Difficult Biliary Stones: A Comprehensive Review of New and Old Lithotripsy Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanical Lithotripsy
3. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy
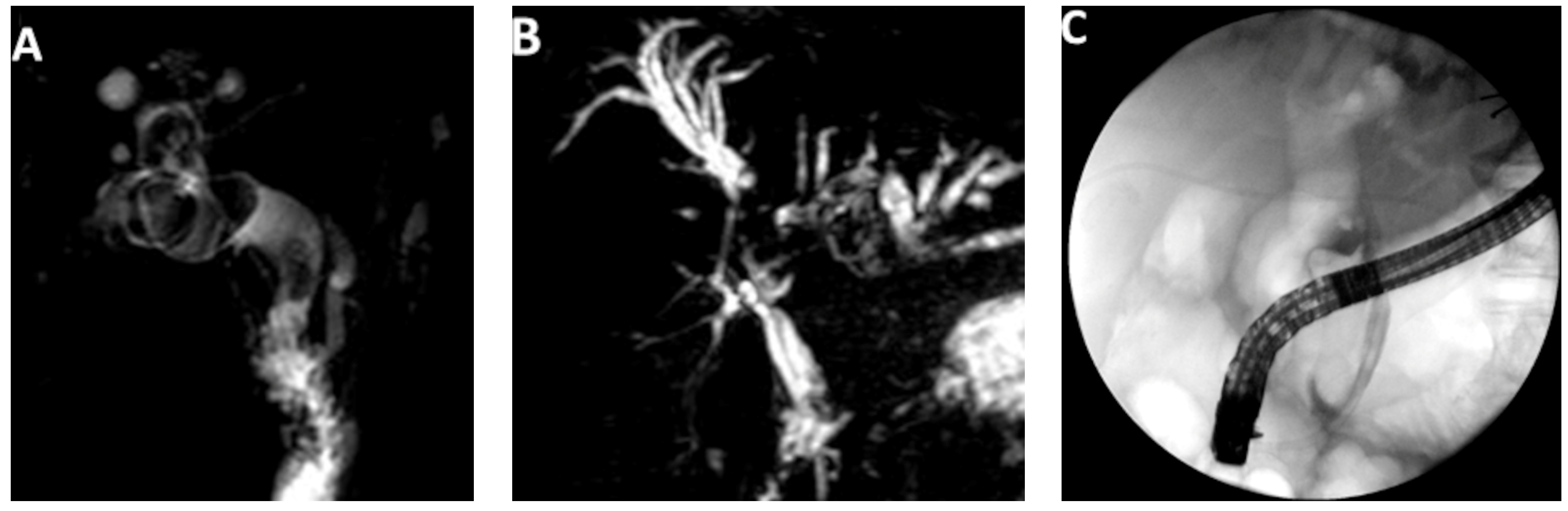
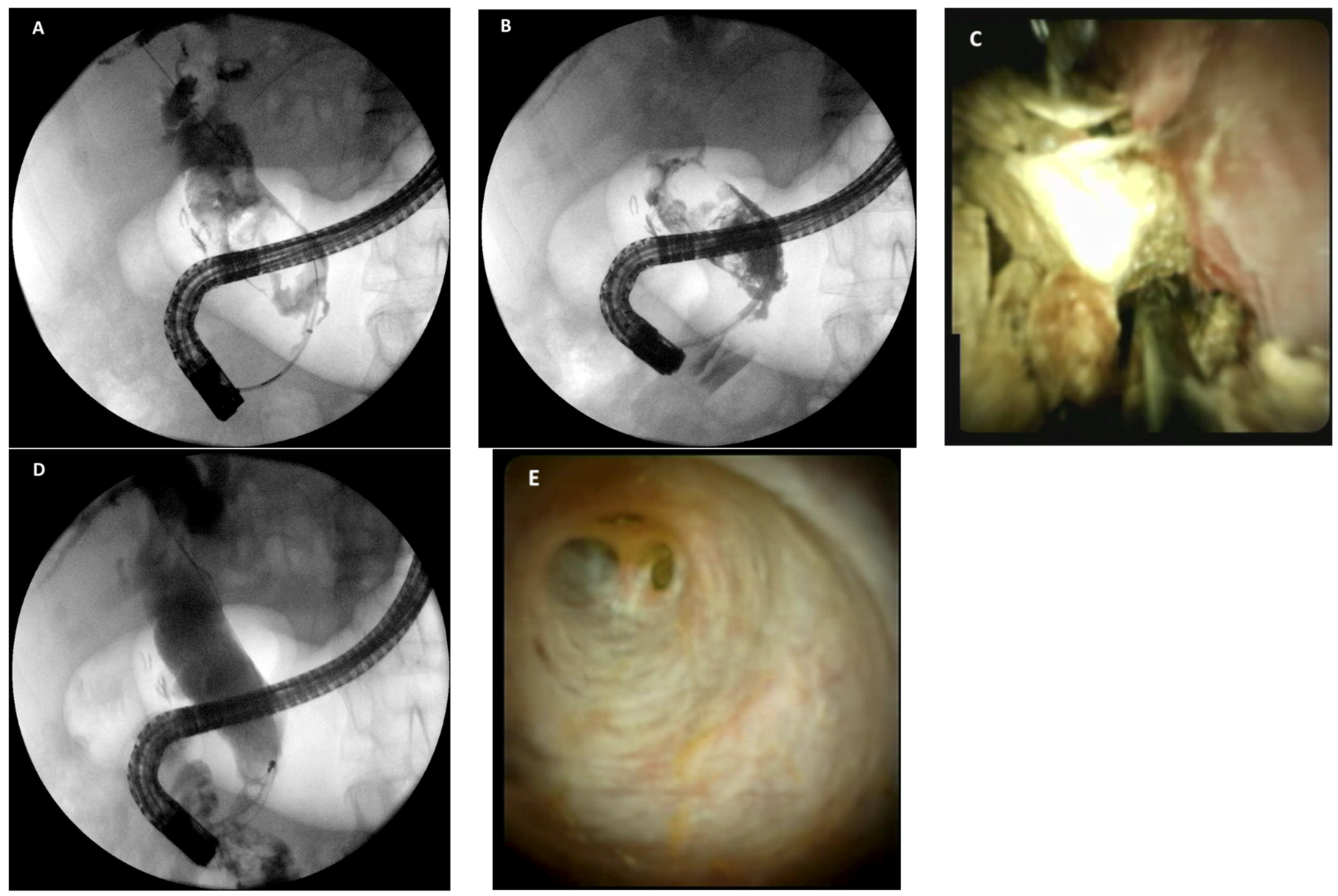
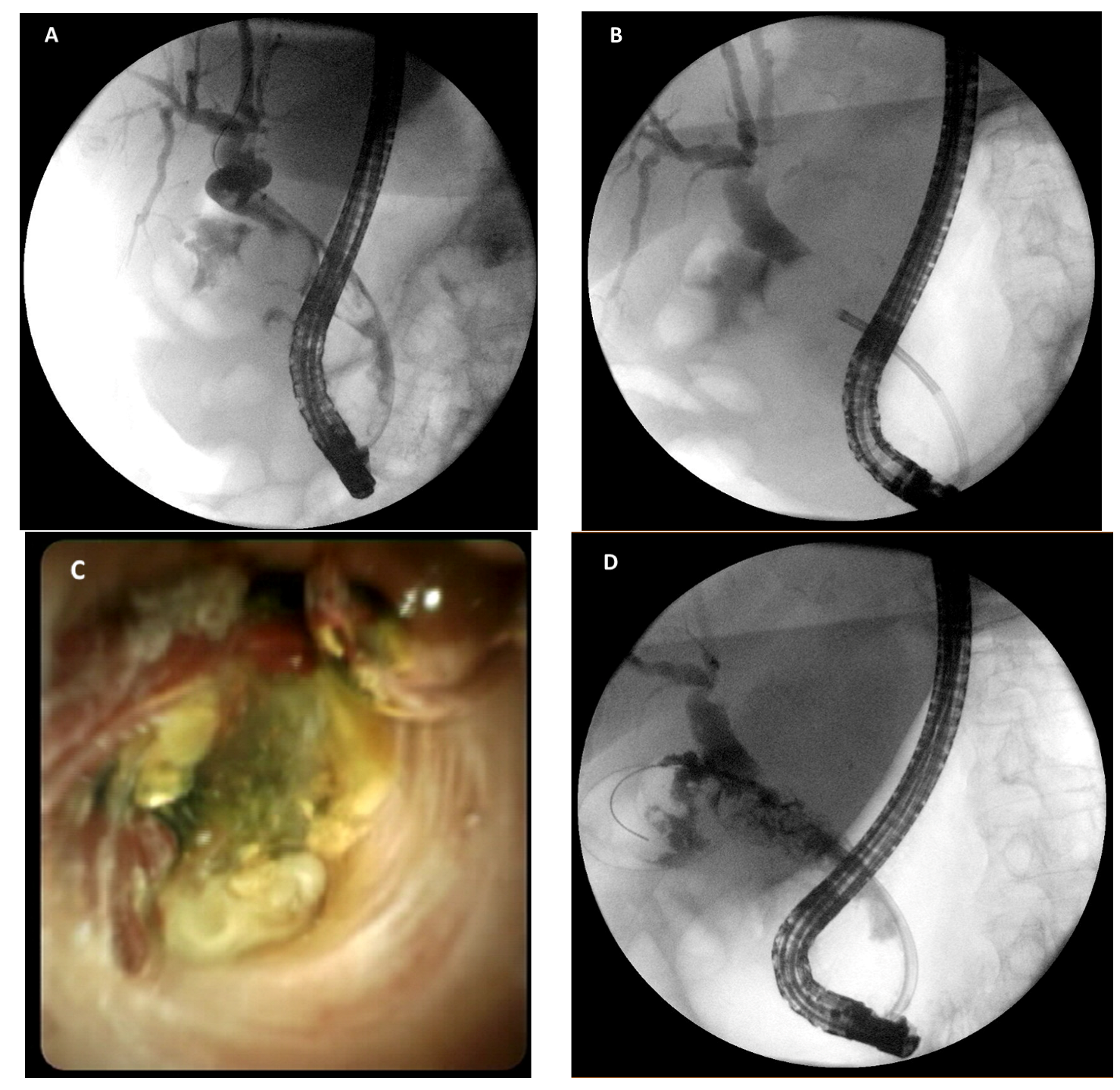
4. Cholangioscopy-Assisted Lithotripsy: The “New” Lithotripsy Technique
5. Percutaneous Bile Duct Stones Treatment
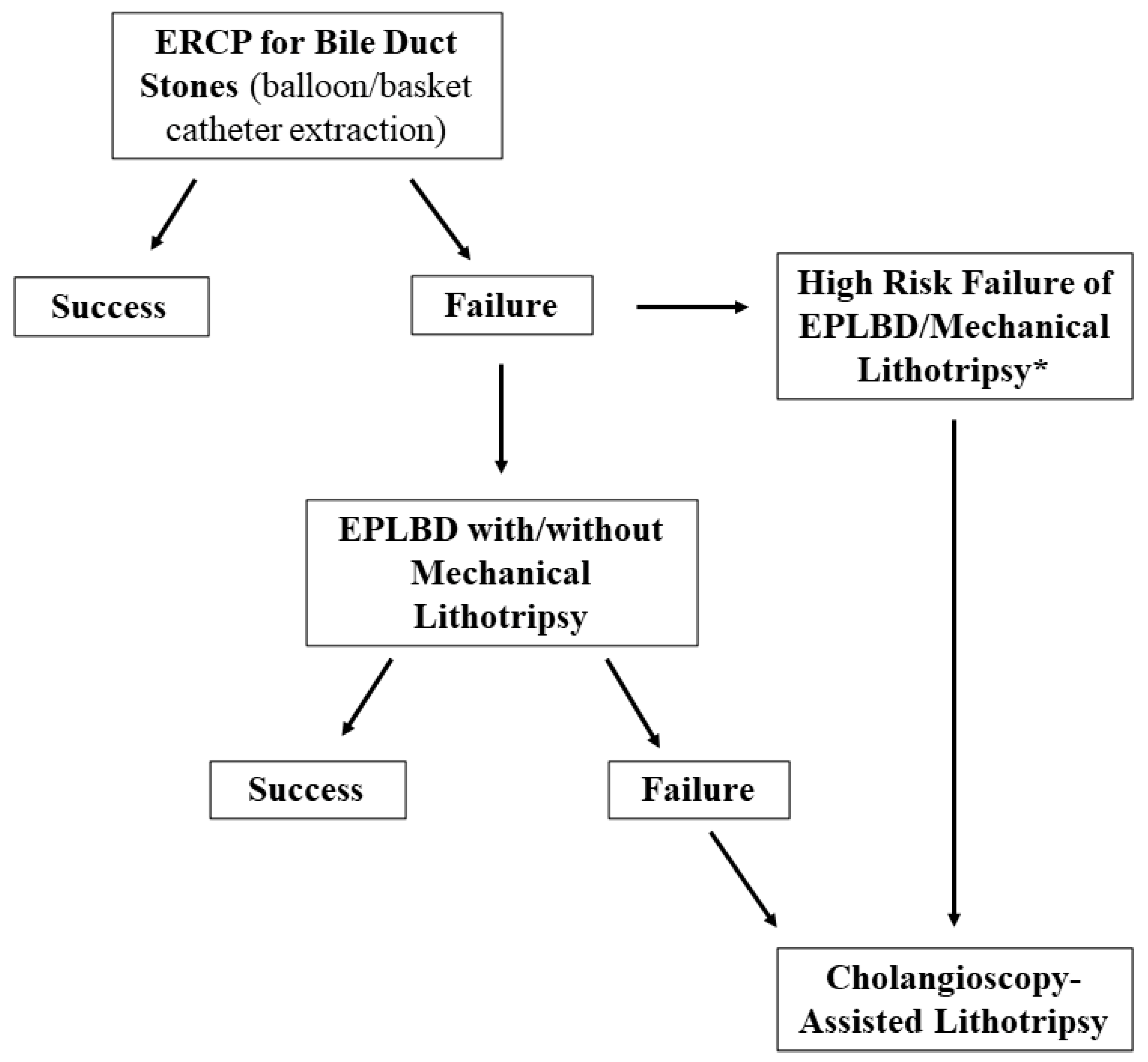
6. Different Approaches for Management of Difficult Biliary Stones
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peery, A.F.; Crockett, S.D.; Murphy, C.C.; Jensen, E.T.; Kim, H.P.; Egberg, M.D.; Lund, J.L.; Moon, A.M.; Pate, V.; Barnes, E.L.; et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2021. Gastroenterology, 2021; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stinton, L.M.; Myers, R.P.; Shaffer, E.A. Epidemiology of gallstones. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracie, W.A.; Ransohoff, D.F. The natural history of silent gallstones: The innocent gallstone is not a myth. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcsherry, C.K.; Ferstenberg, H.; Calhoun, W.F.; Lahman, E.; Virshup, M. The natural history of diagnosed gallstone disease in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. Ann. Surg. 1985, 202, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanzadeh, D.M.; Sørensen, L.T.; Jørgensen, T. A Prediction Rule for Risk Stratification of Incidentally Discovered Gallstones: Results From a Large Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 156–167.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwatari, H.; Kawakami, H.; Hisai, H.; Yane, K.; Onodera, M.; Eto, K.; Haba, S.; Okuda, T.; Ihara, H.; Kukitsu, T.; et al. Balloon catheter versus basket catheter for endoscopic bile duct stone extraction: A multicenter randomized trial. Endoscopy 2016, 48, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, N.; Yasuda, I.; Doi, S.; Iwashita, T.; Shimizu, M.; Mukai, T.; Nakashima, M.; Ban, T.; Kojima, I.; Matsuda, K.; et al. Prospective randomized study of endoscopic biliary stone extraction using either a basket or a balloon catheter: The BasketBall study. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manes, G.; Paspatis, G.; Aabakken, L.; Anderloni, A.; Arvanitakis, M.; Ah-Soune, P.; Barthet, M.; Domagk, D.; Dumonceau, J.-M.; Gigot, J.-F.; et al. Endoscopic management of common bile duct stones: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guideline. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 472–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, I.; Itoi, T. Recent advances in endoscopic management of difficult bile duct stones. Dig. Endosc. 2013, 25, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, U.; Bapaye, S.B.A.; Navarrete, A.M.C.; Bapaye, A.; Bohnacker, S.; Navarrete, C.; Maydeo, A.; Soehendra, N. Advances in therapeutic endoscopic treatment of common bile duct stones. World J. Surg. 1998, 22, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHenry, L.; Lehman, G. Difficult bile duct stones. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2006, 9, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderloni, A. Difficult common bile duct stones: Still “difficult” or just... “different”? Endoscopy 2020, 52, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauri, A.; Horton, R.C.; Davidson, B.R.; Burroughs, A.K.; Dooley, J.S. Endoscopic extraction of bile duct stones: Management related to stone size. Gut 1993, 34, 1718–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Park, D.I.; Cho, Y.K.; Sohn, C.I.; Jeon, W.K.; Kim, B.I.; Choi, S.H. Factors influencing the technical difficulty of endoscopic clearance of bile duct stones. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 66, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.R.; Parsi, M.A.; Aslanian, H.R.; Goodman, A.J.; Lichtenstein, D.R.; Melson, J.; Navaneethan, U.; Pannala, R.; Sethi, A.; Sullivan, S.A.; et al. Biliary and pancreatic lithotripsy devices. VideoGIE 2018, 3, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.-H.; Chu, C.-H.; Wang, T.-E.; Chen, M.