Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health
Abstract
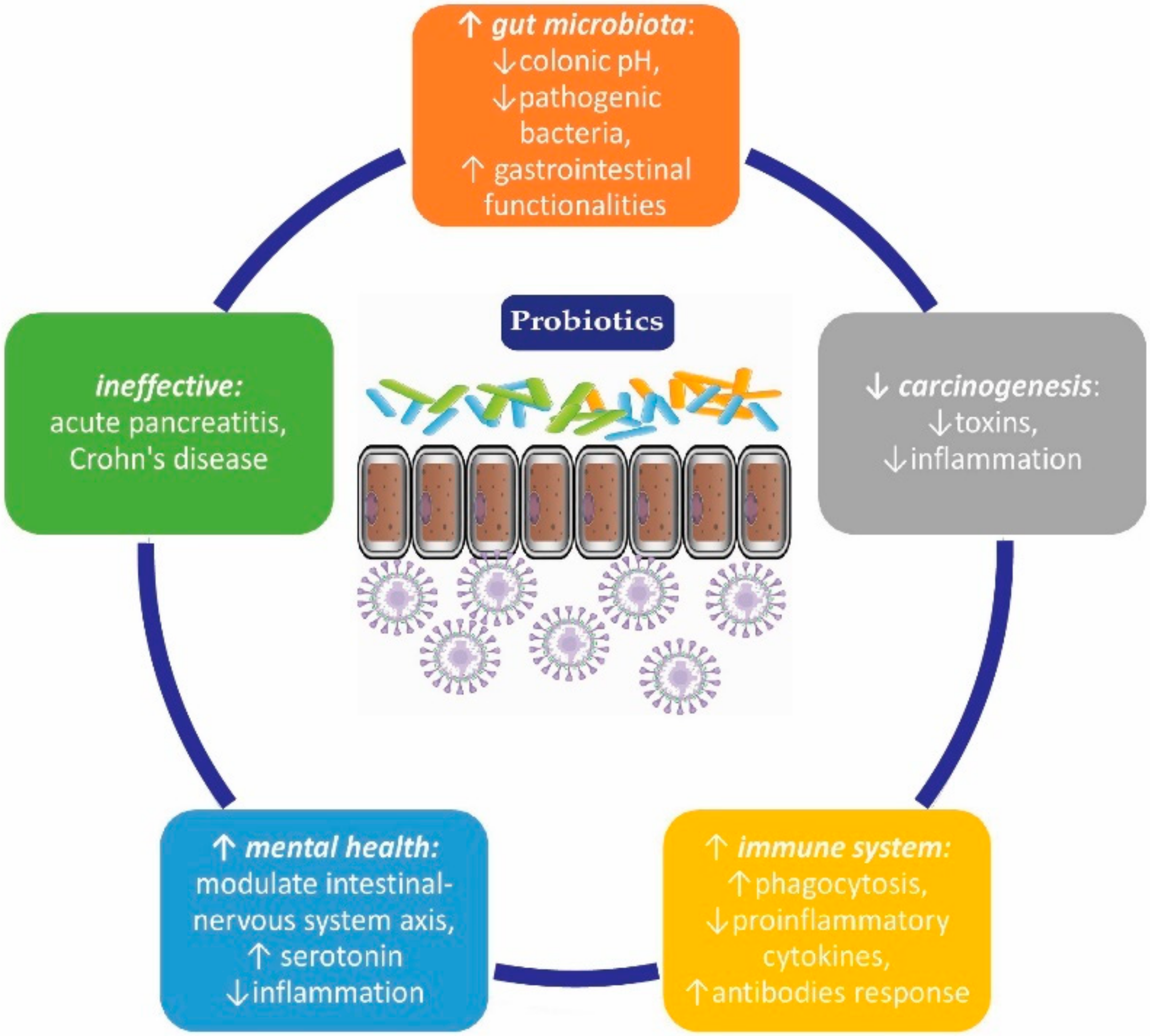
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Effectiveness in Promoting Health: Mechanism of Action of Probiotics
3.1. Use of Probiotics in Gastro-Intestinal (GI) System Disorders
3.1.1. Acute Infectious Diarrhea
3.1.2. Diarrhea Associated with Antibiotic Therapy and Caused by Clostridium difficile
3.1.3. Helicobacter pylori Infection
3.1.4. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD)
3.1.5. Chronic Constipation
3.1.6. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
3.1.7. Hepatic Encephalopathy. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
3.1.8. Celiac Diseases, Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity, Food Allergies
3.1.9. Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease
3.2. Mild and Moderate Depression
3.3. Potential Effect in Reducing Carcinogenesis
3.4. Immunostimulatory Effect
3.5. The Potential of Probiotics in Prophylaxis and Adjuvant Therapy in COVID-19
3.6. Diseases in Which Probiotics are Ineffective
4. Probiotics as Pharmaceutical Dietary Supplements
5. Particular Food Matrices and their Protection Role on Probiotic Viability
6. Probiotics: Safety and Quality Control
6.1. Safety of Probiotics: Side Effects
6.1.1. Systemic Infections
6.1.2. Deleterious Metabolic Activities
6.1.3. Excessive Immune Stimulation in Susceptible Individuals
6.1.4. Gene Transfer
6.2. Quality Control of Probiotics
7. Discussion
8. Limitations and Clinical Pitfalls
9. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salehi, B.; Lopez-Jornet, P.; Pons-Fuster López, E.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Ramírez-Alarcón, K.; Forman, K.; Fernández, M.; Martorell, M.; Setzer, W.N. Plant-derived bioactives in oral mucosal lesions: A key emphasis to curcumin, lycopene, chamomile, aloe vera, green tea and coffee properties. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kumar, N.V.A.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, oxidative stress and antioxidants: Back and forth in the pathophysiology of chronic diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Ata, A.; Kumar, N.V.A.; Sharopov, F.; Ramírez-Alarcón, K.; Ruiz-Ortega, A.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Kobarfard, F.; Zakaria, Z.A.; et al. Antidiabetic potential of medicinal plants and their active components. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayatollahi, A.M.; Ghanadian, M.; Afsharypuor, S.; Choudhary, M.I.; Kobarfard, F.; Rahmati, M. Two new lathyrane type diterpenoids from Euphorbia aellenii. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Z.; Adhikari, A.; Sattar, S.A.; Ayatollahi, S.A.M.; Al-Majid, A.M.A.; Atta Ur, R. Diterpenoids including a novel dimeric conjugate from Salvia leriaefolia. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayatollahi, A.M.; Ghanadian, M.; Afsharypuor, S.; Mesaik, M.A.; Abdalla, O.M.; Shahlaei, M.; Farzandi, G.; Mostafavi, H. Cycloartanes from Euphorbia aellenii Rech. f. and their Antiproliferative Activity. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Neffe-Skocińska, K.; Rzepkowska, A.; Szydłowska, A.