Bioinformatics Approach to Investigating the Immuno-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Periodontitis in the Progression of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Normalization and Annotation of Microarray Data
2.3. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.4. Selection of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Establishment
2.7. Machine Learning for Biomarker Selection and ROC Curve Construction
2.8. Nomogram Construction and Single-Gene Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.9. Immune Infiltration Analysis
2.10. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data Analysis
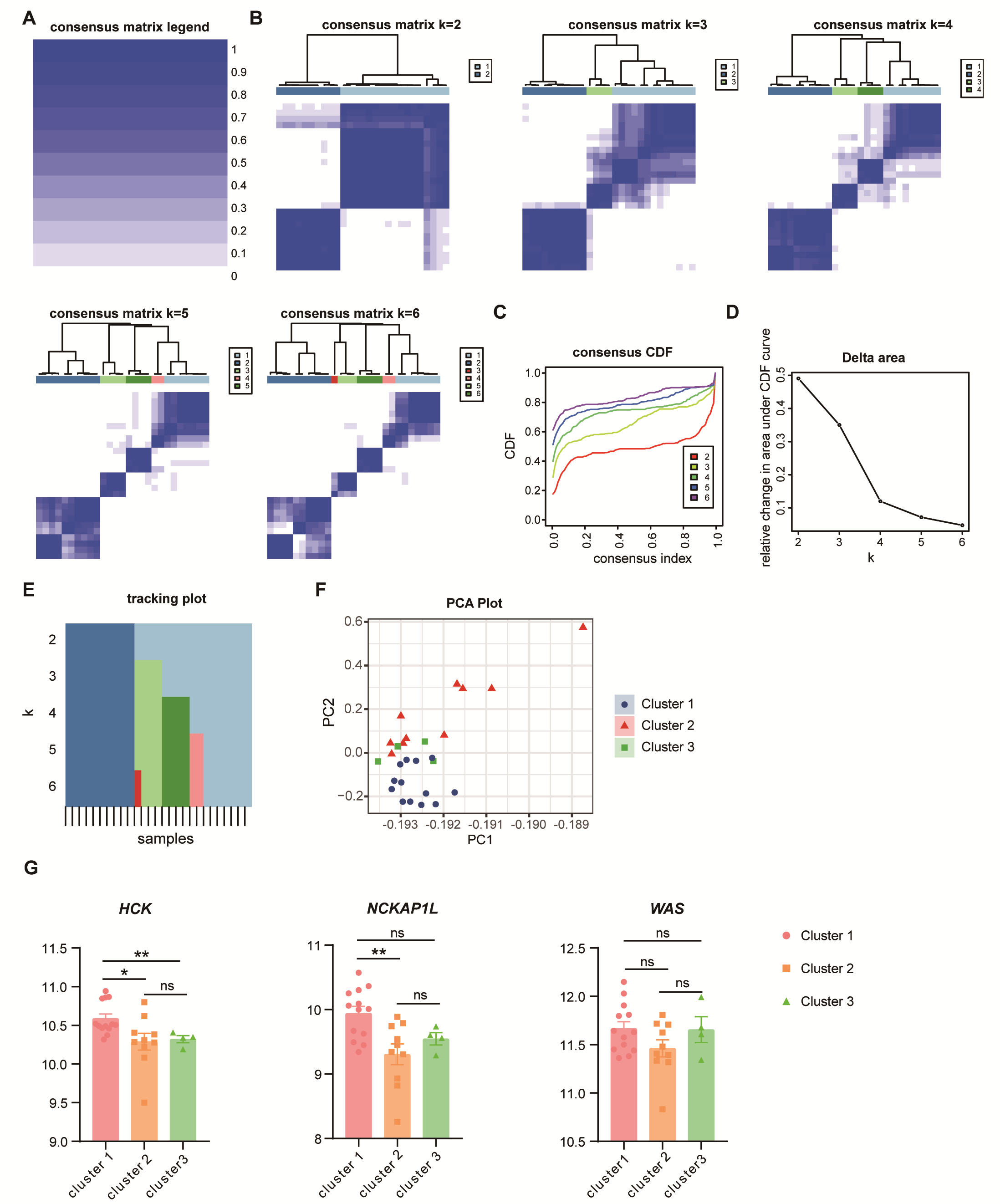
2.11. Consensus Clustering
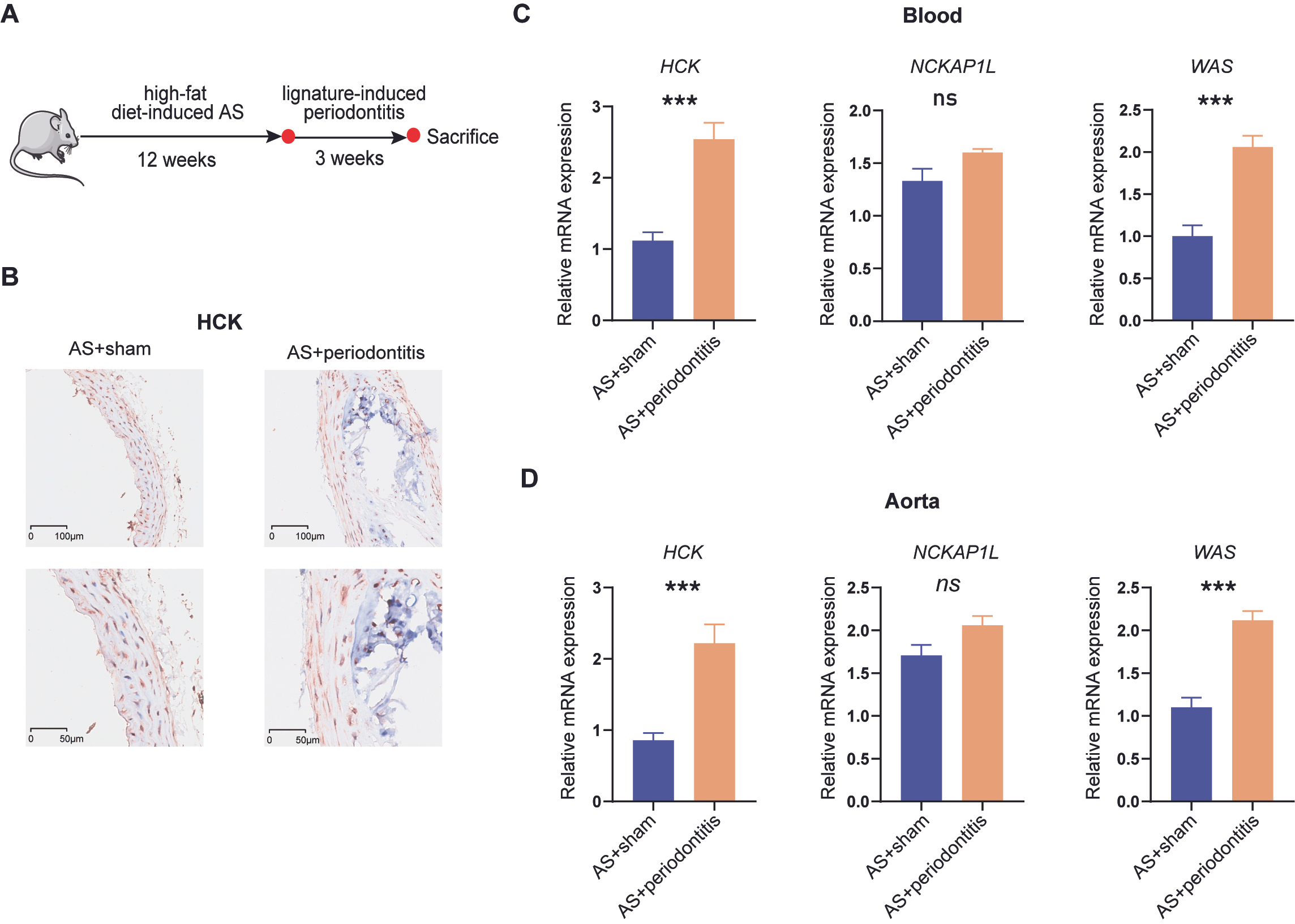
2.12. Establishment of Atherosclerosis Mouse Model
2.13. Establishment of Chronic Periodontitis Mouse Model
2.14. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment
2.15. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (q-RTPCR) Experiment
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Gene Modules Associated with Periodontitis
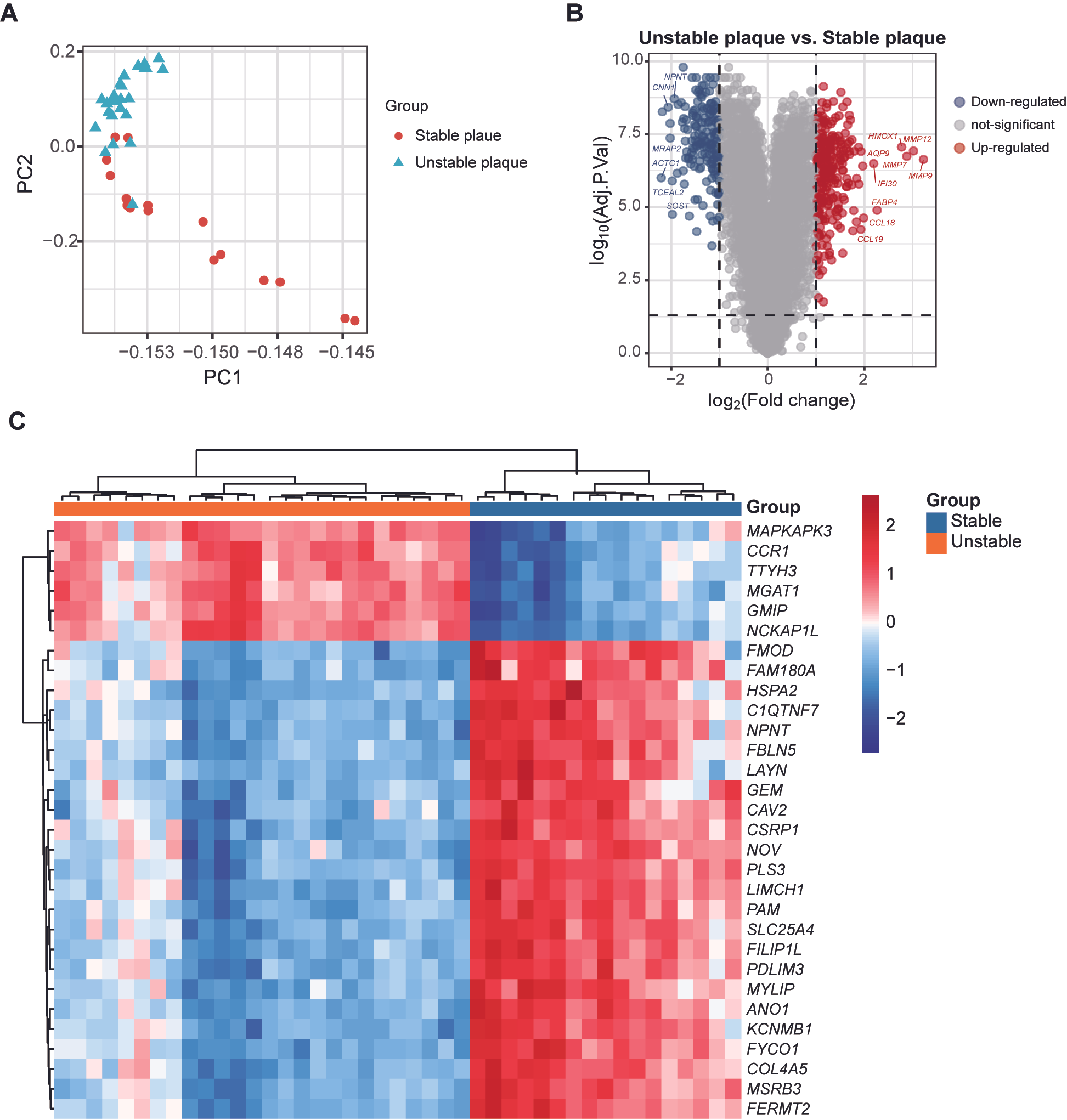
3.2. Different Gene Expression Patterns in Stable and Unstable Atherosclerotic Plaques
3.3. Functional Enrichment and PPI Network of Periodontitis-Related DEGs
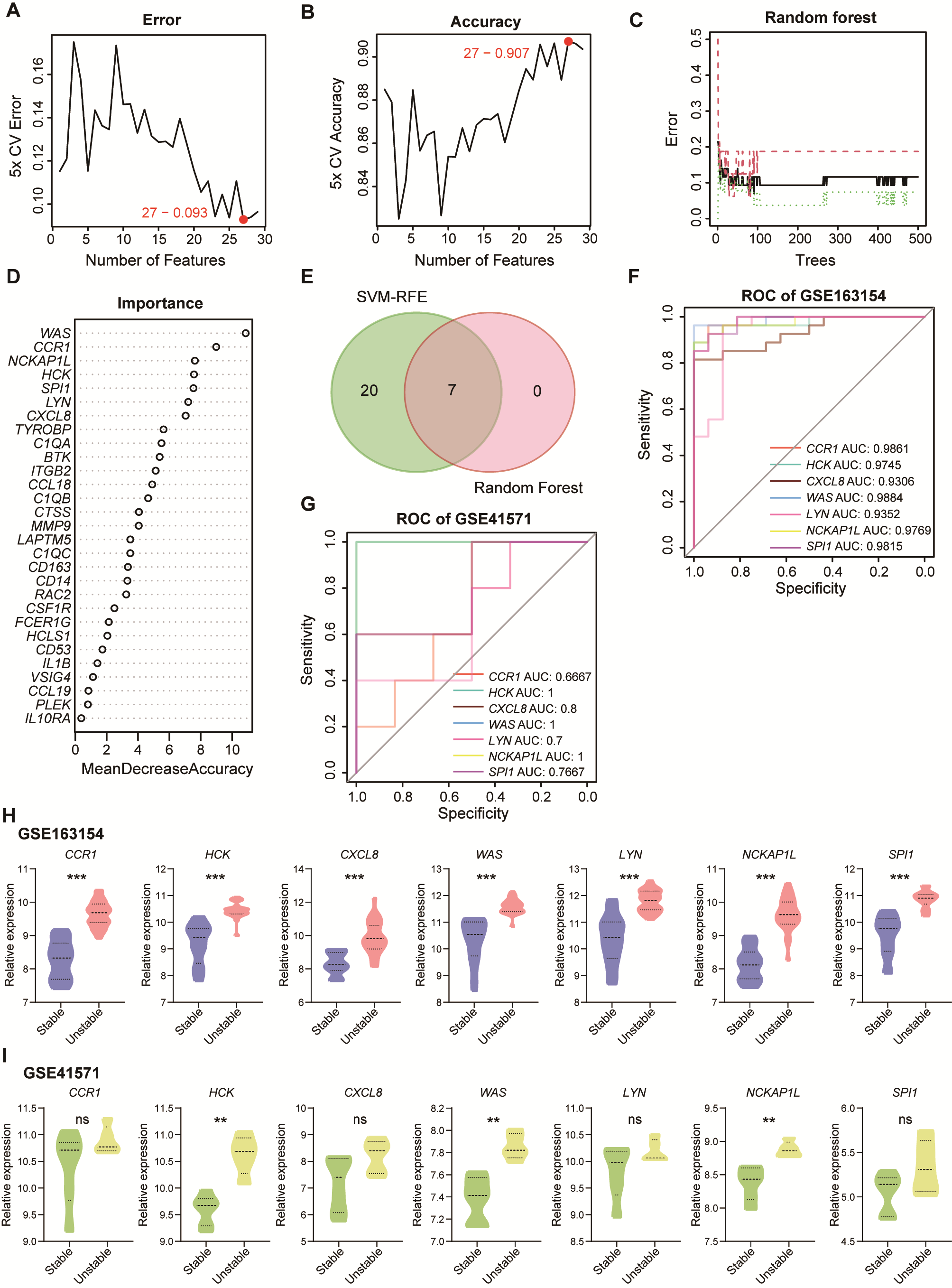
3.4. Identification of Biomarkers for Unstable Plaque Associated with Periodontitis
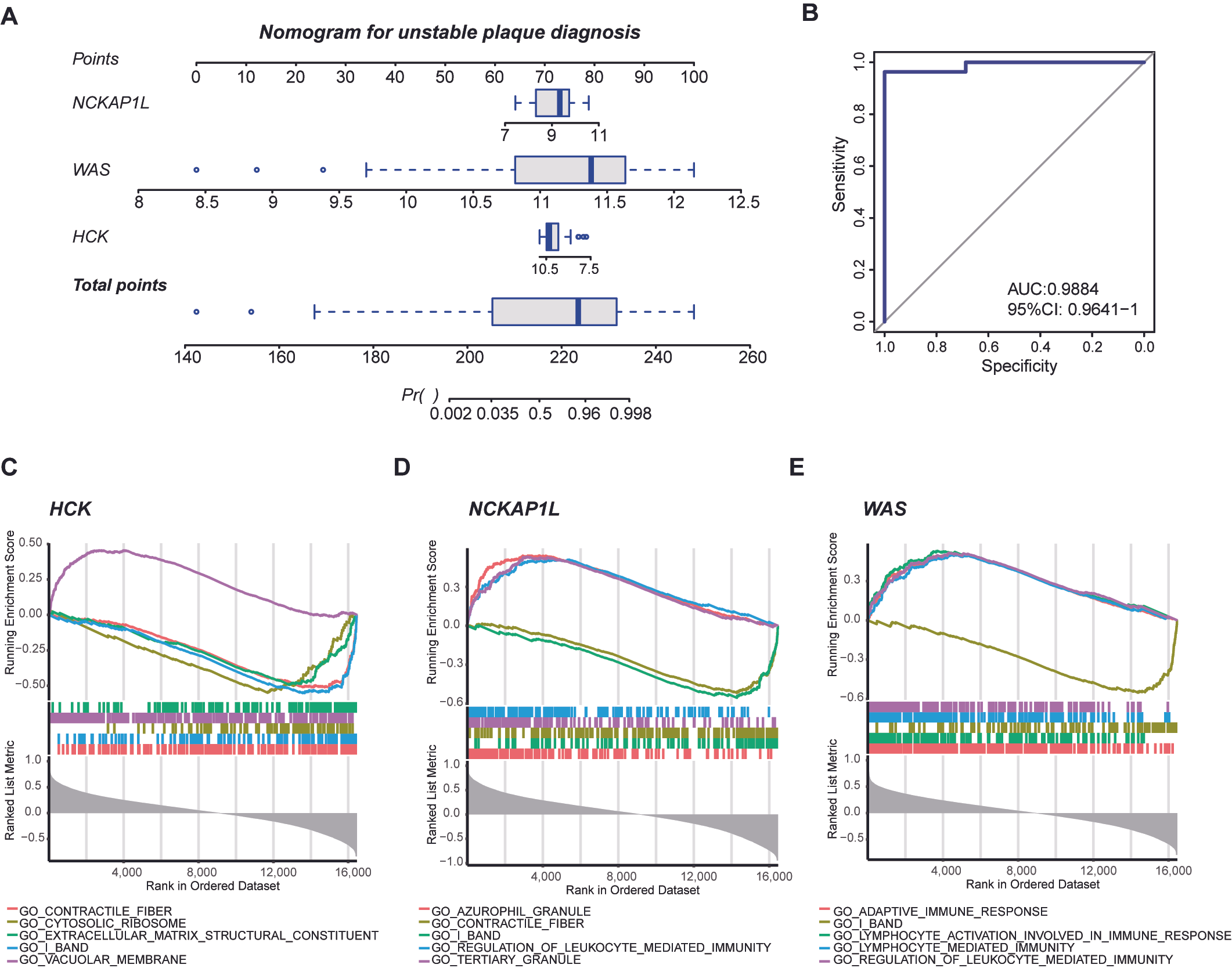
3.5. Nomogram for Diagnosing Unstable Plaques and Single-Gene GSEA of Biomarkers
3.6. Immune Infiltration Landscape of Atherosclerotic Plaques
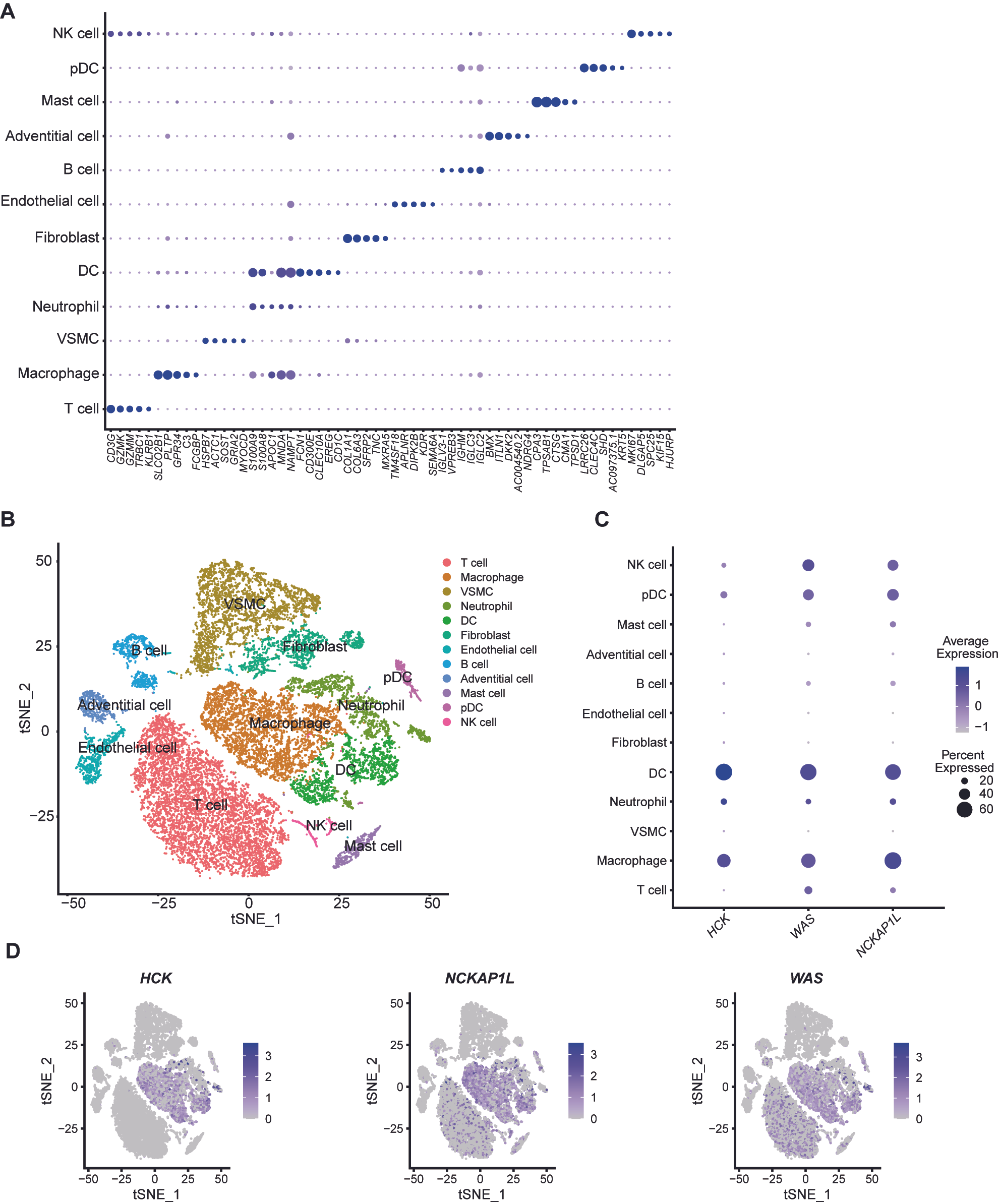
3.7. Characterization of Biomarkers’ Expression in Single-Cell mRNA Data of Unstable Plaques
3.8. Potential Subtypes in Unstable Plaques
3.9. Validation of Periodontitis-Associated Atherosclerotic Biomarker Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CDF | Cumulative Distribution Function |
| DEG | differentially expressed genes |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| FC | fold change |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GSEA | gene set enrichment analysis |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| miRNA | micro RNA |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristics |
