Poria cocos Ethanol Extract Restores MK-801-Induced Cytoskeleton Regulation in Neuro2A and IMR-32 Cells and Locomotor Hyperactivity in C57BL/6 Mice by Modulating the Rho Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the P. cocos Ethanol Extract and MK-801
2.2. Determination and Quantification of the Components in PCEE by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
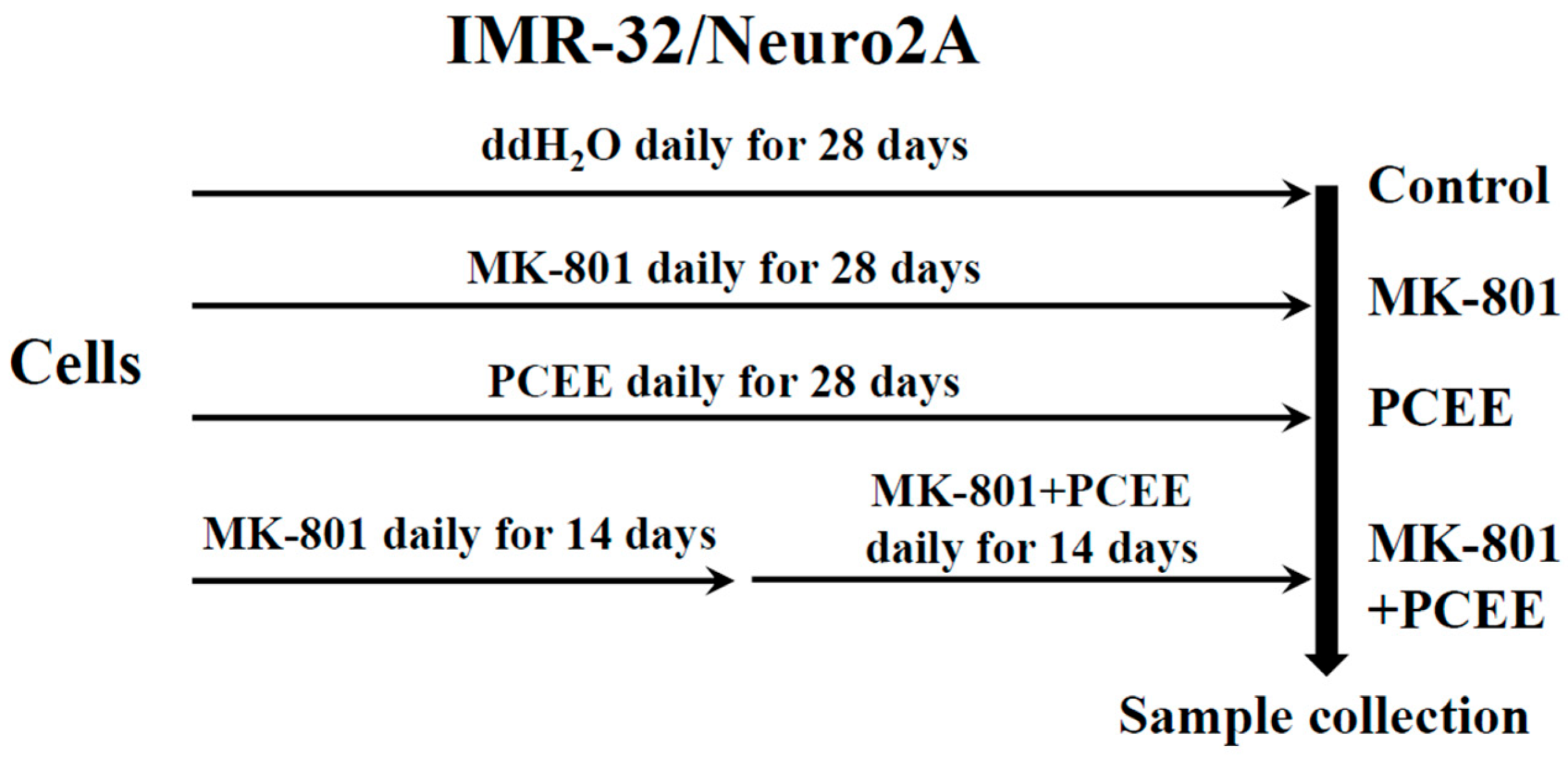
2.3. Cell Culture and Cell Stimulation
2.4. Animal Preparation and Experimental Protocol
2.5. Wound Healing Assay and Transwell Migration Assay
2.6. Total Protein Extraction and Immunoblotting
2.7. Fluorescence Staining of Activated RhoGDI1 and F-Actin
2.8. Open Field Test
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HPLC Confirmed PCEE Contained the Main Components of P. cocos
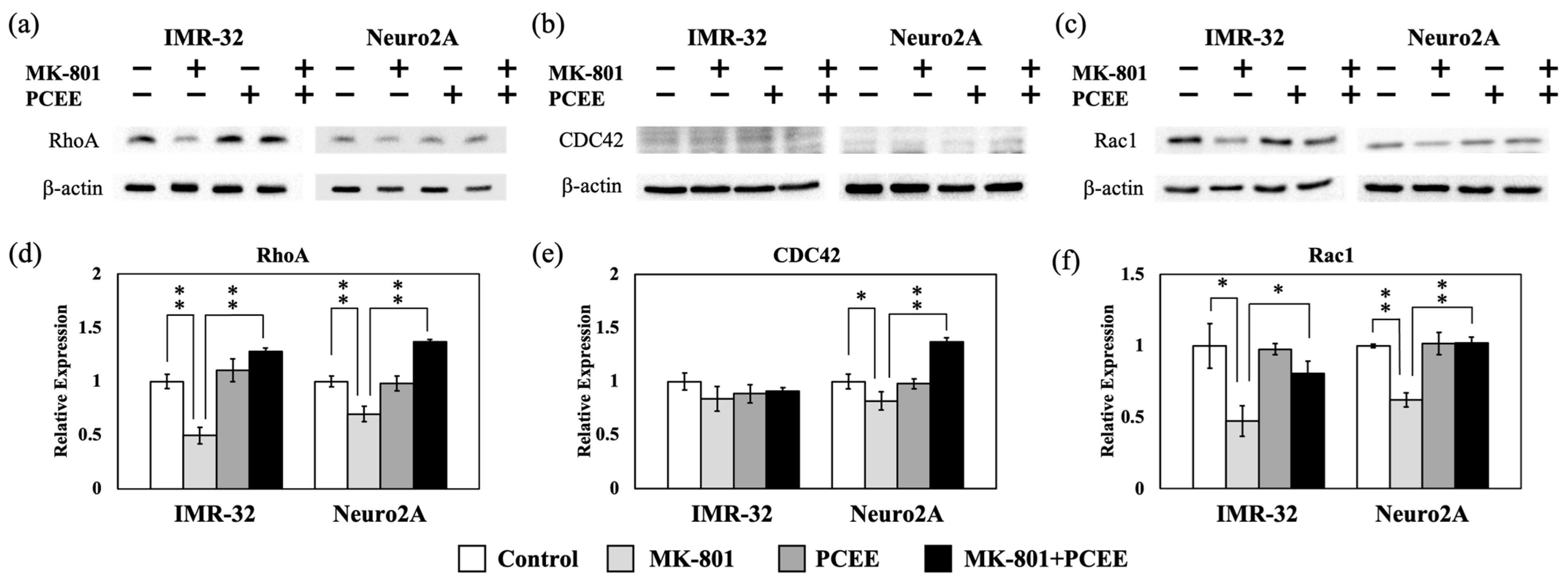
3.2. PCEE Modulates the Expression and Phosphorylation of RhoA, CDC42, and Rac1
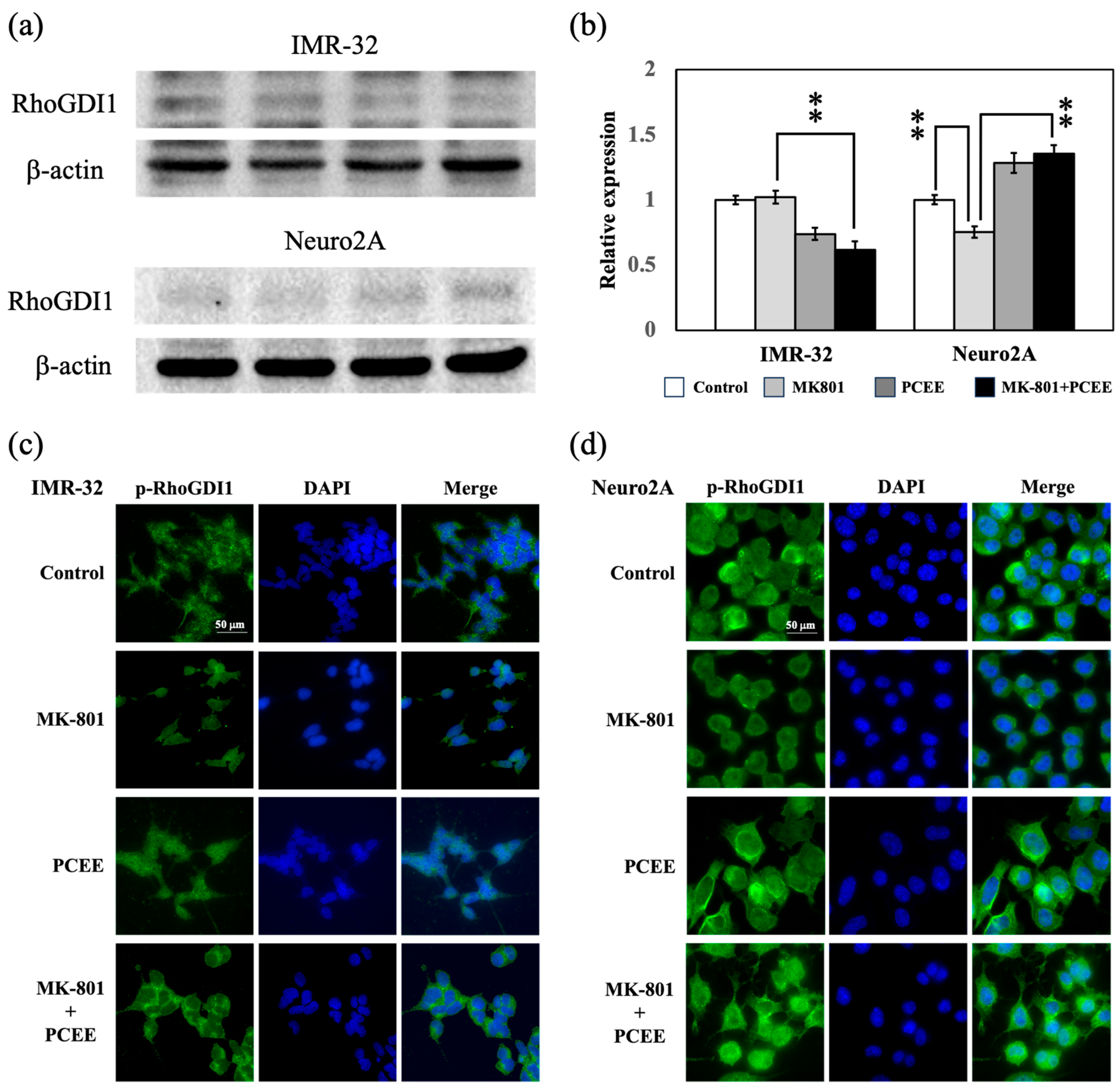
3.3. PCEE Inhibits the MK-801-Induced Phosphorylation of RhoGDI1
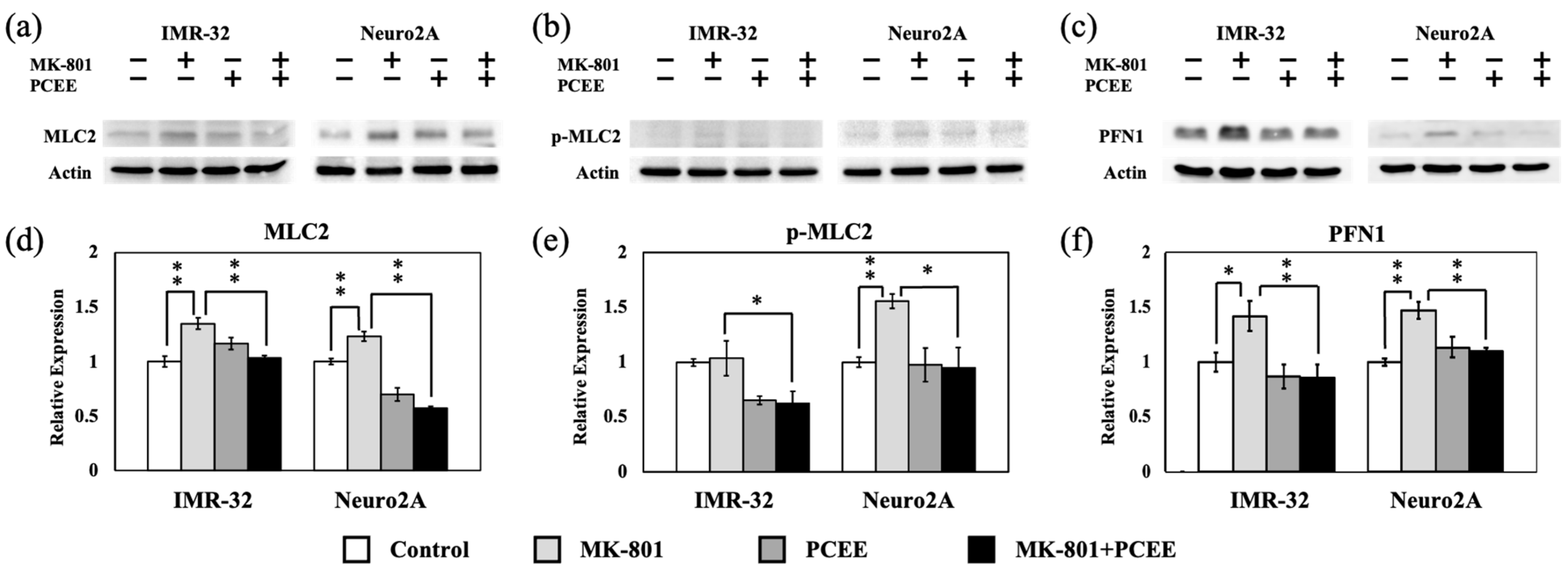
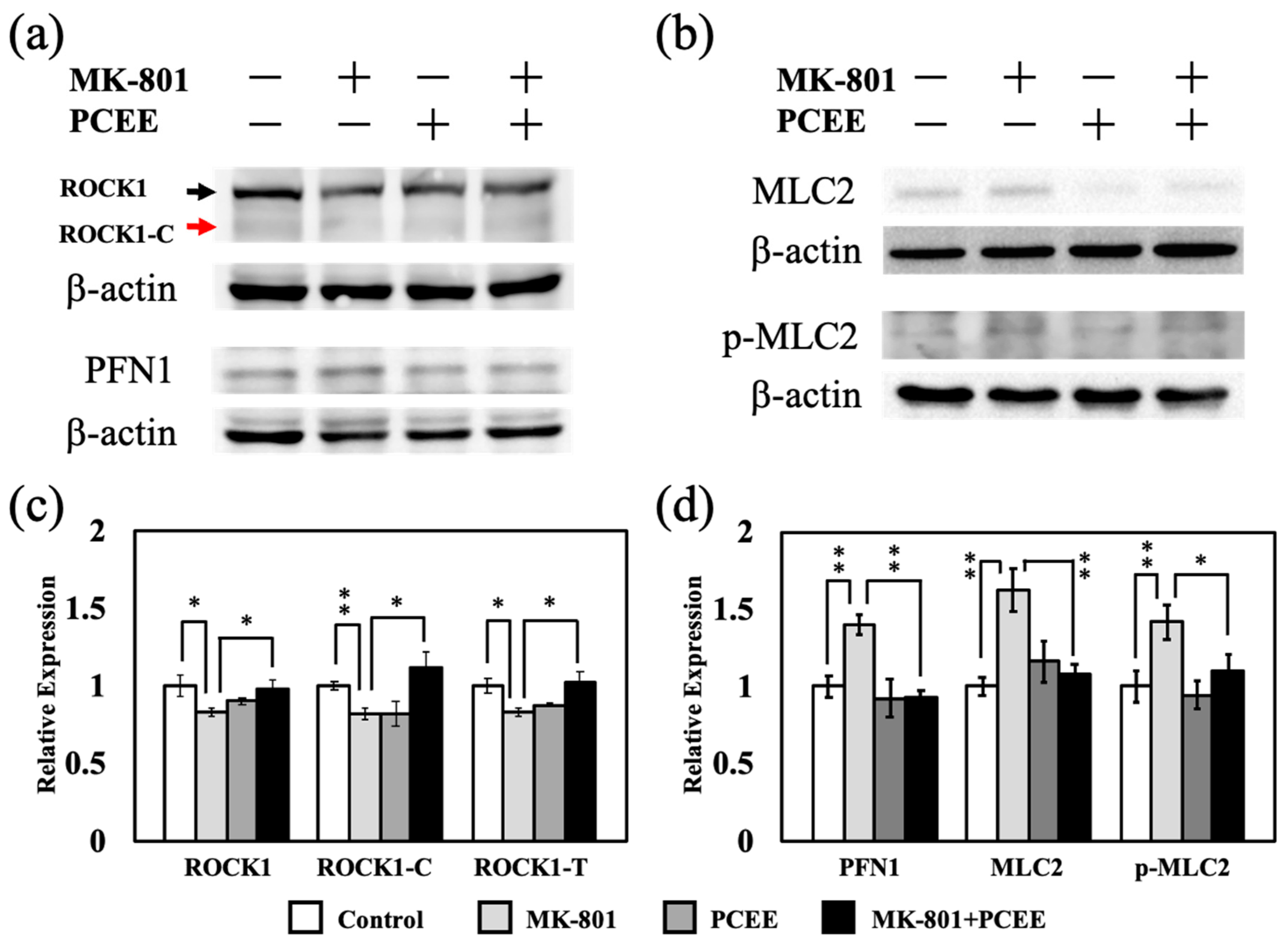
3.4. MK-801 and PCEE Modulate the RhoA/ROCK1 Pathway and Downstream MLC2 and PFN1 Regulation
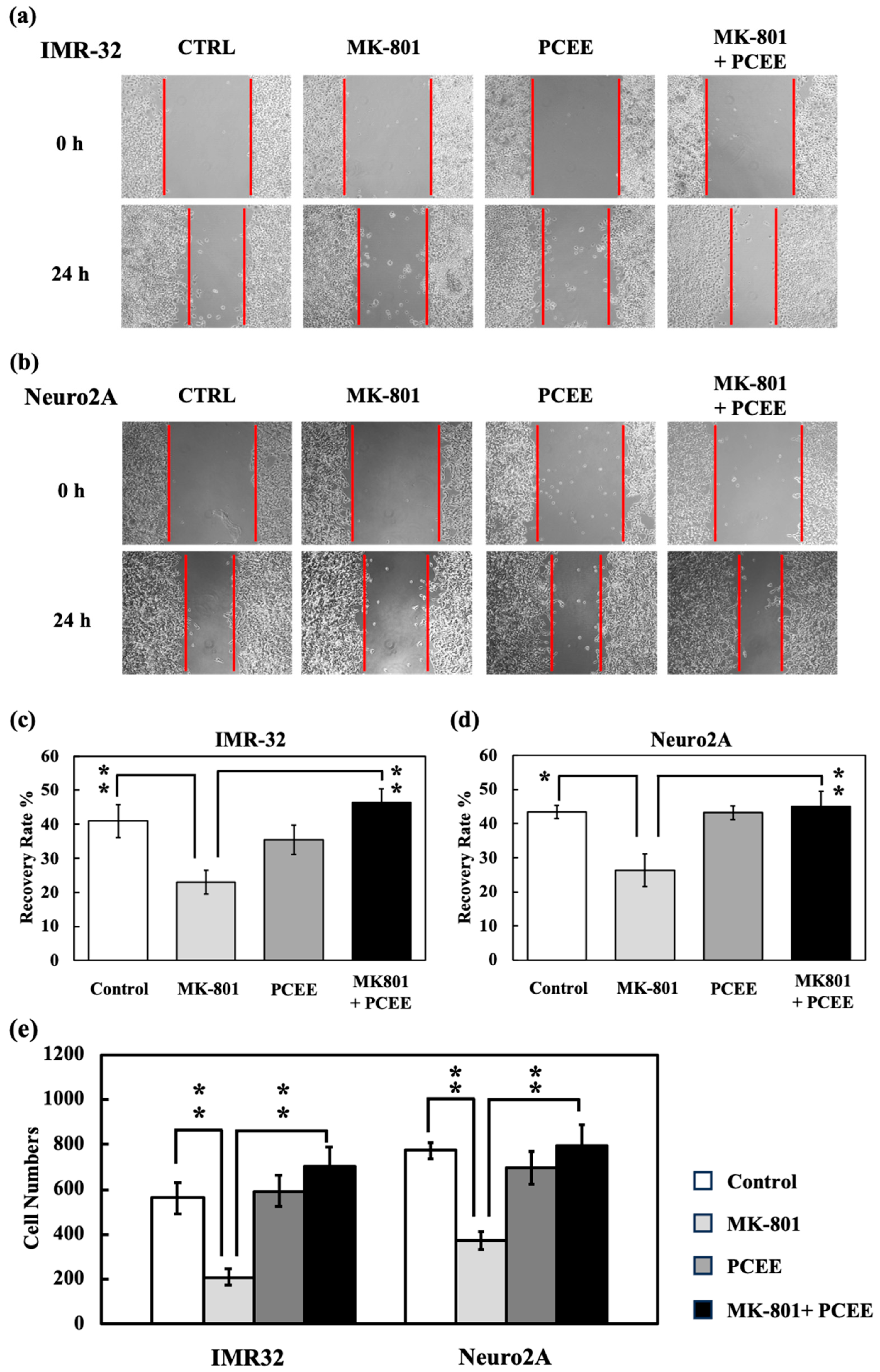
3.5. PCEE Reverses the Inhibitory Effect of MK-801 on Cell Mobility In Vitro
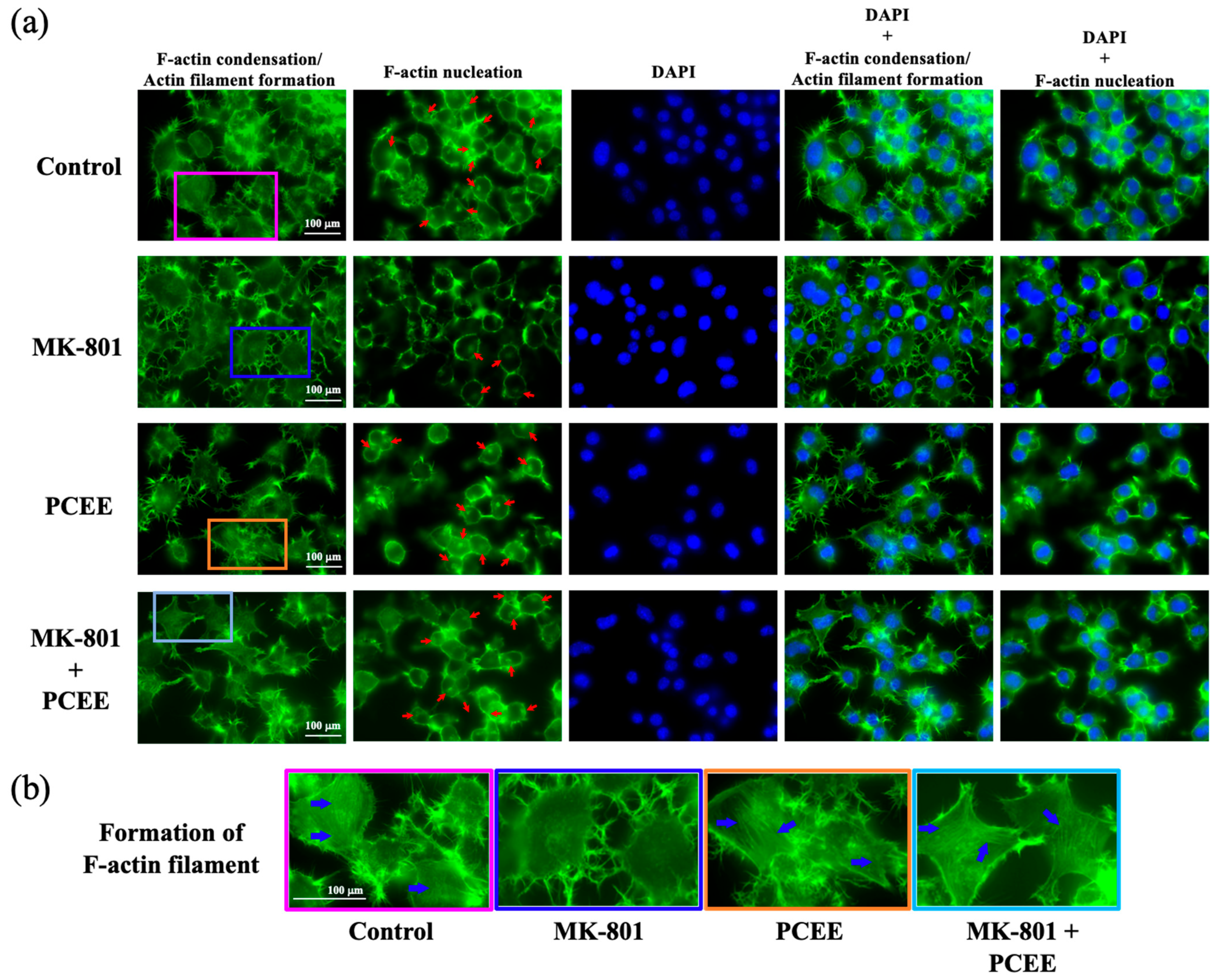
3.6. PCEE Increases the Levels of F-Actin Condensation and Nucleation In Vitro
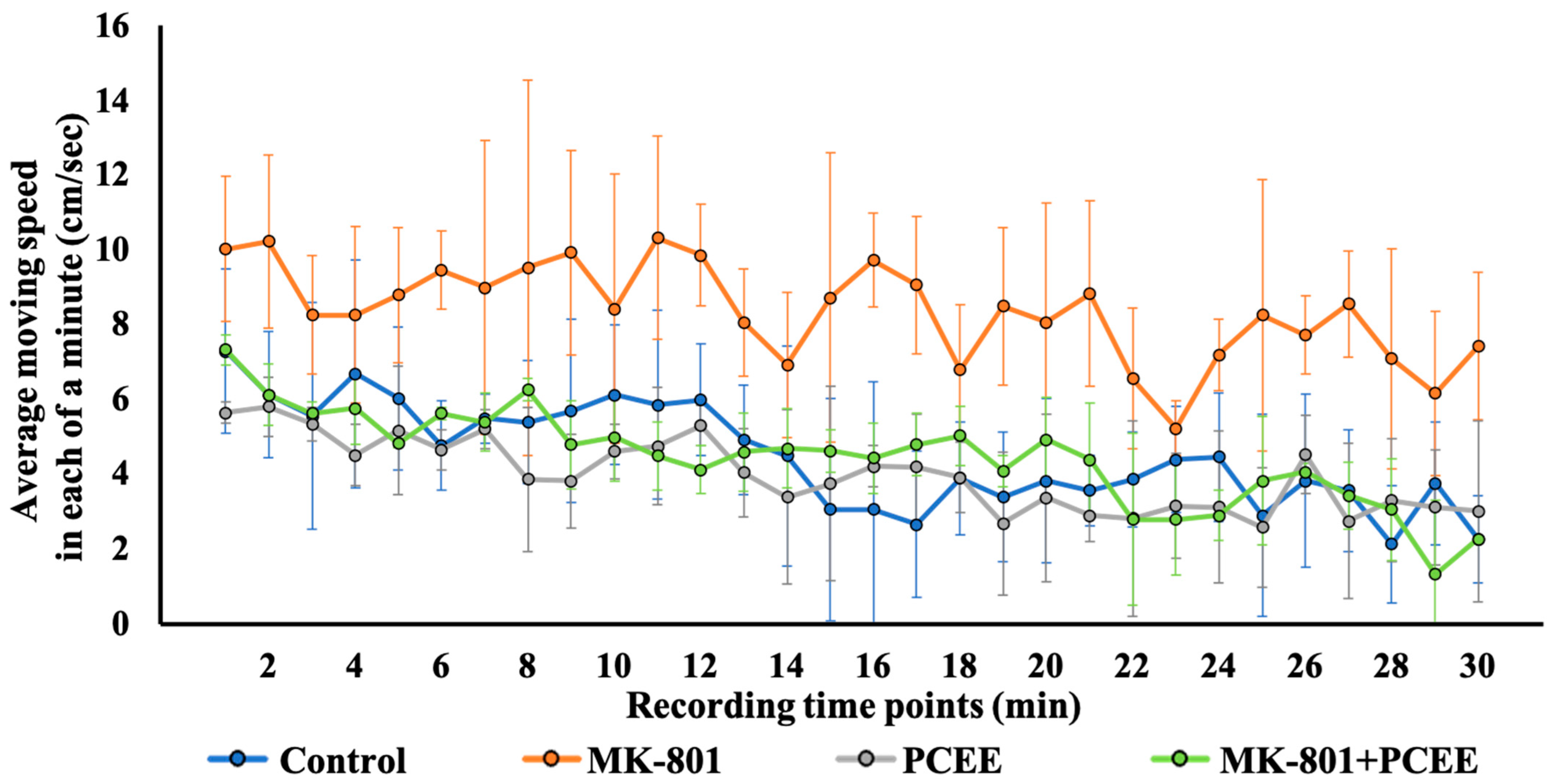
3.7. PCEE Mitigates MK-801-Induced Hyperactivity in Mice
3.8. PCEE Modulates the Expression of Rho Family Proteins in the PFC of C57BL/6 Mice
3.9. Summary of MK-801/PCEE-Induced In Vivo and In Vitro Regulation of Rho Signaling-Related Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCEE | Poria cocos ethanol extract |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| RhoGDI1 | Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor 1 |
| RhoA | Rho family protein (Ras homolog family member A |
| CDC42 | cell division control protein 42 homolog |
| Rac1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