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Trends and possibilities of the use of probiotics in food production. In Alternative and Replacement Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 65–94. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, W.R.; Duncan, S.H. Advanced analytical methodologies to study the microbial metabolome of the human gut. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukalas, D.; Fragoulakis, V.; Sarandi, E.; Docea, A.O.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Tsilimidos, G.; Anamaterou, C.; Fragkiadaki, P.; Aschner, M.; Tsatsakis, A. Targeted metabolomic analysis of serum fatty acids for the prediction of autoimmune diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoukalas, D.; Fragkiadaki, P.; Docea, A.O.; Alegakis, A.K.; Sarandi, E.; Vakonaki, E.; Salataj, E.; Kouvidi, E.; Nikitovic, D.; Kovatsi, L. Association of nutraceutical supplements with longer telomere length. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoukalas, D.; Fragkiadaki, P.; Docea, A.O.; Alegakis, A.K.; Sarandi, E.; Thanasoula, M.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsatsakis, A.; Razgonova, M.P.; Calina, D. Discovery of potent telomerase activators: Unfolding new therapeutic and anti-aging perspectives. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3701–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagchi, T. Traditional food & modern lifestyle: Impact of probiotics. Indian J. Med Res. 2014, 140, 333–335. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Scagnolari, C.; Pugliese, F.; Mastroianni, C.M.; d’Ettorre, G. Probiotics and COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 721–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ettorre, G.; Ceccarelli, G.; Marazzato, M.; Campagna, G.; Pinacchio, C.; Alessandri, F.; Ruberto, F.; Rossi, G.; Celani, L.; Scagnolari, C.; et al. Challenges in the management of SARS-CoV2 infection: The Role of oral bacteriotherapy as complementary therapeutic strategy to avoid the progression of COVID-19. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerry, R.G.; Patra, J.K.; Gouda, S.; Park, Y.; Shin, H.-S.; Das, G. Benefaction of probiotics for human health: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Espinoza, Y.; Gallardo-Navarro, Y. Non-dairy probiotic products. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinque, B.; La Torre, C.; Melchiorre, E.; Marchesani, G.; Zoccali, G.; Palumbo, P.; Di Marzio, L.; Masci, A.; Mosca, L.; Mastromarino, P. Use of probiotics for dermal applications. In Probiotics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, M.; Giri, S. Probiotic functional foods: Survival of probiotics during processing and storage. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 9, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Joint FAO/WHO Working Group Report on Drafting Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; FAO: London, ON, Canada; WHO: London, ON, Canada, 2002; Available online: http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/probiotics2/en/ (accessed on 24 December 2019).
