-
 Long-Standing Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation: A Comprehensive Review and Proposal of a Treatment Algorithm
Long-Standing Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation: A Comprehensive Review and Proposal of a Treatment Algorithm -
 Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)—An Evidence-Based Review of Indications, Efficacy, Harms, and Deprescribing
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)—An Evidence-Based Review of Indications, Efficacy, Harms, and Deprescribing -
 Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Digital Health for Hypertension: Evolving Tools for Precision Cardiovascular Care
Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Digital Health for Hypertension: Evolving Tools for Precision Cardiovascular Care -
 The Journey of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Cutaneous Melanoma: A Brief Narrative Review from Scalpel to Smart Tech
The Journey of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Cutaneous Melanoma: A Brief Narrative Review from Scalpel to Smart Tech -
 The Impact of Basal Inflammatory Status on Post-CABG Atrial and Ventricular Ectopy and Remodeling Pathways
The Impact of Basal Inflammatory Status on Post-CABG Atrial and Ventricular Ectopy and Remodeling Pathways
Journal Description
Medicina
Medicina
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal covering all problems related to medicine. It is the official journal of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences (LUHS) and published monthly online. The Lithuanian Medical Association, the Vilnius University, the Rīga Stradiņš University, the University of Latvia, and the University of Tartu are affiliated to Medicina, which serves as the official journal. Their members receive discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Medicine, General and Internal) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
Formulation of α-Linolenic Acid-Based Microemulsions for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Physicochemical Tests and HET-CAM Assays for Anti-Angiogenic Activities
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2030; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112030 (registering DOI) - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is an age-associated retinal disorder characterized by blood–retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown and pathological angiogenesis, leading to vascular leakage. The intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF agents remains the most effective treatment for neovascular AMD. However, repetitive intravitreal injections
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is an age-associated retinal disorder characterized by blood–retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown and pathological angiogenesis, leading to vascular leakage. The intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF agents remains the most effective treatment for neovascular AMD. However, repetitive intravitreal injections have risks, causing side effects such as cataracts, bleeding, retina damage, and, in severe cases, post-injection endophthalmitis. Hence, the development of innovative drug delivery systems is essential to minimize the risks and discomfort associated with intravitreal injections. Materials and Methods: We developed a microemulsion (ME)-based topical drug delivery system incorporating α-linolenic acid (ALA). In brief, pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were constructed by the water titration method using different combinations of surfactants and cosurfactants (Smix-Cremophor RH 40: Span 80: Transcutol P in ratios of 1:1.05, 1:1:1, 1:1:1.5) containing ALA as the oil phase. Three blank microemulsions (ME1, ME2, and ME3) were prepared and characterized based on the optimized pseudo-ternary phase equilibrium with a Smix ratio of 1:1:1. Results: ME3, with an average particle size of 38.59 nm, was selected as the optimized formulation for developing drug-loaded ME containing Fenofibrate, Axitinib, and Sirolimus. The drug-loaded ME showed particle size (46.94–56.39 nm) and in vitro release displayed sustained and longer time drug release for 240 h. The irritation and antiangiogenic activities were evaluated using the hen’s egg chorioallantoic membrane (HET-CAM) assay employing the optimized ME loaded with each drug. Among the three drug-loaded ME, the Sirolimus ME showed a reduction in blood vessel sprouting in the HET-CAM assay, indicating strong antiangiogenic activity. Treatment with the optimized blank ME and Sirolimus ME significantly (p < 0.05) reduced COX-2 protein expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells, suggesting their potential anti-inflammatory effects. Conclusions: Overall, we suggest that the α-linolenic acid-based Sirolimus microemulsion may serve as a promising topical therapeutic approach for managing AMD and offering a potential alternative to invasive intravitreal injections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Ophthalmology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Emergency Management of Perforated Gastro-Duodenal Ulcers: Surgical Strategies, Outcomes, and Prognostic Determinants in a Tertiary Eastern European Center
by
Oprescu Macovei Anca Monica, Dana Paula Venter, Stefan Mihai, Constantin Oprescu, Andrei Gabriel, Dumitriu Bogdan, Valcea Sebastian, Gheorghiu Alexandra-Oana and Ilie Stan Madalina
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2029; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112029 (registering DOI) - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Perforated gastro-duodenal ulcers (PGDUs) are life-threatening surgical emergencies with high morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to evaluate surgical strategies, outcomes, and prognostic factors in patients treated for PGDUs in a tertiary Eastern European center. Materials and Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Perforated gastro-duodenal ulcers (PGDUs) are life-threatening surgical emergencies with high morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to evaluate surgical strategies, outcomes, and prognostic factors in patients treated for PGDUs in a tertiary Eastern European center. Materials and Methods: We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 156 patients admitted with PGDUs between 2020 and 2024. Data on demographics, risk factors, ulcer location, type of surgical approach, operative details, hospital stay, and mortality were collected. Statistical analysis included chi-square, Mann–Whitney U, and multivariate logistic regression. Results: The mean age was 57.6 ± 15.9 years (range 18–91), with men accounting for 64.7% of cases. Alcohol use was significantly associated with male sex (p = 0.012), while NSAID use was equally distributed. Open surgery was the mainstay of treatment (85.9%), with laparoscopy performed in 12.8% and conversion in 1.9%. Median hospital stay was shorter after laparoscopic repair (7.5 vs. 9 days, p = 0.039. On multivariate analysis, both age and comorbidity burden were independent predictors of mortality (p < 0.01). Conclusions: PGDU management in Eastern Europe remains dominated by open surgery. Laparoscopy, though underutilized, is associated with shorter recovery. Age is the strongest determinant of mortality, highlighting the need for early risk stratification, wider adoption of minimally invasive techniques, and preventive measures targeting modifiable risk factors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastroenterology & Hepatology)
Open AccessArticle
The Microbiological Spectrum and Antibiotic Resistance in Acute Acalculous and Calculous Cholecystitis: A Seven-Year Study in a Tertiary Center
by
Cosmin Vasile Obleaga, Ovidiu Mircea Zlatian, Oana Mariana Cristea, Alexandra Rosu-Pires, Alexandru Marin Pascu, Mirela-Marinela Florescu, Claudiu Marinel Ionele, Ion Rogoveanu, Alexandru Valentin Popescu, Vlad Catanoiu and Sergiu Marian Cazacu
