Effects of 4-Week Inspiratory Muscle Training on Sport Performance in College 800-Meter Track Runners
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Maximal Inspiratory Pressure (MIP) Assessment
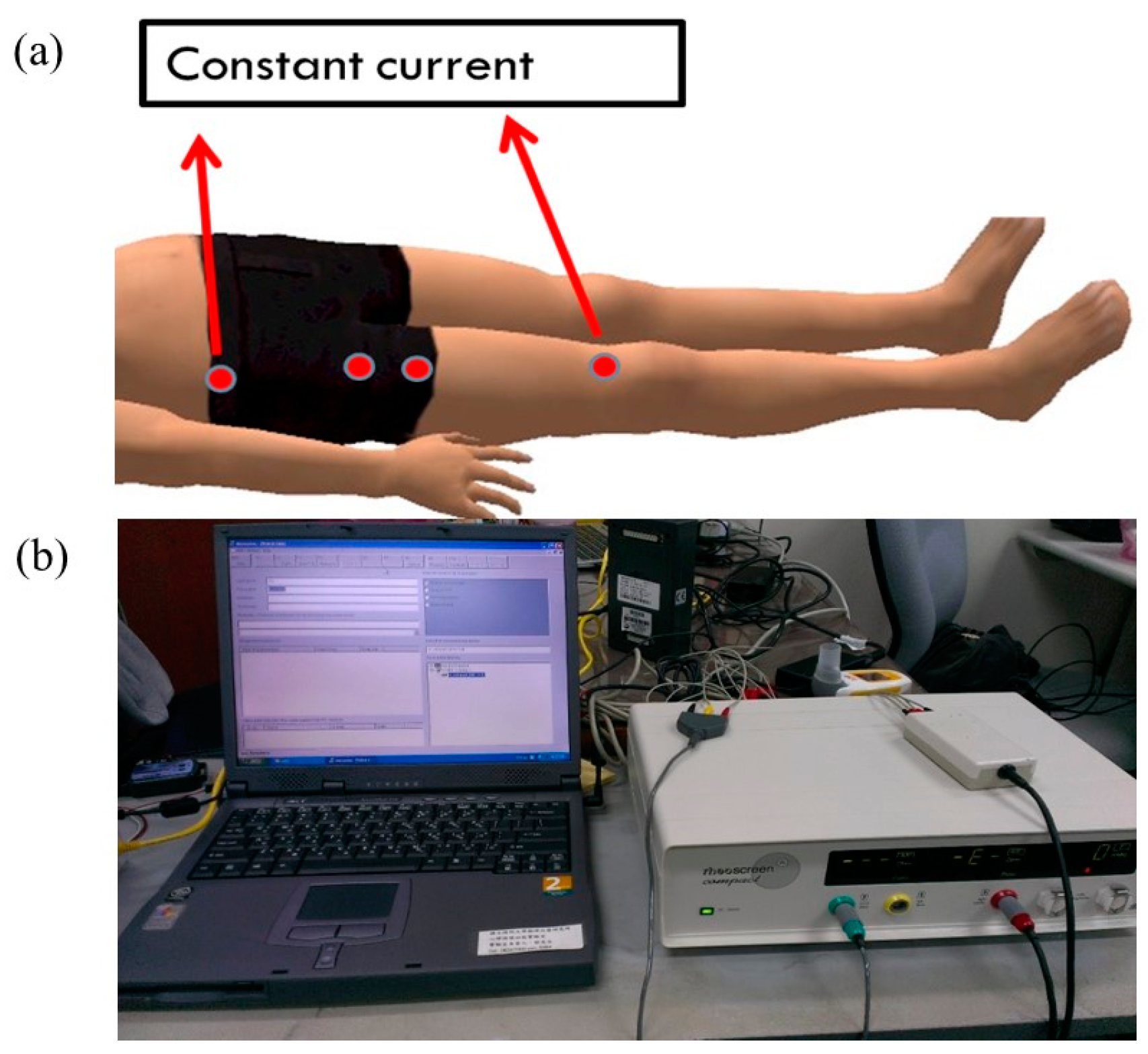
2.3.2. Limb Blood Flow Assessment
2.3.3. Athletic Performance Assessment
2.4. Interventions of Respiratory Muscle Training
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mickleborough, T.D.; Stager, J.M.; Chatham, K.; Lindley, M.R.; Ionescu, A.A. Pulmonary adaptations to swim and inspiratory muscle training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 103, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.B. Respiratory Physiology: The Essentials, 7th ed.; Lippincitt Wolliams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- St. Croix, C.M.; Morgan, B.J.; Wetter, T.J.; Dempsey, J.A. Fatiguing inspiratory muscle work causes reflex sympathetic activation in humans. J. Physiol. 2000, 529, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Romer, L.; Rodman, J.; Miller, J.; Smith, C. Consequences of exercise-induced respiratory muscle work. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2006, 151, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheel, A.W.; Derchak, P.A.; Morgan, B.J.; Pegelow, D.F.; Jacques, A.J.; Dempsey, J.A. Fatiguing inspiratory muscle work causes reflex reduction in resting leg blood flow in humans. J. Physiol. 2001, 537, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, A. Pulmonary system limitations to endurance exercise performance in humans. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 93, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Romer, L.M.; Lovering, A.T.; Haverkamp, H.C.; Pegelow, D.F.; Dempsey, J.A. Effect of inspiratory muscle work on peripheral fatigue of locomotor muscles in healthy humans. J. Physiol. 2006, 571, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, L.M.; Haverkamp, H.C.; Lovering, A.T.; Pegelow, D.F.; Dempsey, J.A. Effect of exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia on quadriceps muscle fatigue in healthy humans. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Howley, E.T. Exercise Physiology: Theory and Application To fitness and Performance, 10th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.A.; Sharpe, G.R.; Brown, P.I. Inspiratory muscle training improves cycling time-trial performance and anaerobic work capacity but not critical power. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 101, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, L.M.; McConnell, A.K.; Jones, D. Inspiratory muscle fatigue in trained cyclists: Effects of inspiratory muscle training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilding, A.E.; Brown, S.; McConnell, A.K. Inspiratory muscle training improves 100 and 200 m swimming performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volianitis, S.; McConnell, A.K.; Koutedakis, Y.; McNaughton, L.; Backx, K.; Jones, D.A. Inspiratory muscle training improves rowing performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.; Kilding, A.E. Exercise-induced inspiratory muscle