Abstract
Caenorhabditis elegans is an important model used for many aspects of biological research. Its genome contains 76 genes coding for cytochromes P450 (P450s), and few data about the biochemical properties of those P450s have been published so far. However, an increasing number of articles have appeared on their involvement in the metabolism of xenobiotics and endobiotics such as fatty acid derivatives and steroids. Moreover, the implication of some P450s in various biological functions of C. elegans, such as survival, dauer formation, life span, fat content, or lipid metabolism, without mention of the precise reaction catalyzed by those P450s, has been reported in several articles. This review presents the state of our knowledge about C. elegans P450s.
1. Introduction
The soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is one of the simplest organisms with a laboratory model status. C. elegans is a transparent worm of about 1 mm in length, found in temperate soil environments [1]. C. elegans is an important model used for many aspects of biological research [2]. It is a non-infectious and non-pathogenic organism that survives by feeding on microbes such as bacteria. With abundant food and low population density, C. elegans has a lifespan of around two or three weeks with a generation time average of three and half days. C. elegans’s developmental stages are eggs, larvae, fertile adults, and post-reproductive adults. C. elegans larvae complete development from embryo to adult with four larval stages (L1–L4) in three days. However, in an environment with limited food and/or high population density, larvae may arrest development at L2 to enter a particular stage called the dauer stage (L2d [3]). The dauer larva has a unique morphology with physiology and metabolism, which allow resistance to environmental stress. The dauer larva can live up to several months, and this stage ends when conditions favor further growth of the larva, now into the L4 stage. The dauer stage is considered to be non-aging because the post-dauer life span is not affected by the length of this stage [4]. The C. elegans model proposes the power of integrated whole animal investigations that are cost- and time-efficient and require minimal infrastructure. It is nowadays a powerful model organism not only for developmental biology but also for aging studies or toxicology [2,5]. C. elegans somatic cell locations and types, as well as networks neurons, have been mapped [6], allowing morphological evaluations of abnormalities induced by toxins and deep neurological/behavioral correlations. Furthermore, genes and signaling pathways appear to be well conserved between C. elegans and humans [7,8]. Despite their different complexity, the number of genes in C. elegans and humans is surprisingly similar (~21.000 genes in humans, ~19.000 genes in C. elegans) [9].
Contrary to toxicity tests using cell cultures, C. elegans toxicity tests provide data from a whole animal with intact and metabolically active digestive, reproductive, endocrine, sensory, and neuromuscular functions. Toxicity ranking, including LD50, in this nematode, has repeatedly been shown to be as predictive as the LD50 rankings using rats or mice [5]. However, the defense mechanisms against xenobiotics in C. elegans have been little studied, although they are essential in toxicological studies. The xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes, and particularly P450-dependent monooxygenases (phase I enzymes), play a key role in these defense mechanisms. In this review, we present the state of our knowledge about C. elegans P450s.
P450s are ubiquitous heme-thiolate proteins involving iron-protoporphyrin IX in their active site that are widely distributed in living organisms [10,11]. The common property to all P450s discovered so far is the peculiar position of the Soret peak of their Fe(II)–CO complex around 450 nm. This redshifted Soret peak is the signature of the presence of a cysteinate ligand from the protein bound to the iron in trans position to the CO ligand [11]. Most P450s catalyze monooxygenase reactions, such as hydroxylations or epoxidations, on a great number of substrates. These reactions require the presence of dioxygen as well as a cofactor, NADPH or NADH, providing the necessary electrons via electron transfer proteins that are very often coupled to P450 inside cell membranes [11]. In the human genome, 57 genes encoding P450s have been identified (drnelson.uthsc.edu (accessed on 24 January 2022)). Some P450s catalyze oxidation steps involved in the biosynthesis and/or biodegradation of endogenous compounds such as steroids, fatty acids, and endocannabinoids [12]. On the other hand, P450s play a key role in the oxidative biotransformation of xenobiotics such as drugs, pesticides, and other environmental chemicals, facilitating their elimination from living organisms [11,12].
We know of over 62,000 bacterial P450s and 85,000 fungal P450s [13]. Since 1989, P450s have been classified according to their degree of identity in their amino acid sequence. Indeed, P450s with a degree of identity greater than 40% belong to the same family and are designated by a number behind the abbreviation P450 or CYP (CYP13, CYP14). When they have a degree of identity greater than 55%, they belong to the same subfamily and are therefore designated by a capital letter behind the number of the family (CYP13A, CYP13B). Finally, isoforms belonging to the same subfamily are differentiated by a number behind the letter of the subfamily (CYP13A1, CYP13A10). Humans have 57 functional P450s classified in 18 families and 43 subfamilies [12,14]. The largest P450s families in humans are 2, 3, and 4, and some of them are even larger in other mammals such as a mouse. As the number of families increased, it was necessary to establish a new reunification. Clans bring together families that belong to the same group (from the same ancestral gene) according to many phylogenetic trees established previously [15]. There are 11 animal P450s clans (clans 2, 3, 4, 7, 19, 20, 26, 46, 51, 74, and mitochondrial or mito). However, not all organisms own all 11 clans. For example, ecdysozoa (insects, crustaceans, nematodes including C. elegans) only have clans 2, 3, 4, and mito [15,16], whereas humans have 10 out of 11 clans, all except clan 74 [17].
The genomic sequence of the nematode C. elegans reveals over 19,000 genes, of which 76 encode for P450s [9]. Studies on this subject, having led to about a hundred articles that will be mentioned below, show that some P450s are involved in the regulation of the transition to the dauer state as well as other physiological functions of the worm. Other P450s are involved in the metabolism and bioactivation or detoxication of xenobiotics. As vertebrates, C. elegans can induce some P450s, in particular through the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) signaling pathway. AhR is a receptor well known for its fundamental role in the metabolism of xenobiotics in vertebrates [18]. Ligands of AhR are hydrophobic xenobiotics including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and halogenated compounds such as benzo (a) pyrene and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-P-dioxin. AhR also has endogenous ligands such as some steroids and kynurenine. Activation of AhR leads to its translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and then its heterodimerization with its partner, the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT), thus forming a transcription factor. The heterodimer AhR/ARNT directly regulates the expression of many genes, including those of some enzymes involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics (P450s of family 1 and glutathione-S-transferases) [19].
In the following, we will review what is presently known about C. elegans P450s.
2. Genetic and Phylogenetic Analysis of C. elegans P450s
C. elegans was the first multicellular organism to have its whole genome sequenced [9] and is the only organism to have its connectome (neuronal “wiring diagram”) completed [20]. It contains 82 P450 genes, including 6 pseudogenes, divided into 16 families (13, 14, 22, 23, 25, 29, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 42, 43, 44) and 26 subfamilies in accordance with the Nelson’s nomenclature [21]. Table 1 shows all the C. elegans P450s grouped by family. Almost all of the C. elegans P450s families appear to be nematode-specific [22], but they correspond to the clans 2, 3, 4, and mito also found in humans [16].