| SVM-RFE | support vector machine recursive feature elimination |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TOM | Topological Overlap Matrix |
| WGCNA | weighted genes co-expression network analysis |
| VSMCs | vascular smooth muscle cells |
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baaten, C.C.F.M.J.; Nagy, M.; Bergmeier, W.; Spronk, H.M.H.; van der Meijden, P.E.J. Platelet biology and function: Plaque erosion vs. rupture. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Cui, Z.Y.; Huang, X.F.; Zhang, D.D.; Guo, R.J.; Han, M. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: Signaling pathways and therapeutic intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.J.; Blankstein, R.; Min, J.K. Outcomes in Stable Coronary Disease: Is Defining High-Risk Atherosclerotic Plaque Important? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, S. What makes a plaque rupture? A simple answer seems too much to ask for. EuroIntervention 2023, 18, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devesa, A.; Ibanez, B.; Malick, W.A.; Tinuoye, E.O.; Bustamante, J.; Peyra, C.; Rosenson, R.S.; Bhatt, D.L.; Stone, G.W.; Fuster, V. Primary Prevention of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Young Adults: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2152–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauerman, H.L.; Ibanez, B. The Edge of Time in Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbab-Zadeh, A.; Fuster, V. The myth of the “vulnerable plaque”: Transitioning from a focus on individual lesions to atherosclerotic disease burden for coronary artery disease risk assessment. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasser, L.; Lamster, I.B. Prevention and management of periodontal diseases and dental caries in the older adults. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 84, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, B.G.; Van Dyke, T.E. The role of inflammation and genetics in periodontal disease. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 83, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, M.; Polizzi, A.; Santonocito, S.; Romano, A.; Lombardi, T.; Isola, G. Impact of Oral Microbiome in Periodontal Health and Periodontitis: A Critical Review on Prevention and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Molina, A.; Buhlin, K.; Klinge, B. Periodontal diseases and association with atherosclerotic disease. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 83, 66–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.D.; Elter, J.R.; Heiss, G.; Couper, D.; Mauriello, S.M.; Offenbacher, S. Relationship of periodontal disease to carotid artery intima-media wall thickness: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, N.; Ahlqvist, J.; Näslund, U.; Buhlin, K.; Gustafsson, A.; Kjellström, B.; Klinge, B.; Rydén, L.; Levring Jäghagen, E. Associations among Periodontitis, Calcified Carotid Artery Atheromas, and Risk of Myocardial Infarction. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G. Interconnection of periodontal disease and comorbidities: Evidence, mechanisms, and implications. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 89, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Yu, X.; Saha, G.; Kalafati, L.; Ioannidis, C.; Mitroulis, I.; Netea, M.G.; Chavakis, T.; Hajishengallis, G. Maladaptive innate immune training of myelopoiesis links inflammatory comorbidities. Cell 2022, 185, 1709–1727.e1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carra, M.C.; Rangé, H.; Caligiuri, G.; Bouchard, P. Periodontitis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A critical appraisal. Periodontol. 2000 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhao, L. PAMPs and DAMPs as the Bridge Between Periodontitis and Atherosclerosis: The Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 856118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chitnis, N.; Monos, D.; Dinh, A. Next-generation sequencing technologies: An overview. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greener, J.G.; Kandathil, S.M.; Moffat, L.; Jones, D.T. A guide to machine learning for biologists. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebschull, M.; Demmer, R.T.; Grün, B.; Guarnieri, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Papapanou, P.N. Gingival tissue transcriptomes identify distinct periodontitis phenotypes. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Goossens, P.; Juhasz, P.; Eijgelaar, W.; Manca, M.; Karel, J.M.H.; Smirnov, E.; Sikkink, C.; Mees, B.M.E.; Waring, O.; et al. Integrative multiomics analysis of human atherosclerosis reveals a serum response factor-driven network associated with intraplaque hemorrhage. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Santibanez-Koref, M.; Polvikoski, T.; Birchall, D.; Mendelow, A.D.; Keavney, B. Increased expression of fatty acid binding protein 4 and leptin in resident macrophages characterises atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Atherosclerosis 2013, 226, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashore, A.C.; Yan, H.; Xue, C.; Zhu, L.Y.; Kim, E.; Mawson, T.; Coronel, J.; Chung, A.; Sachs, N.; Ho, S.; et al. High-Dimensional Single-Cell Multimodal Landscape of Human Carotid Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 930–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.; Meltzer, P.S. GEOquery: A bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1846–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Treviño, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Bai, J.; Chen, J.; Jiang, W.; Yang, K.; Ou, Q.; et al. CellMarker 2.0: An updated database of manually curated cell markers in human/mouse and web tools based on scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D870–D876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutzan, N.; Kajikawa, T.; Abusleme, L.; Greenwell-Wild, T.; Zuazo, C.E.; Ikeuchi, T.; Brenchley, L.; Abe, T.; Hurabielle, C.; Martin, D.; et al. A dysbiotic microbiome triggers T(H)17 cells to mediate oral mucosal immunopathology in mice and humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat0797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature 2021, 592, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianopoulos, I.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Macrophage profiling in atherosclerosis: Understanding the unstable plaque. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2024, 119, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Cao, S.; Chen, M. Integrated analysis and exploration of potential shared gene signatures between carotid atherosclerosis and periodontitis. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Feng, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, S. Shared pyroptosis pathways and crosstalk genes underpin inflammatory links between periodontitis and atherosclerosis. Immunobiology 2025, 230, 152880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.V.O.; Mosley, G.A.; Ross, W.; Dagher, A.; Martins, B.G.D.S.; Fernandes, J.C.H. Revisiting Socransky’s Complexes: A Review Suggesting Updated New Bacterial Clusters (GF-MoR Complexes) for Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Gong, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, B. Bioinformatics analysis and reveal potential crosstalk genetic and immune relationships between atherosclerosis and periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Tumanov, S.; Stanley, C.P.; Kong, S.M.Y.; Nadel, J.; Vigder, N.; Newington, D.L.; Wang, X.S.; Dunn, L.L.; Stocker, R. Destabilization of Atherosclerotic Plaque by Bilirubin Deficiency. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 812–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Ouyang, L.; Yu, C.; Carr, S.M.; Ramprasath, T.; Liu, Z.; Song, P.; Zou, M.H.; Ding, Y. Nicotine exacerbates atherosclerosis and plaque instability via NLRP3 inflammasome activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Theranostics 2023, 13, 2825–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation during the life cycle of the atherosclerotic plaque. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Menon, M.C.; Wang, W.; Fu, J.; Yi, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Mou, L.; Banu, K.; et al. HCK induces macrophage activation to promote renal inflammation and fibrosis via suppression of autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolinska, M.J.; Horwood, N.J.; Page, T.H.; Smallie, T.; Foxwell, B.M. Chemical inhibition of Src family kinases affects major LPS-activated pathways in primary human macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, I.; Cougoule, C.; Drechsler, M.; Bermudez, B.; Koenen, R.R.; Sluimer, J.; Wolfs, I.; Döring, Y.; Herias, V.; Gijbels, M.; et