Association of Two Indices of Insulin Resistance Marker with Abnormal Liver Function Tests: A Cross-Sectional Population Study in Taiwanese Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Study Design
2.2. Clinical Measurements
2.3. Other Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Association between TyG Index and TG/HDL-C Ratio with Abnormal Liver Function
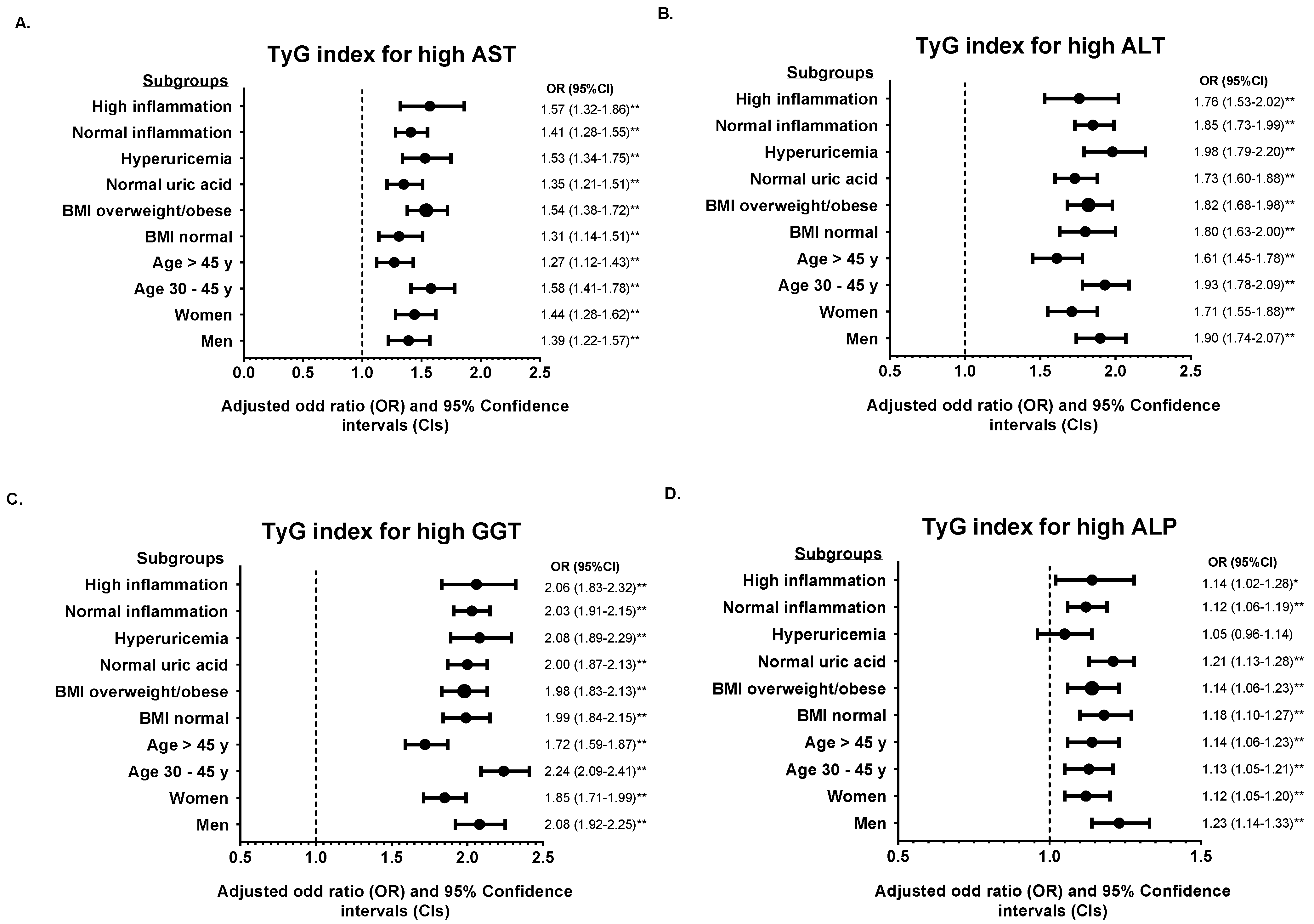
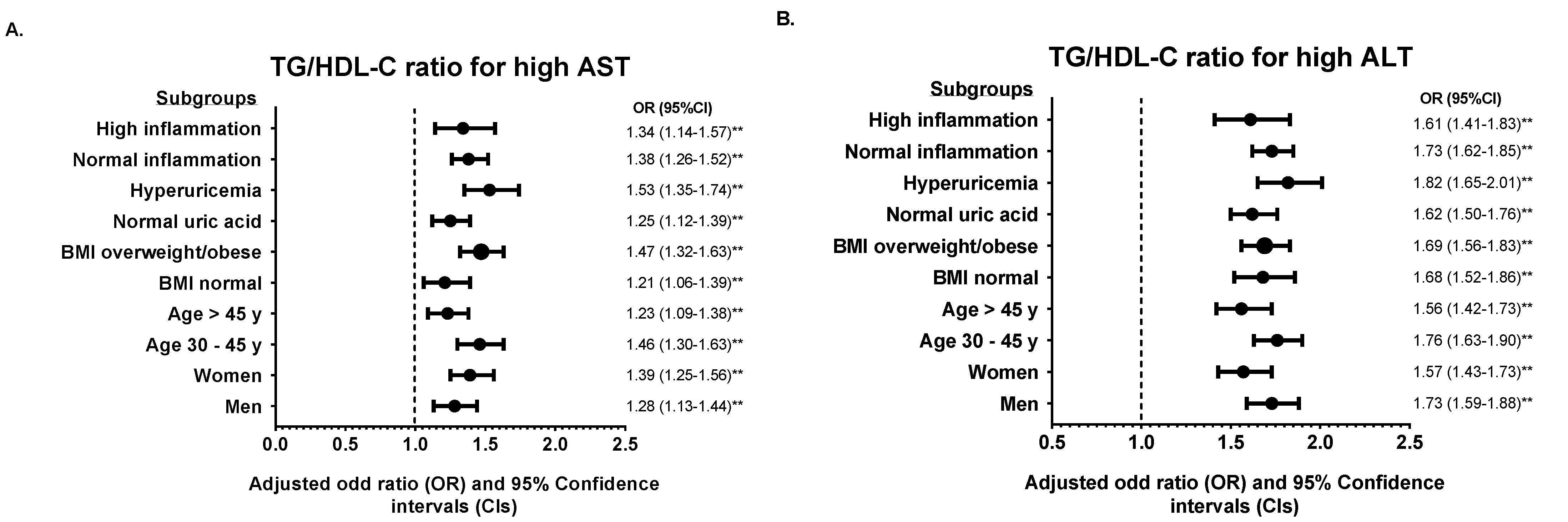
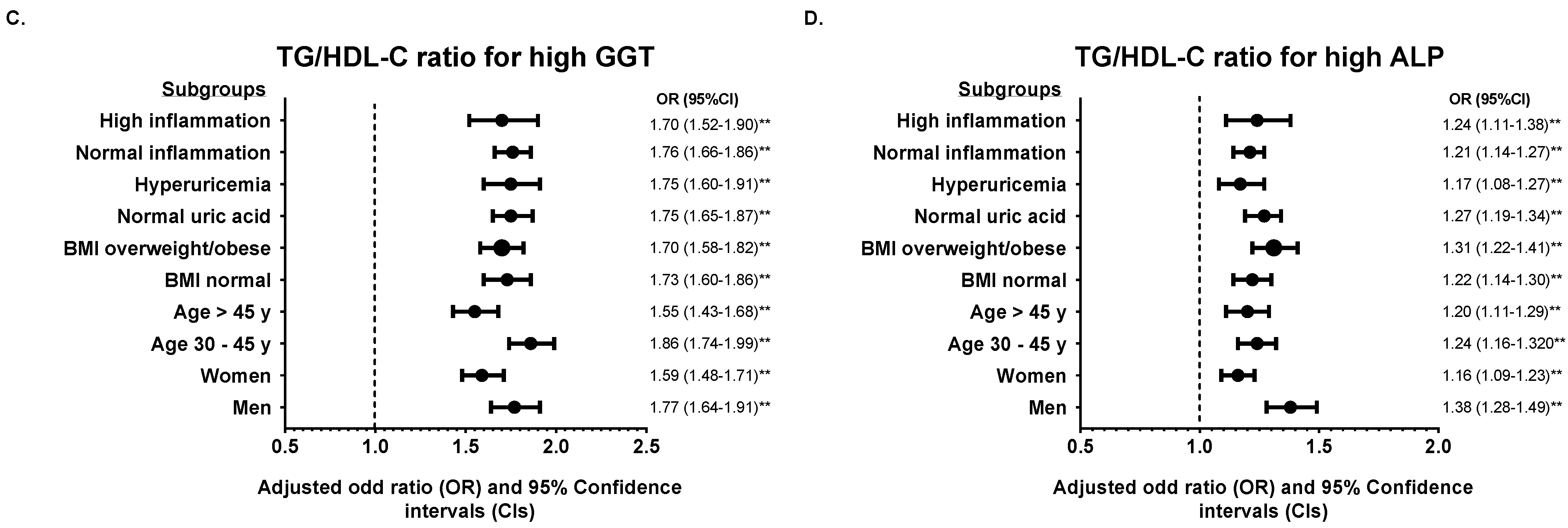
3.3. Subgroup Analysis According to TyG Index and TG/HDL-C Ratio
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballestri, S.; Zona, S.; Targher, G.; Romagnoli, D.; Baldelli, E.; Nascimbeni, F.; Roverato, A.; Guaraldi, G.; Lonardo, A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an almost twofold increased risk of incident type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Shaper, A.G.; Lennon, L.; Whincup, P.H. Hepatic enzymes, the metabolic syndrome, and the risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2913–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nolan, C.J.; Prentki, M. Insulin resistance and insulin hypersecretion in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: Time for a conceptual framework shift. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-S.; Kang, G.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, B.H.; Koo, S.-H. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, Z.; Ahmed, U.; Walayat, S.; Ren, J.; Martin, D.K.; Moole, H.; Sean, K.; Sherri, Y.; Sonu, D. Liver function test in identifying patients with liver disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, R.M.; Flamm, S. AGA technical review on the evaluation of liver chemistry tests. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1367–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sesti, G.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Hribal, M.L.; Sciacqua, A.; Perticone, F. Association of hepatic insulin resistance indexes to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and related biomarkers. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Taniguchi, E.; Itou, M.; Sakata, M.; Sumie, S.; Sata, M. Insulin resistance and chronic liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2011, 3, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.W.; Adams, L.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus: Pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, P.; Lonardo, A.; Anania, F. Liver and diabetes. A vicious circle. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Silva, N.M.G.; Borges, M.C.; Hingorani, A.D.; Engmann, J.; Shah, T.; Zhang, X.; Luan, J.; Langenberg, C.; Wong, A.; Kuh, D.; et al. Liver Function and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Zhyzhneuskaya, S.; Peters, C.; Barnes, A.C.; Aribisala, B.S.