Determination of Body Fat Ratio Standards in Children at Early School Age Using Bioelectric Impedance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandita, A.; Sharma, D.; Pandita, D.; Pawar, S.; Tariq, M.; Kaul, A. Childhood obesity: Prevention is better than cure. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2016, 9, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecký, M. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in children between the ages of 6 and 7 and the attitude of parents towards primary prevention in the Olomouc region. Hygiena 2016, 61, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigos, C.; Hainer, V.; Basdevant, A.; Finer, N.; Fried, M.; Mathus-Vliegen, E.; Micic, D.; Maislos, M.; Roman, G.; Schutz, Y.; et al. Management of obesity in adults: European clinical practice guidelines. Obes. Facts 2008, 1, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunc, V. Obesity—Causes and remedies. Phys. Act. Rev. 2016, 4, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Faith, M.S.; Pietrobelli, A.; Heo, M. What is the best measure of adiposity change in growing children: BMI, BMI %, BMI z-score or BMI centile? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inokuchi, M.; Matsuo, N.; Takayama, J.I.; Hasegawa, T. BMI z-score is the optimal measure of annual adiposity change in elementary school children. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2011, 38, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verjans-Janssen, S.R.B.; van de Kolk, I.; Van Kann, D.H.H.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Gerards, S.M.P.L. Effectiveness of school-based physical activity and nutrition interventions with direct parental involvement on childrens BMI and energy balance-related behaviors—A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyward, V.H.; Wagner, D.R. Applied Body Composition Assessment, 2nd ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Block, G.; Dresser, C.M.; Hartman, A.M.; Carroll, M.D. Nutrient sources in the American diet: Quantitative data from the NHANES II survey. I. Vitamins and minerals. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1985, 122, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremmel, M.; Gerdtham, U.-G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Saha, S. Economic Burden of Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Obesity. Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Report of a WHO Consultation (WHO Technical Report Series 894); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Available online: http://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/obesity/WHO_TRS_894/en/ (accessed on 7 February 2020).
- WHO Child Growth Standards. BMI-for-Age; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: http://www.who.int/childgrowth/standards/bmi_for_age/en/ (accessed on 7 February 2020).
