Inflammatory Disorders of the Central Nervous System Vessels: Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
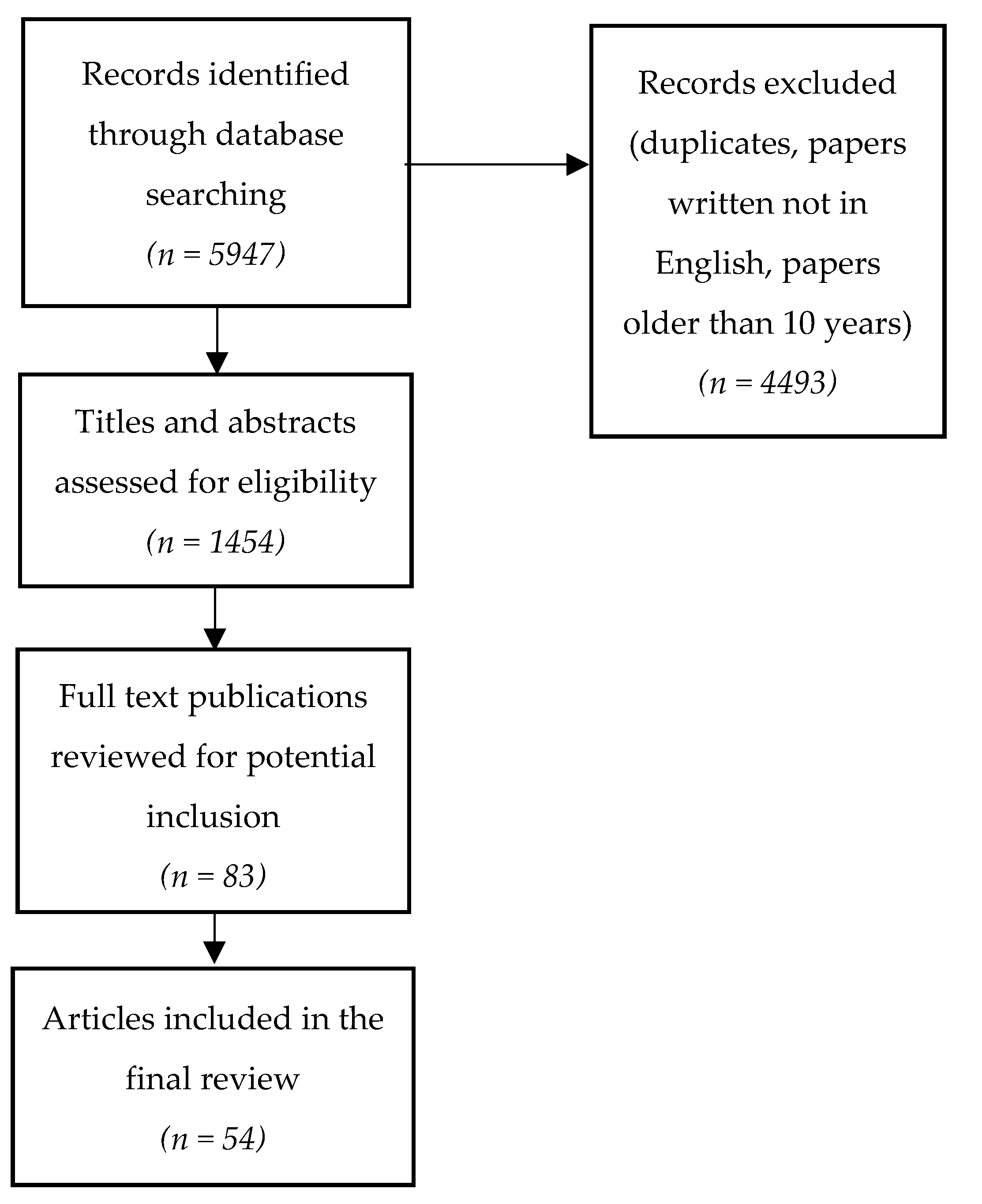
2. Literature Search and Synthesis
3. Primary Vasculitides of the CNS
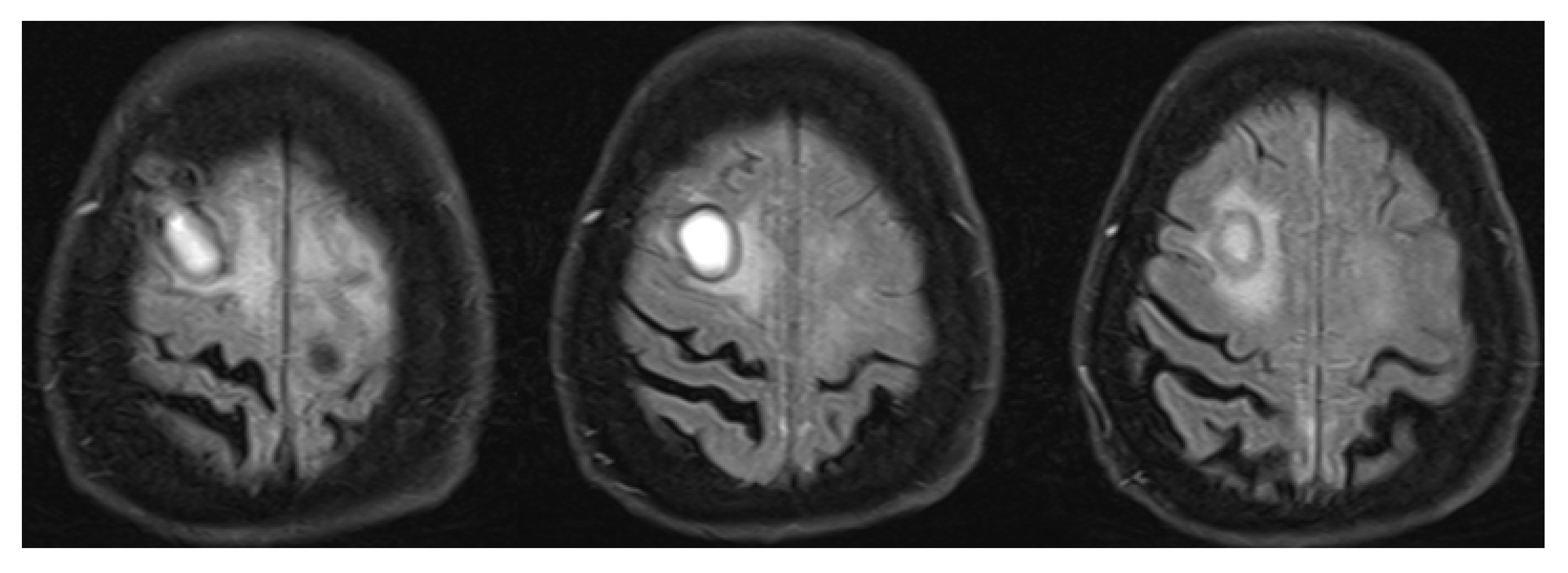
3.1. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System
3.2. Inflammatory Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy (ICAA)
4. Secondary Vasculitides of the Central Nervous System
4.1. Central Nervous System Involvement in Systemic Vasculitis
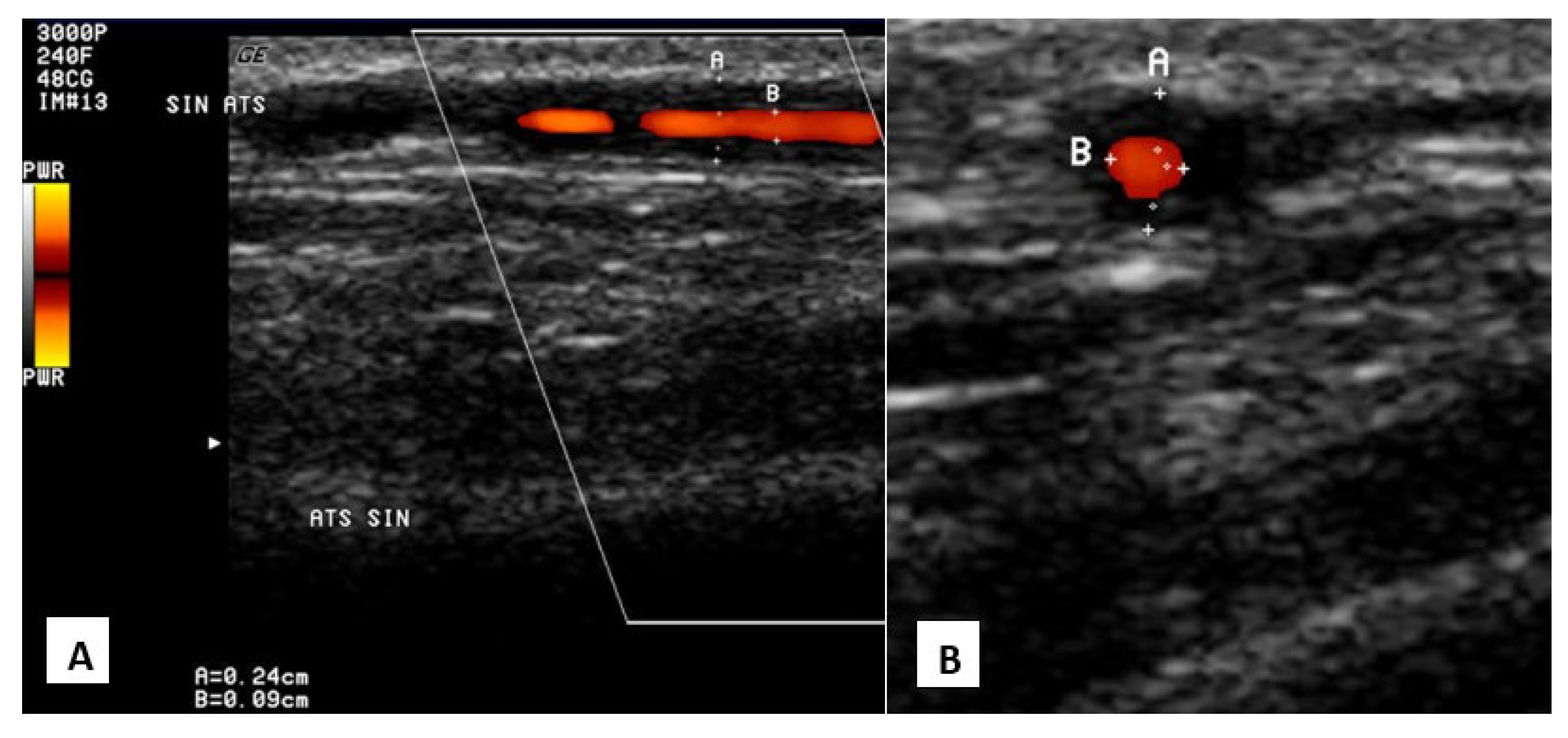
4.1.1. Giant Cell Arteritis
4.1.2. Takayasu Arteritis
4.1.3. Nodular Polyarteritis (Polyarteritis Nodosa)
4.1.4. Kawasaki Disease
4.1.5. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
4.1.6. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
4.1.7. Microscopic Polyangiitis
4.1.8. Henoch-Schoenlein Purpura
4.1.9. Behçet’s Disease
4.2. Central Nervous System Vasculitis Due to Systemic Connective Tissue Diseases
4.2.1. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
4.2.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
5. Future Directions in the Workup of Inflammatory Disorders of the Central Nervous System Vessels
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hajj-Ali, R.A.; Calabrese, L.H. Diagnosis and classification of central nervous system vasculitis. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 48, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjepong, D.; Malik, B.H. Associations and Outcomes Between Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy and Vasculitis in Adults Patients. Cureus 2020, 12, e6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younger, D.S. Eleven Themes in the History of Systemic and Nervous System Vasculitides. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.A.; Loeffler, J.S.; Tarbell, N.J. Late Effects of CNS Radiation Therapy. In Late Effects of Treatment for Brain Tumors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byram, K.; Hajj-Ali, R.A.; Calabrese, L. CNS Vasculitis: An Approach to Differential Diagnosis and Management. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, C.; Picchioni, A.; Telese, R.; Pasi, M.; Failli, Y.; Pracucci, G.; Cammelli, D.; Inzitari, D. “When should primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) be suspected?”: Literature review and proposal of a preliminary screening algorithm. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 3135–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Brown, R.D.; Hunder, G.G. Adult primary central nervous system vasculitis. Lancet 2012, 380, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 37715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soun, J.E.; Song, J.W.; Romero, J.M.; Schaefer, P.W. Central Nervous System Vasculopathies. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 2019, 57, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewells, V.L.; Latchaw, R.E. CNS Vasculitis—An Overview of This Multiple Sclerosis Mimic: Clinical and MRI Implications. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2020, 41, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Brown, R.D.; Christianson, T.J.; Huston, J.; Giannini, C.; Hunder, G.G. Long-term remission, relapses and maintenance therapy in adult primary central nervous system vasculitis: A single-center 35-year experience. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb-Chatterji, M.; Schuster, S.; Häußler, V.; Gerloff, C.; Thomalla, G.; Magnus, T. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: New Potential Imaging Techniques and Biomarkers in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, K.; Samaniego, E.A.; Adams, H.P. Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Central Nervous System Angiitis. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2018, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, J.; Chung, S.A. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2017, 43, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godasi, R.; Pang, G.; Chauhan, S.; Bollu, P.C. Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, T.A.; Jones, A. CNS vasculopathies: Challenging mimickers of primary angiitis of the central nervous system. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 34, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Berkowitz, A.L. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system: Avoiding misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis of a rare disease. Pr. Neurol. 2016, 16, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.; Berlit, P. Primary central nervous system vasculitis—An update on diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 424, 117422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, L.A.; de Souza, A.W.; Grinberg-Dias, G.; Barsottini, O.; Appenzeller, S. Central nervous system vasculitis in adults: An update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, C.M.; Scolding, N.J. The diagnosis of primary central nervous system vasculitis. Pr. Neurol. 2019, 20, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Boysson, H.; Boulouis, G.; Aouba, A.; Bienvenu, B.; Guillevin, L.; Zuber, M.; Touzé, E.; Naggara, O.; Pagnoux, C. Adult primary angiitis of the central nervous system: Isolated small-vessel vasculitis represents distinct disease pattern. Rheumatology 2016, 56, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.H.; Mallek, J.A. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Medicine 1988, 67, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, K.; Iglesias, E.; Nasrallah, M.; González-Álvarez, V.; Suñol, M.; Anton, J.; Saiz, A.; Lancaster, E.; Armangue, T. Anti-MOG encephalitis mimicking small vessel CNS vasculitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2019, 6, e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strunk, D.; Schmidt-Pogoda, A.; Beuker, C.; Milles, L.S.; Korsukewitz, C.; Meuth, S.G.; Minnerup, J. Biomarkers in Vasculitides of the Nervous System. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corovic, A.; Kelly, S.; Markus, H.S. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy associated with inflammation: A systematic review of clinical and imaging features and outcome. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, A.C.; Silva, C.; Albuquerque, L.; Pimentel, J.; Silva, V.; Ferro, J.M. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Associated with Inflammation: Report of 3 Cases and Systematic Review. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwalisz, B. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and related inflammatory disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 424, 117425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshner, H.S.; Bradshaw, M. The Inflammatory Form of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy or “Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation” (CAARI). Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danve, A.; Grafe, M.; Deodhar, A. Amyloid Beta-Related Angiitis—A Case Report and Comprehensive Review of Literature of 94 Cases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Thomas, M.M.; Sipe, A.L.; Benzinger, T.; McConathy, J.; Connolly, S.; Schwetye, K.E. Multimodality Review of Amyloid-related Diseases of the Central Nervous System. RadioGraphics 2016, 36, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvarani, C.; Hunder, G.G.; Morris, J.M.; Brown, R.D.; Christianson, T.; Giannini, C. A -related angiitis: Comparison with CAA without inflammation and primary CNS vasculitis. Neurology 2013, 81, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy: Emerging Concepts. J. Stroke 2015, 17, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciofalo, A.; Gulotta, G.; Iannella, G.; Pasquariello, B.; Manno, A.; Angeletti, D.; Pace, A.; Greco, A.; Altissimi, G.; De Vincentiis, M.; et al. Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA): Pathogenesis, Clinical Aspects and Treatment Approaches. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2019, 15, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, D.S. Treatment of Vasculitis of the Nervous System. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 399–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, D.; Tan, G. Neurological Involvement in Primary Systemic Vasculitis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolding, N. CNS involvement in systemic vasculitides. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 424, 117423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kötter, I.; Lötscher, F. Behçet‘s Syndrome Apart From the Triple Symptom Complex: Vascular, Neurologic, Gastrointestinal, and Musculoskeletal Manifestations. A Mini Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 639758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle-Botero, E.; Abril, A. Lupus Vasculitis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, H.; Chu, L. Neuropsychiatric Lupus Erythematosus: Future Directions and Challenges; a Systematic Review and Survey. Clinics 2020, 75, e1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maz, M.; Chung, S.A.; Abril, A.; Langford, C.A.; Gorelik, M.; Guyatt, G.; Archer, A.M.; Conn, D.L.; Full, K.A.; Grayson, P.C.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Pipitone, N.; Hunder, G.G. Management of primary and secondary central nervous system vasculitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2016, 28, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.E.; Kalot, M.A.; Husainat, N.M.; Dua, A.B.; Byram, K.; Springer, J.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Turgunbaev, M.; Villa-Forte, A.; Gorelik, M.; et al. Kawasaki Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Benefits and Harms of Common Treatments. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sada, K.-E.; Miyauchi, A.; Hashimoto, D.; Ino, R.; Nojima, S.; Yamanaka, S.; Kawamura, M. Recurrent atelectasis and brain infarction in a patient with anti-neutrophil antibody negative eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A case report. BMC Rheumatol. 2021, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, J.M.; Kalot, M.A.; Husainat, N.M.; Byram, K.W.; Dua, A.B.; James, K.E.; Lin, Y.C.; Turgunbaev, M.; Villa-Forte, A.; Abril, A.; et al. Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis and Microscopic Polyangiitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Benefits and Harms of Common Treatments. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygunoğlu, U.; Siva, A. Nervous system involvement in Behçet’s syndrome. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Shi, X.; Gao, X.; Niu, J.; Hu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Clinical features of central nervous system infections and experience in differential diagnosis from neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus in a cohort of 8491 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolopoulos, D.; Fanouriakis, A.; Boumpas, D.T. Update on the pathogenesis of central nervous system lupus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Amorim, J.C.; Torricelli, A.K.; Frittoli, R.B.; Lapa, A.T.; Dertkigil, S.S.J.; Reis, F.; Costallat, L.T.; Junior, M.C.F.; Appenzeller, S. Mimickers of neuropsychiatric manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.; Huang, M.W.; Putterman, C. Advances in the diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arinuma, Y. Antibodies and the brain. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro-Checa, C.; Steup-Beekman, G.M.; Huizinga, T.W.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Ronen, I. Laboratory and Neuroimaging Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Where Do We Stand, Where To Go? Front. Med. 2018, 5, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, M.; Tang, C.C.; Vo, A. Advanced neuroimaging in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Talotta, R.; Masala, I.F.; Gerardi, M.C.; Casale, R.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Central nervous system involvement in rheumatoid arthritis patients and the potential implications of using biological agents. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.C.; Bonow, R.H.; Barros, G.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Kim, L.J.; Levitt, M.R. Magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging in cerebrovascular diseases. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Large vessel  | Takayasu arteritis Giant cell arteritis |
Medium vessel  | Polyarteritis nodosa Kawasaki disease |
Small vessel  | ANCA-associated:
|
Variable vessel  | Behçet’s disease |
| Vasculitis associated with systemic disease | Lupus vasculitis Rheumatoid vasculitis |
| Single organ vasculitis | Primary angiitis of the CNS Inflammatory cerebral amyloid angiopathy |
| Rheumatological causes [5,6,15,16,18]. | Arthritis, skin changes, Raynaud phenomenon, ocular, lung, or kidney involvement Systemic symptoms Peripheral nervous system (PNS) involvement Elevated ESR and CRP Hypochromic anemia Low complement levels Elevated antibody titers:
|
| Infectious causes [5,6,10,15,16,18,23]. | Positive serology for:
|
| Malignancies (intravascular lymphoma, gliomatosis) [5,6,15,16,18]. | History of malignancy Specific MRI spectroscopy findings Atypical cells on the brain biopsy |
| Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome [5,6,15,16,18]. | Acute onset, thunderclap headache Normal cerebrospinal fluid findings Brain MRI normal in 70% of patients Angiographic findings similar to PACNS but usually reversible within 6–12 weeks No inflammatory changes on the brain biopsy |
