An Overview on Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Development of Carbapenem Resistance: Molecular Mechanisms
3. Treatment Modalities
Limited Treatment Options
4. Epidemiology of Carbapenem Resistance
5. Prevalence of CRE
6. Transmission of CRE
6.1. Healthcare Settings
6.2. Colonisation
6.3. Transmission of CRE to the Community
6.4. Screening for Carbapenem Resistance
6.5. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of CRE
6.6. Phenotypic Characterisation
6.6.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
6.6.2. Multi-Disk Mechanism Testing and Combined Disk Synergy Tests
6.6.3. Chromogenic Media
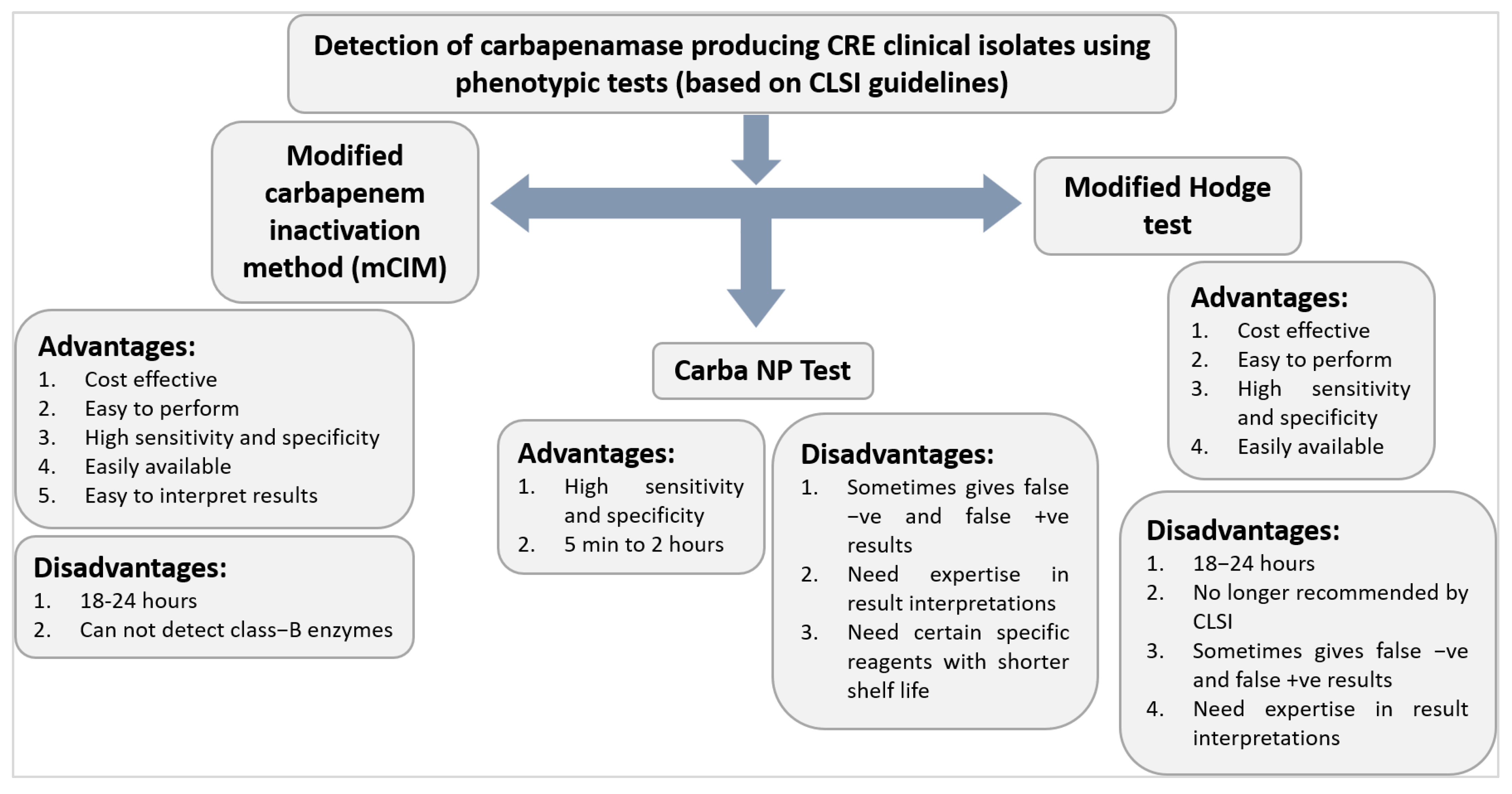
6.6.4. Modified Hodge Test (MHT)
6.6.5. Carba NP
6.6.6. Carbapenem Inactivation Method (CIM) and Modified CIM
6.6.7. Immunochromatographic (IC) Assays
6.6.8. Bio-Analytical Methods—MALDI-TOF MS
6.7. Genotypic Characterisation of CRE: Detection of Carbapenemase Genes
6.7.1. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
6.7.2. Microarrays
6.7.3. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willyard, C. The drug-resistant bacteria that pose the greatest health threats. Nature 2017, 543, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-M.; Lai, C.-C.; Chiang, H.-T.; Lu, M.-C.; Wang, L.-F.; Tsai, T.-L.; Kang, M.-Y.; Jan, Y.-N.; Lo, Y.-T.; Ko, W.-C. Presence of multidrug-resistant organisms in the residents and environments of long-term care facilities in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, B.; Machuca, I.; Pascual, A. Treatment of infections caused by extended-spectrum-b-lactamase-, AmpC-, and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00079-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-J.; Hsieh, C.-F.; Chang, P.-C.; Chen, J.-J.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-C.; Chao, C.-M.; Chuang, Y.-C. Clinical significance of community- and healthcare-acquired carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales isolates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151897. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, C.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chang, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R. Management of infections caused by extended-spectrum b-lactamaseproducing Enterobacteriaceae: Current evidence and future prospects. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Collins, J.J. How antibiotics kill bacteria: From targets to networks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Song, X.; Li, M.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, A.; Sun, H. Global Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Epidemiological Features, Resistance Mechanisms, Detection and Therapy. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 266, 127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerdan, M.B.; Al Hassan, S.; Shaker, W.; El Hajjar, R.; Allam, S.; Zerdan, M.B.; Naji, A.; Zeineddine, N. Carbapenemase Inhibitors: Updates on Developments in 2021. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2022, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Global spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Peghin, M.; Vena, A. Treatment of Infections Due to MDR Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Med. 2019, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.-P.; Wang, S.-F.; Ma, L.; Wang, T.-Y.; Yang, T.-Y.; Siu, L.K.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Lee, P.-S.; Wang, J.-T.; Wu, T.