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2028; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112028 (registering DOI) - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) is rare, mostly in older males, with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, critical illness, or systemic infection. Antibiotherapy before or after cholecystectomy is important for preventing septic shock and postoperative infections. Increasing antibiotic resistance was recently noted
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) is rare, mostly in older males, with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, critical illness, or systemic infection. Antibiotherapy before or after cholecystectomy is important for preventing septic shock and postoperative infections. Increasing antibiotic resistance was recently noted and can complicate antibiotherapy. Materials and Methods: A retrospective study of all patients who underwent cholecystectomy between 2018 and 2024 in the Clinical Emergency Hospital of Craiova was performed. The etiology of AAC, complications, hospitalization duration, mortality, positive bile cultures, and in vitro antibiotic resistance were analyzed. Results: A total of 802 calculous and 54 AAC were recorded. Patients with AAC were predominantly males (OR = 1.767, p = 0.043) with diabetes (OR = 2.049, p = 0.014) and were older (66.6 ± 13.2 versus 61.4 ± 15.6, p = 0.014). Mortality was significantly higher in AAC (18.5 versus 3.6%, OR= 6.058, p < 0.001), with longer hospitalization (mean 9.7 versus 8.4 days) and more perforation. Positive bile cultures were recorded in 60.5–66.2% of cases, with a similar etiology in both forms of acute cholecystitis (mostly Gram-negative species, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus); 10 ESBL Escherichia coli and Klebsiella strains, 11 Staphylococcus aureus MRSA, and 1 Enterococcus VRE strain were recorded. Antibiotic susceptibility in vitro was similar in both AAC and calculous cholecystitis. Significant resistance to cephalosporins and quinolones was recorded; the lowest resistance was noted for amikacin, carbapenems, chloramphenicol, colistin (Gram-negative bacteria), and vancomycin. Conclusions: AAC was encountered in older males with diabetes, with a higher rate of complications and in-hospital mortality. Bile cultures were positive in 60.5–66.2%, predominantly with Gram-negative, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus species. Significant in vitro resistance to cephalosporins and quinolones was found.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends in Infectious Disease Prevention and Control)
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Hemoglobin Levels During Definite Chemoradiotherapy of Patients with Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma on Survival
by
Sandy Hazko, Amed Ahmed, Robert Michael Hermann, Mathias Alexander Sonnhoff, Athanasia Warnecke, Frank Bruns, Robert Blach, Hans Christiansen and Jan-Niklas Becker
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2027; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112027 (registering DOI) - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: This study aims to investigate the impact of hemoglobin (Hb) level changes during radiochemotherapy (RCT) on the survival of patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: This study aims to investigate the impact of hemoglobin (Hb) level changes during radiochemotherapy (RCT) on the survival of patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 97 patients with HNSCC, treated with definitive RCT between January 2016 and October 2021. Hb levels were monitored weekly during RCT. Kaplan–Meier and Cox regression analysis were performed. Results: There was a significant association between Hb levels at the end of RCT and overall survival (p < 0.01). Initial Hb levels and Hb level changes were not significantly associated with survival. In multivariate analysis, a lower body mass index (BMI) and Hb levels at week six were identified as significant prognostic factors. Conclusions: At the end of RCT, rather than baseline levels or changes during treatment, Hb levels are a significant prognostic factor for overall survival in patients with HNSCC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Contemporary Management of Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: A Comprehensive Review
by
Giulia Bertagna, Valentina Scarati, Nicola Troisi and Raffaella Berchiolli
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2026; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112026 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: current guidelines recommend surgical treatment for asymptomatic popliteal artery aneurysm > 20 mm in diameter, although without any suggestion about the preferred treatment choice. The two main treatment options are open surgical repair (OPAR) and endovascular repair (EPAR). Although
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: current guidelines recommend surgical treatment for asymptomatic popliteal artery aneurysm > 20 mm in diameter, although without any suggestion about the preferred treatment choice. The two main treatment options are open surgical repair (OPAR) and endovascular repair (EPAR). Although ER has emerged as a promising technique due to being less invasive, OPAR remains the standard in many centers. The aim of the study is to report and compare outcomes of both endovascular and open repair of asymptomatic PAAs to provide an extensive overview of their current management. Materials and Methods: the present review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Guidelines. Preliminary searches were conducted on MEDLINE, Pubmed, Scopus, and Web of Science from January 2010 to September 2025. Articles were divided into three main groups based on the preferred treatment modality. Early outcomes were technical success, mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), and graft occlusion(s). In mid- and long-term periods, the evaluated outcomes were overall survival, amputation-free survival, primary patency, primary assisted patency, secondary patency, and freedom from reintervention. Results: 21 articles were identified for a total of 9760 patients and 10,062 limbs treated. Technical success was up to 100% for both OPAR and EPAR with low complication rates. Primary patency (79.8% vs. 63.8%; p = 0.012) and freedom from reintervention (82.2% vs. 68.4%; p = 0.021) seem to be better for OPAR than EPAR. Overall survival, amputation free-survival, and secondary patency rates are comparable between the two techniques. Conclusions: although endovascular repair has emerged as a safe and effective approach to treat elective PAAs, long-term data on a large scale are still lacking. Indeed, open surgical repair remains the milestone, due to excellent primary patency rates, regardless of the conduit used.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment Outcomes of Cardiac Myxoma: Twenty Years of Data at a Single Institution
by
Gabriele Jakuskaite, Povilas Jakuska, Rimantas Benetis, Jolanta Justina Vaskelyte and Egle Ereminiene
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2025; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112025 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Cardiac myxoma (CM) is the most common primary benign neoplasm of the heart. This study’s objective was to analyse diagnostic features of CM, surgical data and postoperative courses of patients over a 20-year period in a single institution. Materials and
