Effects of Non-Invasive Radiofrequency Diathermy in Pelvic Floor Disorders: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Literature Search
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Methodological Quality Assessment
3. Results
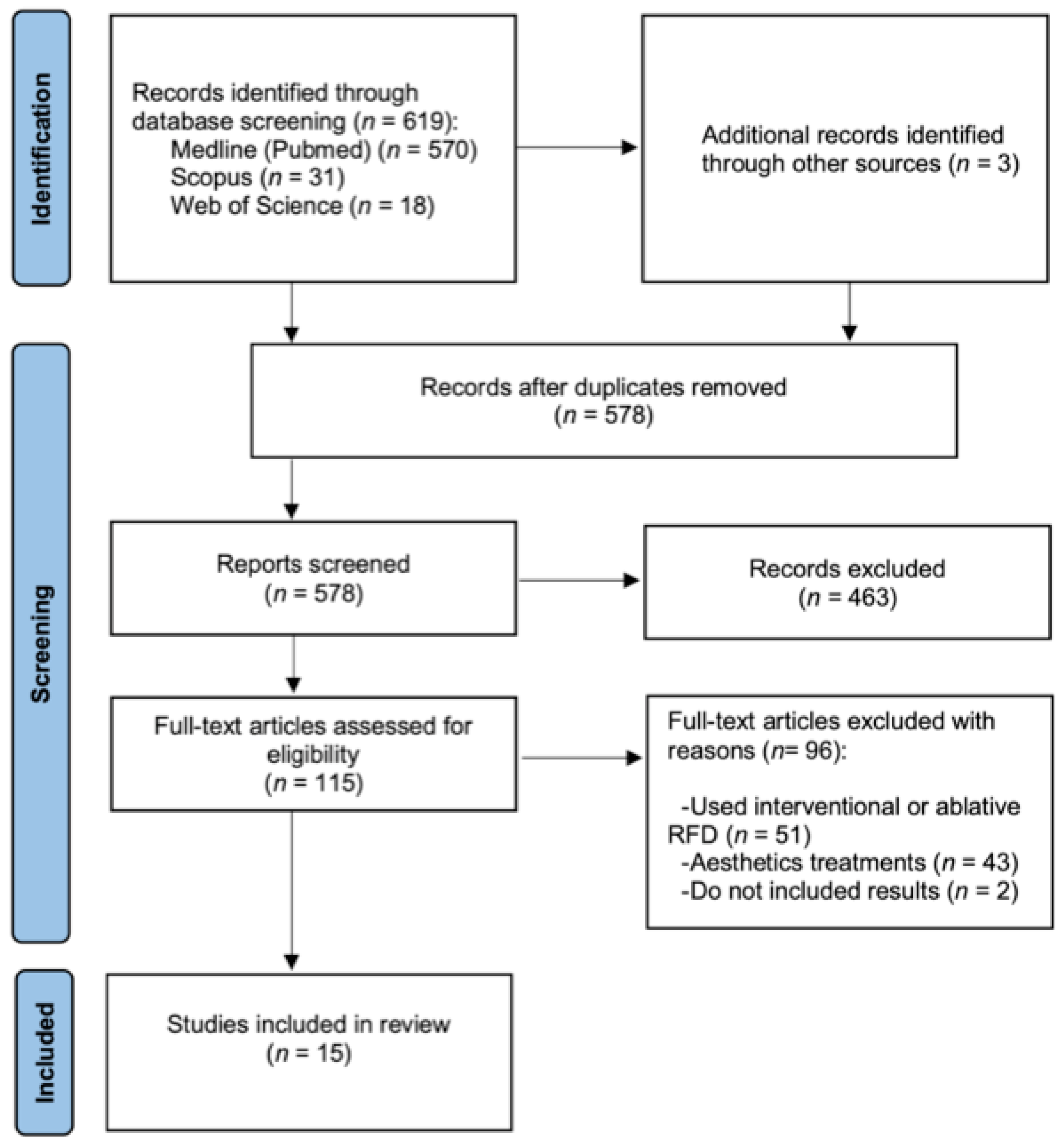
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Studies Included in the Review
3.3. Methodological Quality Assessment
3.4. Synthesis of Outcomes and Questionnaires Used in Studies Included in This Review
3.5. Synthesis of Main Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumaran, B.; Herbland, A.; Watson, T. Continuous-mode 448 kHz capacitive resistive monopolar radiofrequency induces greater deep blood flow changes compared to pulsed mode shortwave: A crossover study in healthy adults. Eur. J. Physiother. 2017, 19, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, B.; Watson, T. Thermal build-up, decay and retention responses to local therapeutic application of 448 kHz capacitive resistive monopolar radiofrequency: A prospective randomised crossover study in healthy adults. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 6736, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, B.; Watson, T. Radiofrequency-based treatment in therapy-related clinical practice—A narrative review. Part II: Chronic conditions. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2015, 20, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltrame, R.; Ronconi, G.; Ferrara, P.E.; Salgovic, L.; Vercelli, S.; Solaro, C.; Ferriero, G. Capacitive and resistive electric transfer therapy in rehabilitation: A systematic review. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2020, 43, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Vera, A.J. Radiofrequency in aesthetics skin treatment: Classification and modalities. J. Dermatol. Res. Ski. Care 2017, 1, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, S.L.; Miller, L.D.; Mishra, K. Pelvic floor physical therapy in the treatment of pelvic floor dysfunction in women. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 31, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.H.; Rawlins, A.; Brinker, C.A. Physical Therapy Treatment of Pelvic Pain. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 28, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz-Cabello, M.; Barrios-Quinta, C.J.; Escobio-Prieto, I.; Sobrino-Sánchez, R.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J.; Espejo-Antúnez, L. Treatment of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome with Dielectric Radiofrequency Diathermy: A Preliminary Single—Group Study with Six-Month Follow-Up. Medicina 2021, 57, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz-Cabello, M.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J.; Aguilar-Ferrándiz, M.E.; Espejo-Antúnez, L. Monopolar dielectric diathermy by emission of radiofrequency in Patellofemoral pain. A single-blind-randomized clinical trial. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2020, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, B.; Watson, T. Treatment using 448 kHz capacitive resistive monopolar radiofrequency improves pain and function in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee joint: A randomised controlled trial. Physiotheraphy 2019, 105, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochsprung, A.; Escudero-Uribe, S.