Table 1.
Genes and pseudogenes (in italics) of P450s in C. elegans.
Some families have only one member (22, 23, 36, 42, 43, and 44) while others are very large, such as family 33 with 18 P450s (Table 1).
To compare the C. elegans and human P450s, a phylogenetic analysis was made. In order to achieve a phylogenetic tree, the sequences of all P450s (humans and C. elegans) were collected from the Uniprot website [23]. All trees were produced thanks to the Phylogeny site [24]: the P450 tree of C. elegans, that of human P450s, then a tree grouping together all these P450s. Subsequently, the creation of a more visual tree was carried out with the Cytoscape software [25].
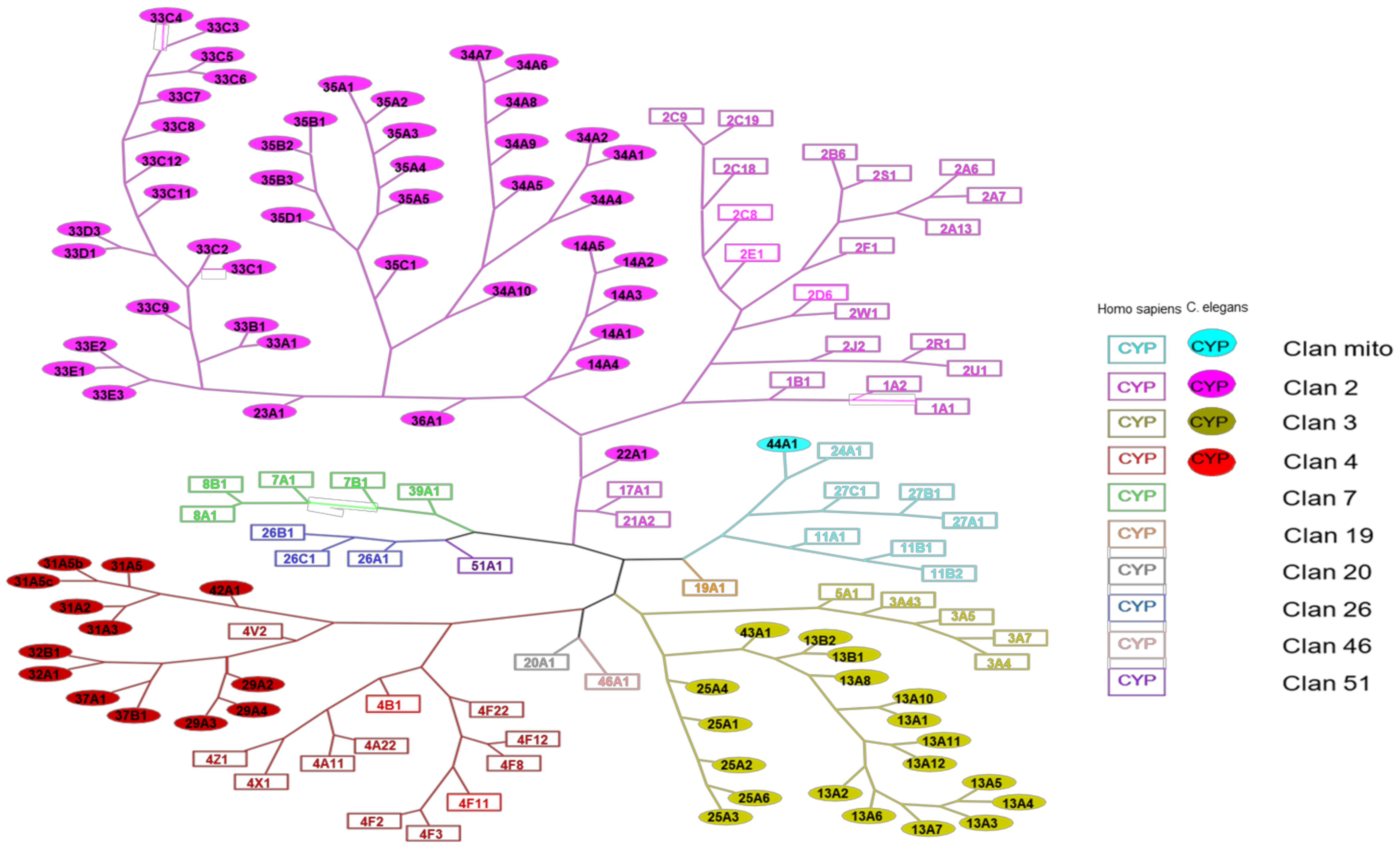
The resulting phylogenetic tree common to humans and C. elegans P450s, shown in Figure 1, indicates interspecies relationships.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree gathering human and C. elegans P450s. The square boxes represent human P450s, while the filled round boxes represent C. elegans P450s. Different colors are assigned according to the clan to which the CYP450s belong.
Human P450s belong to 10 different clans, whereas C. elegans P450s only belong to 4 clans. Some sequences of C. elegans P450s are closer to human P450s sequences than to those of other C. elegans P450s: this is particularly the case for P450s 22A1 (clan 2, close to 17A1 and 21A2) and 44A1 (clan mito, close to 24A1). This also occurs the other way around, as for human P450 4V2 (clan 4) that is found on the tree more closely related to C. elegans P450s 29A, 32, and 37 than to other human P450s of the same family (P450s 4B1, 4F22). P450 13A10 is found in clan 3. It belongs to the same clan as P450 3A4, which is one of the most important human P450 quite often involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics [12]. We also distinguish differences in the distribution of P450s in the clans between humans and C. elegans. Indeed, although clans 2 and 3 present a proportion rather like that expected considering the higher number of P450s in C. elegans than in humans, we can notice that only one of the 76 P450s of the nematode has a mitochondrial sequence. The proportion is, on the other hand, very different for humans who have in this clan 7 P450s out of 57 in total. Clan 4 also has a higher percentage of human P450s (12 P450s out of 57 in total) than C. elegans P450s (13 P450s out of 76 in total). In these two species, the largest P450s clan is clan 2, whereas, in insects, clan 3 is the largest one [22].
P450s can also be classified on an even higher level into groups that contain similar P450 clans across animals, plants, and bacteria [26]. P450 families have emerged and been lost during evolution. For example, P450 51A1 (Sterol 14α-demethylase) required for one step of cholesterol synthesis is evolutionarily old and found in bacteria, plants, and humans. However, it is not found in nematodes or insects that do not synthesize cholesterol de novo. Most of the phylogenetically well-preserved P450 families typically have only one or a few members conserved across many species, whereas unstable P450 families have variable numbers of members in different species. It is believed that the stable P450 families are essential in the synthesis or degradation of endogenous substrates, while the highly diverse P450 families metabolize xenobiotics or secondary metabolites [27,28].
3. Implication of P450s in Biological Functions of C. elegans
Most of the physiological roles of P450s in C. elegans have been determined by the invalidation of P450 expression (knock-out worms or knock-out/gene silencing by RNA interference). Thus, the implication of some P450s in the biological functions of C. elegans without mention of the precise enzymatic reactions catalyzed by those P450s has been reported in several articles (Table 2).

