Are the Morphological Indices of the Vertebrobasilar System Heritable? A Twin Study Based on 3D Reconstructed Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wafa, H.A.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Emmett, E.; Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Wang, Y. Burden of Stroke in Europe: Thirty-Year Projections of Incidence, Prevalence, Deaths, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years. Stroke 2020, 51, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouh, A.M.; Eremke, J.; Ruland, S. Ischemic Posterior Circulation Stroke: A Review of Anatomy, Clinical Presentations, Diagnosis, and Current Management. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wake-Buck, A.K.; Gatenby, J.C.; Gore, J.C. Hemodynamic Characteristics of the Vertebrobasilar System Analyzed Using MRI-Based Models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Lyu, J.; Hou, Z.; He, J.; Mo, D.; Gao, F.; Liu, X.; Sui, B.; Shen, M.; et al. Different risk factors in identical features of intracranial atherosclerosis plaques in the posterior and anterior circulation in high-resolution MRI. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, H.T.; Fu, S.Q.; Yu, M.; Ren, Y.-F.; Ji, P. Basilar artery bending length, vascular risk factors, and pon-tine infarction. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 338, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.M.; Chung, C.-S.; Bang, O.Y.; Yong, S.W.; Joo, I.S.; Huh, K. Vertebral artery dominance contributes to basilar artery curvature and peri-vertebrobasilar junctional infarcts. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.-F.; Dong, X.-F.; Feng, H.-X.; Zhao, H.-Q.; Liu, C.-F. Study on the correlation of vertebral artery dominance, basilar artery curvature and posterior circulation infarction. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2015, 116, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnoki, A.D.; Fejer, B.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Littvay, L.; Lucatelli, P.; Cirelli, C.; Fanelli, F.; Sacconi, B.; Fagnani, C.; Medda, E.; et al. Vertebral Artery Diameter and Flow: Nature or Nurture. J. Neuroimaging 2017, 27, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Forgo, B.; Szabo, H.; Melicher, D.; Metneki, J.; Littvay, L. The Hungarian Twin Registry Update: Turning From a Voluntary to a Population-Based Registry. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2019, 22, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.C.; Nyholt, D.R.; Neuman, R.; Madden, P.A.; Bucholz, K.K.; Todd, R.D.; Nelson, E.C.; Montgomery, G.W.; Martin, N.G. Zygosity diagnosis in the absence of genotypic data: An approach using latent class analysis. Twin Res. 2003, 6, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thomas, J.B.; Antiga, L.; Che, S.L.; Milner, J.S.; Steinman, D.A.; Spence, J.D.; Rutt, B.K.; Steinman, D.A. Variation in the carotid bifurcation geometry of young versus older adults: Implications for geometric risk of atherosclerosis. Stroke 2005, 36, 2450–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiga, L.; Piccinelli, M.; Botti, L.; Ene-Iordache, B.; Remuzzi, A.; Steinman, D.A. An image-based modeling framework for pa-tient-specific computational hemodynamics. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierfelder, K.M.; Baumann, A.B.; Sommer, W.H.; Armbruster, M.; Opherk, C.; Janssen, H. Vertebral artery hypoplasia: Fre-quency and effect on cerebellar blood flow characteristics. Stroke 2014, 45, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Kosmidou, M.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Giannopoulos, S. Is Vertebral Artery Hypoplasia a Predisposing Factor for Posterior Circulation Cerebral Ischemic Events? A Comprehensive Review. Eur. Neurol. 2013, 70, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, L.R. Arterial occlusions: Does size matter? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 2007, 78, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.-C. Twisted Blood Vessels: Symptoms, Etiology and Biomechanical Mechanisms. J. Vasc. Res. 2012, 49, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.M. Aberrant Origin of Vertebral Artery and its Clinical Implications. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 31, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodati, A.; Inzaghi, E.; Cianfarani, S. Epigenetics and In Utero Acquired Predisposition to Metabolic Disease. Front. Genet. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballermann, B.J.; Dardik, A.; Eng, E.; Liu, A. Shear stress and the endothelium. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, S100–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.; Wenz, R.; Maros, M.E.; Böhme, J.; Al-Zghloul, M.; Alonso, A.; Groden, C.; Wenz, H. Anatomical distribution of cerebral microbleeds and intracerebral hemorrhage in vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Nam, H.; Kim, J.-T.; Ha, Y.S.; Oh, S.-Y.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Hur, N.; Kwak, H.-S.; et al. Basilar Artery Angulation in Association with Aging and Pontine Lacunar Infarction: A Multicenter Observational Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2015, 22, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Lim, J.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-S. Basilar Artery Dolichoectasia Is Associated with Paramedian Pontine Infarction. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 27, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Ibrahim, J.G.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; et al. Heritability of Regional Brain Volumes in Large-Scale Neuroimaging and Genetic Studies. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 29, 2904–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Cho, K.-H.; Kang, D.-W.; Kwon, S.U.; Suh, D.C. Basilar artery atherosclerotic disease is related to subacute lesion volume increase in pontine base infarction. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 120, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
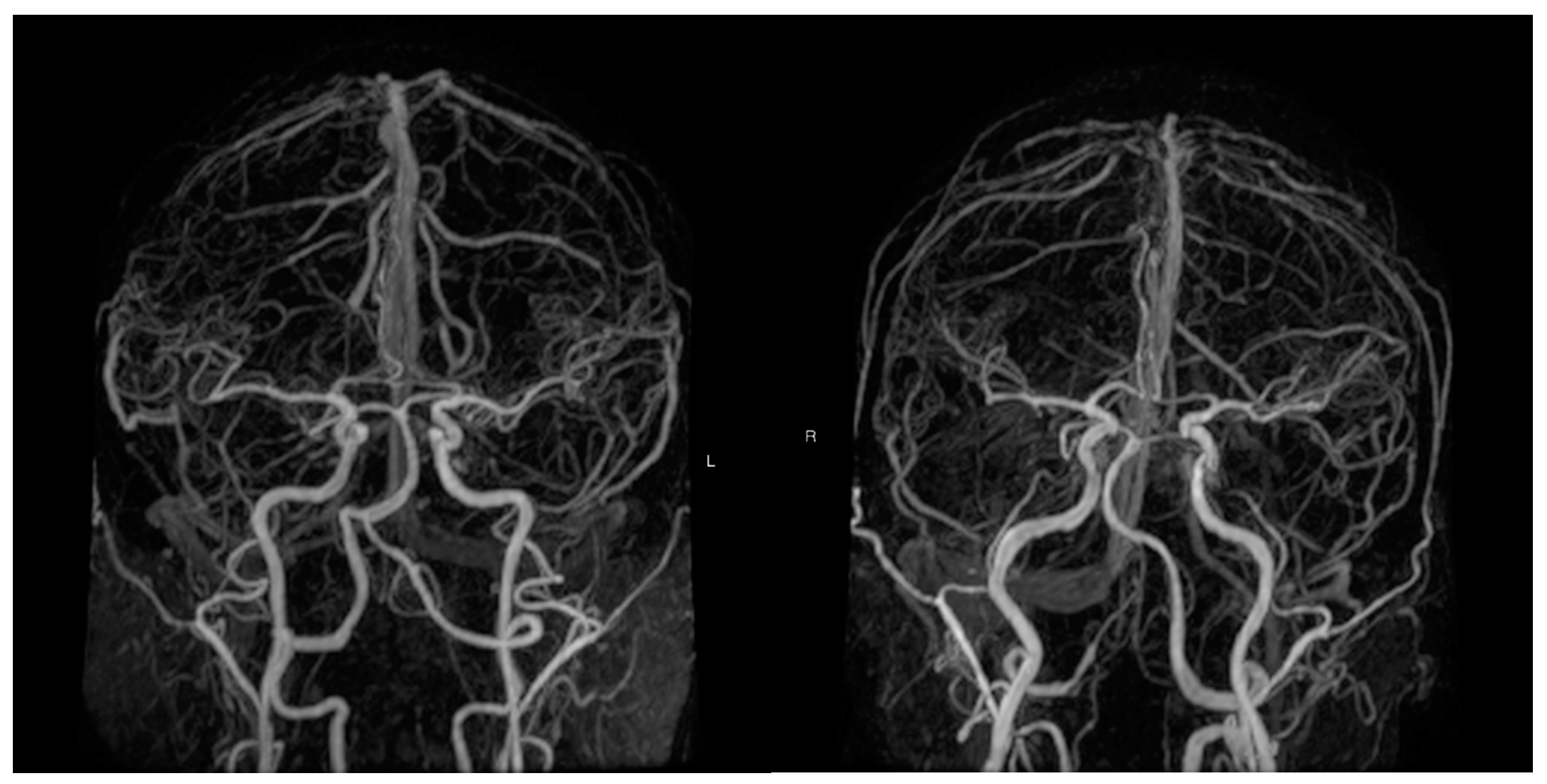