- Vignerová, J.; Riedlová, P.; Bláha, P.; Kobzová, J.; Krejčovský, L.; Brabec, M.; Hrušková, M. Growth Charts. 6th Nation-Wide Anthropological Survey of Children and Adolescents 2001 Czech Republic, 1st ed.; PřF UK a SZÚ: Prague, Czech Republic, 2006; pp. 97–137. Available online: http://www.szu.cz/publikace/data/kniha-6-cav-2001-ke-stazeni. (accessed on 7 February 2020).
- Baumgartner, R.N. Body composition in healthy aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 2000, 904, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gába, A.; Přidalová, M. Age-related changes in body composition in a sample of Czech women aged 18–89 years: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.P.; Going, S.B.; Lohman, T.G.; Harsha, D.W.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Webber, L.S.; Berenson, G.S. Body fatness and risk for elevated blood pressure, total cholesterol, and serum lipoprotein ratios in children and adolescents. Am. J. Public Health 1992, 82, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurson, K.R.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Welk, G.J. Development of youth percent body fat standards using receiver operating characteristic curves. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 41, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaufrère, B.; Morio, B. Fat and protein redistribution with aging: Metabolic considerations. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberka, M.; Stolarz-Skrzypek, K.; Biedroń, M.; Szóstak-Janiak, K.; Partyka, M.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Gasior, Z. Obesity, Visceral Fat, and Hypertension-Related Complications. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2018, 16, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gaal, L.F.; Mertens, I.L.; De Block, C.E. Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature 2006, 444, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunc, V. A movement intervention as a tool of the influence of physical fitness and health. Trends Sport Sci. 2018, 4, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bunc, V. Walking like a tool of physical fitness and body composition influence. Antropomotoryka 2012, 22, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bunc, V.; Skalská, M. Using walking as a tool for fitness and its influence on obesity and overweight individuals. Jacobs J. Obes. 2015, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaar, N.; Aucouturier, J.; Ratel, S.; Rance, M.; Meyer, M.; Duché, P. Effect of physical activity intervention on body composition in young children: Influence of body mass index status and gender. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 96, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roriz, D.E.; Oliveira, M.S.; Teixeira Seabra, A.F.; Ribeiro Maia, J.A. Effects of a recreational physical activity summer camp on body composition, metabolic syndrome and physical fitness in obese children. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2016, 56, 933–938. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenmann, J.C.; Heelan, K.A.; Welk, J.G. Assessing body composition among 3- to 8-year-old children: Anthropometry, BIA, and DXA. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergi, G.; De Rui, M.; Stubbs, B.; Veronese, N.; Manzato, E. Measurement of lean body mass using bioelectrical impedance analysis: A consideration of the pros and cons. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutáč, P.; Kopecký, M. Comparison of body fat using various bioelectrical impedance analyzers in university students. Acta Gymnica 2015, 45, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Bellato, M.; Zago, M.; Cusella, G.; Sforza, C.; Lovecchio, N. BMI and inverted BMI as predictors of fat mass in young people: A comparison across the ages. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2020, 47, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurson, K.R.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Welk, G.J. Body Mass Index Standards Based on Agreement with Health-Related Body Fat. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 41, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech Statistical Office. Statistics. 2018; ČSÚ: Praha, Czech Republic, 2018; Available online: https://vdb.czso.cz/vdbvo2/faces/index.jsf?page=vystup-objekt&pvo=DEM01&z=T&f=TABULKA&skupId=606&katalog=30845&pvo=DEM01&str=v33&evo=v866_!_VUZEMI97-100_1&c=v3~2__RP2019MP12DP31 (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Mirwald, R.L.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.; Bailey, D.A.; Beunen, G.P. An assessment of maturity from anthropometric measurements. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, L.; Müller, E.; Hildebrandt, C.; Kapelari, K.; Raschner, C. The assessment of biological maturation for talent selection—Which method can be used? Sportverletz Sportschaden 2015, 29, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Vignerová, J.; Lhotská, L.; Bláha, P.; Roth, Z. Growth of the Czech child population 0–18 years compared to the World Health Organization growth reference. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 1997, 9, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mialich, M.S.; Sicchieri, J.M.F.; Junior, A.A.J. Analysis of Body Composition: A Critical Review of the Use of Bioelectrical Impedance. Anal. Int. J. Clin. Nutr 2014, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Jan, C.; Ma, Y.; Dong, B.; Zou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Song, Y.; Ma, J.; Sawyer, S.M.; et al. Economic development and the nutritional status of Chinese school-aged children and adolescents from 1995 to 2014: An analysis of five successive national surveys. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutáč, P.; Jurková, S.; Farana, R. Morphological characteristics of young female artistic gymnasts from the Czech Republic. Sci. Gym. J. 2019, 11, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Skår, A.; Meza, T.J.; Fredriksen, P.M. Development of weight and height in Norwegian children: The Health Oriented Pedagogical Project (HOPP). Scand. J. Public Health 2018, 46, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, R.M.; Bouchard, C.; Bar-Or, O. Growth, Maturation, and Physical Activity, 2nd ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 41–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wijnhoven, T.M.A.; van Raaij, J.M.A.; Spinelli, A.; Rito, A.I.; Hovengen, R.; Kunesova, R.; Starc, G.; Rutter, H.; Sjöberg, A.; Petrauskiene, A.; et al. WHO European childhood obesity surveillance initiative 2008: Weight, height and body mass index in 6–9-year-old children. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 8, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/96980/2.3.-Prevalence-of-overweight-and-obesity-EDITED_layouted_V3.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Dabas, A.; Seth, A. Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, A.; Nishimura, R.; Sano, H.; Matsudaira, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Shirasawa, T.; Koide, S.; Takahashi, E.; Tajima, N. Gender differences in the relationship between percent body fat(%BF) and body mass index (BMI) in Japanese children. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 78, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.P.; Ford, A.; Sabin, M.A.; Crowne, E.C.; Shield, J.P. Clinical measures of adiposity and percentage fat loss: Which measure most accurately reflects fat loss and what should we aim for? Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
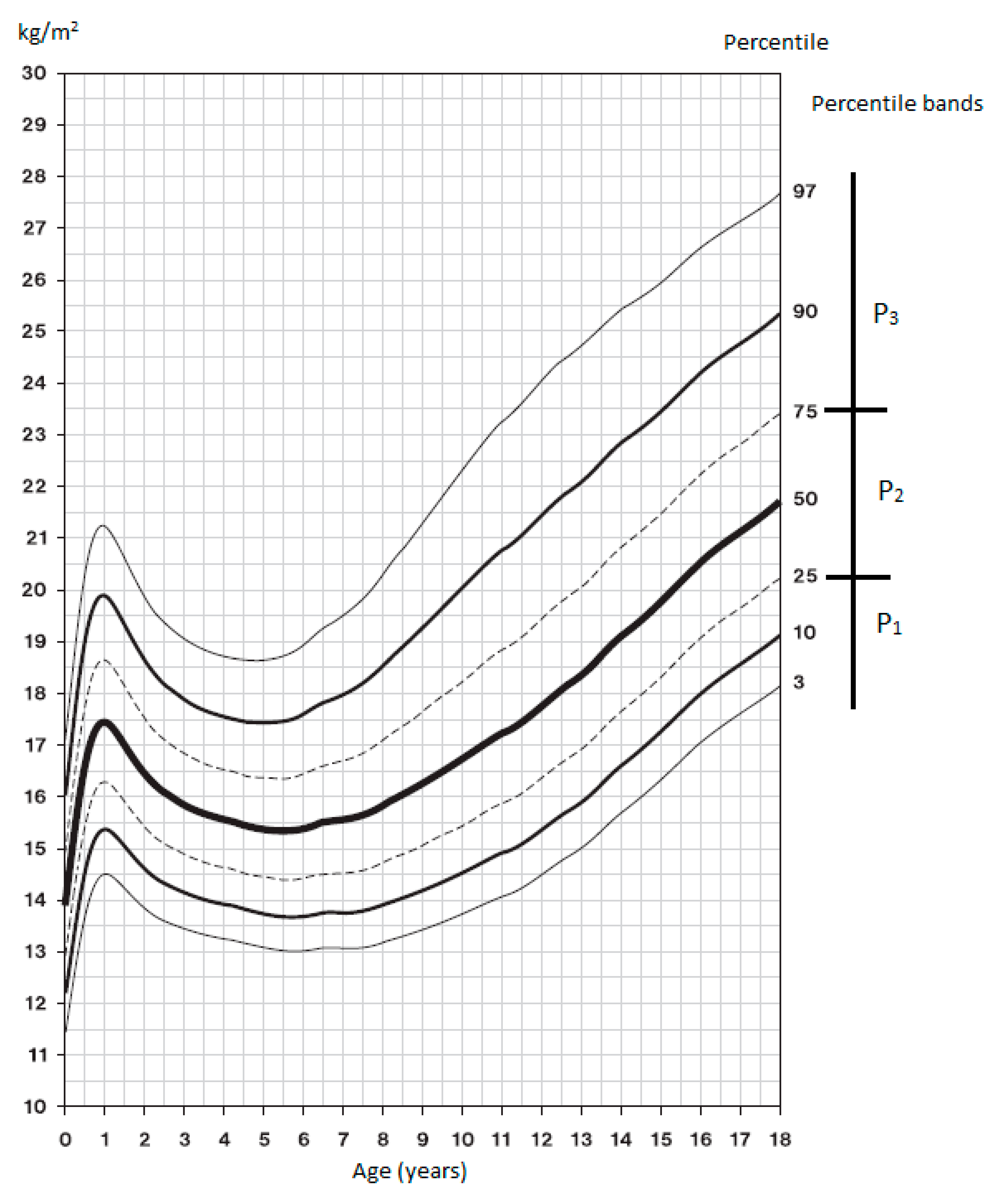


| 6 Years | 7 Years | 8 Years | 9 Years | 10 Years | 11 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | 110 | 138 | 152 | 149 | 159 | 108 |
| Girls | 87 | 165 | 168 | 171 | 156 | 111 |
| Age (years) | P | n (%) | BH (cm) M ± SD | BM (kg) M ± SD | BF (%) M ± SD (95% CI) | VFA (cm2) M ± SD (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | P1 < 25 | 22 (20.0) | 123.1 ± 4.9 | 20.9 ± 1.9 | 11.6 ± 2.1 (10.6, 12.5) | 33.7 ± 8.7 (29.8, 37.6) |
| P2 25–75 | 64 (58.2) | 124.3 ± 5.5 | 23.9 ± 2.4 | 15.2 ± 3.8 (14.3, 16.1) | 36.6 ± 12.4 (34.0, 40.0) | |
| P3 > 75 | 24 (21.8) | 127.8 ± 4.4 | 30.7 ± 3.8 | 25.0 ± 5.8 (22.6, 27.5) | 53.8 ± 15.2 (47.4, 60.2) | |