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peredo-Lovillo, A.; Romero-Luna, H.; Jiménez-Fernández, M. Health promoting microbial metabolites produced by gut microbiota after prebiotics metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Rational use of prebiotics for gut microbiota alterations: Specific bacterial phylotypes and related mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.D.; Kalyanasundram, J.; Sabidi, S.; Song, A.A.-L.; Abdullah, M.; Rahim, R.A.; Yusoff, K. Recovery of recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens fused with cell wall-anchoring motif (LysM) from inclusion bodies using non-denaturing reagent (N-laurylsarcosine). BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusceddu, M.M.; Murray, K.; Gareau, M.G. Targeting the microbiota, from irritable bowel syndrome to mood disorders: Focus on probiotics and prebiotics. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2018, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagia, M.; Basoulis, D.; Konstantopoulou, S.; Dimitriadi, D.; Gyftopoulou, K.; Skarmoutsou, N.; Fakiri, E. Health benefits of probiotics: A review. ISRN Nutr. 2013, 2013, 481651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, T.; Sequoia, J. Probiotics for gastrointestinal conditions: A summary of the evidence. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.U. Clinical uses of probiotics. Medicine 2016, 95, e2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.; Leung, A.A.; Wong, A.H.; Hon, K.L. Travelers’ diarrhea: A clinical review. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2019, 13, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Jass, J.; Sebulsky, M.T.; McCormick, J.K. Potential uses of probiotics in clinical practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- do Espírito Santo, A.P.; Perego, P.; Converti, A.; Oliveira, M.N. Influence of food matrices on probiotic viability–A review focusing on the fruity bases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ołdak, A.; Zielińska, D.; Rzepkowska, A.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Comparison of antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from two different kinds of regional cheeses from Poland: Oscypek and Korycinski cheese. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantegazza, C.; Molinari, P.; D’Auria, E.; Sonnino, M.; Morelli, L.; Zuccotti, G.V. Probiotics and antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children: A review and new evidence on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG during and after antibiotic treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K. What could probiotic do for us? Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2014, 3, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, A.; Pifer, R.; Behrendt, C.L.; Hooper, L.V.; Yarovinsky, F. Gut commensal bacteria direct a protective immune response against Toxoplasma gondii. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowak, K.; Śliżewska, K.; Libudzisz, Z.; Socha, J. Probiotics–health effects. Żywność Nauka Technol. Jakość 2010, 4, 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ungureanu, A.; Zlatian, O.; Mitroi, G.; Drocaş, A.; Ţîrcă, T.; Călina, D.; Dehelean, C.; Docea, A.O.; Izotov, B.N.; Rakitskii, V.N. Staphylococcus aureus colonisation in patients from a primary regional hospital. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8771–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Călina, D.; Roșu, L.; Roșu, A.F.; Ianoşi, G.; Ianoşi, S.; Zlatian, O.; Mitruț, R.; Docea, A.; Rogoveanu, O.; Mitruț, P. Etiological diagnosis and pharmacotherapeutic management of parapneumonic pleurisy. Farmacia 2016, 64, 946–952. [Google Scholar]
- Tanase, A.; Colita, A.; Ianosi, G.; Neagoe, D.; Branisteanu, D.E.; Calina, D.; Docea, A.O.; Tsatsakis, A.; Ianosi, S.L. Rare case of disseminated fusariosis in a young patient with graft vs. host disease following an allogeneic transplant. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 2078–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McFarland, L.; Evans, C.; Goldstein, E. Strain-specificity and disease-specificity of probiotic efficacy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2018, 5, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, M.; Yu, S.; Deng, J.; Yan, Q.; Yang, C.; Xia, G.; Zhou, X. Efficacy of probiotic supplementation therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosu, A.; Patita, M.; Calina, D.; Andreea, N.; Fonseca, C. Multidrug resistant infections in cirrhosis patients. Filodiritto Editore. In Proceedings of the Romanian National Congress of Pharmacy, 17th Edition, Bucharest, Romania, 26–29 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, K.; Tong, X.; Wang, R.; Song, X. The clinical effects of probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e13792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, H.C.; Song, I.S. Simvastatin induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and in tumor xenografts, and attenuates colitis-associated colon cancer in mice. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, L.; Deng, H.; Guo, J.; Shu, H.; Zhang, L. Efficacy and safety of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, C.H.; Chang, S.K. Alteration of gut microbiota and efficacy of probiotics in functional constipation. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 21, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AlFaleh, K.; Anabrees, J. Probiotics for prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Evid. Based Child Health A Cochrane Rev. J. 2014, 9, 584–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docea, A.O.; Gofiță, E.; Călina, D.; Zaharie, S.; Valcea, D.I.; Mitruț, P. Autoimmune disorders due to double antiviral therapy with Peginterferon and Ribavirin in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Farmacia 2016, 64, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Halegoua-DeMarzio, D. Role of probiotics in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Does gut microbiota matter? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shewry, P.R.; Hey, S.J. The contribution of wheat to human diet and health. Food Energy Secur. 2015, 4, 178–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherf, K.A. Immunoreactive cereal proteins in wheat allergy, non-celiac gluten/wheat sensitivity (NCGS) and celiac disease. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akobeng, A.K.; Singh, P.; Kumar, M.; Al Khodor, S. Role of the gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease and potential therapeutic implications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biase, A.R.; Marasco, G.; Ravaioli, F.; Dajti, E.; Colecchia, L.; Righi, B.; D’Amico, V.; Festi, D.; Iughetti, L.; Colecchia, A. Gut microbiota signatures and clinical manifestations in celiac disease children at onset: A pilot study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valitutti, F.; Cucchiara, S.; Fasano, A. Celiac disease and the microbiome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chibbar, R.; Dieleman, L.A. The gut microbiota in celiac disease and probiotics. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galipeau, H.J.; McCarville, J.L.; Huebener, S.; Litwin, O.; Meisel, M.; Jabri, B.; Sanz, Y.; Murray, J.A.; Jordana, M.; Alaedini, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota modulates gluten-induced immunopathology in humanized mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 2969–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henggeler, J.C.; Veríssimo, M.; Ramos, F. Non-coeliac gluten sensitivity: A review of the literature. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, M. Food allergy in adults: Presentations, evaluation, and treatment. Med. Clin. 2020, 104, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, S.; Tortajada-Genaro, L.A.; Maquieira, A.; Martinez, M.-A.G. Biosensors for food allergy detection according to specific IgE levels in serum. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Song, Y.; Wu, W.; Yu, K.; Zhang, G. The gut microbiota, environmental factors, and links to the development of food allergy. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2020, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schülke, S.; Albrecht, M. Mouse models for food allergies: Where do we stand? Cells 2019, 8, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aitoro, R.; Paparo, L.; Amoroso, A.; Di Costanzo, M.; Cosenza, L.; Granata, V.; Di Scala, C.; Nocerino, R.; Trinchese, G.; Montella, M.; et al. Gut Microbiota as a target for preventive and therapeutic intervention against food allergy. Nutrients 2017, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefka, A.T.; Feehley, T.; Tripathi, P.; Qiu, J.; McCoy, K.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Tjota, M.Y.; Seo, G.-Y.; Cao, S.; Theriault, B.R. Commensal bacteria protect against food allergen sensitization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13145–13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boynton, W.; Floch, M. New strategies for the management of diverticular disease: Insights for the clinician. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarpignato, C.; Bertelé, A.; Tursi, A. Probiotics for the Treatment of symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease: Rationale and current evidence. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50 (Suppl. 1), S70–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahner, E.; Bellisario, C.; Hassan, C.; Zullo, A.; Esposito, G.; Annibale, B. Probiotics in the Treatment of diverticular disease: A systematic review. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2016, 25, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Faliva, M.A.; Perna, S.; Giacosa, A.; Peroni, G.; Castellazzi, A.M. Using probiotics in clinical practice: Where are we now? A review of existing meta-analyses. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 521–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogdan, M.; Gofita, E.; Calina, D.C.; Turcu-Stiolica, A.; Docea, A.O.; Balseanu, T.A.; Camen, A.; Popa, G.E.; Rusu, G.; Cristofor, I. New antidepressant medication: Benefits versus adverse effects. In Pharmacokinetics and Adverse Effects of Drugs-Mechanisms and Risks Factors; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum, L.; Hogea, L.M.; Călina, D.; Andreescu, N.; Grădinaru, R.; Ștefănescu, R.; Puiu, M. Modern treatment approaches in psychoses. Pharmacogenetic, neuroimagistic and clinical implications. Farmacia 2017, 65, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Lankatillake, C.; Dias, D.A.; Docea, A.O.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Lobine, D.; Chazot, P.L.; Kurt, B.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Catarina Moreira, A. Impact of natural compounds on neurodegenerative disorders: From preclinical to pharmacotherapeutics. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallace, C.J.K.; Milev, R. The effects of probiotics on depressive symptoms in humans: A systematic review. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2017, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gayathri, D.; Rashmi, B. Anti-cancer properties of probiotics: A natural strategy for cancer prevention. EC Nutr. 2016, 5, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, H. Utilization of natural antioxidants: Green tea extract and Thymbra spicata oil in Turkish dry-fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 2006, 73, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honikel, K.-O. The use and control of nitrate and nitrite for the processing of meat products. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Telese, A.; Marasco, G.; Bazzoli, F.; Zagari, R.M. Gastric cancer prevention strategies: A global perspective. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neffe-Skocińska, K.; Okoń, A.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D.; Dolatowski, Z. Amino acid profile and sensory characteristics of dry fermented pork loins produced with a mixture of probiotic starter cultures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.; Kalam, A.; Sarker, M.; Wan, D. Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics on cytokine profiles. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8063647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, types, sources, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, C.F.; Rodrigues, M.E.; Henriques, M.C. Promising alternative therapeutics for oral candidiasis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2515–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, D.; Chapman, J.; Adeuya, A.; Kim, J.; Chen, F.; Whitehead, T.; Lapidus, A.; Rokhsar, D.; Lebrilla, C.B.; German, J. The genome sequence of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals adaptations for milk utilization within the infant microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18964–18969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akelma, A.Z.; Topcu, Z. Probiotics and allergic disease. World J. Immunol. 