Revised Rainfall Threshold in the Indonesian Landslide Early Warning System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
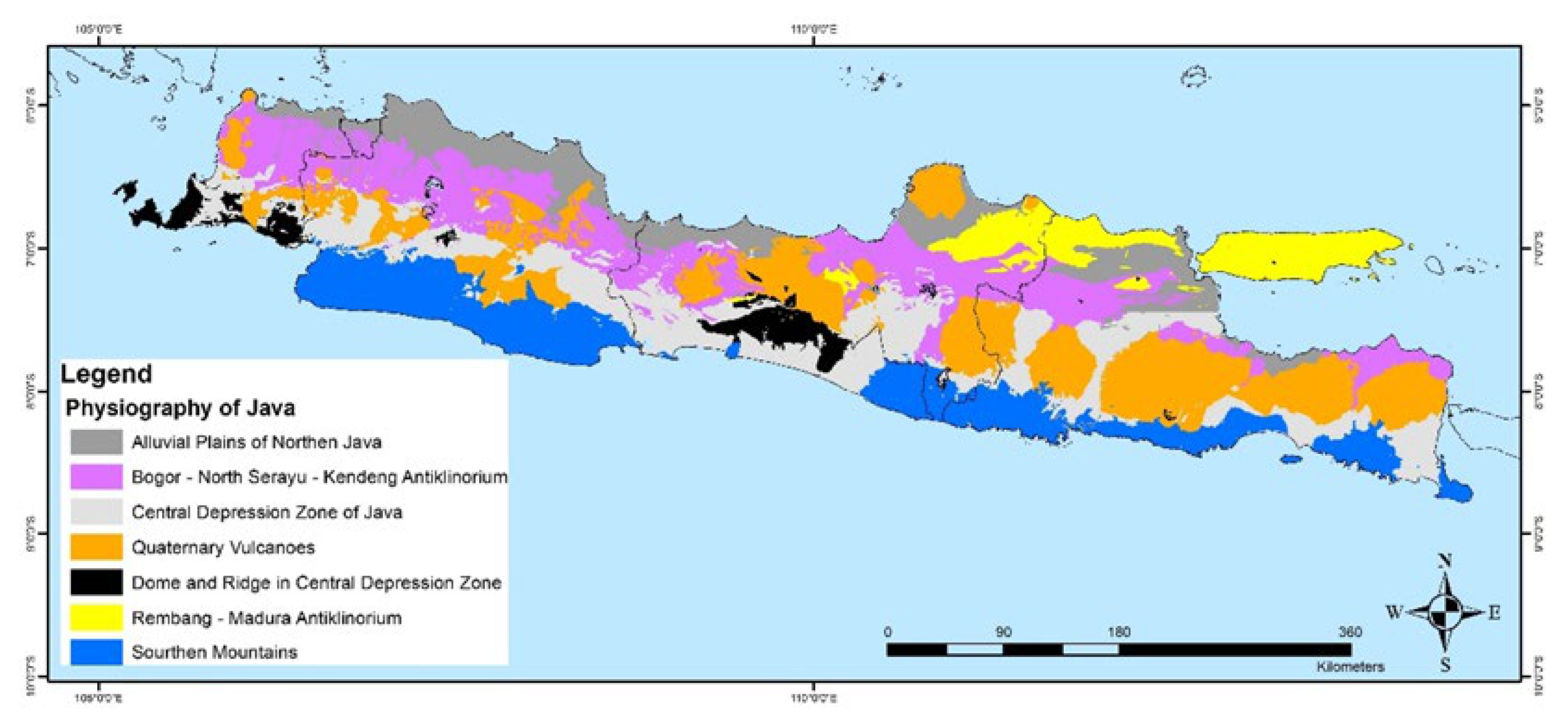
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Landslide Events
2.2.2. Observed Rainfall Data
2.3. Methods
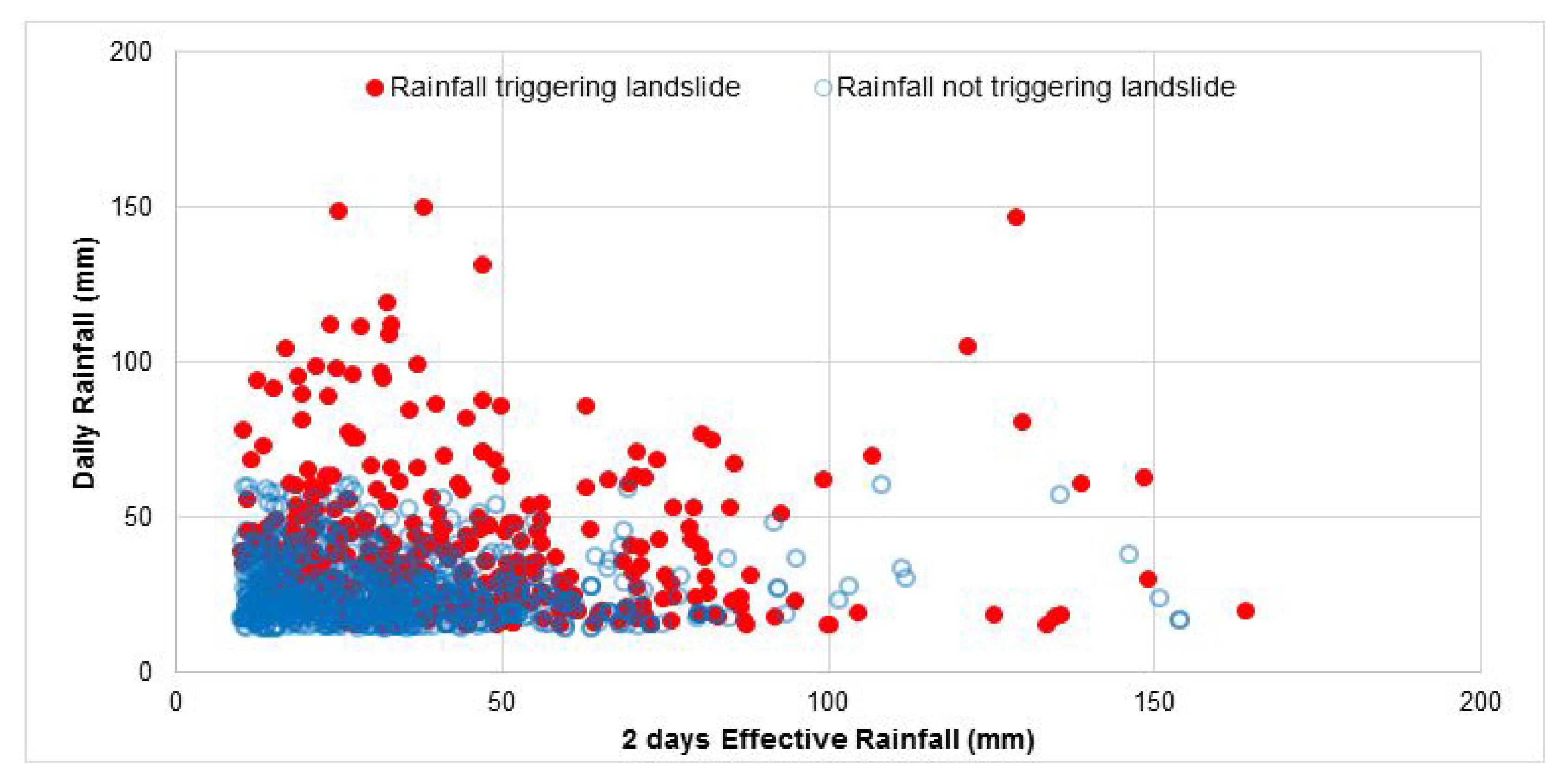
2.3.1. Effective Antecedent Daily Rainfall
2.3.2. Determination of Rainfall Thresholds
2.3.3. Performance Analysis of Rainfall Thresholds
3. Results
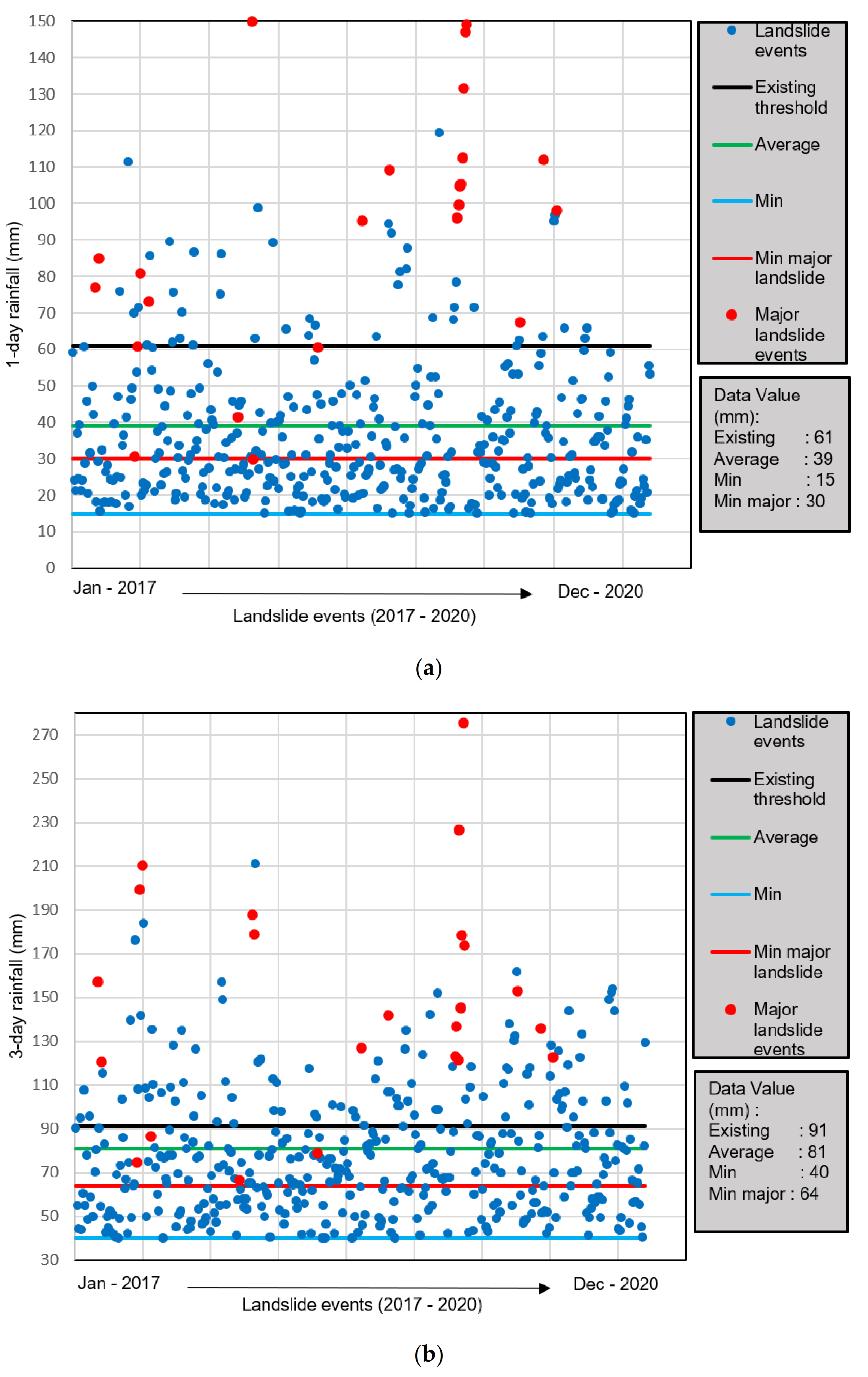
3.1. Rainfall Threshold Results
3.2. Performance Analysis
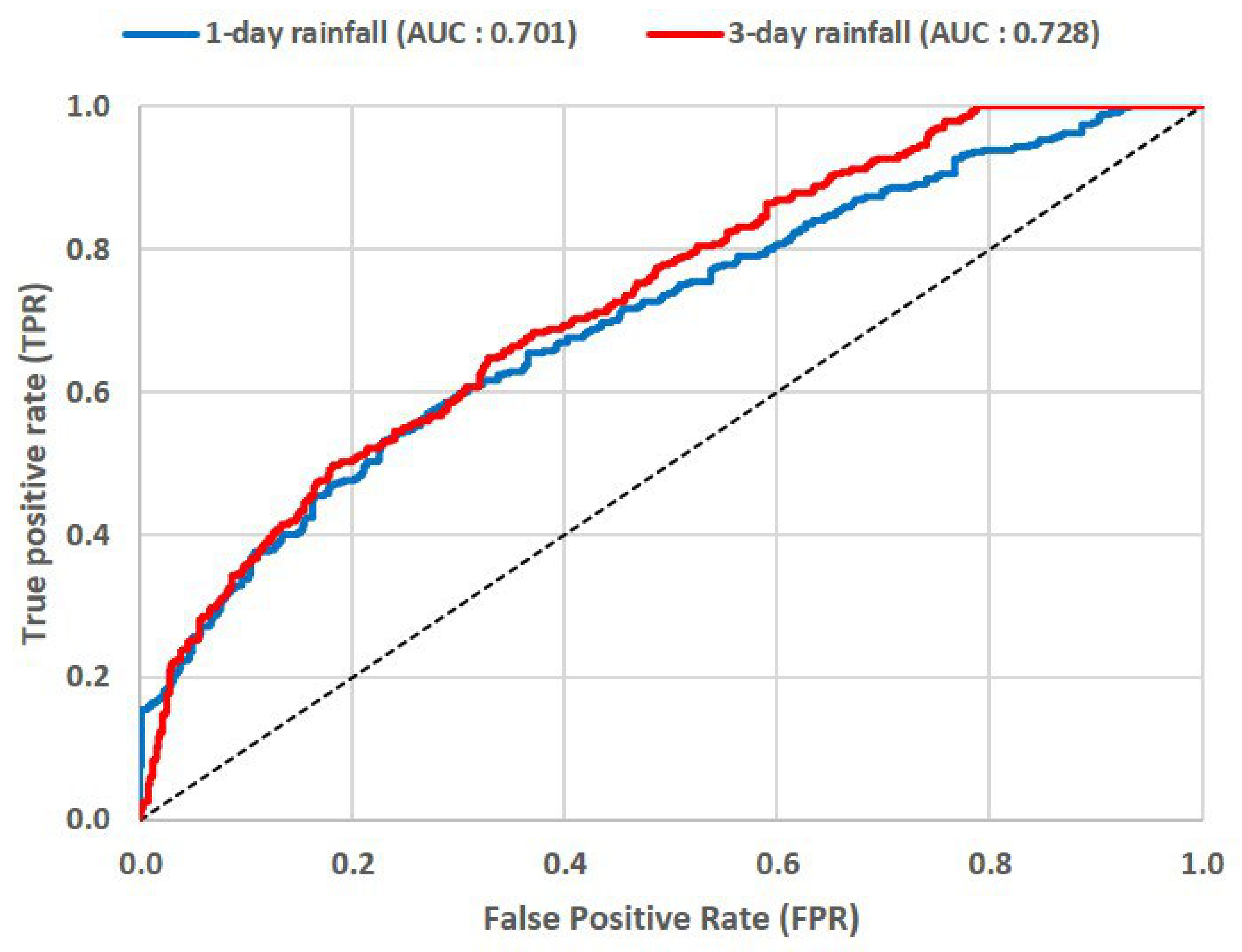
3.2.1. ROC Curve
3.2.2. Confusion Matrix and Statistical Indices
TPR and TNR
Accuracy
Overall Statistical Scores
4. Discussion
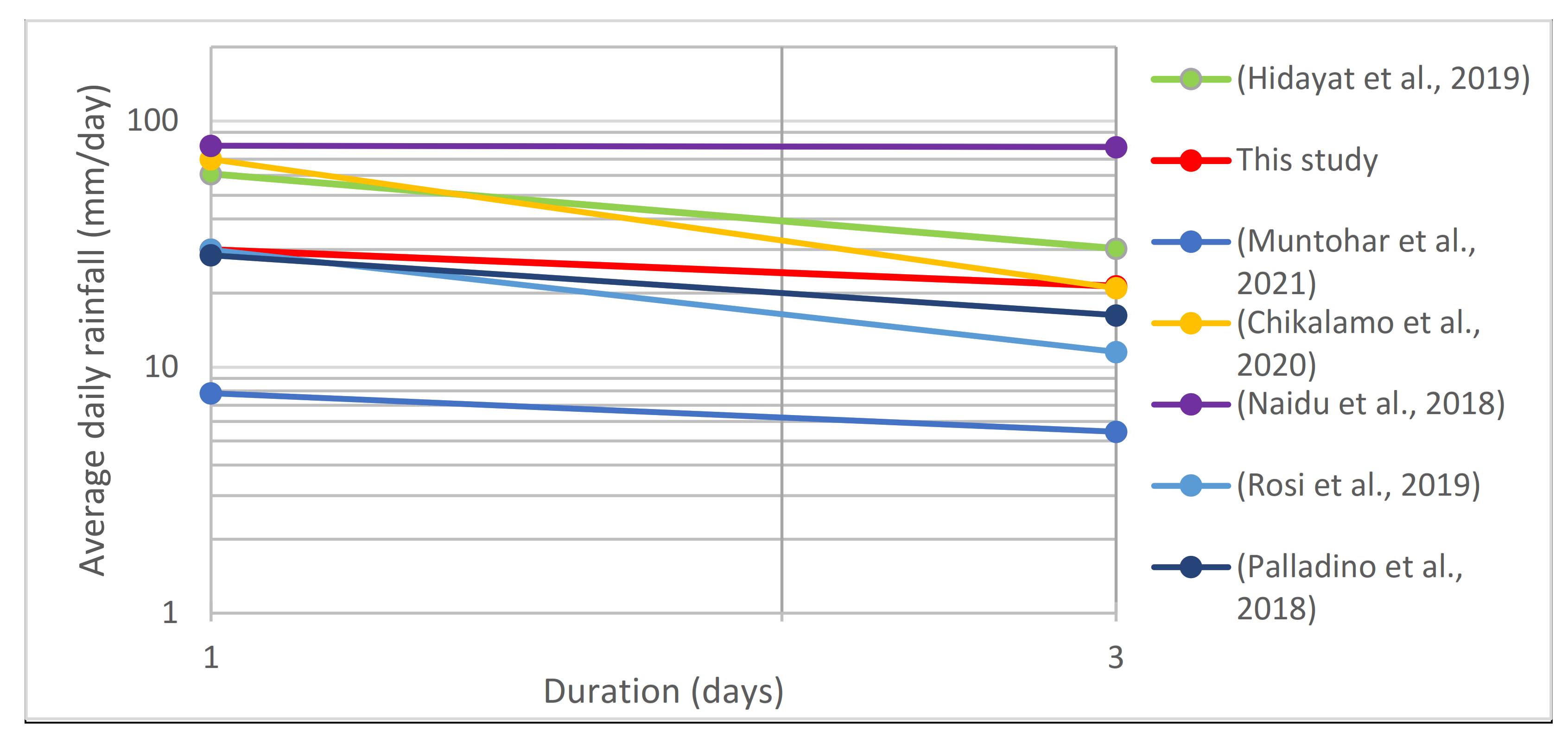
4.1. Worldwide Rainfall Thresholds
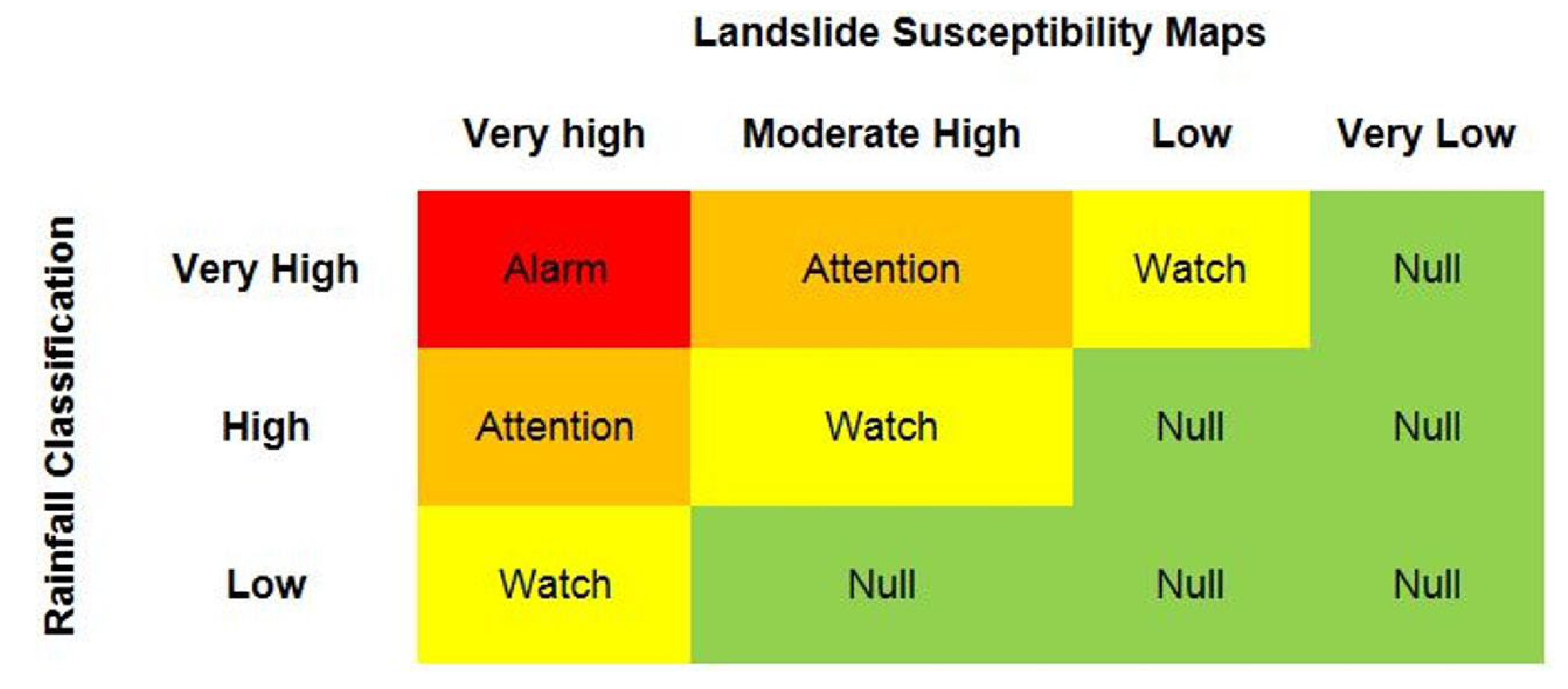
4.2. Implementation in the Balai Sabo-ILEWS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Segoni, S.; Piciullo, L.; Gariano, S.L. A review of the recent literature on rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence. Landslides 2018, 15, 1483–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasse, S.; Nadim, F. Landslide Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategy. In Landslides—Disaster Risk Reduction; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 31–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaciago, G. The SafeLand Compendium of Landslide Risk Mitigation Measures. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Tan, S. Landslide mitigation strategies in southeast Bangladesh: Lessons learned from the institutional responses. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 62, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piciullo, L.; Calvello, M.; Cepeda, J.M. Territorial early warning systems for rainfall-induced landslides. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Gariano, S.L.; Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Marchesini, L.; Rossi, M.; Melillo, M. Geographical landslide early warning systems. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, R.; Sutanto, S.J.; Hidayah, A.; Ridwan, B.; Mulyana, A. Development of a Landslide Early Warning System in Indonesia. Geosciences 2019, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muntohar, A.S.; Mavrouli, O.; Jetten, V.G.; van Westen, C.J.; Hidayat, R. Development of Landslide Early Warning System Based on the Satellite-Derived Rainfall Threshold in Indonesia. In Understanding and Reducing Landslide Disaster Risk; Casagli, N., Tofani, V., Sassa, K., Bobrowsky, P.T., Takara, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, M.T.; Fathani, T.F.; Wilopo, W. Estimating the Velocity of Landslide Movement Using Visco-Plastic Model in Jeruk Sub-village, Kulon Progo District, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. J. Civ. Eng. Forum 2018, 4, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-L.; Chang, C.-H.; Yang, J.-C.; Tung, Y.-K. Physical-based rainfall-triggered shallow landslide forecasting. Smart Water 2018, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwikorita, K.; Djoko, L. Landslide Hazard and Community-based Risk Reduction Effort in Karanganyar and the Surrounding Area, Central Java, Indonesia. J. Mt. Sci. 2011, 8, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Fukuoka, H.; Sassak, K.; Krnawati, D.; Fathani, F. Prototyping an experimental early warning system for rainfall-induced landslides in Indonesia using satellite remote sensing and geospatial datasets. Landslides 2010, 7, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, H.; Wilopo, W.; Wiyoso, T.; Fathani, T.F.; Karnawati, D. Investigation and numerical simulation of the 22 February 2018 landslide-triggered long-traveling debris flow at Pasir Panjang Village, Brebes Regency of Central Java, Indonesia. Landslides 2019, 16, 2219–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardani, S.P.R.; Kodoatie, R.J. Disaster Management in Central Java Province, Indonesia. In Geotechnical Engineering for Disaster Mitigation and Rehabilitation; Liu, H., Deng, A., Chu, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petley, D.N.; Hearn, G.J.; Hart, A.; Rosser, N.J.; Dunning, S.A.; Oven, H.; Mitchell, W.A. Trends in landslide occurrence in Nepal. Nat. Hazards 