The Use of Kappa Free Light Chains to Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background Overview of FLC Usage in MS Diagnostics
1.2. Aim
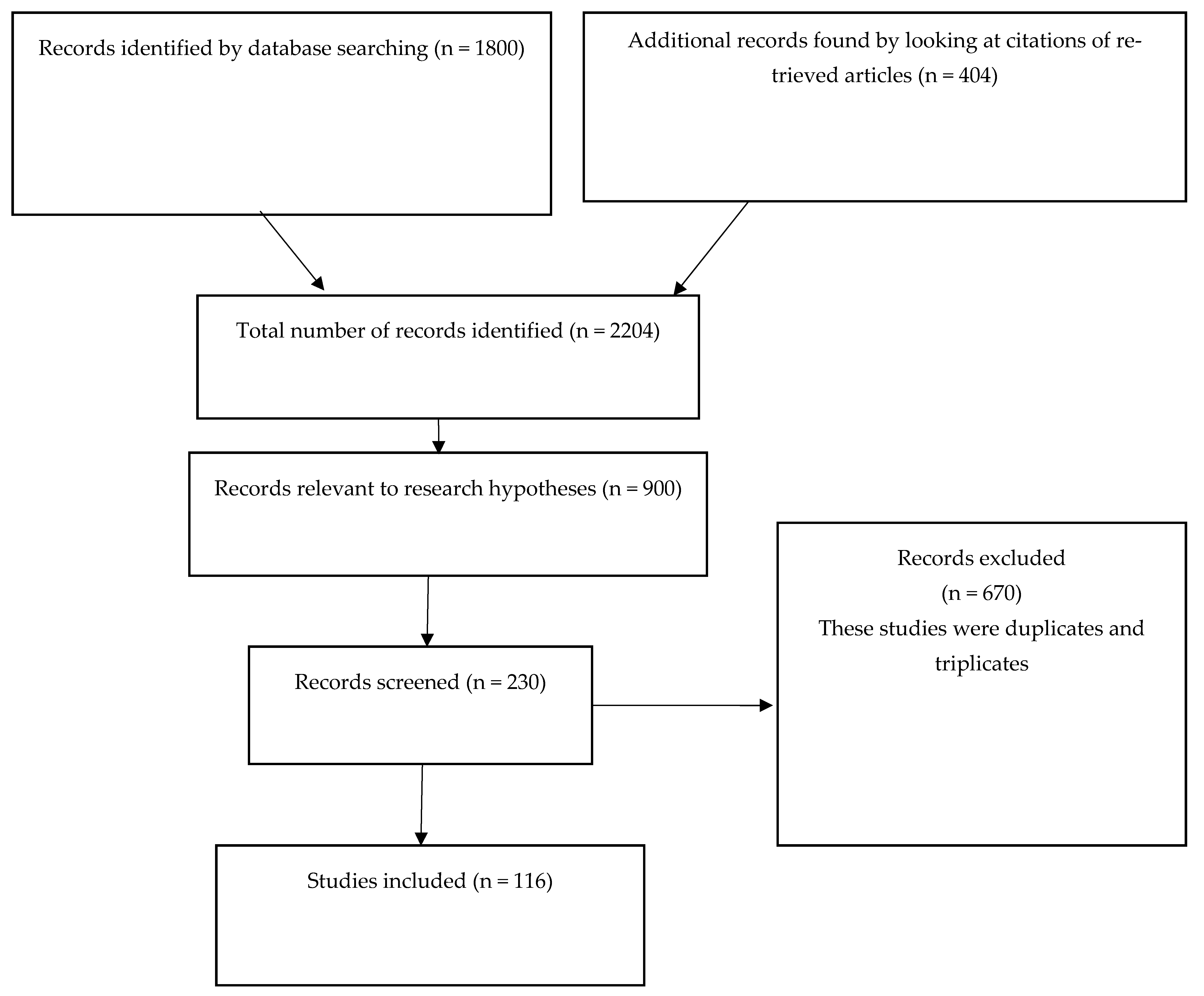
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Data Collection and Analysis Process
3. Results
3.1. Free Light Chains and Immunological Abnormalities
3.2. Free Light Chains and Multiple Sclerosis
3.3. Free Light Chains and Demyelinating Diseases
3.4. The Efficiency of Lambda Free Light Chains in the Diagnosis of Diseases/Multiple Sclerosis
3.5. The Efficiency of Kappa Free Light Chains in Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esparvarinha, M.; Nickho, H.; Mohammadi, H.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Majidi, J. The role of free kappa and lambda light chains in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Livneh, A.; Sela, B.-A. Immunoglobulin Free Light Chain Dimers in Human Diseases. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lock, R.; Saleem, R.; Roberts, E.; Wallage, M.; Pesce, T.; Rowbottom, A.; Cooper, S.; McEvoy, E.; Taylor, J.; Basu, S. A multicentre study comparing two methods for serum free light chain analysis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2013, 50, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenner, E. Serum free light chains in clinical laboratory diagnostics. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 427, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhole, M.V.; Sadler, R.; Ramasamy, K. Serum-free light-chain assay: Clinical utility and limitations. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2014, 51, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muchtar, E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Leung, N.; Lacy, M.Q.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Hayman, S.R.; Kapoor, P.; Hwa, Y.L.; Fonder, A.; et al. Optimizing deep response assessment for AL amyloidosis using involved free light chain level at end of therapy: Failure of the serum free light chain ratio. Leukemia 2018, 33, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoedemakers, R.M.J.; Pruijt, J.F.M.; Hol, S.; Teunissen, E.; Martens, H.; Stam, P.; Melsert, R.; Velthuis, H.T. Clinical comparison of new monoclonal antibody-based nephelometric assays for free light chain kappa and lambda to polyclonal antibody-based assays and immunofixation electrophoresis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2012, 50, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, J.P.; Cobbold, M.; Wang, Y.; Goodall, M.; Bonney, S.L.; Chamba, A.; Birtwistle, J.; Plant, T.; Afzal, Z.; Jefferis, R.; et al. Development of a highly-sensitive multi-plex assay using monoclonal antibodies for the simultaneous measurement of kappa and lambda immunoglobulin free light chains in serum and urine. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 391, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottenberg, J.E.; Seror, R.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Benessiano, J.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Dieude, P.; Dubost, J.J.; Fauchais, A.L.; Goeb, V.; Hachulla, E.; et al. Serum levels of beta2-microglobulin and free light chains of immunoglobulins are associated with systemic disease activity in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Data at enrollment in the prospective ASSESS cohort. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59868. [Google Scholar]
- Groot Kormelink, T.; WAskenase, P.; ARedegeld, F. Immunobiology of antigen-specific immunoglobulin free light chains in chronic inflammatory diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Rigante, D.; Stefanile, A.; Gulli, F.; Marino, M.; Basile, V.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Basile, U. Free light chains and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, M.; Mojib-Yezdani, F.; Braisch, U.; Bachhuber, F.; Lewerenz, J.; Ludolph, A.C.; Otto, M.; Tumani, H. CSF Free Light Chains as a Marker of Intrathecal Immunoglobulin Synthesis in Multiple Sclerosis: A Blood-CSF Barrier Related Evaluation in a Large Cohort. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makshakov, G.; Nazarov, V.; Kochetova, O.; Surkova, E.; Lapin, S.; Evdoshenko, E. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of the Cerebrospinal Fluid Concentration of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in Clinically Isolated Syndrome with Conversion to Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basile, U.; Gulli, F.; Gragnani, L.; Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Mussap, M.; Zignego, A.L. Free light chains: Eclectic multipurpose biomarker. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 451, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, V.D.; Makshakov, G.; Mazing, A.; Surkova, E.; Krasnov, V.S.; Shumilina, M.V.; Totolyan, N.A.; Evdoshenko, E.P.; Lapin, S.V.; Emanuel, V.L.; et al. Diagnostic value of immunoglobulin free light chains at the debut of multiple sclerosis. Zhurnal Nevrol. Psikhiatrii SS Korsakova 2017, 117, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, V.D.; Evdoshenko, E.P.; Makshakov, G.S.; Totolian, A.A.; Lapin, S.V.; Surkova, E.A. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of intrathecal synthesis of immunoglobulin free light chains in multiple sclerosis. Med. Immunol. 