Did the COVID-19 Pandemic Prolong the Time Till Diagnosis and Worsen Outcomes for Children with Acute Appendicitis?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
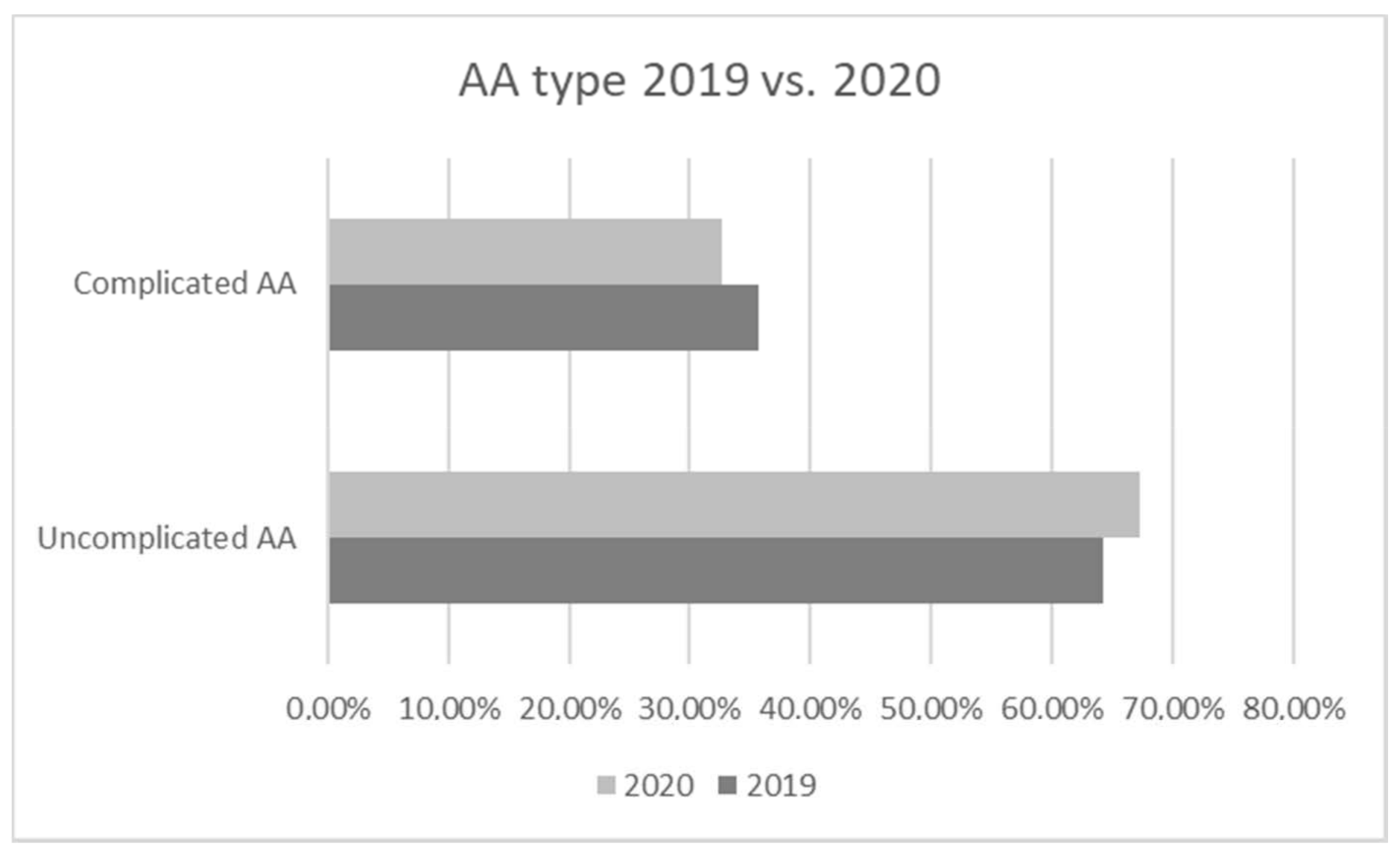
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sartelli, M.; Baiocchi, G.L.; Di Saverio, S.; Ferrara, F.; Labricciosa, F.M.; Ansaloni, L.; Coccolini, F.; Vijayan, D.; Abbas, A.; Abongwa, H.K.; et al. Prospective Observational Study on acute Appendicitis Worldwide (POSAW). World J. Emerg. Surg. 2018, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arlt, A.; Bharti, R.; Ilves, I.; Häsler, R.; Miettinen, P.; Paajanen, H.; Brunke, G.; Ellrichmann, M.; Rehman, A.; Hauser, C.; et al. Characteristic changes in microbial community composition and expression of innate immune genes in acute appendicitis. Innate Immun. 2013, 21, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.S.W.; Hampartzoumian, T.; Lloyd, A.R.; Grimm, M.C. A murine model of appendicitis and the impact of inflammation on appendiceal lymphocyte constituents. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 150, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börekci, H.; Serin, H.I.; Baş, H.; Börekci, E. Relationship between appendicitis and diameter of ileocecal lipomatosis and also ileocecal angle. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2019, 42, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, E.; Avci, V.; Azatçam, M. Parasitic infestation in appendicitis. A retrospective analysis of 660 patients and brief literature review. Saudi Med. J. 2017, 38, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Chavez, F.A.; Peters-Hybki, D.L.; Barber, R.C.; Lindberg, G.M.; Jialal, I.; Munford, R.S.; O’Keefe, G.E. Innate Immunity Genes Influence the Severity of Acute Appendicitis. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L.S.; Toma, I.; Davison, D.; Vaziri, K.; Lee, J.; Lucas, R.; Seneff, M.G.; Nyhan, A.; McCaffrey, T.A. Acute appendicitis: Transcript profiling of blood identifies promising biomarkers and potential underlying processes. BMC Med. Genom. 2016, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubér, M.; Berg, A.; Ekerfelt, C.; Olaison, G.; Andersson, R.E. Different cytokine profiles in patients with a history of gangrenous or phlegmonous appendicitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 143, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubér M Immunopathogenic Aspect of Resolving and Progressing Appendicitis. Ph.D. Thesis, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 2012.
- Cai, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Rong, Z.; Li, W. Clinical Characteristics of 5 COVID-19 Cases with Non-respiratory Symptoms as the First Manifestation in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwanwongse, K.; Shabarek, N. Pseudo-Appendicitis in an Adolescent with COVID-19. Cureus 2020, 12, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.J.; Chavarria, H.D.; Hacking, S.M. A Case of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Mimicking Acute Appendicitis in a COVID-19 Pandemic Area. Cureus 2020, 12, e10722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessheimer, A.J.; Morales, X.; Ginestá, C.; Turrado, V.; Borin, A.; Ausania, F.; Bravo, R.; Fondevila, C.; Lacy, A.M. Where have all the appendicitis gone? patterns of urgent surgical admissions during the COVID19 pandemic. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, e545–e546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapiri, O.; Danziger, C.R.; Krause, I.; Kravarusic, D.; Yulevich, A.; Balla, U.; Bilavsky, E. Delayed diagnosis of paediatric appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, F.; Acar, L.; Berg, A.V.D.; Flemming, S.; Kastner, C.; Müller, S.; Diers, J.; Germer, C.