Genetic Tendency Analysis and Comprehensive Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Leaves and Flowers of Loquat F1 Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Methods and Materials
2.2.1. Materials
2.2.2. Instruments
2.2.3. Extracts for Phenolic and Antioxidant Capacity Measurement
2.2.4. Total Phenolic Content Analysis
2.2.5. Total Flavonoid Content Analysis
2.2.6. Antioxidant Capacity Determination
Free Radical Scavenging Activity Using DPPH Assay
Antioxidant Activity Using ABTS Assay
Ferric-Reducing/Antioxidant Power Assay
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Analysis of Antioxidant Components and Activities of F1 Leaves of “Ninghaibai” and “Oobusa”
3.2. Genetic Analysis of Antioxidant Components and Activities of F1 Flowers of “Ninghaibai” and “Oobusa”
3.3. Comprehensive Evaluation Based on Antioxidant Activity and Components of F1 Leaves and Flowers
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis of Antioxidant Components and Activity of F1 Leaves and Flowers
3.3.2. Principal Component and Cluster Analyses of Comprehensive Antioxidant Activity of F1-Generation Leaves and Flowers
3.3.3. Principal Component and Cluster Analyses of Comprehensive Antioxidant Activity of F1-Generation Leaves and Flowers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, V.; Gupta, P.; Kumar, M. Loquat and its phytochemical potential: A promising application in food technology. eFood 2024, 5, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Priyanka, K.; Sivanand, C. Loquat Antioxidants in Fruits: Properties and Health Benefits, 1st ed.; Nayi, G., Gulzar, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 577–592. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Lin, S.; Jiang, Y.; Ashraf, M. Variation in contents of total phenolics and flavonoids and antioxidant activities in the leaves of 11 Eriobotrya Species. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2008, 63, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Lin, R.; Cheng, K.; Hung, Y.; Cho, C.; Chen, H.; Hwang, S.; Lee, M. Free radical-scavenging activity of Taiwanese native plants. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Biological activities of extracts from loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.): A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1983–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Sun, C.; Chen, K.; Li, X. Flavonoids, phenolics, and antioxidant capacity in the flower of Eriobotrya japonica Lindl. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2935–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; LI, X.; CHEN, J. Comparison of phenolic compound contents and antioxidant capacities of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) fruits. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Sun, C.; Chen, K. Hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidant activity of loquat fruits. J. Food Biochem. 2012, 36, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, A.; Caliskan, O.; Serce, S.; Saracoglu, O.; Kaya, C. Determining total phenolic content and total antioxidant capacity of loquat cultivars grown in Hatay. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2010, 6, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; CHEN, J.; Xie, M. Effect of different light transmittance paper bags on fruit quality and antioxidant capacity in loquat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, J. Commercial quality, major bioactive compound content and antioxidant capacity of 12 cultivars of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) fruits. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Chen, K. Phenolic composition from different loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) cultivars grown in China and their antioxidant properties. Molecules 2015, 20, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Su, J.; Wang, H.; Guan, Z.; Fang, W.; Chen, F.; Zhang, F. Heredity of active compounds and selection of elite hybrids in a segregating F1 population of tea chrysanthemum. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 305, 11366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarska, E.; Gawroński, J.; Jabłońska-Ryś, E.; Zalewska-Korona, M.; Radzki, W.; Sławińska, A. General combining ability and heterosis regarding the phytochemical properties in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) hybrids. Plant Breed. 2017, 136, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaat, F.; Serce, S. Heritability estimates and the variation of pomological traits, total phenolic compounds, and antioxidant capacity in two apricot progenies. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2020, 44, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, D.; Desseva, I.; Tumbarski, Y.; Popova, A.; Pandova, S.; Lante, A. Evaluation of the enzyme inhibition, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of apricots, plums, and their hybrid fruits. Plants 2024, 13, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, V.; Jain, B.; Kaushik, P. Heterosis breeding in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.): Gains and provocations. Plants 2020, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, J.; Crosby, K.; Yoo, K.; Patil, B.; Jifon, J.; Rooney, W. Heterosis in different F1 Capsicum annuum genotypes for fruit traits, ascorbic acid, capsaicin, and flavonoids. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 159, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P.; Reichelt, M.; Augustine, R.; Gershenzon, J.; Bisht, N. Heterotic patterns of primary and secondary metabolites in the oilseed crop Brassica juncea. Heredity 2019, 123, 318–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X. Antioxidant activities and major anthocyanins of myrobalan plum (Prunus cerasifera Ehrh.). J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C388–C393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, J.; Burger, R.; Margit, S. Statistical evaluation of DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, and Folin-Ciocalteu assays to assess the antioxidant capacity of lignins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasoubi, P.; Barzegar, M.; Sahari, M.; Azizi, M. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) peel extracts. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2010, 9, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Yang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, J.; Cheng, S. Evaluation of antioxidant properties of pomegranate peel extract in comparison with pomegranate pulp extract. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippman, B.; Zamir, D. Heterosis: Revisiting the magic. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohge, T.; Scossa, F.; Wendenburg, R.; Frasse, P.; Balbo, I.; Watanabe, M.; Alseekh, S.; Jadhav, S.; Delfin, J.; Lohse, M.; et al. Exploiting natural variation in tomato to define pathway structure and metabolic regulation of fruit polyphenolics in the lycopersicum complex. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidhara, B.; Veena, G.; Rajan, R.; Hudedamani, U.; Hudedamani, A. Screening of mango hybrid population for identifying nutritionally rich hybrids-A special focus on carotenoids. Indian J. Hort. 2020, 77, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhana, M.; Rafii, M.; Ismail, S.; Ramlee, S.; Hosen, M.; Karim, K.; Ikbal, M.; Halidu, J.; Sahmat, S. Growth and yield performances, pathogenicity, heat tolerance, antioxidant activity, and pungency level of anthracnose resistant and heat tolerant inbreed lines and their F1 hybrids of chili (Capsicum annuum L.). Sci. Hortic. 2023, 309, 111606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tian, T.; Zhou, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, W.; Li, M.; Lin, Y.; et al. Fruit sugar and organic acid composition and inheritance analysis in an intraspecific cross of Chinese cherry. LWT 2024, 198, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Peng, Y. Molecular concepts to explain heterosis in crops. Trends Plant Sci. 2024; online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P. Genetic analysis for fruit phenolics content, flesh color, and browning related Traits in Eggplant (Solanum melongena). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, E. Consequences of hybridization and heterozygosity on plant vigor and phenotypic stability. Plant Sci. 2015, 232, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapisarda, P.; Fabroni, S.; Peterek, S.; Russo, G.; Mock, H.P. Juice of New citrus hybrids (Citrus clementina Hort. ex Tan.xC. sinensis L. Osbeck) as a source of natural antioxidants. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, F.; Gomes, D.; Valentão, P.; Gonçalves, R.; Pio, R.; Chagas, E.; Seabra, R.; Andrade, P. Improved loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) cultivars: Variation of phenolics and antioxidative potential. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, D.; Xu, X.; Zhao, T. Analysis of the nutritional composition, biological activities, and phenolic metabolic bioactive module of cherry tomatoes. LWT 2024, 209, 116762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.; Lyu, L.; Li, W. Variation in antioxidant enzyme activity and key gene expression during fruit development of blackberry and blackberry-raspberry hybrids. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzoni, A.; Pritts, M. Applications of principal components analysis to horticultural research. HortScience 1991, 26, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, J.; Martinelli, J. Hierarchical cluster analysis as a tool to manage variation in germplasm collections. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1989, 78, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, P.; Liu, F.; Jia, M.; Liang, J. Seedling evaluation of six walnut rootstock species originated in China based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 265, 109212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Pan, X.; Ou, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W. Comprehensive evaluation of waterlogging tolerance of eleven Canna cultivars at flowering stage. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 296, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Combined evaluation of agronomic and quality traits to explore heat germplasm in celery (Apium graveolens L.). Sci. Hortic. 2023, 317, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Osman, N.; Mohamed, H. Characterization of tomato yellow leaf curl virus resistance genes and genetic variability in commercial tomato F1 hybrids. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 318, 112088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Go, V.; Li, Z.; Lu, Q. A new HPLC–UV method for the quantification of terpenoids and antioxidant activity of commercial loquat leaf tea and preparation. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, P.; Shih, M.; Wu, C.; Hsieh, C.; Chen, M.; Hsieh, S.; Hou, C. Functional evaluation of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) flower water extracts and its potential use in tea. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2023, 2023, 1188178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, A.; Suhag, R.; Thakur, D.; Gupta, V.; Prabhakar, P. Current status of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.): Bioactive functions, preservation approaches, and processed products. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 38, 286–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
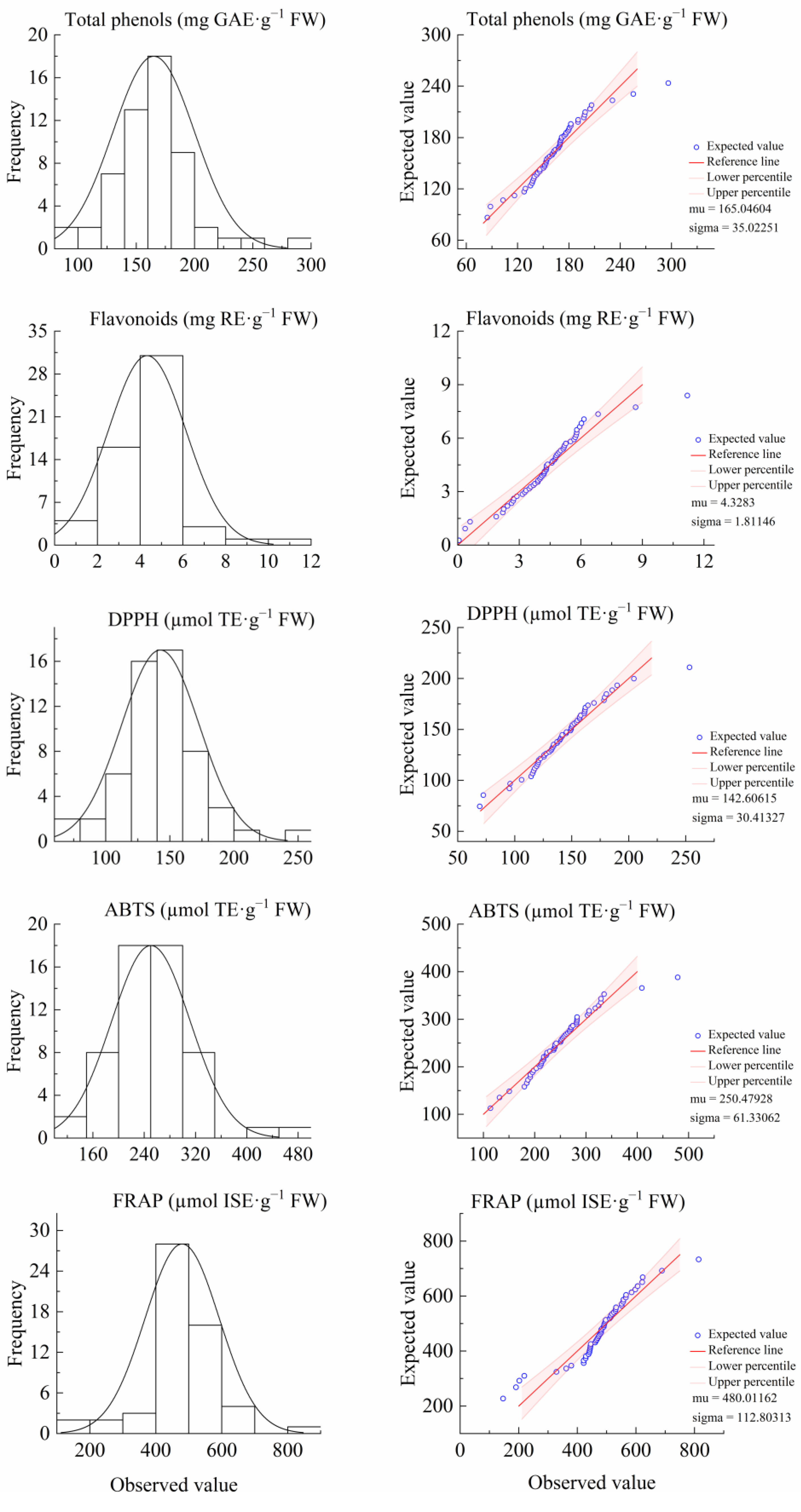
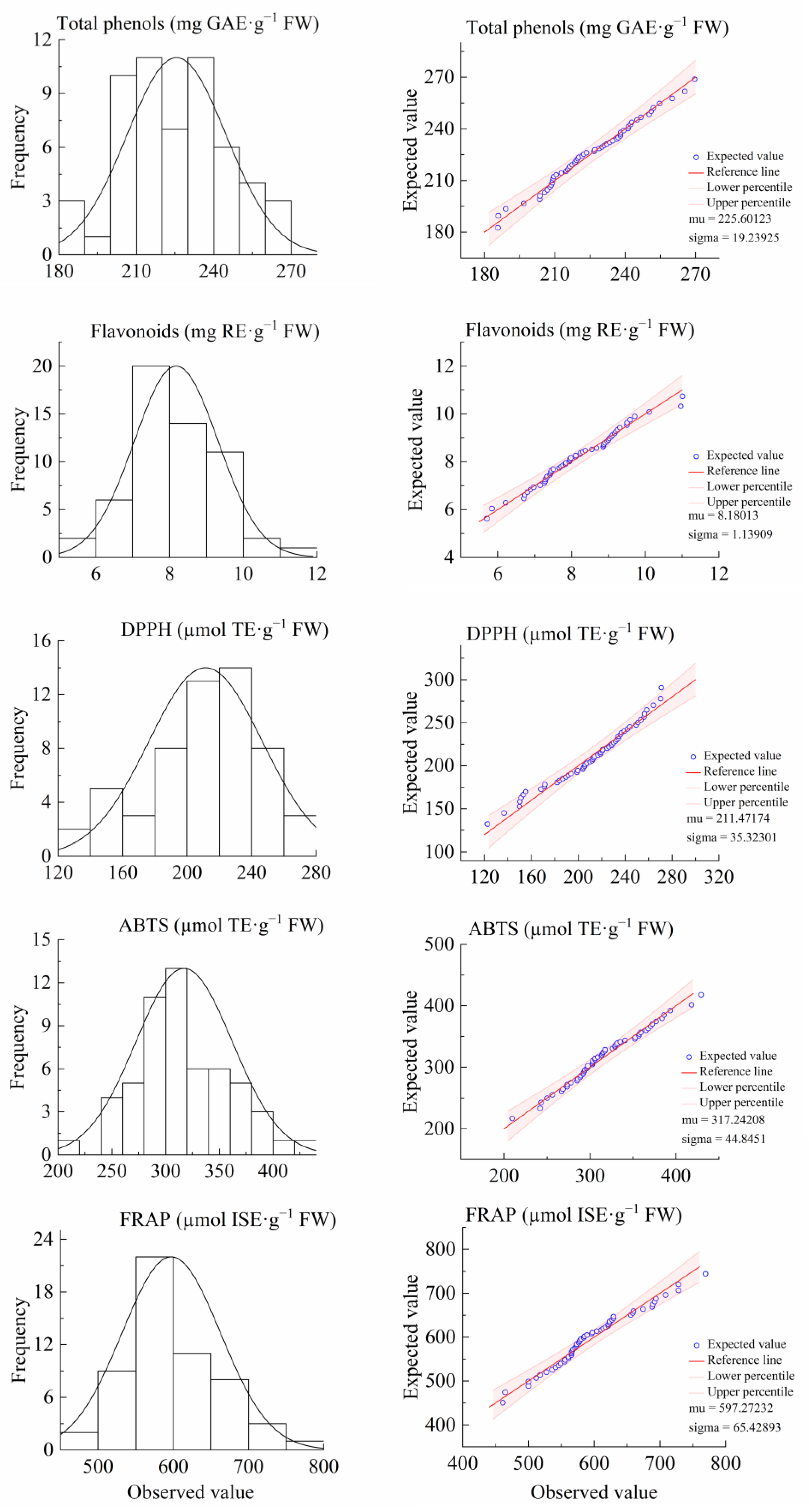


| Characteristic | Oobusa | Ninghaibai | Mid-Parent Value | F1 | Separation Range | CV/% | Ta/% | MPH/% | HH/% | LH/% | Kurt | Skew |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total phenols (mg GAE·g−1 FW) | 242.98 | 169.38 | 206.18 | 165.05 | 84.74~296.34 | 21.22 | 80.05 | −19.95 | 3.57 | 55.36 | 3.53 | 0.89 |
| Flavonoids (mg RE·g−1 FW) | 10.78 | 5.02 | 7.90 | 4.33 | 0.06~11.19 | 41.85 | 54.80 | −45.20 | 1.79 | 69.64 | 3.53 | 0.64 |
| DPPH (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 213.37 | 149.21 | 181.29 | 142.61 | 69.39~253.44 | 21.33 | 78.66 | −21.34 | 1.79 | 59.93 | 2.72 | 0.58 |
| ABTS (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 394.87 | 205.80 | 300.33 | 250.48 | 113.99~478.80 | 24.49 | 83.40 | −16.60 | 3.57 | 19.64 | 3.03 | 0.95 |
| FRAP (µmol ISE·g−1 FW) | 828.24 | 560.88 | 694.56 | 480.01 | 146.61~814.53 | 23.50 | 69.11 | −30.89 | 0 | 83.93 | 2.70 | −0.61 |
| Characteristic | Oobusa | Ninghaibai | Mid Parent Value | F1 | Separation Range | CV/% | Ta/% | MPH/% | HH/% | LH/% | Kurt | Skew |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total phenols (mg GAE·g−1 FW) | 224.14 | 225.06 | 224.60 | 225.60 | 185.70~269.63 | 8.53 | 100.45 | 0.45 | 48.21 | 51.79 | −0.32 | 0.10 |
| Flavonoids (mg RE·g−1 FW) | 8.72 | 8.31 | 8.51 | 8.18 | 5.70~10.96 | 13.81 | 96.13 | −3.87 | 35.71 | 58.93 | −0.25 | 0.96 |
| DPPH (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 224.01 | 224.01 | 224.01 | 211.47 | 122.60~270.96 | 16.70 | 94.40 | −5.60 | 41.07 | 58.93 | −0.23 | 0.94 |
| ABTS (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 293.06 | 306.70 | 299.88 | 317.24 | 209.74~429.41 | 14.14 | 105.79 | 5.79 | 51.79 | 28.57 | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| FRAP (µmol ISE·g−1 FW) | 638.25 | 664.69 | 651.47 | 597.27 | 460.98~769.48 | 10.95 | 91.68 | −8.32 | 16.07 | 78.57 | 0.16 | 0.92 |
| Characteristic | Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | ||
| Leaves | Total phenols (mg GAE·g−1 FW) | 98.13 | 166.03 | 264.92 |
| Flavonoids (mg RE·g−1 FW) | 0.82 | 4.40 | 10.21 | |