Table 2.
Implication of P450s in biological functions of C. elegans.
The silencing of single P450 genes has been described to cause alterations in survival [34,35,37], life span [30,31,32,33,34,35,36], morphology [36,37,38,39,40,41,62], embryonic development [37,42,43], larval development [35,37,42,44], dauer formation [29,30,31,35,45,46,47,48,49,50], reproduction [31,42,51,52,53], fat content [42,47,48,51,53,54,55,56], or lipid metabolism [32,40,42,47,48,50,51,54,55,57,58,59,60,61].
Molecular analyses from several studies allowed a better characterization of the roles of some P450s. It was proposed that P450-dependent eicosanoids may serve as second messengers in the regulation of pharyngeal pumping and food uptake in C. elegans [63]. Some C. elegans P450s are linked to the metabolism of fatty acid-derived signaling molecules [47,55]. The silencing of P450s 31A2 and 31A3 leads to polarization and osmotic defects and to failures in meiosis and embryonic development [42]. P450s 31A2 and 31A3 also appear to be involved in the biosynthesis of lipids that are essential for the correct formation of eggshells [42]. In addition, P450 31A2 is required for sperm motility [64], and it negatively regulates the synthesis of prostaglandins [51]. Similarly, the P450s of the 35A family regulate the levels of several fatty acids and endocannabinoids in C. elegans [54]. Thus, P450s 35A2 and 35A3 are involved in the production of lipids required for eggshell formation [42]. Moreover, the deletion of P450 35A2 affects the lipid regulation and longevity of C. elegans [32]. It was also shown that the hypoxia inducible factor, HIF, regulates C. elegans stress responses and behavior via the nuclear receptor NHR-46 by targeting the gene coding for P450 36A1 [65]. This suggests that P450 36A1 is involved in the biosynthesis of a hormone ligand for this receptor.
Interestingly, there are several P450s that have been implicated in an adaptive response to changing environmental conditions. For example, Cong et al. found six P450 genes (13A8, 13A11, 14A4, 33C2, 33D3, and 35B2), whose expression levels were very low at pH 6.33, while these genes were significantly upregulated when the pH dropped to 3.13 [66].
Only a small number of reactions catalyzed by C. elegans P450s and involving endogenous substrates have been identified so far (Table 3).

Table 3.
Implication of P450s in the metabolism of endogenous compounds in C. elegans.
Thus, microsomes from adult worms oxidize eicosapentaenoic acid, EPA (a polyunsaturated fatty acid that acts as a precursor of prostaglandins, eicosanoids, and tromboxanes), with the main formation of 17,18-epoxy-eicosatetraenoic acid, 17,18-EEQ [47]. This oxidation is NADPH, and cytochrome P450 reductase dependent and is inhibited by usual inhibitors of mammalian arachidonic acid-metabolizing P450s. RNAi gene silencing experiments showed that P450s 29A3 and 33E2, which are related to mammalian P450 family 2, are mainly responsible for the oxidation of EPA into 17,18-EEQ [47]. Further studies using C. elegans P450 33E2 and human P450 reductase expressed in insect cells showed that P450 33E2 catalyzes the epoxygenation of EPA with the formation of 17,18-EEQ and the hydroxylation of arachidonic acid, AA, into 19-hydroxy-AA [55]. This article also showed that P450 33E2 is expressed in the C. elegans pharynx and that 17,18-EEQ is a regulator of the C. elegans pharyngeal pumping activity. More recently, it was reported that C. elegans P450 13A12 and P450 reductase co-expressed in insect cells catalyze the epoxygenation of EPA into 17,18-EEQ and of AA into 14,15-epoxy-eicosatrienoic acid [58] (Table 3). The same article showed that 17,18-EEQ increases the C. elegans locomotion activity.
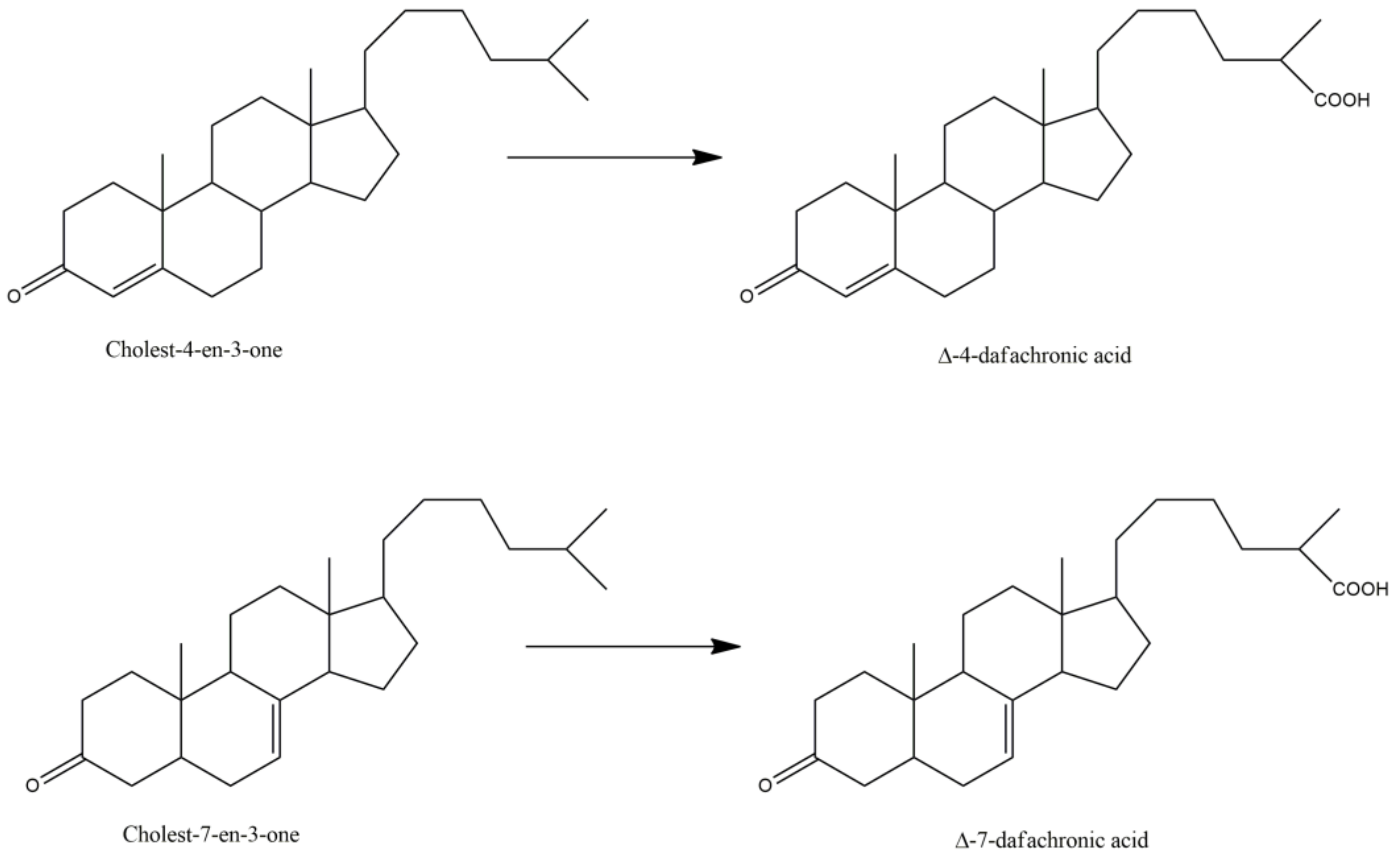
Finally, the most documented C. elegans P450 is called DAF-9 or P450 22A1, with nearly 45 articles that refer to this protein. Indeed, P450 22A1 is involved in several pathways controlling dauer formation [29], life span, and gonadal migration [31,37]. P450 22A1 catalyzes a key step in the biosynthesis of 3-keto-cholestenoic acids, also called dafachronic acids, DAs (Table 3). Those bile acid-like steroids act as ligands of the DAF-12 nuclear receptor that governs C. elegans larval development and adult longevity [37,50,67]. DAF-9 catalyzes the oxidation of a terminal methyl group of the lateral chain of cholest-4-en-3-one or cholest-7-en-3-one with the formation of delta-4- and delta-7-dafachronic acids, respectively (Figure 2) [57,60]. DAF-9 is the equivalent of P450 27A1, the human P450 that catalyzes this oxidation of a terminal methyl group of the lateral chain of 3-keto-steroids in man.