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J.; Izquierdo-Ayuso, G. Effectiveness of monopolar dielectric transmission of pulsed electromagnetic fields for multiple sclerosis-related pain: A pilot study. Neurologia 2021, 36, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Vera, A.J.; García-Romero, J.C.; Alvero-Cruz, J.R.; Lomas-vega, R. Effects of Monopolar Dielectric Radiofrequency Signals on the Symptoms of Fibromyalgia: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Marín, M.; Rodríguez-Almagro, D.; Castellote-Caballero, Y.; Achalandabaso-Ochoa, A.; Lomas-Vega, R.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J. Efficacy of Non-Invasive Radiofrequency-Based Diathermy in the Postoperative Phase of Knee Arthroplasty: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.; Andriessen, A.; Bader, A.; Alinsod, R.; French, E.S.; Guerette, N.; Kolodchenko, Y.; Krychman, M.; Murrmann, S.; Samuels, J. Review and clinical experience exploring evidence, clinical efficacy, and safety regarding nonsurgical treatment of feminine rejuvenation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantash, B.M.; Ubeid, A.A.; Chang, H.; Kafi, R.; Renton, B. Bipolar fractional radiofrequency treatment induces neoelastogenesis and neocollagenesis. Lasers Surg. Med. 2009, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moseley, A.M.; Herbert, R.D.; Sherrington, C.; Maher, C.G. Evidence for physiotherapy practice: A survey of the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro). Aust. J. Physiother. 2002, 48, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connel, D. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quailty of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analysis. 2009. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Bretelle, F.; Fabre, C.; Golka, M.; Pauly, V.; Roth, B.; Bechadergue, V.; Blanc, J. Capacitive–resistive radiofrequency therapy to treat postpartum perineal pain: A randomized study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krychman, M.; Rowan, C.G.; Allan, B.B.; DeRogatis, L.; Durbin, S.; Yacoubian, A.; Wilkerson, D. Effect of Single-Treatment, Surface-Cooled Radiofrequency Therapy on Vaginal Laxity and Female Sexual Function: The VIVEVE I Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Sex. Med. 2017, 14, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanaman Wilson, M.J.; Bolton, J.; Jones, I.T.; Wu, D.C.; Calame, A.; Goldman, M.P. Histologic and Clinical Changes in Vulvovaginal Tissue After Treatment With a Transcutaneous Temperature-Controlled Radiofrequency Device. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruth, J.C. Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of a Novel Radiofrequency Device for Vaginal Treatment. Surg. Technol. Int. 2018, 32, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lordelo, P.; Boas, A.V.; Sodré, D.; Lemos, A.; Tozetto, S.; Brasil, C. New concept for treating female stress urinary incontinence with radiofrequency. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2017, 43, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vicariotto, F.; Raichi, M. Technological evolution in the radiofrequency treatment of vaginal laxity and menopausal vulvo-vaginal atrophy and other genitourinary symptoms: First experiences with a novel dynamic quadripolar device. Minerva Ginecol. 