| Total | MZ | DZ | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zigosity (n paires) | 100 | 67 | 33 | - |
| Age | 51.66 (±14.96) | 49.57 (±14.42) | 56 (±15.23) | 0.004 * |
| Sex (F:M) | 132:67 | 90:44 | 43:23 | - |
| Does weekly exercise | 63.00% | 68.65% | 51.51% | 0.02 * |
| Alcohol consumption once a week | 54.00% | 52.23% | 59.09% | 0.29 |
| Ever Smoked | 27.00% | 28.35% | 24.24% | 0.60 |
| Diagnosed with diabetes | 8.50% | 9.70% | 6.06% | 0.41 |
| Diagnosed with hypertension | 30.50% | 30.60% | 30.30% | 0.95 |
| Diagnosed with dyslipidaemia | 24.50% | 24.62% | 24.24% | 0.97 |
| Height (cm) | 167.95 (±9.12) | 167.90 (±9.27) | 168.05 (±8.86) | 0.91 |
| Weight (kg) | 72.75 (±14.23) | 72.52 (±14.80) | 73.22 (±13.07) | 0.74 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.74 (±4.59) | 25.56 (±4.61) | 26.12 (±4.57) | 0.41 |
| Basilar artery length (mm) | 24.08 (±4.41) | 23.77 (±4.5) | 24.73 (±4.18) | 0.14 |
| Basilar artery diameter (calculated mm) | 3.42 (±0.57) | 3.39 (±0.54) | 3.49 (±0.61) | 0.23 |
| Basilar artery area (mm²) | 9.43 (±3.02) | 9.23 (±2.88) | 9.84 (±3.26) | 0.17 |
| Basilar artery volume (mm³) | 218.28 (±81.32) | 210.47 (±79.24) | 234.49 (±83.79) | 0.05 |
| Basilar artery curvature (mm) | 2.57 (±2.29) | 2.51 (±2.16) | 2.68 (±2.54) | 0.06 |
| Basilar artery tortuosity (%) | 6.37% | 6.03% | 7.08% | 0.35 |
| Basilar artery torsion (%) | 11.29% | 10.59% | 12.57% | 0.19 |
| Left vertebral artery diameter (mm) | 2.44(±0.72) | 2.44 (±0.74) | 2.45 (±0.69) | 0.92 |
| Right vertebral artery diameter (mm) | 2.36 (±0.61) | 2.36 (±0.56) | 2.36 (±0.7) | 0.91 |
| Vertebral artery difference (mm) | 0.75 (±0.62) | 0.71 (±0.61) | 0.82 (±0.66) | 0.22 |
| Left vertebral artery curvature (%) | 7.79% | 7.88% | 7.61% | 0.42 |
| Right vertebral artery curvature (%) | 8.10% | 8.14% | 8.04% | 0.77 |
| Left vertebral artery tortuosity (%) | 11.77% | 11.12% | 13.10% | 0.23 |
| Right vertebral artery tortuosity (%) | 11.57% | 10.71% | 13.35% | 0.07 |
| Left vertebral artery torsion (%) | 12.34% | 12.64% | 11.73% | 0.51 |
| Right vertebral artery torsion (%) | 12.62% | 12.75% | 12.35% | 0.78 |
| Model | AIC | BIC | A | 95% CI | C | 95% CI | E | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basilar artery length (mm) | A-C-E | 1179.85 | 1166.67 | 0.63 | 0.457–0.752 | 0 | 0–0.445 | 0.37 | 0.248–0.543 |
| rMZ: 0.616 (0.434 0.749) | A-E * | 1177.11 | 1165.19 | 0.63 | 0.457–0.752 | 0.37 | 0.248–0.543 | ||
| rDZ: 0.288 (−0.048 0.566) | C-E | 1182.74 | 1170.82 | 0.503 | 0.331–0.641 | 0.497 | 0.359–0.669 | ||
| Basilar artery area (mm²) | A-C-E | 277.860 | 264.687 | 0.13 | 0–0.571 | 0.252 | 0–0.513 | 0.618 | 0.426–0.827 |
| rMZ: 0.361 (0.127 0.558) | A-E | 275.811 | 263.888 | 0.409 | 0.192–0.585 | 0.591 | 0.415–0.808 | ||
| rDZ: 0.346 (0.02 0.606) | C-E * | 275.271 | 263.347 | 0.354 | 0.168–0.516 | 0.646 | 0.484–0.832 | ||
| Basilar artery volume (mm³) | A-C-E | 395.808 | 382.634 | 0.601 | 0.255–0.732 | 0 | 0–0.292 | 0.399 | 0.268–0.576 |
| rMZ: 0.646 (0.474 0.771) | A-E * | 393.073 | 381.149 | 0.601 | 0.424–0.732 | 0.399 | 0.268–0.576 | ||
