Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.3. Echocardiography
2.4. Two-Dimensional (2D) Echocardiography
2.5. Doppler Echocardiography
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kosmala, W.; Marwick, T.H. Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Appleton, C.P.; Gillebert, T.C.; Marino, P.N.; Oh, J.K.; Smiseth, O.A.; Waggoner, A.D.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Pellikka, P.A.; Evangelista, A. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2009, 10, 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Smiseth, O.A.; Appleton, C.P.; Byrd, B.F.; Dokainish, H.; Edvardsen, T.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Gillebert, T.C.; Klein, A.L.; Lancellotti, P.; et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2016, 17, 1321–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.B.; Holland, D.J.; Atherton, J.J.; Whalley, G. New Diastology Guidelines: Evolution, Validation and Impact on Clinical Practice. Heart Lung Circ. 2019, 28, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tawil, J.; Gelzinis, T.A. Differential diagnosis and clinical management of diastolic heart failure: Current best practice. Res. Rep. Clin. Cardiol. 2016, 7, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarasunas, J.; Aidietis, A.; Aidietiene, S. Left atrial strain—An early marker of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with hypertension and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2018, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskas, S.S.; Kansakar, U.; Varzideh, F.; Wilson, S.; Mone, P.; Lombardi, A.; Gambardella, J.; Santulli, G. Heart failure in diabetes. Metabolism 2021, 125, 154910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad-Tarazi, F.M. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and cardiovascular regulation in hypertension. Am. J. Med. 1989, 87, 42S–44S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, Y.; Fok, H.; Simpson, J.; Kentish, J.C.; Shah, A.M.; Chowienczyk, P.J. Reduced First-Phase Ejection Fraction and Sustained Myocardial Wall Stress in Hypertensive Patients with Diastolic Dysfunction: A Manifestation of Impaired Shortening Deactivation That Links Systolic to Diastolic Dysfunction and Preserves Systolic Ejection Fraction. Hypertension 2017, 69, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayor, M.; Enserro, D.M.; Xanthakis, V.; Larson, M.G.; Benjamin, E.J.; Aragam, J.; Mitchell, G.F.; Vasan, R.S. Comorbidities and Cardiometabolic Disease: Relationship with Longitudinal Changes in Diastolic Function. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Simone, G.; Palmieri, V. Diastolic Dysfunction in Arterial Hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2007, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, B.; Zheng, C.; Kang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Prevalence of heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction in China: The China Hypertension Survey, 2012–2015. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Paulus, W.J. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ather, S.; Chan, W.