A role of alpha-tocopherol and phylloquinone in the modulation of uterine contractility and reproductive function in mouse models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Drugs and salts
2.2. Experimental animals
2.3. Ex vivo experimental set-up
2.4. Studies on ex vivo spontaneous uterine contraction
2.5. Studies on ex vivo oxytocin-induced uterine contraction
2.6. Studies on high KCl-induced uterine contraction in ex vivo models
2.7. Studies on some reproductive parameters in vivo
2.8. Data analysis
3. Results
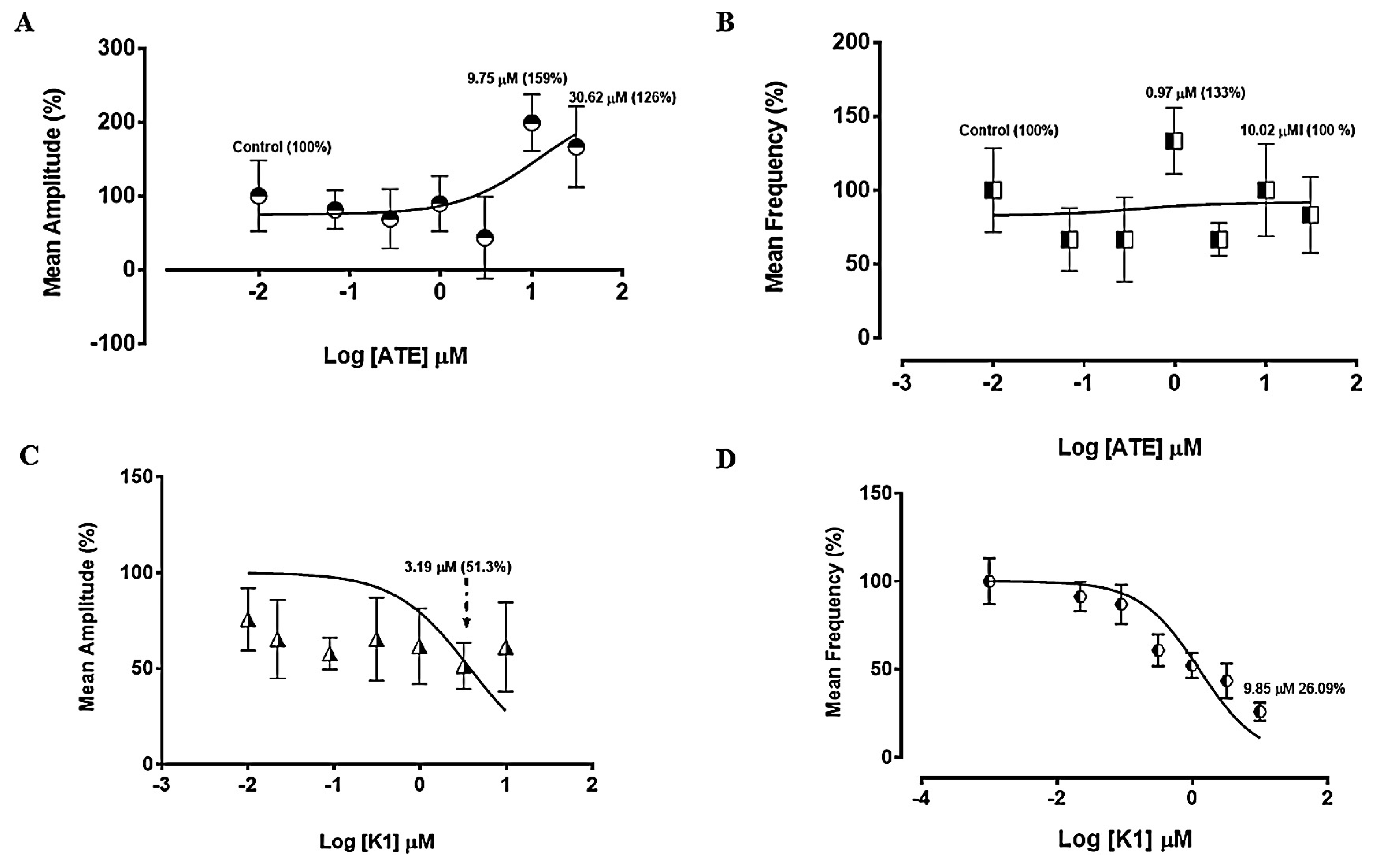
3.1. Experiments on spontaneous uterine contractility
3.1.1. Effect of ATE and K1 on spontaneous uterine contractions
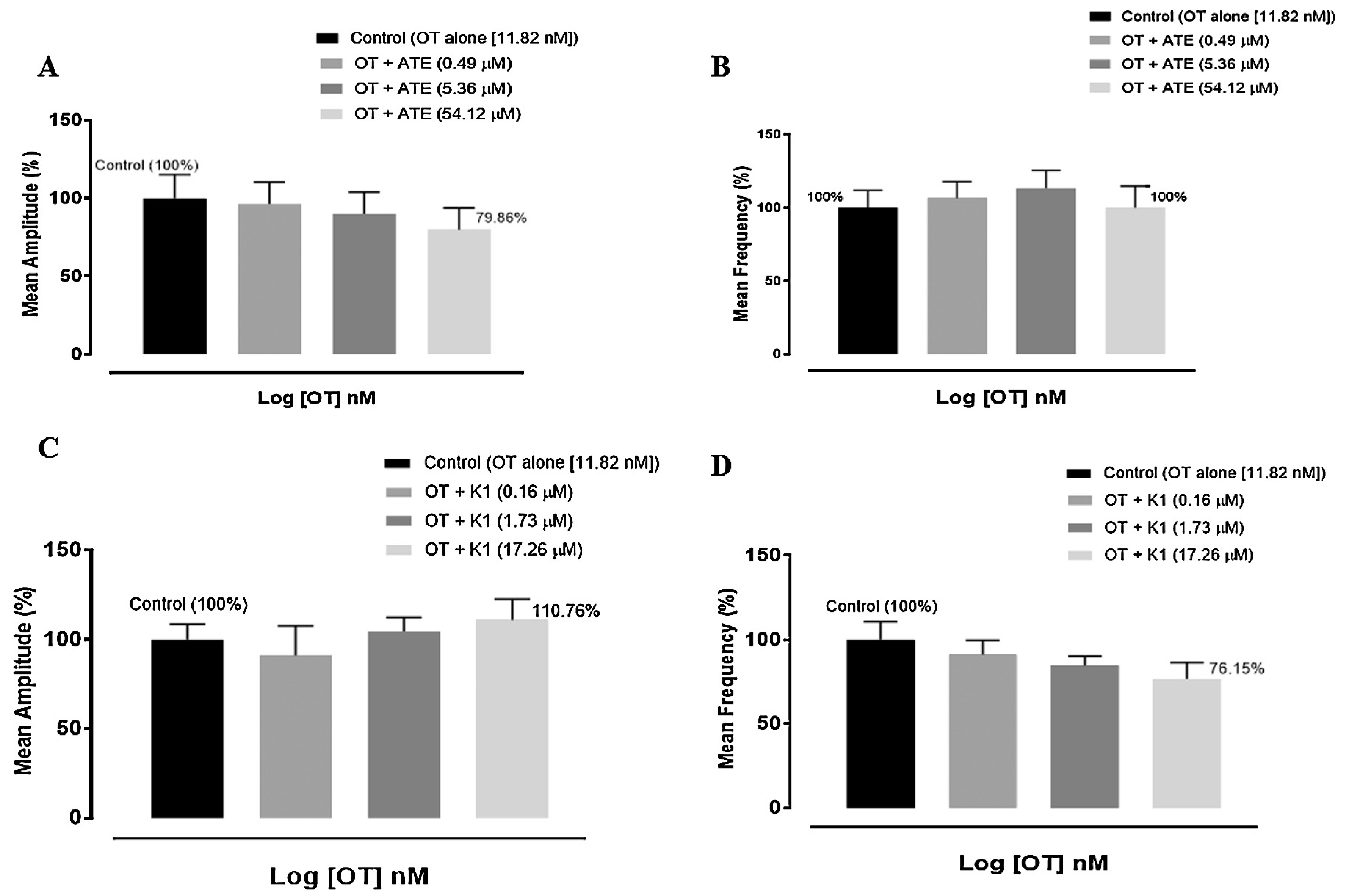
3.2. Effect of ATE and K1 on oxytocin-induced uterine contractions
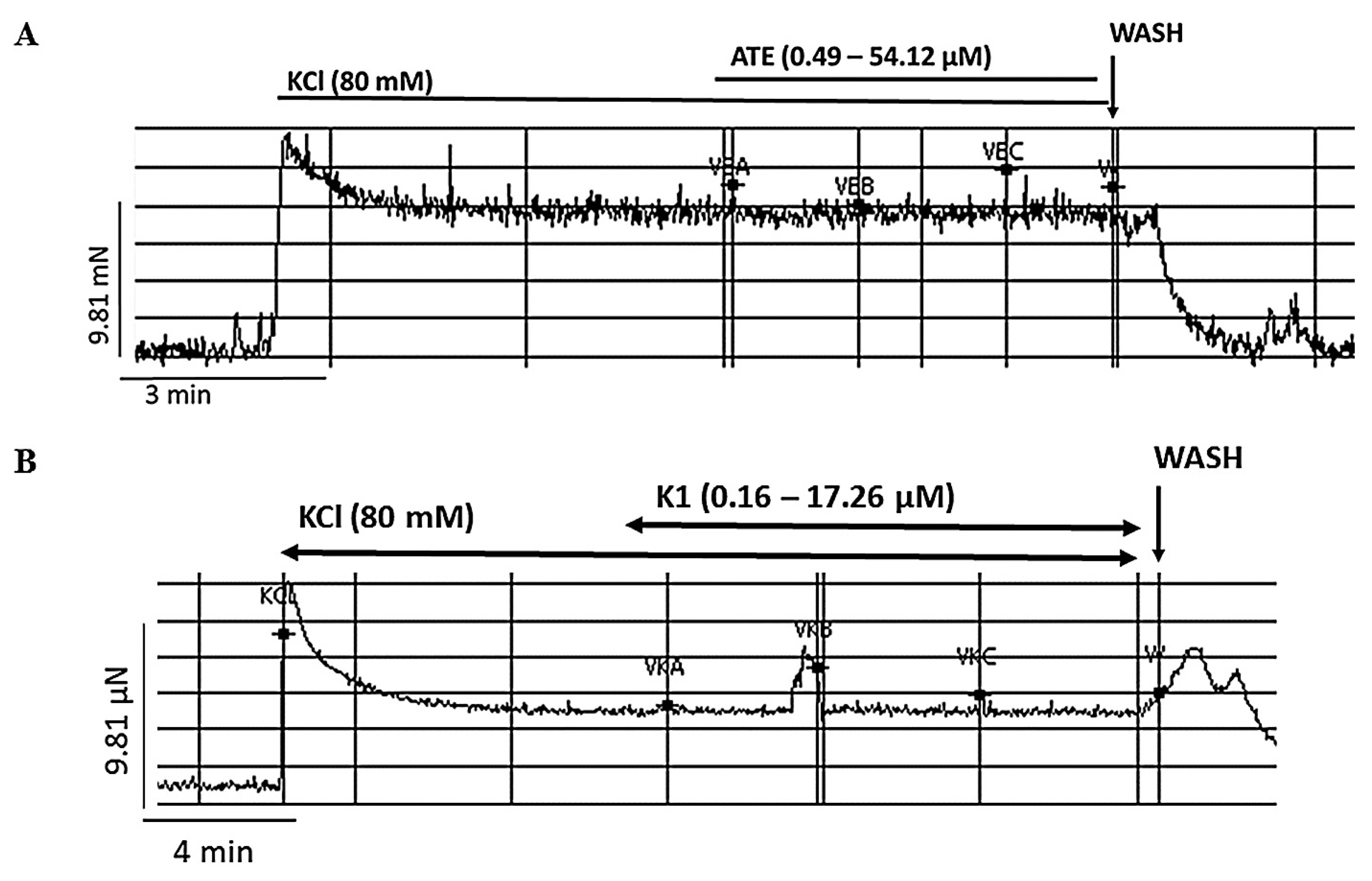
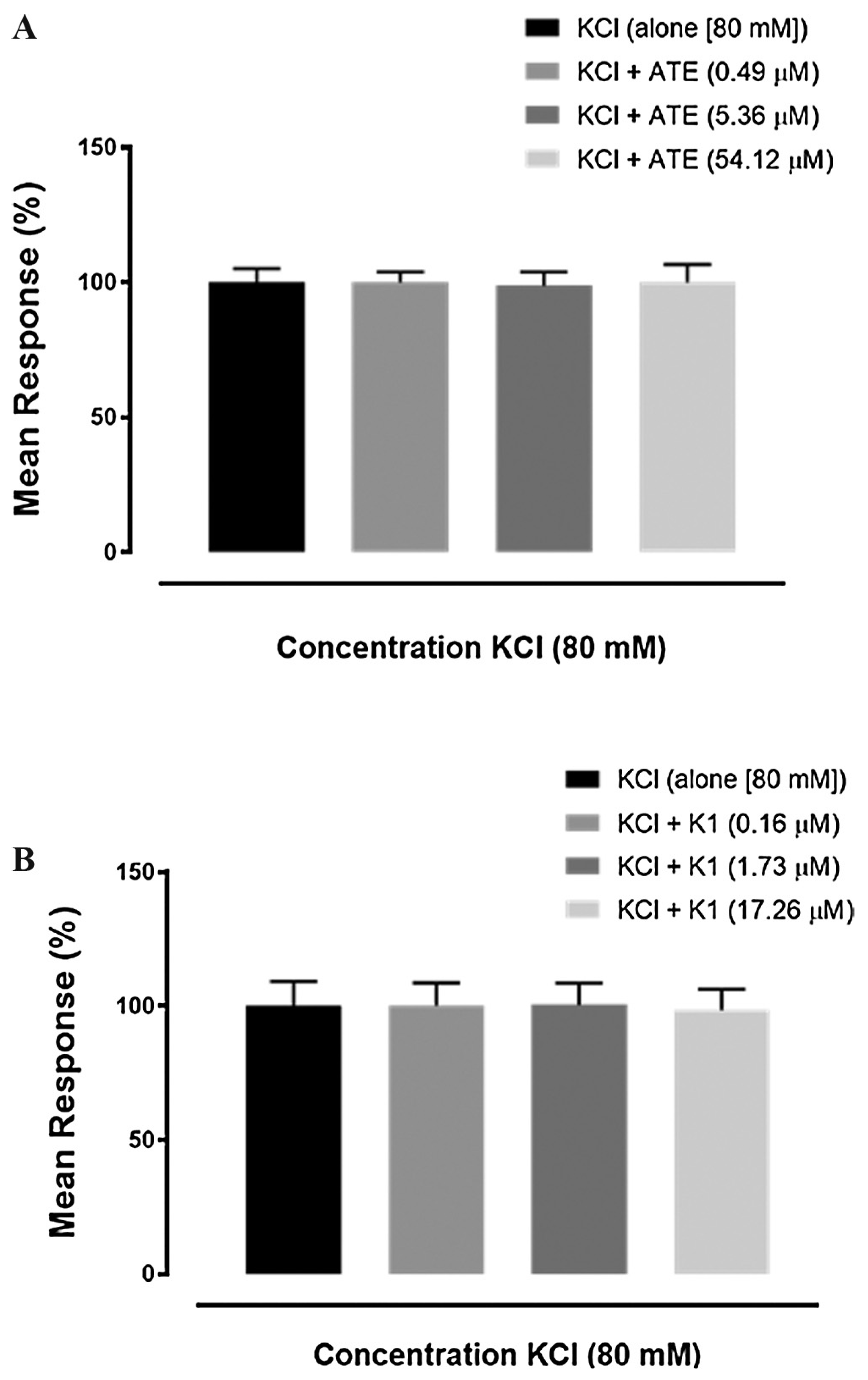
3.3. Effects of ATE and K1 on high KCl-induced uterine contraction
3.4. Effects of ATE on the concentrations of reproductive hormones, on mice body weight and weight of uterus
3.5. Effect of ATE on reproductive tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Funding
Conflict of Interest
Acknowledgments
R E F E R E N C E S
- Okuda, K. Fat soluble vitamins. Nippon Rinsho Jpn J Clin Med 1993, 51, 847–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, EV; Davis, M. The necessity of certain lipins in the diet during growth. J Biol Chem 1913, 15, 167–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, HM; Bishop, KS. On the existence of a hitherto unrecognized dietary factor essential for reproduction. Science 1922, 56, 650–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, ML; Felton, SK; Riek, AE; Bernal-Mizrachi, C. Implications of vitamin D deficiency in pregnancy and lactation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010, 202, 429.