2016, 68, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alinsod, R.M. Transcutaneous temperature controlled radiofrequency for orgasmic dysfunction. Lasers Surg. Med. 2016, 48, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, C.; Romeo, S.; D’Amato, F.; Usala, M.; Letizia Mauro, G.; Caruana, G. Does Transfer Capacitive Resistive Energy Has a Therapeutic Effect on Peyronie’s Disease? Randomized, Single-Blind, Sham-Controlled Study on 96 Patients: Fast Pain Relief. Urol. Int. 2017, 99, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordêlo, P.; Leal, M.R.D.; Brasil, C.A.; Santos, J.M.; Lima, M.C.N.P.C.; Sartori, M.G.F. Radiofrequency in female external genital cosmetics and sexual function: A randomized clinical trial. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2016, 27, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibaschoff, G.; Gonzalez Izasa, P.; Cardona, J.L.; Miklos, J.R.; Moore, R.D. Trascutaneous Temperature Controlled Radiofrequency (TTCRF) for the Treatment of Menopausal Vaginal/Genitourinary Symptoms. Surg. Technol. Int. 2016, 26, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Fortún-Rabadán, R.; Sierra-Artal, B.; Jiménez-Sánchez, C. Effectiveness of intracavitary monopolar dielectric radiofrequency in women with endometriosis-associated pain: A case series. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2022, 46, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, M.; Asghari-azghan, A.; Montazeri, S.; Razzaghi, Z.; Mazloomfard, M.M.; Vafaee, R. Intravaginal Pulsed Contractile Radiofrequency for Stress Urinary Incontinence Treatment; A Safety Study. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2021, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cuadros, M.E.; Kazlauskas, S.G.; Albaladejo-Florin, M.J.; Robles-López, M.; Laborda-Delgado, A.; de la Cal-Alvarez, C.; Pérez-Moro, O. Effectiveness of multimodal rehabilitation (biofeedback plus capacitive–resistive radiofrequency) on chronic pelvic pain and dyspareunia: Prospective study and literature review. Rehabilitacion 2020, 54, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, E.; Ramirez, H.; Westfall, L.; Theodorou, S. Role of Radiofrequency (Votiva, InMode) in Pelvic Floor Restoration. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodré, D.S.M.; Sodré, P.R.S.; Brasil, C.; Teles, A.; Dória, M.; Café, L.E.; Lordelo, P. New concept for treating urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy with radiofrequency: Phase 1 clinical trial. Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 34, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Cuadros, M.E.; Kazlauskas, S.G.; Albaladejo-Florin, M.J.; Robles-López, M.; Laborda-Delgado, A.; de la Cal-Alvarez, C.; Pérez-Moro, O. Efectividad de la rehabilitación multimodal (biofeedback más radiofrecuencia capacitiva-resistiva) sobre el dolor pélvico crónico y la dispareunia: Estudio prospectivo y revisión de la bibliografía. Rehabilitación 2020, 54, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, M.A.; Kristjansson, B.; Griffith, D.; Versi, E. The Incontinence Impact Questionnaire and the Urogenital Distress Inventory: A revisit of their validity in women without a urodynamic diagnosis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 185, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajebrahimi, S.; Corcos, J.; Lemieux, M.C. International consultation on incontinence