A Promising Role of TGF-β Pathway in Response to Regorafenib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
2.2. Sample Processing
2.2.1. DNA and RNA Extraction
2.2.2. Ion Torrent PGM Sequencing
2.2.3. MSI Analysis
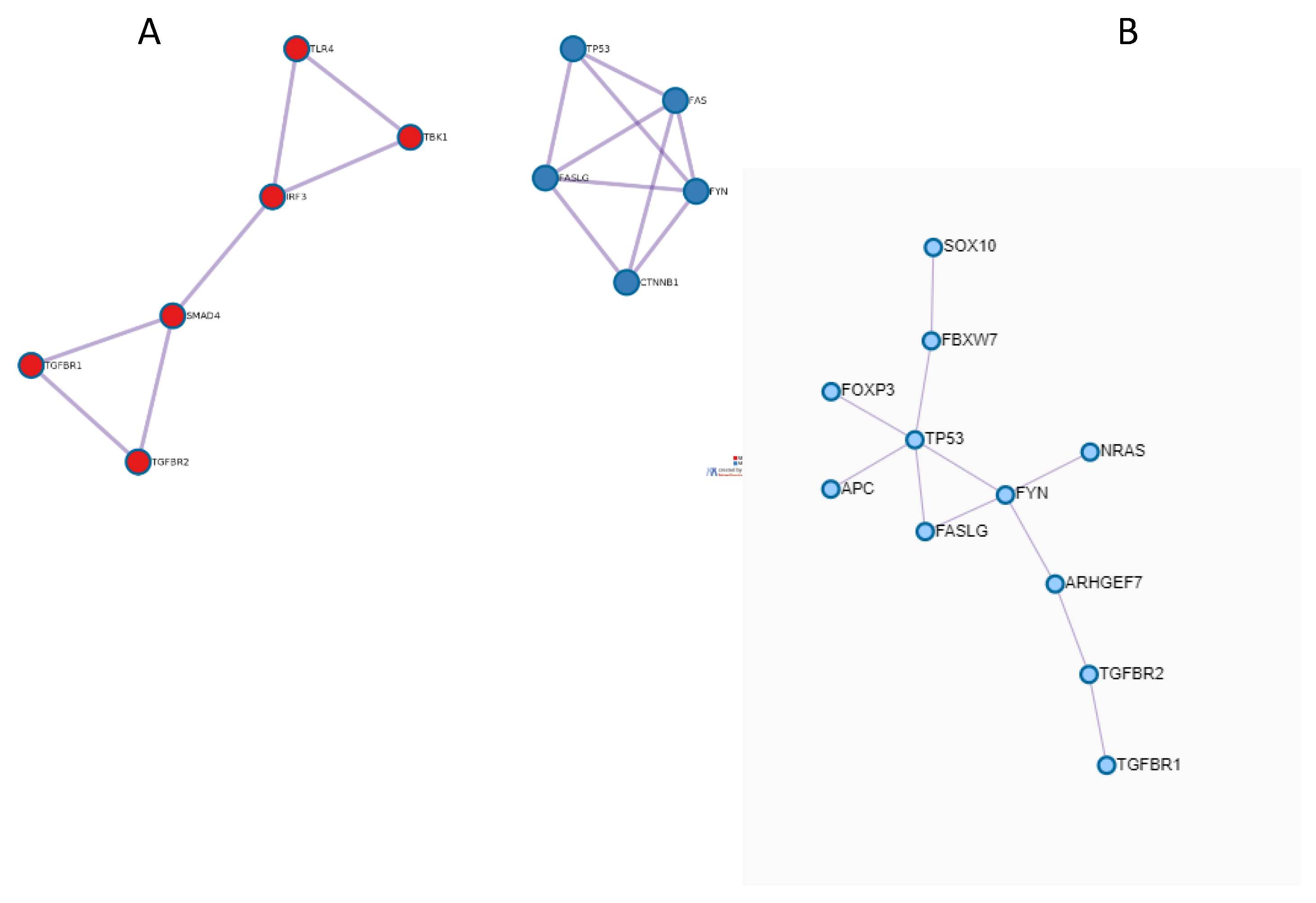
2.3. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mutational Pattern
3.2. Functional Enrichment and PPI Network
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rumpold, H.; Niedersüß-Beke, D.; Heiler, C.; Falch, D.; Wundsam, H.V.; Metz-Gercek, S.; Piringer, G.; Thaler, J. Prediction of mortality in metastatic colorectal cancer in a real-life population: A multicenter explorative analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshani, A.; Hashemzadeh, S.; Asadzadeh, Z.; Shadbad, M.A.; Rasibonab, F.; Safarpour, H.; Jafarlou, V.; Solimando, A.G.; Racanelli, V.; Singh, P.K.; et al. Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen-4 in Colorectal Cancer: Another Therapeutic Side of Capecitabine. Cancers 2021, 13, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, Z.; Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Kazemi, T.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shanehbandi, D.; Hemmat, N.; Derakhshani, A.; Brunetti, O.; Safaei, S.; et al. The combination effect of Prominin1 (CD133) suppression and Oxaliplatin treatment in colorectal cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-X.; Fang, J.-Y. Comprehensive review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Dumas, J.; Adnane, L.; Lynch, M.; Carter, C.A.; Schütz, G.; Thierauch, K.H.; Zopf, D. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): A new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, J.M.; Öhler, L.; Scheithauer, W.; Metges, J.-P.; Dourthe, L.-M.; de Groot, J.W.; Thaler, J.; Yeh, K.-H.; Lin, J.-K.; Falcone, A. Real-world dosing of regorafenib in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): Interim analysis from the prospective, observational CORRELATE study. Liver 2017, 260, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tougeron, D.; Desseigne, F.; Etienne, P.; Dourthe, L.; Mineur, L.; Paule, B.; Hollebecque, A.; Tresch, E.; Spaeth, D.; Michel, P. REBECCA: A large cohort study of regorafenib (REG) in the real-life setting in patients (pts) previously treated for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iv205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothey, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Sobrero, A.; Siena, S.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouché, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, S.; Xu, R.; Yau, T.C.; Ma, B.; Pan, H.; Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; Chi, Y.; Wang, L. Regorafenib plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in Asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CONCUR): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestris, N.; Tommasi, S.; Santini, D.; Russo, A.; Simone, G.; Petriella, D.; Maiello, E.; Tonini, G.; Colucci, G. KRAS mutations and sensitivity to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in metastatic colorectal carcinoma: An open issue. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, P.S.; Wallin, J.J.; Mancao, C. Predictive markers of anti-VEGF and emerging role of angiogenesis inhibitors as immunotherapeutics. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati, G.; Del Gaudio, N.; Scarano, E.; Cifarelli, R.A.; Altucci, L.; Bilancia, D. Unexpected and durable response with regorafenib in a metastatic colorectal cancer patient without KDR mutation: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callebout, E.; Ribeiro, S.M.; Laurent, S.; De Man, M.; Ferdinande, L.; Claes, K.B.; Van der Meulen, J.; Geboes, K.P. Long term response on Regorafenib in non-V600E BRAF mutated colon cancer: A case report. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, K.; Manaka, D.; Kudo, R.; Kanai, S.; Mitsuoka, E.; Kanto, S.; Hamasu, S.; Konishi, S.; Nishitai, R. Metastatic colorectal cancer responsive to regorafenib for 2 years: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, M.; Falcone, R.; Mazzuca, F.; Archibugi, L.; Castaldi, N.; Botticelli, A.; Osti, M.F.; Marchetti, P. The role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in oligometastatic colorectal cancer: Clinical case report of a long-responder patient treated with regorafenib beyond progression. Medicine 2017, 96, e9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, E.; Sforza, V.; Cardone, C.; Capasso, A.; Nappi, A.; Martini, G.; Napolitano, S.; Rachiglio, A.M.; Normanno, N.; Cappabianca, S. Clinical outcome and molecular characterisation of chemorefractory metastatic colorectal cancer patients with long-term efficacy of regorafenib treatment. ESMO Open 2017, 2, e000177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Xia, D.; Xu, E.; Lai, M.; Wu, Y. Mutations of key driver genes in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshani, A.; Silvestris, N.; Hemmat, N.; Asadzadeh, Z.; Abdoli Shadbad, M.; Nourbakhsh, N.S.; Mobasheri, L.; Vahedi, P.; Shahmirzaie, M.; Brunetti, O. Targeting TGF-β-Mediated SMAD Signaling pathway via novel recombinant cytotoxin II: A potent protein from naja naja oxiana venom in Melanoma. Molecules 2020, 25, 5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Qiu, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, H. TGF-β secreted by tumor-associated macrophages promotes proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer via miR-34a-VEGF axis. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. Anti-angiogenic agents in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A promising strategy for cancer treatment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, O.; Calabrese, A.; Palermo, L.; Solimando, A.G.; Argentiero, A. Long-term survival of an advanced colorectal cancer patient treated with Regorafenib: Case report and literature review. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2379–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silvestris, N.; Brunetti, O.; Pinto, R.; Petriella, D.; Argentiero, A.; Fucci, L.; Tommasi, S.; Danza, K.; De Summa, S. Immunological mutational signature in adenosquamous cancer of pancreas: An exploratory study of potentially therapeutic targets. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Markovets, A.; Ahdesmaki, M.; Chapman, B.; Hofmann, O.; McEwen, R.; Johnson, J.; Dougherty, B.; Barrett, J.C.; Dry, J.R. VarDict: A novel and versatile variant caller for next-generation sequencing in cancer research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, K. Genomic variant annotation and prioritization with ANNOVAR and wANNOVAR. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinform. (Oxf. Engl. ) 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Prete, M.; Giampieri, R.; Loupakis, F.; Prochilo, T.; Salvatore, L.; Faloppi, L.; Bianconi, M.; Bittoni, A.; Aprile, G.; Zaniboni, A. Prognostic clinical factors in pretreated colorectal cancer patients receiving regorafenib: Implications for clinical management. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabernero, J.; Lenz, H.-J.; Siena, S.; Sobrero, A.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouché, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C. Analysis of circulating DNA and protein biomarkers to predict the clinical activity of regorafenib and assess prognosis in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A retrospective, exploratory analysis of the CORRECT trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; Granetto, C.; Falletta, A.; Paccagnella, M.; Abbona, A.; Fea, E.; Fabozzi, T.; Nigro, C.L.; Merlano, M.C. Circulating cytokines and outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with regorafenib. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Sakai, Y. Transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway in colorectal cancer and its tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, I.; Sun, W.; Tang, L.; Feng, J. Roles of Smads family and alternative splicing variants of Smad4 in different cancers. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marisa, L.; de Reyniès, A.; Duval, A.; Selves, J.; Gaub, M.P.; Vescovo, L.; Etienne-Grimaldi, M.-C.; Schiappa, R.; Guenot, D.; Ayadi, M. Gene expression classification of colon cancer into molecular subtypes: Characterization, validation, and prognostic value. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Bradshaw, A.-D.; Gera, S.; Dewan, M.Z.; Xu, R. The TGF-β/Smad4 signaling pathway in pancreatic carcinogenesis and its clinical significance. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothey, A.; Prager, G.; Yoshino, T. The mechanism of action of regorafenib in colorectal cancer: A guide for the community physician. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. USA 2019, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar]


| Category | GO | Description | LogP |
|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | −10 |
| Reactome Gene Sets | R-HSA-3304349 | Loss of Function of SMAD2/3 in Cancer | −9.5 |
| Reactome Gene Sets | R-HSA-3304351 | Signaling by TGF-beta Receptor Complex in Cancer | −9.3 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0045351 | type I interferon biosynthetic process | −8.9 |
| Reactome Gene Sets | R-HSA-936964 | Activation of IRF3/IRF7 mediated by TBK1/IKK epsilon | −8.2 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0003198 | epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation | −8 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0032727 | positive regulation of interferon-alpha production | −7.8 |