| 7 | P1 < 25 | 20 (14.5) | 126.3 ± 5.4 | 21.9 ± 2.1 | 10.8 ± 2.5 (9.6, 12.0) | 30.7 ± 9.5 (26.1, 35.2) |
| P2 25–75 | 76 (55.1) | 126.4 ± 4.5 | 24.6 ± 2.3 | 15.1 ± 3.6 (14.3, 16.0) | 34.3 ± 12.1 (31.5, 37.1) | |
| P3 > 75 | 42 (30.4) | 130.7 ± 4.6 | 32.7 ± 5.5 | 25.2 ± 7.6 (22.9, 27.6) | 57.5 ± 20.4 (51.2, 63.9) | |
| 8 | P1 < 25 | 20 (13.1) | 132.5 ± 4.7 | 24.6 ± 2.1 | 11.7 ± 3.4 (10.1, 13.4) | 30.1 ± 11.4 (24.7, 35.6) |
| P2 25–75 | 73 (48.0) | 133.4 ± 5.5 | 28.3 ± 2.7 | 16.3 ± 4.1 (15.4, 17.3) | 35.6 ± 11.8 (32.8, 38.4) | |
| P3 > 75 | 59 (38.9) | 135.9 ± 6.2 | 36.2 ± 5.4 | 26.6 ± 7.8 (24.5, 28.6) | 62.1 ± 21.4 (56.5, 67.7) | |
| 9 | P1 < 25 | 22 (14.8) | 134.6 ± 4.8 | 25.8 ± 1.9 | 12.1 ± 3.2 (10.7, 13.6) | 24.9 ± 13.8 (18.6, 31.2) |
| P2 25–75 | 68 (45.6) | 138.5 ± 6.1 | 31.5 ± 3.2 | 16.7 ± 3.3 (15.9, 17.5) | 35.4 ± 10.9 (31.0, 37.5) | |
| P3 > 75 | 59 (39.6) | 141.5 ± 6.2 | 40.2 ± 6.8 | 27.1 ± 7.0 (25.3, 28.9) | 67.5 ± 21.9 (61.8, 73.2) | |
| 10 | P1 < 25 | 27 (17.0) | 142.7 ± 9.5 | 29.6 ± 4.1 | 10.7 ± 3.6 (9.3, 12.2) | 20.4 ± 10.6 (16.1, 24.7) |
| P2 25–75 | 68 (42.8) | 142.7 ± 6.0 | 34.1 ± 3.7 | 16.7 ± 5.2 (15.4, 18.0) | 35.7 ± 14.7 (30.3, 36.9) | |
| P3 > 75 | 64 (40.2) | 145.2 ± 4.9 | 45.4. ± 7.3 | 29.8 ± 6.5 (28.1, 31.4) | 77.7 ± 25.1 (71.4, 83.9) | |
| 11 | P1 < 25 | 20 (18.5) | 147.8 ± 4.0 | 32.7 ± 1.9 | 13.2 ± 3.6 (11.5, 15.0) | 23.7 ± 9.8 (19.0, 28.4) |
| P2 25–75 | 46 (42.6) | 147.9 ± 6.3 | 37.9 ± 4.0 | 16.8 ± 4.2 (15.5, 18.0) | 39.0 ± 14.2 (36.1, 44.9) | |
| P3 > 75 | 42 (38.9) | 151.5 ± 6.2 | 51.0 ± 7.2 | 29.8 ± 7.5 (27.4, 32.1) | 83.9 ± 27.9 (75.2, 92.6) |
| Age (years) | P | n (%) | BH (cm) M ± SD | BM (kg) M ± SD | BF (%) M ± SD (95% CI) | VFA (cm2) M ± SD (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | P1 < 25 | 24 (27.6) | 120.3 ± 4.2 | 19.4 ± 1.9 | 12.1 ± 2.6 (11.0, 13.3) | 28.7 ± 13.0 (23.1, 34.3) |
| P2 25–75 | 41 (47.1) | 120.8 ± 5.3 | 22.3 ± 2.2 | 18.0 ± 4.3 (16.7, 19.4) | 37.8 ± 13.4 (35.5, 42.1) | |
| P3 > 75 | 22 (25.3) | 124.8 ± 5.1 | 29.0 ± 5.2 | 28.2 ± 5.3 (25.9, 30.6) | 56.8 ± 14.2 (50.5, 63.1) | |
| 7 | P1 < 25 | 39 (23.6) | 124.5 ± 9.0 | 20.6 ± 2.1 | 12.7 ± 3.6 (11.5, 13.9) | 26.5 ± 10.4 (23.1, 30.0) |
| P2 25–75 | 74 (44.8) | 124.4 ± 5.7 | 23.9 ± 2.6 | 18.6 ± 4.0 (17.4, 19.3) | 34.7 ± 13.1 (31.6, 37.8) | |
| P3 > 75 | 52 (31.6) | 128.7 ± 5.8 | 31.4 ± 4.6 | 29.1 ± 6.2 (27.4, 30.8) | 58.2 ± 17.9 (53.2, 63.2) | |
| 8 | P1 < 25 | 44 (26.2) | 129.5 ± 5.2 | 22.5 ± 2.2 | 11.3 ± 4.3 (9.9, 12.6) | 20.5 ± 12.5 (16.6., 24.3) |
| P2 25–75 | 76 (45.2) | 133.4 ± 6.2 | 28.1 ± 3.2 | 18.1 ± 3.8 (17.2, 19.0) | 33.7 ± 13.8 (30.5, 36.8) | |
| P3 > 75 | 48 (28.6) | 134.5 ± 4.2 | 35.8. ± 4.9 | 30.1 ± 6.2 (28.3, 31.9) | 62.8 ± 17.1 (57.9, 67.8) | |