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beulens, JWJ; Booth, SL; van den Heuvel, EGHM; Stoecklin, E; Baka, A; Vermeer, C. The role of menaquinones (vitamin K2) in human health. Br J Nutr 2013, 110, 1357–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyose, C; Muramatsu, R; Kameyama, Y; Ueda, T; Igarashi, O. Biodiscrimination of alpha-tocopherol stereoisomers in humans after oral administration. Am J Clin Nutr 1997, 65, 785–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ganzoury, MM; El-Farrash, RA; Saad, AA; Ali, MS; El-Bhbiti, AR; Selem, AM. Antenatal administration of vitamin K1: relationship to vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors and incidence rate of periventricular–intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants; Egyptian randomized controlled trial. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2014, 27, 816–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, MG; Sies, H. Vitamin E in humans: demand and delivery. Annu Rev Nutr 1996, 16, 321–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, S. Insights into the uterus. Exp Physiol 2007, 92, 621–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, S. Uterine contraction and physiological mechanisms of modulation. Am J Physiol: Cell Physiol 1993, 264, C1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdyga, T; Wray, S; Noble, K. In situ calcium signaling: no calcium sparks detected in rat myometrium. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2007, 1101, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togashi, K. Uterine contractility evaluated on cine magnetic resonance imaging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2007, 1101, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulletti, C; Ziegler, DD; Polli, V; Diotallevi, L; Ferro, ED; Flamigni, C. Uterine contractility during the menstrual cycle. Hum Reprod 2000, 15, 81–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, S; Noble, K. Sex hormones and excitation–contraction coupling in the uterus: the effects of oestrous and hormones. J Neuroendocrinol 2008, 20, 451–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, EA; Taylor, PJ; Zheng, XH; Ballard, G; Levi, CS; Kredentser, JV. Characterization of subendometrial myometrial contractions throughout