2007, 43, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, F.; Fathani, F. A Coupled Hydrology/Slope Kinematics Model for Developing Early Warning Criteria in the Kalitlaga Landslide, Banjarnegara, Indonesia. In Progress of Geo-Disaster Mitigation Technology in Asia; Wang, F., Miyajima, M., Li, T., Shan, W., Fathani, T.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebes, B.; Glade, T. Landslide Early Warning Systems—Fundamental Concepts and Innovative Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayat, R.; Zahro, A.A. Penentuan Ambang Curah Hujan untuk Memprediksi Kejadian Longsor. J. Sumber Daya Air 2020, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Hu, H.; Lu, H.; Hou, A. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network: Validation of GPM and TRMM Over TP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, P.; Crosta, G.; Sosio, R. Approaches for defining thresholds and return periods for rainfall-triggered shallow landslides. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1444–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrian, E.; Susanto, R.D. Identification of three dominant rainfall regions within Indonesia and their relationship to sea surface temperature. Int. J. Clim. 2003, 23, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastra, D.; Idham, N.C. The Proposals of Landslide Spatial-Mitigation Strategy in Indonesia; A literature study from the events of 2010–2015. MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 280, 01010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. A New Interpretation of Java’s Structure. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First Annual Convention, Jakarta, Indonesia, 14–16 May 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bemmelen, R.W. The Geology of Indonesia; Nijhoff: Hague, The Netherlands, 1970; Available online: http://catalog.hathitrust.org/api/volumes/oclc/1517019.html (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Dsikowitzky, L.; Damara, A.; Ferse, S.C.; Irianto, H.E.; Jennerjahn, T.C.; Lukas, M.C.; Nordhaus, I.; Pohlmann, T.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Sugma, K.; et al. Java Island, Indonesia. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 459–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadmoko, D.S.; Lavigne, F.; Samodra, G. Application of a semiquantitative and GIS-based statistical model to landslide susceptibility zonation in Kayangan Catchment, Java, Indonesia. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 437–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BPS (Badan Pusat Statistik). Statistical Surveys of the Indonesian Government. 2021. Available online: https://www.bps.go.id (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Antronicol, L.; Bartolini, D.; Deganutti, A.M.; Gariano, S.L.; Iovne, G.; Luciani, S.; Luino, F.; Melillo, M.; et al. Catalogue of Rainfall Events with Shallow Landslides and New Rainfall Thresholds in Italy. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory; Lollino, G., Giordan, D., Crosta, G.B., Corominas, J., Azzam, R., Wasowski, J., Sciarra, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samodra, G.; Chen, G.; Sartohadi, J.; Kasama, K. Generating landslide inventory by participatory mapping: An example in Purwosari Area, Yogyakarta, Java. Geomorphology 2018, 306, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-L.; Chen, H.-F. Effects of degree of saturation on shallow landslides triggered by rainfall. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh-Tuan, L.; Matsumoto, J.; Ngo-Duc, T.; Nodzu, M.I.; Inoue, T. Evaluation of satellite precipitation products over Central Vietnam. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.; Huffman, G. Evaluation of the potential of NASA multi-satellite precipitation analysis in global landslide hazard assessment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L22402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.; Huffman, G. Use of satellite remote sensing data in the mapping of global landslide susceptibility. Nat. Hazards 2007, 43, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J. Satellite Remote Sensing for Global Landslide Monitoring. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2007, 88, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, T.