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Cardiac myxoma (CM) is the most common primary benign neoplasm of the heart. This study’s objective was to analyse diagnostic features of CM, surgical data and postoperative courses of patients over a 20-year period in a single institution. Materials and Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients with diagnosed and pathologically confirmed CM who underwent surgical resection in our hospital from 1 January 2004 to 1 January 2024. Data was assessed and analysed from medical records. Results: The study included 76 patients (mean age, 61.7 ± 12.6 years; 60.5% female). The majority of patients (93.7%) had symptoms, most commonly presenting with dyspnoea (64.5%), chest pain (39.5%) and arrhythmias (35.5%). Myxomas were found in the left atrium (89.5%), right atrium (9.2%) and left ventricle (1.3%). Isolated tumour extirpation surgery was performed in 50 patients (65.8%). During the early postoperative period, arrhythmias were the most common complication (n = 16, 21.1%). Early in-hospital mortality occurred in two patients due to cardiopulmonary failure. In the late postoperative period, 11 deaths (14.9%) were observed 4 to 17.5 years after surgery. No recurrence of CM was found in any patient during the follow-up period, yet tumours of other localisations were detected in nine patients. Conclusions: Surgery is the first-line treatment for CM, with a good prognosis. Although during the late postoperative period no cardiac tumour recurrence was observed in our study, 12.2% patients were newly diagnosed with non-cardiac neoplasms. Therefore, we suggest monitoring patients not only for cardiac disorders but also for the occurrence of extracardiac tumours.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Temporal Trends of Dengue Surveillance in Sardinia, Italy: Implications of Climate Change on Human and Entomological Monitoring
by
Giovanna Deiana, Isabella Figoni, Antonella Arghittu, Guglielmo Campus, Giuseppe Satta, Cipriano Foxi, Andrea Piana, Paolo Castiglia and Marco Dettori
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2024; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112024 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Climate change is modifying the ecological and climatic conditions that influence the distribution and activity of arthropod vectors. Rising temperatures and prolonged warm seasons have favored the establishment of Aedes albopictus in Mediterranean regions, increasing the risk of autochthonous Dengue
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Climate change is modifying the ecological and climatic conditions that influence the distribution and activity of arthropod vectors. Rising temperatures and prolonged warm seasons have favored the establishment of Aedes albopictus in Mediterranean regions, increasing the risk of autochthonous Dengue transmission. Therefore, this study describes the evolution of Dengue surveillance in Sardinia between 2018 and 2024, integrating human and entomological data to assess trends, system performance, and implications for prevention and control. Materials and Methods: Data on human cases were retrieved from national notification systems (namely PREMAL, arbo.iss.it) and the New Health Information System. Entomological surveillance data were obtained from the Experimental Zooprophylactic Institute of Sardinia. Mosquitoes were collected using BG-Sentinel® traps and ovitraps, covering major cities and points of entry. Descriptive analyses were conducted for both datasets. Results: Sixteen Dengue cases were reported during the study period, all imported and laboratory-confirmed in 81% of cases. Most patients were adults (mean age 38 years), and 77% required hospitalization. The most frequent travel origins were Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America. No autochthonous cases were identified. Entomological surveillance showed a progressive increase in Aedes albopictus captures from 2020 onwards, with seasonal peaks between September and October. Despite intensified sampling and expanded geographic coverage, no mosquito pools tested positive for the Dengue virus. Conclusions: Although no locally acquired Dengue infections have been detected, the widespread and increasing presence of Aedes albopictus indicates that Sardinia meets the ecological prerequisites for possible autochthonous transmission. Strengthening the timeliness and completeness of human surveillance, improving clinicians’ awareness of reporting requirements, promoting vaccination for travelers, and maintaining continuous entomological monitoring are essential to prevent and promptly manage future outbreaks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends in Infectious Disease Prevention and Control)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Risk Factors for QRS-Fragmentation in Patients with STEMI Undergoing PCI
by
Florian Tinhofer, Rosana Rakhimova, Elena A. Badykova, Lukas Fiedler, Dilvin Semo, Christoph C. Kaufmann, Irina A. Lakman, Eduard F. Agletdinov, Dimitry M. Grishaev, Ksenia A. Cheremisina, Anastasia V. Baraboshkina, Lukas J. Motloch, Rudin Pistulli and Naufal S. Zagidullin
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2023; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112023 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Despite modern therapy algorithms, ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) substantially contributes to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality worldwide. Early Risk assessment is crucial to guide therapy allocation, especially in countries with limited healthcare resources. Electrocardiographic parameters such as QRS fragmentation (fQRS)
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Despite modern therapy algorithms, ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) substantially contributes to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality worldwide. Early Risk assessment is crucial to guide therapy allocation, especially in countries with limited healthcare resources. Electrocardiographic parameters such as QRS fragmentation (fQRS) evolved as an important prognostic marker. The underlying mechanisms and specific risk factors for the occurrence of fQRS in patients with STEMI undergoing PCI have not been analyzed yet. Materials and Methods: Between 09/2020 and 06/2021, out of 179 consecutive patients with STEMI undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI), 122 patients were included in this study. The occurrence of fQRS was analyzed and correlated to clinical as well as biochemical parameters. Results: In this population, the fQRS pattern was present in 33.6% (n = 41) of patients. Besides gender, no statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics or comorbidities were observed between the two groups. In univariable logistic regression analysis, both glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (p = 0.050) and C-reactive protein (CRP) (p = 0.014) were significantly associated with the presence of fQRS. However, in the multivariable logistic regression model, only CRP levels on admission remained independently associated with fQRS (OR = 3.44, 95% CI: 1.95; 6.05), (p = 0.029). Conclusions: In this analysis, a correlation between fQRS and CRP levels in patients with STEMI undergoing pPCI could be demonstrated. Consequently, fQRS might serve as a marker for extensive inflammation in the context of myocardial ischemia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Exercise Modulation of the Myostatin–FOXO Pathway in Murine Models of Cancer Cachexia: A Systematic Review
by
Zahra Zare, Mahfoodha Al Kitani and Shahnaz Shahrbanian
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2022; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112022 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Cancer cachexia is a debilitating metabolic syndrome highly prevalent in colorectal cancer (CRC), characterized by progressive skeletal muscle wasting. The myostatin–FOXO signaling pathway contributes to this process by activating the E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF-1 and Atrogin-1. Exercise is a