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Mathers, J.C.; Sattar, N.; Lean, M.E.J. Remission of Human Type 2 Diabetes Requires Decrease in Liver and Pancreas Fat Content but Is Dependent upon Capacity for β Cell Recovery. Cell Metabolism 2018, 28, 547–556.e543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tam, C.S.; Xie, W.; Johnson, W.D.; Cefalu, W.T.; Redman, L.M.; Ravussin, E. Defining insulin resistance from hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, T.M.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Cai, Y.; Qin, R.; Zhao, B.; Li, X. Association between triglyceride glucose index and abnormal liver function in both urban and rural Chinese adult populations: Findings from two independent surveys. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e18265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radikova, Z. Assessment of insulin sensitivity/resistance in epidemiological studies. Endocr. Regul. 2003, 37, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2008, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Reaven, G.M. Comparison of two methods using plasma triglyceride concentration as a surrogate estimate of insulin action in nondiabetic subjects: Triglycerides × glucose versus triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Metabolism 2011, 60, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, T.; Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Lin, X.; Xie, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X. The triglyceride and glucose index (TyG) is an effective biomarker to identify nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin, T.; Reaven, G.; Abbasi, F.; Lamendola, C.; Saad, M.; Waters, D.; Simon, J.; Krauss, R.M. Is there a simple way to identify insulin-resistant individuals at increased risk of cardiovascular disease? Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.R.; Carbajal, H.A.; Espeche, W.G.; Leiva Sisnieguez, C.E.; March, C.E.; Balbín, E.; Dulbecco, C.A.; Aizpurúa, M.; Marillet, A.G.; Reaven, G.M. Comparison of the abilities of the plasma triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the metabolic syndrome to identify insulin resistance. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2013, 10, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vega, G.L.; Barlow, C.E.; Grundy, S.M.; Leonard, D.; DeFina, L.F. Triglyceride-to-high-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio is an index of heart disease mortality and of incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in men. J. Investig. Med. 2014, 62, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, T.V.; Marini, M.A.; Succurro, E.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G. Relationships of surrogate indexes of insulin resistance with insulin sensitivity assessed by euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp and subclinical vascular damage. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2019, 7, e000911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Health Executive Yuan (Taiwan). Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults in Taiwan; Department of Health Executive Yuan: Taipei, Taiwan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian, A.V.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Cushman, W.C.; Green, L.A.; Izzo Jr, J.L.; Jones, D.W.; Materson, B.J.; Oparil, S.; Wright Jr, J.T.; et al. Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1206–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Ou, J.; Wei, Q.; Gu, J. The comparison of dyslipidemia and serum uric acid in patients with gout and asymptomatic hyperuricemia: A cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syauqy, A.; Hsu, C.Y.; Rau, H.H.; Chao, J.C. Association of dietary patterns, anthropometric measurements, and metabolic parameters with C-reactive protein and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in middle-aged and older adults with metabolic syndrome in Taiwan: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limdi, J.K.; Hyde, G.M. Evaluation of abnormal liver function tests. Postgrad Med. J. 2003, 79, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Guo, X.F.; Zhang, X.G.; Yu, S.S.; Yang, H.M.; Jiang, M.H.; Sun, G.Z.; Sun, Y.X. Association between elevated serum alanine aminotransferase and cardiometabolic risk factors in rural Chinese population: A cross-sectional study. Bmc Cardiovasc. Disor. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syauqy, A.; Hsu, C.Y.; Rau, H.H.; Kurniawan, A.L.; Chao, J.C. Association of Sleep Duration and Insomnia Symptoms with Components of Metabolic Syndrome and Inflammation in Middle-Aged and Older Adults with Metabolic Syndrome in Taiwan. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurniawan, A.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Rau, H.H.; Lin, L.Y.; Chao, J.C. Dietary patterns in relation to testosterone levels and severity of impaired kidney function among middle-aged and elderly men in Taiwan: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Du, Z.; Wang, M.; Mao, Y.; Mao, W. A longitudinal epidemiological study on the triglyceride and glucose index and the incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yki-Järvinen, H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014, 2, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lu, J.; Qin, P.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Q. The triglyceride-glucose index is associated with the severity of hepatic steatosis and the presence of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in Chinese adults. Lipid Health Dis. 2020, 19, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Folli, F.; DeFronzo, R.A. The product of triglycerides and glucose as index of insulin resistance. Validation in the SAM study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3351. [Google Scholar]