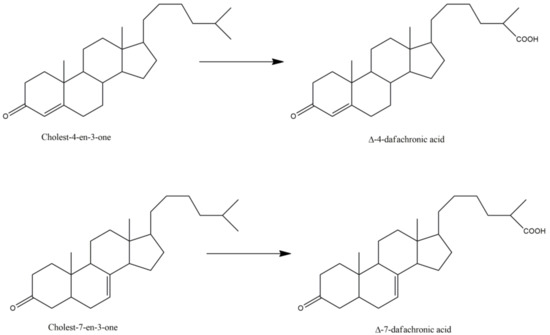
Figure 2.
P450 22A1 (DAF-9) catalyzed oxidation of cholesten-3-ones into dafachronic acids.
Several redox systems are involved in the transfer of electrons from NADPH or NADH for dioxygen reduction at the P450 active site [68]. In all the above-mentioned oxidations catalyzed by microsomal type P450s, electrons from NADPH should be transferred to the P450 active site by a P450 reductase, analogous to human P450 reductase, that is encoded by the C. elegans emb-8 gene [69]. During embryonic development, emb-8 activity is essential for normal interactions between the pronucleus/centrosome complex and the posterior cortex and, thus, for proper anterior-posterior polarity. Emb-8 is also required for the formation of the secreted eggshell [69]. EMB-8 plays an important role in fatty acid modification. For instance, as mentioned in the previous paragraph, oxidation of EPA to 17,18-EEQ by adult worm microsomes is NADPH and P450 reductase dependent [47], and C. elegans P450 13A12 and P450 reductase co-expressed in insect cells catalyze the oxidation of EPA into 17,18-EEQ and of AA into 14,15-epoxy-eicosatrienoic acid [58].
The nature of the protein(s) responsible for electron transfer to the only C. elegans mitochondrial P450, P450 44A1, is less clear. In C. elegans mitochondrion, the Y62E10A.6 and Y73FBA.27 genes are coding for an adrenodoxin reductase and a ferredoxin, respectively [9]. If P450 44A1 functions as a genuine mitochondrial P450, those proteins would supply electrons to P450 44A1, even though it was argued that C. elegans lacks classical mitochondrial-type P450 [22]. More data on the nature and roles of P450 44A1 are required to answer those questions.
4. P450s of C. elegans and Xenobiotics
4.1. Induction of C. elegans P450s by Xenobiotics
As shown in Table 4, many C. elegans P450s are induced after the exposition of the worm to various xenobiotics. Thus, ethanol acts as an inducer of P450s 13A12, 13B1, 25A1, 25A2, 29A2, 32B1, 33B1, 33C6, 34A4, 4A6, 35A3, 35A5, 35B1, 35B2, 35C1, 36A1 and 37B1 [70,71], and caffeine is an inducer of P450s 13A8, 13A12, 14A1, 14A2, 14A4, 14A5, 32A1, 33C3, 33C4, 33C6, 33C7, 33C9, 33E1, 33E2, 33E3, 33E4, 34A7, 34A9, 35A2, 35A3, 35A4, 35A5, 35B1, 35B2, and 43A1 [72]. Interestingly, drugs such as primaquine and lansoprazole are inducers of several members of family 35 (35A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, B1, B2, and C1) and P450 31A3 [73,74,75], whereas rifampicin is an inducer of P450 13A7 [76]. Many pesticides, such as atrazine, fenitrothion, DDT, dichlorvos, rotenone, and thiabendazole are inducers of members of family 35 [73,74,75,77,78,79], whereas endosulfan, cypermethrin, chlorpyrifos, rotenone, and dichlorvos are inducers of P450 34A9 [77], and glyphosate and paraquat of P450 29A2 [77]. Aromatic and polyaromatic molecules, such as beta-naphthoflavone, fluoranthene, bisphenol A, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), act as inducers of several members of family 35 [56,73,74,75,80,81,82]. PCBs are anthropogenic molecules that were produced to be used as dielectric and coolant fluids in electrical devices. They are highly stable and therefore can accumulate in fat tissues. PCB 52 is one among many congeners. It is noteworthy that PCB 52 is also an inducer of P450s 34A6, 14A3, and 14A5 [56,75,83]. Ethidium bromide is an inducer of several members of families 33 and 35 [84,85]. Metal ions related to Cd are inducers of P450s 13A4,13A5, 13A6, 13A7, 14A4, 29A2, 33C5, 33C7, 34A9, and 35A2 [86], whereas those related to Zn, Cu, and Al induce P450s 29A2, 34A9, and 35A2 [87]. Other organic compounds have also been described as inducers of several P450s of C. elegans (Table 4) [88,89,90,91,92].

Table 4.
Induction of C. elegans P450s by xenobiotics.
It is also noteworthy that an endogenous molecule such as progesterone acts as an inducer of P450s 25A2, 25A6, 29A2, 37A1, and 37B1 [93].
4.2. Metabolism of Xenobiotics by C. elegans P450s
Several Phase I and Phase II enzymes involved in xenobiotics metabolism in most living organisms, such as P450-dependent monooxygenases, dehydrogenases, UDP-glucuronyl transferases, and glutathione transferases, are present in C. elegans [95]. They are upregulated in long-lived C. elegans dauer larva [35]. As they are involved in the metabolism and elimination of potentially toxic endobiotics and xenobiotics, these data suggested that those compounds may be the major determinants of molecular damages that cause aging in C. elegans [35].
