Cisplatin-Mediated IL-6 and IDO1 Suppression in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Implications for Tumor Microenvironment Modulation In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Cells
2.2. Evidence of Eligible MSC Classification
2.3. Stromal Cell Differentiation and Histological Staining
2.4. Flow Cytometry and Surface Characterization
2.5. Cytotoxicity Evaluation with the 3-[4,5 Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium-bromid (MTT) Assay
2.6. Migration Analysis with the Scratch Assay
2.7. Protein Determination with Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.9. Illustration of Data and Statistical Evaluation
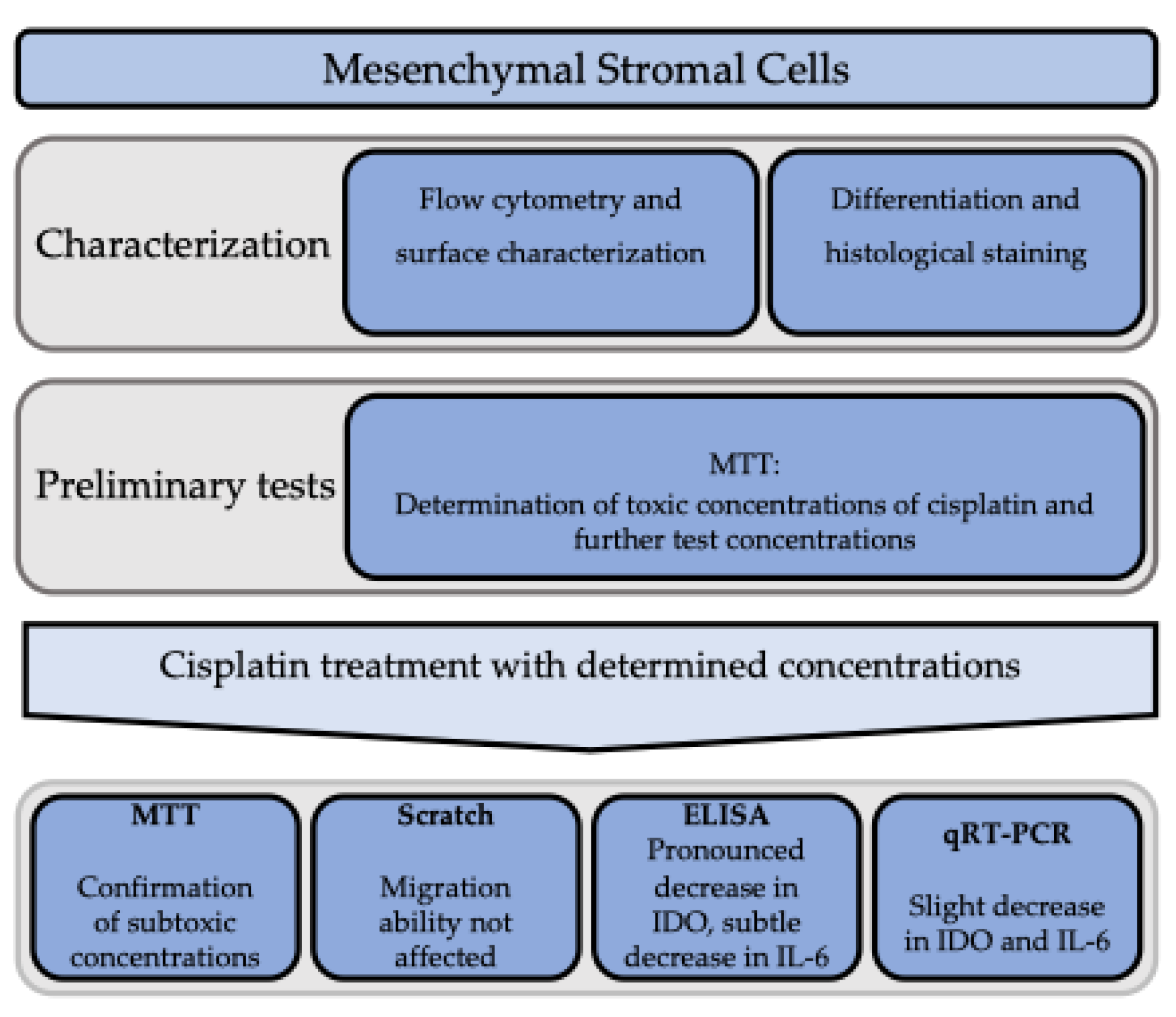
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
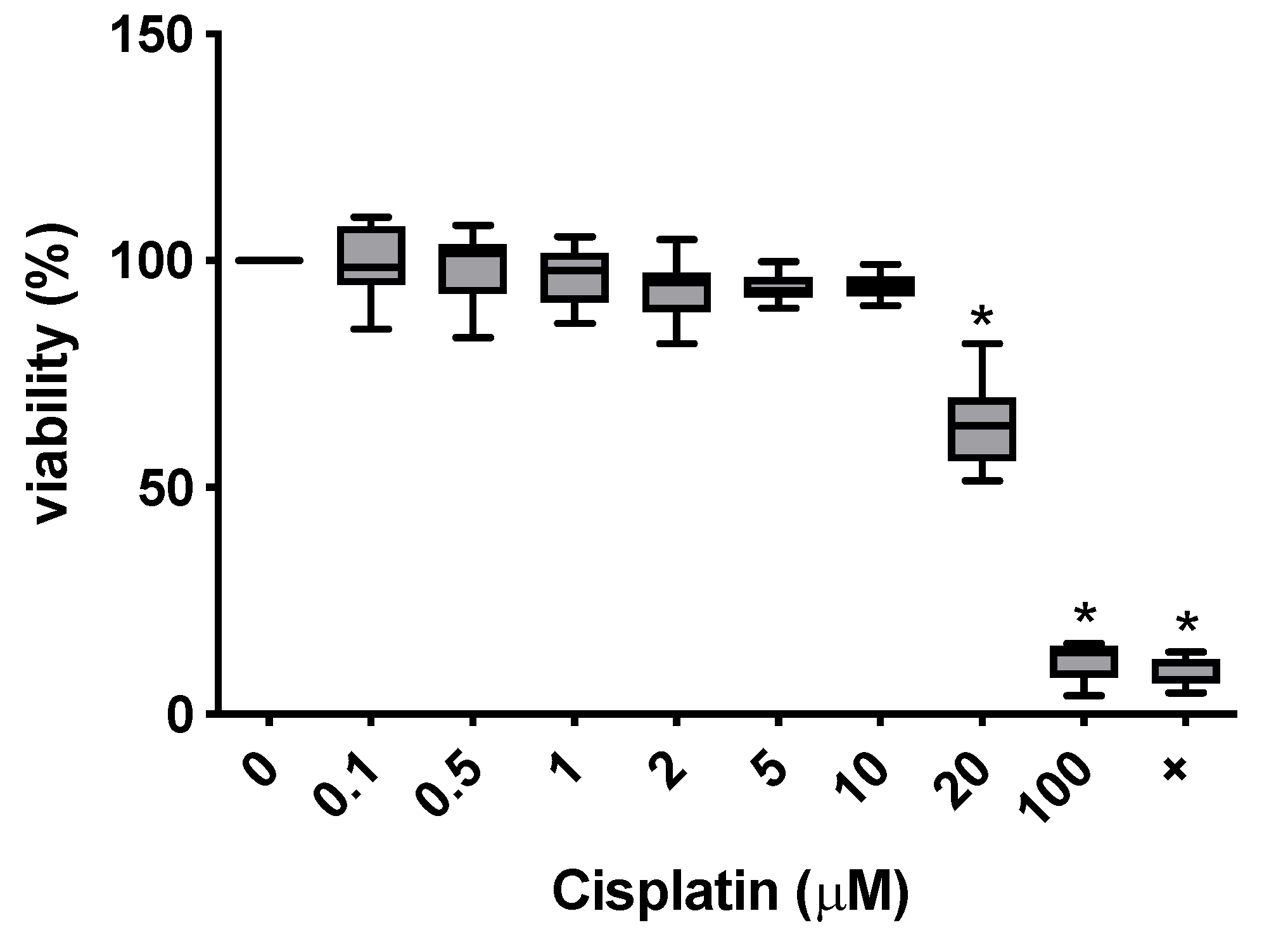
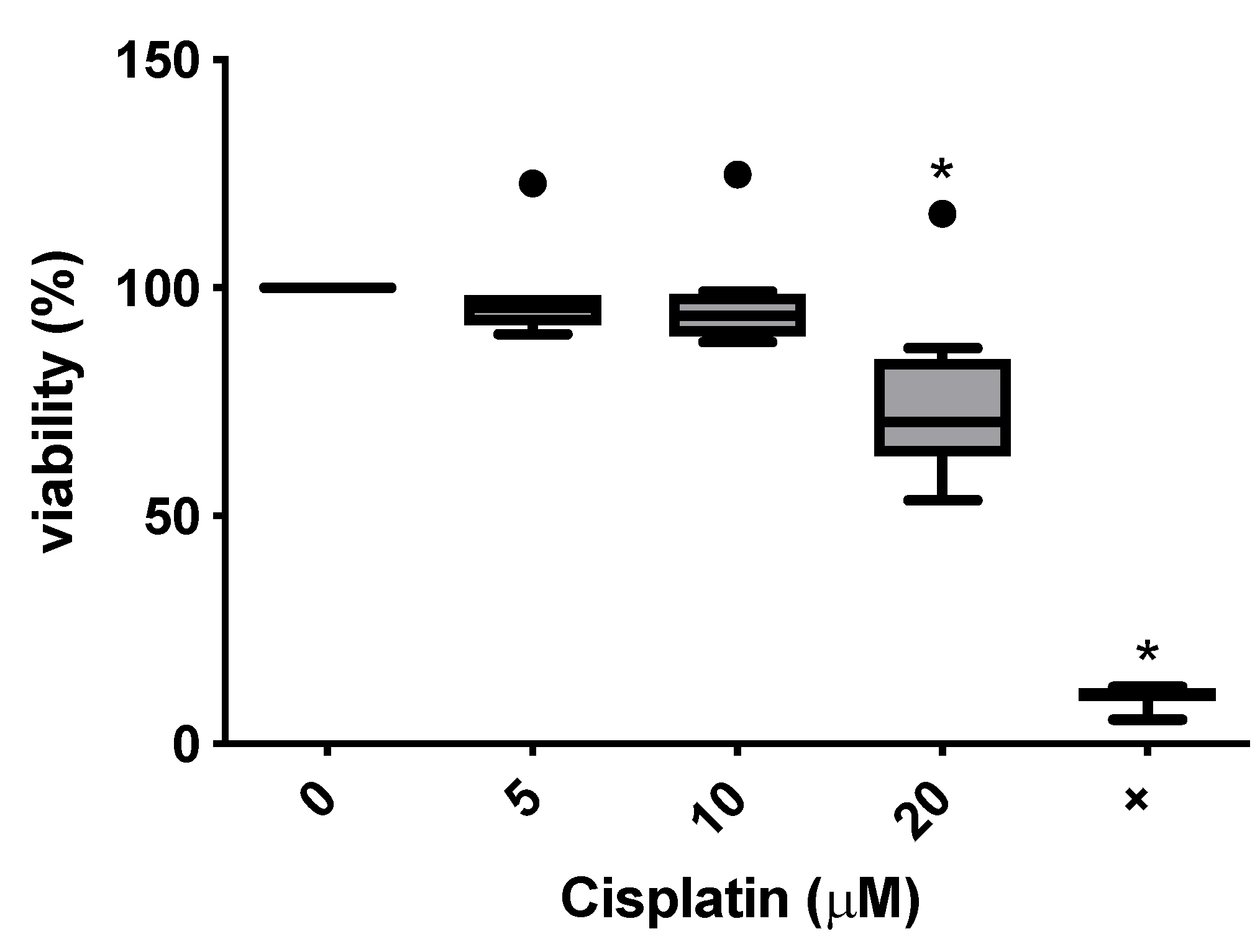
3.2. Toxicity of Cisplatin in the MTT Assay
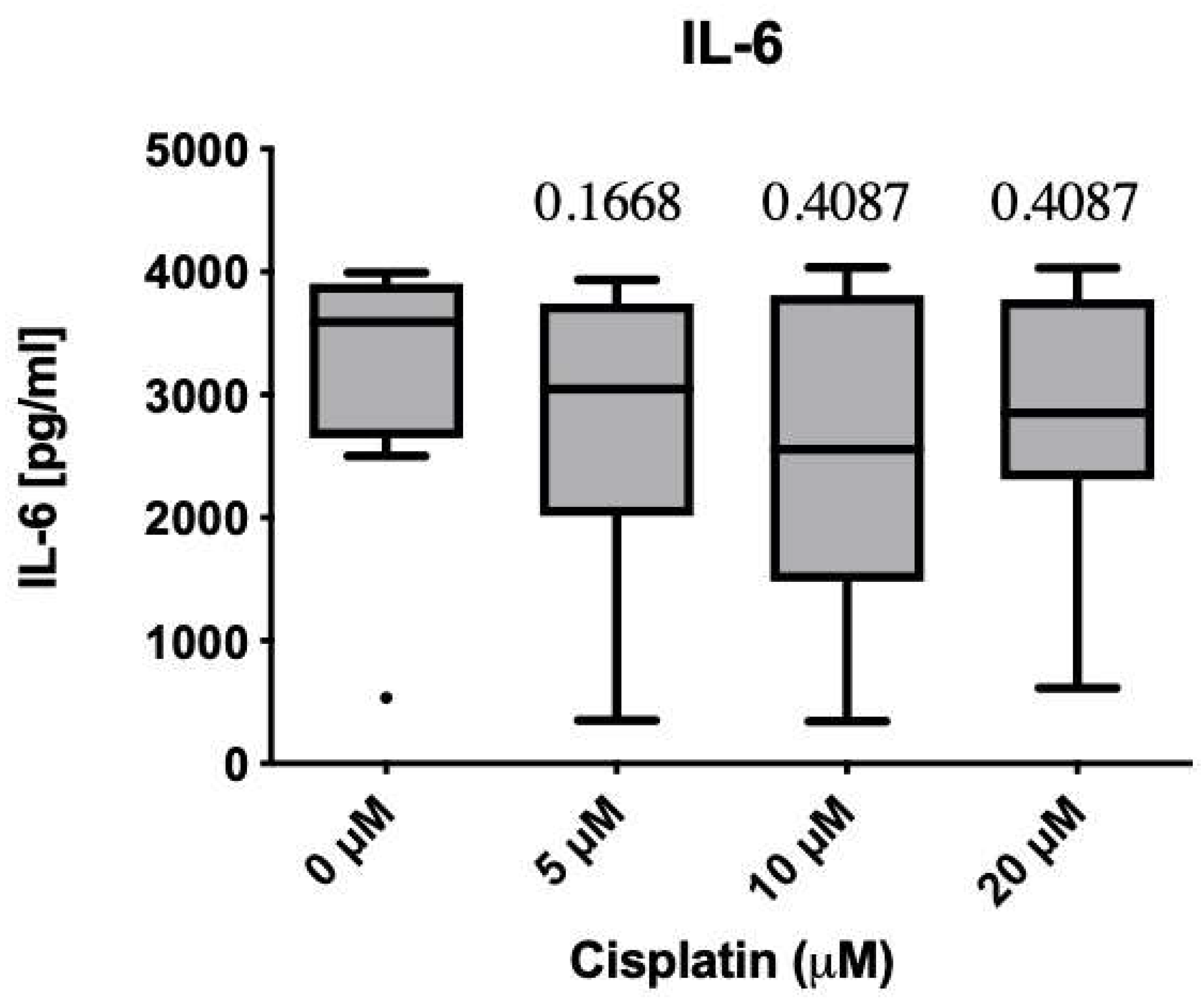
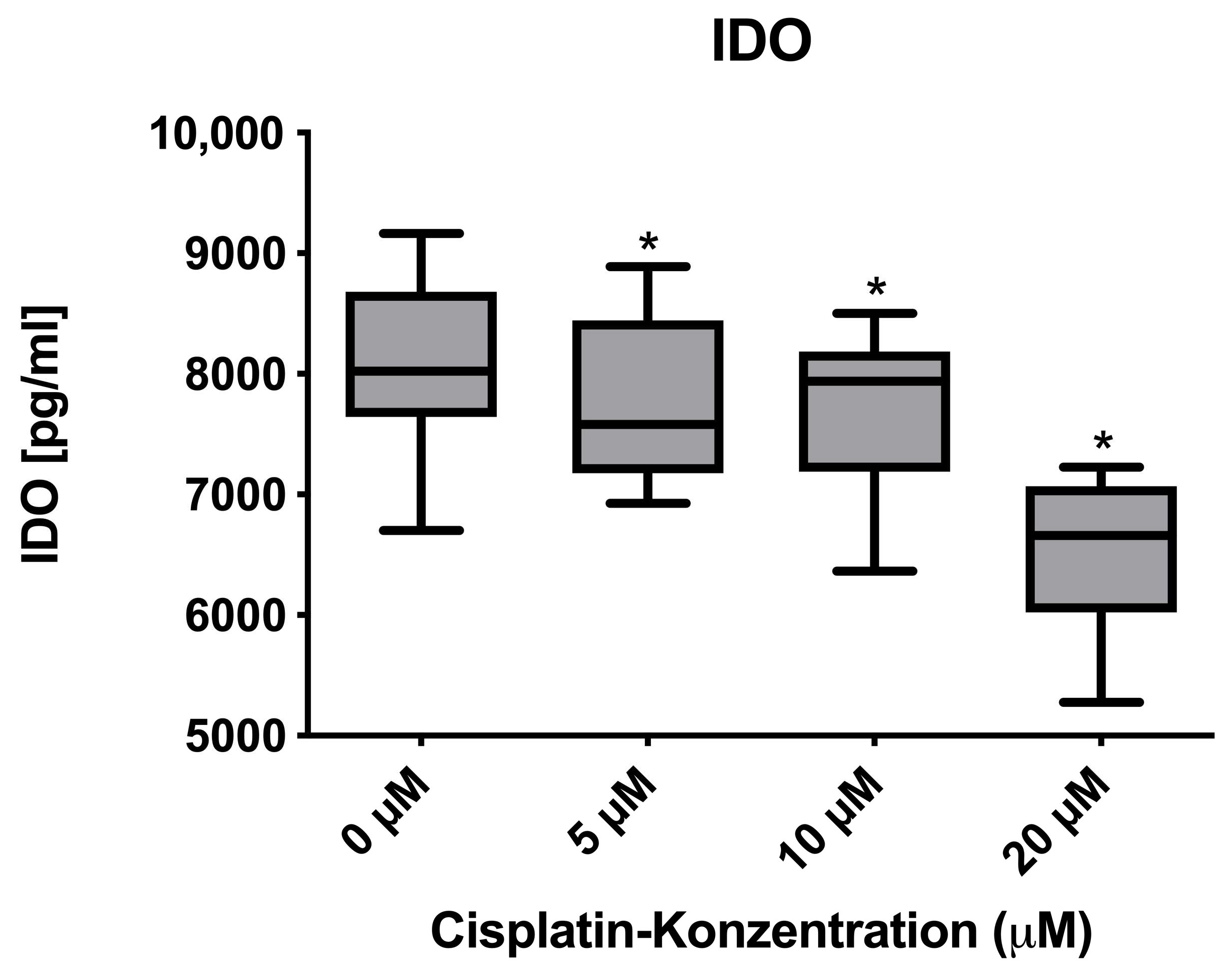
3.3. Immunomodulatory Effects on Protein and mRNA Levels
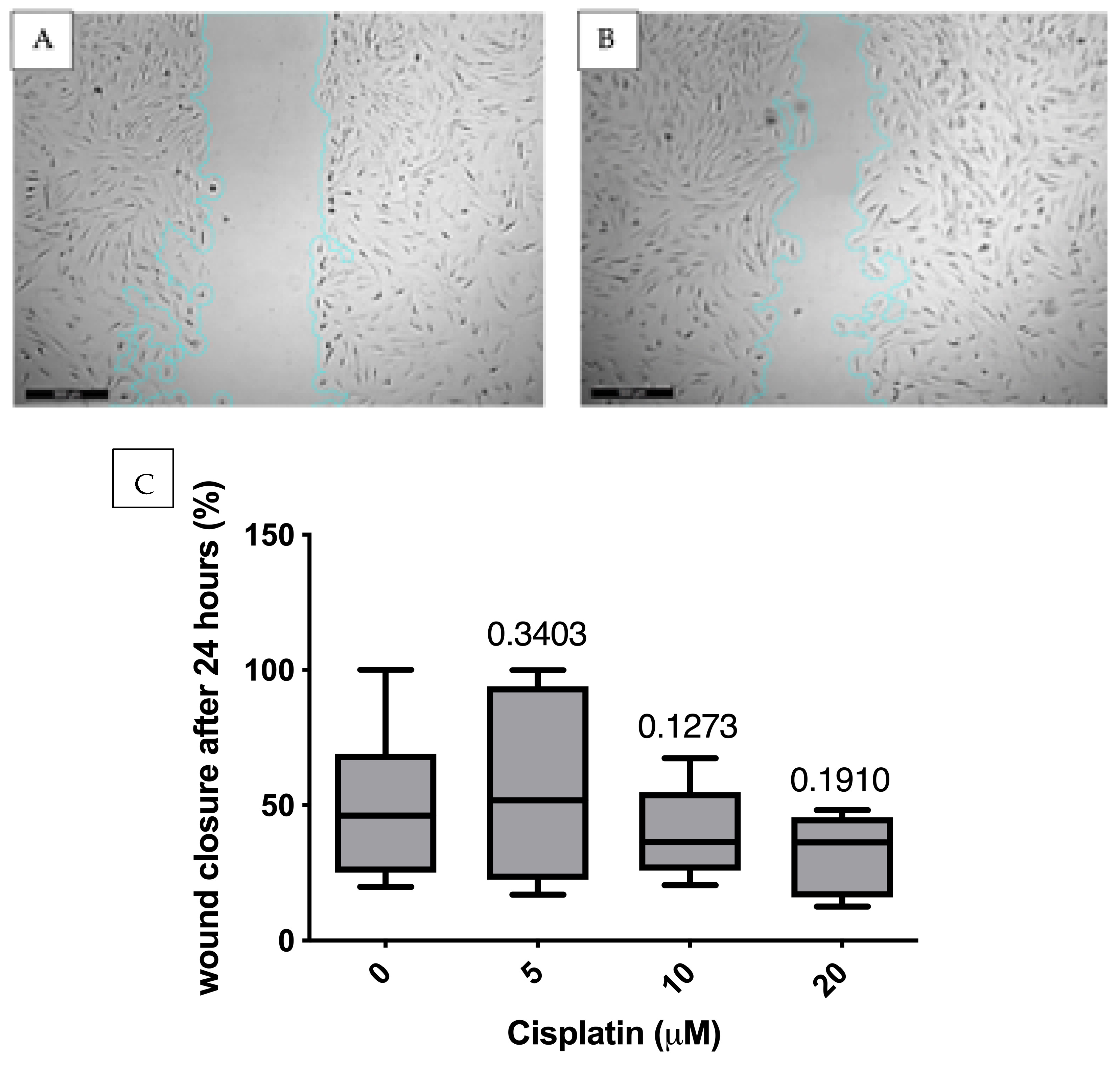
3.4. Migration Analysis Using Scratch Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mushahary, D.; Spittler, A.; Kasper, C.; Weber, V.; Charwat, V. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytom. Part A 2018, 93, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, B.C.; Cao, T.; Haider, H.K.; Wang, D.Z.; Sim, E.K.; Ng, S.C. An overview and synopsis of techniques for directing stem cell differentiation in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 315, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trounson, A.; McDonald, C. Stem Cell Therapies in Clinical Trials: Progress and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, N.; Amu, S.; Iacobaeus, E.; Boberg, E.; Le Blanc, K. Current perspectives on mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for graft versus host disease. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, S.; Prange, J.A.; Baumgartner, V.; Mohr-Haralampieva, D.; Eberli, D. Adult stem cell sources for skeletal and smooth muscle tissue engineering. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebel, C.; Burdick, J.A. Engineering Stem and Stromal Cell Therapies for Musculoskeletal Tissue Repair. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosson, S.; Otte, E.A.; Hezaveh, H.; Cooper-White, J.J. Concise review: Tailoring bioengineered scaffolds for stem cell applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacakova, L.; Zarubova, J.; Travnickova, M.; Musilkova, J.; Pajorova, J.; Slepicka, P.; Kasalkova, N.S.; Svorcik, V.; Kolska, Z.; Motarjemi, H.; et al. Stem cells: Their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells—A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Hou, J.; Shao, C.; Wang, Y. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbie, L.; Buckanovich, R.J.; Coffman, L. Carcinoma-Associated Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Architects of the Pro-tumorigenic Tumor Microenvironment. Stem Cells 2022, 40, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Scholtemeijer, M.; Shah, K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immunomodulation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, A.R.R.; Dahlke, M.H. Immunomodulation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Mechanisms of Action of Living, Apoptotic, and Dead MSCs. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tam, P.K.H. Immunomodulatory Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Potential Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R.; Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Z.; Song, S.; Ge, H. IDO1 Expression Increased After Neoadjuvant Therapy Predicts Poor Pathologic Response and Prognosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ma, F.; Yu, D. The diverse effects of cisplatin on tumor microenvironment: Insights and challenges for the delivery of cisplatin by nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.J.M.; Theodoropoulos, G.