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Cancer cachexia is a debilitating metabolic syndrome highly prevalent in colorectal cancer (CRC), characterized by progressive skeletal muscle wasting. The myostatin–FOXO signaling pathway contributes to this process by activating the E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF-1 and Atrogin-1. Exercise is a promising non-pharmacological strategy, but its effects on this pathway in CRC cachexia remain unclear. This review aimed to synthesize preclinical evidence on the impact of exercise on the myostatin–FOXO axis. Materials and Methods: A comprehensive search was performed in PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, and Science Direct from inception through August 2025. Eligible studies included murine CRC models (C26 or ApcMin/+) exposed to aerobic, resistance, or combined exercise interventions, with outcomes assessing myostatin, FOXO, MuRF-1, or Atrogin-1. Study quality was appraised using the CAMARADES 10-item checklist. Results: eleven studies met the criteria, with quality scores ranging from 6 to 8. Aerobic exercise, particularly voluntary wheel running, most consistently reduced MuRF-1 expression and systemic inflammation, whereas resistance and eccentric training exerted stronger inhibitory effects on FOXO and Atrogin-1. Myostatin was directly measured in two studies, yielding inconsistent results. Resistance and eccentric training promoted anabolic signaling (e.g., mTORC1), whereas aerobic protocols improved oxidative capacity. Variability in exercise type, intensity, and duration contributed to heterogeneity across findings. Conclusions: Exercise attenuates skeletal muscle catabolism in CRC-induced cachexia, mainly through modulation of the myostatin–FOXO pathway and downstream ligases. However, limited direct data on myostatin and methodological heterogeneity underscore the need for standardized protocols and translational studies. This review provides the first focused synthesis of exercise-mediated regulation of this pathway in CRC cachexia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sports Medicine and Sports Traumatology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Association of Abdominal Circumference with Stepping Reaction Time and Functional Balance Among Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Shaikha Jadi M. Alsaheli, Danah Alyahya, Faizan Kashoo, Rima Almutairi, Aamal Almutairi, Muhannad Aloufi, Nouf Alsahli, Saud Alsahli, Turki Alzhrani and Shagun Agarwal
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2021; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112021 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Abdominal obesity significantly impacts postural control and fall risk, yet its specific association with stepping reaction time (SRT), a critical component of balance recovery, remains underexplored in obese individuals. This study investigated the relationship between abdominal circumference (AC) and SRT
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Abdominal obesity significantly impacts postural control and fall risk, yet its specific association with stepping reaction time (SRT), a critical component of balance recovery, remains underexplored in obese individuals. This study investigated the relationship between abdominal circumference (AC) and SRT while considering gender and body mass index (BMI). Materials and Methods: Cross-sectional observational study conducted at Majmaah University Virtual Reality Laboratory using advanced motion capture technology. In this cross-sectional study, 199 adults (104 males, 89 females) underwent AC measurement and SRT assessment using the Stability and Balance Learning Environment Apparatus (STABLE) with motion capture technology. Multiple linear regression analyses were performed to identify associations between the variables. Results: The regression model for right SRT was statistically significant (F(8, 184) = 10.24, p < 0.001), explaining 30.8% of variance. Limits of stability with legs apart was negatively associated with right SRT (β = −0.144, p = 0.039), while left SRT was strongly associated (β = 0.451, p < 0.001). AC did not show any association with either right or left SRT. Males demonstrated significantly faster left SRT than females (b = −0.061, p = 0.048), and age was positively associated with left SRT (β = 0.203, p = 0.002). Conclusions: While AC shows correlation with overall obesity measures, it is not significantly associated with stepping reaction time when evaluated concurrently with balance performance and demographic factors. Limits of stability, age, and gender were more consistently associated with stepping reaction time. The cross-sectional design of this study precludes causal inference; longitudinal investigations are necessary to confirm these associations before implementing targeted fall prevention strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Epidemiology & Public Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
SIRI as a Prognostic Marker in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer
by
Hikmet Akar, Ferhat Ekinci, Atike Pınar Erdoğan and Mustafa Şahbazlar
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2020; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112020 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Systemic inflammation plays a critical role in cancer progression and prognosis. The Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), a novel marker integrating neutrophil, monocyte, and lymphocyte counts, has been suggested as a prognostic indicator in various malignancies. This study aimed to
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Systemic inflammation plays a critical role in cancer progression and prognosis. The Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), a novel marker integrating neutrophil, monocyte, and lymphocyte counts, has been suggested as a prognostic indicator in various malignancies. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic significance of SIRI in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer receiving first-line chemotherapy. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included 147 patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer who received first-line chemotherapy or best supportive care between 2010 and 2024. Clinical and laboratory data were collected from medical records. Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were assessed using the Kaplan–Meier method, and prognostic factors were identified by univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Results: The median OS and PFS were 7 and 4 months, respectively. Multivariate analysis revealed that ECOG ≥ 2 (HR: 2.094, p = 0.019), liver metastasis (HR: 2.039, p = 0.027), and each unit increase in SIRI (HR: 1.156, p < 0.001) were independent predictors of poorer OS. Patients with SIRI > 1.86 had significantly shorter OS compared to those with SIRI ≤ 1.86 (median OS: 4 vs. 9 months, p = 0.019). Conclusions: SIRI is an independent prognostic marker for survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer patients undergoing first-line and subsequent lines of chemotherapy. These inflammation-based markers are simple, cost-effective tools that could be integrated into routine clinical practice to aid in risk assessment and treatment planning.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Coronary Intravascular Imaging: A Comprehensive Review of Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions
by
Giustina Iuvara, Marco Franzino, Gabriele Carciotto, Tommaso De Ferrari, Stefania Lo Giudice, Francesco Pallante, Federico Giannino, Manuela Ajello, Sofia Tomasi, Luigi Sciortino, Gabriele Monciino, Walter Licandri, Rodolfo Caminiti, Vittorio Virga, Francesco Costa, Antonio Micari and Giampiero Vizzari
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2019; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112019 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Intravascular imaging has revolutionized the assessment and management of coronary artery disease, providing unparalleled insights into plaque morphology, lesion severity, and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) optimization. This comprehensive review explores the current landscape of intravascular imaging, detailing the principles and clinical utility of
[...] Read more.