-J.; Lin, C.C. Outcome of simple use of mechanical lithotripsy of difficult common bile duct stones. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Tandon, R.K.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K.; Batra, Y. Predictors of unsuccessful mechanical lithotripsy and endoscopic clearance of large bile duct stones. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2004, 59, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbi, D.; Van Os, E.C.; Aberger, F.J.; Derfus, G.A.; Erickson, R.; Meier, P.; Nelson, U.; Nelson, P.; Shaw, M.; Gostout, C.J. Clinical application of a new disposable lithotripter: A prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1999, 49, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolletta, L.; Costamagna, G.; Bianco, M.A.; Rotondano, G.; Piscopo, R.; Mutignani, M.; Marmo, R. Endoscopic mechanical lithotripsy of difficult common bile duct stones. Br. J. Surg. 1997, 84, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Hintze, R.E.; Adler, A.; Veltzke, W. Outcome of mechanical lithotripsy of bile duct stones in an unselected series of 704 patients. Hepatogastroenterology 1996, 43, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, J.; Sivak, M.V., Jr. Mechanical lithotripsy of large common bile duct stones. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 1993, 60, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.J.; Mackie, R.D.; Moore, J.P.; Dorsher, P.J.; Freeman, M.L.; Meier, P.B.; Potter, T.; Hutton, S.W.; Vennes, J.A. Results of a multicenter trial using a mechanical lithotripter for the treatment of large bile duct stones. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 88, 730–733. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, J.K.; Yoon, W.J.; Lee, J.K.; Kon Ryu, J.; Kim, Y.T.; Bum Yoon, Y.B. How to predict the outcome of endoscopic mechanical lithotripsy in patients with difficult bile duct stones? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Howell, U.A.; Carr-Locke, D.; Wilcox, C.M.; Chak, A.; Raijman, I.; Watkins, J.L.; Schmalz, M.J.; Geenen, J.E.; Catalano, M.F. Mechanical lithotripsy of pancreatic and biliary stones: Complications and available treatment options collected from expert centers. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoz, G.; Tekesin, O.; Ozutemiz, A.O.; Gunsar, F. Biliary sphincterotomy plus dilation with a large balloon for bile duct stones that are difficult to extract. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2003, 57, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, D.K.; Reddy, N.D.; Rerknimitr, R.; Ratanachu-Ek, Y.; Khor, C.J.L.; Itoi, T.; Yasuda, I.; et al. International consensus guidelines for endoscopic papillary large-balloon dilation. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.G.; Cheon, Y.K.; Cho, Y.D.; Moon, J.H.; Park, D.H.; Lee, T.H.; Choi, H.J.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, M.S. Small sphincterotomy combined with endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation versus sphincterotomy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4298–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, A.Y.B.; Cheung, F.K.Y.; Hu, B.; Pan, Y.M.; Lai, L.H.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Wong, S.K.H.; Chan, F.K.L.; Lau, J.Y.W. Randomized trial of endoscopic sphincterotomy with balloon dilation versus endoscopic sphincterotomy alone for removal of bile duct stones. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 341–345.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Pang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Guo, R.; Zhai, H.; Dong, Y.; Jia, X. Dilation-Assisted Stone Extraction: An Alternative Method for Removal of Common Bile Duct Stones. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 59, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Lei, S.; Gong, W.; Gu, H.