2015, 17, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraro, D.; Trovati, A.; Bedin, R.; Natali, P.; Franciotta, D.; Santangelo, M.; Camera, V.; Vitetta, F.; Varani, M.; Trenti, T.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid kappa and lambda free light chains in oligoclonal band-negative patients with suspected multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosello, S.; Basile, U.; De Lorenzis, E.; Gulli, F.; Canestrari, G.; Napodano, C.; Parisi, F.; Pocino, K.; Di Mario, C.; Tolusso, B.; et al. Free light chains of immunoglobulins in patients with systemic sclerosis: Correlations with lung involvement and inflammatory milieu. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, U.; La Rosa, G.; Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Cappannoli, L.; Gulli, F.; Cianfrocca, C.; Di Stasio, E.; Biasucci, L.M. Free light chains a novel biomarker of cardiovascular disease. A pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Rathbone, E.; Durant, L.; Kinsella, J.; Parker, A.R.; Hassan-Smith, G.; Douglas, M.R.; Curnow, S.J. Cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin light chain ratios predict disease progression in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.P. Free Immunoglobulin Light Chains in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespi, I.; Sulas, M.G.; Mora, R.; Naldi, P.; Vecchio, D.; Comi, C.; Cantello, R.; Bellomo, G. Combined use of kappa free light chain index and isoelectrofocusing of cerebrospinal fluid in diagnosing multiple sclerosis: Performances and costs. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinier, S.; Puthenparampil, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Toffanin, E.; Ruggero, S.; Gallo, P.; Plebani, M. Free light chains in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients negative for IgG oligoclonal bands. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 496, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeman, D.; Hradílek, P.; Švagera, Z.; Mojžíšková, E.; Woznicová, I.; Zapletalová, O. Detection of oligoclonal IgG kappa and IgG lambda bands in cerebrospinal fluid and serum with Hevylite™ antibodies. Comparison with the free light chain oligoclonal pattern. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeman, D.; Kušnierová, P.; Švagera, Z.; Všianský, F.; Byrtusová, M.; Hradílek, P.; Kurková, B.; Zapletalová, O.; Bartoš, V. Assessment of Intrathecal Free Light Chain Synthesis: Comparison of Different Quantitative Methods with the Detection of Oligoclonal Free Light Chains by Isoelectric Focusing and Affinity-Mediated Immunoblotting. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hampson, J.; Turner, A.; Stockley, R. Polyclonal free light chains: Promising new biomarkers in inflammatory disease. Curr. Biomark. Find. 2014, 4, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gudowska-Sawczuk, M.; Tarasiuk, J.; Kułakowska, A.; Kochanowicz, J.; Mroczko, B. Kappa Free Light Chains and IgG Combined in a Novel Algorithm for the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkenbecher, P.; Konen, F.F.; Wurster, U.; Witte, T.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.-W.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T. Reiber’s Diagram for Kappa Free Light Chains: The New Standard for Assessing Intrathecal Synthesis? Diagnostics 2019, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berek, K.; Bsteh, G.; Auer, M.; Di Pauli, F.; Grams, A.; Milosavljevic, D.; Poskaite, P.; Schnabl, C.; Wurth, S.; Zinganell, A.; et al. Kappa-Free Light Chains in CSF Predict Early Multiple Sclerosis Disease Activity. Neurol.-Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Gulli, F.; Rossi, E.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Marino, M.; Basile, U. Mono/polyclonal free light chains as challenging biomarkers for immunological abnormalities. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2022, 108, 155–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presslauer, S.; Milosavljevic, D.; Huebl, W.; Aboulenein-Djamshidian, F.; Krugluger, W.; Deisenhammer, F.; Senel, M.; Tumani, H.; Hegen, H. Validation of kappa free light chains as a diagnostic biomarker in multiple sclerosis and clinically isolated syndrome: A multicenter study. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 22, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtner, K.M.; Shosha, E.; Bryant, S.C.; Andreguetto, B.D.; Murray, D.L.; Pittock, S.J.; Willrich, M.A.V. CSF free light chain identification of demyelinating disease: Comparison with oligoclonal banding and other CSF indexes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2018, 56, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan-Smith, G.; Durant, L.; Tsentemeidou, A.; Assi, L.; Faint, J.; Kalra, S.; Douglas, M.; Curnow, S. High sensitivity and specificity of elevated cerebrospinal fluid kappa free light chains in suspected multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 276, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, M. Different roles of urinary light chains and serum light chains as potential biomarkers for monitoring disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Peer J. 2022, 