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Ramasubbu, K.; Zachariah, A.A.; Wehrens, X.H.T.; Deswal, A. Impact of noncardiac comorbidities on morbidity and mortality in a predominantly male population with heart failure and preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Carson, P.E.; Komajda, M.; McKelvie, R.; Zile, M.R.; Ptaszynska, A.; Staiger, C.; Donovan, J.M.; Massie, B.M. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Clinical characteristics of 4133 patients enrolled in the I-PRESERVE trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, P.; Gambardella, J.; Pansini, A.; de Donato, A.; Martinelli, G.; Boccalone, E.; Matarese, A.; Frullone, S.; Santulli, G. Cognitive Impairment in Frail Hypertensive Elderly Patients: Role of Hyperglycemia. Cells 2021, 10, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, S.M.L.; Yasmin; McEniery, C.M.; Mäki-Petäjä, K.M.; Booth, A.D.; Cockcroft, J.R.; Wilkinson, I.B. Isolated systolic hypertension is characterized by increased aortic stiffness and endothelial dysfunction. Hypertension 2007, 50, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.L. Heart failure in women. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2015, 12, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorop, O.; Heinonen, I.; van Kranenburg, M.; van de Wouw, J.; de Beer, V.J.; Nguyen, I.T.N.; Octavia, Y.; van Duin, R.W.B.; Stam, K.; van Geuns, R.-J.; et al. Multiple common comorbidities produce left ventricular diastolic dysfunction associated with coronary microvascular dysfunction, oxidative stress, and myocardial stiffening. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, W.J.; Tschöpe, C. A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandt, M.M.; Nguyen, I.T.N.; Krebber, M.M.; van de Wouw, J.; Mokry, M.; Cramer, M.J.; Duncker, D.J.; Verhaar, M.C.; Joles, J.A.; Cheng, C. Limited synergy of obesity and hypertension, prevalent risk factors in onset and progression of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6666–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pessoa-Amorim, G.; Mancio, J.; Vouga, L.; Ribeiro, J.; Gama, V.; Bettencourt, N.; Fontes-Carvalho, R. Impaired Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of New-onset Atrial Fibrillation After Aortic Valve Replacement Independently of Left Atrial Size. Rev. Española De Cardiol. 2018, 71, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes-Carvalho, R.; Sampaio, F.; Teixeira, M.; Ruivo, C.; Ribeiro, J.; Azevedo, A.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Ribeiro, V.G. Left atrial deformation analysis by speckle tracking echocardiography to predict exercise capacity after myocardial infarction. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2018, 37, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, M.; Pastore, M.C.; Righini, F.M.; Mandoli, G.E.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Lisi, M.; Nistor, D.; Sparla, S.; Curci, V.; Di Tommaso, C.; et al. Prognostic value of left atrial strain in patients with moderate asymptomatic mitral regurgitation. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 35, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oike, F.; Usuku, H.; Yamamoto, E.; Yamada, T.; Egashira, K.; Morioka, M.; Nishi, M.; Komorita, T.; Hirakawa, K.; Tabata, N.; et al. Prognostic value of left atrial strain in patients with wild-type transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 5316–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M. Left atrial strain in patients with arterial hypertension. Int. Cardiovasc. Forum J. 2015, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Addetia, K.; Maffessanti, F.; Mor-Avi, V.; Lang, R.M. LA Strain for Categorization of LV Diastolic Dysfunction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Medvedofsky, D.; Mediratta, A.; Balaney, B.; Kruse, E.; Ciszek, B.; Shah, A.P.; Blair, J.E.; Maffessanti, F.; Addetia, K.; et al. Peak left atrial strain as a single measure for the non-invasive assessment of left ventricular filling pressures. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 35, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondillo, S.; Cameli, M.; Caputo, M.L.; Lisi, M.; Palmerini, E.; Padeletti, M.; Ballo, P. Early Detection of Left Atrial Strain Abnormalities by Speckle-Tracking in Hypertensive and Diabetic Patients with Normal Left Atrial Size. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2011, 24, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebjam, M.; Mazareei, A.; Lotfi-Tokaldany, M.; Ghaffari-Marandi, N.; Zoroufian, A.; Sheikhfatollahi, M. Comparison of Left Atrial Function between Hypertensive Patients with Normal Atrial Size and Normotensive Subjects Using Strain Rate Imaging Technique. Arch. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 2, e16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Değirmenci, H.; Duman, H.; Demirelli, S.; Bakirci, E.; Hamur, H.; Inci, S.; Simsek, Z.; Askin, L.; Arısoy, A.; Lazoglu, Z. Assessment of effect of irbesartan and nebivolol on the left atrium volume and deformation in the patients with mild-moderate hypertension. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.-Y.; Sun, J.P.; Lee, A.P.-W.; Yang, X.S.; Ji, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.-M.; Wang, J.-G. Left Atrial Function as Assessed by Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Hypertension. Medicine 2015, 94, e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.A.; Belyavskiy, E.; Aravind-Kumar, R.; Kropf, M.; Frydas, A.; Braunauer, K.; Marquez, E.; Krisper, M.; Lindhorst, R.; Osmanoglou, E.; et al. Potential Usefulness and Clinical Relevance of Adding Left Atrial Strain to Left Atrial Volume Index in the Detection of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Gómez, A.M.; Sierra, L.T.; Mora, N.M.; Toledo, E.; Alonso, A.; Uriarte, M.G.; Sanchez, C.S.; Portillo, M.P.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Arellano, E.E.; et al. Left atrial strain improves echocardiographic classification of diastolic function in patients with metabolic syndrome and overweight-obesity. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 348, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, F.; D’Elia, N.; Nolan, M.T.; Marwick, T.H.; Negishi, K. Normal Ranges of Left Atrial Strain by Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2017, 30, 59–70.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frydas, A.; Morris, D.A.; Belyavskiy, E.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kropf, M.; Tadic, M.; Roessig, L.; Lam, C.S.P.; Shah, S.J.; Solomon, S.D.; et al. Left atrial strain as sensitive marker of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Khan, F.H.; Remme, E.W.; Ohte, N.; García-Izquierdo, E.; Chetrit, M.; Moñivas-Palomero, V.; Mingo-Santos, S.; Andersen, Ø.S.; Gude, E.; et al. Determinants of left atrial reservoir and pump strain and use of atrial strain for evaluation of left ventricular filling pressure. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 23, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizu, T.; Seo, Y.; Kameda, Y.; Kawamura, R.; Kimura, T.; Shimojo, N.; Xu, D.; Murakoshi, N.; Aonuma, K. Left Ventricular Strain and Transmural Distribution of Structural Remodeling in Hypertensive Heart Disease. Hypertension 2014, 63, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, M.; Khan, F.; Stoklosa, T.; Iannaccone, A.; Negishi, K.; Marwick, T.H. Prognostic Implications of LV Strain Risk Score in Asymptomatic Patients with Hypertensive Heart Disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göksülük, H.; Habibova, U.; Ongun, A.; Akbulut, M.; Özyüncü, N.; Kürklü, T.S.T.; Erol, C. Evaluation of the effect of dipping pattern in hypertensive patients on the left ventricular systolic functions by two-dimensional strain analysis. Echocardiography 2017, 34, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Group with Normal LAP N = 104 (57.77%) Mean ± SD or % | Group with Elevated LAP N = 76 (42.22%) Mean ± SD or % | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.11 ± 6.15 | 54.95 ± 7.2 | 0.07 |
| Gender (f) | 55.4% | 44.6% | 0.1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.32 ± 3.58 | 28.93 ± 4.14 | 0.2 |
| History of hypertension ≤ 5 years | 58 (55.8%) | 2 (2.6%) | <0.0001 |
| History of hypertension 5–10 years | 46 (44.2%) | 14 (18.4%) | 0.0003 |
| History of hypertension ≥ 10 years | 0 | 60 (78.9%) | <0.0001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 126.2 ± 12.4 | 128 ± 15.4 | 0.33 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 72 ± 10.2 | 75 ± 13.3 | 0.08 |
| HR (bpm) | 75 ± 20.1 | 78 ± 25.4 | 0.37 |
| History of diabetes | 23 (22.1%) | 30 (39.4%) | 0.01 |
| Smoking history | 26 (25%) | 36 (47%) | 0.002 |
| History of hyperlipidemia | 20 (19.2%) | 28 (36.8%) | 0.008 |
| Number of antihypertensive agents/day ≤ 2 | 58 (55%) | 46 (44%) | 0.1 |
| Number of antihypertensive agents/day > 2 | 36 (47%) | 40 (52%) | 0.5 |
| Users of β blockers | 28 (26.9%) | 22 (28.9%) | 0.7 |
| Users of ACE/ARB | 52 (50%) | 47 (61.8%) | 0.1 |
| Users of CCB | 34 (32.7%) | 32 (42.1%) | 0.1 |
| Users of Thiazides | 36 (34.6%) | 30 (39.5%) | 0.5 |
| Parameter | Group with Normal LAP N = 104 (57.77%) Mean ± SD or % | Group with Elevated LAP N = 76 (42.22%) Mean ± SD or % | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| IVS/PLW (cm) | 1.17 ± 0.12 | 1.27 ± 0.14 | <0.0001 |
| LVDd (cm) | 4.7 (4.3; 5.1) | 4.7 (4.4; 5.1) | 0.38 |
| LVDs (cm) | 2.9 (2.6; 3.2) | 2.9 (2.7; 3.3) | 0.19 |
| EF (%) | 63 (60; 63) | 61 (59; 63) | 0.007 |
| LVMi (g/m2) | 90.46 ± 15.42 | 113.32 ± 29.99 | <0.0001 |
| Vp (cm/s) | 52.87 ± 7.14 | 47.3 ± 4.52 | <0.0001 |
| E/e’ ratio | 10.42 ± 2.23 | 15.13 ± 3.86 | <0.0001 |
| IVRT (mm/s) | 85.48 ± 12.54 | 71.07 ± 18.01 | <0.0001 |
| LA (cm) | 3.7 (3.4–3.9) | 4.3 (3.9–4.6) | <0.0001 |
| LAVi (mL/m2) | 34 (28.61–46.17) | 35.80 (41.93–57.05) | <0.0001 |
| LVM (g) | 182.2 (154.1–204) | 215.03 (196.75–250) | <0.0001 |
| E-wave (m/s) | 0.7 (0.6–0.8) | 0.9 (0.7–1.0) | <0.0001 |
| E/A ratio | 0.94 (0.75–1.19) | 1.19 (0.83–1.4) | 0.002 |
| DTE (ms) | 163 (141–185) | 132.5 (121.5–143) | <0.0001 |