Intravascular imaging has revolutionized the assessment and management of coronary artery disease, providing unparalleled insights into plaque morphology, lesion severity, and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) optimization. This comprehensive review explores the current landscape of intravascular imaging, detailing the principles and clinical utility of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT). We discuss the role of these technologies in various clinical scenarios, ranging from stable coronary artery disease to acute coronary syndromes, emphasizing their ability to refine diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic decision-making. A key focus is placed on their application in identifying vulnerable plaques, a critical step in preventing adverse cardiovascular events. Furthermore, we highlight the role of intravascular imaging in guiding PCI, improving stent deployment, and reducing procedural complications. Finally, we explore emerging imaging modalities and technological advancements poised to further enhance coronary assessment, including hybrid imaging techniques. In addition to established modalities, this review examines emerging imaging technologies and the growing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and hybrid imaging systems, which hold promise for automated plaque characterization, improved reproducibility, and enhanced decision support during PCI. By summarizing the latest evidence and future directions, this review aims to provide a comprehensive reference for clinicians and researchers seeking to optimize the use of intravascular imaging in contemporary cardiovascular practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal Imaging Techniques in Myocardial Ischemia: Current Applications and Future Prospects)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Novel Visual Grade and Hounsfield Unit Predict Adequate Bone Strength for Cementless Total Knee Arthroplasty
by
Dong Hwan Lee, Dai-Soon Kwak, Sheen-Woo Lee, Yong Deok Kim, Nicole Cho and In Jun Koh
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2018; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112018 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The use of cementless total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is increasing, but established methods for assessing bone quality to prevent early failure remain undefined. Current preoperative assessments using central bone mineral density (BMD) do not accurately reflect peripheral bone quality,
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The use of cementless total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is increasing, but established methods for assessing bone quality to prevent early failure remain undefined. Current preoperative assessments using central bone mineral density (BMD) do not accurately reflect peripheral bone quality, and intraoperative evaluation is subjective. This study aimed to establish objective assessment methods by analyzing the correlations between a novel visual grading system, CT Hounsfield units (HU), and actual bone strength. Materials and Methods: This prospective study included 131 patients undergoing posterior-stabilized TKA. We developed a novel visual grading system (Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor) based on femoral cutting surface characteristics. CT HUs were measured preoperatively by an assisting surgeon in the box bone area. Femoral box specimens underwent indentation testing to determine their actual bone strength. Minimum Required Strength (MRS) was defined at 2.5-fold the patient’s body weight, and Estimated Withstanding Strength (EWS) was determined by scaling first failure load using area ratios. Patients were classified as “cementless suitable” (EWS > MRS) or “cemented mandatory” (EWS < MRS). Correlations were assessed using Spearman’s rank correlation for visual grade and Pearson correlation for Hounsfield units. ROC curve analysis determined diagnostic accuracy. Results: Visual grade exhibited an exceptionally robust relationship to bone strength (Spearman ρ = 0.903, p < 0.01), whereas HU showed substantial correlation (Pearson r = 0.660, p < 0.01, R2 = 0.435). Visual grading achieved excellent diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 0.974, sensitivity 95.1%, specificity 95.9%) using “Good” grade as cutoff. HU demonstrated AUC of 0.938 with 92.7% sensitivity and 81.6% specificity at a cutoff value of 65.2. Conclusions: Our novel visual grading system and CT HU demonstrated excellent correlations with actual distal femoral bone strength and outstanding diagnostic performance for identifying cementless TKA candidates. Unlike traditional subjective intraoperative assessments such as the “thumb test”, this system provides objective visual criteria directly correlated with actual bone strength. Preoperative HU screening with intraoperative visual grading can help prevent early failure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Knee Surgery: From Diagnosis to Recovery)
►▼
Show Figures
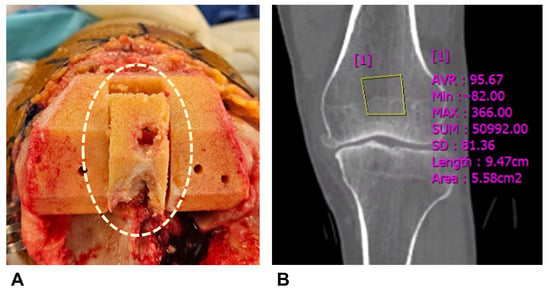
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Gut Microbiota–Metabolic Axis: Emerging Insights from Human and Experimental Studies on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Narrative Review
by
Mohammed Saad Alqahtani
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2017; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112017 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
The rapidly advancing field of gut microbiota research has revealed its pivotal role in human health, with growing evidence implicating microbial dysbiosis in the development of metabolic diseases, particularly type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This narrative review synthesizes recent findings on the complex,
[...] Read more.