- Adiels, M.; Westerbacka, J.; Soro-Paavonen, A.; Häkkinen, A.-M.; Vehkavaara, S.; Caslake, M.J.; Packard, C.; Olofsson, S.-O.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Taskinen, M.R.; et al. Acute suppression of VLDL 1 secretion rate by insulin is associated with hepatic fat content and insulin resistance. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hamaguchi, M.; Fukuda, T.; Nakamura, N.; Ohbora, A.; Kato, T.; Kojima, T.; Fukui, M. Triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is an independent predictor of incident fatty liver; a population-based cohort study. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, N.; Peng, L.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y. Triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as a surrogate for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study. Lipid Health Dis 2019, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Qin, H.; Qiu, S.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y. Correlation of triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among the non-obese Chinese population with normal blood lipid levels: A retrospective cohort research. Lipid Health Dis 2019, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kang, H.-T.; Shim, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-R. The association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in the general Korean population: Based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2007–2009. Diabetes Res. Clin Pract 2012, 97, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmez, A.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Saglam, M.; Unal, H.U.; Gok, M.; Cetinkaya, H.; Karaman, M.; Haymana, C.; Eyileten, T.; Oguz, Y.; et al. The role of plasma triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio to predict cardiovascular outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Lipid Health Dis 2015, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K. Who needs to care about small, dense low-density lipoproteins? Int J. Clin Pract 2007, 61, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; Katsiki, N.; Montalto, G.; Isenovic, E.R.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Rizzo, M. Lipoprotein subfractions in metabolic syndrome and obesity: Clinical significance and therapeutic approaches. Nutrients 2013, 5, 928–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christou, G.A.; Kiortsis, D.N. Adiponectin and lipoprotein metabolism. Obes Rev. 2013, 14, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | All | Quintiles of TyG Index | pa | Quintiles of TG/HDL-C Ratio | pa | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (4.73–7.89) | Q2 (7.90–8.20) | Q3 (8.21–8.51) | Q4 (8.52–8.90) | Q5 (8.91–11.86) | Q1 (0.04–0.87) | Q2 (0.88–1.27) | Q3 (1.28–1.84) | Q4 (1.85–2.91) | Q5 (2.92–19.95) | ||||
| N | 133,867 | 26,762 | 26,786 | 267,40 | 26,806 | 26,773 | 26,779 | 26,775 | 26,768 | 26,783 | 26,762 | ||
