A Preliminary Retrospective Study to Assess the Short-Term Safety of Traditional Smooth or Microtextured Silicone Gel-Filled Breast Implants in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Patients and Setting
2.2. Treatment Protocol
2.3. Patient Evaluation and Criteria
2.4. Statistical Analysis of the Patient Data
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. Incidences of Postoperative Complications by the Breast Implants
3.3. Results of Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacerda, M.A.C.; Carvalho, G.; Uggioni, M.L.R.; Bavaresco, D.V.; Simon, C.S.; Cruz, M.; Silva, F.; Rosa, M.I. Accuracy of Ultrasonography in Breast Implant Rupture Diagnosis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 14, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, Y.A. Cosmetic Surgery and Self-esteem in South Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Bang, S.I.; Heo, C.Y. BellaGel breast implant: 4-year results of a prospective cohort study. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2019, 53, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, G.P.; Gabriel, A. Breast implant design. Gland Surg. 2017, 6, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Headon, H.; Kasem, A.; Mokbel, K. Capsular Contracture after Breast Augmentation: An Update for Clinical Practice. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2015, 42, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mempin, M.; Hu, H.; Chowdhury, D.; Deva, A.; Vickery, K. The A, B and C’s of Silicone Breast Implants: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, Biofilm and Capsular Contracture. Materials 2018, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nava, M.B.; Rancati, A.; Angrigiani, C.; Catanuto, G.; Rocco, N. How to prevent complications in breast augmentation. Gland Surg. 2017, 6, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashar, B.S. Assessing the Risks of Breast Implants and FDA’s Vision for the National Breast Implant Registry. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Silicone Gel-Filled Breast Implant Market 2020 By Type [Silicone Implant, Structured Implants and others], By Application [Mastoplasty, Breast Reconstruction, Breast Augmentation Surgery and Others]: Global Forecast to 2026 and COVID-19 Impact Outlook. Available online: https://transiliencemarketresearch.com/shop/pharmaceutical/global-silicone-gel-filled-breast-implant-market-2020-by-type-silicone-implant-structured-implants-and-othersby-application-mastoplasty-breast-reconstructionbreast-augmentation-surgery-and-othe/ (accessed on 17 March 2021).