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; Zhi, F. A Preliminary Comparison of Endoscopic Sphincterotomy, Endoscopic Papillary Large Balloon Dilation, and Combination of the Two in Endoscopic Choledocholithiasis Treatment. Med Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karsenti, D.; Coron, E.; Vanbiervliet, G.; Privat, J.; Kull, E.; Bichard, P.; Perrot, B.; Quentin, V.; Duriez, A.; Cholet, F.; et al. Complete endoscopic sphincterotomy with vs. without large-balloon dilation for the removal of large bile duct stones: Randomized multicenter study. Endoscopy 2017, 49, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madhoun, M.F.; Wani, S.; Hong, S.; Tierney, W.M.; Maple, J.T. Endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation reduces the need for mechanical lithotripsy in patients with large bile duct stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diag. Ther. Endosc. 2014, 2014, 309618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.M.; Hu, B. Endoscopic sphincterotomy plus large-balloon dilation vs. endoscopic sphincterotomy for choledocholithiasis: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 9453–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.J.; Kim, T.N. Prospective comparative study of endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation and endoscopic sphincterotomy for removal of large bile duct stones in patients above 45 years of age. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.C.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, S.G.; Kim, S.S.; Shin, S.J.; Lee, K.M.; Yoo, B.M. Endoscopic large-balloon dilation alone versus endoscopic sphincterotomy plus large-balloon dilation for the treatment of large bile duct stones. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, M.A.; Abdelshafy, M.; Ahmed, M.Y.; Rezk, A.G.; Taha, A.M.; Hussein, H.M. Endoscopic Papillary Large Balloon Dilation Versus Endoscopic Sphincterotomy for Retrieval of Large Choledocholithiasis: A Prospective Randomized Trial. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2017, 27, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, H.; Kawahata, S.; Mukai, T.; Doi, S.; Iwashita, T.; Ban, T.; Ito, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Hayashi, T.; Sasahira, N.; et al. Multicenter randomized trial of endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation without sphincterotomy versus endoscopic sphincterotomy for removal of bile duct stones: MARVELOUS trial. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsinelos, P.; Kountouras, J.; Paroutoglou, G.; Chatzimavroudis, G.; Zavos, C. Combination of endoprostheses and oral ursodeoxycholic acid or placebo in the treatment of difficult to extract common bile duct stones. Dig. Liver Dis. 2008, 40, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Moon, J.H.; Koo, H.C.; Kang, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Jeong, S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, H.G. Effect of biliary stenting combined with ursodeoxycholic acid and terpene treatment on retained common bile duct stones in elderly patients: A multicenter study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2418–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, A.; Nakayama, Y.; Kajiyama, M.; Kato, N.; Kamijima, T.; Graham, D.Y.; Tanaka, N. Biliary stenting in the management of large or multiple common bile duct stones. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 1200–1203.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Han, J.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.M.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, S.-J. Is the addition of choleretic agents in multiple double-pigtail biliary stents effective for difficult common bile duct stones in elderly patients? A prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.D.; Zhu, Q.H.; Huang, Q.K. Endoscopic sphincterotomy plus endoprostheses in the treatment of large or multiple common bile duct stones. Dig. Endosc. 2011, 23, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Hawes, R.; Lawrence, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lv, W. Analysis of plastic stents in the treatment of large common bile duct stones in 45 patients. Dig. Endosc. 2011, 23, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.C.; Ng, E.K.; Chung, S.C.; Lai, C.W.; Lau, J.Y.; Sung, J.J.; Leung, J.W.C.; Li, A.K.C. Common bile duct stones become smaller after endoscopic biliary stenting. Endoscopy 1998, 30, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, D.W.; Paik, W.H.