| Gender | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| Men | 41,510 (31.0) | 3413 (8.2) | 5996 (14.4) | 8547 (20.6) | 10,859 (26.2) | 12,695 (30.6) | 2706 (6.5) | 5148 (12.4) | 7954 (19.2) | 11,120 (26.8) | 14,582 (35.1) | ||
| Women | 92,357 (69.0) | 23,349 (25.3) | 20,790 (22.5) | 18,193 (19.7) | 15,947 (17.3) | 14,078 (15.2) | 24,073 (26.0) | 21,627 (23.4) | 18,814 (20.4) | 15,663 (17.0) | 12,180 (13.2) | ||
| Age group | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| 30–45 y | 88,682 (66.2) | 22,433 (25.3) | 20,081 (22.6) | 17,489 (19.7) | 15,414 (17.4) | 13,265 (15.0) | 20,874 (23.5) | 19,174 (21.6) | 17,347 (19.6) | 15,975 (18.0) | 15,312 (17.3) | ||
| >45 y | 45,185 (33.8) | 4329 (9.6) | 6705 (14.8) | 9251 (20.5) | 11,392 (25.2) | 13,508 (29.9) | 5905 (13.1) | 7601 (16.8) | 9421 (20.9) | 10,808 (23.9) | 11,450 (25.3) | ||
| Marital status b | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| No | 33,776 (26.2) | 7822 (23.2) | 7057 (20.9) | 6527 (19.3) | 6314 (18.7) | 6056 (17.9) | 7863 (23.3) | 7129 (21.1) | 6646 (19.7) | 6210 (18.4) | 5928 (17.5) | ||
| Yes | 95,054 (73.8) | 17,908 (18.8) | 18,686 (19.7) | 19,248 (20.3) | 19,492 (20.5) | 19,720 (20.7) | 17,859 (18.8) | 18,638 (19.6) | 19,107 (20.1) | 19,585 (20.6) | 19,865 (20.9) | ||
| Educational attainment c | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| Low | 82,975 (62.5) | 14,897 (18.0) | 15,948 (19.2) | 16,635 (20.0) | 17,274 (20.8) | 18,221 (22.0) | 15,544 (18.7) | 16,243 (19.6) | 16,870 (20.3) | 17,003 (20.5) | 17,315 (20.9) | ||
| High | 49,821 (37.5) | 11,680 (23.4) | 10,621 (21.3) | 9891 (19.9) | 9320 (18.7) | 8309 (16.7) | 11,042 (22.2) | 10,308 (20.7) | 9681 (19.4) | 9566 (19.2) | 9224 (18.5) | ||
| Annual income d | 0.023 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| Low (<800,000 NTD) | 74,266 (59.1) | 14,990 (20.2) | 15,057 (20.3) | 14,858 (20.0) | 14,671 (19.7) | 14,690 (19.8) | 15,230 (20.5) | 15,232 (20.5) | 15,024 (20.2) | 14,640 (19.7) | 14,140 (19.1) | ||
| High (>810,000 NTD) | 51,314 (40.9) | 10,264 (20.0) | 10,147 (19.8) | 10,153 (19.8) | 10,403 (20.3) | 10,347 (20.1) | 9937 (19.4) | 9884 (19.3) | 10,063 (19.6) | 10,435 (20.3) | 10,995 (21.4) | ||
| Physical activity status | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| Inactive | 74,021 (55.3) | 15,897 (21.5) | 15,101 (20.4) | 14,441 (19.5) | 14,197 (19.2) | 14,385 (19.4) | 15,898 (21.5) | 15,174 (20.5) | 14,625 (19.8) | 14,227 (19.2) | 14,097 (19.0) | ||
| Active | 59,846 (44.7) | 10,865 (18.2) | 11,685 (19.5) | 12,299 (20.5) | 12,609 (21.1) | 12,388 (20.7) | 10,881 (18.2) | 11,601 (19.4) | 12,143 (20.3) | 12,556 (21.0) | 12,665 (21.1) | ||
| Sleeping time | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| < 6 h | 30,418 (22.7) | 5562 (18.3) | 5722 (18.8) | 6092 (20.0) | 6339 (20.8) | 6703 (22.1) | 5864 (19.3) | 5774 (19.0) | 6122 (20.1) | 6271 (20.6) | 6387 (21.0) | ||