-L. The plasmid-mediated fosfomycin resistance determinants and synergy of fosfomycin and meropenem in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumonia isolates in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Alhumaid, S.; Mutair, A.A.; Garout, M.; Abulhamayel, Y.; Halwani, M.A.; Alestad, J.H.; Bshabshe, A.A.; Sulaiman, T.; AlFonaisan, M.K. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Combating High Antimicrobial Resistance Rates. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbediwi, M.; Li, Y.; Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Li, X.; Xie, S.; Rajkovic, A.; Feng, Y.; Fang, W.; Rankin, S.C. Global burden of colistin-resistant bacteria: Mobilized colistin resistance genes study (1980–2018). Microorganisms 2019, 7, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Rapid Risk Assessment: Plasmid-mediated colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Stockholm: ECDC. 2016. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/media/en/publications/Publications/enterobacteriaceae-risk-assessment-diseases-caused-by-antimicrobial-resistant-microorganisms-europe-june-2016.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Giamarellou, H.; Galani, L.; Baziaka, F.; Karaiskos, I. Effectiveness of a double-carbapenem regimen for infections in humans due to carbapenemase-producing pandrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2388–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.F.; Simkins, J.; Beduschi, T.; Tekin, A.; Aragon, L.; Pérez-Cardona, A.; Prado, C.E.; Morris, M.I.; Abbo, L.M.; Cantón, R. Successful treatment of Carbapenemase-producing pandrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5903–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douka, E.; Perivolioti, E.; Kraniotaki, E.; Fountoulis, K.; Economidou, F.; Tsakris, A.; Skoutelis, A.; Routsi, C. Emergence of a pandrug-resistant VIM-1-producing Providencia stuartii clonal strain causing an outbreak in a Greek intensive care unit. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2015, 45, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zowawi, H.M.; Forde, B.M.; Alfaresi, M.; Alzarouni, A.; Farahat, Y.; Chong, T.-M.; Yin, W.-F.; Chan, K.-G.; Li, J.; Schembri, M.A. Stepwise evolution of pandrug-resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafur, A.; Lakshmi, V.; Kannain, P.; Murali, A.; Thirunarayan, M. Emergence of Pan-drug resistance amongst gram negative bacteria! The First case series from India. J. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2014, 4, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljaaly, K.; Alharbi, A.; Alshehri, S.; Ortwine, J.K.; Pogue, J.M. Plazomicin: A novel aminoglycoside for the treatment of resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Drugs 2019, 79, 243–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Khalid, H.; Mushtaq, M.; Basha, S.; Rabaan, A.A.; Garout, M.; Halwani, M.A.; Al Mutair, A.; Alhumaid, S.; Al Alawi, Z. The Molecular Characterization of Virulence Determinants and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Human Bacterial Uropathogens. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, N.; Zeshan, B.; Qadri, M.M.A.; Ishaq, M.; Afzal, M.; Ahmed, N. Phenotypic and genotypic evaluation of antibiotic resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria isolated from surgical intensive care unit patients in Pakistan. Jundishapur. J. Microbiol. 2021, 14, e113008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Facility Guidance for Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales(CRE)—November 2015 Update CRE Toolkit. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/hai/organisms/cre/cre-toolkit/ (accessed on 4 June 2016).