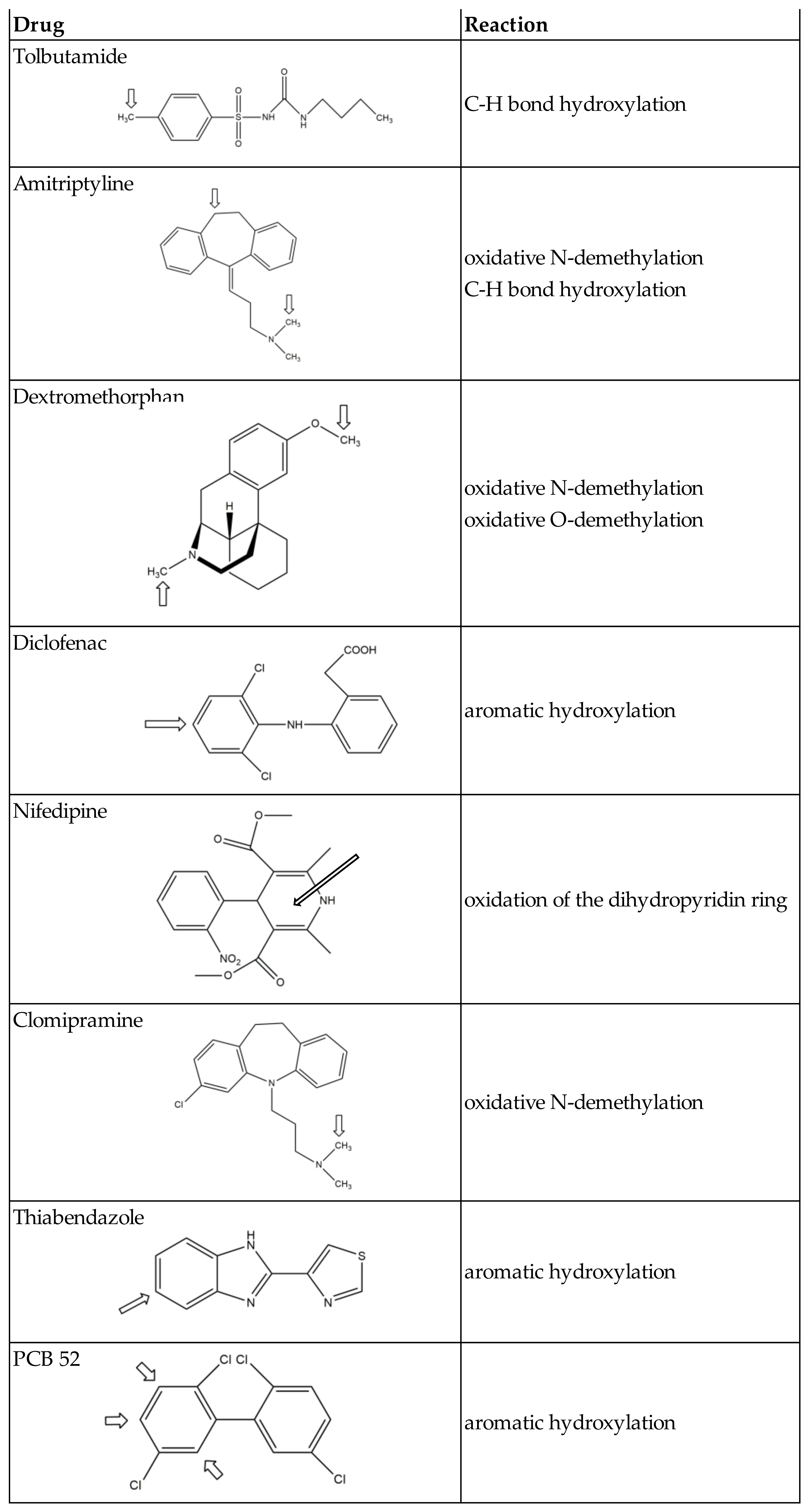
First results showing that C. elegans P450s are responsible for the metabolism of xenobiotics were concerned with a worldwide distributed pollutant, 2,2′,5,5′-tetrachloro-biphenyl, PCB 52 [83]. Metabolism of PCB 52 by C. elegans leads to C3- and C4- and/or C6-hydroxy-PCB 52. Experiments using RNAi and P450- mutant strains showed that P450 34A6 and members of the P450 14A family were involved in these aromatic hydroxylations (Table 5 and Figure 3). A few years later, it was reported that C. elegans hydroxylates thiabendazole in position 5 of its aromatic ring and that P450 35D1 is responsible for this reaction [96] (Table 5 and Figure 3).

Table 5.
Metabolism of xenobiotics by C. elegans: implication of P450s.

Figure 3.
Oxidations of xenobiotics by C. elegans (arrows indicate the oxidation site(s)).
Even more recently, a study of the metabolism by C. elegans of a series of drugs well known to be oxidized in humans by P450s of families 1, 2, and 3 was published [97]. Tolbutamide, amitriptyline, dextromethorphan, diclofenac, nifedipine, and clomipramine that are oxidized by P450s of families 2 and 3 in humans were found to undergo similar oxidations by C. elegans. However, phenacetin that is oxidized into paracetamol by P450 1A2 in humans is not oxidized by C. elegans. These data would indicate the lack of equivalents of P450s of family 1 in C. elegans [97]. Experiments of P450 gene inactivation by RNAis showed that tolbutamide hydroxylation by C. elegans is mainly dependent on P450 34A9 and to a lesser extent on P450s 36A1 and 34A10 (Table 5). Those P450s are the homologs of P450s of family 2 (2C8, 2C9, and 2C19) that are responsible for this hydroxylation in humans. However, the oxidative N-demethylation and C-H bond hydroxylation of amitriptyline were found to be catalyzed by several C. elegans P450s are the equivalents of human P450s of families 2,3, and 4, whereas those reactions are mainly catalyzed by P450 2D6 in humans [97].
Other experiments have shown that some P450s play a role in the development of toxic effects of several xenobiotics for C. elegans. Thus, the DNA damages and growth inhibition caused by aflatoxin B1, a mycotoxin, in C. elegans were reported to depend on the P450 reductase of this organism, even though the involved P450s were not determined [98] (Table 6). The toxic effects of fenitrothion for C. elegans also appear to derive from the formation of reactive metabolites mainly by P450 35A2 [79] (Table 6). Quite recent data have shown that the genotoxic effects of benzo(a)pyrene, B(a)P on C. elegans do not depend on P450s equivalent to those of human family 1A that do not seem to exist in C. elegans but depend on P450s 35A2, 35A3, and 35A5 [99].

Table 6.
Implication of P450s in the biological effects of xenobiotics on C. elegans.