| ≥ 6 h | 103,449 (77.3) | 21,200 (20.5) | 21,064 (20.3) | 20,648 (20.0) | 20,467 (19.8) | 20,070 (19.4) | 20,915 (20.2) | 21,001 (20.3) | 20,646 (20.0) | 20,512 (19.8) | 20,375 (19.7) | ||
| Sleeping condition e | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| Insomnia | 82,648 (62.2) | 17,272 (20.9) | 16,883 (20.4) | 16,416 (19.9) | 16,213 (19.6) | 15,864 (19.2) | 17,465 (21.1) | 17,174 (20.8) | 16,677 (20.2) | 15,989 (19.3) | 15,343 (18.6) | ||
| Sleep well | 50,215 (37.8) | 9306 (18.5) | 9700 (19.3) | 10,141 (20.2) | 10,371 (20.7) | 10,697 (21.3) | 9106 (18.1) | 9393 (18.7) | 9877 (19.7) | 10,616 (21.1) | 112,23 (22.4) | ||
| Smoker f | 27,727 (21.1) | 3854 (13.9) | 4582 (16.5) | 5324 (19.2) | 6268 (22.6) | 7699 (27.8) | <0.001 | 3668 (13.2) | 4212 (15.2) | 5154 (18.6) | 6282 (22.7) | 8411 (30.3) | <0.001 |
| Alcoholic drinker | 16,105 (12.0) | 2194 (13.6) | 2624 (16.3) | 3195 (19.8) | 3597 (22.4) | 4495 (27.9) | <0.001 | 2472 (15.4) | 2598 (16.1) | 3009 (18.7) | 3610 (22.4) | 4416 (27.4) | <0.001 |
| Presence of diseases | |||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 19,476 (14.6) | 1043 (5.4) | 2040 (10.5) | 3385 (17.4) | 5170 (26.5) | 7838 (40.2) | <0.001 | 1539 (7.9) | 2469 (12.7) | 3687 (18.9) | 5154 (26.5) | 6627 (34.0) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 5824 (4.4) | 121 (2.1) | 213 (3.6) | 379 (6.5) | 884 (15.2) | 4227 (72.6) | <0.001 | 276 (4.7) | 455 (7.8) | 872 (15.0) | 1501 (25.8) | 2720 (46.7) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular | 3667 (2.7) | 386 (10.5) | 519 (14.2) | 671 (18.3) | 836 (22.8) | 1255 (34.2) | <0.001 | 487 (13.3) | 558 (15.2) | 742 (20.2) | 856 (23.3) | 1024 (28.0) | <0.001 |
| Hyperuricemia | 31,232 (23.3) | 2116 (6.8) | 3607 (11.6) | 5353 (17.1) | 8256 (26.4) | 11,900 (38.1) | <0.001 | 2015 (6.4) | 3558 (11.4) | 5374 (17.2) | 8215 (26.3) | 12,070 (38.7) | <0.001 |
| Reduced renal function | 3642 (2.7) | 182 (5.0) | 376 (10.3) | 597 (16.4) | 955 (26.2) | 1532 (42.1) | <0.001 | 279 (7.6) | 458 (12.6) | 674 (18.5) | 913 (25.1) | 1318 (36.2) | <0.001 |
| High inflammation | 22,120 (16.5) | 3170 (14.3) | 3589 (16.2) | 4245 (19.2) | 4941 (22.3) | 6175 (28.0) | <0.001 | 2979 (13.5) | 3643 (16.5) | 4384 (19.8) | 5192 (23.5) | 5922 (26.7) | |
| Liver function status | |||||||||||||
| High AST | 7650 (5.72) | 561 (7.3) | 763 (10.0) | 1163 (15.2) | 1692 (22.1) | 3471 (45.4) | <0.001 | 641 (8.4) | 814 (10.6) | 1168 (15.3) | 1795 (23.5) | 3232 (42.2) | <0.001 |
| High ALT | 15,853 (11.8) | 800 (5.0) | 1342 (8.5) | 2350 (14.8) | 3948 (24.9) | 7413 (46.8) | <0.001 | 863 (5.4) | 1301 (8.2) | 2276 (14.4) | 4001 (25.2) | 7412 (46.8) | |
| High GGT | 24,035 (18.0) | 1212 (5.0) | 2152 (9.0) | 3570 (14.9) | 6037 (25.1) | 11,064 (46.0) | <0.001 | 1478 (6.1) | 2249 (9.4) | 3692 (15.4) | 6076 (25.3) | 10,540 (43.8) | <0.001 |