The rapidly advancing field of gut microbiota research has revealed its pivotal role in human health, with growing evidence implicating microbial dysbiosis in the development of metabolic diseases, particularly type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This narrative review synthesizes recent findings on the complex, bidirectional relationship between the gut microbiota–metabolic axis and T2DM, drawing upon data from human and experimental studies published in the past decade. Patients with T2DM consistently demonstrate marked gut dysbiosis, characterized by reduced microbial diversity and depletion of beneficial butyrate-producing taxa such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Roseburia intestinalis. In contrast, increases in pro-inflammatory bacteria including Escherichia-Shigella and Lactobacillus are commonly observed. Such compositional changes are linked to metabolic dysfunction through altered microbial metabolites, including elevated trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), which has been associated with insulin resistance and increased diabetes risk. Moreover, gut microbiota imbalances correlate with systemic inflammation, as indicated by higher levels of cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-6. These findings underscore the gut microbiota’s central role in energy metabolism and inflammation in T2DM. Understanding these mechanisms could inform novel therapeutic and preventive strategies—such as microbiota-targeted dietary, probiotic, or pharmacologic interventions—to improve metabolic outcomes and enhance clinical management of diabetes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastroenterology & Hepatology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sodium Phenylbutyrate Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss in Rats
by
Bakiye Akbaş, Gülseren Dinç, Ahmet Akbaş, Nadir Adnan Hacım, Gülçin Ercan, Hatice Aygün and Oytun Erbaş
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2016; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112016 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Estrogen deficiency after menopause accelerates bone loss through oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines. Sodium phenylbutyrate (SP), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, exhibits antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects, but its impact on postmenopausal osteoporosis remains unclear. Materials and Methods: Thirty female Wistar
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Estrogen deficiency after menopause accelerates bone loss through oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines. Sodium phenylbutyrate (SP), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, exhibits antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects, but its impact on postmenopausal osteoporosis remains unclear. Materials and Methods: Thirty female Wistar rats were divided into control, ovariectomy (OVX), and OVX+SPB groups (n = 10 each). After 12 weeks, bone mineral density (BMD), histomorphometry, bone marrow biomarkers (MDA, TNF-α, IL-6, RANKL), and plasma Cathepsin K were evaluated. Results: OVX induced trabecular deterioration with reduced number, area, and thickness (all p < 0.001), increased separation (p < 0.001), and decreased femoral and lumbar BMD (p < 0.001). SPB significantly improved these indices (TN, p < 0.05; TA, p < 0.01; TH, p < 0.05; femoral BMD, p < 0.05; lumbar BMD, p < 0.001; TS, p = 0.001). OVX elevated MDA, TNF-α, IL-6, RANKL, and Cathepsin K (all p < 0.001), which were significantly reduced by SPB (MDA, p < 0.001; TNF-α, p < 0.01; IL-6, p < 0.01; RANKL, p < 0.001; Cathepsin K, p < 0.001). Conclusions: SPB mitigates OVX-induced oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokine release, and osteoclast-mediated resorption, resulting in partial but significant improvements across biochemical, structural, and histomorphometric parameters in estrogen-deficient rats. Given its established clinical safety profile, SPB emerges as a cost-effective candidate for repurposing in postmenopausal osteoporosis, warranting further translational and clinical studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Post-PCI Inflammation and Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Metabolic Risk Factors: A Retrospective Observational Study
by
Alexandra Manuela Buzle, Corina Cinezan, Paul Sextil Sasu, Adrian Tudor Cura, Marc Cristian Ghitea, Evelin Claudia Ghitea, Maria Flavia Gîtea, Aura Bianca Luncan, Timea Claudia Ghitea and Mircea Ioachim Popescu
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2015; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112015 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a known precursor of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), particularly in patients with metabolic comorbidities. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) may exacerbate LVDD via systemic inflammation. This study
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a known precursor of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), particularly in patients with metabolic comorbidities. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) may exacerbate LVDD via systemic inflammation. This study aimed to explore the association between post-procedural systemic inflammation and the severity of diastolic dysfunction in patients with ACS and metabolic comorbidities. Materials and Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted in 181 patients with ACS who underwent PCI. Inflammatory markers (leukocytes, neutrophils, and C-reactive protein [CRP]) measured at 24–48 h post-intervention were analyzed in relation to diastolic dysfunction, assessed by echocardiography. Multivariable ordinal logistic regression and correlation analyses were performed. Results: CRP showed a non-significant trend toward association with more advanced diastolic dysfunction (p = 0.081). Hypertension had a positive but nonsignificant coefficient. Other metabolic comorbidities (diabetes, dyslipidemia, and obesity) were not significantly associated. The correlation between N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and troponin was exploratory. NT-proBNP was the only marker significantly correlated with high-sensitivity troponin (TrHS) at 48 h, indicating a link between myocardial injury and wall stress. Conclusions: CRP may be weakly associated with the severity of diastolic dysfunction post-PCI. However, classical metabolic comorbidities were not independently predictive. Post-PCI inflammation showed only modest, non-significant trends toward diastolic impairment, warranting confirmation in larger prospective studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Seroprevalence in Cryptogenic Cirrhosis: From Evidence of High Frequency to the Impact on Disease Progression
by
Serkan Yaraş, Osman Özdoğan, Seda Tezcan Ülger, Gönül Aslan, Eyüp Naci Tiftik and Orhan Sezgin