10, e13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, J.L.; Phillips, A.C.; Drayson, M.; Campbell, J.P. Serum free light chains are reduced in endurance trained older adults: Evidence that exercise training may reduce basal inflammation in older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 77, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernardi, G.; Biagioli, T.; Malpassi, P.; De Michele, T.; Vecchio, D.; Repice, A.M.; Lugaresi, A.; Mirabella, M.; Clerici, V.T.; Crespi, I. The contribute of cerebrospinal fluid free light-chain assay in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases in an Italian multicenter study. Mult. Scler. J. 2021, 28, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draborg, A.H.; Lydolph, M.C.; Westergaard, M.; Olesen Larsen, S.; Nielsen, C.T.; Duus, K.; Jacobsen, S.; Houen, G. Elevated concentrations of serum immunoglobulin free light chains in systemic lupus erythematosus patients to disease activity, inflammatory status, B cell activity, and Epstein-Barr virus antibodies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyoshi, N.; Iuliano, L.; Tomono, S.; Ohshima, H. Implications of cholesterol autoxidation products in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 Revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenstein, I.; Rasch, S.; Axelsson, M.; Novakova, L.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Lycke, J. Kappa free light chain index as a diagnostic biomarker in multiple sclerosis: A real-world investigation. J. Neurochem. 2021, 159, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.; Arneth, B.; Koehler, J.; Lotz, J.; Lackner, K.J. Kappa Free Light Chains in Cerebrospinal Fluid as Markers of Intrathecal Immunoglobulin Synthesis. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arrambide, G.; Tintore, M. CSF examination still has value in the diagnosis of MS—Commentary. Mult. Scler. J. 2016, 22, 997–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalla, P.; Caropreso, P.; Limoncelli, S.; Bosa, C.; Pasanisi, M.; Schillaci, V.; Alteno, A.; Costantini, G.; Giordana, M.; Mengozzi, G.; et al. Kappa free light chains index in the differential diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis from Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders and other immune-mediated central nervous system disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 339, 577122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leurs, C.E.; Twaalfhoven, H.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.I.; van Pesch, V.; Dujmovic, I.; Drulovic, J.; Castellazzi, M.; Bellini, T.; Pugliatti, M.; Kuhle, J.; et al. Kappa free light chains is a valid tool in the diagnostics of MS: A large multicenter study. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 26, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desplat-Jégo, S.; Feuillet, L.; Pelletier, J.; Bernard, D.; Chérif, A.A.; Boucraut, J. Quantification of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in CerebroSpinal Fluid by Nephelometry. J. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 25, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranti, F.; Pieri, M.; Centonze, D.; Buttari, F.; Bernardini, S.; Dessi, M. Determination of kFLC and K Index in cerebrospinal fluid: A valid alternative to assess intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 263, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Malekzadeh, A.; Leurs, C.; Bridel, C.; Killestein, J. Body-fluid biomarkers for multiple sclerosis- the long road to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, R.A.; Katzmann, J.A.; Therneau, T.M.; Larson, D.; Benson, J.; Clark, R.J.; Melton, L.J., III; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.K.; et al. Immunoglobulin free light chain ratio is an independent risk factor for progression of smoldering (asymptomatic) multiple myeloma. Blood. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2008, 111, 785–789. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, G.P.; Carr-Smith, H.D.; Drayson, M.T.; Morgan, G.J.; Child, J.A.; Bradwell, A.R. Serum free light chains for monitoring multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 126, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, M.; Gjelstrup, M.C.; Stilund, M.; Christensen, T.; Petersen, T.; Møller, H.J. Cerebrospinal fluid free kappa light chains and kappa index perform equal to oligoclonal bands in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2018, 57, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegen, H.; Walde, J.; Milosavljevic, D.; Aboulenein-Djamshidian, F.; Senel, M.; Tumani, H.; Deisenhammer, F.; Presslauer, S. Free light chains in the cerebrospinal fluid. Comparison of different methods to determine intrathecal synthesis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, N.; Yao, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Qin, Y.; et al. The prognostic utility and the association of serum light chains (free and total) and absolute lymphocyte count in patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duell, F.; Evertsson, B.; Al Nimer, F.; Sandin, Å.; Olsson, D.; Olsson, T.; Khademi, M.; Hietala, M.A.; Piehl, F.; Hansson, M. Diagnostic accuracy of intrathecal kappa free light chains compared with OCBs in MS. Neurol.-Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochtler, T.; Hegenbart, U.; Heiss, C.; Benner, A.; Cremer, F.; Volkmann, M.; Ludwig, J.; Perz, J.B.; Ho, A.D.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. Evaluation of the serum-free light chain test in untreated patients with AL amyloidosis. Haematologica 2008, 93, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freedman, M.S.; Thompson, E.J.; Deisenhammer, F.; Giovannoni, G.; Grimsley, G.; Keir, G.; Öhman, S.; Racke, M.K.; Sharief, M.; Sindic, C.J.M.; et al. Recommended standard of cerebrospinal fluid analysis in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: A consensus statement. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Clark, R.J.; Abraham, R.S.; Bryant, S.; Lymp, J.F.; Bradwell, A.R.; Robert, A.K. Serum reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for free kappa and free lambda immunoglobulin light chains: Relative sensitivity for detection of monoclonal light chains. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement (reprinted from Annals of Internal Medicine). Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 89, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, I.; Vecchio, D.; Serino, R.; Saliva, E.; Virgilio, E.; Sulas, M.G.; Bellomo, G.; Dianzani, U.; Cantello, R.; Comi, C. K Index is a Reliable Marker of Intrathecal Synthesis, and an Alternative to IgG Index in Multiple Sclerosis Diagnostic Work-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nazarov, V.; Makshakov, G.; Kalinin, I.; Lapin, S.; Surkova, E.; Mikhailova, L.; Gilburd, B.; Skoromets, A.; Evdoshenko, E. Concentrations of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in Cerebrospinal Fluid predict increased level of brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Ganelin-Cohen, E.; Golderman, S.; Livneh, A. Diagnostic utility of kappa free light chains in multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraro, D.; Bedin, R.; Natali, P.; Franciotta, D.; Smolik, K.; Santangelo, M.; Immovilli, P.; Camera, V.; Vitetta, F.; Gastaldi, M.; et al. Kappa Index Versus CSF Oligoclonal Bands in Predicting Multiple Sclerosis and Infectious/Inflammatory CNS Disorders. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, D.; Bellomo, G.; Serino, R.; Virgilio, E.; Lamonaca, M.; Dianzani, U.; Cantello, R.; Comi, C.; Crespi, I. Intrathecal kappa free light chains as markers for multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Aizenbud, B.M.; Golderman, S.; Yaskariev, R.; Sela, B.-A. Free light chain monomers in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 229, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Disanto, G.; Dobson, R.; Adiutori, R.; Bianchi, L.; Topping, J.; Bestwick, J.; Meier, U.-C.; Marta, M.; Costa, G.D.; et al. Conversion from clinically isolated syndrome to multiple sclerosis: A large multicentre study. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 21, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konen, F.F.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Witte, T.; Sühs, K.W.; Grothe, M.; Hannich, M.J.; Süße, M.; Skripuletz, T. Kappa Free Light Chains in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Inflammatory and Non-Inflammatory Neurological Diseases. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arneth, B. Author’s Response to Professor Reiber’s second letter concerning our article: High sensitivity of free lambda and free kappa light chains for the detection of intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis in cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 120, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, L.M.; Espiño, M.; Costa-Frossard, L.; Muriel, A.; Jiménez, J.; Álvarez-Cermeño, J.C. High levels of cerebrospinal fluid free kappa chains predict conversion to multiple sclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pröbstel, A.-K.; Sanderson, N.S.R.; Derfuss, T. B Cells and Autoantibodies in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16576–16592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süße, M.; Feistner, F.; Holbe, C.; Grothe, M.; Nauck, M.; Dressel, A.; Hannich, M.J. Diagnostic value of Kappa Free Light Chains in Patiens with one isolated band in isoelectric focusing. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 507, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süße, M.; Reiber, H.; Grothe, M.; Petersmann, A.; Nauck, M.; Dressel, A.; Hannich, M.J. Free light chain kappa and the polyspecific immune response in MS and CIS—Application of the hyperbolic reference range for most reliable data interpretation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 346, 577287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, M.; Storto, M.; Pignalosa, S.; Zenobi, R.; Buttari, F.; Bernardini, S.; Centonze, D.; Dessi, M. κ−FLC Index utility in multiple sclerosis diagnosis: Further confirmation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 309, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, R.A.; Rajkumar, S.V. Criteria for diagnosis, staging, risk stratification and response assessment of multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2009, 23, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasilj, M.; Kes, V.B.; Vrkic, N. Relevance of κ−FLC quantification to differentiate clinically isolated syndrome from multiple sclerosis at clinical onset. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 174, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geervani, V.; Mohanaih, D.R.P. Extraction of object in multi-views based on LDA approach. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. Res. 2017, 6, 5166–5171. [Google Scholar]