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Han, D.; Srivastava, P.K.; Ishak, A.M. Performance evaluation of the TRMM precipitation estimation using ground-based radars from the GPM validation network. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 77, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zipser, E.J. The global distribution of largest, deepest, and most intense precipitation systems: Largest, Deepest and Strongest Storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3591–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glade, T.; Crozier, M.; Smith, P. Applying Probability Determination to Refine Landslide-triggering Rainfall Thresholds Using an Empirical ‘Antecedent Daily Rainfall Model. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2000, 157, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikalamo, E.E.; Mavrouli, O.C.; Ettema, J.; van Westen, C.J.; Muntohar, A.S.; Mustofa, A. Satellite-derived rainfall thresholds for landslide early warning in Bogowonto Catchment, Central Java, Indonesia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 89, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalubowila, P.; Lokupitiya, E.; Halwatura, D.; Jayathissa, G. Threshold rainfall ranges for landslide occurrence in Matara district of Sri Lanka and findings on community emergency preparedness. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 52, 101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zêzere, J.L.; Trigo, R.M.; Trigo, I.F. Shallow and deep landslides induced by rainfall in the Lisbon region (Portugal): Assessment of relationships with the North Atlantic Oscillation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hiura, H.; Shino, K.; Sassa, K.; Fukuoka, H. Quantitative assessment on the influence of heavy rainfall on the crystalline schist landslide by monitoring system -case study on Zentoku landslide, Japan. Landslides 2005, 2, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Berdine, G. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Southwest Respir. Crit. Care Chron. 