the menstrual cycle in normal fertile women. Fertil Steril 1991, 55, 771–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, G; Leyendecker, G. Uterine peristaltic activity during the menstrual cycle: characterization, regulation, function and dysfunction. Reprod Biomed Online 2002, 4 Suppl 3, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, K; Lyons, EA; Ballard, G; Levi, CS; Lindsay, DJ. Contractions of the inner third of the myometrium. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990, 162, 679–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrowsmith, S; Kendrick, A; Wray, S. Drugs acting on the pregnant uterus. Obstet Gynaecol Reprod Med 2010, 20, 241–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafor, EE; Lim, CV; Rowan, EG; Edrada-Ebel, R. The leaves of Ficus exasperata Vahl (Moraceae) generates uterine active chemical constituents. J Ethnopharmacol 2013, 145, 803–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbold, A; Crowther, CA. Vitamin E supplementation in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskovic, R; Gargaun, L; Oren, D; Djulus, J; Koren, G. Pregnancy outcome following high doses of Vitamin E supplementation. Reprod Toxicol 2005, 20, 85–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederberg, J; Simán, CM; Eriksson, UJ. Combined treatment with vitamin E and vitamin C decreases oxidative stress and improves fetal outcome in experimental diabetic pregnancy. Pediatr Res 2001, 49, 755–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruthi, S; Wahner-Roedler, DL; Torkelson, CJ; Cha, SS; Thicke, LS; Hazelton, JH; et al. Vitamin E and evening primrose oil for management of cyclical mastalgia: a randomized pilot study. Altern Med Rev 2010, 15, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lanza, E; Forman, MR; Johnson, EJ; Muesing, RA; Graubard, BI; Beecher, GR. alpha-Tocopherol concentrations in plasma but not in lipoproteins fluctuate during the menstrual cycle in healthy premenopausal women. J Nutr 1998, 128, 1150–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvis-Offiah, U; Bafor, EE. Evaluation