| rDZ: 0.016 (−0.316 0.347) | C-E | 401.440 | 389.516 | 0.452 | 0.281–0.596 | 0.548 | 0.404–0.719 | ||
| Basilar artery curvature (mm) | A-C-E | 1244.914 | 1231.741 | 0 | 0–0.371 | 0.164 | 0–0.347 | 0.836 | 0.653–1 |
| rMZ: 0.117 (−0.133 0.354) | A-E | 1242.810 | 1230.887 | 0.174 | 0–0.388 | 0.826 | 0.612–1 | ||
| rDZ: 0.231 (−0.098 0.514) | C-E * | 1242.179 | 1230.255 | 0.164 | 0–0.347 | 0.836 | 0.653–1 | ||
| Basilar artery tortuosity (%) | A-C-E | 611.919 | 598.746 | 0.099 | 0–0.627 | 0.395 | 0–0.618 | 0.507 | 0.345–0.699 |
| rMZ: 0.492 (0.275 0.663) | A-E | 610.983 | 599.059 | 0.515 | 0.32–0.664 | 0.485 | 0.336–0.68 | ||
| rDZ: 0.464 (0.162 0.686) | C-E * | 609.296 | 597.373 | 0.475 | 0.297–0.621 | 0.525 | 0.379–0.703 | ||
| Basilar artery torsion (%) | A-C-E | -201.823 | -214.996 | 0 | 0–0.239 | 0 | 0–0.196 | 1 | 0.761–1 |
| rMZ: −0.003 (−0.246 0.241) | C-E | -204.558 | -216.482 | 0 | 0–0.196 | 1 | 0.804–1 | ||
| rDZ: −0.016 (−0.345 0.317) | E * | -207.233 | -217.967 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Left vertebral artery diameter (mm) | A-C-E | 453.901 | 440.727 | 0.003 | 0–0.436 | 0.229 | 0–0.412 | 0.768 | 0.563–0.965 |
| rMZ: 0.255 (0.011 0.473) | A-E | 451.515 | 439.592 | 0.249 | 0.03–0.445 | 0.751 | 0.555–0.97 | ||
| rDZ: 0.213 (−0.124 0.506) | C-E * | 451.166 | 439.242 | 0.232 | 0.035–0.412 | 0.768 | 0.588–0.965 | ||
| Right vertebral artery diameter (mm) | A-C-E | 151.110 | 137.936 | 0.181 | 0–0.601 | 0.257 | 0–0.559 | 0.562 | 0.39–0.765 |
| rMZ: 0.454 (0.236 0.629) | A-E | 148.959 | 137.035 | 0.453 | 0.254–0.612 | 0.547 | 0.388–0.746 | ||
| rDZ: 0.339 (0.016 0.598) | C-E * | 148.656 | 136.732 | 0.41 | 0.228–0.564 | 0.59 | 0.436–0.772 | ||
| Vertebral artery difference (mm) | A-C-E | 588.849 | 575.675 | 0.23 | 0–0.444 | 0 | 0–0.29 | 0.77 | 0.556–1 |
| rMZ: 0.306 (0.064 0.514) | A-E * | 586.114 | 574.190 | 0.23 | 0–0.444 | 0.77 | 0.556–1 | ||
| rDZ: −0.089 (−0.405 0.248) | C-E | 587.741 | 575.817 | 0.144 | 0–0.335 | 0.856 | 0.665–1 | ||
| Left vertebral artery curvature (%) | A-C-E | 57.607 | 44.434 | 0.064 | 0–0.522 | 0.274 | 0–0.494 | 0.662 | 0.474–0.858 |
| rMZ: 0.349 (0.116 0.547) | A-E | 55.443 | 43.519 | 0.358 | 0.148–0.535 | 0.642 | 0.465–0.852 | ||
| rDZ: 0.284 (−0.061 0.567) | C-E * | 54.900 | 42.976 | 0.329 | 0.139–0.495 | 0.671 | 0.505–0.861 | ||
| Right vertebral artery curvature (%) | A-C-E | 48.395 | 35.221 | 0.216 | 0–0.428 | 0 | 0–0.292 | 0.784 | 0.572–1 |
| rMZ: 0.27 (0.027 0.483) | A-E * | 45.659 | 33.735 | 0.216 | 0–0.428 | 0.784 | 0.572–1 | ||
| rDZ: −0.066 (−0.381 0.263) | C-E | 46.984 | 35.060 | 0.141 | 0–0.327 | 0.859 | 0.673–1 | ||
| Left vertebral artery tortuosity (%) | A-C-E | 509.755 | 496.581 | 0.339 | 0–0.635 | 0.124 | 0–0.522 | 0.536 | 0.365–0.769 |
| rMZ: 0.409 (0.185 0.594) | A-E * | 507.207 | 495.284 | 0.476 | 0.263–0.638 | 0.524 | 0.362–0.737 | ||
| rDZ: 0.349 (0.018 0.611) | C-E | 508.125 | 496.202 | 0.386 | 0.2–0.545 | 0.614 | 0.455–0.8 | ||
| Right vertebral artery tortuosity (%) | A-C-E | 490.434 | 477.260 | 0.557 | 0.043–0.711 | 0 | 0–0.391 | 0.443 | 0.289–0.659 |