-T.; Lock, J.F.; L’Hoest, H.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on appendicitis treatment in Germany—A population-based analysis. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, R.; Lee, J.; Howell, J. Rate of Pediatric Appendiceal Perforation at a Children’s Hospital during the COVID-19 Pandemic Compared with the Previous Year. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2027948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somers, K.; Elwahab, S.A.; Raza, M.Z.; O’Grady, S.; DeMarchi, J.; Butt, A.; Burke, J.; Robb, W.; Power, C.; McCawley, N.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on management and outcomes in acute appendicitis: Should these new practices be the norm? Surgeon 2021, 19, e310–e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvizdic, Z.; Vranic, S. Decreased number of acute appendicitis cases in pediatric population during the COVID-19 pandemic: Any link? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 56, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, M.Y.; Bauerle, W.; Eriksson, E.; Azar, F.K.; Evans, H.L.; Johnson, M.; Lawless, R.A.; Lottenberg, L.; Sanchez, S.E.; Simianu, V.V.; et al. Where did the patients go? Changes in acute appendicitis presentation and severity of illness during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: A retrospective cohort study. Surgery 2021, 169, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankel, J.; Keinan, A.; Blich, O.; Koussa, M.; Helou, B.; Shay, S.; Zugayar, D.; Pikarsky, A.; Mazeh, H.; Spira, R.; et al. The Decreasing Incidence of Acute Appendicitis during COVID-19: A Retrospective Multi-centre Study. World J. Surg. 2020, 44, 2458–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, A.G.; CAMIN Study Group; Oldhafer, K.J.; Conze, S.; Thasler, W.E.; von Schassen, C.; Hauer, T.; Huber, T.; Germer, C.-T.; Günster, S.; et al. Appendicitis during the COVID-19 lockdown: Results of a multicenter analysis in Germany. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basamh, M.; Rajendiran, A.; Chung, W.Y.; Runau, F.; Sangal, S. Management of appendicitis during the COVID pandemic: Lessons from the first month of the outbreak. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, e450–e451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cen, L.-S. Managing acute appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic in Jiaxing, China. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Pergola, E.; Sgrò, A.; Rebosio, F.; Vavassori, D.; Fava, G.; Codrich, D.; Montanaro, B.; Leva, E.; Schleef, J.; Cheli, M.; et al. Appendicitis in Children in a Large Italian COVID-19 Pandemic Area. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 600320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, T. Auswirkung der COVID-19-Pandemie auf die Appendizitis bei COVID-19-negativen Kindern. Mon. Kinderheilkd. 2021, 169, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Khan, M.A.; Rehman, I.U.; Uzair, M. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on presentation, treatment and outcome of paediatric surgical emergencies. J. Ayub. Med. Coll. Abbottabad. 2021, 32 (Suppl. S1), S621–S624. [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Archer, P.; Blackall, S.; Campbell, H.; Boyd, D.; Patel, B.; McBride, C. Increased incidence of complicated appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Paediatr. Child Heal. 2020, 56, 1313–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Li, M.; Zhou, H.