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2014; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112014 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) is increasingly recognized as a cause of chronic infection in immunocompromised patients, but its precise role in cryptogenic cirrhosis (CC) is unclear. CC is defined as liver cirrhosis in which all known causes, including
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) is increasingly recognized as a cause of chronic infection in immunocompromised patients, but its precise role in cryptogenic cirrhosis (CC) is unclear. CC is defined as liver cirrhosis in which all known causes, including viral, autoimmune, metabolic, and alcohol-related etiologies, have been meticulously excluded. We aimed to address this gap by definitively assessing HEV’s etiological contribution in CC through seroprevalence comparison and evaluating its long-term prognostic impact on disease progression and adverse clinical outcomes. Materials and Methods: This is a retrospective, single-center, observational, and longitudinal cohort study, conducted between July 2017 and June 2025. The study included 52 CC patients, whose diagnosis was strictly confirmed by excluding all known etiologies, and 900 healthy blood donors from the same region. CC patients were retrospectively followed for five years to assess long-term clinical outcomes. We compared HEV seropositive and seronegative patients for accelerated disease progression (assessed by follow-up MELD-Na scores) and cirrhosis-related death. We employed multivariable logistic regression to adjust for demographic confounders in the prevalence comparison and multivariable COX regression for survival analysis to determine the independent prognostic role of HEV seropositivity. Results: The anti-HEV IgG seroprevalence in CC patients (42.3%) was significantly higher than in healthy donors (12.8%) (p < 0.001). Multivariable logistic regression confirmed CC status as an independent predictor of HEV seropositivity (Adjusted OR = 6.142, p < 0.001). During the five-year follow-up, the cirrhosis-related death rate was significantly higher in the anti-HEV IgG positive group (36.4% vs. 13.4%; p = 0.047), and their follow-up MELD-Na score was significantly higher (p = 0.029). However, multivariable COX analysis did not sustain anti-HEV IgG positivity as an independent risk factor for death (p = 0.294). Conclusions: HEV exposure is independently and significantly higher in CC patients. While anti-HEV IgG positivity correlates with higher mortality and accelerated disease progression in univariable analysis, its lack of independent prognostic significance suggests it may primarily function as a marker for a more advanced stage of CC or underlying immune dysfunction. Further rigorous prospective studies are necessary to precisely define HEV’s long-term prognostic role and evaluate its impact on disease progression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastroenterology & Hepatology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Oxidative DNA Damage and Repair
by
Adnan Ayna, Cuneyt Caglayan and Seyithan Taysi
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2013; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112013 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
DNA is continuously exposed to endogenous and exogenous factors that induce oxidative modifications leading to mutations and genomic instability. Oxidative DNA damage plays a dual role, contributing to physiological signaling at low levels while promoting mutagenesis, carcinogenesis and degenerative diseases when unpaired. Among
[...] Read more.
DNA is continuously exposed to endogenous and exogenous factors that induce oxidative modifications leading to mutations and genomic instability. Oxidative DNA damage plays a dual role, contributing to physiological signaling at low levels while promoting mutagenesis, carcinogenesis and degenerative diseases when unpaired. Among various lesions, an oxidized base, such as 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG), is one of the major biomarkers of oxidative stress and genomic damage. Cells have evolved sophisticated repair processes, including base excision repair (BER), nucleotide excision repair (NER), and mismatch repair (MMR), to maintain genomic integrity. Dysregulation or polymorphism of these repair genes has been linked with cancer, neurologic, and cardiovascular disorders. This review discusses an overview of what is presently known concerning oxidative DNA damage and repair mechanisms, particularly emphasizing their molecular players, signaling routes, and human disease implications. It further refers to the latest advances in CRISPR-based technologies and multi-omics approaches that are redefining our understanding of DNA damage response (DDR) networks and creating new frontiers for therapeutic interventions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Genetics and Molecular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Incidence of New Fractures in Patients Treated with Kyphoplasty/Vertebroplasty or Conservative Methods
by
Alper Tabanli, Hakan Yilmaz, Hüseyin Berk Benek, Mehmet Akif Ercan, Gulsen Ozgenc, Cafer Ak, Onur Bologur, Emrah Akcay and Alaettin Yurt
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2012; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112012 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) are a common cause of morbidity in the elderly, often resulting in pain, reduced mobility, and diminished quality of life. Treatment options include conservative management, vertebroplasty (VP), and kyphoplasty (KP). This study aimed to compare
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) are a common cause of morbidity in the elderly, often resulting in pain, reduced mobility, and diminished quality of life. Treatment options include conservative management, vertebroplasty (VP), and kyphoplasty (KP). This study aimed to compare the clinical outcomes and complication rates of patients treated with kyphoplasty/vertebroplasty versus conservative methods and identify risk factors associated with the development of new fractures. Materials and Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients diagnosed with OVCFs who were treated either surgically (KP/VP) or conservatively between January 2020 and January 2025. Inclusion criteria encompassed vertebral height loss on CT, STIR hyperintensity on MRI, and a T-score below −2.5. Patients were followed for at least one year. Clinical evaluations included pain scores (VAS), functional status (ODI), and quality of life assessments. Complications and new fracture rates were recorded. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify risk factors influencing fracture recurrence. Results: A total of 132 patients were analyzed: 65 in the KP/VP group and 67 in the conservative treatment group. The KP/VP group achieved better postoperative pain results (3.2 ± 1.0 vs. 4.0 ± 1.2) with a significant difference of −0.8 (95% CI: −1.2 to −0.4, p = 0.032) and better mobility results (ODI: 4.5 ± 0.8 vs. 3.9 ± 0.9) with a significant difference of 0.6 (95% CI: 0.3–0.9, p = 0.047) and improved quality of life scores (6.7 ± 1.1 vs. 5.9 ± 1.3) with a significant difference of 0.8 (95% CI: 0.4–1.2, p = 0.041). The incidence of new fractures was similar between groups (15.4% vs. 17.9%, p = 0.678). Overall complication rates were 7.7% in the KP/VP group versus 11.9% in the conservative group (p = 0.435). The results from logistic regression analysis showed that age (adjusted OR: 2.48, 95% CI: 1.20–5.13), low bone mineral density (adjusted OR: 0.31, 95% CI: 0.15–0.63), and cement leakage (adjusted OR: 3.10, 95% CI: 1.21–7.99) were identified as risk factors for new fractures. The study found that outdoor activity (adjusted OR: 0.38, 95% CI: 0.20–0.73) and anti-osteoporosis treatment (adjusted OR: 0.17, 95% CI: 0.04–0.79) acted as protective factors against new fractures. The KP/VP group required half the time to recover from their injuries because they used their braces for 3.0 ± 0.5 months instead of 6.0 ± 1.0 months (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty were more effective than conservative treatment in improving pain, mobility, and quality of life in patients with OVCFs. Although the incidence of new fractures did not differ significantly between groups, surgical treatment demonstrated lower complication rates and significantly faster recovery, as evidenced by reduced brace use duration. These findings support the use of KP/VP as a viable option for managing OVCFs in appropriately selected patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Spinal Neurosurgery: Current Treatment and Future Options)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Importance of Secondary Prevention in Coronary Heart Disease
by
Svetlana Mosteoru, Nilima Rajpal Kundnani, Andreea Rus, Simona Ilin, Veronica Ciocan, Nicolae Albulescu, Marioara Nicula Neagu, Laura Gaita and Dan Gaita
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2011; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112011 - 10 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: The present study evaluates documentation and control of cardiovascular risk factors (RFs) in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) during routine outpatient visits at a single tertiary center in western Romania and places these findings in descriptive context relative
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The present study evaluates documentation and control of cardiovascular risk factors (RFs) in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) during routine outpatient visits at a single tertiary center in western Romania and places these findings in descriptive context relative to SURF-CHD reports from Europe. Materials and Methods: We have enrolled 136 consecutive patients between 18 and 80 years old with coronary artery disease attending routine outpatient clinic check-ups between May 2019 and July 2020. All patients had been diagnosed with acute coronary syndrome or stable angina pectoris and had been treated either by PCI or CABG. Comparisons with SURF-CHD were primarily descriptive due to non-harmonized denominators and lack of patient-level data; inferential testing was limited to variables with clear n/N in both cohorts. Results: Most patients (81%) were males with a mean age of 61.7 years. 93.4% of the patients had undergone PCI, and 4.4% had coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). Regarding risk factors, 25% were current smokers, while 50% were former smokers and the mean BMI value was 29.9 (±6.07). While most patients (80.1%) revealed no previous history of dyslipidemia, 62.5% had no previous history of arterial hypertension, and 84.6% had no previous history of diabetes mellitus. Mean LDL cholesterol levels after a major coronary event remained 93.55 (±43.52) mg/dL, mean HbA1c levels were 7.86 (±1.40)%, while mean systolic blood pressure was 129 (±14.9) mmHg. Conclusions: In this single-center audit, several modifiable RFs remained suboptimally controlled despite established CHD. These results should not be generalized nationally; rather, they highlight center-level opportunities for improving secondary prevention and underscore the need for multicenter, nationally representative registries in Romania.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Challenges and Prospects in Clinical Cardiology and Angiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Medicina Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Clinics and Practice, Cosmetics, JCM, Medicina, Dermato, LabMed, Psychology International
Advances in Psychodermatology
Topic Editors: Jacek C. Szepietowski, Andrzej JaworekDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topic in
Cardiogenetics, Hearts, JCDD, JCM, Medicina
Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease—Chances and Risks, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Alexander E. Berezin, Michael LichtenauerDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
JFMK, Medicina, Therapeutics, Healthcare, JCM, Rheumato
New Trends in Physiotherapy Care: Improvements in Functionality, Pain Management, and Quality of Life
Topic Editors: Carlos Bernal-Utrera, Ernesto Anarte-Lazo, Juan José González GerezDeadline: 3 March 2026
Topic in
Diagnostics, Geriatrics, JCDD, Medicina, JPM, Medicines
New Research on Atrial Fibrillation
Topic Editors: Michele Magnocavallo, Domenico G. Della Rocca, Stefano Bianchi, Pietro Rossi, Antonio BisignaniDeadline: 31 March 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Medicina
Advances in Interstitial Lung Diseases: From Diagnosis to Treatment
Guest Editors: Jacobo Sellarés, Jaume Bordas-MartinezDeadline: 15 November 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Adenomyosis and Endometriosis-Related Infertility
Guest Editors: Simone Ferrero, Giuseppe GulloDeadline: 20 November 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Dermato-Engineering and AI Assessment in Dermatology Practice
Guest Editors: Emmanouil Karampinis, Paweł PietkiewiczDeadline: 20 November 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Advances in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis in Clinical Medicine
Guest Editors: Marko Barešić, Joško MitrovićDeadline: 20 November 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Advances in Cornea, Cataract, and Refractive Surgery
Collection Editor: Ivo Guber
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Interventional Oncology
Collection Editors: François Cornelis, Matthias Barral, Adrian Kastler, Dimitrios Filippiadis
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Interdisciplinary Medicine – The Key For Personalized Medicine
Collection Editor: Camelia Diaconu
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Frontiers in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editors: Jimmy T. Efird, Tithi Biswas











