Physical Fitness and Body Composition in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Measures
2.3. Physical Fitness Measures
2.4. Other Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
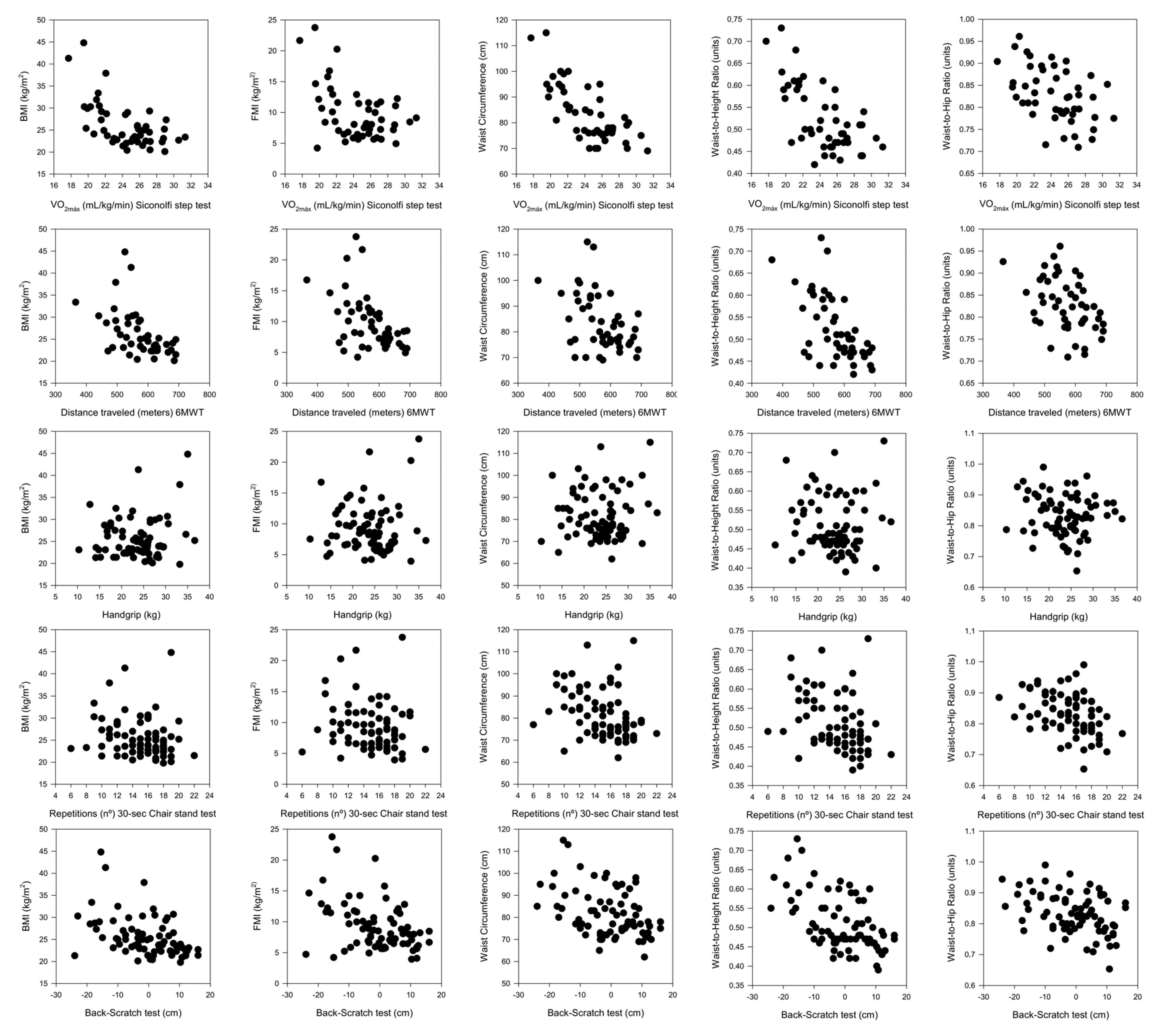
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Somers, E.C.; Marder, W.; Cagnoli, P.; Lewis, E.E.; DeGuire, P.; Gordon, C.; Helmick, C.G.; Wang, L.; Wing, J.J.; Dhar, J.P.; et al. Population-based incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus: The Michigan Lupus Epidemiology and Surveillance program. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipen, Y.; Strauss, B.J.; Morand, E.F. Body composition in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 37, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hak, A.E.; Karlson, E.W.; Feskanich, D.; Stampfer, M.J.; Costenbader, K.H. Systemic lupus erythematosus and the risk of cardiovascular disease: Results from the nurses’ health study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2009, 61, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichile, T.; Petri, M. Prevention and management of co-morbidities in SLE. Presse Med. 2014, 43, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fors-Nieves, C.E.; Izmirly, P.M. Mortality in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Updated Review. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, P.; Gregorich, S.; Yazdany, J.; Trupin, L.; Julian, L.; Yelin, E.; Criswell, L.A. Obesity and its measurement in a community-based sample of women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2011, 63, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltz, G.; Aguirre, M.T.; Sanderson, M.; Fadden, M.K. The role of fat mass index in determining obesity. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2010, 22, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.G.; Schutz, Y.; Dupertuis, Y.M.; Pichard, C. Body composition interpretation. Contributions of the fat-free mass index and the body fat mass index. Nutrition 2003, 19, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koning, L.; Merchant, A.T.; Pogue, J.; Anand, S.S. Waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular events: Meta-regression analysis of prospective studies. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 850–856. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, F.B.; Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Lee, D.; Ruiz, J.R.; Blair, S.N.; Sui, X. Fitness and Fatness as Health Markers through the Lifespan: An overview of Current Knowledge. Prog. Prev. Med. 2018, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Linauskas, A.; Overvad, K.; Symmons, D.; Johansen, M.B.; Steengard-Pedersen, K.; de Thurah, A. Body fat percentage, waist circumference and obesity as risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis—A Danish cohort study. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2018, 7, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, A.; Hurtado, G.F.; Martínez, M.; Mendoza, C. Análisis de la composición corporal en mujeres adultas con lupus eritematoso sistémico. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 950–951. [Google Scholar]
- Vadacca, M.; Margiotta, D.; Rigon, A.; Cacciapaglia, F.; Coppolino, G.; Amoroso, A.; Afeltra, A. Adipokines and systemic lupus erythematosus: Relationship with metabolic sindrome and cardiovascular disease risk factors. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, C.J.; Deedwania, P.; Ortega, F.B. Obesity is rarely healthy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 678–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rámirez-Vélez, R.; Meneses-Echavez, J.F.; González-Ruíz, K.; Correa, J.E. Fitness muscular y riesgo cardio-metabólico en adultos jóvenes colombianos. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prioreschi, A.; Brage, S.; Westgate, K.; Norris, S.A.; Micklesfield, L.K. Cardiorespiratory fitness levels and associations with physical activity and body composition in young South African adults from Soweto. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sui, X.; Huang, S.; Lavie, C.J.; Wang, Z.; Blair, S.N. Secular change in cardiorespiratory fitness and body composition in women: The Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, K.M.; Tucker, L.B.; Potts, J.E.; McKenzie, D.C. Fitness, fatigue, disease activity and quality of life in pediatric lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyser, R.E.; Rus, V.; Cade, W.T.; Kalappa, N.; Flores, R.H.; Handwerger, B.S. Evidence for aerobic insufficiency in women with systemic Lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 49, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbán-Méndez, C.; Soriano-Maldonado, A.; Vargas-Hitos, J.A.; Sáez-Urán, L.M.; Rosales-Castillo, A.; Morillas-de-Laguno, P.; Gavilán-Carrera, B.; Jiménez-Alonso, J. Cardiorespiratory fitness and age-related arterial stiffness in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.J.; Miyake, C.N.; Benatti, F.B.; Silva, C.A.; Sallum, A.M.; Borba, E.; de Sá-Pinto, A.L.; Bonfá, E.; Gualano, B. Reduced aerobic capacity and quality of life in physically inactive patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with mild or inactive disease. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2016, 68, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tench, C.; Bentley, D.; Vleck, V.; McCurdie, I.; White, P.; P’Cruz, D. Aerobic fitness, fatigue, and physical disability in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balsamo, S.; Nascimento, C.; Tibana, R.A.; de Santana, F.S.; da Mota, L.M.; Dos Santos-Neto, L.L. The quality of life of patients with lupus erythematosus influences cardiovascular capacity in 6-minute walk test. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2013, 53, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Maldonado, A.; Morillas-de-Laguno, P.; Sabio, J.M.; Gavilán-Carrera, B.; Rosales-Castillo, A.; Montalbán-Méndez, C.; Sáez-Urán, L.M.; Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; Vargas-Hitos, J.A. Effects of 12-week Aerobic Exercise on Arterial Stiffness, Inflammation, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Women with Sytemic Lupus Erythematosus: Non-Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.S.; Trupin, L.; Schmajuk, G.; Barton, J.; Margaretten, M.; Yazdany, J.; Yelin, E.H.; Katz, P.P. Muscle strength, muscle mass, and physical disability in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2015, 67, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.S.; Trupin, L.; Schmajuk, G.; Barton, J.; Margaretten, M.; Yazdany, J.; Yelin, E.H.; Katz, P.P. Muscle strength and Changes in Physical Function in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2015, 67, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1997, 40, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siconolfi, S.F.; Garber, C.E.; Lasater, T.M.; Carleton, R.A. A simple, valid step test for estimating maximal oxygen uptake in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1985, 121, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcora, S.M.; Casanova, F.; Fortes, M.B.; Maddison, P.J. Validity and reliability of the Siconolfi Step Test for assessment of physical fitness in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2007, 57, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikli, R.E.; Jones, C.J. Functional Fitness Normative Scores for Community-Residing Older Adults, Ages 60-94. J. Aging Phys. Activ. 1999, 7, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.J.; Rikli, R.E.; Beam, W.C. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community-residing older adults. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport. 1999, 70, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ruiz, J.; Mesa, J.L.; Gutiérrez, A.; Castillo, M.J. Hand size influences optimal grip span in women but not men. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2002, 27, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, B.; Mosca, M.; Gordon, C. Assessment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and use of lupus disease activity indices. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 19, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladman, D.; Ginzler, E.; Goldsmith, C.; Fortin, P.; Liang, M.; Urowitz, M.; Bacon, P.; Bombardieri, S.; Hanly, J.; Hay, E.; et al. The development and initial validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1996, 39, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipen, Y.; Briganti, E.M.; Strauss, B.J.; Littlejohn, G.O.; Morand, E.F. Three year follow-up of body composition changes in pre-menopausal women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999, 38, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keevil, V.L.; Khaw, K.T. Overadjustment in regression analyses: Considerations when evaluating relationships between body mass index, muscle strength, and body size. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogun, J.A.; Akinloye, A.A.; Adendola, S.A. Grip strength as a function of age, height, body weight and Quetelet index. Physiother. Theory Pract. 1991, 7, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, S.S.; Segev, S.; Novikov, I.; Dankner, R. Waist circumference vs body mass index in association with cardiorespiratory fitness in healthy men and women: A cross sectional analysis of 403 subjects. Nutr. J. 2013, 15, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesser, I.A.; Dick, T.J.; Guenette, J.A.; Hoogbruin, A.; Mackey, D.C.; Singer, J.; Lear, S.A. The association between cardiorespiratory fitness and abdominal adiposity in postmenopausal, physically inactive South Asian women. Prev. Med. Rep. 2015, 21, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with diminished total and abdominal obesity independent of body mass index. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, S.W.; Fitzgerald, S.J.; McAuley, P.A.; Barlow, C.E. Cardiorespiratory fitness, adiposity, and all-cause mortality in women. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.L.; Katzmarzyk, P.; Nichaman, M.Z.; Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N.; Ross, R. Cardiorespiratory fitness is associated with lower abdominal fat independent of body mass index. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Ross, R.; Leon, A.S.; Skinner, J.S.; Rao, D.C.; Wilmore, J.H.; Rankinen, T.; Bouchard, C. Fitness alters the associations of BMI and waist circumference with total and abdominal fat. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, S.A.; Luben, R.; Keevil, V.L.; Moore, S.; Dalzell, N.; Bhaniani, A.; Khawaja, A.P.; Foster, P.; Brayne, C.; Wareham, N.J.; et al. Cohort profile: A prospective cohort study of objective physical and cognitive capability and visual health in an ageing population of men and women in Norfolk (EPIC-Norfolk 3). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.B.; Haggerty, C.L.; Goodpaster, B.; Harris, T.; Kritchevsky, S.; Nevitt, M.; Miles, T.P.; Visser, M. Strength and muscle quality in a well-functioning cohort of older adults: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keevil, V.L.; Luben, R.; Dalzell, N.; Hayat, S.A.; Sayer, A.A.; Wareham, N.J.; Khaw, K.T. Cross-sectional associations between different measures of obesity and muscle strength in men and women in a British cohort study. J. Nutr. Health. Aging 2015, 19, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevill, A.M.; Holder, R.L. Modelling handgrip strength in the presence of confounding variables: Results from the Allied Dunbar National Fitness Survey. Ergonomics 2000, 43, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulac, M.C.; Carvalho, L.P.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M. Functional capacity depends on lower limb muscle strength rather than on abdominal obesity in active postmenopausal women. Menopause 2018, 25, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, R.; Cooper, R.; Aihie-Sayer, A.; Ben-Schlomo, Y.; Cooper, C.; Deary, I.J.; Demakakos, P.; Gallacher, J.; Martin, R.M.; McNeill, G.; et al. Body mass index, muscle strength and physical performance in older adults from eight cohort studies: The HALCyon programme. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrypnik, D.; Bogdanski, P.; Madry, E.; Karolkiewicz, J.; Ratajczak, M.; Krysciak, J.; Pupek-Musialik, D.; Walkowiak, J. Effects of Endurance and Endurance Strength Training on Body Composition and Physical Capacity in Women with Abdominal Obesity. Obes. Facts 2015, 8, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, I.; Farinatti, P.; De Souza, M.G.; Manhanini, D.P.; Balthazar, E.; Dantas, D.L.; De Andrade Pinto, E.H.; Bouskela, E.; Kraemer-Aguiar, L.G. Effects of Resistance Training on Obese Adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L.; Eagon, J.C.; Trujillo, M.E.; Scherer, P.E.; Klein, S. Visceral fat adipokines secretion is associated with systemic inflammation in obese humans. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaap, L.A.; Plujim, S.M.; Deeg, D.J.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Colbert, L.H.; Pahor, M.; Rubin, S.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; et al. Higher inflammatory marker levels in older persons: Associations with 5-year change in muscle mass and muscle strength. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Kuller, L.H.; Broudeau, R.; Kammerer, C.; de Rekeneire, N.; Harris, T.B.; Schwartz, A.V.; Tylavsky, F.A.; et al. Accelerated loss of skeletal muscle strength in older adults with type 2 diabetes: The health, aging, and body composition study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Wijndaele, K.; Lee, D.C.; Sharp, S.J.; Wareham, N.; Brage, S. Independent and joint associations of grip strength and adiposity with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in 403,199 adults: The UK Biobank study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.A.; Menezes, T.N.; Melo, R.L.; Pedraza, D.F. Handgrip strength and flexibility and their association with anthropometric variables in the elderly. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2013, 59, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.R.; Souza, J.M.; Lebrão, M.L.; de Fátima, M. Nutritional status and physical performance of erderly in the city of São Paulo. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2007, 53, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorio-Arenas, E.; Ruiz-Cabello, P.; Camiletti-Moiron, D.; Moratalla-Cecilia, N.; Aranda, P.; Lopez-Jurado, M.; Llopis, J.; Aparicio, V.A. The associations between physical fitness and cardiometabolic risk and body-size phenotypes in perimenopausal women. Maturitas 2016, 92, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.V.; Hung, C.Y.; Li, C.M.; Lin, Y.H.; Wang, T.G.; Tsai, K.S.; Han, D.S. Reduced flexibility associated with metabolic syndrome in community-dwelling elders. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Dashottar, A.; Borstad, J.D. Scapula kinematics differ by body mass index. J. Appl. Biomech. 2013, 29, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R. Mitigating cellular inflammation in older adults: A randomized controlled trial of Tai Chi Chih. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2012, 20, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, N.T.; Scheuermann, B.W. Cardiovascular Responses to Skeletal Muscle Stretching: “Stretching” the Truth or a New Exercise Paradigm for Cardiovascular Medicine? Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2507–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.A.; Frisoli, A.; Pinheiro, M.M.; Szejnfeld, V.L. Sarcopenia and aging: Etiological aspects and therapeutic options. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2006, 46, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Timóteo, R.P.; Silva, A.F.; Micheli, D.C.; Candido-Murta, E.F.; Freire, M.; Teodoro, R.B.; Lima, F.M.; Martins Tavares Murta, B.; Bertoncello, D. Increased flexibility, pain reduction and unaltered levels of IL-10 and CD11b + lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus were associated with kinesiotherapy. Lupus 2018, 27, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| N | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 77 | 43.2 | 13.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 77 | 65.1 | 11.1 |
| Height (cm) | 77 | 160.1 | 6.8 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 77 | 25.5 | 4.5 |
| FMI (kg/m2) | 77 | 9.23 | 3.87 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 77 | 81.7 | 10.7 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 77 | 98.1 | 9.9 |
| Waist-to-height ratio (units) | 77 | 0.51 | 0.07 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio (units) | 77 | 0.83 | 0.06 |