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Deng, W. Complicated appendicitis are common during the epidemic period of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Asian J. Surg. 2020, 43, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.W.; Prieto, J.; Ikeda, D.S.; Lewis, P.R.; Benzer, E.M.; Van Gent, J.-M. Perforated Appendicitis: An Unintended Consequence During the Coronavirus-19 Pandemic. Mil. Med. 2021, 186, e94–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeramo, C.A.; Dreifuss, N.H.; Schlottmann, F.; Rotholtz, N.A. More Severe Presentations of Acute Appendicitis During COVID-19. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 25, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Valencia, S.; Guerrero, A. Acute Appendicitis During Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Changes in Clinical Presentation and CT Findings. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 17, 1011–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turanli, S.; Kiziltan, G. Did the COVID-19 Pandemic Cause a Delay in the Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis? World J. Surg. 2021, 45, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, S.; Chhetri, R.K.; Thapa, N. Comparison of acute appendicitis before and within lockdown period in COVID-19 era: A retrospective study from rural Nepal. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaele, A.; Cervone, A.; Ruffoli, M.; Cereda, E.; Avolio, L.; Parigi, G.B.; Riccipetitoni, G. Critical factors conditioning the management of appendicitis in children during COVID-19 Pandemic: Experience from the outbreak area of Lombardy, Italy. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, e529–e530. [Google Scholar]
- Gerall, C.D.; DeFazio, J.R.; Kahan, A.M.; Fan, W.; Fallon, E.M.; Middlesworth, W.; Stylianos, S.; Zitsman, J.L.; Kadenhe-Chiweshe, A.V.; Spigland, N.A.; et al. Delayed presentation and sub-optimal outcomes of pediatric patients with acute appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 56, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheath, C.; Abdelrahman, M.; MacCormick, A.; Chan, D. Paediatric appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 57, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.V.; Groome, P.A.; Merchant, S.J.; Lajkosz, K.; Nanji, S.; Brogly, S.B. Timing of surgery and the risk of complications in patients with acute appendicitis: A population-level case-crossover study. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018, 85, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, W.; Bedwani, N.H.; Smith, C.; Shatkar, V. Investigation and management of suspected appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, e337–e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, R.; Lucocq, J.; Ekpete, N.O.; Ain, N.U.; Lim, S.K.; Alwash, A.; Bibi, S.; Alijani, A. Management of appendicitis during COVID-19 pandemic; short-term outcomes. Scott. Med. J. 2020, 65, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keohane, C.A.; Rogers, S.; Gardner, R.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Salzberg, C.A.; Yu, T.; Yoon, C.S.; Williams, D.H.; Wien, M.F.; Landrigan, C.P.; et al. After Performing Nighttime Procedures. Jama 2009, 302, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury, P.; Warnock, G.; Whalen, T. Risks of complications by attending physicians after performing nighttime procedures. Can. J. Surg. 2012, 55, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirian, I. The impact of sleep deprivation on surgeons’ performance during night shifts. Dan. Med. J. 2014, 61, B4912. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Zhao, X.