of the effects of oxytocin and diethylstilboestrol on mouse oestrous cycle using an index. J Med Biomed Res 2014, 13, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Green, EL. Biology of the laboratory mouse; The Blakiston Company: Philadelphia, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, KR; Taft, RA. Reproductive Biology of the Laboratory Mouse The mouse in biomedical research: normative biology husbandry and models. 2007; vol. 3, pp. 91–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champlin, AK; Dorr, DL; Gates, AH. Determining the stage of the estrous cycle in the mouse by the appearance of the vagina. Biol Reprod 1973, 8, 491–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafor, EE; Eyohan, SE; Omoruyi, O; Elvis-Offiah, UB; Ayinde, BA; Eze, GI; et al. Preliminary endocrinological, histological and haematological investigation of Alchornea laxiflora (Euphorbiaceae) leaf extract effects on the ovary, uterus and cervix of mouse models. J Sci Pract Pharm 2016, 2, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, LE; Hales, C. Labelled antibodies and immunological assay systems. Nature 1968, 219, 186–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequin, RM. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Chem 2005, 51, 2415–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, M. The physiological mechanism of uterine contraction with emphasis on calcium ion. Calcium Signal 2014, 1, 1168–76. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, HN; Mitchell, BF. Physiological pathways and molecular mechanisms regulating uterine contractility. Hum Reprod Update 2010, 16, 725–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, RJ; Allen, MJ; Nandi, M; Giles, H; Thornton, S. Spontaneous contractions of myometrium from humans, non-human primate and rodents are sensitive to selective oxytocin receptor antagonism in vitro. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2001, 108, 960–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, S; Kupittayanant, S; Shmygol, A; Smith, RD; Burdyga, T. The physiological basis of uterine contractility: a short review. Exp Physiol 2001, 86, 239–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrowsmith, S; Wray, S. Oxytocin: its mechanism of action and receptor signalling in the myometrium. J Neuroendocrinol 2014, 26, 356–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackler, AM; Ducsay, CA; Veldhuis, JD; Yellon, SM. Maturation of spontaneous and agonist-induced uterine contractions in the peripartum mouse uterus. Biol Reprod 1999, 61, 873–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T; Honda, K; Fukuoka, T; Negoro, H; Wakabayashi, K. Release of oxytocin during suckling and parturition in the rat. J Endocrinol 1985, 105, 339–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, WY; Chen, DL. Myometrial oxytocin receptors and prostaglandin in the parturition process in the rat. Biol Reprod 1992, 46, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bolton, TB; Prestwich, SA; Zholos, AV; Gordienko, DV. Excitation–contraction coupling in gastrointestinal and other smooth muscles. Annu Rev Physiol 1999, 61, 85–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxatto, HB; Diaz, S. The place of progesterone in human contraception. J Steroid Biochem 1987, 27, 991–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres-Bartho, J; Halasz, M; Palkovics, T. Progesterone in pregnancy; receptor–ligand interaction and signaling pathways. J Reprod Immunol 2009, 83, 60–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groom, GV; Griffiths, K. Effect of the anti-oestrogen tamoxifen on plasma levels of luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, prolactin, oestradiol and progesterone in normal pre-menopausal women. J Endocrinol 1976, 70, 421–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivier, C; Rivier, J; Vale, W. Inhibin-mediated feedback control of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in the female rat. Science 1986, 234, 205–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khallouki, F; de