- Sung, J.Y.; Jeong, J.P.; Moon, D.S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, W.S.; Song, K.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, H.G.; Kim, J.H. Short-term Safety of Augmentation Mammaplasty Using the BellaGel Implants in Korean Women. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H. Association of the BellaGel® Breast Implant Scandal with the Poly Implant Prothèse Fraud: A Review of Literatures. J. Surg. Open Access 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.S.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, H.C.; Jeong, J.P.; Sung, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. Short-term treatment outcomes and safety of two representative brands of the fifth-generation silicone gel-filled breast implants in Korea. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H. The Manufacturer’s Deliberate Modification of the Shell Structure of the BellaGel® SmoothFine in Violation of the Regulatory Requirement. J. Surg. Open Access 2021, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Paik, N.S.; Nam, S.Y.; Cho, Y.; Park, H.K. The Emerging Crisis of Stakeholders in Implant-based Augmentation Mammaplasty in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deva, A.K.; Cuss, A.; Magnusson, M.; Cooter, R. The “Game of Implants”: A Perspective on the Crisis-Prone History of Breast Implants. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2019, 39, S55–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anne, K.G.; Graf, R. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) and the Textured Breast Implant Crisis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, W.P., Jr.; Rios, J.L.; Smith, S.J. Enhancing patient outcomes in aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery using triple antibiotic breast irrigation: Six-year prospective clinical study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 46S–52S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, T.A.; Ahmad, J.; Rohrich, R.J. Capsular contracture with breast implants in the cosmetic patient: Saline versus silicone—A systematic review of the literature. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biau, D.J.; Hamadouche, M. Estimating implant survival in the presence of competing risks. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, J.M.; Gatti, M.E.; Schaffner, A.D.; Hill, L.M.; Spear, S.L. Effect of incision choice on outcomes in primary breast augmentation. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2012, 32, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiener, T.C. Relationship of incision choice to capsular contracture. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araco, A.; Gravante, G.; Araco, F.; Delogu, D.; Cervelli, V.; Walgenbach, K. A retrospective analysis of 3000 primary aesthetic breast augmentations: Postoperative complications and associated factors. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2007, 31, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlan, M.; Nuti, G.; Wang, H.; Decker, S.; Perry, T. Breast implant surface texture impacts host tissue response. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 88, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça Munhoz, A.; Santanelli, D.; Pompeo, F.; De Mezerville, R. Nanotechnology, nanosurfaces and silicone gel breast implants: Current aspects. Case Rep. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2017, 4, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munhoz, A.M.; Clemens, M.W.; Nahabedian, M.Y. Breast Implant Surfaces and Their Impact on Current Practices: Where We Are Now and Where Are We Going? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doloff, J.C.; Veiseh, O.; de Mezervill, R.; Sforza, M.; Perry, T.A.; Haupt, J.; Jamiel, M.; Chambers, C.; Nash, A.; Aghlara-Fotovat, S.; et al. The surface topography of silicone breast implants mediates the foreign body response in mice, rabbits and humans. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calobrace, M.B.; Schwartz, M.R.; Zeidler, K.R.; Pittman, T.A.; Cohen, R.; Stevens, W.G. Long-Term Safety of Textured and Smooth Breast Implants. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2017, 38, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montemurro, P.; Tay, V.K.S. Transitioning From Conventional Textured to Nanotextured Breast Implants: Our Early Experience and Modifications for Optimal Breast Augmentation Outcomes. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2021, 41, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calobrace, M.B.; Capizzi, P.J. The biology and evolution of cohesive gel and shaped implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 6S–11S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnsley, G.P.; Sigurdson, L.J.; Barnsley, S.E. Textured surface breast implants in the prevention of capsular contracture among breast augmentation patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.H.; Samuel, M.; Tan, B.K.; Song, C. Capsular contracture in subglandular breast augmentation with textured versus smooth breast implants: A systematic review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, H.G., Jr.; Kumpf, A.L. Aesthetic breast surgery: Emerging trends and technologies. Mo. Med. 2010, 107, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barr, S.; Bayat, A. Breast implant surface development: Perspectives on development and manufacture. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2011, 31, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bengtson, B.P.; Eaves, F.F., III. High-resolution ultrasound in the detection of silicone gel breast implant shell failure: Background, in vitro studies, and early clinical results. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2012, 32, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Handel, N.; Jensen, J.A.; Black, Q.; Waisman, J.R.; Silverstein, M.J. The fate of breast implants: A critical analysis of complications and outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Mu, D.; Wang, K.; Zhu, S.; He, Y.; Luan, J. Chinese women’s preferences and concerns regarding incision location for breast augmentation surgery: A survey of 216 patients. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2015, 39, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, H.B. Transaxillary endoscopic breast augmentation. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2014, 41, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Variables | Values |