questionnaire short form: Comparison of physician versus patient completion and immediate and delayed self-administration. Urology 2004, 63, 1076–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.; Brown, C.; Heiman, J.; Leiblum, S.; Meston, C.; Shabsigh, R.; Ferguson, D.; D’agostino, R. The Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI): A Multidimensional Self-Report Instrument for the Assessment of Female Sexual Function D’Agostino (2000) The Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI): A Multidimensional Self-Report Instrument for the Assessment of Female Sexual Function. J. Sex Marital Ther. 2011, 26, 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, P.; Avery, K.; Gardener, N.; Donovan, J. The international consultation on incontinence modular questionnaire: www.iciq.net. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krhut, J.; Zachoval, R.; Smith, P.P.; Rosier, P.F.W.M.; Valansk, L.; Martan, A.; Zvara, P. Pad Weight Testing in the Evaluation of Urinary Incontinence. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014, 33, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A.; López-de-Celis, C.; Lucha-López, O.M.; González-Rueda, V.; Tricás-Moreno, J.M.; Simon, M.; Hidalgo-García, C. Thermal and non-thermal effects of capacitive–resistive electric transfer application on different structures of the knee: A cadaveric study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmolenko, P.S.; Moon, E.J.; Landon, C.; Manzoor, A.; Hochman, D.W.; Viglianti, B.L.; Dewhirst, M.W. Thresholds for thermal damage to normal tissues: An update. Int. J. Hyperth. 2011, 27, 320–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.F.; de Oliveira, P.; Silva, F.K.B.A.; da Costa, A.C.S.; Pereira, C.R.A.; Casenave, S.; Valentim Silva, R.M.; Araújo-Neto, L.G.; Santos-Filho, S.D.; Aizamaque, E.; et al. Radiofrequency treatment induces fibroblast growth factor 2 expression and subsequently promotes neocollagenesis and neoangiogenesis in the skin tissue. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albornoz-Cabello, M.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J.; de la Cruz-Torres, B. Efficacy of monopolar dielectric transmission radio frequency in panniculus adiposus and cellulite reduction Efficacy of monopolar dielectric transmission radio frequency in panniculus adiposus and cellulite reduction. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2017, 19, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| DATABASES | SEARCH STRATEGY |
|---|---|
| PubMed Medline | (radiofrequency therapy [mh] OR radiofrequency therapy [tiab] OR “radiofrequency” [tiab] OR hyperthermia, induced [mh] OR hyperthermia, induced [tiab] OR induced hyperthermia [tiab] OR diathermy [mh] OR diathermy [tiab] OR capacitive–resistive therapy [tiab] OR dielectric radiofrequency [tiab] OR dielectric radiofrequency therapy [tiab]) AND (pelvic floor [mh] or pelvic floor [tiab] OR pelvic floor disorders [mh] OR pelvic floor disorders [tiab] OR pelvic floor diseases [tiab] OR pelvic floor dysfunction [tiab] OR urogenital diseases [mh] OR urogenital diseases [tiab] OR female urogenital diseases [tiab]) |
| SCOPUS | (TITLE-ABS-KEY ((“radiofrequency” OR “diathermy” OR “capacitive–resistive” OR “hyperthermia”)) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY ((“pelvic floor” OR “pelvic floor disorders” OR “pelvic floor diseases” OR “female urogenital diseases” OR “pelvic floor dysfunction”))) |