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). NIAID’s Antibacterial Resistance Program: Current Status and Future Directions 2014. Available online: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/sites/default/files/arstrategicplan2014.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2017).
- Bush, K. Proliferation and significance of clinically relevant β-lactamases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1277, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaber, M.J.; Lev, B.; Israeli, A.; Solter, E.; Smollan, G.; Rubinovitch, B.; Shalit, I.; Carmeli, Y. Containment of a country-wide outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Israeli hospitals via a nationally implemented intervention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Cunningham, M.A.; Mire, J.; Tesar, C.; Sacchettini, J.; Joachimiak, A. NDM-1, the ultimate promiscuous enzyme: Substrate recognition and catalytic mechanism. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) Tracking CRE infections. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/hai/organisms/cre/TrackingCRE.html#CREmap (accessed on 4 June 2016).
- Gonçalves, I.R.; Ferreira, M.; Araujo, B.; Campos, P.; Royer, S.; Batistão, D.; Souza, L.; Brito, C.; Urzedo, J.; Gontijo-Filho, P. Outbreaks of colistin-resistant and colistin susceptible KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Brazilian intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 94, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergönül, Ö.; Aydin, M.; Azap, A.; Başaran, S.; Tekin, S.; Kaya, Ş.; Gülsün, S.; Yörük, G.; Kurşun, E.; Yeşilkaya, A. Healthcare-associated Gram-negative bloodstream infections: Antibiotic resistance and predictors of mortality. J Hosp. Infect. 2016, 94, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGann, P.; Snesrud, E.; Maybank, R.; Corey, B.; Ong, A.C.; Clifford, R.; Hinkle, M.; Whitman, T.; Lesho, E.; Schaecher, K.E. Escherichia coli harboring mcr-1 and blaCTX-M on a novel IncF plasmid: First report of mcr-1 in the USA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guh, A.Y.; Bulens, S.N.; Mu, Y.; Jacob, J.T.; Reno, J.; Scott, J.; Wilson, L.E.; Vaeth, E.; Lynfield, R.; Shaw, K.M. Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales in 7 US Communities, 2012–2013. JAMA 2015, 314, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, S.K.; Singh, R.; Chang, J.; Gombosev, A.; Tjoa, T.; Zahn, M.; Steger, P.; Huang, S.S. Emergence of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in Orange County, California, and support for early regional strategies to limit spread. Am. J. Infect. Control 2017, 45, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.J.; Lin, M.Y.; Weinstein, R.A.; Trick, W.E. Spread of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales among Illinois healthcare facilities: The role of patient sharing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Satlin, M.J.; Chen, L.; Patel, G.; Gomez-Simmonds, A.; Weston, G.; Kim, A.C.; Seo, S.K.; Rosenthal, M.E.; Sperber, S.J.; Jenkins, S.G. Multicenter clinical and molecular epidemiological analysis of bacteremia due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) in the CRE epicenter of the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02349-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. 2013. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/ (accessed on 17 January 2018).