-F.; Li, M.-M.; Cui, H.-L. A clinical prediction model for complicated appendicitis in children younger than five years of age. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardeni, D.; Hirschl, R.B.; Drongowski, R.A.; Teitelbaum, D.H.; Geiger, J.D.; Coran, A.G. Delayed versus immediate surgery in acute appendicitis: Do we need to operate during the night? J. Pediatr. Surg. 2004, 39, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, S.T.; van Dijk, A.H.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Boermeester, M.A. Meta-analysis of in-hospital delay before surgery as a risk factor for complications in patients with acute appendicitis. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.M.; Kwak, B.S.; Park, Y.J. Is a One Night Delay of Surgery Safe in Patients with Acute Appendicitis? Ann. Coloproctology 2018, 34, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canal, C.; Lempert, M.; Birrer, D.L.; Neuhaus, V.; Turina, M. Short-term outcome after appendectomy is related to preoperative delay but not to the time of day of the procedure: A nationwide retrospective cohort study of 9224 patients. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, C.-M.; Latz, H.; Kraemer, J.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Graeber, S.; Glanemann, M.; Simon, A. Acute appendicitis in children: Can surgery be postponed? Short-term results in a cohort of 225 children. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohba, G.; Komori, K.; Hirobe, S. The necessity of nighttime appendectomies: Is appendicitis an emergency? Afr. J. Paediatr. Surg. 2020, 17, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Duration | 2019/Non-Pandemic | 2020/Pandemic | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of symptoms from start to ER 1 | 24 [4;120] | 24 [3;120] | p = 0.658 |
| Time from ER to Department 1 | 0.98 [0.35;3] | 2.85 [0.5;16.95] | p < 0.001 * |
| Time from Department to OR 1 | 2.66 [0.17;20.07] | 5.31 [0.1;17.4] | p = 0.03 * |
| Time from the beginning of symptoms to OR 1 | 27.77 [6.58;122.83] | 33.54 [12.87;144.17] | p = 0.095 |
| Duration of operation 1 | 1.1 [0,5;3] | 1 [0.5;3.75] | p = 0.749 |
| Length of stay at the hospital 2 | 6 [1;20] | 6 [2;14] | p = 0.074 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vansevičienė, I.; Bučinskaitė, D.; Malcius, D.; Lukošiūtė-Urbonienė, A.; Beržanskis, M.; Čekanauskas, E.; Barauskas, V. Did the COVID-19 Pandemic Prolong the Time Till Diagnosis and Worsen Outcomes for Children with Acute Appendicitis? Medicina 2021, 57, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111234
Vansevičienė I, Bučinskaitė D, Malcius D, Lukošiūtė-Urbonienė A, Beržanskis M, Čekanauskas E, Barauskas V. Did the COVID-19 Pandemic Prolong the Time Till Diagnosis and Worsen Outcomes for Children with Acute Appendicitis? Medicina. 2021; 57(11):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111234
Chicago/Turabian StyleVansevičienė, Idilė, Danielė Bučinskaitė, Dalius Malcius, Aušra Lukošiūtė-Urbonienė, Mindaugas Beržanskis, Emilis Čekanauskas, and Vidmantas Barauskas. 2021. "Did the COVID-19 Pandemic Prolong the Time Till Diagnosis and Worsen Outcomes for Children with Acute Appendicitis?" Medicina 57, no. 11: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111234
APA StyleVansevičienė, I., Bučinskaitė, D., Malcius, D., Lukošiūtė-Urbonienė, A., Beržanskis, M., Čekanauskas, E., & Barauskas, V. (2021). Did the COVID-19 Pandemic Prolong the Time Till Diagnosis and Worsen Outcomes for Children with Acute Appendicitis? Medicina, 57(11), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111234






