Pustular Psoriasis and Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Epidemiology
2. Pathophysiology
3. Clinical Features
4. Histopathologic Features
5. Differential Diagnosis
6. Treatment
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, H.; Ryan, T.J. Generalized pustular psoriasis. A clinical and epidemiological study of 104 cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 1968, 80, 771–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beylot, C.; Bioulac, P.; Doutre, M.S. Pustuloses exanthématiques aiguës généralisées. A propos de 4 cas [Acute generalized exan-thematic pustuloses (four cases) (author’s transl)]. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 1980, 107, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bachelez, H. Pustular Psoriasis: The Dawn of a New Era. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoegler, K.M.; John, A.M.; Handler, M.Z.; Schwartz, R.A. Generalized pustular psoriasis: A review and update on treatment. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twelves, S.; Mostafa, A.S.; Dand, N.; Burri, E.; Farkas, K.; Wilson, R.; Cooper, H.L.; Irvine, A.; Oon, H.; Kingo, K.; et al. Clinical and genetic differences between pustular psoriasis subtypes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 143, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunasso, A.M.G.; Massone, C. Psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis: An endless debate? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, e335–e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunasso, A.M.G.; Massone, C. Recent advances in palmoplantar pustulosis. Fac. Rev. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognia, J.L.; Schaffer, J.V.; Cerroni, L. Dermatology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bachelez, H.; Choon, S.-E.; Marrakchi, S.; Burden, A.D.; Tsai, T.-F.; Morita, A.; Turki, H.; Hall, D.B.; Shear, M.; Baum, P.; et al. Inhibition of the Interleukin-36 Pathway for the Treatment of Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Aboud, D.M.A.; Crane, J.S.; Kumar, S. Pustular Psoriasis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, S.; Kubo, H.; Morishima, H.; Goto, R.; Zheng, R.; Nakagawa, H. Guselkumab, a human interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis: Efficacy and safety analyses of a 52-week, phase 3, multicenter, open-label study. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, B.; Richards, L.; Menter, A. Treatment of two patients with generalized pustular psoriasis with the interleukin-1β inhibitor gevokizumab. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-M.; Jin, H.-Z. Biologics in the treatment of pustular psoriasis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Kromer, C.; Gerdes, S.; Linker, C.; Magnolo, N.; Sabat, R.; Reich, K.; Mössner, R. A multi-center open-label study of apremilast in palmoplantar pustulosis (APLANTUS). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, A.V.; Damiani, G.; Genovese, G.; Gattorno, M. A dermatologic perspective on autoinflammatory diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 110, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Znajewska-Pander, A.; Owczarek, W.; Maciejewska-Radomska, A.; Placek, W. Clinicopathologic ret-rospective analysis of annular pustular psoriasis. Acta Derm. Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018, 27, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Sidoroff, A.; Dunant, A.; Viboud, C.; Halevy, S.; Bavinck, J.N.B.; Naldi, L.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Fagot, J.-P.; Roujeau, J.-C. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoroff, A.; Halevy, S.; Bavinck, J.N.B.; Vaillant, L.; Roujeau, J.-C. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—A clinical reaction pattern. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2001, 28, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, A.; Das, S.; Sarda, A.; Pal, D.; Biswas, P. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis: An update. Indian J. Dermatol. 2018, 63, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatkowski, J.; Schwartz, R.A. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokura, Y.; Mori, T.; Hino, R. Psoriasis and other Th17-mediated skin diseases. J. UOEH 2010, 32, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halevy, S.; Kardaun, S.H.; Davidovici, B.; Wechsler, J.; EuroSCAR and RegiSCAR Study Group. The spectrum of histopathological features in acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A study of 102 cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Kiyokawa, C.; Mori, O.; Miyasato, M.; Chidgey, M.A.; Garrod, D.R.; Kobayashi, Y.; Komori, K.; Ishii, K.; Amagai, M.; et al. Human Desmocollin 1 (Dsc1) Is an Autoantigen for the Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Type of IgA Pemphigus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 109, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsi, A.C.; Rosman, I.S. Histopathology of Cutaneous Inflammatory Disorders in Children. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2018, 21, 115–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-T.; Chu, C.-Y. Treatments for Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goh, T.K.; Pang, S.M.; Thirumoorthy, T.; Goh, S.G.N. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis and toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by carbamazepine. Singap. Med. J. 2008, 49, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Berki, D.M.; Choon, S.-E.; Burden, A.D.; Allen, M.H.; Arostegui, J.I.; Chaves, A.; Duckworth, M.; Irvine, A.D.; Mockenhaupt, M.; et al. IL36RN mutations define a severe autoinflammatory phenotype of generalized pustu-lar psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 135, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choon, S.E.; Lai, N.M.; Mohammad, N.A.; Nanu, N.M.; Tey, K.E.; Chew, S.F. Clinical profile, morbidity, and outcome of adult-onset generalized pustular psoriasis: Analysis of 102 cases seen in a tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia. Int. J. Dermatol. 2013, 53, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Terui, T. Palmoplantar pustulosis: Current understanding of disease definition and pathomechanism. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 98, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotz, C.; Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Haddad, C.; Bouvresse, S.; Ortonne, N.; Duong, T.; Ingen-Housz-Oro, S.; Roujeau, J.; Wolkenstein, P.; Chosidow, O. Systemic involvement of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A retrospective study on 58 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, D.E. Lever’s Histopathology of the Skin; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Isom, J.; Braswell, D.S.; Siroy, A.; Auerbach, J.; Motaparthi, K. Clinical and histopathologic features differentiating acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and pustular psoriasis: A retrospective series. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, P.J.; Khachemoune, A. Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis: A Review of 30 Years of Progress. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruta, D.; Ishii, N.; Hamada, T.; Ohyama, B.; Fukuda, S.; Koga, H.; Imamura, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Karashima, T.; Nakama, T.; et al. IgA pemphigus. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 29, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguier, M.; Aubin, F.; Delaporte, E.; Pagès, C.; Paul, C.; Beylot-Barry, M.; Goujon, C.; Rybojad, M.; Bachelez, H.; Groupe de Recherche sur le Psoriasis de la Société Française de Dermatologie. Efficacy and Safety of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors in Acute Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zangrilli, A.; Papoutsaki, M.; Talamonti, M.; Chimenti, S. Long-term efficacy of adalimumab in generalized pustular psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2008, 19, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, U.; Kinoshita, A.; Sekigawa, I.; Takamori, K.; Suga, Y. Successful treatment with adalimumab in a patient with psoriatic arthritis and generalized pustular psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2012, 39, 1071–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghate, J.V.; Alspaugh, C.D. Adalimumab in the management of palmoplantar psoriasis. Derm. Online J. 2009, 15, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Daudén, E.; Santiago-Et-Sánchez-Mateos, D.; Sotomayor-López, E.; García-Díez, A. Ustekinumab: Effective in a patient with severe recalcitrant generalized pustular psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 1346–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imafuku, S.; Honma, M.; Okubo, Y.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M.; Morita, A.; Seko, N.; Kawashima, N.; Ito, S.; Shima, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis: A 52-week analysis from phase III open-label multicenter Japanese study. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Nakajo, K.; Ishii, T.; Morisaki, Y.; Aoki, T.; Cameron, G.S.; Osuntokun, O.O.; Akasaka, T.; Asano, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab treatment for Japanese patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and generalized pustular psoriasis: Results from a 52-week, open-label, phase 3 study (UNCOVER-J). J. Dermatol. 2016, 44, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamasaki, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Kubo, Y.; Ootaki, K.; Japanese Brodalumab Study Group. Efficacy and safety of brodalumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis and psoriatic erythroderma: Results from a 52-week, open-label study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 176, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmidt, E.; Wetter, D.A.; Ferguson, S.B.; Pittelkow, M.R. Psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis associated with tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors: The Mayo Clinic experience, 1998 to 2010. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, e179–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, S.; Bishnoi, A.; Narang, T.; Handa, S. Secukinumab-induced paradoxical pustular psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 44, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenk, K.S.; Claros, J.M.; Ehrlich, A. Flare of pustular psoriasis after initiating ustekinumab therapy. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2011, 23, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marovt, M.; Marko, P.B. Apremilast monotherapy for palmoplantar pustulosis: Report of three cases. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Syring, F.; Ludwig, R.J.; Thaçi, D. Successful Treatment of Refractory Palmoplantar Pustular Psoriasis With Apremilast: A Case Series. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 543944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, C.; Nakamura, M.; Sekhon, S.; Yan, D.; Wu, J.J.; Liao, W.; Bhutani, T. Generalized pustular psoriasis treated with apremilast in a patient with multiple medical comorbidities. JAAD Case Rep. 2017, 3, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halevy, S. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 9, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.E.; Jones, J.M. Recognition and Management of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions (Including Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis). Med. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 105, 577–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingen-Housz-Oro, S.; Hotz, C.; Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Sbidian, E.; Hemery, F.; Chosidow, O.; Wolkenstein, P. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A retrospective audit of practice between 1994 and 2011 at a single centre. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 172, 1455–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


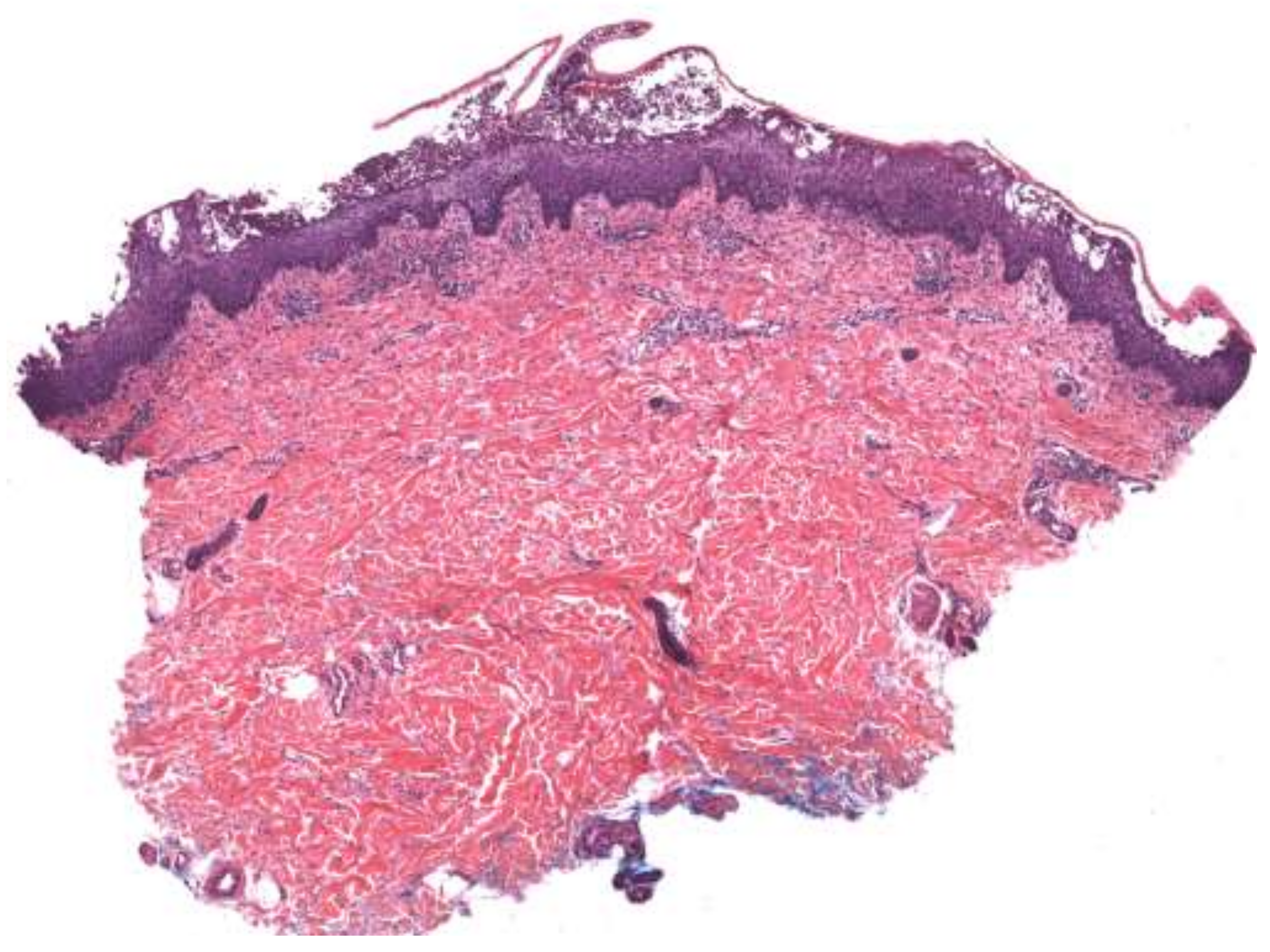
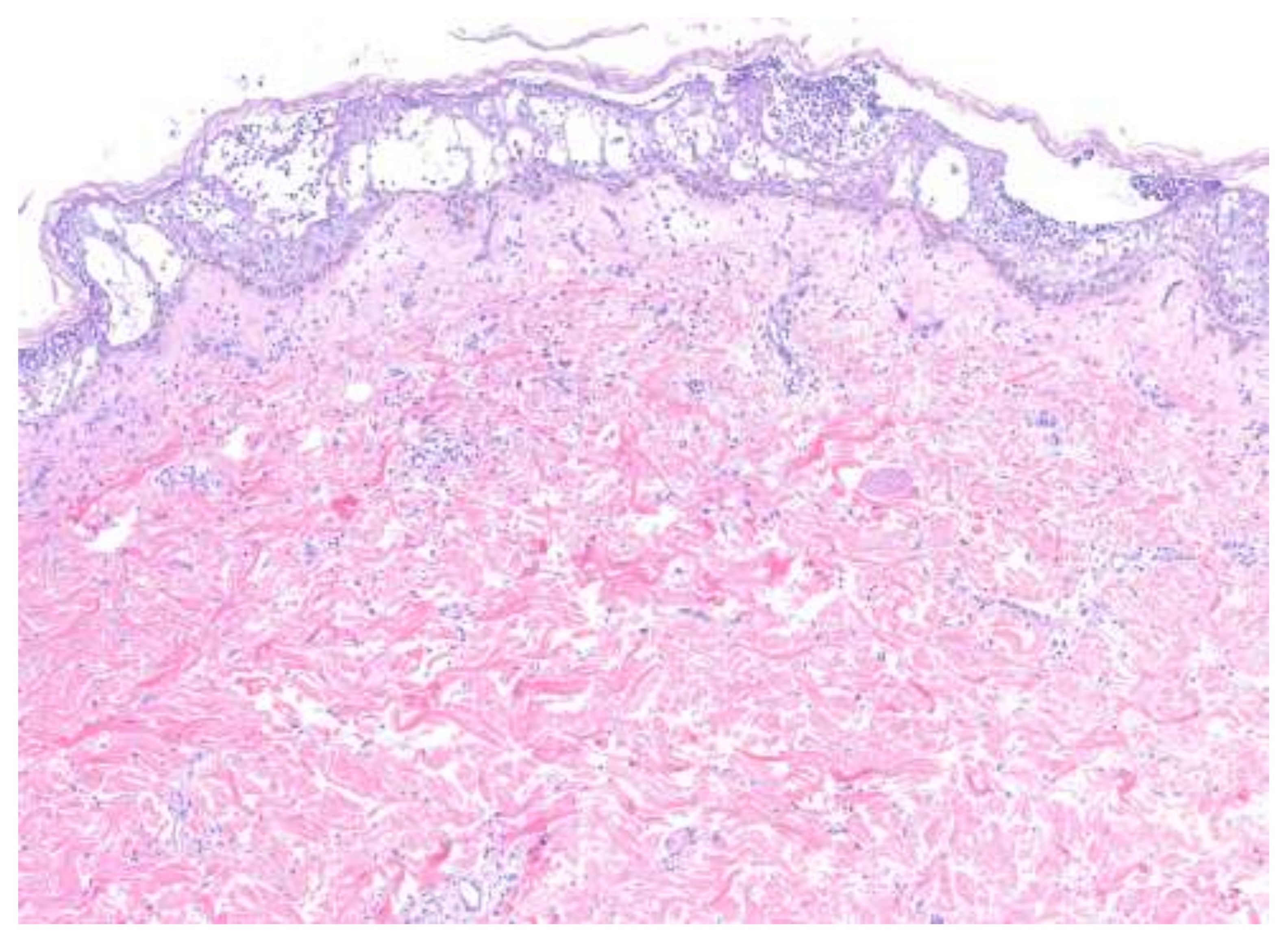
| Disease | Clinical Morphology | Demographic | Pathology | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) | All PP subtypes contain sterile pustules [3]. Disseminated, painful erythematous lesions covered with aseptic pustules [3,8]. Severe systemic symptoms, including fever, malaise, fatigue, and arthritis, may be present [3,4]. | Fifth decade of life with slight female predominance [4]. | Pathogenesis: Disruption of the interleukin-36 pathway plays a major role (mutations in IL36RN), although there is significant heterogeneity in the gene pathways implicated [3,9,10]. The innate immune system, environmental factors, and genetic susceptibility all contribute [7]. Histopathology: Spongiform pustules of Kogoj in the epidermis and microabscesses of Munro [3,4]. Parakeratosis and psoriasiform hyperplasia [8]. | Topical corticosteroids, oral retinoids (i.e., acitretin), cyclosporine, methotrexate, TNF-α inhibitors (i.e., adalimumab), anti-IL-17 monoclonal antibody (i.e., secukinumab), anti-IL-23 monoclonal antibody (i.e., guselkumab), anti-IL-1β monoclonal antibodies (i.e., gevokizumab and canakinumab), IL-1R inhibitor (i.e., anakinra), PDE-4 inhibitor (i.e., apremilast) [3,4,7,9,11,12,13,14]. |