2016, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calina, D.; Docea, A.O.; Golokhvast, K.S.; Sifakis, S.; Tsatsakis, A.; Makrigiannakis, A. Management of endocrinopathies in pregnancy: A review of current evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, D.-J.; Oh, S.; Lim, K.-T. The anti-allergic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum L67 and its application to yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9372–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguli, K.; Collado, M.C.; Rautava, J.; Lu, L.; Satokari, R.; von Ossowski, I.; Reunanen, J.; de Vos, W.M.; Palva, A.; Isolauri, E.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and its SpaC pilus adhesin modulate inflammatory responsiveness and TLR-related gene expression in the fetal human gut. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llewellyn, A.; Foey, A. Probiotic modulation of innate cell pathogen sensing and signaling events. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rask, C.; Adlerberth, I.; Berggren, A.; Ahrén, I.L.; Wold, A.E. Differential effect on cell-mediated immunity in human volunteers after intake of different lactobacilli. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 172, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitetta, L.; Saltzman, E.T.; Thomsen, M.; Nikov, T.; Hall, S. Adjuvant probiotics and the intestinal microbiome: Enhancing vaccines and immunotherapy outcomes. Vaccines 2017, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, G.; Korenaga, H.; Nagamine, R.; Kawahara, S.; Takeda, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Dashnyam, B.; Yoshida, T.; Kono, T.; Sakai, M. Elevated cytokine responses to Vibrio harveyi infection in the Japanese pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) treated with Lactobacillus paracasei spp. paracasei (06TCa22) isolated from the Mongolian dairy product. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdeano, C.M.; Cazorla, S.I.; Dumit, J.M.L.; Vélez, E.; Perdigón, G. Beneficial effects of probiotic consumption on the immune system. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Docea, A.O.; Tsatsakis, A.; Albulescu, D.; Cristea, O.; Zlatian, O.; Vinceti, M.; Moschos, S.A.; Tsoukalas, D.; Goumenou, M.; Drakoulis, N. A new threat from an old enemy: Re-emergence of coronavirus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calina, D.; Docea, A.O.; Petrakis, D.; Egorov, A.M.; Ishmukhametov, A.A.; Gabibov, A.G.; Shtilman, M.I.; Kostoff, R.; Carvalho, F.; Vinceti, M. Towards effective COVID-19 vaccines: Updates, perspectives and challenges. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Nasiruddin, M.; Khan, I.N.; Mishra, S.K.; Kudrat-E-Zahan, M.; Riaz, T.A.; Ali, E.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Mubarak, M.S.; Martorell, M.; et al. A perspective on emerging therapeutic interventions for COVID-19. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojewodzic, M.W. Bacteriophages could be a potential game changer in the trajectory of coronavirus disease (COVID-19). PHAGE 2020, 1, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, D.; Mohanty, A. Gut microbiota and Covid-19-possible link and implications. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 198018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.B.; Tolonen, A.C.; Xavier, R.J. Human genetic variation and the gut microbiome in disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infusino, F.; Marazzato, M.; Mancone, M.; Fedele, F.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Severino, P.; Ceccarelli, G.; Santinelli, L.; Cavarretta, E.; Marullo, A.G.M.; et al. Diet supplementation, probiotics, and nutraceuticals in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A scoping review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liévin-Le Moal, V.; Servin, A.L. Anti-infective activities of lactobacillus strains in the human intestinal microbiota: From probiotics to gastrointestinal anti-infectious biotherapeutic agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 167–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.K.; Shin, C. The microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric disorders: Pathophysiological mechanisms and novel treatments. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegari, A.; Kheyrolahzadeh, K.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Sharifi, S.; Memar, M.Y.; Zununi Vahed, S. The battle of probiotics and their derivatives against biofilms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrakis, D.; Margină, D.; Tsarouhas, K.; Tekos, F.; Stan, M.; Nikitovic, D.; Kouretas, D.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsatsakis, A. Obesity—A risk factor for increased COVID-19 prevalence, severity and lethality (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Sharopov, F.; Docea, A.O.; Can Karaca, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kahveci Karıncaoglu, D.; Gülseren, G.; Şenol, E.; Demircan, E. Diet, lifestyle and cardiovascular diseases: Linking pathophysiology to cardioprotective effects of natural bioactive compounds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, B.; Yu, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, W.; Tang, C.; Gao, Y.; Luo, K. Ultrahard nanotwinned cubic boron nitride. Nature 2013, 493, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trinchieri, V.; Laghi, L.; Vitali, B.; Parolin, C.; Giusti, I.; Capobianco, D.; Mastromarino, P.; De Simone, C. Efficacy and safety of a multistrain probiotic formulation depends from manufacturing. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, H.; Koning, C.; Mulder, L.; Rombouts, F.; Beynen, A. Monostrain, multistrain and multispecies probiotics—A comparison of functionality and efficacy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 96, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Islas, A.Á.; Jiménez-Fernández, M.; Cantú-Lozano, D.; Urrea-García, G.R.; Luna-Solano, G. Effect of the freeze-drying process on the physicochemical and microbiological properties of mexican kefir grains. Processes 2019, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Simone, C. The unregulated probiotic market. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cinque, B.; La Torre, C.; Lombardi, F.; Palumbo, P.; Evtoski, Z.; Santini, S., Jr.; Falone, S.; Cimini, A.; Amicarelli, F.; Cifone, M.G. VSL# 3 probiotic differently influences IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cell status and function. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3530–3539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gareau, M.G.; Sherman, P.M.; Walker, W.A. Probiotics and the gut microbiota in intestinal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shori, A.B. Influence of food matrix on the viability of probiotic bacteria: A review based on dairy and non-dairy beverages. Food Biosci. 2016, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wong, F.S.; Wen, L. Type 1 diabetes and gut microbiota: Friend or foe? Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 98, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, M.Z.; Qadir, M.I.; Hussain, T.; Janbaz, K.H.; Khan, Y.H.; Ahmad, B. Probiotics and their beneficial effects against various diseases. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 405–415. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, H.L.; Callaway, L.K.; Nitert, M.D. Probiotics: A potential role in the prevention of gestational diabetes? Acta Diabetol. 2012, 49, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-J. Foodomics: A novel approach for food microbiology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 96, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terpou, A.; Papadaki, A.; Lappa, I.K.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Bosnea, L.A.; Kopsahelis, N. Probiotics in food systems: Significance and emerging strategies towards improved viability and delivery of enhanced beneficial value. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, H. Technological aspects of probiotic functional food development. Nutrafoods 2012, 11, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, C.; Bertolino, M.; Zeppa, G.; Cocolin, L. Evaluation of toma piemontese PDO cheese as a carrier of putative probiotics from table olive fermentations. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Klaenhammer, T.R.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Pot, B.; Johansen, E.; Heimbach, J.T.; Marco, M.L.; Tennilä, J.; Ross, R.P.; Franz, C. Effects of genetic, processing, or product formulation changes on efficacy and safety of probiotics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1309, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neffe, K.; Kolozyn-Krajewska, D. Potential uses of probiotic bacteria in ripening meat products. Zywnosc Nauka Technol. Jakosc (Poland) 2010, 17, 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Neffe-Skocinska, K.; Gierejkiewicz, M.; Kolozyn-Krajewska, D. Optimization of fermentation conditions for dry-aged sirloins with probiotic bacteria added. Zywnosc Nauka Technol. Jakosc 2011, 18, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójciak, K.; Dolatowski, Z.; Okoń, A. The effect of probiotic strains on oxidative stability of cured pork meat products. Fleischwirtschaft 2012, 1, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, S.-K.; Ewe, J.-A.; Tham, C.S.-C.; Liong, M.-T. Carriers of probiotic microorganisms. In Probiotics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 191–220. [Google Scholar]
- Kołożyn-Krajewska, D.; Dolatowski, Z.J. Probiotic meat products and human nutrition. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, T.D.; Axelsson, L.; Naterstad, K.; Elsser, D.; Budde, B.B. Identification of potential probiotic starter cultures for Scandinavian-type fermented sausages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 105, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkkila, S.; Suihko, M.L.; Eerola, S.; Petaja, E.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Dry sausage fermented by Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 64, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holko, I.; Hrabě, J.; Šalaková, A.; Rada, V. The substitution of a traditional starter culture in mutton fermented sausages by Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arihara, K.; Itoh, M. UV-induced Lactobacillus gasseri mutants resisting sodium chloride and sodium nitrite for meat fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 56, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumarasamy, P.; Holley, R.A. Survival of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in dry fermented sausages containing micro-encapsulated probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldrá, F.; Reig, M. Innovations for healthier processed meats. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.V.; Vijayendra, S.V.N.; Reddy, O.V.S. Trends in dairy and non-dairy probiotic products-a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6112–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Kurvinen, T.; Rissanen, P. Use of a probiotic Bifidobacterium in a dry food matrix, an in vivo study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Capanoglu, E.; Adrar, N.; Catalkaya, G.; Shaheen, S.; Jaffer, M.; Giri, L.; Suyal, R.; Jugran, A.K.; Calina, D. Cucurbits plants: A key emphasis to its pharmacological potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Capanoglu, E.; Adrar, N.; Catalkaya, G.; Shaheen, S.; Jaffer, M.; Giri, L.; Suyal, R.; Jugran, A.K. Cucurbita plants: From farm to industry. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehi, B.; Shivaprasad Shetty, M.; V Anil Kumar, N.; Živković, J.; Calina, D.; Oana Docea, A.; Emamzadeh-Yazdi, S.; Sibel Kılıç, C.; Goloshvili, T.; Nicola, S. Veronica plants—Drifting from farm to traditional healing, food application, and phytopharmacology. Molecules 2019, 24, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batista, C.; Barros, L.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C. Nutritional and nutraceutical potential of rape (Brassica napus L. var. napus) and “tronchuda” cabbage (Brassica oleraceae L. var. costata) inflorescences. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Kinetic studies for the preparation of probiotic cabbage juice: Impact on phytochemicals and bioactivity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Possemiers, S.; Marzorati, M.; Verstraete, W.; Van de Wiele, T. Bacteria and chocolate: A successful combination for probiotic delivery. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopalan, V.; Shriner, K.A.; Wong-Beringer, A. Regulatory oversight and safety of probiotic use. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, D.E.; Fraser, C.; Palumbo, F.; Ravel, F.; Rowthorn, J.; Schwartz, V. Final Report. Federal Regulation of Probiotics: An Analysis of the Existing Regulatory Framework and Recommendations for Alternative Frameworks; White Paper; University Maryland Francis King Carey School of Law: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2016; Available online: http://www.law.umaryland.edu (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Doron, S.; Snydman, D.R. Risk and safety of probiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, S129–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whelan, K.; Myers, C.E. Safety of probiotics in patients receiving nutritional support: A systematic review of case reports, randomized controlled trials, and nonrandomized trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardeau, M.; Guguen, M.; Vernoux, J.P. Beneficial lactobacilli in food and feed: Long-term use, biodiversity and proposals for specific and realistic safety assessments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Akkermans, L.M.; Haller, D.; Hammerman, C.; Heimbach, J.T.; Hörmannsperger, G.; Huys, G. Safety assessment of probiotics for human use. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, S.; Arakawa, C.; Kohira, R.; Fujita, Y.; Fuchigami, T.; Mugishima, H. A case of D-lactic acid encephalopathy associated with use of probiotics. Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruseler-van Embden, J.; Van Lieshout, L.; Gosselink, M.; Marteau, P. Inability of Lactobacillus casei strain GG, L. acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium bifidum to degrade intestinal mucus glycoproteins. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 30, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Wolf, P.G.; Gaskins, H.R. Taurocholic acid metabolism by gut microbes and colon cancer. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Ghosh, M.; Ganguli, A. Mitogenic response and probiotic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolated from indigenously pickled vegetables and fermented beverages. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Crittenden, R.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S. Safety evaluation of probiotics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Hu, T.; Qu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Dong, A. Plasmids from food lactic acid bacteria: Diversity, similarity, and new developments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13172–13202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franz, C.M.; Huch, M.; Abriouel, H.; Holzapfel, W.; Gálvez, A. Enterococci as probiotics and their implications in food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Tomar, S.K.; Goswami, P.; Sangwan, V.; Singh, R. Antibiotic resistance among commercially available probiotics. Food Res. Int. 2014, 57, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammor, M.S.; Flórez, A.B.; Van Hoek, A.H.; Clara, G.; Aarts, H.J.; Margolles, A.; Mayo, B. Molecular characterization of intrinsic and acquired antibiotic resistance in lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 14, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueimonde, M.; Sanchez, B.; de los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G.; Margolles, A. Antibiotic resistance in probiotic bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Tuomola, E.; Crittenden, R.; Playne, M.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Quality assurance criteria for probiotic bacteria. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 393s–398s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, M.; Andonova, L.; Peikova, L.; Zlatkov, A. Probiotics–Health benefits, classification, quality assurance and quality control–Review. Pharmacia 2014, 61, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Huys, G.; Botteldoorn, N.; Delvigne, F.; De Vuyst, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Pot, B.; Dubois, J.J.; Daube, G. Microbial characterization of probiotics–Advisory report of the working group “8651 probiotics” of the Belgian superior health council (SHC). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1479–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mianzhi, Y.; Shah, N.P. Contemporary nucleic acid-based molecular techniques for detection, identification, and characterization of Bifidobacterium. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 987–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, W.H.; Haberer, P.; Geisen, R.; Björkroth, J.; Schillinger, U. Taxonomy and important features of probiotic microorganisms in food and nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 365s–373s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandok, H.; Shah, P.; Akare, U.R.; Hindala, M.; Bhadoriya, S.S.; Ravi, G.; Sharma, V.; Bandaru, S.; Rathore, P.; Nayarisseri, A. Screening, isolation and identification of probiotic producing lactobacillus acidophilus strains EMBS081 & EMBS082 by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2015, 7, 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- Shokryazdan, P.; Faseleh Jahromi, M.; Liang, J.B.; Ho, Y.W. Probiotics: From isolation to application. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wosinska, L.; Cotter, P.D.; O’Sullivan, O.; Guinane, C. The potential impact of probiotics on the gut microbiome of athletes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, M.L.; Romanuk, T.N. A meta-analysis of probiotic efficacy for gastrointestinal diseases. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, T.F.; Casarotti, S.N.; de Oliveira, G.L.V.; Penna, A.L.B. The impact of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on the biochemical, clinical, and immunological markers, as well as on the gut microbiota of obese hosts. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, P.A.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.J.; Cani, P.D.; Mercenier, A.; MacDonald, T.T.; Garcia-Ródenas, C.L.; Wells, J.M. Can probiotics modulate human disease by impacting intestinal barrier function? Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogsan, C.S.B.; Ferreira, L.; Maldonado, C.; Perdigon, G.; Almeida, S.R.d.; Oliveira, M.N.d. Fermented or unfermented milk using Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis HN019: Technological approach determines the probiotic modulation of mucosal cellular immunity. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Rescigno, A.; Dettori, T.; Calina, D.; Docea, A.O.; Singh, L.; Cebeci, F.; Özçelik, B.; Bhia, M.; Dowlati Beirami, A. Avocado–soybean unsaponifiables: A panoply of potentialities to be exploited. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenster, K.; Freeburg, B.; Hollard, C.; Wong, C.; Rønhave Laursen, R.; Ouwehand, A.C. The Production and Delivery of probiotics: A review of a practical approach. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ranadheera, R.; Baines, S.; Adams, M. Importance of food in probiotic efficacy. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.; Ruelaz, A.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J.N.; Suttorp, M.J.; Johnsen, B.; Shanman, R.; Slusser, W.; Fu, N. Safety of probiotics used to reduce risk and prevent or treat disease. Evid. Rep. Technol. Assess. 2011, 200, 1–645. [Google Scholar]
- Marteau, P. Safety aspects of probiotic products. Näringsforskning 2001, 45, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Govender, M.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; van Vuuren, S.; Pillay, V. A review of the advancements in probiotic delivery: Conventional vs. non-conventional formulations for intestinal flora supplementation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Celiberto, L.S.; Pinto, R.A.; Rossi, E.A.; Vallance, B.A.; Cavallini, D.C.U. Isolation and Characterization of potentially probiotic bacterial strains from mice: Proof of concept for personalized probiotics. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salehi, B.; Calina, D.; Docea, A.O.; Koirala, N.; Aryal, S.; Lombardo, D.; Pasqua, L.; Taheri, Y.; Marina Salgado Castillo, C.; Martorell, M. Curcumin’s nanomedicine formulations for therapeutic application in neurological diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardona, F.; Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Tulipani, S.; Tinahones, F.J.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I. Benefits of polyphenols on gut microbiota and implications in human health. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sireswar, S.; Dey, G.; Sreesoundarya, T.; Sarkar, D. Design of probiotic-fortified food matrices influence their antipathogenic potential. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas, M.; Muñoz-González, I.; Cueva, C.; Jiménez-Girón, A.; Sánchez-Patán, F.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Moreno-Arribas, M.; Bartolomé, B. A survey of modulation of gut microbiota by dietary polyphenols. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 850902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti-Silva, A.C.; de Souza-Borges, P.K. Sensory characteristics, brand and probiotic claim on the overall liking of commercial probiotic fermented milks: Which one is more relevant? Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Gastrointestinal Diseases/Disorders | Effect of Probiotics | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Efficacy of probiotics in gastrointestinal diseases | ||
| Acute Bacterial Infectious Diarrhea | ↓duration of the disease, ↓the risk of prolongation over four days | [28] |
| ↓ the number of daily stools | ||
| Traveler’s diarrhea | preventive effect | [29] |
| Acute viral diarrhea | no significant difference between the group of patients who received the probiotic containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and the control group | [30] |
| Diarrhea associated with antibiotic therapy | prevents or lessens the course of diarrhea | [33,34] |
| ↓stool frequency, ↑recovery, ↓disease duration | [40] | |
| Helicobacter pylori Infection | adjunct to antibiotic therapy to eradicate Helicobacter pylori infection | [41] |
| Ulcerative Colitis, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Functional Abdominal Pain | it cannot be concluded whether the use of probiotics has a general benefit in the evolution of these diseases. | [43] |
| ↑remission rate in adults with ulcerative colitis, not maintaining remission, ↓symptoms, ↑ quality of life | [45] | |
| Chronic Constipation | ↑ average number of stools per week | [46] |
| Necrotizing Enterocolitis | ↓the risk of severe necrotizing enterocolitis, ↓ mortality | [47] |
| Hepatic encephalopathy | ↓ risk of developing hepatic encephalopathy | [48] |
| Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis | ↑liver function | [49] |
| Celiac Diseases, Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity, Food Allergy | ↑protection from gluten-induced pathology | [56] |
| ↑protection against peanut allergy | [60] | |
| ↑ immune reactions, ↑levels of antibodies | [61] | |
| Symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease | the therapeutic effect is not fully known | [66] |
| Ineffectiveness of probiotics in gastro-intestinal disease | ||
| Pancreatitis | Ineffective | [67] |
| Crohn’s disease | Insufficient evidence | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.; Dimitrijević, M.; Aleksić, A.; Neffe-Skocińska, K.; Zielińska, D.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D.; Salehi, B.; Milton Prabu, S.; et al. Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health. Medicina 2020, 56, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090433
Sharifi-Rad J, Rodrigues CF, Stojanović-Radić Z, Dimitrijević M, Aleksić A, Neffe-Skocińska K, Zielińska D, Kołożyn-Krajewska D, Salehi B, Milton Prabu S, et al. Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health. Medicina. 2020; 56(9):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090433
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharifi-Rad, Javad, Célia F. Rodrigues, Zorica Stojanović-Radić, Marina Dimitrijević, Ana Aleksić, Katarzyna Neffe-Skocińska, Dorota Zielińska, Danuta Kołożyn-Krajewska, Bahare Salehi, Selvaraj Milton Prabu, and et al. 2020. "Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health" Medicina 56, no. 9: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090433
APA StyleSharifi-Rad, J., Rodrigues, C. F., Stojanović-Radić, Z., Dimitrijević, M., Aleksić, A., Neffe-Skocińska, K., Zielińska, D., Kołożyn-Krajewska, D., Salehi, B., Milton Prabu, S., Schutz, F., Docea, A. O., Martins, N., & Calina, D. (2020). Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health. Medicina, 56(9), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090433