| 9 | P1 < 25 | 35 (20.5) | 136.8 ± 5.1 | 26.1 ± 2.0 | 13.9 ± 3.7 (12.6, 15.2) | 23.7 ± 11.3 (19.8, 27.6) |
| P2 25–75 | 97 (56.7) | 137.0 ± 5.7 | 30.5 ± 3.1 | 18.7 ± 4.3 (17.9, 19.6) | 34.3 ± 16.1 (31.0, 37.5) | |
| P3 > 75 | 39 (22.8) | 138.5 ± 7.3 | 39.5 ± 6.9 | 31.5 ± 6.3 (29.4, 33.5) | 69.2 ± 20.0 (62.8, 75.7) | |
| 10 | P1 < 25 | 24 (15.4) | 140.5 ± 6.7 | 28.7 ± 2.7 | 15.1 ± 3.6 (13.5, 16.6) | 23.0 ± 11.8 (17.9, 28.1) |
| P2 25–75 | 85 (54.5) | 142.9 ± 6.5 | 34.0 ± 3.8 | 18.6 ± 4.8 (17.6, 19.7) | 33.6 ± 15.2 (30.3, 36.9) | |
| P3 > 75 | 47 (30.1) | 147.6 ± 6.9 | 46.7 ± 7.3 | 32.4 ± 6.7 (30.5, 34.4) | 81.2 ± 21.8 (74.8, 87.6) | |
| 11 | P1 < 25 | 22 (19.8) | 145.2 ± 7.7 | 31.1 ± 3.4 | 13.4 ± 3.5 (11.8, 15.0) | 19.9 ± 9.6 (15.5, 24.3) |
| P2 25–75 | 62 (55.9) | 151.1 ± 7.1 | 39.4 ± 4.6 | 19.4 ± 4.3 (18.3, 20.5) | 40.5 ± 17.2 (36.1, 44.9) | |
| P3 > 75 | 27 (24.3) | 152.2 ± 6.5 | 52.5 ± 8.9 | 31.8 ± 7.2 (28.9, 34.6) | 82.3 ± 28.8 (70.9, 93.7) |
| Age (years) | P | Boys | Girls | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ BF (%) | Δ VFA (cm2) | Δ BF (%) | Δ VFA (cm2) | ||
| 6 | P1 vs. P2 | −3.6 *** | −2.9 NS | −5.9 *** | −9.1 * |
| P2 vs. P3 | −9.8 *** | −16.6 *** | −10.2 *** | −19.0 *** | |
| 7 | P1 vs. P2 | −4.3 *** | −3.6 NS | −5.9 *** | −8.2 ** |
| P2 vs. P3 | −10.2 *** | −23.2 *** | −10.8 *** | −23.5 *** | |
| 8 | P1 vs. P2 | −4.6 *** | −5.5 NS | −6.8 *** | −13.2 *** |
| P2 vs. P3 | −10.2 *** | −26.5 *** | −12.1 *** | −29.2 *** | |
| 9 | P1 vs. P2 | −4.6 *** | −10.5 ** | −4.8 *** | −10.6 ** |
| P2 vs. P3 | −10.4 *** | −32.2 *** | −12.7 *** | −35.0 *** | |
| 10 | P1 vs. P2 | −6.0 *** | −15.3 *** | −3.5 ** | −10.6 ** |
| P2 vs. P3 | −13.1 *** | −42.0 *** | −13.8 *** | −47.7 *** | |
| 11 | P1 vs. P2 | −3.6 ** | −15.3 *** | −6.0 *** | −20.6 *** |
| P2 vs. P3 | −13.0 *** | −44.8 *** | −12.3 *** | −41.8 *** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kutac, P.; Bunc, V.; Sigmund, M. Determination of Body Fat Ratio Standards in Children at Early School Age Using Bioelectric Impedance. Medicina 2020, 56, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120641
Kutac P, Bunc V, Sigmund M. Determination of Body Fat Ratio Standards in Children at Early School Age Using Bioelectric Impedance. Medicina. 2020; 56(12):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120641
Chicago/Turabian StyleKutac, Petr, Václav Bunc, and Martin Sigmund. 2020. "Determination of Body Fat Ratio Standards in Children at Early School Age Using Bioelectric Impedance" Medicina 56, no. 12: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120641
APA StyleKutac, P., Bunc, V., & Sigmund, M. (2020). Determination of Body Fat Ratio Standards in Children at Early School Age Using Bioelectric Impedance. Medicina, 56(12), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56120641