fatigue during swimming: The effect of race distance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, T.M.K.; Jones, A.Y.M. Target-flow Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Running Performance in Recreational Runners: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Hong Kong Physiother. J. 2009, 27, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E. Running strategy of female middle distance runners attempting the 800 m and 1500 m “Double” at a major championship: A performance analysis and qualitative investigation. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2005, 5, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, T.; Yamanaka, R.; Hagiwara, M.; Oriishi, M.; Suzuki, Y. The 400- and 800-m Track Running Induces Inspiratory Muscle Fatigue in Trained Female Middle-Distance Runners. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickleborough, T.D.; Nichols, T.; Lindley, M.R.; Chatham, K.; Ionescu, A.A. Inspiratory flow resistive loading improves respiratory muscle function and endurance capacity in recreational runners. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, M.; Enright, P.; Stukovsky, K.; Jiang, R.; Barr, R. Performance of maximal inspiratory pressure tests and MIP reference equations for four ethnic groups. Respir. Care 2009, 54, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, Z.; Kapreli, E.; Konstantinidou, I.; Oldham, J.; Strimpakos, N. Test/retest reliability of maximum mouth pressure measurements with the MicroRPM in healthy volunteers. Respir. Care 2011, 56, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irzmańska, E.; Charłusz, M.; Irzmański, R. The use of impedance plethysmography to evaluate the impact of increasing physical activity on blood flow in the lower extremities involving footwear comfort—A preliminary report. Clin. Exp. Med. Lett. 2011, 52, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hanon, C.; Thomas, C.; Chevalier, J.-M.L.; Gajer, B.; Vandewalle, H. How does VO2 evolve during the 800 m? New Studies in Athletics. IAAF 2002, 17, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- HajGhanbari, B.; Yamabayashi, C.; Buna, T.R.; Coelho, J.D.; Freedman, K.D.; Morton, T.A.; Palmer, S.A.; Toy, M.A.; Walsh, C.; Sheel, A.W.; et al. Effects of respiratory muscle training on performance in athletes: A systematic review with meta-analyses. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1643–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.J.; Romer, L.M.; Kelly, J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; DiMenna, F.J.; Jones, A.M. Inspiratory muscle training enhances pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics and high-intensity exercise tolerance in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, C.A.; Babcock, M.A.; McClaran, S.R.; Pegelow, D.F.; Nickele, G.A.; Nelson, W.B.; Dempsey, J.A. Respiratory muscle work compromises leg blood flow during maximal exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 82, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicks, C.R.; Morgan, D.W.; Fuller, D.K.; Caputo, J.L. The influence of respiratory muscle training upon intermittent exercise performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.K.; Fu, F.H.; Chung, P.K.; Eston, R.; Lu, K.; Quach, B.; Nie, J.; So, R. The effect of inspiratory muscle training on high-intensity, intermittent running performance to exhaustion. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.K.; Fu, F.H.; Eston, R.; Chung, P.K.; Quach, B.; Lu, K. Chronic and acute inspiratory muscle loading augment the effect of a 6-week interval program on tolerance of high-intensity intermittent bouts of running. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3041–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Anthropological Information | IMT Group (N = 11) Mean ± SD | Control Group (N = 9) Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (M:F) | 8:3 | 6:3 | 0.10 |
| Age, years | 21.64 ± 2.06 | 20.78 ± 1.48 | 0.31 |
| Height, cm | 170.59 ± 6.7 | 172.33 ± 9.94 | 0.64 |
| Weight, kg | 61.46 ± 6.92 | 63.39 ± 14.33 | 0.69 |
| IMT * Group | Control Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre (N = 10) (Mean ± SD) | Post (N = 10) (Mean ± SD) | Pre (N = 10) (Mean ± SD) | Post (N = 10) (Mean ± SD) | |
| MIP (cmH2O) | 112.95 ± 27.13 † | 131.09 ± 28.20 † | 116.33 ± 40.56 | 117.00 ± 36.40 |
| Blood flow change rate (%) | 19.91 ± 11.65 | 9.63 ± 7.62 | 5.33 ± 7.45 | 13.50 ± 7.48 |
| 800-m test (sec) | 162.97 ± 24.96 | 156.75 ± 20.73 | 166.67 ± 21.83 | 167.60 ± 20.73 |
| Within-Subject (Pre-Post) | Between-Subject (Group) | Interaction (Group × Pre-Post) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p Value | Partial Eta Squared | F | p Value | Partial Eta Squared | F | p Value | Partial Eta Squared | Power | |
| MIP (cmH2O) | 10.966 | 0.004 * | 0.379 | 0.136 | 0.717 | 0.007 | 9.466 | 0.007 * | 0.345 | 0.829 |
| Blood flow change rate (%) | 0.272 | 0.609 | 0.015 | 2.443 | 0.135 | 0.119 | 20.691 | 0.000 * | 0.535 | 0.990 |
| 800-m test (s) | 3.932 | 0.063 | 0.179 | 0.541 | 0.471 | 0.029 | 7.174 | 0.015 * | 0.285 | 0.717 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Ho, C.-C.; Lee, P.-F.; Chou, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-W.; Chou, L.-W. Effects of 4-Week Inspiratory Muscle Training on Sport Performance in College 800-Meter Track Runners. Medicina 2021, 57, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010072
Chang Y-C, Chang H-Y, Ho C-C, Lee P-F, Chou Y-C, Tsai M-W, Chou L-W. Effects of 4-Week Inspiratory Muscle Training on Sport Performance in College 800-Meter Track Runners. Medicina. 2021; 57(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yun-Chi, Hsiao-Yun Chang, Chien-Chang Ho, Po-Fu Lee, Yi-Chen Chou, Mei-Wun Tsai, and Li-Wei Chou. 2021. "Effects of 4-Week Inspiratory Muscle Training on Sport Performance in College 800-Meter Track Runners" Medicina 57, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010072
APA StyleChang, Y.-C., Chang, H.-Y., Ho, C.-C., Lee, P.-F., Chou, Y.-C., Tsai, M.-W., & Chou, L.-W. (2021). Effects of 4-Week Inspiratory Muscle Training on Sport Performance in College 800-Meter Track Runners. Medicina, 57(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57010072