On the contrary, C. elegans P450s may be involved in the detoxication of some xenobiotics. This is the case of P450 13A7, an equivalent of human P450 3A4, that mitigates tetrabromobisphenol A-induced toxicity for C. elegans [94]. This is also the case of P450s of the 35 family, P450s 35A1, 35A2, 35A4, 35B3, and 35C1, that are responsible for the detoxication of 3-bromopyruvate [100] (Table 6). Finally, it was recently reported that the expression of Zebrafish P450 1A1 in C. elegans protects it from the toxic effects of B(a)P and other polyaromatic hydrocarbons [101].
5. Conclusions
The C. elegans genome contains 76 genes coding for P450s. Phylogenetic analysis shows that they are homologous to mammalian P450s of families 2, 3, and 4. Many compounds, including drugs, pesticides, polyaromatic molecules, metal ions, ethanol, or caffeine, act as inducers of C. elegans P450s (Table 2). Very few data about the biochemical properties of those P450s have been published so far. Thus, no spectroscopic or structural study of those P450s has been reported so far. However, an increasing number of articles have appeared on reactions catalyzed by them in the metabolism of xenobiotics (Table 5 and Table 6 and Figure 3) and of endobiotics such as fatty acid derivatives and steroids (Table 3 and Figure 2). Moreover, the implication of some P450s in various biological functions of C. elegans without mention of the precise reaction catalyzed by those P450s has been reported in several articles (Table 2). These preliminary studies at the biological level may pave the way to decipher the enzymatic reactions catalyzed by these P450s. Invalidation of the expression of several P450s has shown their implication in C. elegans survival, morphology, embryonic development, growth, larval development, dauer formation, life span, reproduction, movement, pharyngeal pumping, fat content, or lipid composition and metabolism. All the data reported so far for each P450 are schematically summarized in Table 7. Moreover, because of the importance of the use of C. elegans as a model in biology and toxicology, more complete knowledge of its P450s appears to be important in the near future.

Table 7.
Data presently reported on each C. elegans P450.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale); CNRS (Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique); Université Paris Descartes (Bourse de l’école doctorale MTCI). The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
17:18-EEQ: 17,18-epoxy-eicosatetraenoic acid; AA, arachidonic acid; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; ARNT, aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; BaP, benzo(a)pyrene; C. elegans, Caenorhabditis elegans; DAs, dafachronic acids; DDT, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; KO, knock-out; LD50, lethal dose 50; P450, cytochrome P450; PCB 52, 2,2′,5,5′-tetrachloro-biphenyl.
References
- Brusca, R.; Moore, W.; Shuster, S. (Eds.) Invertebrates; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Meneely, P.; Dahlberg, C.; Rose, J. Working with Worms: Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model Organism. Curr. Protoc. Essent. Lab. Tech. 2019, 19, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassada, R.C.; Russell, R.L. The dauerlarva, a post-embryonic developmental variant of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 1975, 46, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klass, M.; Hirsh, D. Non-ageing developmental variant of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1976, 260, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, P.R. The C. elegans model in toxicity testing. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.G.; Southgate, E.; Thomson, J.N.; Brenner, S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1986, 314, 1–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletta, T.; Hengartner, M.O. Finding function in novel targets: C. elegans as a model organism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.C.; Williams, P.L.; Benedetto, A.; Au, C.; Helmcke, K.J.; Aschner, M.; Meyer, J.N. Caenorhabditis elegans: An emerging model in biomedical and environmental toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 106, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium CES. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: A platform for investigating biology. Science 1998, 282, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, D.; Renaud, J.P. Heme-Thiolate Proteins Different from Cytochromes Catalyzing Monooxygenation. In Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; de Montellano, O.P.R., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 537–574. [Google Scholar]
- De Montellano, O.P.R. Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich, F.P. Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. In Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry, 4th ed.; de Montellano, O.P.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 523–785. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R. Cytochrome P450 diversity in the tree of life. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018, 1866, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, P.B. The cytochrome P450 superfamily: Biochemistry, evolution and drug metabolism in humans. Curr Drug Metab. 2002, 3, 561–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R. Cytochrome P450 and the individuality of species. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 369, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, W.S.; Marko, P.B.; Nelson, D.R. The cytochrome P450 (CYP) gene superfamily in Daphnia pulex. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.R.; Goldstone, J.V.; Stegeman, J.J. The cytochrome P450 genesis locus: The origin and evolution of animal cytochrome P450s. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero-Navarro, S.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.M. New Trends in Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Biology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larigot, L.; Juricek, L.; Dairou, J.; Coumoul, X. AhR signaling pathways and regulatory functions. Biochim. Open 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.J.; Jarrell, T.A.; Brittin, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Bloniarz, A.E.; Yakovlev, M.A.; Nguyen, K.C.Q.; Tang, L.T.; Bayer, E.A.; Duerr, J.S.; et al. Whole-animal connectomes of both Caenorhabditis elegans sexes. Nature 2019, 571, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R. A world of cytochrome P450s. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R. Metazoan cytochrome P450 evolution. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 121, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt, version 2021.4; EMBL-EBI: Cambridge, UK, 2021.