|---|---|
| Age (years old) | 31.59 ± 8.32 |
| Sex | |
| Men | 0 (0.0%) |
| Women | 2612 (100.0%) |
| Height (cm) | 162.31 ± 7.66 |
| Weight (kg) | 51.42 ± 6.03 |
| FU period (months) | 14.47 ± 2.46 (12–17) |
| Purpose of surgery | |
| Aesthetic augmentation mammaplasty | 2612 (100.0%) |
| Mode of incision | |
| Trans-axillary incision | 2416 (92.5%) |
| IMF incision | 124 (4.7%) |
| Peri-areolar incision | 72 (2.8%) |
| Type of pocket | |
| Subpectoral pocket | 1860 (71.21%) |
| Subglandular pocket | 752 (28.79%) |
| Volume of breast implant (cc) | |
| ≤245 | 52 (2.0%) |
| 250–295 | 404 (15.5%) |
| 300–345 | 1280 (49.0%) |
| 350–395 | 716 (27.4%) |
| ≥400 | 168 (6.1%) |
| Surface topography of breast implant | |
| Microtextured | 2364 (90.5%) |
| Smooth | 248 (9.5%) |
| Profile of breast implant | |
| Ultra-high | 180 (6.9%) |
| High | 2252 (86.2%) |
| Medium | 168 (6.4%) |
| Low | 12 (0.5%) |
| Variables | Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sebbin® Sublimity (n = 1072) | BellaGel® SmoothFine (n = 944) | Motiva Ergonomix™ (n = 312) | Mentor® MemoryGel™ Xtra (n = 152) | BellaGel® Smooth (n = 84) | Eurosilicone Round Collection™ (n = 36) | Natrelle® INSPIRA™ (n = 12) | |
| Age (years old) | 31.01 ± 7.26 | 30.81 ± 8.44 | 34.19 ± 8.62 | 28.82 ± 7.83 | 40.62 ± 11.43 | 33.00 ± 6.93 | 45.33 ± 3.21 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Women | 1072 (100.00%) | 944 (100.00%) | 312 (100.00%) | 152 (100.00%) | 84 (100.00%) | 36 (100.00%) | 12 (100.00%) |
| Height (cm) | 162.64 ± 4.94 | 161.77 ± 10.81 | 163.58 ± 5.09 | 160.74 ± 5.18 | 163.11 ± 6.00 | 161.67 ± 4.82 | 159.67 ± 2.52 |
| Weight (kg) | 51.15 ± 5.56 | 51.43 ± 6.01 | 52.29 ± 5.78 | 50.37 ± 6.70 | 55.70 ± 9.02 | 50.00 ± 6.76 | 42.00 ± 1.73 |
| FU period (months) | 12.12 ± 0.73 | 12.19 ± 0.27 | 12.68 ± 0.58 | 12.71 ± 0.36 | 12.67 ± 0.29 | 12.89 ± 0.04 | 12.77 ± 0.66 |
| Purpose of surgery | |||||||
| Aesthetic augmentation mammaplasty | 1072 (100.00%) | 944 (100.00%) | 312 (100.00%) | 152 (100.00%) | 84 (100.00%) | 36 (100.00%) | 12 (100.00%) |
| Mode of incision | |||||||
| Trans-axillary incision | 1036 (96.64%) | 868 (91.95%) | 268 (85.90%) | 144 (94.74%) | 56 (66.67%) | 36 (100.00%) | 8 (66.67%) |
| IMF incision | 16 (1.49%) | 68 (8.62%) | 28 (8.97%) | 8 (5.26%) | 4 (4.76%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Peri-areolar incision | 20 (1.87%) | 8 (0.57%) | 16 (5.13%) | 0 (0.00%) | 24 (28.57%) | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (33.33%) |
| Type of pocket | |||||||
| Subpectotal pocket | 841 (78.45%) | 551 (58.37%) | 253 (81.09%) | 118 (77.63%) | 67 (79.76%) | 24 (66.67%) | 6 (50.00%) |
| Subglandular pocket | 231 (21.55%) | 393 (41.63%) | 59 (18.91%) | 34 (22.37%) | 17 (20.24%) | 12 (33.33%) | 6 (50.00%) |
| Volume of breast implant (cc) | |||||||
| ≤245 | 4 (1.49%) | 2 (0.57%) | 3 (3.85) | 1 (2.63%) | 2 (9.52%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (33.33%) |