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.K.; Ryu, J.K.; Kim, Y.-T. Factors associated with complete clearance of difficult common bile duct stones after temporary biliary stenting followed by a second ERCP: A multicenter, retrospective, cohort study. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veld, J.V.; Van Huijgevoort, N.C.M.; Boermeester, M.A.; Besselink, M.G.; Van Delden, O.M.; Fockens, P.; Van Hooft, J.E. A systematic review of advanced endoscopy-assisted lithotripsy for retained biliary tract stones: Laser, electrohydraulic or extracorporeal shock wave. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, H.; Zillinger, C.; Born, P.; Ott, R.; Allescher, H.; Rösch, T.; Classen, M. Randomized study of intracorporeal laser lithotripsy versus extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy for difficult bile duct stones. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1998, 47, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobs, R.; Adamek, H.E.; Maier, M.; Krömer, M.; Benz, C.; Martin, W.R.; Riemann, J.F. Fluoroscopically guided laser lithotripsy versus extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for retained bile duct stones: A prospective randomised study. Gut 1997, 40, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertan, A. Treatment of gallstones by extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecinato, P.; Fuccio, L.; Azzaroli, F.; Lisotti, A.; Correale, L.; Hassan, C.; Buonfiglioli, F.; Cariani, G.; Mazzella, G.; Bazzoli, F.; et al. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for difficult common bile duct stones: A comparison between 2 different lithotripters in a large cohort of patients. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringali, A.; Lemmers, A.; Meves, V.; Terheggen, G.; Pohl, J.; Manfredi, G.; Häfner, M.; Costamagna, G.; Devière, J.; Neuhaus, H.; et al. Intraductal biliopancreatic imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) technology review. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderloni, A.; Fugazza, A.; Troncone, E.; Carrara, S.; Rovati, A.; Spaggiari, P.; Repici, A. Direct per-oral pancreatoscopy as a diagnostic tool for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2018, 27, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaerel, P.; Gevers, A.M.; De Bruecker, Y.; Sunaert, S.; Wilms, G. Stroke caused by cerebral air embolism during endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2003, 57, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiou, M.; Raftopoulos, S.; Antonio Chirinos, J.; May, G.R. Air embolism complicated by left hemiparesis after direct cholangioscopy with an intraductal balloon anchoring system. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 75, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J.; Stollberger, C.; Bastovansky, A. Cardiac and cerebral air embolism from endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, Y.; Okano, N.; Ito, K.; Suzuki, T.; Mimura, T. Effectiveness of peroral cholangioscopy and narrow band imaging for endoscopically diagnosing the bile duct cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2009, 21 (Suppl. 1), S101–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsi, M.A.; Stevens, T.; Collins, J.; Vargo, J.J. Utility of a prototype peroral video cholangioscopy system with narrow-band imaging for evaluation of biliary disorders (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.K.; Pleskow, D.K. SpyGlass single-operator peroral cholangiopancreatoscopy system for the diagnosis and therapy of bile-duct disorders: A clinical feasibility study (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 65, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komanduri, S.; Thosani, N.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Aslanian, H.R.; Enestvedt, B.K.; Manfredi, M.; Maple, J.T.; Navaneethan, U.; Pannala, R.; Parsi, M.A.; et al. Cholangiopancreatoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, J.H.; Cha, S.W.; Ryu, C.B.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, S.J.; Cheon, Y.K.; Cho, Y.