| DPPH (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 88.41 | 143.60 | 223.81 | |
| ABTS (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 158.91 | 249.20 | 427.59 | |
| FRAP (µmol ISE·g−1 FW) | 189.70 | 493.71 | 777.32 | |
| Flowers | Total phenols (mg GAE·g−1 FW) | 236.30 | 225.43 | 213.54 |
| Flavonoids (mg RE·g−1 FW) | 8.18 | 8.20 | 8.12 | |
| DPPH (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 223.39 | 211.44 | 204.50 | |
| ABTS (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 324.50 | 317.57 | 290.44 | |
| FRAP (µmol ISE·g−1 FW) | 612.78 | 598.23 | 596.46 | |
| Characteristic | PC1 | PC2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Total phenols (mg GAE·g−1 FW) | 0.934 | 0.177 |
| Flavonoids (mg RE·g−1 FW) | 0.940 | 0.075 | |
| DPPH (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 0.943 | 0.124 | |
| ABTS (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | 0.885 | 0.106 | |
| FRAP (µmol ISE·g−1 FW) | 0.923 | 0.168 | |
| Flowers | Total phenols (mg GAE·g−1 FW) | −0.266 | 0.883 |
| Flavonoids (mg RE·g−1 FW) | −0.120 | 0.537 | |
| DPPH (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | −0.213 | 0.606 | |
| ABTS (µmol TE·g−1 FW) | −0.210 | 0.599 | |
| FRAP (µmol ISE·g−1 FW) | −0.055 | 0.868 | |
| Eigenvalues/% | 4.458 | 2.640 | |
| Rate of variance/% | 44.575 | 26.397 | |
| Rate of cumulative variances/% | 44.575 | 70.973 | |
| Germplasm No. | PC1 | PC2 | PC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score | Rank | Score | Rank | Score | Rank | |
| ND107 | 7.532 | 1 | 0.592 | 22 | 4.951 | 1 |
| Oobusa | 5.529 | 2 | 1.357 | 12 | 3.977 | 2 |
| ND128 | 5.034 | 3 | −0.842 | 43 | 2.849 | 3 |
| ND082 | 1.369 | 8 | 1.674 | 9 | 1.482 | 4 |
| ND167 | 1.028 | 12 | 2.235 | 4 | 1.477 | 5 |
| ND142 | 0.205 | 25 | 3.474 | 2 | 1.421 | 6 |
| ND036 | 1.614 | 6 | 0.794 | 18 | 1.309 | 7 |
| ND135 | 2.365 | 5 | −0.796 | 42 | 1.189 | 8 |
| ND088 | 2.467 | 4 | −1.216 | 45 | 1.097 | 9 |
| ND093 | 0.626 | 20 | 1.832 | 7 | 1.075 | 10 |
| ND120 | 0.646 | 19 | 1.495 | 10 | 0.962 | 11 |
| ND121 | 0.688 | 16 | 1.313 | 13 | 0.920 | 12 |
| ND139 | 1.414 | 7 | −0.060 | 30 | 0.865 | 13 |
| ND165 | 0.269 | 24 | 1.806 | 8 | 0.841 | 14 |
| ND159 | 0.606 | 21 | 1.116 | 15 | 0.796 | 15 |
| ND164 | −0.972 | 43 | 3.459 | 3 | 0.676 | 16 |
| ND123 | −0.184 | 33 | 1.864 | 6 | 0.578 | 17 |
| ND099 | 0.667 | 17 | 0.386 | 26 | 0.563 | 18 |
| ND031 | 0.606 | 22 | 0.308 | 28 | 0.495 | 19 |
| ND125 | 0.178 | 26 | 0.997 | 17 | 0.482 | 20 |
| ND084 | 0.948 | 13 | −0.355 | 35 | 0.463 | 21 |
| ND050 | −1.334 | 48 | 3.494 | 1 | 0.462 | 22 |
| ND146 | 0.651 | 18 | 0.016 | 29 | 0.415 | 23 |
| ND136 | −0.270 | 35 | 1.466 | 11 | 0.376 | 24 |
| Ninghaibai | 0.158 | 27 | 0.656 | 21 | 0.343 | 25 |
| ND156 | 0.540 | 23 | −0.165 | 33 | 0.277 | 26 |
