A Heart Rate Step Function Response Method for the Evaluation of Pulse Wave Velocity as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardio-Vascular Events
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
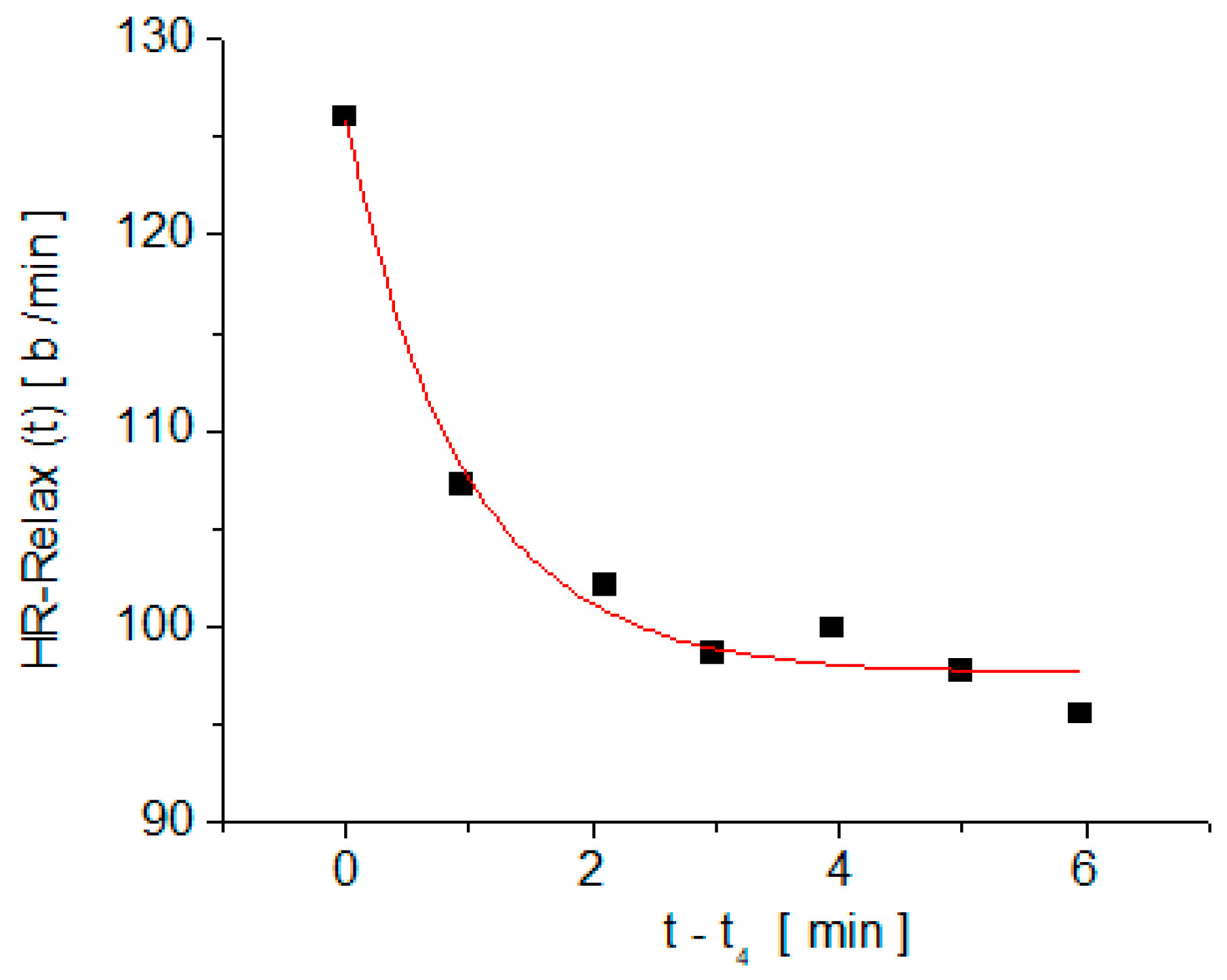
3. Results
4. Discussion
- After a moderate physical effort and a resting time of at least 6 min, the HR remains at values larger than 80 b/min;
- The relaxation time, τ, in a physical effort test of moderate intensity is larger than 1 min;
- The HR measured after the subject is raised from the supine position to the orthostatic position is larger than 100 b/min;
- Resting HR is larger than 80 b/min.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Technical Information Site of Power Supply Design, Tech Web. Available online: https://techweb.rohm.com/knowledge/dcdc/dcdc-ldo/dcdc-ldo02/9697 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Scafe, B.K.P. Principles of Dielectrics, Revised ed.; Oxford University Press: London, England, 1998; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Fannin, P.C.; Marin, C.N.; Couper, C. On the significance of the area under the after-effect function curve of a magnetic fluid. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Mendoza-Halliday, D.; Ting, J.T.; Kaiser, T.; Sun, X.; Bastos, A.M.; Wimmer, R.D.; Guo, B.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; et al. An Ultra-Sensitive Step-Function Opsin for Minimally Invasive Optogenetic Stimulation in Mice and Macaques. Neuron 2020, 107, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, H.; Pyari, G.; Roy, S. Co-expressing fast channelrhodopsin with step-function opsin overcomes spike failure due to photocurrent desensitization in optogenetics: A theoretical study. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 026032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, N.; Unekawa, M.; Murata, J.; Tomita, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Nakahara, J.; Takuwa, H.; Kanno, I.; Matsui, K.; Tanaka, K.F.; et al. Differential pial and penetrating arterial responses examined by optogenetic activation of astrocytes and neurons. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Lamm, S.H.; Ferdosi, H.; Boroje, I.J. Aortic Elasticity and Arsenic Exposure: A Step Function rather than a Linear Function. Risk Anal. 2021, 41, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, E.; Hsueh, L.; McConeghy, K.W.; Stefan Gravenstein, S.; Saade, E. Major adverse cardiovascular event definitions used in observational analysis of administrative databases: A systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, F.J.; Geddes, L.A.; Babbs, C.F.; Bourland, J.D. Relationship between Pulse-Wave Velocity and Arterial Elasticity. Purdue University, Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering Faculty Publications. 1986. Available online: http://docs.lib.purdue.edu/bmepubs/78 (accessed on 13 August 2022).
- Van Bortel, L.M.; Duprez, D.; Starmans-Kool, M.J.; Safar, M.E.; Giannattasio, C.; Cockcroft, J.; Kaiser, D.R.; Thuillez, C. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness, Task Force III: Recommendations for user procedures. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Reference Values for Arterial Stiffness’ Collaboration. Determinants of pulse wave velocity in healthy people and in the presence of cardiovascular risk factors: ‘establishing normal and reference values’. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2338–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.L.; Russell, B.S.; Fendrich, M.; Finkelstein-Fox, L.; Hutchison, M.; Becker, J. Americans’ COVID-19 Stress, Coping, and Adherence to CDC Guidelines. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Kosmopoulou, F.; Alexopoulos, N.; Ioakeimidis, N.; Siasos, G.; Stefanadis, C. Acute mental stress has a prolonged unfavorable effect on arterial stiffness and wave reflections. Psychosom. Med. 2006, 68, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Noguchi, H.; Rolfe, P.; Yamakoshi, T.; Matsuoka, Y. Differential effect of two mental stress tasks on arterial stiffness. Jpn. Psychol. Res. 2019, 61, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, D.; Nishiwaki, M.; Takahara, R.; Hotta, N. The effectiveness of bench step exercise for ameliorating acute mental stress-induced arterial stiffening. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 122, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, I.; Iurciuc, M.; Popescu, F.G.; Iurciuc, S.; Popoiu, C.M.; Marin, C.N.; Ursoniu, S.; Fira-Mladinescu, C. Pulse wave velocity, a predictor for major adverse cardiovascular events and its correlation with the general stress level of health care workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Medicina 2022, 56, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, W.L.; Wilmore, J.H.; Costill, D.L. Physiology of Sport and Exercise, 5th ed.; Human Kinetics: Leeds, UK, 2011; pp. 182–183. [Google Scholar]
- Iurciuc, S.; Avram, C.; Turi, V.; Militaru, A.; Avram, A.; Cimpean, A.M.; Iurciuc, M. Physical Training, Hemodynamic Parameters and Arterial Stiffness: Friends or Foes of the Hypertensive Patient? Vivo 2016, 30, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, D.T.; Martin, J.S.; Casey, D.P.; Braith, R.W. Exercise Training Reduces Peripheral Arterial Stiffness and Myocardial Oxygen Demand in Young Prehypertensive Subjects. Am. J. Hypertens. 2013, 26, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.; Ficarra, S.; Nakamura, M.; Paoli, A.; Bellafore, M.; Palma, A.; Bianco, A. Effects of Different Long-Term Exercise Modalities on Tissue Stiffness. Sports Med. Open 2022, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ya, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of exercise training on arterial stiffness in obese and overweight children: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 2633–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhao, M.X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Sun, L. Arterial stiffness acute changes following aerobic exercise in males with and without hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujie, S.; Sanada, K.; Hamaoka, T.; Iemitsu, M. Time-dependent relationships between exercise training-induced changes in nitric oxide production and hormone regulation. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 166, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haesler, E.; Lyon, X.; Pruvot, E.; Kappenberger, L.; Hayoz, D. Confounding effects of heart rate on pulse wave velocity in paced patients with a low degree of atherosclerosis. J. Hypertens. 2004, 22, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.; Spronck, B.; Kiat, H.; Barin, E.; Reesink, K.D.; Delhaas, T.; Avolio, A.P.; Butlin, M. Heart Rate Dependency of Large Artery Stiffness. Hypertension 2016, 68, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentilin, A.; Tarperi, C.; Cevese, A.; Mattioli, A.V.; Schena, F. Estimation of carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity from finger photoplethysmography signal. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 075011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calbet, J.A.; Lundby, C. Skeletal muscle vasodilatation during maximal exercise in health and disease. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 6285–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žikić, D.; Žikić, K. Wave propagation through a viscous fluid-filled elastic tube under initial pressure: Theoretical and biophysical model. Eur. Biophys. J. 2022, 51, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, G.; Spronck, B.; Avolio, A.P.; Tap, L.; Vaudo, G.; Anastasio, F.; Van Den Meiracker, A.; Mattace-Raso, F. Age-Specific Acute Changes in Carotid-Femoral Pulse Wave Velocity with Head-up Tilt. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020, 33, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Mean Value | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 26.27 years | 3.23 years |
| Anthropometric measurements | ||
| Body Height | 1.71 m | 0.09 m |
| Body Weight | 66.72 kg | 15.89 kg |
| Body Mass Index | 22.76 kg/m2 | 3.97 kg/m2 |
| Arteriograph measurements | ||
| Systolic BP (SBP-Art) | 116.05 mmHg | 9.20 mmHg |
| Diastolic BP (DBP-Art) | 67.72 mmHg | 8.12 mmHg |
| Heart rate (HR-Art) | 69.91 b/min | 11.31 b/min |
| PWV | 7.34 m/s | 1.32 m/s |
| Regression Equation | Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient | Significance 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation of PWV with yo | PWV = 4.130 + 0.045∙yo | 0.395 | 0.017 |
| Correlation of PWV with τ | PWV = 6.640 + 1.097∙τ | 0.329 | 0.049 |
| Correlation of PWV with A | - | −0.090 | 0.599 |
| Regression Equation | Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient | Significance 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation of PWV with HR-Art | PWV = 3.353 + 0.057∙HR-Art | 0.490 | 0.002 |
| Correlation of PWV with HR-Pre | PWV = 2.932 + 0.052∙HR-Pre | 0.479 | 0.003 |
| Correlation of PWV with HR-4min | PWV = 4.907 + 0.022∙HR-4min | 0.245 | 0.150 |
| Correlation of PWV with HR-6min | PWV = 3.774 + 0.049∙HR-6min | 0.433 | 0.008 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marin, I.; Popescu, F.G.; Pauncu, E.-A.; Apostol, A.; Ivan, V.M.; Marin, C.N.; Fira-Mladinescu, O.; Ursoniu, S. A Heart Rate Step Function Response Method for the Evaluation of Pulse Wave Velocity as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardio-Vascular Events. Medicina 2022, 58, 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111633
Marin I, Popescu FG, Pauncu E-A, Apostol A, Ivan VM, Marin CN, Fira-Mladinescu O, Ursoniu S. A Heart Rate Step Function Response Method for the Evaluation of Pulse Wave Velocity as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardio-Vascular Events. Medicina. 2022; 58(11):1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111633
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarin, Ioana, Florina Georgeta Popescu, Elena-Ana Pauncu, Adrian Apostol, Viviana Mihaela Ivan, Catalin Nicolae Marin, Ovidiu Fira-Mladinescu, and Sorin Ursoniu. 2022. "A Heart Rate Step Function Response Method for the Evaluation of Pulse Wave Velocity as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardio-Vascular Events" Medicina 58, no. 11: 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111633
APA StyleMarin, I., Popescu, F. G., Pauncu, E.-A., Apostol, A., Ivan, V. M., Marin, C. N., Fira-Mladinescu, O., & Ursoniu, S. (2022). A Heart Rate Step Function Response Method for the Evaluation of Pulse Wave Velocity as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardio-Vascular Events. Medicina, 58(11), 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111633