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, M.S.; et al. Endoscopic treatment of retained bile-duct stones by using a balloon catheter for electrohydraulic lithotripsy without cholangioscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2004, 60, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberger, J.; Tex, S.; Maiss, J.; Hahn, E. Management of difficult common bile duct stones. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 13, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpimanmas, S.; Chantawibul, S.; Ratanachu-Ek, T. Pulse dye laser lithotripsy for large biliary tract stones. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2000, 83, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blind, P.J.; Lundmark, M. Management of bile duct stones: Lithotripsy by laser, electrohydraulic, and ultrasonic techniques. Report of a series and clinical review. Eur. J. Surg. 1998, 164, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejleh, M.P.; Thaker, A.M.; Kim, S.; Muthusamy, V.R.; Sedarat, A. Cholangioscopy-guided retrieval basket and snare for the removal of biliary stones and retained prostheses. VideoGIE 2019, 4, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.H.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, Y.N.; Yoo, H.W.; Yang, J.K.; Cha, S.W.; Cho, Y.D.; Park, S.H. A Preliminary Study on the Efficacy of Single-Operator Cholangioscopy with a New Basket for Residual Stone Retrieval after Mechanical Lithotripsy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, N.; Nelles, S.E.; Haber, G.B.; Kim, Y.-I.; Kortan, P.K. Electrohydraulic lithotripsy in 111 patients: A safe and effective therapy for difficult bile duct stones. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 2330–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piraka, C.; Shah, R.J.; Awadallah, N.S.; Langer, D.A.; Chen, Y.K. Transpapillary cholangioscopy-directed lithotripsy in patients with difficult bile duct stones. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swahn, F.; Edlund, G.; Enochsson, L.; Svensson, C.; Lindberg, B.; Arnelo, U. Ten years of Swedish experience with intraductal electrohydraulic lithotripsy and laser lithotripsy for the treatment of difficult bile duct stones: An effective and safe option for octogenarians. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korrapati, P.; Ciolino, J.; Wani, S.; Shah, J.; Watson, R.; Muthusamy, V.R.; Klapman, J.; Komanduri, S. The efficacy of peroral cholangioscopy for difficult bile duct stones and indeterminate strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Int. Open 2016, 4, E263–E275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mccarty, T.R.; Gulati, R.; Rustagi, T. Efficacy and safety of peroral cholangioscopy with intraductal lithotripsy for difficult biliary stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J.; Sahakian, A.; Ko, C.; Jayaram, P.; Lane, C.; Yu, C.Y.; Kankotia, R.; Laine, L. Randomized trial of cholangioscopy-guided laser lithotripsy versus conventional therapy for large bile duct stones (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maydeo, A.P.; Rerknimitr, R.; Lau, J.Y.; Aljebreen, A.; Niaz, S.K.; Itoi, T.; Ang, T.L.; Reichenberger, J.; Seo, D.W.; Ramchandani, M.K.; et al. Cholangioscopy-guided lithotripsy for difficult bile duct stone clearance in a single session of ERCP: Results from a large multinational registry demonstrate high success rates. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokemeyer, A.; Gerges, C.; Lang, D.; Bettenworth, D.; Kabar, I.; Schmidt, H.; Neuhaus, H.; Ullerich, H.; Lenze, F.; Beyna, T. Digital single-operator video cholangioscopy in treating refractory biliary stones: A multicenter observational study. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maydeo, A.; Kwek, B.E.A.; Bhandari, S.; Bapat, M.; Dhir, V. Single-operator cholangioscopy-guided laser lithotripsy in patients with difficult biliary and pancreatic ductal stones (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, O.I.B.; Bekkali, N.L.; Raijman, I.; Sturgess, R.; Sejpal, D.V.; Aridi, H.D.; Sherman, S.; Shah, R.J.; Kwon, R.S.; Buxbaum, J.L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Digital Single-Operator Cholangioscopy for Difficult Biliary Stones. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxbaum, J.L.; Fehmi, S.M.A.; Sultan, S.; Fishman, D.S.; Qumseya, B.J.; Cortessis, V.K.; Schilperoort, H.; Kysh, L.; Matsuoka, L.; Yachimski, P.; et al. ASGE guideline on the role of endoscopy in the evaluation and management of choledocholithiasis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 1075–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Beckingham, I.; El Sayed, G.; Gurusamy, K.; Sturgess, R.; Webster, G.; Young, T. Updated guideline on the management of common bile duct stones (CBDS). Gut 2017, 66, 765–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pemberton, M.; Wells, A.D. The Mirizzi syndrome. Postgrad. Med. J. 1997, 73, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Siwo, E.A.; Khu, M.; Tian, Y. Current trends in the management of Mirizzi Syndrome: A review of literature. Medicine 2018, 97, e9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yuan, T.; Sun, X.; Zheng, M. A Minimally Invasive Strategy for Mirizzi Syndrome Type II: Combined Endoscopic With Laparoscopic Approach. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan. Tech. 2016, 26, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Cai, W.; Qin, M. Combined laparoscopic and endoscopic treatment for Mirizzi syndrome. Hepatogastroenterology 2011, 58, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi, T.; Sakai, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Ishihara, T.; Yokosuka, O. Long-term follow-up after peroral cholangioscopy-directed lithotripsy in patients with difficult bile duct stones, including Mirizzi syndrome: An analysis of risk factors predicting stone recurrence. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 25, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, H.; Bseiso, B.; Al-Salem, A. Successful laser lithotripsy using peroral SpyGlass cholangioscopy in a patient with Mirizzi syndrome. Endoscopy 2011, 43, E166–E167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhandari, S.; Bathini, R.; Sharma, A.; Maydeo, A. Usefulness of single-operator cholangioscopy-guided laser lithotripsy in patients with Mirizzi syndrome and cystic duct stones: Experience at a tertiary care center. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, H.K.; Park, C.; Kim, T.H. Minimally Invasive Approach Using Digital Single-Operator Peroral Cholangioscopy-Guided Electrohydraulic Lithotripsy and Endoscopic Nasogallbladder Drainage for the Management of HighGrade Mirizzi Syndrome. Clin. Endosc. 2021, 54, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binmoeller, K.F.; Thonke, F.; Soehendra, N. Endoscopic treatment of Mirizzi’s syndrome. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1993, 39, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.; Popa, D.; Neumann, H.; Wilcox, C.M.; Mönkemüller, K. ERCP with the overtube-assisted enteroscopy technique: A systematic review. Endoscopy 2014, 46, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mönkemüller, K.; Fry, L.C.; Bellutti, M.; Neumann, H.; Malfertheiner, P. ERCP with the double balloon enteroscope in patients with Roux-en-Y anastomosis. Surg. Endosc. 2009, 23, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.Y.; Song, T.J. Recent advances in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in Billroth II gastrectomy patients: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3091–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, H.A.; Venbrux, A.C.; Coleman, J.; Prescott, C.A.; Johnson, M.S.; Osterman, F.A., Jr.; Cameron, J.L. Intrahepatic stones. The transhepatic team approach. Ann. Surg. 1994, 219, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Ikeda, S.; Tanaka, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Kuroda, Y. Choledochoscopic electrohydraulic lithotripsy and lithotomy for stones in the common bile duct, intrahepatic ducts, and gallbladder. Ann. Surg. 1989, 210, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Li, X.; Jiang, P.; Jiang, Y.; Shuai, L.; He, Y.; Li, Z. Variations of ABCB4 and ABCB11 genes are associated with primary intrahepatic stones. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, W.