Circulating Proteins Implicated in Health and Diseases. Cancers 2021, 13, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, R.; Sakata, S.; Gong, B.; Seto, Y.; Takemoto, A.; Takagi, S.; Ninomiya, H.; Yanagitani, N.; Nakao, M.; Mun, M.; et al. Solubile PD-L1 works as a decoy in lung cancer immunotherapy via alternative polyadenylation. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e153323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zeng, Y.; Du, W.; Zhu, J.; Shen, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. The EGFR pathway is involved in the regulation of PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.V.; Greulich, H.; Sellers, W.R.; Meyerson, M.; Frank, D.A. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for the oncogenic effects of non-small-cell lung cancer-associated mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3162–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Tang, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, T.; Qin, T.; et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR Activation Mediates the Immune Escape in EGFR-Driven NSCLC: Implication for Optional Immune Targeted Therapy for NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Nie, J.; Dai, L.; Hu, W.; Chen, X.; Han, J.; Ma, X.; Tian, G.; et al. Circulating PD-L1 in NSCLC patients and the correlation between the level of PD-L1 expression and the clinical characteristics. Thorac. Cancer 2015, 6, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Choi, H.; Lee, S.M. Parametric and non-parametric estimation of reference intervals for routine laboratory tests: An analysis of health check-up data for 260 889 young men in the South Korean military. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e062617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.D.; Qin, B.D.; You, P.; Cai, J.; Zang, Y.S. The prognostic value of TP53 and its correlation with EGFR mutation in advanced non-small cell lung cancer, an analysis based on cBioPortal data base. Lung Cancer 2018, 123, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Hu, L.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Pu, L.; Xiong, S. The Prognostic Significance of Soluble Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 86, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Si, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ni, R.; Wang, J. Elevated serum soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 concentration as a potential marker for poor prognosis in small cell lung cancer patients with chemotherapy. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, D.; Roksandić-Milenković, M.; Kotur-Stevuljević, J.; Ćeriman, V.; Vukanić, I.; Samardžić, N.; Popević, S.; Ilić, B.; Gajić, M.; Simon, M.; et al. Soluble sPD-L1 and Serum Amyloid A1 as Potential Biomarkers for Lung Cancer. J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 38, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X.; Xing, Y.F.; Shi, M.H.; Chen, Y.J. Level of soluble programmed death-1 ligand 1 in peripheral blood of patients with advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutated lung adenocarcinoma and its clinical implications. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 96, 3870–3874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Xi, Q.; Zhao, X.; Ji, M.; Hu, G. Plasma levels of soluble programmed death ligand-1 may be associated with overall survival in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients receiving thoracic radiotherapy. Medicine 2017, 96, e6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, Y.; Wakui, H.; Utsumi, H.; Sagawa, Y.; Hosomi, Y.; Kuwano, K.; Homma, S. Soluble Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 as a Novel Biomarker for Nivolumab Therapy for Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, 410–417.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, A.; Julie, C.; Dumenil, C.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Tisserand, J.; Dumoulin, J.; Giraud, V.; Labrune, S.; Chinet, T.; Emile, J.F.; et al. Predictive role of plasmatic biomarkers in advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated by nivolumab. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1452581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomi, M.; Ahmed, T.; Addo, S.; Kooshki, M.; Palmieri, D.; Levine, B.J.; Ruiz, J.; Grant, S.; Petty, W.J.; Triozzi, P.L. Circulating immune biomarkers as predictors of the response to pembrolizumab and weekly low dose carboplatin and paclitaxel in NSCLC and poor PS: An interim analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronca, R.S.; Liu, X.; Harrington, S.M.; Enninga, E.A.L.; Kottschade, L.A.; Koo, C.W.; McWilliams, R.R.; Block, M.S.; Nevala, W.K.; Markovic, S.; et al. Bim and soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) as predictive biomarkers of response to anti-PD-1 therapy in patients with melanoma and lung carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, S11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, H. Prognostic value of soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Immunotherapy 2022, 14, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.B.; Song, X. Analysis of soluble programmed death-1 ligand-1 of lung cancer patients with different characteristics. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 8690–8696. [Google Scholar]
- Tiako Meyo, M.; Jouinot, A.; Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Fabre, E.; Wislez, M.; Alifano, M.; Leroy, K.; Boudou-Rouquette, P.; Tlemsani, C.; Khoudour, N.; et al. Predictive Value of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1, VEGFA, CD40 Ligand and CD44 for Nivolumab Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Bu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, A.; Wu, X.; Cheng, X.; Xing, X.; Du, H.; et al. Level of circulating PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced gastric cancer and its clinical implications. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 26, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vecchiarelli, S.; Passiglia, F.; D’Incecco, A.; Gallo, M.; De Luca, A.; Rossi, E.; D’Incà, F.; Minuti, G.; Landi, L.; Bennati, C.; et al. Circulating programmed death ligand-1 (cPD-L1) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17554–17563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, S.F.; Demuth, C.; Weber, B.; Sorensen, B.S.; Meldgaard, P. Increase in soluble PD-1 is associated with prolonged survival in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib. Lung Cancer 2016, 100, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Zhao, Z.; Arooj, S.; Fu, Y.; Liao, G. Soluble PD-1: Predictive, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Value for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).