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, C.; Sha, W.; Feun, L.G.; Lampidis, T.J.; Savaraj, N.; Wangpaichitr, M. Targeting the Kynurenine Pathway for the Treatment of Cisplatin-Resistant Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Ran, R.; Li, X.; Ling, H.; Wen, F.; Yu, T. IDO1 Modulates the Sensitivity of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin through ROS/p53-Dependent Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Ren, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Rabson, A.B.; Roberts, A.I.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Mesenchymal stem cells use IDO to regulate immunity in tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Biasi, A.R.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Adusumilli, P.S. Cisplatin-induced antitumor immunomodulation: A review of preclinical and clinical evidence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5384–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolekova, S.; Matuskova, M.; Bohac, M.; Toro, L.; Durinikova, E.; Tyciakova, S.; Demkova, L.; Gursky, J.; Kucerova, L. Cisplatin-induced mesenchymal stromal cells-mediated mechanism contributing to decreased antitumor effect in breast cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabosch, S.; Bulatovic, M.; Zeng, F.; Ma, T.; Zhang, L.; Ross, M.; Brozick, J.; Fang, Y.; Tseng, G.; Kim, E.; et al. Cisplatin-induced immune modulation in ovarian cancer mouse models with distinct inflammation profiles. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2380–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudenschild, C.C.; Schwartz, S.M. Endothelial regeneration. II. Restitution of endothelial continuity. Lab. Investig. 1979, 41, 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Bellagamba, B.C.; Abreu, B.R.; Grivicich, I.; Markarian, C.F.; Chem, E.; Camassola, M.; Nardi, N.B.; Dihl, R.R. Human mesenchymal stem cells are resistant to cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of cisplatin in vitro. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.L.; Hsu, Y.T.; Wu, C.C.; Lai, Y.Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.C.; Wu, T.C.; Hung, C.F. Dose-dense chemotherapy improves mechanisms of antitumor immune response. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koufos, N.; Michailidou, D.; Xynos, I.D.; Tomos, P.; Athanasiadou, K.; Kosmas, C.; Tsavaris, N. Modulation of peripheral immune responses by paclitaxel-ifosfamide-cisplatin chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Mirza, N.; Fricke, I.; Chiappori, A.; Thompson, P.; Williams, N.; Bepler, G.; Simon, G.; Janssen, W.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Combination of p53 cancer vaccine with chemotherapy in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, M.; Cereda, V.; di Bari, M.G.; Formica, V.; Spila, A.; Jochems, C.; Farsaci, B.; Donahue, R.; Gulley, J.L.; Schlom, J.; et al. Effects of conventional therapeutic interventions on the number and function of regulatory T cells. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e27025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchikawa, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Yamamura, Y.; Shichinohe, T.; Hirano, S.; Kondo, S. The immunological impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on the tumor microenvironment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, G.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Song, H. Preconditioning chemotherapy with cisplatin enhances the antitumor activity of cytokine-induced killer cells in a murine melanoma model. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2012, 27, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.W.; Hung, C.F.; Alvarez, R.D.; Trimble, C.; Huh, W.K.; Kim, D.; Chuang, C.M.; Lin, C.T.; Tsai, Y.C.; He, L.; et al. Pretreatment with cisplatin enhances E7-specific CD8+ T-Cell-mediated antitumor immunity induced by DNA vaccination. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3185–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.; Shamsasenjan, K.; Ahmadi, M.; Beheshti, S.A.; Saleh, M. Mesenchymal stem cells and natural killer cells interaction mechanisms and potential clinical applications. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najar, M.; Fayyad-Kazan, M.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Fayyad-Kazan, H.; Lagneaux, L. Mesenchymal stromal cells of the bone marrow and natural killer cells: Cell interactions and cross modulation. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgaard, R.B.; Zamarin, D.; Li, Y.; Gasmi, B.; Munn, D.H.; Allison, J.P.; Merghoub, T.; Wolchok, J.D. Tumor-Expressed IDO Recruits and Activates MDSCs in a Treg-Dependent Manner. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forteza, M.J.; Polyzos, K.A.; Baumgartner, R.; Suur, B.E.; Mussbacher, M.; Johansson, D.K.; Hermansson, A.; Hansson, G.K.; Ketelhuth, D.F.J. Activation of the Regulatory T-Cell/Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Axis Reduces Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Mice. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracho-Sanchez, E.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Brusko, M.A.; Wallet, M.A.; Keselowsky, B.G. Dendritic Cells Treated with Exogenous Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Maintain an Immature Phenotype and Suppress Antigen-specific T cell Proliferation. J. Immunol. Regen. Med. 2019, 5, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Volarevic, A.; Djonov, V.G.; Jovicic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell: A Friend or Foe in Anti-Tumor Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lob, S.; Konigsrainer, A. Is IDO a key enzyme bridging the gap between tumor escape and tolerance induction? Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2008, 393, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Choi, H.K.; Lee, K.J.; Jung, J.Y.; Hur, G.Y.