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, J.K.; Song, B.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-T.; Yoon, Y.B. Long-term clinical outcomes of biliary cast syndrome in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplant. 2013, 19, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, K.S.; Chiang, H.J.; Shih, S.C. Limitations of percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy in the removal of complicated biliary calculi. World J. Surg. 1989, 13, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, T. Percutaneous Cholangioscopy for Management of Retained Biliary Tract Stones and Intrahepatic Stones. Endoscopy 1989, 21 (Suppl. 1), 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, K.R.; Falchuk, K.R.; Clouse, M.E. Biliary duct stones: Update on 54 cases after percutaneous transhepatic removal. Radiology 1989, 170, 999–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Jan, Y.Y.; Lee, T.Y. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy. Br. J. Surg. 1987, 74, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Seo, D.W.; Myung, S.J.; Park, E.T.; Lim, B.C.; Kim, H.J.; Yoo, K.S.; Park, H.J.; Joo, Y.H.; Kim, M.H.; et al. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic treatment for hepatolithiasis: An evaluation of long-term results and risk factors for recurrence. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 53, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.-H.; Tsai, C.-C.; Mo, L.-R.; Yang, C.-T.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Yau, M.-P.; Yueh, S.-K. Percutaneous choledochoscopic biliary tract stone removal: Experience in 645 consecutive patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 1993, 17, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okugawa, T.; Tsuyuguchi, T.; Ando, T.; Ishihara, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yugi, H.; Saisho, H. Peroral cholangioscopic treatment of hepatolithiasis: Long-term results. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 56, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Yang, J.C.; Yang, C.C.; Yeh, Y.H.; Chou, D.A.; Mo, L.R.; Yueh, S.K.; Nien, C.K. Long-term outcome of percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotomy for hepatolithiasis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, C.; Vázquez, A.G.; Tringali, A.; Verde, J.M.; Dertmann, T.; Houghton, E.; Cina, A.; Beyna, T.; Begnis, F.S.; Pizzicannella, M.; et al. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy using a single-operator cholangioscope (pSOC), a retrospective, observational, multicenter study. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 6724–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, H.; Beyna, T. Percutaneous single-operator video cholangioscopy using a novel short disposable endoscope: First clinical case with treatment of a complex biliary stone and inaccessible papilla after Roux-en-Y reconstructive surgery. VideoGIE 2021, 6, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, N.; Kahriman, G.; Mavili, E. Percutaneous transhepatic removal of bile duct stones: Results of 261 patients. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 35, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kint, J.F.; Bergh, J.E.V.D.; Van Gelder, R.E.; Rauws, E.A.; Gouma, D.J.; Van Delden, O.M.; Laméris, J.S. Percutaneous treatment of common bile duct stones: Results and complications in 110 consecutive patients. Dig. Surg. 2015, 32, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.Y.; Sutton, B.; Navaneethan, U.; Hawes, R.; Varadarajulu, S. Efficacy of Single-Operator Cholangioscopy-Guided Lithotripsy Compared With Large Balloon Sphincteroplasty in Management of Difficult Bile Duct Stones in a Randomized Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2349–2356.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angsuwatcharakon, P.; Kulpatcharapong, S.; Ridtitid, W.; Boonmee, C.; Piyachaturawat, P.; Kongkam, P.; Pareesri, W.; Rerknimitr, R. Digital cholangioscopy-guided laser versus mechanical lithotripsy for large bile duct stone removal after failed papillary large-balloon dilation: A randomized study. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzini, T.; Moura, R.N.; Bonifácio, P.; Luz, G.O.; De Souza, T.F.; Dos Santos, M.E.L.; Rodela, G.L.; Ide, E.; Herman, P.; Montagnini, A.L.; et al. Complex biliary stones management: Cholangioscopy versus papillary large balloon dilation-A randomized controlled trial. Endosc. Int. Open 2018, 6, E131–E138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Facciorusso, A.; Gkolfakis, P.; Ramai, D.; Tziatzios, G.; Lester, J.; Crinò, S.F.; Frazzoni, L.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Arvanitakis, M.; Blero, D.; et al. Endoscopic Treatment of Large Bile Duct Stones: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprez, P.H.; Durán, R.G.; Moreels, T.; Furneri, G.; Demma, F.; Verbeke, L.; Van der Merwe, S.; Laleman, W. The economic impact of using single-operator cholangioscopy for the treatment of difficult bile duct stones and diagnosis of indeterminate bile duct strictures. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrajhi, S.; Barkun, A.; Adam, V.; Callichurn, K.; Martel, M.; Brewer, O.; Khashab, M.A.; Forbes, N.; Almadi, M.A.; Chen, Y.I. Early cholangioscopy-assisted electrohydraulic lithotripsy in difficult biliary stones is cost-effective. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanidis, G.; Viazis, N.; Pleskow, D.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Theocharis, L.; Christodoulou, C.; Kotsikoros, N.; Giannousis, J.; Sgouros, S.; Rodias, M.; et al. Large balloon dilation vs. mechanical lithotripsy for the management of large bile duct stones: A prospective randomized study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Stone-related Factors
|
Bile Duct-related Factors
|
| Post-Surgical Anatomy (e.g., long biliary limbs) |
| Patient’s Clinical Conditions (e.g., severe acute cholangitis) |
| Low Experienced Endoscopist |
| Inadequate Setting (e.g., out-of-hours ERCP with non-dedicated staff) |
| Author, Year [Ref.] | No. of Centers | Techniques | Definition of Difficult Stones | No. of Patients | Success Rate | p | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stefanidis et al., 2011 [112] | 1 | Sphincterotomy + EPLBD vs. Mechanical Lithotripsy | Large > 12 mm | 45 45 | 44/45 (97.7%) 41/45 (91.1%) | 0.36 | 2/45 (4.4%) 9/45 (20%) |
| Franzini et al., 2017 [108] | 1 | SOC-EHL vs. Sphincterotomy + EPLBD | Multiple (>10), large >15 mm, above strictures, disproportion CBD/stone > 2 mm | 50 50 | 37/48 (77.1%) 36/50 (72%) | >0.05 | 2/48 (4.2%) 6/50 (12%) |
| Buxbaum et al., 2017 [71] | 1 | SOC-LL vs. Conventional Therapies | Large > 10 mm | 42 18 | 39/42 (92.9%) 12/18 (66.7%) | <0.01 | 4/42 (9.5%) 2/18 (11.1%) |
| Angsuwatchakaron et al., 2019 [107] | 2 | SOC-LL vs. Mechanical Lithotripsy | Failed extraction after Sphincterotomy + EPLBD | 16 16 | 16/16 (100%) 10/16 (63%) | 0.009 | 2/16 (12.5%) 1/16 (6.3%) |
| Bang et al., 2020 [106] | 1 | SOC-LL vs. Sphincterotomy + EPLBD | Failed extraction with balloon/basket catheters | 33 33 | 31/33 (93.9%) 24/33 (72.7%) | 0.021 | 3/33 (9.1%) 1/33 (3%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troncone, E.; Mossa, M.; De Vico, P.; Monteleone, G.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G. Difficult Biliary Stones: A Comprehensive Review of New and Old Lithotripsy Techniques. Medicina 2022, 58, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010120
Troncone E, Mossa M, De Vico P, Monteleone G, Del Vecchio Blanco G. Difficult Biliary Stones: A Comprehensive Review of New and Old Lithotripsy Techniques. Medicina. 2022; 58(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010120
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroncone, Edoardo, Michelangela Mossa, Pasquale De Vico, Giovanni Monteleone, and Giovanna Del Vecchio Blanco. 2022. "Difficult Biliary Stones: A Comprehensive Review of New and Old Lithotripsy Techniques" Medicina 58, no. 1: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010120
APA StyleTroncone, E., Mossa, M., De Vico, P., Monteleone, G., & Del Vecchio Blanco, G. (2022). Difficult Biliary Stones: A Comprehensive Review of New and Old Lithotripsy Techniques. Medicina, 58(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010120