al. Hck/Fgr Kinase Deficiency Reduces Plaque Growth and Stability by Blunting Monocyte Recruitment and Intraplaque Motility. Circulation 2015, 132, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.N.; Rosenzwajg, M.; Carapito, R.; Shahrooei, M.; Konantz, M.; Khan, A.; Miao, Z.; Groß, M.; Tranchant, T.; Radosavljevic, M.; et al. NCKAP1L defects lead to a novel syndrome combining immunodeficiency, lymphoproliferation, and hyperinflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20192275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Staehling-Hampton, K.; Appleby, M.W.; Brunkow, M.E.; Habib, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ramsdell, F.; Liggitt, H.D.; Freie, B.; Tsang, M.; et al. A point mutation in the murine Hem1 gene reveals an essential role for Hematopoietic protein 1 in lymphopoiesis and innate immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2899–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, O.D.; Rentel, M.C.; Ott, A.; Brown, G.E.; Jedrychowski, M.; Yaffe, M.B.; Gygi, S.P.; Cantley, L.C.; Bourne, H.R.; Kirschner, M.W. Hem-1 complexes are essential for Rac activation, actin polymerization, and myosin regulation during neutrophil chemotaxis. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Borek, D.; Padrick, S.B.; Gomez, T.S.; Metlagel, Z.; Ismail, A.M.; Umetani, J.; Billadeau, D.D.; Otwinowski, Z.; Rosen, M.K. Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex. Nature 2010, 468, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.A.; Comrie, W.A.; Poli, M.C.; Similuk, M.; Oler, A.J.; Faruqi, A.J.; Kuhns, D.B.; Yang, S.; Vargas-Hernández, A.; Carisey, A.F.; et al. HEM1 deficiency disrupts mTORC2 and F-actin control in inherited immunodysregulatory disease. Science 2020, 369, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, E.; Thrasher, A.J. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein: Emerging mechanisms in immunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancliff, P.J.; Blundell, M.P.; Cory, G.O.; Calle, Y.; Worth, A.; Kempski, H.; Burns, S.; Jones, G.E.; Sinclair, J.; Kinnon, C.; et al. Two novel activating mutations in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein result in congenital neutropenia. Blood 2006, 108, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoenkam, J.; Paensuwan, P.; Wipa, P.; Schamel, W.W.A.; Pongcharoen, S. Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein: Roles in Signal Transduction in T Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 674572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, E.; Rai, R.; Lötscher, J.; Hollinshead, M.; Markelj, G.; Thaventhiran, J.; Worth, A.; Cavazza, A.; Hess, C.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; et al. Wiskott Aldrich syndrome protein regulates non-selective autophagy and mitochondrial homeostasis in human myeloid cells. Elife 2020, 9, e55547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, L.; An, Y.; Song, W.; et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein maintains regulatory T cell tolerance by modulating their surface IL-2 receptor levels. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 149, 103336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snapper, S.B.; Rosen, F.S.; Mizoguchi, E.; Cohen, P.; Khan, W.; Liu, C.H.; Hagemann, T.L.; Kwan, S.P.; Ferrini, R.; Davidson, L.; et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein-deficient mice reveal a role for WASP in T but not B cell activation. Immunity 1998, 9, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvez, R.; Lafouresse, F.; De Meester, J.; Galy, A.; Valitutti, S.; Dupré, L. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein permits assembly of a focused immunological synapse enabling sustained T-cell receptor signaling. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.J. Macrophages in Atherosclerosis Regression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvalho, J.M.; Fernandes, J.C.H.; Castilho, R.M.; Fernandes, G.V.O. The Macrophage’s Role on Bone Remodeling and Osteogenesis: A Systematic Review. Clinic Rev. Bone Miner. Metab. 2023, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, A.C. Inflammation Resolution: Implications for Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.L.A.; Schmidt, V.F.; Öcal, O.; von Thaden, A.; Dietrich, O.; Popper, B.; Elges, S.; Seidensticker, M.; Ricke, J.; Kimm, M.A.; et al. A minimally invasive animal model of atherosclerosis and neointimal hyperplasia for translational research. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2025, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| GSE Number | Platform | PMID | Samples | Source Types | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE16134 | GPL570 | 24646639 | 240 Periodontitis and 70 Control | Gingival tissue | Test dataset |
| GSE163154 | GPL6104 | 37920458 | 16 Stable plaque and 27 Unstable plaque | Carotid plaque | Test dataset |
| GSE41571 | GPL570 | 23122912 | 6 Stable plaque and 5 Unstable plaque | Carotid plaque | Validation dataset |
| GSE253904 | GPL24676 | 38385291 | 6 Unstable plaque | Carotid plaque | Validation dataset |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.; Xie, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Y.; Wang, B. Bioinformatics Approach to Investigating the Immuno-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Periodontitis in the Progression of Atherosclerosis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030197
Yang W, Xie J, Zhao X, Li X, Liu Q, Sun J, Zhang R, Wei Y, Wang B. Bioinformatics Approach to Investigating the Immuno-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Periodontitis in the Progression of Atherosclerosis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(3):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030197
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wenling, Jianhua Xie, Xing Zhao, Xuelian Li, Qingyi Liu, Jinpeng Sun, Ruiyu Zhang, Yumiao Wei, and Boyuan Wang. 2025. "Bioinformatics Approach to Investigating the Immuno-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Periodontitis in the Progression of Atherosclerosis" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 3: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030197
APA StyleYang, W., Xie, J., Zhao, X., Li, X., Liu, Q., Sun, J., Zhang, R., Wei, Y., & Wang, B. (2025). Bioinformatics Approach to Investigating the Immuno-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Periodontitis in the Progression of Atherosclerosis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(3), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030197