| 250–295 | 36 (13.43%) | 28 (12.14%) | 16 (20.51%) | 11 (28.95%) | 5 (23.81%) | 4 (44.44%) | 1 (33.33%) |
| 300–345 | 146 (54.48%) | 126 (53.39%) | 27 (34.62%) | 14 (36.84%) | 4 (19.05%) | 2 (22.22%) | 1 (33.33%) |
| 350–395 | 66 (24.63%) | 80 (33.90%) | 17 (21.79%) | 10 (26.32%) | 3 (14.29%) | 3 (33.34%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| ≥400 | 16 (5.97%) | 0 (0.00%) | 15 (19.23%) | 2 (5.26%) | 8 (38.10%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Surface topography of breast implant | |||||||
| Microtextured | 1072 (100.00%) | 944 (100.00%) | 312 (100.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 36 (100.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Smooth | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 152 (100.00%) | 84 (100.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 12 (100.00%) |
| Profile of breast implant | |||||||
| Ultra-high | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 180 (57.69%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| High | 1040 (97.01%) | 848 (90.68%) | 96 (30.77%) | 152 (100.00%) | 72 (85.71%) | 36 (100.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Medium | 32 (2.99%) | 88 (9.32%) | 36 (11.54%) | 0 (0.00%) | 12 (14.29%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Non-applicable | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 12 (100.00%) |
| Values | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sebbin® Sublimity (n = 1072) | BellaGel® SmoothFine (n = 944) | MotivaErgonomixTM (n = 312) | Mentor® MemoryGel™ Xtra (n = 152) | BellaGel® Smooth (n = 84) | Eurosilicone Round Collection™ (n = 36) | Natrelle® INSPIRA™ (n = 12) | |
| Total incidences | 88 (8.21%) | 92 (9.75%) | 40 (12.82%) | 8 (5.26%) | 12 (14.29%) | 0 (0.00%) | 8 (66.67%) |
| Early hematoma | 4 (0.37%) | 4 (0.42%) | 4 (1.28%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Early seroma | 28 (2.61%) | 60 (6.36%) | 20 (6.41%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (33.33%) |
| Rupture | 4 (0.37%) | 4 (0.42%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (33.33%) |
| Capsular contracture | 20 (1.87%) | 12 (1.27%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Rippling | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (4.76%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Shape deformation | 28 (2.61%) | 8 (0.85%) | 12 (3.85%) | 4 (2.63%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Infection | 4 (0.37%) | 4 (0.42%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (4.76%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Stretch deformities with skin excess | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (1.28%) | 4 (2.63%) | 4 (4.76%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Breast Implants | N | n | Censored Values | TTE (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
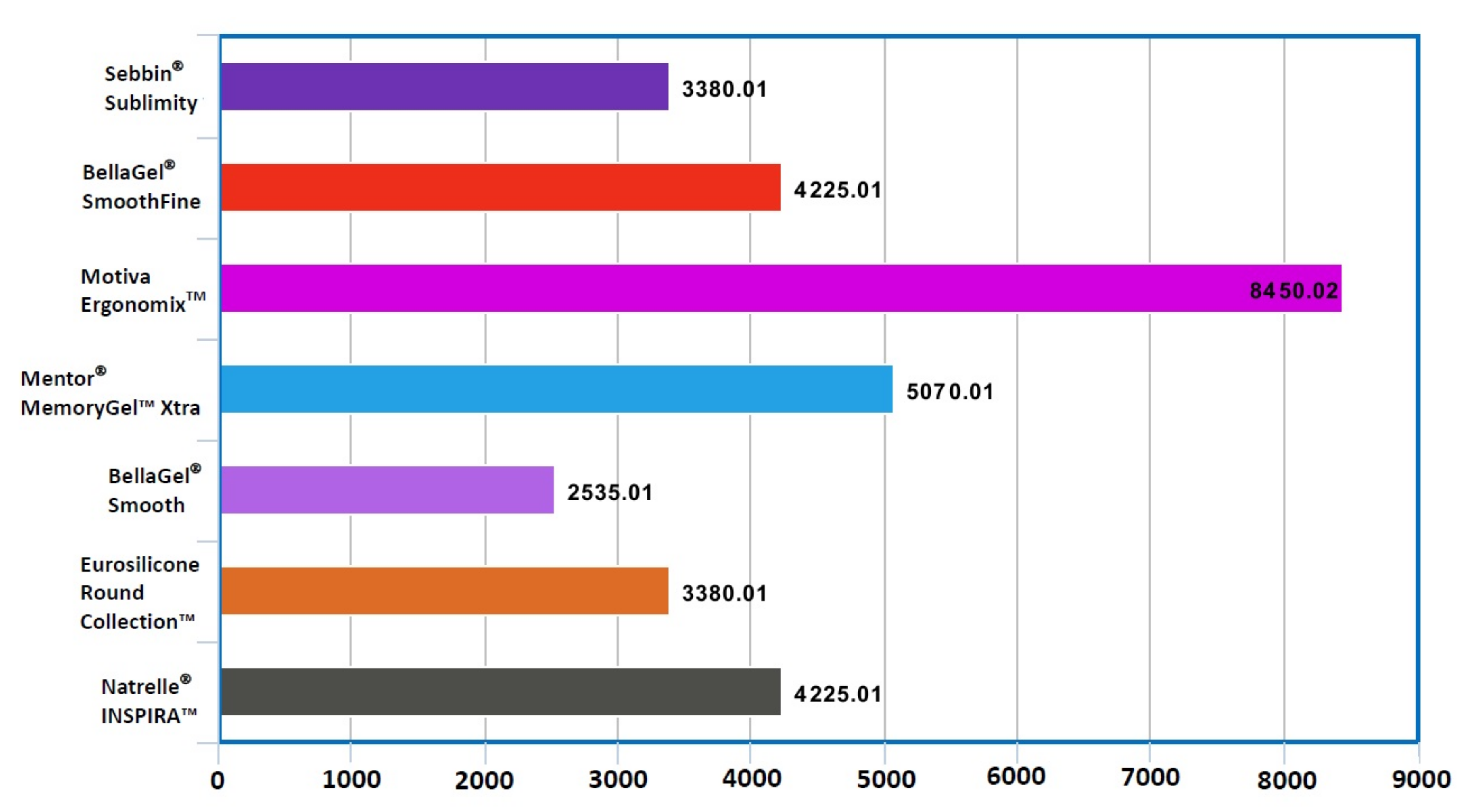
| Total | 2612 | 248 | 2364 (90.5%) | 1564.32 ± 75.52 (1416.39–1712.32) |
| Sebbin® Sublimity (n = 1072) | 1072 | 88 | 984 (91.8%) | 1322.00 ± 51.20 (1221.64–1422.32) |