| ROCK1 | Rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 1 |
| MLC2 | myosin light chain 2 |
| PFN1 | profilin-1 |
| PA | pachymic acid |
| TA | tumulosic acid |
| DTA | dehydrotumulosic acid |
| PPA | polyporenic acid C |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| PFC | prefrontal cortex |
References
- Bergeron, R.; Coyle, J.T. NAAG, NMDA receptor and psychosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1360–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adell, A. Brain NMDA Receptors in Schizophrenia and Depression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, N.M.; Unal, G. Vortioxetine improved negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia in subchronic MK-801 model in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 444, 114365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janus, A.; Lustyk, K.; Pytka, K. MK-801 and cognitive functions: Investigating the behavioral effects of a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacology 2023, 240, 2435–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qiu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.L. NMDA Receptor Antagonist MK801 Protects Against 1-Bromopropane-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, M.; Sobue, A.; Kushima, I.; Wang, C.; Arioka, Y.; Kato, H.; Kodama, A.; Kubo, H.; Ito, N.; Sawahata, M.; et al. ARHGAP10, which encodes Rho GTPase-activating protein 10, is a novel gene for schizophrenia risk. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.; El-Sibai, M. Signaling networks of Rho GTPases in cell motility. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosas-Molist, E.; Samain, R.; Kohlhammer, L.; Orgaz, J.L.; George, S.L.; Maiques, O.; Barcelo, J.; Sanz-Moreno, V. Rho GTPase signaling in cancer progression and dissemination. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 455–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, A.; Stradal, T.E.; Rottner, K. Signalling Pathways Controlling Cellular Actin Organization. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 235, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, N.; Santos, M.D. Dendritic Spines in Learning and Memory: From First Discoveries to Current Insights. Adv. Neurobiol. 2023, 34, 311–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiering, D.; Hodgson, L. Dynamics of the Rho-family small GTPases in actin regulation and motility. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, M.; Nakayama, M.; Kaibuchi, K. Rho-kinase/ROCK: A key regulator of the cytoskeleton and cell polarity. Cytoskeleton 2010, 67, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, X.; Surma, M.; Vemula, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Kapur, R.; Wei, L. Distinct roles for ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the regulation of cell detachment. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raftopoulou, M.; Hall, A. Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev. Biol. 2004, 265, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Bae, Y.H.; Roy, P. Molecular insights on context-specific role of profilin-1 in cell migration. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2012, 6, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, E.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Wu, W.; Xu, Y.X.Z.; Zhou, P.; Tu, W.; Lou, X.; Rao, G.; et al. Profilin 1 knockdown prevents ischemic brain damage by promoting M2 microglial polarization associated with the RhoA/ROCK pathway. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 1198–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherfils, J.; Zeghouf, M. Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 269–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.S.; Langeslag, M.; ten Klooster, J.P.; Hordijk, P.L.; Jalink, K.; Collard, J.G. Calcium signaling regulates translocation and activation of Rac. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39413–39421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovas, A.; Couchman, J.R. RhoGDI: Multiple functions in the regulation of Rho family GTPase activities. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Xie, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Du, Y.; Huo, C.; Wang, Q. Comparison of triterpene compounds of four botanical parts from Poria cocos (Schw.) wolf using simultaneous qualitative and quantitative method and metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.L. Chemical constituents and pharmacological properties of Poria cocos. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Choe, K.; Park, J.S.; Khan, A.; Kim, M.W.; Park, T.J.; Kim, M.O. O-Cyclic Phytosphingosine-1-Phosphate Protects against Motor Dysfunctions and Glial Cell Mediated Neuroinflammation in the Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Models. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tian, H.; Bao, Y. The immunomodulatory effect of Poria cocos polysaccharides is mediated by the Ca2+/PKC/p38/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoobi, Z.; Ataei, S.; Riahi, E.; Parviz, M.; Sehati, F.; Zare, M.; Angizeh, R.; Ashabi, G.; Hosseindoost, S. Neuroprotective effects of MK-801 against cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.M.; Hao, X.B.; Hong, Y.X.; Zhao, S.S.; Chen, X.C.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. NMDARs antagonist MK801 suppresses LPS-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction by regulating subunits of NMDARs via the CaM/CaMKII/ERK pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, C.T.; Tzeng, I.S.; Kuo, C.Y.; Tsai, F.M.; Chen, M.L. Poria cocos Regulates Cell Migration and Actin Filament Aggregation in B35 and C6 Cells by Modulating the RhoA, CDC42, and Rho Signaling Pathways. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6854860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.H.; Phillips, T.J. MK-801 potentiates ethanol’s effects on locomotor activity in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1998, 59, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainetdinov, R.R.; Mohn, A.R.; Bohn, L.M.; Caron, M.G. Glutamatergic modulation of hyperactivity in mice lacking the dopamine transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11047–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, A.; Gonzalez-Billault, C. Crosstalk between Rac1-mediated actin regulation and ROS production. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 116, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogucka-Janczi, K.; Harms, G.; Coissieux, M.M.; Bentires-Alj, M.; Thiede, B.; Rajalingam, K. ERK3/MAPK6 dictates CDC42/RAC1 activity and ARP2/3-dependent actin polymerization. Elife 2023, 12, e85167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Chen, T.L.; Chen, R.M. Cytoskeleton interruption in human hepatoma HepG2 cells induced by ketamine occurs possibly through suppression of calcium mobilization and mitochondrial function. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.L. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis revealed antipsychotic drugs induced protein expression modulations in C6 glioma cells. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Welch, W.J.; Diprospero, N.A.; Diamond, M.I. Phosphorylation of profilin by ROCK1 regulates polyglutamine aggregation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 5196–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.B.; Kullmann, J.A.; Witke, W. Role of the actin-binding protein profilin1 in radial migration and glial cell adhesion of granule neurons in the cerebellum. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2012, 6, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.C.; Duan, X.; Cui, X.S.; Kim, N.H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.C. Profilin 1 plays feedback role in actin-mediated polar body extrusion in mouse oocytes. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2018, 30, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; An, W.; Chu, J. Effect of water extract of Poria on cytosolic free calcium concentration in brain nerve cells of neonatal rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 1998, 18, 293–295. [Google Scholar]