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariano, S.L.; Brunetti, M.; Iovine, G.; Melillo, M.; Peruccacci, S.; Terranova, O.; Vennari, C.; Huzzetti, F. Calibration and validation of rainfall thresholds for shallow landslide forecasting in Sicily, southern Italy. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, S.; Sajinkumar, K.S.; Oommen, T.; Anuja, V.J.; Samuel, R.A.; Muraleedharan, C. Early warning system for shallow landslides using rainfall threshold and slope stability analysis. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, M.R.; Viero, A.; Turconi, L.; Brunetti, M.; Peruccacci, S.; Melillo, M.; Luino, F.; Deganutti, A.; Guzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for the activation of shallow landslides in the Italian Alps: The role of environmental conditioning factors. Geomorphology 2018, 303, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Canavesi, V.; Segoni, S.; Nery, T.D.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Landslides in the Mountain Region of Rio de Janeiro: A Proposal for the Semi-Automated Definition of Multiple Rainfall Thresholds. Geosciences 2019, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzzetti, F.; Peruccacci, S.; Rossi, M.; Stark, C.P. Rainfall thresholds for the initiation of landslides in central and southern Europe. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2007, 98, 239–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Lagomarsino, D.; Fanti, R.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Integration of rainfall thresholds and susceptibility maps in the Emilia Romagna (Italy) regional-scale landslide warning system. Landslides 2015, 12, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradhan, A.M.S.; Lee, S.-R.; Kim, Y.-T. A shallow slide prediction model combining rainfall threshold warnings and shallow slide susceptibility in Busan, Korea. Landslides 2019, 16, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, M.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Hürlimann, M. Debris-flow forecasting at regional scale by combining susceptibility mapping and radar rainfall. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.F. Predicting global landslide spatiotemporal distribution: Integrating landslide susceptibility zoning techniques and real-time satellite rainfall estimates. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Tofani, V.; Rosi, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Combination of Rainfall Thresholds and Susceptibility Maps for Dynamic Landslide Hazard Assessment at Regional Scale. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BSN (Badan Standardisasi Nasional). SNI 8291Penyusunan dan Penentuan Zona Kerentanan Gerakan Tanah. 2016. Available online: https://pesta.bsn.go.id/produk/detail/10848-sni82912016 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Park, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-R.; Kim, Y.-T.; Kang, S.; Lee, D.-H. A Regional-Scale Landslide Early Warning System Based on the Sequential Evaluation Method: Development and Performance Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model Predictions | Landslide Events | |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |
| ≤Threshold | TP | FP |
| >Threshold | FN | TN |
| Statistical Indices | Description | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity/true positive rate (TPR) | The proportion of positive cases of landslide events that are correctly detected by the threshold | |
| Specificity/true negative rate (TNR) | The proportion of negative cases of landslide events that are correctly detected by the threshold | |
| Accuracy | The proportion of correct predictions overall |
| AUC Value | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | No discrimination, random guesses |
| 0.5 < AUC ≤ 0.6 | Poor discrimination |
| 0.6 < AUC ≤ 0.7 | Acceptable discrimination |
| 0.7 < AUC ≤ 0.8 | Excellent discrimination |
| 0.9 < AUC | Outstanding discrimination |
| Method | Threshold Line | Duration | Threshold (mm) | Contingency Table * | Av. ** TPR | Av. TNR | Av. Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Existing threshold | 1 Day | 61 | 59 | 1 | 0.21 | 0.97 | 0.70 |
| 361 | 749 | |||||||
| 3 Days | 91 | 120 | 44 | |||||
| 300 | 706 | |||||||
| 2nd | Average | 1 Day | 39 | 155 | 79 | 0.38 | 0.89 | 0.71 |
| 265 | 671 | |||||||