- Livorsi, D.J.; Chorazy, M.L.; Schweizer, M.L.; Balkenende, E.C.; Blevins, A.E.; Nair, R.; Samore, M.H.; Nelson, R.E.; Khader, K.; Perencevich, E.N. A systematic review of the epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in the United States. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netikul, T.; Kiratisin, P. Genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales and the spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumonia ST340 at a university hospital in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotiprasitsakul, D.; Srichatrapimuk, S.; Kirdlarp, S.; Pyden, A.D.; Santanirand, P. Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A 5-year experience at a tertiary care hospital. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.-Q.; Du, X.-X.; Yu, Y.-S.; Shen, P.; Chen, Y.-G.; Li, L.-J. Plasmid-mediated KPC-2 in a Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate from China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Chan, E.W.-c.; Zhou, H.; Chen, S. Prevalence and genetic characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales strains in China. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017, 17, 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Jin, L.; Gu, B.; Xie, L.; Yang, C.; Ma, X.; Li, H. Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales Infections: Report from the China CRE Network. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01882-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-López, S.; Dominguez, M.; Conejo, M.; Pascual, A.; Rodriguez-Bano, J. Lessons from an outbreak of metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella oxytoca in an intensive care unit: The importance of time at risk and combination therapy. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 89, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgari, E.; Gartzonika, C.; Vrioni, G.; Politi, L.; Priavali, E.; Levidiotou-Stefanou, S.; Tsakris, A. The Balkan region: NDM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 clonal strain causing outbreaks in Greece. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabák, J.; Walková, R.; Študentová, V.; Chudáčková, E.; Bergerová, T. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Czech Republic in 2011. Euro Surveill. 2013, 18, 20626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zweigner, J.; Gastmeier, P.; Kola, A.; Klefisch, F.-R.; Schweizer, C.; Hummel, M.A. A carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae outbreak following bronchoscopy. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 936–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharbi, M.; Moore, L.; Gilchrist, M.; Thomas, C.; Bamford, K.; Brannigan, E.; Holmes, A. Forecasting carbapenem resistance from antimicrobial consumption surveillance: Lessons learnt from an OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae outbreak in a West London renal unit. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2015, 46, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambri, V. Successful containment and infection control of a Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae outbreak in an Italian hospital. New Microbiol. 2014, 37, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Brizendine, K.D.; Richter, S.S.; Cober, E.D.; van Duin, D. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae urinary tract infection following solid organ transplantation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, P.; Perl, T.M. Combating the spread of carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae: A battle that infection prevention should not lose. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, D.; Masarwa, S.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Mishali, H.; Fridental, I.; Rubinovitch, B.; Smollan, G.; Carmeli, Y.; Schwaber, M.J.; Israel, P. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in post-acute-care facilities in Israel. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucleo, E.; Caltagirone, M.; Marchetti, V.M.; D’Angelo, R.; Fogato, E.; Confalonieri, M.; Reboli, C.; March, A.; Sleghel, F.; Soelva, G. Colonization of long-term care facility residents in three Italian Provinces by multidrug-resistant bacteria. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.; Mc Namara, C.; Doody, O. Healthcare workers’ experiences of caring for patients colonized with carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) in an acute hospital setting–A scoping review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Zeshan, B.; Naveed, M.; Afzal, M.; Mohamed, M. Antibiotic resistance profile in relation to virulence genes fimH, hlyA and usp of uropathogenic E. coli isolates in Lahore, Pakistan. Trop. Biomed 2019, 36, 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Tischendorf, J.; de Avila, R.A.; Safdar, N. Risk of infection following colonization with carbapenem-resistant Enterobactericeae: A systematic review. Am. J. Infect Control. 2016, 44, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, I.; Sprecher, H.; Finkelstein, R.; Hadad, S.; Neuberger, A.; Hussein, K.; Raz-Pasteur, A.; Lavi, N.; Saad, E.; Henig, I. Eradication of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales gastrointestinal colonization with nonabsorbable oral antibiotic treatment: A prospective controlled trial. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2013, 41, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lübbert, C.; Lippmann, N.; Busch, T.; Kaisers, U.X.; Ducomble, T.; Eckmanns, T.; Rodloff, A.C. Long-term carriage of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-2-producing K pneumoniae after a large single-center outbreak in Germany. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2014, 42, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizny Gordon, A.E.; Mathers, A.J.; Cheong, E.Y.; Gottlieb, T.; Kotay, S.; Walker, A.S.; Peto, T.E.; Crook, D.W.; Stoesser, N. The Hospital Water Environment as a Reservoir for Carbapenem-Resistant Organisms Causing Hospital-Acquired Infections-A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofteland, S.; Naseer, U.; Lislevand, J.H.; Sundsfjord, A.; Samuelsen, Ø. A long-term low-frequency hospital outbreak of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae involving Intergenus plasmid diffusion and a persisting environmental reservoir. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, R.A.; Johnson, R.C.; Conlan, S.; Ramsburg, A.M.; Dekker, J.P.; Lau, A.F.; Khil, P.; Odom, R.T.; Deming, C.; Park, M. Genomic Analysis of Hospital Plumbing Reveals Diverse Reservoir of Bacterial Plasmids Conferring Carbapenem Resistance. MBio 2018, 9, e02011-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlan, S.; Thomas, P.J.; Deming, C.; Park, M.; Lau, A.F.; Dekker, J.P.; Snitkin, E.S.; Clark, T.A.; Luong, K.; Song, Y. Single-molecule sequencing to track plasmid diversity of hospital-associated carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 254ra126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, R.; Frank, K.M.; Jacobs, M.R.; Wilson, B.; Kaye, K.; Donskey, C.J.; Perez, F.; Endimiani, A.; Bonomo, R.A. Intestinal carriage of Carbapenemase-producing organisms: Current status of surveillance methods. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbuch, D.; Tridello, G.; Hoek, J.; Mikulska, M.; Akan, H.; Yaňez San Segundo, L.; Pabst, T.; Özçelik, T.; Klyasova, G.; Donnini, I. Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Negative Rods Causing Bacteremia in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: Intercontinental Prospective Study of the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the European Bone Marrow Transplantation Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, I.; Eldegla, H.E.; Nasef, N.; Shouman, B.; Abdel-Hady, H.; Shabaan, A.E. Risk factors and clinical outcomes for carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative late-onset sepsis in a neonatal intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 97, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Infection Control Measures to prevent The Transmission of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteralesthrough Cross-Border Transfer of Patients; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014.