- Lisek, M.; Zylinska, L.; Boczek, T. Ketamine and Calcium Signaling-A Crosstalk for Neuronal Physiology and Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomski, N.J.; Morrison, P.; Meyer, A. Antipsychotic medication side effect assessment tools: A systematic review. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2016, 50, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; He, J.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, P. Immunomodulatory Activity and Its Mechanisms of Two Polysaccharides from Poria cocos. Molecules 2023, 29, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.E.; Teixeira, A.L. Inflammation in psychiatric disorders: What comes first? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1437, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lian, P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, K. Pachymic acid inhibits tumorigenesis in gallbladder carcinoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 17781–17788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Castillo, V.; Sliva, D. CDC20 associated with cancer metastasis and novel mushroom-derived CDC20 inhibitors with antimetastatic activity. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Chu, Z.; Ni, T.; Ou, S.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Poria Acid, Triterpenoids Extracted from Poria cocos, Inhibits the Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopaske, G.T.; Dorph-Petersen, K.A.; Sweet, R.A.; Pierri, J.N.; Zhang, W.; Sampson, A.R.; Lewis, D.A. Effect of chronic antipsychotic exposure on astrocyte and oligodendrocyte numbers in macaque monkeys. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, A.C.; Crum, W.R.; Lerch, J.P.; Chege, W.; Natesan, S.; Modo, M.; Cooper, J.D.; Williams, S.C.; Kapur, S. Reduced cortical volume and elevated astrocyte density in rats chronically treated with antipsychotic drugs-linking magnetic resonance imaging findings to cellular pathology. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Cheda, B.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Joglar, B.