| 3 Days | 81 | 168 | 93 | |||||
| 252 | 657 | |||||||
| 3rd | Minimum | 1 Day | 15 | 417 | 693 | 0.99 | 0.14 | 0.45 |
| 3 | 57 | |||||||
| 3 Days | 40 | 417 | 590 | |||||
| 3 | 160 | |||||||
| 4th | Minimum of major landslides | 1 Day | 30 | 229 | 186 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.68 |
| 191 | 564 | |||||||
| 3 Days | 64 | 272 | 245 | |||||
| 148 | 505 | |||||||
| Method | Threshold Line | TPR | TNR | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Existing threshold | Not Good | Good | Good |
| 2nd | Average | Not Good | Good | Good |
| 3rd | Minimum | Good | Not Good | Not Good |
| 4th | Minimum of major landslides | Good | Good | Good |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuniawan, R.A.; Rifa’i, A.; Faris, F.; Subiyantoro, A.; Satyaningsih, R.; Hidayah, A.N.; Hidayat, R.; Mushthofa, A.; Ridwan, B.W.; Priangga, E.; et al. Revised Rainfall Threshold in the Indonesian Landslide Early Warning System. Geosciences 2022, 12, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030129
Yuniawan RA, Rifa’i A, Faris F, Subiyantoro A, Satyaningsih R, Hidayah AN, Hidayat R, Mushthofa A, Ridwan BW, Priangga E, et al. Revised Rainfall Threshold in the Indonesian Landslide Early Warning System. Geosciences. 2022; 12(3):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030129
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuniawan, Ragil Andika, Ahmad Rifa’i, Fikri Faris, Andy Subiyantoro, Ratna Satyaningsih, Alidina Nurul Hidayah, Rokhmat Hidayat, Akhyar Mushthofa, Banata Wachid Ridwan, Eka Priangga, and et al. 2022. "Revised Rainfall Threshold in the Indonesian Landslide Early Warning System" Geosciences 12, no. 3: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030129
APA StyleYuniawan, R. A., Rifa’i, A., Faris, F., Subiyantoro, A., Satyaningsih, R., Hidayah, A. N., Hidayat, R., Mushthofa, A., Ridwan, B. W., Priangga, E., Muntohar, A. S., Jetten, V. G., Westen, C. J. v., Bout, B. V. d., & Sutanto, S. J. (2022). Revised Rainfall Threshold in the Indonesian Landslide Early Warning System. Geosciences, 12(3), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12030129








