Diagnosing a Patient with Erdheim-Chester Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
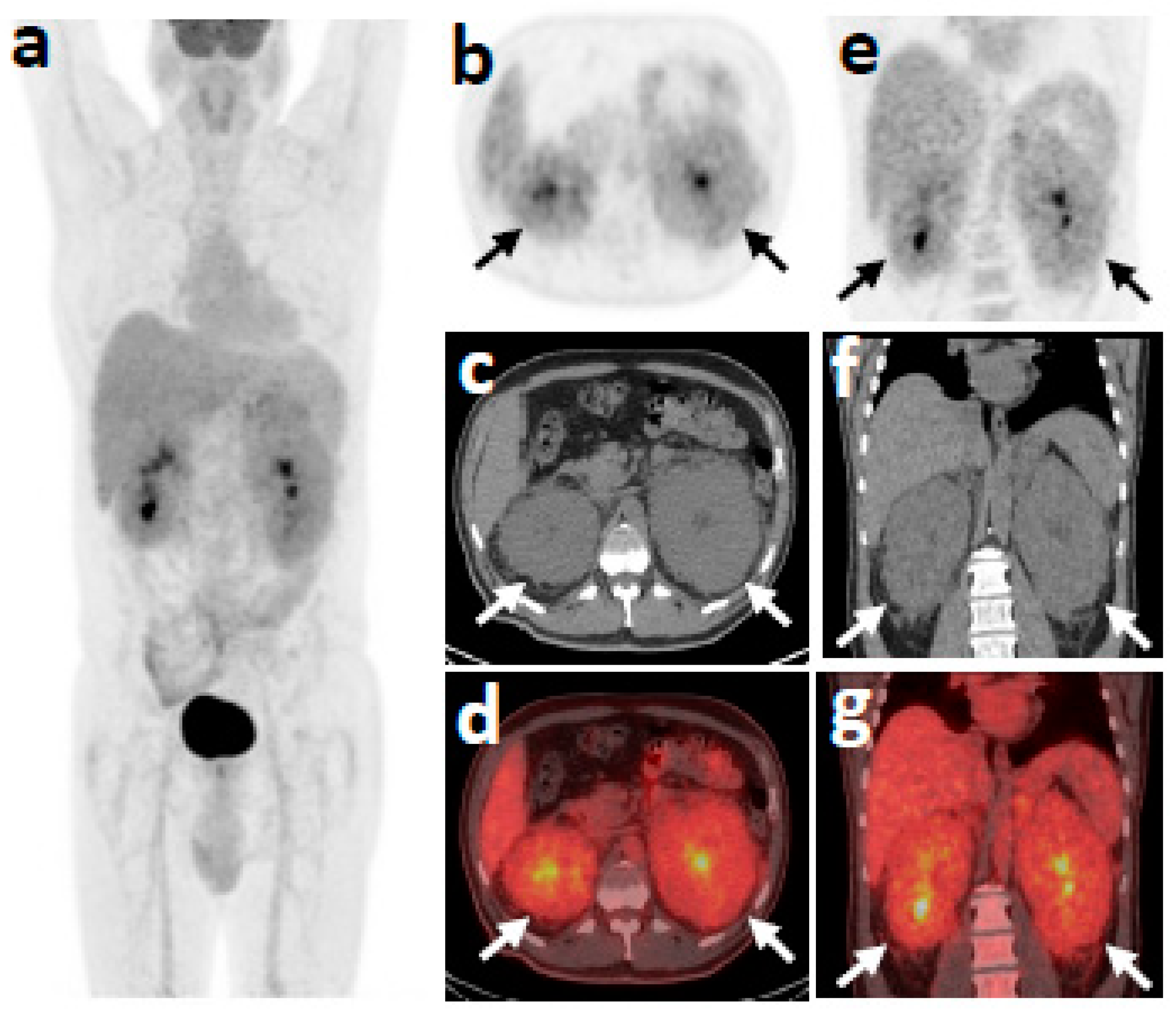
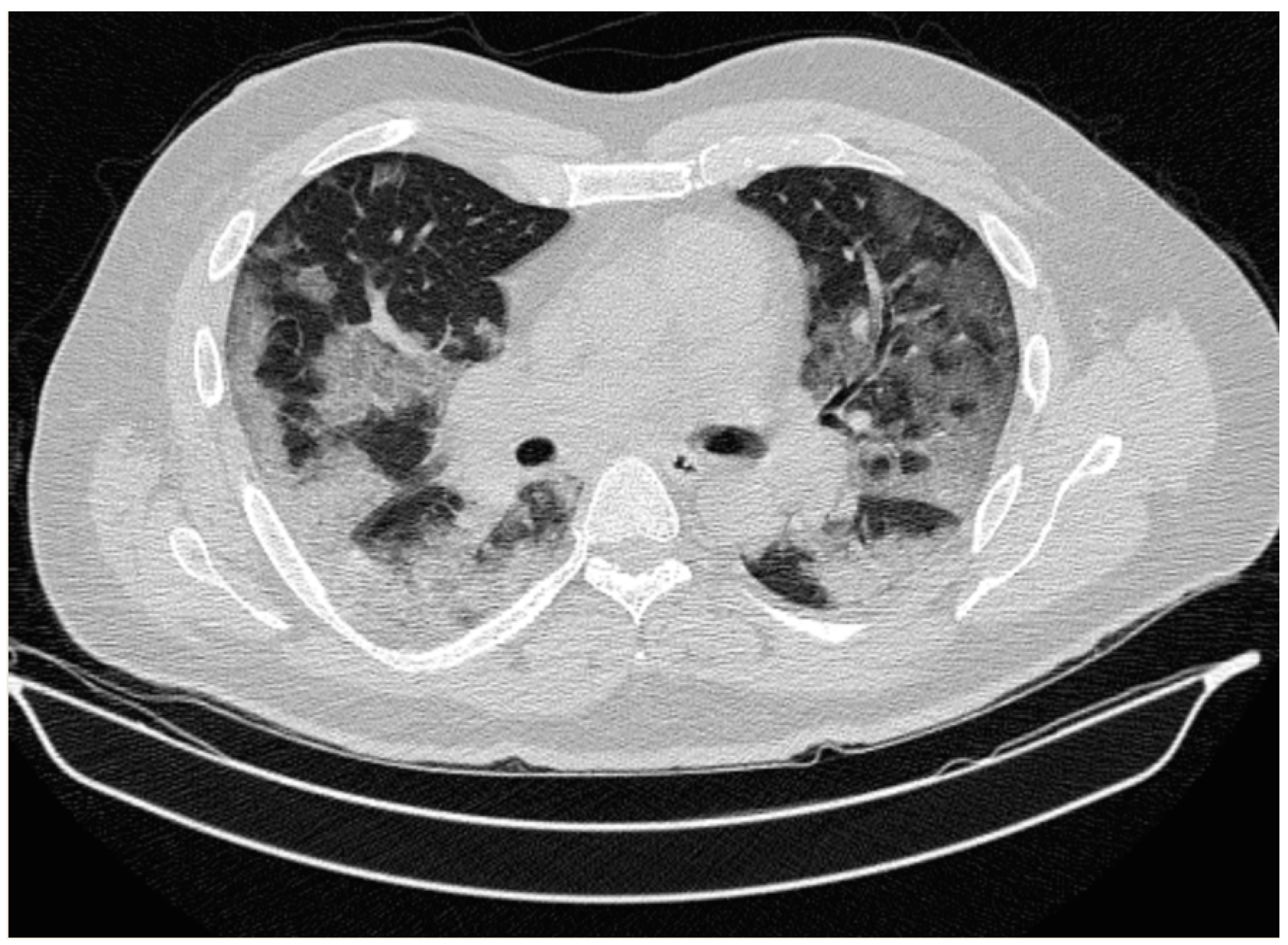
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Haroche, J.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Amoura, Z. Erdheim-Chester disease. Blood 2020, 135, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood Am. Soc. Hematol. 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emile, J.-F.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Collin, M.; Fraitag, S.; Idbaih, A.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Rollins, B.J.; Donadieu, J.; Haroche, J. Histiocytosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, L. The Untold Toll—The Pandemic’s Effects on Patients without COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2368–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.F.; Al Sium, S.M.; Anwar, S. Research and Management of Rare Diseases in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era: Challenges and Countermeasures. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 640282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, B.A.; Lortholary, O.; Cunha, C. Fever of Unknown Origin: A Clinical Approach. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 1138.e1–1138.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goyal, G.; Heaney, M.L.; Collin, M.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Vaglio, A.; Durham, B.H.; Hershkovitz-Rokah, O.; Girschikofsky, M.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Toyama, K.; et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: Consensus recommendations for evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment in the molecular era. Blood 2020, 135, 1929–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Veras, J.I.; O’Brien, K.J.; Boyd, L.C.; Dave, R.H.; Durham, B.H.; Xi, L.; Malayeri, A.A.; Chen, M.Y.; Gardner, P.J.; Enriquez, J.R.A.; et al. The clinical spectrum of Erdheim-Chester disease: An observational cohort study. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mariampillai, A.; Sivapiragasam, A.; Kumar, A.; Hindenburg, A.; Cunha, B.A.; Zhou, J. Erdheim–Chester disease: A rare cause of recurrent fever of unknown origin mimicking lymphoma. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 46, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Kim, K.H.; Suh, K.J.; Yoh, K.A.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Roh, E.Y.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, J.H. A Unique Case of Erdheim-Chester Disease with Axial Skeleton, Lymph Node, and Bone Marrow Involvement. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 48, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, G.; Young, J.R.; Koster, M.J.; Tobin, W.O.; Vassallo, R.; Ryu, J.H.; Davidge-Pitts, C.J.; Hurtado, M.D.; Ravindran, A.; Sartori Valinotti, J.C.; et al. The Mayo Clinic Histiocytosis Working Group Consensus Statement for the Diagnosis and Evaluation of Adult Patients with Histiocytic Neoplasms: Erdheim-Chester Disease, Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, and Rosai-Dorfman Disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 2054–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gianfreda, D.; Musetti, C.; Nicastro, M.; Maritati, F.; Cobelli, R.; Corradi, D.; Vaglio, A. Erdheim-Chester Disease as a Mimic of IgG4-Related Disease. Medicine 2016, 95, e3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkaya, N.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Durham, B.; Pichardo, J.D.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Hameed, M.R.; Busam, K.J.; Travis, W.D.; Diamond, E.L.; Dogan, A. The histopathology of Erdheim–Chester disease: A comprehensive review of a molecularly characterized cohort. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (Revised 4th). Int. Agency Res. Cancer 2017, 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, S.; Sinaii, N.; Irizarry-Caro, J.A.; Gahl, W.A.; Estrada-Veras, J.I.; Dave, R.; Papadakis, G.Z.; Tirosh, A.; Abel, B.S.; Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; et al. Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Patients with Erdheim-Chester Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2019169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, S.; Irizarry-Caro, J.A.; Sinaii, N.; Gahl, W.A.; Estrada-Veras, J.I.; Dave, R.H.; Gochuico, B.R.; Papadakis, G.Z.; Patronas, N.; Stratakis, C.A.; et al. Pituitary Imaging Abnormalities and Related Endocrine Disorders in Erdheim–Chester Disease. Cancers 2021, 13, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limongelli, G.; Iucolano, S.; Monda, E.; Elefante, P.; De Stasio, C.; Lubrano, I.; Caiazza, M.; Mazzella, M.; Fimiani, F.; Galdo, M.; et al. Diagnostic issues faced by a rare disease healthcare network during COVID-19 outbreak: Data from the Campania Rare Disease Registry. J. Public Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halley, M.C.; Stanley, T.; Maturi, J.; Goldenberg, A.J.; Bernstein, J.A.; Wheeler, M.T.; Tabor, H.K. “It seems like COVID-19 now is the only disease present on Earth”: Living with a rare or undiagnosed disease during the COVID-19 pandemic. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampe, C.; MetabERN Collaboration Group; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Bellettato, C.M.; Paneghetti, L.; Van Lingen, C.; Bond, S.; Brown, C.; Finglas, A.; Francisco, R.; et al. The impact of COVID-19 on rare metabolic patients and healthcare providers: Results from two MetabERN surveys. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Laboratory Parameter | Patient Value on Admission | Reference Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | 11.9 g/dL | 14.0–18.0 g/dL |
| Mean Corpuscular Volume | 79 fL | 80.0–99.0 fL |
| Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin | 28.3 pg | 27.0–32.0 pg |
| Reticulocytes | 0.9% | 0–2% |
| White Blood Cells | 6.59 Κ/μL | 3.8–10.5 K/μL |
| Neutrophils | 3.9 K/μL | 1.6–6.5 K/μL |
| Monocytes | 0.45 Κ/μL | 0.2–1.0 Κ/μL |
| Platelets | 398 K/μL | 150–450 Κ/μL |
| Ferritin | 135 ng/mL | 0–400 ng/mL |
| Urea | 34 mg/dL | 10–50 mg/dL |
| Creatinine | 1.02 mg/dL | 0.50–1.20 mg/dL |
| AST | 11 U/L | 0–38 U/L |
| ALT | 7 U/L | 0–40 U/L |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation rate | 35 mm | 0–20 mm |
| CRP | 1.55 mg/dL | 0.0–0.8 mg/dL |
| HbA1c | 6.8% | 4–6% |
| TSH | 3.01 μIU/mL | 0.27–4.20 μIU/mL |
| FT3 | 3.6 pmol/L | 3.1–6.8 pmol/L |
| FT4 | 16.4 pmol/L | 12.0–22.0 pmol/L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaiafa, G.; Pilalas, D.; Koletsa, T.; Daios, S.; Arsos, G.; Hatzidakis, A.; Protopapas, A.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Savopoulos, C. Diagnosing a Patient with Erdheim-Chester Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Medicina 2021, 57, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101001
Kaiafa G, Pilalas D, Koletsa T, Daios S, Arsos G, Hatzidakis A, Protopapas A, Stamatopoulos K, Savopoulos C. Diagnosing a Patient with Erdheim-Chester Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Medicina. 2021; 57(10):1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaiafa, Georgia, Dimitrios Pilalas, Triantafyllia Koletsa, Stylianos Daios, Georgios Arsos, Adam Hatzidakis, Adonis Protopapas, Kostas Stamatopoulos, and Christos Savopoulos. 2021. "Diagnosing a Patient with Erdheim-Chester Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic" Medicina 57, no. 10: 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101001
APA StyleKaiafa, G., Pilalas, D., Koletsa, T., Daios, S., Arsos, G., Hatzidakis, A., Protopapas, A., Stamatopoulos, K., & Savopoulos, C. (2021). Diagnosing a Patient with Erdheim-Chester Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Medicina, 57(10), 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101001