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, C.; Shim, J.J.; In, K.H.; et al. The immune tolerance of cancer is mediated by IDO that is inhibited by COX-2 inhibitors through regulatory T cells. J. Immunother. 2009, 32, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanikas, V.; Zamanakou, M.; Kerenidi, T.; Dahabreh, J.; Hevas, A.; Nakou, M.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Germenis, A.E. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) expression in lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, M.; Baumann, H.; Freer, G.; Freudenberg, M.; Lamers, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Zinkernagel, R.; Bluethmann, H.; Kohler, G. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature 1994, 368, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Snick, J. Interleukin-6: An overview. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1990, 8, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashizume, M.; Hayakawa, N.; Mihara, M. IL-6 trans-signalling directly induces RANKL on fibroblast-like synovial cells and is involved in RANKL induction by TNF-alpha and IL-17. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, B.; Majidzadeh, A.K.; Ghadirian, R.; Mosayebzadeh, M.; Farahmand, L. Recruited bone marrow derived cells, local stromal cells and IL-17 at the front line of resistance development to anti-VEGF targeted therapies. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonov, D.C.; Ignatova, M.M.K.; Ananiev, J.R.; Gulubova, M.V. IL-6 Activities in the Tumour Microenvironment. Part 1. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, E.H.; Millan-Barea, L.R.; Zhuang, I.; Goulet, D.R.; Frose, J.; Hemann, M.T. Microenvironmental IL-6 inhibits anti-cancer immune responses generated by cytotoxic chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Riester, Z.; Huser, L.; Sticht, C.; Siebenmorgen, A.; Groth, C.; Hu, X.