Medina, P; Caze-Subra, S; Bystricky, K; Balaguer, P; Poirot, M; et al. Molecular and biochemical analysis of the estrogenic and proliferative properties of vitamin E compounds. Front Oncol 2015, 5, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janne, O; Kontula, K; Luukkainen, T; Vihko, R. Oestrogen-induced progesterone receptor in human uterus. J Steroid Biochem 1975, 6, 501–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künzel, J; Geisler, K; Maltaris, T; Müller, A; Hoffmann, I; Schneider, H; et al. Effects of interactions between progesterone and prostaglandin on uterine contractility in a perfused swine uterus model. In Vivo (Brooklyn) 2014, 28, 467–76. [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich, R; Henning, J; Maltaris, T; Hoffmann, I; Oppelt, PG; Cupisti, S; et al. Extracorporeal perfusion of the swine uterus: effect of human seminal plasma. Andrologia 2012, 44, 543–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, J; Herbison, AE. Oestrogen, kisspeptin, GPR54 and the pre-ovulatory luteinising hormone surge. J Neuroendocrinol 2009, 21, 305–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, SI. Human physiology, 12th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Perusquía, M; Navarrete, E. Evidence that 17alpha-estradiol is biologically active in the uterine tissue: antiuterotonic and antiuterotrophic action. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2005, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, AH; Jacobson, KA; Rose, J; Zeller, R. Preparation of slides and coverslips for microscopy. Cold Spring Harbor Protoc 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegg, MA; Meinen, S. Histopathology in hematoxylin & eosin stained muscle sections. Neuromuscul Netw 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, JD; Roman, SD; McGowan, E; Sutherland, RL; Clarke, CL. Preferential stimulation of human progesterone receptor B expression by estrogen in T-47D human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 1995, 270, 30693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathalla, MF. Incessant