| High ALP | 28,568 (21.3) | 3393 (11.9) | 5056 (17.7) | 6080 (21.3) | 6748 (23.6) | 7291 (25.5) | <0.001 | 3564 (12.5) | 5037 (17.6) | 5837 (20.4) | 6652 (23.3) | 7478 (26.2) | <0.001 |
| Dietary score | |||||||||||||
| Western style | 9.8 ± 2.3 | 9.9 ± 2.2 | 9.8 ± 2.2 | 9.7 ± 2.3 | 9.8 ± 2.3 | 9.8 ± 2.4 | 0.385 | 9.8 ± 2.2 | 9.7 ± 2.2 | 9.7 ± 2.3 | 9.8 ± 2.3 | 10.0 ± 2.4 | <0.001 |
| Vege-seafood style | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 8.5 + 2.0 | 8.4 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 2.0 | <0.001 | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 8.5 ± 1.9 | 0.002 |
| American breakfast style | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.4 ± 1.4 | <0.001 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 5.4 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Anthropometry | |||||||||||||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.0 ± 3.5 | 20.8 ± 2.5 | 21.7 ± 2.9 | 22.8 ± 3.2 | 24.1 ± 3.4 | 25.4 ± 3.5 | <0.001 | 20.7 ± 2.5 | 21.7 ± 2.9 | 22.9 ± 3.2 | 24.1 ± 3.4 | 25.4 ± 3.4 | <0.001 |
| Body fat, % | 27.8 ± 7.1 | 25.1 ± 5.5 | 26.3 ± 6.3 | 27.7 ± 7.0 | 29.2 ± 7.3 | 30.8 ± 7.5 | <0.001 | 25.2 ± 5.6 | 26.7 ± 6.4 | 28.0 ± 7.1 | 29.2 ± 7.5 | 30.0 ± 7.4 | <0.001 |
| WHR | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| Blood biochemistry | |||||||||||||
| FBG, mg/dL | 99.4 ± 19.6 | 91.6 ± 6.9 | 94.6 ± 7.4 | 97.1 ± 8.5 | 100.1 ± 11.0 | 113.4 ± 36.4 | <0.001 | 93.7 ± 9.9 | 95.8 ± 12.3 | 98.5 ± 16.3 | 101.7 ± 20.4 | 107.2 ± 29.4 | <0.001 |
| TG, mg/dL | 105.8 ± 66.1 | 47.3 ± 8.4 | 67.5 ± 7.4 | 88.4 ± 10.1 | 120.7 ± 16.9 | 205.2 ± 77.6 | <0.001 | 49.5 ± 11.1 | 68.7 ± 13.0 | 88.8 ± 17.1 | 119.3 ± 24.0 | 202.9 ± 79.0 | <0.001 |
| TC, mg/dL | 194.8 ± 35.2 | 177.6 ± 30.1 | 186.2 ± 31.3 | 193.9 ± 32.1 | 202.9 ± 33.8 | 213.5 ± 36.7 | <0.001 | 186.4 ± 31.9 | 188.0 ± 32.9 | 192.7 ± 34.2 | 200.0 ± 35.4 | 207.2 ± 36.8 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 115.2 ± 31.7 | 99.5 ± 26.2 | 109.0 ± 28.3 | 117.1 ± 29.6 | 124.9 ± 31.4 | 125.5 ± 34.5 | <0.001 | 100.7 ± 27.4 | 109.5 ± 28.8 | 117.2 ± 30.3 | 124.9 ± 31.6 | 123.7 ± 33.6 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 59.1 ± 15.3 | 68.6 ± 14.9 | 63.9 ± 14.4 | 59.6 ± 14.0 | 54.8 ± 13.0 | 48.6 ± 11.3 | <0.001 | 75.6 ± 13.9 | 65.0 ± 11.4 | 58.3 ± 10.4 | 52.1 ± 9.3 | 44.4 ± 8.3 | <0.001 |
| Insulin resistance indexes | |||||||||||||
| TyG index | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | 8.7 ± 0.1 | 9.3 ± 0.3 | <0.001 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 8.4 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 9.2 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL-C ratio | 2.0 ± 1.7 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 2.3 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 1.8 | <0.001 |
| High AST | High ALT | High GGT | High ALP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | |
| TyG index | ||||||||