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W465–W469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, O. Divergent structures of Caenorhabditis elegans cytochrome P450 genes suggest the frequent loss and gain of introns during the evolution of nematodes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gotoh, O. Evolution of cytochrome p450 genes from the viewpoint of genome informatics. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.H. Rapid birth-death evolution specific to xenobiotic cytochrome P450 genes in vertebrates. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e672007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.S.; Riddle, D.L. Mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans that form dauer-like larvae. Dev. Biol. 1988, 126, 270–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerisch, B.; Antebi, A. Hormonal signals produced by DAF-9/cytochrome P450 regulate C. elegans dauer diapause in response to environmental cues. Development 2004, 131, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerisch, B.; Weitzel, C.; Kober-Eisermann, C.; Rottiers, V.; Antebi, A. A hormonal signaling pathway influencing C. elegans metabolism, reproductive development, and life span. Dev. Cell 2001, 1, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanikia, S.; Hylands, P.; Sturzenbaum, S.R. The double mutation of cytochrome P450’s and fatty acid desaturases affect lipid regulation and longevity in C. elegans. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2015, 2, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Sun, H. Functional genomic approach to identify novel genes involved in the regulation of oxidative stress resistance and animal lifespan. Aging Cell 2007, 6, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kenyon, C. Regulation of the longevity response to temperature by thermosensory neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElwee, J.J.; Schuster, E.; Blanc, E.; Thomas, J.H.; Gems, D. Shared transcriptional signature in Caenorhabditis elegans Dauer larvae and long-lived daf-2 mutants implicates detoxification system in longevity assurance. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44533–44543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.T.; McCarroll, S.A.; Bargmann, C.I.; Fraser, A.; Kamath, R.S.; Ahringer, J.; Li, H.; Kenyon, C. Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2003, 424, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.; Albert, P.S.; Riddle, D.L. DAF-9, a cytochrome P450 regulating C. elegans larval development and adult longevity. Development 2002, 129, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, R.S.; Fraser, A.G.; Dong, Y.; Poulin, G.; Durbin, R.; Gotta, M.; Kanapin, A.; Le Bot, N.; Moreno, S.; Sohrmann, M.; et al. Systematic functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome using RNAi. Nature 2003, 421, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rual, J.F.; Ceron, J.; Koreth, J.; Hao, T.; Nicot, A.S.; Hirozane-Kishikawa, T.; Vandenhaute, J.; Orkin, S.H.; Hill, D.E.; van den Heuvel, S.; et al. Toward improving Caenorhabditis elegans phenome mapping with an ORFeome-based RNAi library. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelson, A.V.; Klimczak, R.R.; Thompson, D.B.; Carr, C.E.; Ruvkun, G. Identification of Caenorhabditis elegans genes regulating longevity using enhanced RNAi-sensitive strains. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2007, 72, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Simmer, F.; Moorman, C.; van der Linden, A.M.; Kuijk, E.; van den Berghe, P.V.; Kamath, R.S.; Fraser, A.G.; Ahringer, J.; Plasterk, R.H. Genome-wide RNAi of C. elegans using the hypersensitive rrf-3 strain reveals novel gene functions. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, E122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benenati, G.; Penkov, S.; Muller-Reichert, T.; Entchev, E.V.; Kurzchalia, T.V. Two cytochrome P450s in Caenorhabditis elegans are essential for the organization of eggshell, correct execution of meiosis and the polarization of embryo. Mech. Dev. 2009, 126, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnichsen, B.; Koski, L.B.; Walsh, A.; Marschall, P.; Neumann, B.; Brehm, M.; Alleaume, A.M.; Artelt, J.; Bettencourt, P.; Cassin, E.; et al. Full-genome RNAi profiling of early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2005, 434, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, M.H.; Kawasaki, I.; Shim, Y.H. A circulatory transcriptional regulation among daf-9, daf-12, and daf-16 mediates larval development upon cholesterol starvation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannich, J.T.; Entchev, E.V.; Mende, F.; Boytchev, H.; Martin, R.; Zagoriy, V.; Theumer, G.; Riezman, I.; Riezman, H.; Knolker, H.J.; et al. Methylation of the sterol nucleus by STRM-1 regulates dauer larva formation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, V.L.; Simonsen, K.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, D.; Riddle, D.L. RNAi screen of DAF-16/FOXO target genes in C. elegans links pathogenesis and dauer formation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e159022010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulas, J.; Schmidt, C.; Rothe, M.; Schunck, W.H.; Menzel, R. Cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism of eicosapentaenoic acid in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 472, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.M.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Shui, G. Sequestration of polyunsaturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids of Caenorhabditis elegans dauer larva attenuates eicosanoid biosynthesis for prolonged survival. Redox. Biol. 2017, 12, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magner, D.B.; Antebi, A. Caenorhabditis elegans nuclear receptors: Insights into life traits. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 19, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motola, D.L.; Cummins, C.L.; Rottiers, V.; Sharma, K.K.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, H.E.; Auchus, R.J.; Antebi, A.; et al. Identification of ligands for DAF-12 that govern dauer formation and reproduction in C. elegans. Cell 2006, 124, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, H.D.; Prasain, J.K.; Dorand, D.; Miller, M.A. A heterogeneous mixture of F-series prostaglandins promotes sperm guidance in the Caenorhabditis elegans reproductive tract. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e10032712013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleemann, G.; Jia, L.; Emmons, S.W. Regulation of Caenorhabditis elegans male mate searching behavior by the nuclear receptor DAF-12. Genetics 2008, 180, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Roh, J.Y.; Park, Y.K.; Park, K.; Choi, J. Ecotoxicological investigation of CeO(2) and TiO(2) nanoparticles on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using gene expression, growth, fertility, and survival as endpoints. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 29, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarnio, V.; Lehtonen, M.; Storvik, M.; Callaway, J.C.; Lakso, M.; Wong, G. Caenorhabditis Elegans Mutants Predict Regulation of Fatty Acids and Endocannabinoids by the CYP-35A Gene Family. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosel, M.; Wild, W.; Bell, A.; Rothe, M.; Lindschau, C.; Steinberg, C.E.; Schunck, W.H.; Menzel, R. Eicosanoid formation by a cytochrome P450 isoform expressed in the pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, R.; Yeo, H.L.; Rienau, S.; Li, S.; Steinberg, C.E.; Sturzenbaum, S.R. Cytochrome P450s and short-chain dehydrogenases mediate the toxicogenomic response of PCB52 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 370, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilaniu, H.; Fabrizio, P.; Witting, M. The Role of Dafachronic Acid Signaling in Development and Longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans: Digging Deeper Using Cutting-Edge Analytical Chemistry. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Ellieva, A.; Ma, D.K.; Ju, J.; Nehk, E.; Konkel, A.; Falck, J.R.; Schunck, W.H.; Menzel, R. CYP-13A12 of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is a PUFA-epoxygenase involved in behavioural response to reoxygenation. Biochem. J. 2014, 464, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, S.T.; Ivens, A.; Butler, V.; Ravikumar, S.P.; Laing, R.; Woods, D.J.; Gilleard, J.S. The transcriptional response of Caenorhabditis elegans to Ivermectin exposure identifies novel genes involved in the response to reduced food intake. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e313672012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanti, P.; Bose, N.; Bethke, A.; Judkins, J.C.; Wollam, J.; Dumas, K.J.; Zimmerman, A.M.; Campbell, S.L.; Hu, P.J.; Antebi, A.; et al. Comparative metabolomics reveals endogenous ligands of DAF-12, a nuclear hormone receptor, regulating C elegans development and lifespan. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.K.; Wang, Z.; Motola, D.L.; Cummins, C.L.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Auchus, R.J. Synthesis and activity of dafachronic acid ligands for the C. elegans DAF-12 nuclear hormone receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ceron, J.; Rual, J.F.; Chandra, A.; Dupuy, D.; Vidal, M.; van den Heuvel, S. Large-scale RNAi screens identify novel genes that interact with the C. elegans retinoblastoma pathway as well as splicing-related components with synMuv B activity. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Falck, J.R.; Rothe, M.; Schunck, W.H.; Menzel, R. Role of CYP eicosanoids in the regulation of pharyngeal pumping and food uptake in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2110–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubagawa, H.M.; Watts, J.L.; Corrigan, C.; Edmonds, J.W.; Sztul, E.; Browse, J.; Miller, M.A. Oocyte signals derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids control sperm recruitment in vivo. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pender, C.L.; Horvitz, H.R. Hypoxia-inducible factor cell non-autonomously regulates C. elegans stress responses and behavior via a nuclear receptor. eLife 2018, 7, e36828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, P.; Xie, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L. Transcriptome Analysis of the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans in Acidic Stress Environments. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, M.; Chaudhari, S.N.; Balachandran, R.S.; Vagasi, A.S.; Kipreos, E.T. Dafachronic acid inhibits C. elegans germ cell proliferation in a DAF-12-dependent manner. Dev. Biol. 2017, 432, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, F.; Bichet, A.; Ewen, K.M.; Bernhardt, R. Cytochrome P450 systems—Biological variations of electron transport chains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007, 1770, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappleye, C.A.; Tagawa, A.; Le Bot, N.; Ahringer, J.; Aroian, R.V. Involvement of fatty acid pathways and cortical interaction of the pronuclear complex in Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic polarity. BMC. Dev. Biol. 2003, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patananan, A.N.; Budenholzer, L.M.; Eskin, A.; Torres, E.R.; Clarke, S.G. Ethanol-induced differential gene expression and acetyl-CoA metabolism in a longevity model of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 61, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, J.; Aarnio, V.; Heikkinen, L.; Lakso, M.; Wong, G. Chronic ethanol exposure increases cytochrome P-450 and decreases activated in blocked unfolded protein response gene family transcripts in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2013, 27, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Kawasaki, I.; Gong, J.; Shim, Y.H. Caffeine induces high expression of cyp-35A family genes and inhibits the early larval development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, R.; Bogaert, T.; Achazi, R. A systematic gene expression screen of Caenorhabditis elegans cytochrome P450 genes reveals CYP35 as strongly xenobiotic inducible. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 395, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Rodel, M.; Kulas, J.; Steinberg, C.E. CYP35: Xenobiotically induced gene expression in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 438, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, K.; Menzel, R. Expression profiling of five different xenobiotics using a Caenorhabditis elegans whole genome microarray. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrapani, B.P.; Kumar, S.; Subramaniam, J.R. Development and evaluation of an in vivo assay in Caenorhabditis elegans for screening of compounds for their effect on cytochrome P450 expression. J. Biosci. 2008, 33, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, C.; Lafayette, I.; Antoniou-Kourounioti, M.; Gutierrez, C.; Martin, J.R.; Chowdhuri, D.K.; De Pomerai, D.I. Use of transgenic GFP reporter strains of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans to investigate the patterns of stress responses induced by pesticides and by organic extracts from agricultural soils. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.M.; Rayson, S.J.; Flemming, A.J.; Urwin, P.E. Adaptive and specialised transcriptional responses to xenobiotic stress in Caenorhabditis elegans are regulated by nuclear hormone receptors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e699562013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.Y.; Choi, J. Cyp35a2 gene expression is involved in toxicity of fenitrothion in the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Cui, C.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, K. The chronic toxicity of bisphenol A to Caenorhabditis elegans after long-term exposure at environmentally relevant concentrations. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.D.; Lin, K.F. Ecotoxicological evaluation of low-concentration bisphenol A exposure on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and intrinsic mechanisms of stress response in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.D.; Lin, K.F. Ecotoxicity of bisphenol A to Caenorhabditis elegans by multigenerational exposure and variations of stress response in vivo across generations. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, P.; Muller, M.; Kruger, A.; Steinberg, C.E.; Menzel, R. Cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism of PCB52 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 488, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.C.; Rooney, J.P.; Ryde, I.T.; Bernal, A.J.; Bess, A.S.; Crocker, T.L.; Ji, A.Q.; Meyer, J.N. Effects of early life exposure to ultraviolet C radiation on mitochondrial DNA content, transcription, ATP production, and oxygen consumption in developing Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, A.L.; Meyer, J.N. Effects of reduced mitochondrial DNA content on secondary mitochondrial toxicant exposure in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mitochondrion 2016, 30, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; McBride, S.J.; Boyd, W.A.; Alper, S.; Freedman, J.H. Toxicogenomic analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans reveals novel genes and pathways involved in the resistance to cadmium toxicity. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Choi, J. Assessment of stress-related gene expression in the heavy metal-exposed nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: A potential biomarker for metal-induced toxicity monitoring and environmental risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2946–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baberschke, N.; Steinberg, C.E.; Saul, N. Low concentrations of dibromoacetic acid and N-nitrosodimethylamine induce several stimulatory effects in the invertebrate model Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, H.J.; Ahn, J.M.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1)-flavin containing monooxygenase-2 (FMO-2) signaling acts in silver nanoparticles and silver ion toxicity in the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 270, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Miwa, S.; Isomura, K.; Tsutsumiuchi, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Miwa, J. Acrylamide-responsive genes in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.Y.; Jung, I.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, J. Toxic effects of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate on mortality, growth, reproduction and stress-related gene expression in the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicology 2007, 237, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, M.; Kim, S.K.; Berdichevsky, A.; Guarente, L. A role for SIR-2.1 regulation of ER stress response genes in determining C. elegans life span. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodia, N.; Won, S.J.; Novillo, A.; Wieland, M.; Li, C.; Callard, I.P. Caenorhabditis elegans as an environmental monitor using DNA microarray analysis. Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 2001, 948, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Luo, Q.; Cao, X.; Cui, C.; Lin, K.; Huang, K. Toxicological assessment and underlying mechanisms of tetrabromobisphenol A exposure on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, T.H.; Dodd, A.K. Xenobiotic detoxification in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Exp. Zool. A Comp. Exp. Biol. 2006, 305, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.M.; Flemming, A.J.; Urwin, P.E. NHR-176 regulates cyp-35d1 to control hydroxylation-dependent metabolism of thiabendazole in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, P.H.; Perry, S.J.; Stevens, A.J.; Flemming, A.J. Comparative metabolism of xenobiotic chemicals by cytochrome P450s in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.C.; Goldstone, J.V.; Boyd, W.A.; Freedman, J.H.; Meyer, J.N. Caenorhabditis elegans generates biologically relevant levels of genotoxic metabolites from aflatoxin B1 but not benzo[a]pyrene in vivo. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 118, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbass, M.; Chen, Y.; Arlt, V.M.; Sturzenbaum, S.R. Benzo[a]pyrene and Caenorhabditis elegans: Defining the genotoxic potential in an organism lacking the classical CYP1A1 pathway. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.M.; Lu, Z.L.; Yu, Y.; Chen, G.; Ma, R.; Kou, W.; Lan, Y.M. Toxicity and metabolism of 3-bromopyruvate in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.B.; Hartman, J.H.; Luz, A.L.; Wilson, J.Y.; Dinyari, A.; Meyer, J.N. Zebrafish CYP1A expression in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans protects from exposures to benzo[a]pyrene and a complex polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixture. Toxicology 2020, 440, 152473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, P.; Matthijssens, F.; Vlaeminck, C.; Braeckman, B.P.; Vanfleteren, J.R. Effects of sod gene overexpression and deletion mutation on the expression profiles of reporter genes of major detoxification pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herholz, M.; Cepeda, E.; Baumann, L.; Kukat, A.; Hermeling, J.; Maciej, S.; Szczepanowska, K.; Pavlenko, V.; Frommolt, P.; Trifunovic, A. KLF-1 orchestrates a xenobiotic detoxification program essential for longevity of mitochondrial mutants. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, Q.; Kong, Y.; Wu, S.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.O. Specific regulation of thermosensitive lipid droplet fusion by a nuclear hormone receptor pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8841–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).