- Tintore, M.; Rovira, A.; Rio, J.; Tur, C.; Pelayo, R.; Nos, C.; Téllez, N.; Perkal, H.; Comabella, M.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; et al. Do oligoclonal bands add information to MRI in first attacks of multiple sclerosis? Neurology 2008, 70, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpendale, M.S.T.; Cowperthwaite, D.J.; David Fracchia, F. 3-dimensional pliable surfaces: For the effective presentation of visual information. Ucalgary Ca. 2012, 101, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Izneid, T.; Rauf, A.; Shariati, M.A.; Khalil, A.A.; Imran, M.; Rebezov, M.; Uddin, S.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Rengasamy, K.R. Sesquiterpenes and their derivatives-natural anticancer compounds: An update. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voortman, M.M.; Stojakovic, T.; Pirpamer, L.; Jehna, M.; Langkammer, C.; Scharnagl, H.; Reindl, M.; Ropele, S.; Seifert-Held, T.; Archelos, J.-J.; et al. Prognostic value of free light chains lambda and kappa in early multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2016, 23, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presslauer, S.; Milosavljevic, D.; Brücke, T.; Bayer, P.; Hübl, W. Elevated levels of kappa free light chains in CSF support the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, M.; Tumani, H.; Lauda, F.; Presslauer, S.; Mojib-Yezdani, R.; Otto, M.; Brettschneider, J. Cerebrospinal Fluid Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chain in Clinically Isolated Syndrome and Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrambide, G.; Espejo, C.; Carbonell-Mirabent, P.; Dieli-Crimi, R.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Castillo, M.; Auger, C.; Cárdenas-Robledo, S.; Castilló, J.; Cobo-Calvo, Á.; et al. The kappa free light chain index and oligoclonal bands have a similar role in the McDonalds Criteria. Brain 2022, awac220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presslauer, S.; Milosavljevic, D.; Huebl, W.; Parigger, S.; Schneider-Koch, G.; Bruecke, T. Kappa Free Light Chains. Diagnostic and Prognostic Relevance in MS and CIS. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeCarli, C.; Menegus, M.A.; Rudick, R.A. Free light chains in multiple sclerosis and infections of the CNS. Neurology 1987, 37, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, P.; Bedin, R.; Bernardi, G.; Corsini, E.; Cocco, E.; Schirru, L.; Crespi, I.; Lamonaca, M.; Sala, A.; Nicolò, C.; et al. On Behalf Of Rirems Rising Researchers In Ms. Inter-laboratory concordance of cerebrospinal fluid and serum kappa free light chain measurements. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huss, A.; Mojib-Yezdani, F.; Bachhuber, F.; Fangerau, T.; Lewerenz, J.; Otto, M.; Tumani, H.; Senel, M. Association of Cerebrospinal Kappa Free Light Chains with the intrathecal polyspecific antiviral immune response in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 498, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootla, B.; Denic, A.; Keegan, B.M.; Winters, J.L.; Astapenko, D.; Warrington, A.E.; Bieber, A.J.; Rodriguez, M. Evidence for the Role of B Cells and Immunoglobulins in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H. Software for cerebrospinal fluid diagnostics and statistics. Rev. Cuba. Investig. Biomédicas 2020, 39, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, B.N.; Luxton, R.W.; Thompson, E.J. A study of immunoglobulin G in the cerebrospinal fluid of 1007 patients with suspected neurological disease using isoelectric focusing and the Log IgG-Index. A comparison and diagnostic applications. Brain 2014, 113 Pt 5, 1269–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Petzold, A.; Bennett, J.L.; Berven, F.S.; Brundin, L.; Comabella, M.; Franciotta, D.; Frederiksen, J.L.; Fleming, J.O.; Furlan, R.; et al. A consensus protocol for the standardization of cerebrospinal fluid collection and biobanking. Neurology 2009, 73, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deisenhammer, F.; Bartos, A.; Egg, R.; Gilhus, N.E.; Giovannoni, G.; Rauer, S.; Sellebjerg, F. Guidelines on routine cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Report from an EFNS task force. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Diaz, C.T.; de las Heras Flórez, S.; Carretero Perez, M.; Hernández Pérez, M.Á.; Martín García, V. Evaluation of Kappa Index as a Tool in the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis: Implementation in Routine Screening Procedure. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinker, T.; Trinkaus, K.; Cross, A.H. Elevated CSF free kappa light chains correlate with disability prognosis in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2006, 67, 1288–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, R.; Merlini, G.; Miguel, J.S.; Ludwig, H.; Hajek, R.; Palumbo, A.; Jagannath, S.; Blade, J.; Lonial, S.