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J.S.; Umansky, V. IL-6 regulates CCR5 expression and immunosuppressive capacity of MDSC in murine melanoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Groth, C.; Lasser, S.; Arkhypov, I.; Petrova, V.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. IL-6 as a major regulator of MDSC activity and possible target for cancer immunotherapy. Cell Immunol. 2021, 359, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, E.H.; Gilbert, L.A.; Hemann, M.T. A senescence secretory switch mediated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation controls chemoprotective endothelial secretory responses. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, L.A.; Hemann, M.T. DNA damage-mediated induction of a chemoresistant niche. Cell 2010, 143, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, W.; Collins, M.A.; Bednar, F.; Rakshit, S.; Zetter, B.R.; Stanger, B.Z.; Chung, I.; Rhim, A.D.; di Magliano, M.P. Interleukin-6 is required for pancreatic cancer progression by promoting MAPK signaling activation and oxidative stress resistance. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6359–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, A.; Bhatt, A.N. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 11553–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
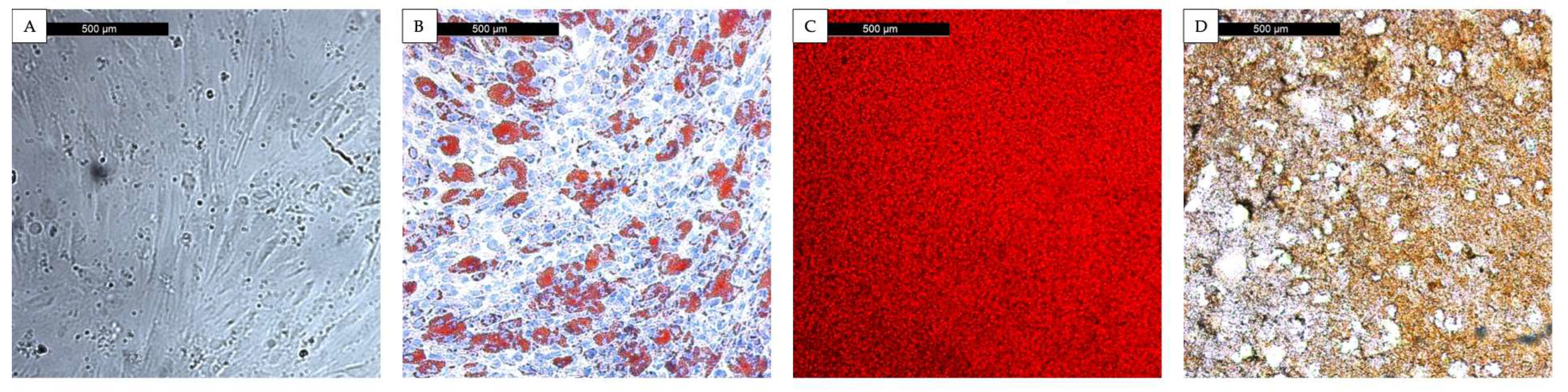



| Antibody | Source |
|---|---|
| APC mouse anti-human CD90 (559689) | Becton Dickinson GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany |
| FITC mouse anti-human CD105 (555690) | Becton Dickinson GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany |
| FITC mouse anti-human CD45 (555482) | Becton Dickinson GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany |
| PE mouse anti-human CD31 (555446) | Becton Dickinson GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany |
| PE mouse anti-human CD34 (550761) | Becton Dickinson GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany |
| PE mouse anti-human CD73 (550257) | Becton Dickinson GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany |
| FITC, Alexa Fluor® 488 goat anti-mouse IgG, 1:1000 | Life Technologies Corporation, Carlsbad, CA, USA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Fournier, A.; Würflein, E.; Moratin, H.; Stöth, M.; Ehret Kasemo, T.; Herrmann, M.; Goncalves, M.; Hagen, R.; Hackenberg, S.; Gehrke, T.; et al. Cisplatin-Mediated IL-6 and IDO1 Suppression in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Implications for Tumor Microenvironment Modulation In Vitro. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040231
von Fournier A, Würflein E, Moratin H, Stöth M, Ehret Kasemo T, Herrmann M, Goncalves M, Hagen R, Hackenberg S, Gehrke T, et al. Cisplatin-Mediated IL-6 and IDO1 Suppression in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Implications for Tumor Microenvironment Modulation In Vitro. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(4):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040231
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Fournier, Armin, Erik Würflein, Helena Moratin, Manuel Stöth, Totta Ehret Kasemo, Marietta Herrmann, Miguel Goncalves, Rudolf Hagen, Stephan Hackenberg, Thomas Gehrke, and et al. 2025. "Cisplatin-Mediated IL-6 and IDO1 Suppression in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Implications for Tumor Microenvironment Modulation In Vitro" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 4: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040231
APA Stylevon Fournier, A., Würflein, E., Moratin, H., Stöth, M., Ehret Kasemo, T., Herrmann, M., Goncalves, M., Hagen, R., Hackenberg, S., Gehrke, T., & Scherzad, A. (2025). Cisplatin-Mediated IL-6 and IDO1 Suppression in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Implications for Tumor Microenvironment Modulation In Vitro. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(4), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040231