| rMZ: 0.477 (0.248 0.655) | A-E * | 487.698 | 475.775 | 0.557 | 0.341–0.711 | 0.443 | 0.289–0.659 | ||
| rDZ: 0.281 (−0.048 0.556) | C-E | 492.061 | 480.138 | 0.385 | 0.199–0.544 | 0.615 | 0.456–0.801 | ||
| Left vertebral artery torsion (%) | A-C-E | -183.109 | -196.283 | 0.057 | 0–0.271 | 0 | 0–0.23 | 0.943 | 0.729–1 |
| rMZ: 0.078 (−0.167 0.316) | C-E | -185.738 | -197.662 | 0.039 | 0–0.233 | 0.961 | 0.767–1 | ||
| rDZ: −0.06 (−0.395 0.292) | E * | -188.263 | -198.997 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Right vertebral artery torsion (%) | A-C-E | -165.418 | -178.592 | 0 | 0–0.168 | 0 | 0–0.186 | 1 | 0.814–1 |
| rMZ: −0.1 (−0.336 0.149) | C-E | -168.154 | -180.078 | 0 | 0–0.186 | 1 | 0.814–1 | ||
| rDZ: 0.225 (−0.104 0.512) | E * | -170.829 | -181.563 | 1 | 1 |
| -2LL_Base | -2LL_Reduced | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basilar area | 242.4058 | 280.1872 | <0.001 |
| Basilar volume | 360.3536 | 401.4033 | <0.001 |
| Basilar diameter | 292.5449 | 330.3450 | <0.001 |
| Left VA curvature | 22.15288 | 37.39575 | 0.05 |
| Right VA curvature | 12.94010 | 39.96847 | <0.001 |
| Left VA diameter | 418.4466 | 435.5442 | 0.03 |
| Basilar length | 1144.393 | 1165.349 | 0.01 |
| Model | Smoking (Binary) | Height (cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Left VA diameter | 0.22 (0.002, 0.435) | Not significant |
| Basilar diameter | 0.212 (0.049, 0.375) | 0.025 (0.012, 0.037) |
| Basilar volume | Not significant | 0.03 (0.015, 0.045) |
| Basilar area | 0.188 (0.043, 0.332) | 0.022 (0.011, 0.033) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szalontai, L.; Jokkel, Z.; Horvath, T.; Piroska, M.; Forgo, B.; Olah, C.; Kostyal, L.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Tarnoki, A.D. Are the Morphological Indices of the Vertebrobasilar System Heritable? A Twin Study Based on 3D Reconstructed Models. Medicina 2021, 57, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57020127
Szalontai L, Jokkel Z, Horvath T, Piroska M, Forgo B, Olah C, Kostyal L, Tarnoki DL, Tarnoki AD. Are the Morphological Indices of the Vertebrobasilar System Heritable? A Twin Study Based on 3D Reconstructed Models. Medicina. 2021; 57(2):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57020127
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzalontai, Laszlo, Zsofia Jokkel, Tamas Horvath, Marton Piroska, Bianka Forgo, Csaba Olah, Laszlo Kostyal, David L. Tarnoki, and Adam D. Tarnoki. 2021. "Are the Morphological Indices of the Vertebrobasilar System Heritable? A Twin Study Based on 3D Reconstructed Models" Medicina 57, no. 2: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57020127
APA StyleSzalontai, L., Jokkel, Z., Horvath, T., Piroska, M., Forgo, B., Olah, C., Kostyal, L., Tarnoki, D. L., & Tarnoki, A. D. (2021). Are the Morphological Indices of the Vertebrobasilar System Heritable? A Twin Study Based on 3D Reconstructed Models. Medicina, 57(2), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57020127