| Web of Science | TS = ((* radiofrequency * OR * diathermy * OR * capacitive–resistive * OR * dielectric * OR * hyperthermia *)) AND TS = ((* pelvic floor * OR * pelvic floor disorders * OR * pelvic floor diseases * OR * female urogenital diseases * OR * pelvic floor dysfunction *)) |
| Author, Year | Study | Disorder | n | Outcomes | Intervention | Results | PEDro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bretelle et al., 2020 | RCT | Postpartum perineal pain | 60 EG(29) CG(31) | Perineal Pain (VAS), discomfort while walking and sitting (yes/no), analgesic intake | EG: 15′ of RFD (range 300–500 KHz) 1st and 2nd day of postpartum; CG: the same but sham therapy | Improvements in discomfort while walking and analgesic Intake in favor of experimental group, not in perineal pain (VAS) | 5/10 |
| Krychman et al., 2017 | RCT | Sexual function | 186 EG(123) CG(63) | Sexual function (FSFI, FSDS-R) | EG: cooled RFD (90 J/cm2); CG: RFD (1 J/cm2) | Improvements of 1.8 points in FSFI (p = 0.031) and 2.42 in FSDS-R | 6/10 |
| Pavone et al., 2017 | RCT | Peyronie’s disease | 96 EG(64) CG(32) | Erectile function (IIEF-5), quality of life (SF-36), pain during erection (VAS), penis curvature (°) | EG: 3 sessions (in 3 days) 5–8′ CAP (45%W) and 3′ RES (40%W); CG: the same without energy transfer | 2-point (VAS) reduction in pain during erection (p > 0.01), no changes in IIEF-5 or curvature | 5/10 |
| Lordelo et al., 2016 | RCT | Sexual function | 43 EG(21) CG(22) | Sexual function (FSFI) | EG: 8 sessions of RFD (7 days between session). RFD applied until tissue reached 39–41 °C, then 2′ more of treatment; CG: previously heated gel with no emission | 3.51 points (FSFI) of improvement for experimental group (p > 0.03) | 7/10 |
| Leibaschoff et al., 2016 | RCT | Menopausal Urinary Symptoms | 20 EG(10) CG(10) | Stress urinary incontinence (UDI-6, ICQ-SF UI), dyspareunia and dryness (VAS); Vaginal Health (VHI) | EG: 3–5′ RFD 40–45°; CG: sham RFD (the same without any heat) | Improvements in ICQ-SF UI and UDI-6 (p < 0.01) for experimental group | 5/10 |
| Author, Year | Study | Disorder | n | Outcomes | Intervention | Results | NOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fortún et al., 2022 | Case series | Endometriosis-related pain | 5 | Sex interference (EHP), MTP, pain (VAS), allodynia, neuropathic pain component (DN4) | 25 RFD sessions along 3 menstrual cycles, 30′ per session | Improvements in sex interference, dysmenorrhea intensity, myofascial and referral pain. | *** |
| Razaghi et al. 2021 | Case series | Stress urinary incontinence | 28 | Urinary incontinence (I-QOL, Q-tip test, 24 h pad test) | Once a week for 3 weeks, 10′ heating at 40 °C the vaginal wall (pulsed emission at 20–40 w and 1000–300 kHz) | Significant improvements in I-QOL score and the pad test | ** |
| Fernández-Cuadros et al., 2020 | Prospective study | Women chronic pelvic pain and dyspareunia | 37 | Pain (VAS), pelvic floor muscles strength (mmHg) | 8 session of pelvic floor muscles therapeutic exercise and 15′ RFD (5′capacitive +10′resistive) | Improvements in pain (3.52 VAS points) and muscle strength (both p < 0.0001) | *** |
| Dayan et al., 2019 | Case series | Postpartum restoration | 50 | Pelvic muscle tone and maximal contraction (biofeedback device) | 2 (n = 31) or 3 (n = 19) sessions of RFD | Improvement in maximal pelvic floor contraction, no changes in tone | *** |