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group guidelines for serum-free light chain analysis in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Leukemia 2008, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Annunziata, P.; Giorgio, A.; De Santi, L.; Zipoli, V.; Portaccio, E.; Amato, M.P.; Clerici, R.; Scarpini, E.; Moscato, G.; Iudice, A.; et al. Absence of cerebrospinal fluid oligoclonal bands is associated with delayed disability progression in relapsing-remitting MS patients treated with interferon-β. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 244, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, F.G.; Hirst, C.L.; Pickersgill, T.P.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Robertson, N.P.; Scolding, N.J. CSF oligoclonal band status informs prognosis in multiple sclerosis: A case control study of 100 patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Matsui, M.; Inoue, I.; Awata, T.; Katayama, S.; Murakoshi, T. Free immunoglobulin light chain: Its biology and implications in diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage 2004, 23, S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadeh, R.S.; Bryant, S.C.; McKeon, A.; Weinshenker, B.; Murray, D.L.; Pittock, S.J. Willrich MAV CSF Kappa Free Light Chains: Cutoff Validation for Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2022, 97, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konen, F.F.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Wurster, U.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Möhn, N.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.W.; Hannich, M.J.; Grothe, M.; Witte, T.; et al. The influence of Renal Function Impairment on Kappa Free Light Chains in Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2021, 13, 11795735211042166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetani, L.; Di Carlo, M.; Brachelente, G.; Valletta, F.; Eusebi, P.; Mancini, A.; Gentili, L.; Borrelli, A.; Calabresi, P.; Sarchielli, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid free light chains compared to oligoclonal bands as biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 339, 577108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, D.B. Multiple sclerosis: Assay of free immunoglobulin light chains. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobson, R.; Ramagopalan, S.; Davis, A.; Giovannoni, G. Cerebrospinal fluid oligoclonal bands in multiple sclerosis and clinically isolated syndromes: A meta-analysis of prevalence, prognosis and effect of latitude. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostouli, M.; Christidi, F.; Zalonis, I.; Nikolaou, C.; Lyrakos, D.; Triantafyllou, N.; Evdokimidis, I.; Kilidireas, C. Clinical and cognitive implications of cerebrospinal fluid oligoclonal bands in multiple sclerosis patients. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenkenbecher, P.; Konen, F.F.; Wurster, U.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.-W.; Pul, R.; Witte, T.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T. The Persisting Significance of Oligoclonal Bands in the Dawning Era of Kappa Free Light Chains for the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valencia-Vera, E.; Garcia-Ripoll, A.M.-E.; Enguix, A.; Abalos-Garcia, C.; Segovia-Cuevas, M.J. Application of κ free light chains in cerebrospinal fluid as a biomarker in multiple sclerosis diagnosis: Development of a diagnosis algorithm. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2017, 56, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinl, E.; Derfuss, T.; Krumbholz, M.; Pröbstel, A.-K.; Hohlfeld, R. Humoral autoimmunity in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 306, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudani, N.; Djidjik, R.; Ghaffor, M. Comments on CSF κFLC assay evaluation in assessing intrathecal synthesis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 266, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, P.; Tomassetti, S.; Merli, A.; Polli, V. Serum free light-chain assay for the detection and monitoring of multiple myeloma and related conditions. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2012, 4, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Süße, M.; Hannich, M.; Petersmann, A.; Zylla, S.; Pietzner, M.; Nauck, M.; Dressel, A. Kappa free light chains in cerebrospinal fluid to identify patients with oligoclonal bands. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Golderman, S.; Yahalom, G.; Yeskaraev, R.; Ziv, T.; Aizenbud, B.M.; Sela, B.A.; Livneh, A. Free light chains monomer dimer patterns in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 390, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, B.; Birklein, F. High sensitivity of free lambda and free kappa light chains for detection of intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis in cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 119, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, D.A.; Lopes, J.; da Silva, A.; Morais, C.; Vasconcelos, J.; Lima, I.; Carneiro, C.; Neves, E. Kappa Free Light Chains: Diagnostic Performance in Multiple Sclerosis and utility in a clinical laboratory. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 528, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Abid, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Muneer, S.; Khan, S.; de Oliveira, M.H.S.; Kausar, R.; Siddiqui, I. Evaluation of CSF kappa free ligh chains for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS): A comparision with oligoclonal bands (OCB) detection via isoelectric focusing (IEF) coupled with immunoblotting. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 28, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegen, H.; Berek, K.; Deisenhammer, F. Cerebrospinal fluid kappa free light chains as biomarker in multiple sclerosis—From diagnosis to prediction of disease activity. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2022, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliozzi, R.; Cross, A.H. Can CSF biomarkers predict future MS disease activity and severity? Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konen, F.F.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.-W.; Tumani, H.; Süße, M.; Skripuletz, T. The Increasing Role of Kappa Free Light Chains in the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Cells 2021, 10, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Key Findings from the Literature | Supporting Studies | n | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free light chains are essential in altering polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) functions and aiding in PMN prestimulation. | Esparvarinha et al. [1], Napodano et al. [11] | 900 | p < 0.005 |
| High concentrations of kappa and lambda free light chains are evident in the serum of multiple myeloma patients. | Kaplan et al. [2], Lock et al. [3], Bhole et al. [5], Muchtar et al. [6], Gottenberg et al. [9], Gurtner et al. [32], Jiang et al. [34], Draborg et al. [37] | 1001/2771 | p < 0.0001 |
| There is a comparable clinical difference in the specificity and sensitivity of diagnosing monoclonal plasma proliferative disorders between a monoclonal free light chain (FLC) assay and a polyclonal antibody-based assay. | Hoedemakers et al. [7], Campbell et al. [8] | 671/890 | p < 0.0001 |
| Positive implications of immunoglobulin free light chains in the early diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. | 4 studies, n = 1640 Nazarov et al. [15], Nazarov et al. [16], Rathbone et al. [20], Bernardi et al. [36] | 1242/1640 | p ≥ 0.320 |
| Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) kappa free light chain is a more profound and earlier intrathecal immunoglobulin marker in comparison to oligoclonal bands (OCBs). | 6 studies n = 3054 Ferraro et al. [17], Bosello et al. [18]. Basile [19], Altinier et al. [23], Zeman et al. [24]. Zeman et al. [25] | 2333/3054 | p ≥ 5.7 |
| Key Findings from the Literature | Supporting Studies | Studies Against |
|---|---|---|
| κ-FLC concentrations in CSF are higher in patients with clinically validated multiple sclerosis | 16 studies; n = 3040 (Hassan-Smith [33], Gudowska-Sawczuk et al. [27], Rosenstein et al. [40], Fischer et al. [41], Leurs et al. [47], Villar et al. [67], Süße et al. [69], Süße et al. [70], Vasilj et al. [73], Voortman et al. [78], Presslauer et al. [79], Senel et al. [80], Presslauer et al. [82], Rinker et al. [92], Nakano et al. [96], Ramsden [101], and Messaoudani et al. [107]). n = 2033/3040 p < 0.001 | - |
| κ-FLC concentrations in CSF can be used to predict multiple sclerosis | 8 studies; n = 1800 (Presslauer et al. [31], Mead et al. [49], Han et al. [52], Rathbone et al. [20], Kaplan et al. [60], Vecchio et al. [62], Annunziata et al. [94], Saadeh et al. [98], Bernardi et al. [36], and Abid et al. [113]). n = 981/1800 p < 0.005 | - |
| κ-FLC index cutoff values are a novel tool in the determination of intrathecal synthesis of κ-FLCs | 9 studies; n = 2450 (Cavalla et al. [43], Freedman et al. [55], Katzmann et al. [56], Pieri et al. [71], Arrambide et al. [81], McLean et al. [88], and Dispenzieri et al. [93]). n = 1721/2450 p < 0.005 | 5 studies, n = 1341 (Geervani et al. [74], DeCarli et al. [83], Teunissen et al. [89], Deisenhammer et al. [90,114], and Sanz Diaz et al. [91] and Magliozzi et al [115]) |
| Reiber’s diagram provides accurate measurements of κ-FLCs and the associated accuracy of multiple sclerosis (MS ) diagnosis | 5 studies, n =1447 (Schwenkenbecher et al. [28], Konen et al. [65], Reiber et al. [87], Arneth et al. [66,111], and Duranti et al. [46]). n = 911/1447 p < 0.013 | - |
| κ-FLC index is a better predictor of MS than the use of CSF OCBs | 11 studies, n = 2700 (Leurs et al. [81], Desplat-Jégo et al. [45], Duranti et al. [46], Dispenzieri et al. [93], Duell et al. [53], Bochtler et al. [91], Tintore et al. [75], Ferraro et al. [61], Gaetani et al. [100], Konen et al. [116], and Sanz et al. [91]). n = 2321/2700 p < 0.091 | 5 studies, n = 1200 (Christiansen et al. [50], Presslauer et al. [82], Crespi et al. [58], Natali et al. [84], and Joseph et al. [95]) |
| κ-FLC concentration in CSF is the future of MS diagnosis | 12 studies, n = 3150 (Polman et al. [39], Pröbstel et al. [68], Kyle et al. [72], Carpendale et al. [76], Abu-Izneid et al. [77], Wootla et al. [86], Smith et al. [97], Dobson et al. [102], Anagnostouli et al. [103], Valencia-Vera et al. [105], Meinl et al. [106], and Hegen et al. [114]). n = 2776/3150 p < 0.0001 | - |