| Multiple sclerosis [10]. | Less contrast-enhancing lesions (compared to PACNS in which 90% of lesions enhance contrast) No vessel wall changes |
| Anti-MOG encephalitis [23]. | Positive MOG antibodies in the CSF No vessel wall changes Absence of fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel wall on the brain biopsy |
| Sneddon’s syndrome [16]. | Younger women are affected (20–40 y.o.) Livedo rash Antiphospholipid antibodies positive in 50–80% Headache is not so common Psychiatric complications occur later in the course of the disease |
| PACNS | CAARI | ABRA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive decline | 50–70% [17] | 48–76% [25,28] | 71% [29] |
| Focal neurological symptoms | 25–30% [17] | 46% [25,28] | 51% [29] |
| Severe headache | 50–60% [17] | 32–41% [25,28] | 35% [29] |
| Seizures | 25–30% [17] | 31% [25,28] | 30% [29] |
| Elevated ESR or CRP [31] | Uncommon | Up to 30% | |
| Elevated CSF protein [31] | 80–90% | 71% | |
| CSF pleocytosis [31] | 80–90% | 44% | |
| Intracranial hemorrhage [31] | 8% | 20% | 14% |
| Meningeal gadolinium enhancement [31] | 12% | 56% | 57% |
| Disorder | Frequency of CNS Involvement (%) | Disorder | Frequency of CNS Involvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic lupus erythematosus [36,37] | 30–50% | Granulomatosis with polyangiitis [38] | 7–11% |
| Giant cell arteritis [33] | 30% | Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis [38] | 6–10% |
| Takayasu arteritis [38] | 10–20% | Henoch-Schoenlein purpura [38] | 0.65–8% |
| Polyarteritis nodosa [38] | 5–25% | Kawasaki disease [38] | 5.1% |
| Microscopic polyangiitis [36] | 11% | Behçet’s disease [39] | 3–30% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ekkert, A.; Šaulytė, M.; Jatužis, D. Inflammatory Disorders of the Central Nervous System Vessels: Narrative Review. Medicina 2022, 58, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101446
Ekkert A, Šaulytė M, Jatužis D. Inflammatory Disorders of the Central Nervous System Vessels: Narrative Review. Medicina. 2022; 58(10):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101446
Chicago/Turabian StyleEkkert, Aleksandra, Marta Šaulytė, and Dalius Jatužis. 2022. "Inflammatory Disorders of the Central Nervous System Vessels: Narrative Review" Medicina 58, no. 10: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101446
APA StyleEkkert, A., Šaulytė, M., & Jatužis, D. (2022). Inflammatory Disorders of the Central Nervous System Vessels: Narrative Review. Medicina, 58(10), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58101446






