Prognosis of Subcutaneous Mastectomy for Special Types of Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Surgical Treatment
2.2. Pathological Analysis
2.3. Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Prognosis between IDC and STBC
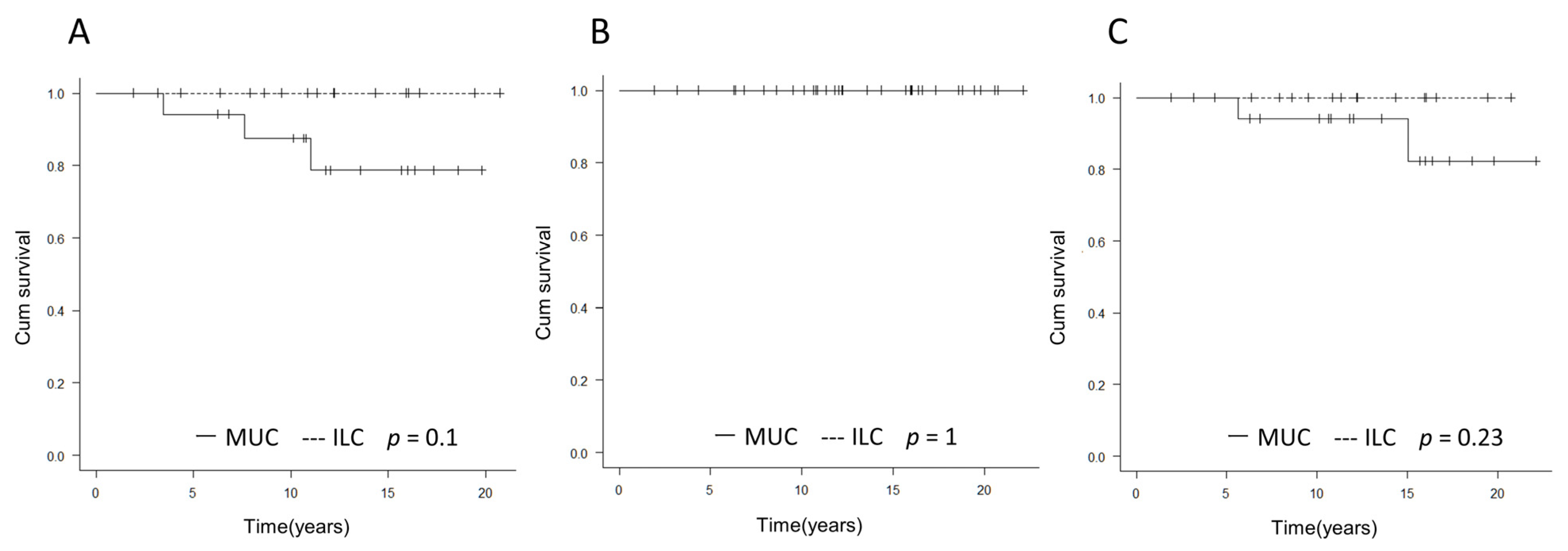
3.2. Comparison of Prognosis between MUC and ILC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanec, Z.; Žic, R.; Budi, S.; Stanec, S.; Milanovic, R.; Vlajcic, Z.; Roje, Ž.; Rudman, F.; Martic, K.; Held, R.; et al. Skin and nipple-areola complex sparing mastectomy in breast cancer patients: 15-year experience. Ann Plast. Surg. 2014, 73, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missana, M.C.; Laurent, I.; Germain, M.; Lucas, S.; Barreau, L. Long-term oncological results after 400 skin-sparing mastectomies. J. Visc. Surg. 2013, 150, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, J.D.; Salibian, A.A.; Lee, J.; Harris, K.; Axelrod, D.M.; Guth, A.A.; Shapiro, R.L.; Schnabel, F.R.; Karp, N.S.; Choi, M. Oncologic Trends, Outcomes, and Risk Factors for Locoregional Recurrence: An Analysis of Tumor-to-Nipple Distance and Critical Factors in Therapeutic Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, J.D.; Salibian, A.A.; Lee, J.; Harris, K.; Axelrod, D.M.; Guth, A.A.; Shapiro, R.L.; Schnabel, F.R.; Karp, N.S.; Choi, M. Equivalent survival after nipple-sparing compared to non-nipple-sparing mastectomy: Data from California, 1988–2013. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 160, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Breast Tumours; WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, Ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019; pp. 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, N.H.G.M.; Van Esser, S.; Van Den Bosch, M.A.A.J.; Storm, R.K.; Plaisier, P.W.; Van Dalen, T.; Diepstraten, S.C.E.; Weits, T.; Westenend, P.J.; Stapper, G.; et al. Preoperative MRI and surgical management in patients with nonpalpable breast cancer: The Monet-Randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.M.; Loo, C.E.; Wobbes, T.; Bult, P.; Barentsz, J.O.; Gilhuijs, K.G.; Boetes, C. The impact of preoperative breast MRI on the re-excision rate in invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 119, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luini, A.; Aguilar, M.; Gatti, G.; Fasani, R.; Botteri, E.; Brito, J.A.D.; Maisonneuve, P.; Vento, A.R.; Viale, G. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast, an unusual disease with worse prognosis: The experience of the European Institute of Oncology and review of the literature. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 101, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jung, S.-Y.; Ro, J.Y.; Kwon, Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Park, I.H.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, H.S.; et al. Metaplastic breast cancer: Clinicopathological features and its prognosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirot, F.; Chaltiel, D.; Lakhdar, A.B.; Mathieu, M.C.; Rimareix, F.; Conversano, A. Squamous cell carcinoma of the breast, are there two entities with distinct prognosis? A series of 39 patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, J.D.; Gospodararowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C. Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 8th ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda, H.; Akiyama, F.; Kurosumi, M.; Sakamoto, G.; Watanabe, T. Establishment of histological criteria for high-risk node-negative breast carcinoma for a multi-institutional randomized clinical trial of adjuvant therapy. Japan National Surgical Adjuvant Study of Breast Cancer (NSAS-BC) Pathology Section. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 28, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giacalone, P.L.; Rathat, G.; Daures, J.P.; Benos, P.; Azria, D.; Rouleau, C. New concept for immediate breast reconstruction for invasive cancers: Feasibility, oncological safety and esthetic outcome of post-neoadjuvant therapy immediate breast reconstruction versus delayed breast reconstruction: A prospective pilot study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 122, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.M.; Paik, H.-J.; Park, S.; Yi, H.W.; Nam, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.K.; Yu, J.; Bae, S.Y.; Lee, J.E. Oncologic Outcomes after Immediate Breast Reconstruction following Total Mastectomy in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Matched Case-Control Study. J. Breast Cancer 2017, 20, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livi, L.; Paiar, F.; Meldolesi, E.; Talamonti, C.; Simontacchi, G.; Detti, B.; Salerno, S.; Bianchi, S.; Cardona, G.; Biti, G.P. Tubular carcinoma of the breast: Outcome and loco-regional recurrence in 307 patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 31, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, T.; Abi Raad, R.; Goldberg, S.; Assaad, S.I.; Gadd, M.; Smith, B.L.; Powell, S.N.; Taghian, A.G. Tubular carcinoma of the breast: A retrospective analysis and review of the literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005, 93, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestalozzi, B.C.; Zahrieh, D.; Mallon, E.; Gusterson, B.A.; Price, K.N.; Gelber, R.D.; Holmberg, S.B.; Lindtner, J.; Snyder, R.; Thürlimann, B.; et al. Distinct clinical and prognostic features of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: Combined results of 15 International Breast Cancer Study Group clinical trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3006–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvieto, E.; Maiorano, E.; Bottiglieri, L.; Maisonneuve, P.; Rotmensz, N.; Galimberti, V.; Luini, A.; Brenelli, F.; Gatti, G.; Viale, G. Clinicopathologic characteristics of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: Results of an analysis of 530 cases from a single institution. Cancer 2008, 113, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomone, D.S.; Juan, G.; Eli, A. A retrospective review with long term follow up of 11,400 cases of pure mucinous breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 111, 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.Y.; Choi, M.-Y.; Cho, D.H.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, S.J.; Yang, J.H. Mucinous carcinoma of the breast in comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma: Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis. J. Breast Cancer 2011, 14, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Total (254) | IDC (211) | STBC (43) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean) | 26–72 (46) | 26–72 (45) | 31–64 (48) | ||
| Type of subcutaneous mastectomy | Skin sparing mastectomy | 166 | 145 | 21 | 1 |
| Nipple sparing mastectomy | 88 | 75 | 13 | ||
| Operation on axillary lymph nodes | Sentinel Lymph node biopsy | 129 | 113 | 16 | 0.493 |
| Sentinel Lymph node biopsy → Axillary lymph node dissection | 45 | 37 | 8 | ||
| Axillary lymph node dissection | 80 | 70 | 10 | ||
| Reconstruction method | TRAM/VRAM | 31 | 26 | 5 | 0.623 |
| DIEP | 43 | 38 | 5 | ||
| LD | 63 | 54 | 9 | ||
| TE | 117 | 102 | 15 | ||
| Post mastectomy irradiation | No | 247 | 215 | 32 | 0.338 |
| Yes | 7 | 5 | 2 | ||
| Histological type | Invasive ductal carcinoma | 211 | 211 | - | - |
| Special type | 43 | - | 43 | ||
| Mucinous carcinoma | 17 | - | 17 | ||
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 17 | - | 17 | ||
| Apocrine carcinoma | 6 | - | 6 | ||
| Tubular carcinoma | 1 | - | 1 | ||
| Invasive micropapillary carcinoma | 2 | - | 2 | ||
| Tumor size | 1 | 150 | 137 | 13 | 0.0651 |
| 2 | 94 | 78 | 16 | ||
| 3 | 10 | 5 | 5 | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | No | 179 | 155 | 24 | 0.856 |
| Yes | 75 | 65 | 10 | ||
| Nuclear grade | 1 | 143 | 113 | 30 | 0.0004 |