| Impetigo herpetiformis | All PP subtypes contain sterile pustules [3]. See GPP. | GPP during third trimester of pregnancy [3]. | Pathogenesis: see GPP. Histopathology: see GPP. | Cyclosporine, systemic corticosteroids [3,4] |
| Palmoplantar pustular psoriasis (PPPP) | All PP subtypes contain sterile pustules [3]. Pustules intermixed with yellow-brown macules on palms and soles [7,8,15]. | Slight female predominance [4,5] | Pathogenesis: Mutations in IL36RN make up a significantly smaller proportion of cases compared to GPP [4,5]. Mutations in AP1S3 and CARD14, as well as abnormalities of eccrine sweat glands, have been implicated in PPPP [7]. Histopathology: see GPP; on acral skin. | See GPP. |
| Acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau | All PP subtypes contain sterile pustules [3]. Pustular lesions overlying erythematous, scaling skin on the tips of the fingers and toes [3,4,8]. | Slight female predominance [4,5]. | Pathogenesis: see GPP. Histopathology: see GPP, on acral skin. | Topical corticosteroids, calcipotriene [3,4] |
| Annular pustular psoriasis | All PP subtypes contain sterile pustules [3]. Pustules located circumferentially on erythematous skin lesions. Lesions present on limbs, buttocks, abdomen. Can present with fever and malaise [16]. | More common in children [16]. | Pathogenesis: see GPP. Histopathology: see GPP. | See GPP. |
| Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis | Sterile, pin-sized pustules overlying edematous and erythematous skin. Often appears on the face or intertriginous areas before spreading to the trunk and limbs [17]. Acutely accompanied by fever, neutrophilia, and eosinophilia [18]. | More common in adults with a slight female predominance [17]. | Pathogenesis: Drug-specific T-cell predominantly infiltrates with neutrophil accumulation mediated by IL-8 and GM-CSF [19,20,21]. Th17 cells are also involved in neutrophil activation [21]. Mutations in IL36RN found in some patients [20]. Histopathology: Spongiform subcorneal or intraepidermal pustules ± necrotic keratinocytes, vacuolar interface dermatitis, dermal eosinophilia, psoriasiform hyperplasia [17,22]. | Typically resolves within 2 weeks of discontinuation of the offending drug [20,23]. Topical steroids are often used for symptomatic relief [20]. Systemic corticosteroids or cyclosporine are useful in severe cases or with extracutaneous involvement [24,25]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sussman, M.; Napodano, A.; Huang, S.; Are, A.; Hsu, S.; Motaparthi, K. Pustular Psoriasis and Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis. Medicina 2021, 57, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101004
Sussman M, Napodano A, Huang S, Are A, Hsu S, Motaparthi K. Pustular Psoriasis and Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis. Medicina. 2021; 57(10):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101004
Chicago/Turabian StyleSussman, Morgan, Anthony Napodano, Simo Huang, Abhirup Are, Sylvia Hsu, and Kiran Motaparthi. 2021. "Pustular Psoriasis and Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis" Medicina 57, no. 10: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101004
APA StyleSussman, M., Napodano, A., Huang, S., Are, A., Hsu, S., & Motaparthi, K. (2021). Pustular Psoriasis and Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis. Medicina, 57(10), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101004