| ND130 | 0.115 | 28 | 0.510 | 24 | 0.262 | 27 |
| ND043 | 0.715 | 15 | −0.750 | 41 | 0.170 | 28 |
| ND124 | −1.050 | 44 | 1.932 | 5 | 0.059 | 29 |
| ND079 | 1.366 | 9 | −2.192 | 53 | 0.043 | 30 |
| ND116 | 1.083 | 10 | −1.822 | 50 | 0.002 | 31 |
| ND081 | 0.772 | 14 | −1.371 | 46 | −0.025 | 32 |
| ND117 | −0.147 | 32 | −0.148 | 32 | −0.147 | 33 |
| ND090 | −0.682 | 40 | 0.714 | 19 | −0.163 | 34 |
| ND162 | 0.069 | 31 | −0.731 | 40 | −0.229 | 35 |
| ND069 | 1.037 | 11 | −2.919 | 55 | −0.434 | 36 |
| ND045 | −1.107 | 45 | 0.667 | 20 | −0.447 | 37 |
| ND166 | −0.901 | 42 | −0.175 | 34 | −0.631 | 38 |
| ND106 | −1.292 | 47 | 0.407 | 25 | −0.660 | 39 |
| ND026 | 0.092 | 29 | −1.963 | 52 | −0.672 | 40 |
| ND134 | −0.532 | 37 | −1.009 | 44 | −0.709 | 41 |
| ND154 | −0.869 | 41 | −0.643 | 37 | −0.785 | 42 |
| ND085 | −0.359 | 36 | −1.758 | 49 | −0.880 | 43 |
| ND086 | −0.570 | 39 | −1.461 | 47 | −0.902 | 44 |
| ND029 | −1.886 | 53 | 0.556 | 23 | −0.978 | 45 |
| ND004 | −0.557 | 38 | −1.705 | 48 | −0.984 | 46 |
| ND122 | −1.371 | 49 | −0.721 | 39 | −1.129 | 47 |
| ND028 | 0.087 | 30 | −3.246 | 58 | −1.153 | 48 |
| ND037 | −1.860 | 52 | −0.098 | 31 | −1.205 | 49 |
| ND119 | −1.772 | 51 | −0.358 | 36 | −1.246 | 50 |
| ND127 | −0.263 | 34 | −3.124 | 56 | −1.327 | 51 |
| ND089 | −1.172 | 46 | −1.941 | 51 | −1.458 | 52 |
| ND007 | −2.704 | 55 | 0.342 | 27 | −1.571 | 53 |
| ND024 | −1.496 | 50 | −3.190 | 57 | −2.126 | 54 |
| ND080 | −2.223 | 54 | −2.238 | 54 | −2.229 | 55 |
| ND148 | −4.359 | 56 | 1.206 | 14 | −2.289 | 56 |
| ND149 | −5.629 | 58 | 1.020 | 16 | −3.156 | 57 |
| ND150 | −4.911 | 57 | −0.689 | 38 | −3.341 | 58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Ge, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Xu, H. Genetic Tendency Analysis and Comprehensive Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Leaves and Flowers of Loquat F1 Generation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47010058
Zhu Q, Li X, Ge H, Wang Z, Wang B, Chen J, Xu H. Genetic Tendency Analysis and Comprehensive Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Leaves and Flowers of Loquat F1 Generation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Qixuan, Xiaoying Li, Hang Ge, Zhixuan Wang, Binjun Wang, Junwei Chen, and Hongxia Xu. 2025. "Genetic Tendency Analysis and Comprehensive Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Leaves and Flowers of Loquat F1 Generation" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47010058
APA StyleZhu, Q., Li, X., Ge, H., Wang, Z., Wang, B., Chen, J., & Xu, H. (2025). Genetic Tendency Analysis and Comprehensive Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Leaves and Flowers of Loquat F1 Generation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47010058