| Q1 | 0.83 (0.74–0.93) ** | 0.86 (0.77–0.97) * | 0.65 (0.59–0.71) ** | 0.69 (0.63–0.75) ** | 0.56 (0.52–0.61) ** | 0.61 (0.56–0.65) ** | 0.55 (0.52–0.58) ** | 0.56 (0.53–0.59) ** |
| Q2 | 0.85 (0.77–0.94) ** | 0.87 (0.78–0.96) ** | 0.76 (0.71–0.82) ** | 0.79 (0.73–0.85) ** | 0.76 (0.72–0.81) ** | 0.79 (0.75–0.84) ** | 0.83 (0.79–0.86) ** | 0.83 (0.79–0.87) ** |
| Q3 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q4 | 1.13 (1.04–1.23) ** | 1.07 (0.98–1.16) | 1.32 (1.24–1.41) ** | 1.25 (1.17–1.33) ** | 1.47 (1.40–1.54) ** | 1.35 (1.29–1.43) ** | 1.10 (1.05–1.15) ** | 1.07 (1.02–1.11) ** |
| Q5 | 1.79 (1.66–1.94) ** | 1.45 (1.33–1.57) ** | 2.18 (2.05–2.31) ** | 1.85 (1.73–1.97) ** | 2.71 (2.58–2.85) ** | 2.04 (1.93–2.15) ** | 1.19 (1.14–1.25) ** | 1.13 (1.07–1.19) ** |
| TG/HDL-C ratio | ||||||||
| Q1 | 0.98 (0.88–1.09) | 0.91 (0.81–1.01) | 0.82 (0.75–0.90) ** | 0.78 (0.71–0.85) ** | 0.72 (0.67–0.77) ** | 0.61 (0.57–0.66) ** | 0.59 (0.56–0.62) ** | 0.60 (0.57–0.64) ** |
| Q2 | 0.91 (0.82–1.00) | 0.90 (0.81–0.99) * | 0.81 (0.75–0.87) ** | 0.80 (0.74–0.87) ** | 0.81 (0.77–0.87) ** | 0.79 (0.74–0.84) ** | 0.86 (0.82–0.90) ** | 0.87 (0.83–0.91) ** |
| Q3 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q4 | 1.14 (1.05–1.23) ** | 1.10 (1.01–1.19) * | 1.30 (1.22–1.38) ** | 1.25 (1.18–1.33) ** | 1.37 (1.30–1.44) ** | 1.32 (1.25–1.39) ** | 1.15 (1.10–1.20) ** | 1.11 (1.06–1.16) ** |
| Q5 | 1.66 (1.53–1.79) ** | 1.38 (1.27–1.49) ** | 2.02 (1.90–2.14) ** | 1.71 (1.61–1.82) ** | 2.23 (2.12–2.34) ** | 1.75 (1.66–1.84) ** | 1.34 (1.28–1.41) ** | 1.21 (1.16–1.27) ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurniawan, A.-L.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chao, J.C.-J.; Paramastri, R.; Lee, H.-A.; Jallow, A.-W. Association of Two Indices of Insulin Resistance Marker with Abnormal Liver Function Tests: A Cross-Sectional Population Study in Taiwanese Adults. Medicina 2022, 58, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010004
Kurniawan A-L, Hsu C-Y, Chao JC-J, Paramastri R, Lee H-A, Jallow A-W. Association of Two Indices of Insulin Resistance Marker with Abnormal Liver Function Tests: A Cross-Sectional Population Study in Taiwanese Adults. Medicina. 2022; 58(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurniawan, Adi-Lukas, Chien-Yeh Hsu, Jane C.-J. Chao, Rathi Paramastri, Hsiu-An Lee, and Amadou-Wurry Jallow. 2022. "Association of Two Indices of Insulin Resistance Marker with Abnormal Liver Function Tests: A Cross-Sectional Population Study in Taiwanese Adults" Medicina 58, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010004
APA StyleKurniawan, A.-L., Hsu, C.-Y., Chao, J. C.-J., Paramastri, R., Lee, H.-A., & Jallow, A.-W. (2022). Association of Two Indices of Insulin Resistance Marker with Abnormal Liver Function Tests: A Cross-Sectional Population Study in Taiwanese Adults. Medicina, 58(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58010004