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Involvement of microglial RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway activation in the dopaminergic neuron death. Role of angiotensin via angiotensin type 1 receptors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 47, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govek, E.E.; Newey, S.E.; Van Aelst, L. The role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolias, K.F.; Duman, J.G.; Um, K. Control of synapse development and plasticity by Rho GTPase regulatory proteins. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 94, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Boku, S.; Watanabe, N.; Fujita, A.; Iwamatsu, A.; Obinata, T.; Ohashi, K.; Mizuno, K.; Narumiya, S. Signaling from Rho to the actin cytoskeleton through protein kinases ROCK and LIM-kinase. Science 1999, 285, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Active Compound | Stand Curve 1, 5, 10, 50, and 100 mg/mL | R2 | mg/100 mg PCEE | Mean ± S.D. (mg/100 mg PCEE) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch1 | Batch2 | Batch3 | ||||
| TA | Y = 8494.41X + 950.361 | 0.99996 | 16.188 | 17.411 | 16.809 | 16.803 ± 0.612 |
| PA | Y = 6765.41X − 415.930 | 0.99961 | 28.266 | 30.427 | 29.335 | 29.343 ± 1.081 |
| DTA | Y = 21,148.8X + 3179.20 | 0.99996 | 11.385 | 12.196 | 11.736 | 11.772 ± 0.407 |
| PPA | Y = 16,091.0X + 856.040 | 0.99993 | 8.387 | 9.008 | 8.68 | 8.692 ± 0.311 |
| Time Interval of Test | Group (n = 3) | Mean of Moving Speed (cm/s) | Standard Deviation (SD) of Moving Speed | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–30 min | Control | 4.5078 | 2.1682 | <0.01 # |
| MK-801 | 8.3722 | 2.3778 | ||
| PCEE | 3.9898 | 1.5851 | <0.01 ‡ | |
| MK-801 + PCEE | 4.4522 | 1.5314 | ||
| 10–20 min | Control | 4.1233 | 2.2342 | <0.01 # |
| MK-801 | 8.6100 | 2.2233 | ||
| PCEE | 3.9680 | 1.565 | <0.01 ‡ | |
| MK-801 + PCEE | 4.5867 | 0.782 |
| C57BL/6 | NuoroA | IMR-32 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK-801 | PCEE | MK801 + PCEE | MK-801 | PCEE | MK801 + PCEE | MK-801 | PCEE | MK801 + PCEE | |
| RhoGDI1 | D | N | N | D | I | I | N | D | D |
| p-RhoGDI1 | - | - | - | D | N | N | D | N | N |