| BellaGel® SmoothFine (n = 944) | 944 | 92 | 852 (90.3%) | 1458.4 ± 65.76 (1329.56–1587.28) |
| MotivaErgonomixTM (n = 312) | 312 | 40 | 272 (87.2%) | 1528.00 ± 157.92 (1218.48–1837.56) |
| Mentor®MemoryGel™Xtra (n = 152) | 152 | 8 | 144 (94.7%) | 698.4 ± 52.64 (595.28–801.52) |
| BellaGel® Smooth (n = 84) | 84 | 12 | 72 (85.7%) | 1138.72 ± 161.28 (822.6–1454.84) |
| Eurosilicone Round Collection™ (n = 36) | 36 | 0 | 36 (100.0%) | 0.00 ± 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Natrelle® INSPIRA™ (n = 12) | 12 | 8 | 4 (33.3%) | 380.00 ± 170.88 (45.04–714.96) |
| Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
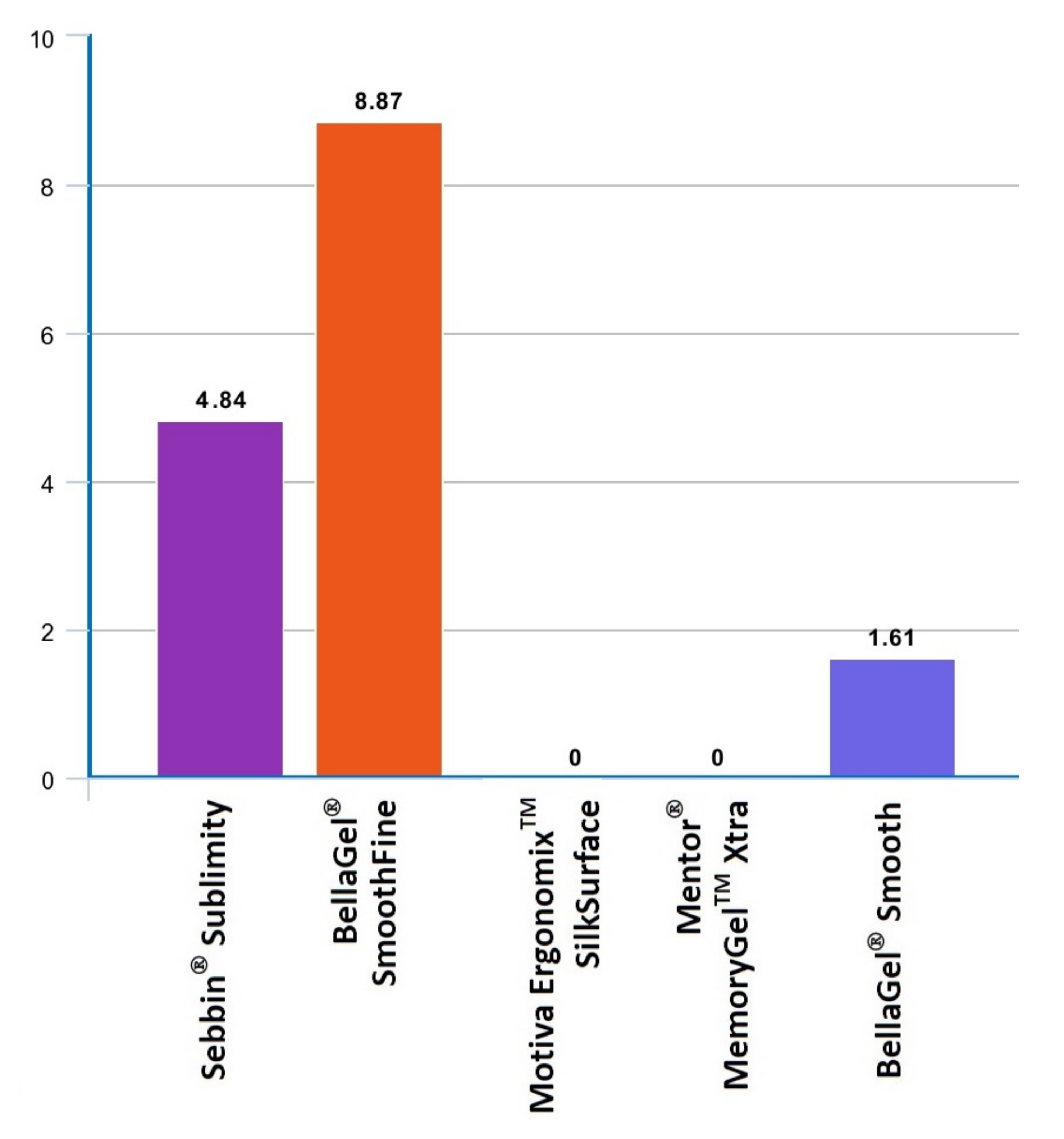
| Sebbin® Sublimity (n = 16) | BellaGel® SmoothFine (n = 68) | Motiva ErgonomixTM (n = 28) | Mentor® MemoryGel™ Xtra (n = 8) | BellaGel® Smooth (n = 4) | |
| Total incidences | 6 (4.84%) | 11 (8.87%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 2 (1.61%) |
| Early hematoma | 1 (0.81%) | 1 (0.81%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Early seroma | 1 (0.81%) | 3 (2.42%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Rupture | 1 (0.81%) | 2 (1.61%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Capsular contracture | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Rippling | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (0.81%) |
| Shape deformation | 2 (1.61%) | 3 (2.42%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| Infection | 1 (0.81%) | 2 (1.61%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (0.81%) |
| Stretch deformities with skin excess | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.; Kim, R.; Kim, T.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Jeong, C.; Lee, J.H. A Preliminary Retrospective Study to Assess the Short-Term Safety of Traditional Smooth or Microtextured Silicone Gel-Filled Breast Implants in Korea. Medicina 2021, 57, 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57121370
Han S, Kim R, Kim TS, Park JH, Kim SS, Jeong C, Lee JH. A Preliminary Retrospective Study to Assess the Short-Term Safety of Traditional Smooth or Microtextured Silicone Gel-Filled Breast Implants in Korea. Medicina. 2021; 57(12):1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57121370
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Sanghyuk, Robert Kim, Tae Seob Kim, Jung Heum Park, Seung Soo Kim, Cheol Jeong, and Ji Heui Lee. 2021. "A Preliminary Retrospective Study to Assess the Short-Term Safety of Traditional Smooth or Microtextured Silicone Gel-Filled Breast Implants in Korea" Medicina 57, no. 12: 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57121370
APA StyleHan, S., Kim, R., Kim, T. S., Park, J. H., Kim, S. S., Jeong, C., & Lee, J. H. (2021). A Preliminary Retrospective Study to Assess the Short-Term Safety of Traditional Smooth or Microtextured Silicone Gel-Filled Breast Implants in Korea. Medicina, 57(12), 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57121370