| Study | Study Question/Hypothesis | n | p-Value | Reported Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leurs et al. 2020 [44] | Can kappa free light chain (κ-FLC) and lambda free light chain (λ-FLC) indices serve as diagnostic biomarkers in multiple sclerosis? | 745 | p < 0.001 | Compared with OCBs, the κ-FLC index is more sensitive but less specific for diagnosing CIS/MS. |
| Christiansen et al. 2018 [50] | Comparative diagnostic performance of CSF FLC with OCB and Immunoglobulin G (IgG) index. | 96/230 | p < 0.094 | Using only the absolute concentration of CSF-kappa is a logistic advantage in clinical laboratories. |
| Crespi et al. 2019 [58] | Is the κ-FLC index a reliable marker of intrathecal synthesis and an alternative to the IgG index in multiple sclerosis diagnostic work-up? | 385 | p < 0.0001 | Results confirmed the previous proposal to use the κ-FLC index as a highly sensitive and easy-to-detect first-line marker in CSF analysis for intrathecal synthesis. |
| Rathbone et al. 2018 [20] | Do free light chains (FLCs) as biomarkers for confirming a diagnosis of MS show greater sensitivity and specificity than OCBs? | 43 | p < 0.026 | CSF immunoglobulin κ: λ ratios, determined at the time of diagnostic lumbar puncture, predict MS disease progression and may therefore be useful prognostic markers for early therapeutic stratification. |
| Vecchio et al. 2020 [62] | What is the role of κ-FLCs in the diagnostic work-up for MS? | 406 | p < 0.001 | κ-FLCs provided high sensitivity and decent specificity for MS diagnosis. |
| Arneth et al. 2009 [66,111] | Immunoglobulin free light chain concentrations measured in the CSF of patients with neurological disorders. | 20 | p < 0.001 | The high sensitivity of lambda light chains for the detection of intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis may be of benefit in establishing clinical diagnoses. |
| Villar et al. 2012 [67] | What is the accuracy of CSF κ-FLC measurement to predict the conversion of CIS patients to MS? | 133/374 | p < 0.001 | High CSF κ-FLC concentration accurately predicts the conversion of CIS patients to MS. |
| Süße et al. 2020 [70] | What is the application and interpretation of κ-FLC data in quotient diagrams with a hyperbolic reference range? | 98/400 | p < 0.001 | The evaluation of κ-FLC with a hyperbolic reference range in quotient diagrams is superior to other analytical methods, such as the linear κ-FLC index. |
| Voortman et al. 2016 [78] | What is the prognostic value of κ-FLC in OCB-positive patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) suggestive of MS and early MS? | 48/61 | p < 0.05 | Increased intrathecal synthesis of κ-FLC in CIS/MS supports its diagnostic contribution. |
| Presslauer et al. 2016 [82] | What is the diagnostic accuracy of intrathecal κ-FLC synthesis? | 70/438 | p ≥ 5.9 | Findings support the diagnostic value of intrathecal κ-FLC synthesis in CIS and MS patients and demonstrate a valid, easier, and rater-independent alternative to OCB detection. |
| Ferraro et al. 2020 [61] | What is the diagnostic accuracy of the κ-FLC index in comparison with OCB detection in predicting MS? | 84/540 | p ≥5.8 | The κ-FLC index has a slightly higher sensitivity and lower specificity than CSF OCB, and both markers supply the clinician with useful, complementary information. |
| Saadeh et al. 2021 [98] | What are the reference values for FLC measures? What is their accuracy with regard to the diagnosis of MS? | 70/1224 | p ≥ 5.9 | CSF κ-FLCs may not replace OCBs, but they may support diagnosis in MS as a quantitative parameter. |
| Duranti et al. 2013 [46] | Is the κ-FLC index more accurate than other parameters? | 33/80 | p < 0.001 | Nephelometric assay for κ-FLCs in CSF reliably detects intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis and discriminates multiple sclerosis patients. |
| Valencia-Vera et al. 2018 [105] | What is the diagnostic value of κ-FLC and its inclusion in a procedure algorithm along with OCB interpretation? | 123 | p < 0.001 | κ-FLC determination is rapid and automatized, but it has no higher sensitivity or specificity than OCB in MS diagnosis. |
| Süße et al. 2018 [109] | Can the determination of the κ-FLC index be used to predict the presence of OCBs? | 46/295 | p < 0.86 | Determination of the κ-FLC index provided a quantitative parameter that could be used as an initial diagnostic step in inflammatory central nervous system disorders before measuring OCBs. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arneth, B.; Kraus, J. The Use of Kappa Free Light Chains to Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina 2022, 58, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111512
Arneth B, Kraus J. The Use of Kappa Free Light Chains to Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina. 2022; 58(11):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111512
Chicago/Turabian StyleArneth, Borros, and Jörg Kraus. 2022. "The Use of Kappa Free Light Chains to Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis" Medicina 58, no. 11: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111512
APA StyleArneth, B., & Kraus, J. (2022). The Use of Kappa Free Light Chains to Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina, 58(11), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111512