ovulation – a factor in ovarian neoplasia? Lancet 1971, 2, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, JT; Pike, MC; Ross, RK; Louie, EW; Roy, S; Henderson, BE. “Incessant ovulation” and ovarian cancer. Lancet 1979, 314, 170–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, PA; Balleine, RL; McGowan, EM; Clarke, CL. Heterogeneity of progesterone receptors A and B expression in human endometrial glands and stroma. Hum Reprod 2000, 15 Suppl 3, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H; Ishi, K; Ann Serna, V; Kakazu, R; Bulun, SE; Kurita, T. Progesterone is essential for maintenance and growth of uterine leiomyoma. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2433–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, TE; Bazer, FW. Biology of progesterone action during pregnancy recognition and maintenance of pregnancy. Front Biosci 2002, 7, d1879–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, C; Ferenczy, A; Toft, DO; Shyamala, G. Immunocytochemical study of progesterone receptors in hyperplastic and neoplastic endometrial tissues. Cancer Res 1988, 48, 6132–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huszar, GB; Michael, PW. Relationship between myometrial and cervical functions in pregnancy and labor. Semin Perinatol 1991, 15, 97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Challis, JRG; Lye, SJ. Parturition. In The physiology of reproduction; Knobil, E, Neill, JD, Eds.; Raven Press: New York, 1994; pp. 985–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Luque, EH; Ramos, JG; Rodriguez, Ha; Muñoz de Toro, MM. Dissociation in the control of cervical eosinophilic infiltration and collagenolysis at the end of pregnancy or after pseudopregnancy in ovariectomized steroid-treated rats. Biol Reprod 1996, 55, 1206–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]


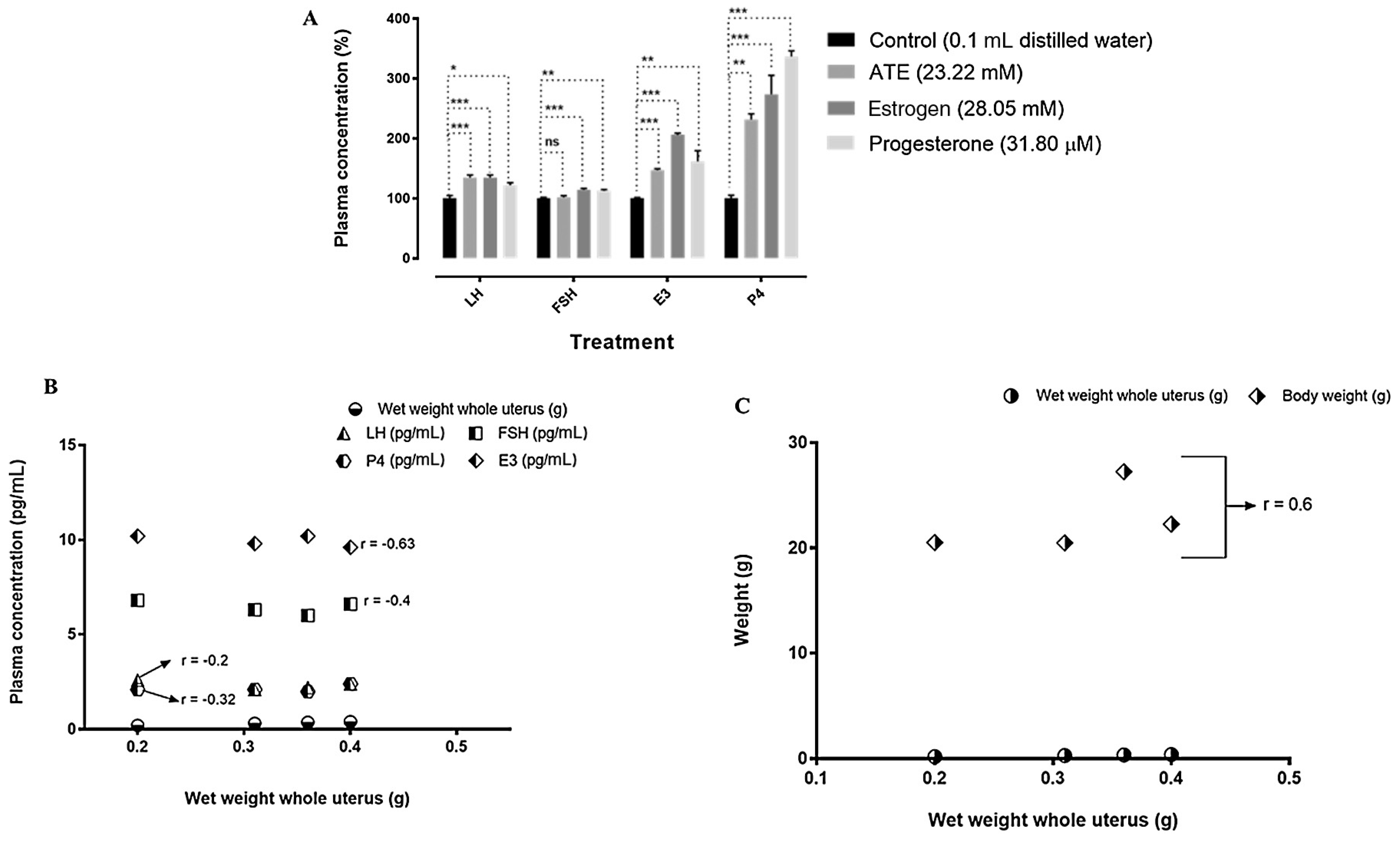
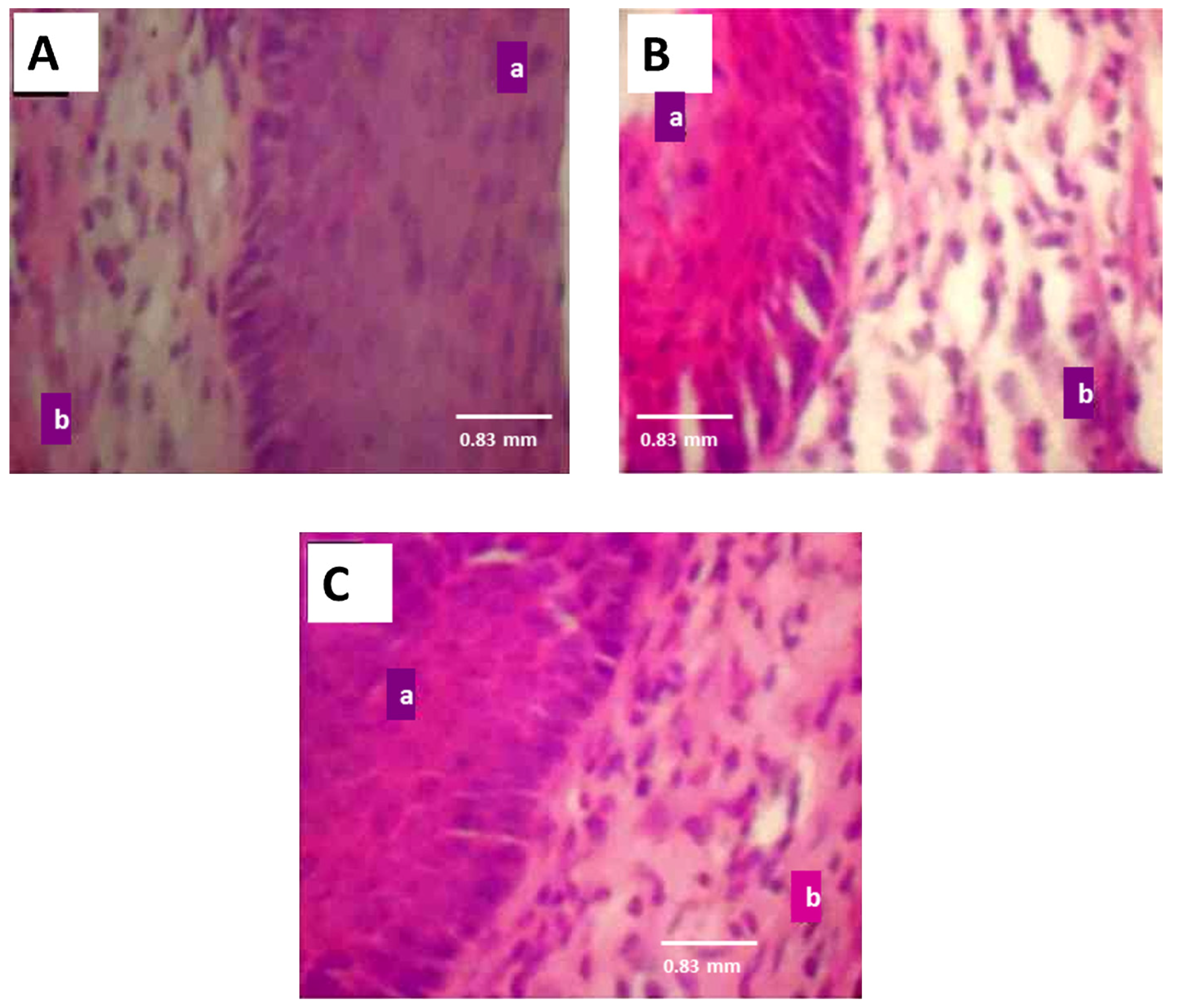
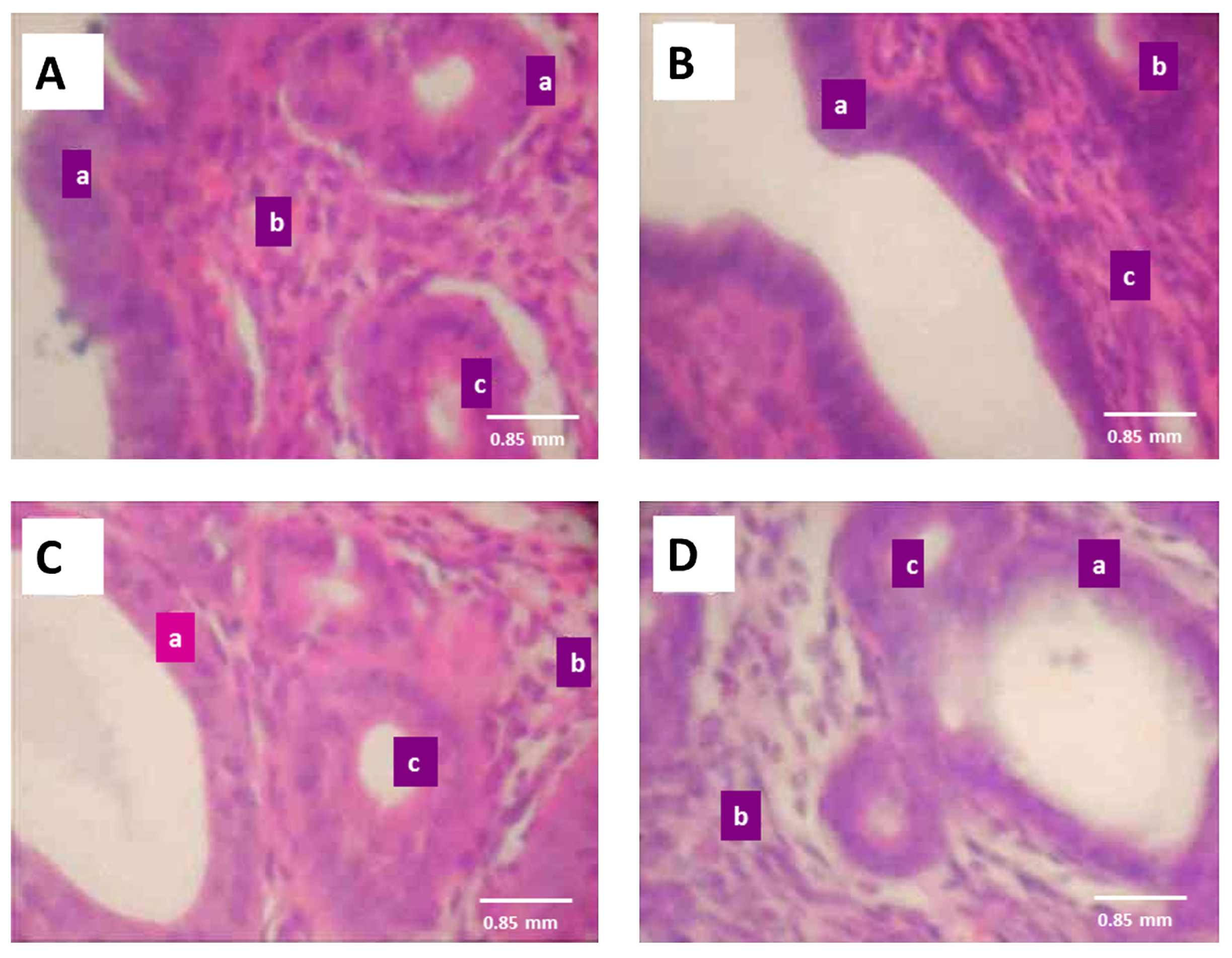
| Groups | Weight, g | |
|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Day 7 | |