| e’ (m/s) | 0.06 (0.05–0.08) | 0.05 (0.05–0.06) | <0.0001 |
| LVGS (%) | −17.62 (−19.35–15.36) | −14.58 (−15.5–−13.39) | <0.0001 |
| LAS (%) | 34.75 (27.16–38.45) | 15.84 (12.22–21.35) | <0.0001 |
| RVDd (cm) | 2.4 (2.2; 2.6) | 2.4 (2.1; 2.6) | 0.93 |
| TR Vmax (m/s) | 1.95 (0–2.48) | 2.1 (1.05–2.75) | 0.04 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 24.6 ± 3.2 | 23.8 ± 4.6 | 0.1 |
| RVs’ (cm/s) | 14 ± 2.1 | 13.6 ±1.9 | 0.1 |
| MR mild | 14 (35.9%) | 25 (64.1%) | 0.003 |
| TR mild | 12 (33.3%) | 24 (66.7%) | 0.001 |
| Parameter | Univariant | Multivariant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | |
| LVMi (g/m2) | 1.063 (1.038–1.088) | <0.0005 | / | ns |
| LVGS % | 1.325 (1.169–1.503) | <0.0005 | / | ns |
| Vp (cm/s) | 0.825 (0.766–0.889) | <0.0005 | / | ns |
| DTE (ms) | 0.984 (0.976–0.993) | <0.0005 | 0.990 (0.981–0.998) | 0.021 |
| LAS % | 0.830 (0.790–0.872) | <0.0005 | 0.834 (0.793–0.876) | 0.000 |
| Parameter | AUC | Std. Error | p Value | Cut-off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E/e’ | 0.879 | 0.027 | <0.0005 | 12.35 | 82.9 | 77.9 |
| LAVi (mL/m2) | 0.689 | 0.040 | <0.0005 | 39.90 | 75.0 | 66.3 |
| LVMi (g/m2) | 0.763 | 0.035 | <0.0005 | 97.33 | 76.3 | 66.3 |
| GLS (%) | 0.800 | 0.033 | <0.0005 | −15.90 | 85.5 | 70.2 |
| TR V max (m/s) | 0.587 | 0.043 | =0.046 | 2.47 | 40.8 | 75.0 |
| Vp (cm/s) | 0.761 | 0.035 | <0.0005 | 50.50 | 84.2 | 65.4 |
| DTE (ms) | 0.764 | 0.040 | <0.0005 | 142.00 | 75.0 | 74.0 |
| LAS (%) | 0.885 | 0.025 | <0.0005 | 24.27 | 78.9 | 84.6 |
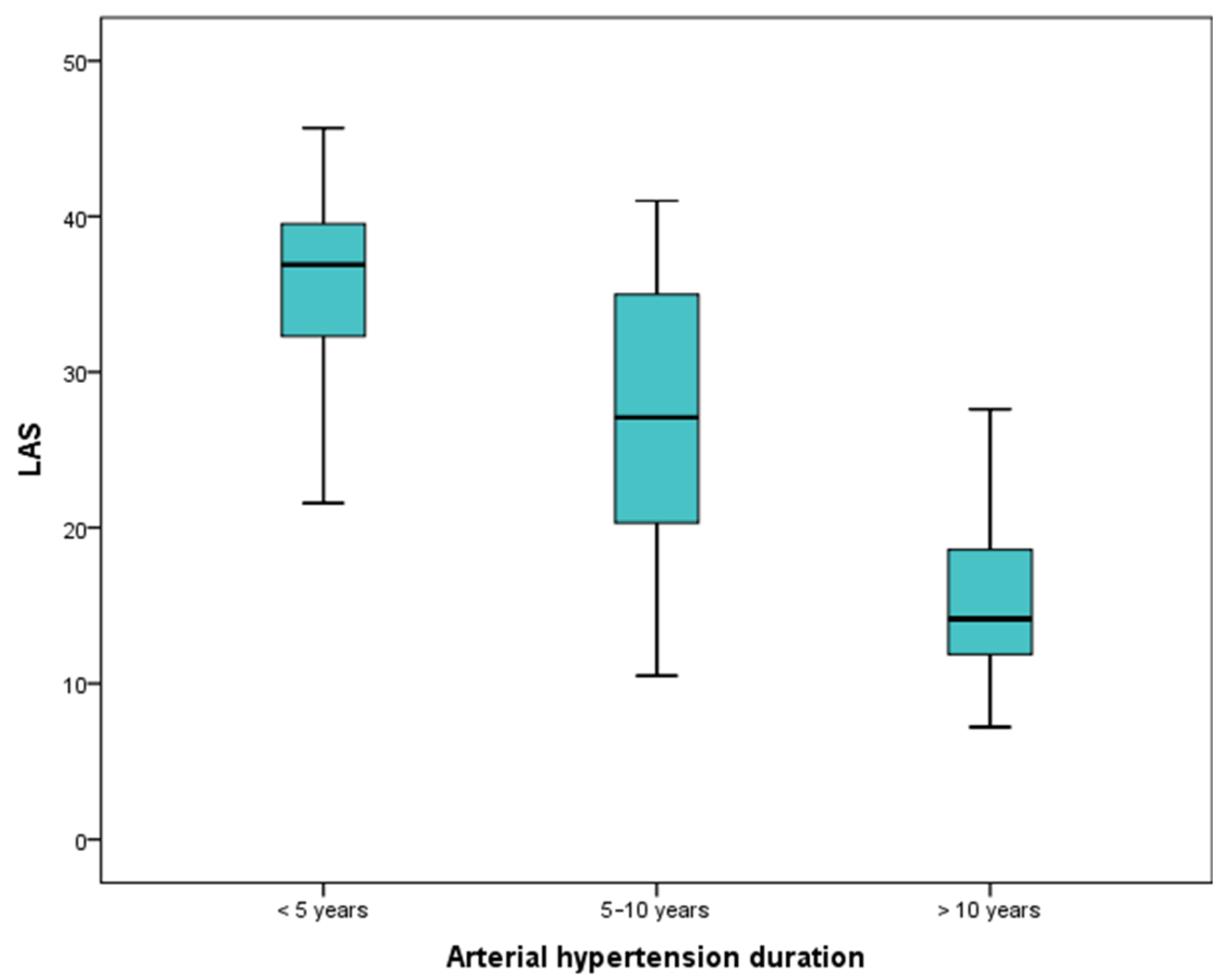
| Parameter | History of Hypertension ≤ 5 Years | History of Hypertension 5–10 Years | History of Hypertension ≥ 10 Years | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAS % | 36.9 (32.2; 41.2) | 27 (20.5; 35) | 14.1 (11.8; 19.4) | 0.000 |
| LAS ≤ 24.27 | 59 (98.3%) | 38 (63.3%) | 1 (11.7%) | 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miljković, T.; Ilić, A.; Milovančev, A.; Bjelobrk, M.; Stefanović, M.; Stojšić-Milosavljević, A.; Tadić, S.; Golubović, M.; Popov, T.; Petrović, M. Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Arterial Hypertension. Medicina 2022, 58, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58020156
Miljković T, Ilić A, Milovančev A, Bjelobrk M, Stefanović M, Stojšić-Milosavljević A, Tadić S, Golubović M, Popov T, Petrović M. Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Arterial Hypertension. Medicina. 2022; 58(2):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58020156
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiljković, Tatjana, Aleksandra Ilić, Aleksandra Milovančev, Marija Bjelobrk, Maja Stefanović, Anastazija Stojšić-Milosavljević, Snežana Tadić, Miodrag Golubović, Tanja Popov, and Milovan Petrović. 2022. "Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Arterial Hypertension" Medicina 58, no. 2: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58020156
APA StyleMiljković, T., Ilić, A., Milovančev, A., Bjelobrk, M., Stefanović, M., Stojšić-Milosavljević, A., Tadić, S., Golubović, M., Popov, T., & Petrović, M. (2022). Left Atrial Strain as a Predictor of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients with Arterial Hypertension. Medicina, 58(2), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58020156