- Fournier, S.; Desenfant, L.; Monteil, C.; Nion-Huang, M.; Richard, C.; Jarlier, V. Efficiency of different control measures for preventing carbapenemase-producing enterobacteria and glycopeptide-resistant Enterococcus faecium outbreaks: A 6-year prospective study in a French multihospital institution, January 2010 to December 2015. Euro Surveill. 2018, 23, 17–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Health Care Facilities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manges, A.R.; Johnson, J.R. Food-borne origins of Escherichia coli causing extraintestinal infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluytmans, J.A.; Overdevest, I.T.; Willemsen, I.; Kluytmans-Van Den Bergh, M.F.; Van Der Zwaluw, K.; Heck, M.; Rijnsburger, M.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Johnston, B.D. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from retail chicken meat and humans: Comparison of strains, plasmids, resistance genes, and virulence factors. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kola, A.; Kohler, C.; Pfeifer, Y.; Schwab, F.; Kühn, K.; Schulz, K.; Balau, V.; Breitbach, K.; Bast, A.; Witte, W. High prevalence of extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales in organic and conventional retail chicken meat, Germany. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2631–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfel, G.; Galler, H.; Luxner, J.; Petternel, C.; Reinthaler, F.F.; Haas, D.; Kittinger, C.; Grisold, A.J.; Pless, P.; Feierl, G. Multiresistant bacteria isolated from chicken meat in Austria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 12582–12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodousi, A.; Bonura, C.; Di Noto, A.M.; Mammina, C. Extended-Spectrum ss-Lactamase, AmpC-Producing, and Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Escherichia coli in retail broiler chicken meat, Italy. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, P.; López-Cerero, L.; Torres, E.; del Carmen Gómez-Sánchez, M.; Serrano, L.; Sánchez-Ortiz, M.D.N.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Pascual, A. Increased raw poultry meat colonization by extended spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in the south of Spain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 159, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoek, A.H.; Veenman, C.; van Overbeek, W.M.; Lynch, G.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Blaak, H. Prevalence and characterization of ESBL- and AmpC-producing Enterobacterales on retail vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, N.; Wareham, D.W.; Guerra, B.; Teale, C. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales and non-Enterobacterales from animals and the environment: An emerging public health risk of our own making? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, M.; Sekizuka, T.; Yamashita, A.; Kuroda, M.; Fujii, Y.; Murata, M.; Lee, K.-i.; Joshua, D.I.; Balakrishna, K.; Bairy, I. Distribution and relationships of antimicrobial resistance determinants among extended-spectrum cephalosporin or carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from rivers and sewage treatment plants in India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, N.; Poirel, L.; Bessa, L.J.; Barbosa-Vasconcelos, A.; da Costa, P.M.; Nordmann, P. VIM-1, VIM-34, and IMP-8 Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli Strains Recovered from a Portuguese River. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2585–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, R.; Daniels-Haardt, I.; Becker, K.; Mellmann, A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Mevius, D.; Schwarz, S.; Jurke, A. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in wildlife, food-producing and companion animals—A systematic review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomão, M.C.; Maristela, P.F.; Levin Anna, S.S. Patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in emergency room; is this a real problem? Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotb, S.; Lyman, M.; Ismail, G.; Abd El Fattah, M.; Girgis, S.A.; Etman, A.; Hafez, S.; El-Kholy, J.; Zaki, M.E.; Hebat-allah, G.R.; et al. Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Egyptian intensive care units using National Healthcare–associated Infections Surveillance Data, 2011–2017. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, M.; Deshpande, L.M.; Mendes, R.E.; Canton, R.; Sader, H.S.; Jones, R.N. Variations in the occurrence of resistance phenotypes and carbapenemase genes among Enterobacteriaceae isolates in 20 years of the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance program. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, S23–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.D.; Carmeli, Y.; Walton, A.L.; Schwaber, M.J. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A strategic roadmap for infection control. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, R.F.; D’Souza, A.W.; Dantas, G. The rapid spread of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 29, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnin, R.A.; Jousset, A.B.; Emeraud, C.; Oueslati, S.; Dortet, L.; Naas, T. Genetic diversity, biochemical properties, and detection methods of minor carbapenemases in Enterobacterales. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltagirone, M.; Nucleo, E.; Spalla, M.; Zara, F.; Novazzi, F.; Marchetti, V.M.; Piazza, A.; Bitar, I.; De Cicco, M.; Paolucci, S. Occurrence of extended spectrum β-lactamases, KPC-type, and MCR-1.2-producing Enterobacteriaceae from wells, river water, and wastewater treatment plants in Oltrepo Pavese area, northern Italy. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.M.; Mathema, B.; Larson, E.L. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in the community: A scoping review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, P.S.; Domitrovic, T.N.; Moretto, V.T.; Santos, C.S.; Ponce-Terashima, R.; Reis, M.G.; Barbosa, L.M.; Blanton, R.E.; Bonomo, R.A.; Perez, F. Antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from surface waters in urban Brazil highlights the risks of poor sanitation. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Tahir, K.; Aslam, S.; Cheema, S.M.; Rabaan, A.A.; Turkistani, S.A.; Garout, M.; Halwani, M.A.; Aljeldah, M.; Al Shammari, B.R.; et al. Heavy Metal (Arsenic) Induced Antibiotic Resistance among Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Bacteria of Nosocomial Origin. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kost, K.; Yi, J.; Rogers, B.; Jerris, R. Comparison of clinical methods for detecting carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Pract. Lab. Med. 2017, 8, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zahrani, I.A. Routine detection of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacilli in clinical laboratories. A review of current challenge. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, E.B.; Aurbach, U.; Wisplinghoff, H. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Laboratory Detection and Infection Control Practices. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.; Humphries, R. Clinical and laboratory considerations for the rapid detection of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2017, 8, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 8.0. 2018. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Richter, S.S.; Marchaim, D. Screening for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Who, When, and How? Virulence 2017, 8, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI (Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibilty Testing, Supplement, M100S28, 28th ed.; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, M.; Lutgring, J.D.; Ansari, U.; Lawsin, A.; Albrecht, V.; McAllister, G.; Daniels, J.; Lonsway, D.; McKay, S.L.; Beldavs, Z. Molecular characterization of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales collected in the United States. Microbial Drug Resistance 2022, 28, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.; Voets, G.; Scharringa, J.; Voskuil, S.; Fluit, A.; Rottier, W.; Leverstein-Van Hall, M.; Stuart, J.C. A disc diffusion assay for detection of class A, B and OXA-48 carbapenemases in Enterobacterales using phenyl boronic acid, dipicolinic acid and temocillin. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, I.A.; Alsiri, B.A. The emergence of carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates producing OXA-48 and NDM in the Southern (Asir) province, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, D.; Peirano, G.; Lascols, C.; Lloyd, T.; Church, D.L.; Pitout, J.D. Laboratory detection of Enterobacterales that produce carbapenemases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3877–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakris, A.; Poulou, A.; Bogaerts, P.; Dimitroulia, E.; Pournaras, S.; Glupczynski, Y. Evaluation of a new phenotypic OXA-48 disk test for differentiation of OXA-48 carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales clinical isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simner, P.J.; Martin, I.; Opene, B.; Tamma, P.D.; Carroll, K.C.; Milstone, A.M. Evaluation of Multiple Methods for Detection of Gastrointestinal Colonization of Carbapenem-Resistant Organisms from Rectal Swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1664–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarakolu, P.; Day, K.; Sidjabat, H.; Kamolvit, W.; Lanyon, C.; Cummings, S.; Paterson, D.; Akova, M.; Perry, J. Evaluation of a new chromogenic medium, chromID OXA-48, for recovery of carbapenemase producing Enterobacterales from patients at a university hospital in Turkey. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girlich, D.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Comparison of the SUPERCARBA, CHROM agar KPC, and Brilliance CRE screening media for detection of Enterobacterales with reduced susceptibility to carbapenems. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Quintanilla, M.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. CHROMagar mSuperCARBA and RAPIDECR Carba NP test for detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniadek, T.J.; Carroll, K.C.; Simner, P.J. Carbapenem-Resistant Non-Glucose-Fermenting Gram-Negative Bacilli: The Missing Piece to the Puzzle. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgring, J.D.; Limbago, B.M. The Problem of Carbapenemase- Producing-Carbapenem-Resistant-Enterobacterales Detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.; Gupta, R.; Raut, S.S.; Nataraj, G.; Mehta, P.R. Carba NP as a simpler, rapid, cost-effective, and a more sensitive alternative to other phenotypic tests for detection of carbapenem resistance in routine diagnostic laboratories. J. Lab. Physicians. 2017, 9, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Študentová, V.; Izdebski, R.; Oikonomou, O.; Pfeifer, Y.; Petinaki, E.; Hrabák, J. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry meropenem hydrolysis assay with NH4HCO3, a reliable tool for direct detection of carbapenemase activity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Kashiwa, M.; Arai, K.; Nagano, N.; Saito, R. Comparison of the Modified-Hodge test, Carba NP test, and carbapenem inactivation method as screening methods for carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2016, 128, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glupczynski, Y.; Evrard, S.; Ote, I.; Mertens, P.; Huang, T.-D.; Leclipteux, T.; Bogaerts, P. Evaluation of two new commercial immunochromatographic assays for the rapid detection of OXA-48 and KPC carbapenemases from cultured bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareham, D.W.; Phee, L.M.; Abdul Momin, M.H.F. Direct detection of carbapenem resistance determinants in clinical specimens using immunochromatographic lateral flow devices. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1997–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabak, J.; Chudackova, E.; Walkova, R. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight (maldi-tof) mass spectrometry for detection of antibiotic resistance mechanisms: From research to routine diagnosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabák, J.; Walková, R.; Študentová, V.; Chudáčková, E.; Bergerová, T. Carbapenemase activity detection by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3222–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabak, J.; Chudackova, E.; Papagiannitsis, C.C. Detection of carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae: A challenge for diagnostic microbiological laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, S.; Damodaran, S.; Gopi, R.; Bakthavatchalam, Y.D.; Veeraraghavan, B. Rapid Screening for Carbapenem Resistant Organisms: Current Results and Future Approaches. J. Clin. Diagn Res. 2015, 9, DM01–DM03. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, J.A. Staphylococci. In Molecular Typing in Bacterial Infections; Ivano de Filippis, M.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas, S.; Shore, A.C.; Coleman, D.C.; Humphreys, H.; Hughes, D.F. DNA microarray genotyping and virulence and antimicrobial resistance gene profiling of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream isolates from renal patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4349–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Nielsen, E.M.; Kaas, R.S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. Evaluation of whole genome sequencing for outbreak detection of Salmonella enterica. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köser, C.U.; Holden, M.T.; Ellington, M.J.; Cartwright, E.J.; Brown, N.M.; Ogilvy-Stuart, A.L.; Hsu, L.Y.; Chewapreecha, C.; Croucher, N.J.; Harris, S.R. Rapid whole-genome sequencing for investigation of a neonatal MRSA outbreak. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabaan, A.A.; Eljaaly, K.; Alhumaid, S.; Albayat, H.; Al-Adsani, W.; Sabour, A.A.; Alshiekheid, M.A.; Al-Jishi, J.M.; Khamis, F.; Alwarthan, S.; et al. An Overview on Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Medicina 2022, 58, 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111675
Rabaan AA, Eljaaly K, Alhumaid S, Albayat H, Al-Adsani W, Sabour AA, Alshiekheid MA, Al-Jishi JM, Khamis F, Alwarthan S, et al. An Overview on Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Medicina. 2022; 58(11):1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111675
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabaan, Ali A., Khalid Eljaaly, Saad Alhumaid, Hawra Albayat, Wasl Al-Adsani, Amal A. Sabour, Maha A. Alshiekheid, Jumana M. Al-Jishi, Faryal Khamis, Sara Alwarthan, and et al. 2022. "An Overview on Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales" Medicina 58, no. 11: 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111675
APA StyleRabaan, A. A., Eljaaly, K., Alhumaid, S., Albayat, H., Al-Adsani, W., Sabour, A. A., Alshiekheid, M. A., Al-Jishi, J. M., Khamis, F., Alwarthan, S., Alhajri, M., Alfaraj, A. H., Tombuloglu, H., Garout, M., Alabdullah, D. M., Mohammed, E. A. E., Yami, F. S. A., Almuhtaresh, H. A., Livias, K. A., ... Ahmed, N. (2022). An Overview on Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. Medicina, 58(11), 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111675










