Comparison of WBGTs over Different Surfaces within an Athletic Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Does the WBGT vary by athletic surface (artificial turf, hardcourt tennis, and grass)?
- (2)
- Is a single monitoring station able to capture local WBGT conditions in an athletic complex?
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
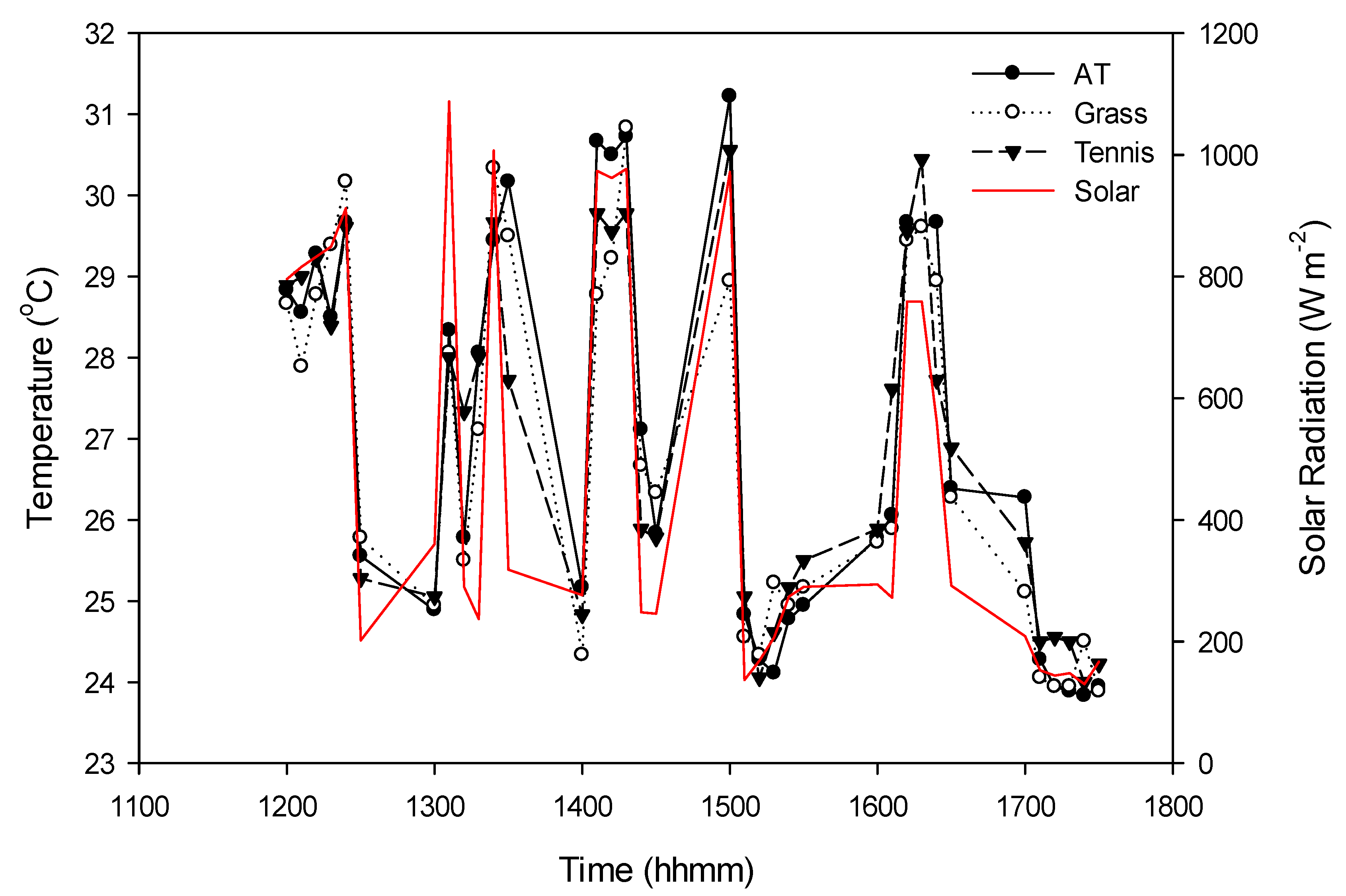
3.1. Weather Conditions
3.2. Differences in WBGT among Athletic Surfaces
3.3. Differences in Microclimates among Athletic Surfaces
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casa, D.J.; Stearns, R.L. Preventing Sudden Death in Sport and Physical Activity; Jones & Bartlett: Burlington, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Casa, D.J.; Millard-Stafford, M.; Moran, D.S.; Pyne, S.W.; Roberts, W.O. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exertional heat illness during training and competition. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casa, D.J.; DeMartini, J.K.; Bergeron, M.F.; Csillan, D.; Eichner, E.R.; Lopez, R.M.; Ferrara, M.S.; Miller, K.C.; O’Connor, F.; Sawka, M.N.; et al. National Athletic Trainers’ Association position statement: Exertional heat illnesses. J. Athl. Train. 2015, 50, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuvront, S.N.; Cauro, E.M.; Heavens, K.R.; Karis, J.; Santee, W.R.; Anos, C.T.; D’Hemecourt, P.D. Effect of WBGT Index Measurement Location on Heat Stress Category Classification. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1958–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor, L.J.; Pryor, R.R.; Grundstein, A.; Casa, D.J. The heat strain of various athletic surfaces: A comparison between observed and modeled wet-bulb globe temperatures. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, B.; Vincent, H.K.; Bruner, M.; Smith, S.M. Comparison of wet bulb globe temperature measured on-site vs. estimated and the impact on activity modification in high school football. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State High School Safety Policies. Available online: https://ksi.uconn.edu/high-school-state-policies-2/ (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Williams, T.B. Microclimatic temperature relationships over different surfaces. J. Geogr. 1991, 9, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskirk, E.R.; Mclaughlin, E.R.; Loomis, J.L. Microclimate over artificial turf. J. Health Phys. Educ. Recreat. 1971, 42, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNitt, A.S. Synthetic turf in the USA: Trends and issues. Int. Turfgrass Soc. Res. 2005, 10, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Petrass, L.A.; Twomey, D.M.; Harvey, J.T.; Otago, L.; Le Rossignol, P. Comparison of surface temperatures of different synthetic turf systems and natural grass: Have advances in synthetic turf technology made a difference. J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2015, 229, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, D.M.; Petrass, L.A.; Harvey, J.T.; Otago, L.; Le Rossignol, P. Selection of management of sports grounds: Does surface heat matter? J. Facil. Plan. Des. Manag. 2016, 4, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jim, C.Y. Solar-terrestrail radiant-energy regimes and temperature anomalies of natural and artificial turf. Appl. Energy 2016, 173, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendelin, W.W.; Krahenbuhl, G.S.; Schact, C.A. Athletic field microclimates and heat stress. J. Saf. Res. 1976, 8, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.F.; Pulley, G.E. Synthetic Surface Heat Studies; Brigham Young University: Provo, UT, USA, 2002; Available online: https://aces.nmsu.edu/programs/turf/documents/brigham-young-study.