| RhoA | D | I | I | D | N | I | D | N | I |
| CDC42 | D | N | N | D | N | I | D | N | N |
| Rac1 | N | I | I | D | N | N | D | N | N |
| p-RhoA | I | N | N | N | N | I | I | D | N |
| p-CDC42 | D | N | N | I | N | N | D | D | D |
| p-Rac1 | D | I | I | D | N | N | I | D | N |
| ROCK1 | D | D | N | D | D | N | I | I | N |
| MLC2 | I | D | N | I | D | D | I | N | N |
| p-MLC2 | I | N | N | I | N | N | N | D | D |
| PFN1 | I | N | N | I | N | N | I | N | N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.-Y.; Lu, C.-W.; Lin, T.-Y.; Tzeng, I.-S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, M.-L. Poria cocos Ethanol Extract Restores MK-801-Induced Cytoskeleton Regulation in Neuro2A and IMR-32 Cells and Locomotor Hyperactivity in C57BL/6 Mice by Modulating the Rho Signaling Pathway. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050312
Chang Y-Y, Lu C-W, Lin T-Y, Tzeng I-S, Chen Y-C, Chen M-L. Poria cocos Ethanol Extract Restores MK-801-Induced Cytoskeleton Regulation in Neuro2A and IMR-32 Cells and Locomotor Hyperactivity in C57BL/6 Mice by Modulating the Rho Signaling Pathway. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(5):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050312
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Ya-Ying, Cheng-Wei Lu, Tzu-Yu Lin, I-Shiang Tzeng, Yi-Chyan Chen, and Mao-Liang Chen. 2025. "Poria cocos Ethanol Extract Restores MK-801-Induced Cytoskeleton Regulation in Neuro2A and IMR-32 Cells and Locomotor Hyperactivity in C57BL/6 Mice by Modulating the Rho Signaling Pathway" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 5: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050312
APA StyleChang, Y.-Y., Lu, C.-W., Lin, T.-Y., Tzeng, I.-S., Chen, Y.-C., & Chen, M.-L. (2025). Poria cocos Ethanol Extract Restores MK-801-Induced Cytoskeleton Regulation in Neuro2A and IMR-32 Cells and Locomotor Hyperactivity in C57BL/6 Mice by Modulating the Rho Signaling Pathway. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(5), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47050312