| Control (0.1 mL distilled water) | 21.00 ± 1.30 | 21.00 ± 0.85 |
| ATE (10 mg/kg) | 23.00 ± 1.70 | 23.00 ± 1.60 |
| Estrogen (10 mg/kg) | 22.00 ± 0.93 | 22.00 ± 1.30 |
| Progesterone (0.01 mg/kg) | 24.00 ± 1.20 | 24.00 ± 0.98 |
| Values are presented in mean ± SEM; n = 4. | ||
| Groups | Weight, g |
|---|---|
| Day 7 | |
| Control (0.1 mL distilled water) | 0.33 ± 0.07 |
| ATE (10 mg/kg) | 0.32 ± 0.15 |
| Estrogen (10 mg/kg) | 0.34 ± 0.02 |
| Progesterone (0.01 mg/kg) | 0.26 ± 0.02 |
| Values are presented in mean ± SEM; n = 4. | |
© 2017 The Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier Sp. z o.o. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bafor, E.E.; Ebidame, V.O.; Elvis-Offiah, U.B.; Omoruyi, O.; Eze, G.I.; Igbinuwen, O.; Braimoh, K.P. A role of alpha-tocopherol and phylloquinone in the modulation of uterine contractility and reproductive function in mouse models. Medicina 2017, 53, 190-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medici.2017.05.002
Bafor EE, Ebidame VO, Elvis-Offiah UB, Omoruyi O, Eze GI, Igbinuwen O, Braimoh KP. A role of alpha-tocopherol and phylloquinone in the modulation of uterine contractility and reproductive function in mouse models. Medicina. 2017; 53(3):190-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medici.2017.05.002
Chicago/Turabian StyleBafor, Enitome E., Victory O. Ebidame, Uloma B. Elvis-Offiah, Osemelomen Omoruyi, Gerald I. Eze, Osamwonyi Igbinuwen, and Kadiri P. Braimoh. 2017. "A role of alpha-tocopherol and phylloquinone in the modulation of uterine contractility and reproductive function in mouse models" Medicina 53, no. 3: 190-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medici.2017.05.002
APA StyleBafor, E. E., Ebidame, V. O., Elvis-Offiah, U. B., Omoruyi, O., Eze, G. I., Igbinuwen, O., & Braimoh, K. P. (2017). A role of alpha-tocopherol and phylloquinone in the modulation of uterine contractility and reproductive function in mouse models. Medicina, 53(3), 190-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medici.2017.05.002