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Kopec, R.J. Response of the wet-bulb-globe-thermometer heat stress index to selected land use surfaces. Southeast. Geogr. 1977, 17, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate of Georgia. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/climatenormals/clim60/states/Clim_GA_01.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Santee, W.; Matthew, W.; Blanchard, L. Effects of meteorological parameters on adequate evaluation of the thermal environment. J. Therm. Biol. 1994, 19, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglou, C.P.; Minard, D. Control of heat casualties at military training centers. Arch. Indust. Health 1957, 16, 302–316. [Google Scholar]
- Users Guide Kestrel 5400 Heat Stress Tracker. Available online: https://kestrelinstruments.com/mwdownloads/download/link/id/14/ (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Kestrel Certificate of Conformity. Available online: https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0084/9012/t/11/assets/5000_Certificate_of_Conformity_specs.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Athens-Clarke WeatherSTEM. Available online: https://athensclarke.weatherstem.com/ (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Henry, J.A.; Dirks, S.E.; Marotz, G.A. Urban and rural humidity distributions: Relationships to surface materials and land use. J. Climatol. 1985, 5, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljegren, J.C.; Carhart, R.A.; Lawday, P.; Tschopp, S.; Sharp, R. Modeling the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature Using Standard Meteorological Measurements. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2008, 5, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, J.O.; Pielke, R.A., Sr.; Eastman, J.; Mahmood, R.; Hubbard, K.G. Impact of irrigation on midsummer surface fluxes and temperature under dry synoptic conditions: A regional atmospheric model study of the U.S. High Plains. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| AT WBGT | Grass WBGT | Tennis WBGT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry-bulb Temperature | 0.52 | 0.32 | 0.50 |
| Dewpoint Temperature | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.15 |
| Solar Radiation | 0.60 | 0.65 | 0.66 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grundstein, A.; Cooper, E. Comparison of WBGTs over Different Surfaces within an Athletic Complex. Medicina 2020, 56, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56060313
Grundstein A, Cooper E. Comparison of WBGTs over Different Surfaces within an Athletic Complex. Medicina. 2020; 56(6):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56060313
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrundstein, Andrew, and Earl Cooper. 2020. "Comparison of WBGTs over Different Surfaces within an Athletic Complex" Medicina 56, no. 6: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56060313
APA StyleGrundstein, A., & Cooper, E. (2020). Comparison of WBGTs over Different Surfaces within an Athletic Complex. Medicina, 56(6), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56060313