| Sodre et al., 2019 | One-arm clinical trial | Men urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy | 10 | Pelvic floor muscular strength unidigital introduction (OGS), urinary incontinence (ICIQ-SF and ICIQ-OAB) | Endoanal RFD at 1 MHz and 3–4 kilojoules, 41 °C temperature (once temperature was reached, application stayed for 2′) | Decrease in urinary loss (n = 9) and resolution in n = 3 | *** |
| Wilson et al., 2018 | Non-randomized trial | Women stress urinary incontinence and orgasmic dysfunction | 10 | Sexual satisfaction (MSSQ and FSFI) | 3 RFD at 4-week intervals, 30′ per session at a temperature of 42–45 °C | Non-significative Improvements in stress urinary incontinence nor orgasmic dysfunction | * |
| Caruth et al., 2018 | Case series | Women urinary incontinence | 30 | Urinary incontinence (ICIQ-UI and IIQ), pelvic floor impact (PFIQ-7) | RFD in vaginal canal: Group 1 (16–20′), Group 2 (10–12′), Group 3 (6–8′), 43 °C maximum | Improvements for all outcomes at two months follow-up (p < 0.001) | * |
| Lordelo et al., 2017 | Case series | Women stress urinary incontinence | 10 | Pelvic floor muscular strength unidigital introduction (OGS), urinary loss (pad test) | Urethral meatus RFD, once per week along 5 weeks, 39–41 °C temperature (once temperature was reached, application stayed for 2′) | General improvement (p = 0.028) in urinary loss: 70% show reduction, 20% resolve and 30% worsening (pad test) | *** |
| Vicariotto et al., 2016 | Case series | Premenopausal and postmenopausal symptoms | 25 | Urinary incontinence (PISQ-12) | Four 10′ sessions of RFD, one each 10 days | Improvements in self-perceived dysuria/urinary incontinence and sexual function | * |
| Alinsod et al., 2016 | Case series | Women orgasmic dysfunction | 25 | Self-perceived time to orgasm | Three 25′ sessions of RFD in a month, elevating temperature between 40 and 45 °C on clitoris region | Reduction of 50% in time to orgasm | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Gutiérrez, M.D.; López-Garrido, Á.; Cortés-Pérez, I.; Obrero-Gaitán, E.; León-Morillas, F.; Ibáñez-Vera, A.J. Effects of Non-Invasive Radiofrequency Diathermy in Pelvic Floor Disorders: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2022, 58, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030437
González-Gutiérrez MD, López-Garrido Á, Cortés-Pérez I, Obrero-Gaitán E, León-Morillas F, Ibáñez-Vera AJ. Effects of Non-Invasive Radiofrequency Diathermy in Pelvic Floor Disorders: A Systematic Review. Medicina. 2022; 58(3):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030437
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Gutiérrez, María Dolores, Álvaro López-Garrido, Irene Cortés-Pérez, Esteban Obrero-Gaitán, Felipe León-Morillas, and Alfonso Javier Ibáñez-Vera. 2022. "Effects of Non-Invasive Radiofrequency Diathermy in Pelvic Floor Disorders: A Systematic Review" Medicina 58, no. 3: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030437
APA StyleGonzález-Gutiérrez, M. D., López-Garrido, Á., Cortés-Pérez, I., Obrero-Gaitán, E., León-Morillas, F., & Ibáñez-Vera, A. J. (2022). Effects of Non-Invasive Radiofrequency Diathermy in Pelvic Floor Disorders: A Systematic Review. Medicina, 58(3), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58030437