| Canonical Pathways | M185 | PID ALK1 PATHWAY | −7.7 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0003272 | endocardial cushion formation | −7.6 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0035666 | TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway | −7.5 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0032647 | regulation of interferon-alpha production | −7.5 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0032728 | positive regulation of interferon-beta production | −7.4 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0032607 | interferon-alpha production | −7.4 |
| Reactome Gene Sets | R-HSA-2173789 | TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs | −7.4 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0002756 | MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway | −7.3 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0060317 | cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition | −7.2 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0003203 | endocardial cushion morphogenesis | −7.2 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:2000826 | regulation of heart morphogenesis | −7 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0060412 | ventricular septum morphogenesis | −6.9 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0003197 | endocardial cushion development | −6.9 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:1901216 | positive regulation of neuron death | −8.9 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:2001233 | regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | −8.9 |
| KEGG Pathway | hsa05162 | Measles | −8.4 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0097190 | apoptotic signaling pathway | −8 |
| Reactome Gene Sets | R-HSA-109581 | Apoptosis | −7.8 |
| Reactome Gene Sets | R-HSA-5357801 | Programmed Cell Death | −7.8 |
| KEGG Pathway | hsa05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | −7.6 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0010942 | positive regulation of cell death | −7.6 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0043523 | regulation of neuron apoptotic process | −7.5 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:2001234 | negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | −7.4 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0051402 | neuron apoptotic process | −7.3 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0070266 | necroptotic process | −7.3 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0097300 | programmed necrotic cell death | −7.1 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0043525 | positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process | −6.9 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:1901214 | regulation of neuron death | −6.9 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0070265 | necrotic cell death | −6.8 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:0070997 | neuron death | −6.7 |
| KEGG Pathway | hsa01524 | Platinum drug resistance | −6.6 |
| KEGG Pathway | hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | −6.5 |
| GO Biological Processes | GO:2001237 | negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | −6.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Summa, S.; Danza, K.; Pilato, B.; Matera, G.; Fasano, R.; Calabrese, A.; Lacalamita, R.; Silvestris, N.; Tommasi, S.; Argentiero, A.; et al. A Promising Role of TGF-β Pathway in Response to Regorafenib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Report. Medicina 2021, 57, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111241
De Summa S, Danza K, Pilato B, Matera G, Fasano R, Calabrese A, Lacalamita R, Silvestris N, Tommasi S, Argentiero A, et al. A Promising Role of TGF-β Pathway in Response to Regorafenib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Report. Medicina. 2021; 57(11):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111241
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Summa, Simona, Katia Danza, Brunella Pilato, Giuseppina Matera, Rossella Fasano, Angela Calabrese, Rosanna Lacalamita, Nicola Silvestris, Stefania Tommasi, Antonella Argentiero, and et al. 2021. "A Promising Role of TGF-β Pathway in Response to Regorafenib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Report" Medicina 57, no. 11: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111241
APA StyleDe Summa, S., Danza, K., Pilato, B., Matera, G., Fasano, R., Calabrese, A., Lacalamita, R., Silvestris, N., Tommasi, S., Argentiero, A., & Brunetti, O. (2021). A Promising Role of TGF-β Pathway in Response to Regorafenib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Case Report. Medicina, 57(11), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57111241