| 2 | 59 | 55 | 4 | ||
| 3 | 52 | 52 | 0 | ||
| Estrogen receptor | Positive | 223 | 192 | 31 | 0.441 |
| Negative | 31 | 28 | 3 | ||
| HER2 | Positive | 20 | 19 | 1 | 1 |
| Negative | 234 | 201 | 33 | ||
| Lymphatic vessel invasion | Positive | 36 | 32 | 4 | 0.811 |
| Negative | 218 | 188 | 30 | ||
| Blood vessel invasion | Positive | 17 | 16 | 1 | 0.32 |
| Negative | 237 | 204 | 33 | ||
| Adjuvant chemotherapy | No | 191 | 164 | 27 | 1 |
| Yes | 63 | 56 | 7 | ||
| Distant Metastasis | No | 228 | 197 | 31 | 0.586 |
| Yes | 26 | 23 | 3 | ||
| Survival | Alive | 233 | 199 | 34 | 0.03 |
| Dead | 21 | 21 | 0 | ||
| Local Recurrence | No | 237 | 205 | 32 | 0.745 |
| Yes | 17 | 15 | 2 | ||
| Characteristics | Total (34) | Mucinous Carcinoma (17) | Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (17) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean) | 31–64 (48) | 31–62 (45) | 38–64 (50) | - | |
| Type of subcutaneous mastectomy | Skin sparing mastectomy | 21 | 7 | 14 | 0.0324 |
| Nipple sparing mastectomy | 13 | 10 | 3 | ||
| Operation on axillary lymph nodes | Sentinel Lymph node biopsy | 16 | 8 | 8 | 0.18 |
| Sentinel Lymph node biopsy → Axillary lymph node dissection | 8 | 2 | 6 | ||
| Axillary lymph node dissection | 10 | 7 | 3 | ||
| Reconstruction method | TRAM/VRAM | 5 | 2 | 3 | 0.223 |
| DIEP | 5 | 1 | 4 | ||
| LD | 9 | 7 | 2 | ||
| TE | 15 | 7 | 8 | ||
| Post mastectomy irradiation | No | 32 | 17 | 15 | 0.485 |
| Yes | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Pure/Mixed type | Pure | 19 | 7 | 12 | 0.166 |
| Mixed | 15 | 10 | 5 | ||
| Tumor size | 1 | 13 | 6 | 7 | 0.0262 |
| 2 | 16 | 11 | 5 | ||
| 3 | 5 | 0 | 5 | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | No | 24 | 14 | 10 | 0.259 |
| Yes | 10 | 3 | 7 | ||
| Nuclear grade | 1 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Estrogen receptor | Positive | 31 | 14 | 17 | 0.227 |
| Negative | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| HER2 | Positive | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Negative | 33 | 16 | 17 | ||
| Lymphatic vessel invasion | Positive | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Negative | 30 | 15 | 15 | ||
| Blood vessel invasion | Positive | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Negative | 33 | 17 | 16 | ||
| Adjuvant chemotherapy | No | 27 | 16 | 11 | 0.0854 |
| Yes | 7 | 1 | 6 | ||
| Distant Metastasis | No | 31 | 14 | 17 | 0.227 |
| Yes | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Survival | Alive | 34 | 17 | 17 | 1 |
| Dead | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Local Recurrence | No | 32 | 15 | 17 | 0.485 |
| Yes | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakagawa, T.; Oda, G.; Mori, H.; Uemura, N.; Onishi, I.; Sagawa, N.; Fujioka, T.; Mori, M.; Kubota, K.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Prognosis of Subcutaneous Mastectomy for Special Types of Breast Cancer. Medicina 2022, 58, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010112
Nakagawa T, Oda G, Mori H, Uemura N, Onishi I, Sagawa N, Fujioka T, Mori M, Kubota K, Ishikawa T, et al. Prognosis of Subcutaneous Mastectomy for Special Types of Breast Cancer. Medicina. 2022; 58(1):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010112
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakagawa, Tsuyoshi, Goshi Oda, Hiroki Mori, Noriko Uemura, Iichiro Onishi, Noriko Sagawa, Tomoyuki Fujioka, Mio Mori, Kazunori Kubota, Toshiaki Ishikawa, and et al. 2022. "Prognosis of Subcutaneous Mastectomy for Special Types of Breast Cancer" Medicina 58, no. 1: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010112
APA StyleNakagawa, T., Oda, G., Mori, H., Uemura, N., Onishi, I., Sagawa, N., Fujioka, T., Mori, M., Kubota, K., Ishikawa, T., Okamoto, K., & Uetake, H. (2022). Prognosis of Subcutaneous Mastectomy for Special Types of Breast Cancer. Medicina, 58(1), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010112