| Back-Scratch test (cm) | 76 | −0.8 | 9.6 |
| Handgrip strength (kg) | 76 | 23.6 | 5.3 |
| Chair stand test (rep) | 77 | 14.9 | 3.1 |
| 6MWT (m) | 49 | 570.8 | 71.7 |
| VO2max estimated (mL/kg/min) | 49 | 24.4 | 3.2 |
| SLEDAI (score) | 77 | 0.68 | 1.5 |
| SDI (score) | 77 | 0.55 | 1.11 |
| Duration of SLE (years) | 77 | 13.9 | 10.1 |
| Accumulated corticosteroid dose (last 3 years; mg) | 77 | 2875 | 2677 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 77 | 18 | |
| Diabetes (%) | 77 | 1 | |
| Arterial hypertension (%) | 77 | 17 | |
| Smokers (%) | 77 | 53 | |
| Statins intake (%) | 77 | 18 | |
| Antidiabetic drugs intake (%) | 77 | 3 | |
| Corticosteroid dose (%; mg/d) | 77 | 65 |
| β | B | SE | CI 95% | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siconolfi VO2max * | ||||||
| Body Mass Index | −1.14 | −1.83 | 0.26 | −2.35 | −1.30 | <0.001 |
| Fat Mass Index | −1.05 | −1.41 | 0.24 | −1.91 | −0.91 | <0.001 |
| Waist Circumference | −1.09 | −3.73 | 0.50 | −4.74 | −2.71 | <0.001 |
| Waist-to-Height Ratio | −0.90 | −0.02 | 0.00 | −0.02 | −0.01 | <0.001 |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio | −0.30 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.01 | 0.00 | 0.151 |
| 6MWT * | ||||||
| Body Mass Index | −0.57 | −0.04 | 0.01 | −0.06 | −0.01 | <0.001 |
| Fat Mass Index | −0.65 | −0.03 | 0.00 | −0.05 | −0.02 | <0.001 |
| Waist Circumference | −0.35 | −0.05 | 0.02 | −0.10 | −0.00 | 0.029 |
| Waist-to-Height Ratio | −0.53 | −0.001 | 0.00 | −0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio | −0.22 | <0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.162 |
| Handgrip | ||||||
| Body Mass Index | −0.16 | −0.14 | 0.05 | −0.24 | −0.04 | 0.006 |
| Fat Mass Index | −0.29 | −0.21 | 0.05 | −0.31 | −0.11 | <0.001 |
| Waist Circumference | −0.19 | −0.40 | 0.14 | −0.69 | −0.11 | 0.007 |
| Waist-to-Height Ratio | −0.29 | −0.004 | 0.00 | −0.01 | −0.00 | 0.001 |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio | −0.15 | −0.002 | 0.00 | −0.00 | 0.00 | 0.246 |
| Chair Stand Test | ||||||
| Body Mass Index | −0.23 | −0.33 | 0.24 | −0.81 | 0.14 | 0.168 |
| Fat Mass Index | −0.29 | −0.36 | 0.20 | −0.77 | 0.04 | 0.083 |
| Waist Circumference | −0.35 | −1.20 | 0.55 | −2.30 | −0.09 | 0.033 |
| Waist-to-Height Ratio | −0.36 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.01 | −0.00 | 0.030 |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio | −0.41 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.01 | −0.00 | 0.011 |
| Back-Scratch | ||||||
| Body Mass Index | −0.43 | −0.20 | 0.05 | −0.31 | −0.09 | <0.001 |
| Fat Mass Index | −0.44 | −0.18 | 0.05 | −0.28 | −0.09 | <0.001 |
| Waist Circumference | −0.36 | −0.40 | 0.13 | −0.66 | −0.14 | 0.003 |
| Waist-to-Height Ratio | −0.48 | −0.004 | 0.00 | −0.01 | −0.00 | <0.001 |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio | −0.29 | −0.002 | 0.00 | −0.00 | −0.00 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sola-Rodríguez, S.; Gavilán-Carrera, B.; Vargas-Hitos, J.A.; Sabio, J.M.; Morillas-de-Laguno, P.; Soriano-Maldonado, A. Physical Fitness and Body Composition in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicina 2019, 55, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020057
Sola-Rodríguez S, Gavilán-Carrera B, Vargas-Hitos JA, Sabio JM, Morillas-de-Laguno P, Soriano-Maldonado A. Physical Fitness and Body Composition in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicina. 2019; 55(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020057
Chicago/Turabian StyleSola-Rodríguez, Sergio, Blanca Gavilán-Carrera, José Antonio Vargas-Hitos, José Mario Sabio, Pablo Morillas-de-Laguno, and Alberto Soriano-Maldonado. 2019. "Physical Fitness and Body Composition in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Medicina 55, no. 2: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020057
APA StyleSola-Rodríguez, S., Gavilán-Carrera, B., Vargas-Hitos, J. A., Sabio, J. M., Morillas-de-Laguno, P., & Soriano-Maldonado, A. (2019). Physical Fitness and Body Composition in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Medicina, 55(2), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55020057






