Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment-Overview
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
3. Clinical Diagnosis and Manifestation
3.1. Ulcerative Colitis
3.2. Crohn’s Disease
3.3. Indeterminate Colitis
4. Core Tip
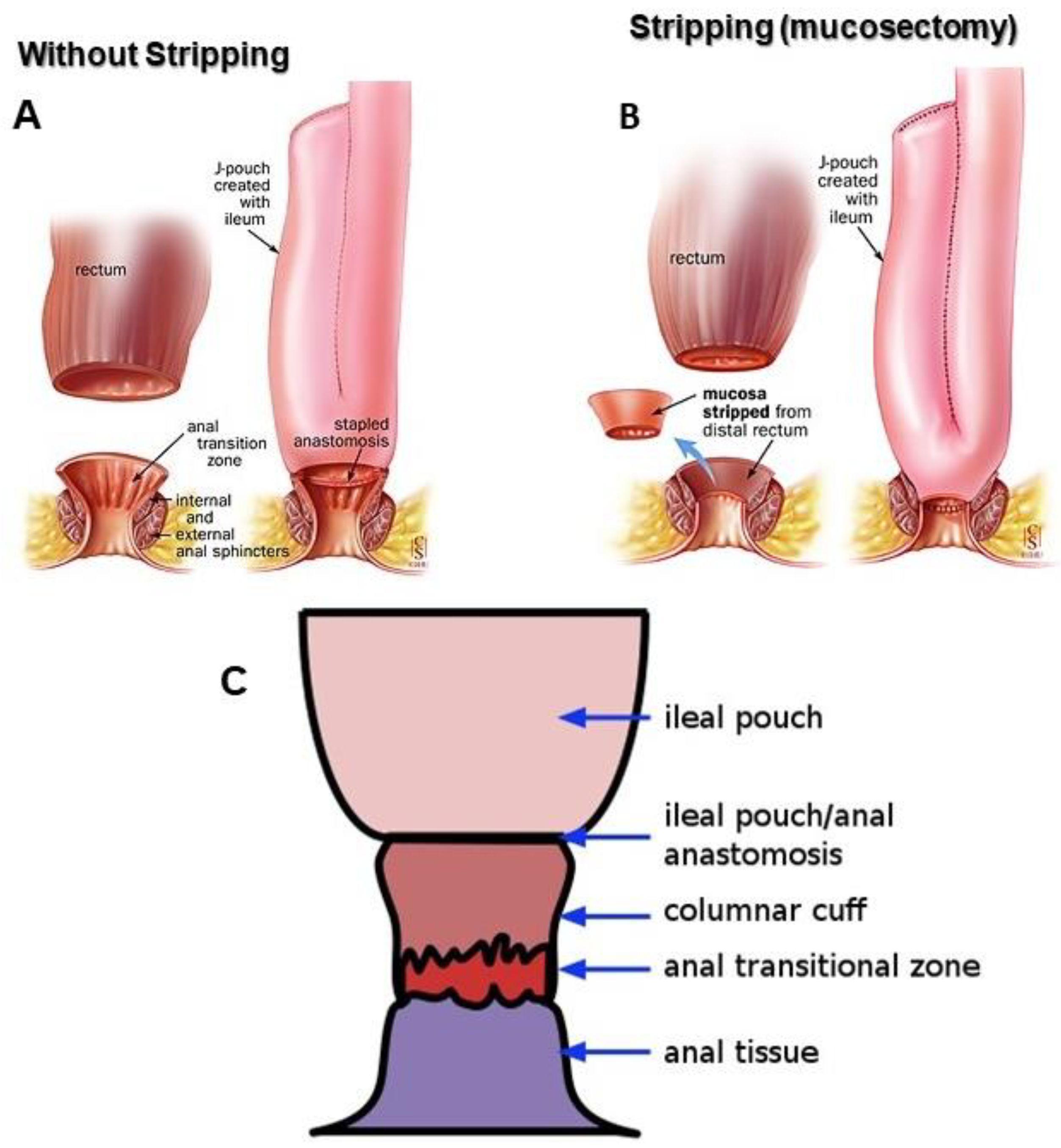
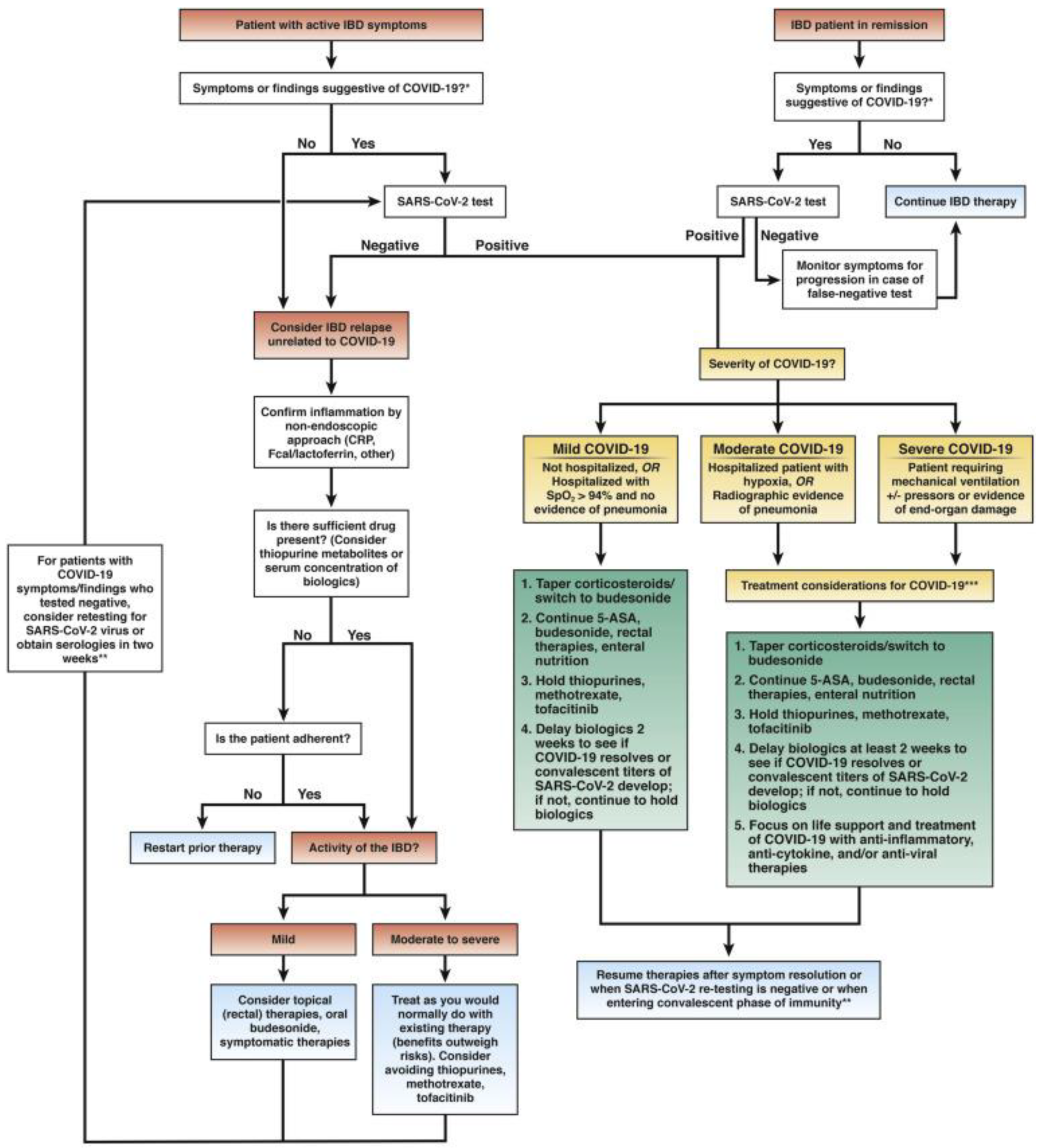
5. Surgical Treatment
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M’Koma, A.E. The Multifactorial Etiopathogeneses Interplay of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Overview. Gastrointest. Disord. 2018, 1, 75–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conrad, K.; Roggenbuck, D.; Laass, M.W. Diagnosis and classification of ulcerative colitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosti, P.A.; Stahl, T.J.; Sokol, A.I. Surgical repair of rectovaginal fistulas in patients with Crohn’s disease. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 171, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, O.H.; Rogler, G.; Hahnloser, D.; Thomsen, O.O. Diagnosis and management of fistulizing Crohn’s disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, R.S.; Chebli, J.M.F.; Amarante, H.; Flores, C.; Parente, J.M.L.; Ramos, O.; Fernandes, M.; Rocha, J.J.R.; Feitosa, M.R.; Feres, O.; et al. Quality of life, work productivity impairment and healthcare resources in inflammatory bowel diseases in Brazil. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5862–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciberras, M.; Karmiris, K.; Nascimento, C.; Tabone, T.; Nikolaou, P.; Theodoropoulou, A.; Mula, A.; Goren, I.; Yanai, H.; Amir, H.; et al. Mental health, work presenteeism and exercise in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Ueno, F.; Matsui, T.; Hirai, F.; Inoue, N.; Kato, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Koganei, K.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for inflammatory bowel disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 305–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapasi, R.; Glatter, J.; Lamb, C.A.; Acheson, A.G.; Andrews, C.; Arnott, I.D.; Barrett, K.J.; Bell, G.; Bhatnagar, G.; Bloom, S.; et al. Consensus standards of healthcare for adults and children with inflammatory bowel disease in the UK. Front. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amiot, A.; Bouguen, G.; Bonnaud, G.; Bouhnik, Y.; Hagege, H.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Abitbol, V.; Malamut, G.; Boruchowicz, A.; Siproudhis, L.; et al. Clinical guidelines for the management of inflammatory bowel disease: Update of a French national consensus. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.T.; Feuerstein, J.D.; Wang, A.Y.; Cohen, R.D. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Expert Commentary. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.D.; Korolkova, O.Y.; Sakwe, A.M.; Geiger, T.M.; James, S.D.; Muldoon, R.L.; Herline, A.J.; Goodwin, J.S.; Izban, M.G.; Washington, M.K.; et al. Human alpha defensin 5 is a candidate biomarker to delineate inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179710. [Google Scholar]
- M’Koma, A.E.; Wise, P.E.; Muldoon, R.L.; Schwartz, D.A.; Washington, M.K.; Herline, A.J. Evolution of the restorative proctocolectomy and its effects on gastrointestinal hormones. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2007, 22, 1143–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Kochhar, G.; Navaneethan, U.; Farraye, F.A.; Schwartz, D.A.; Iacucci, M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Dryden, G.; Cross, R.; Bruining, D.H.; et al. Practical guidelines on endoscopic treatment for Crohn’s disease strictures: A consensus statement from the Global Interventional Inflammatory Bowel Disease Group. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Nikfar, S.; Rezaie, A.; Abdollahi, M. A meta-analysis of antibiotic therapy for active ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, F.; Fuss, I.J.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E.; Blumberg, R.S.; Strober, W. Oxazolone colitis, a Th2 colitis model resembling ulcerative colitis, is mediated by IL-13-producing NK-T cells. Immunity 2002, 17, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmaily, H.; Sanei, Y.; Abdollahi, M. Autoantibodies and an immune-based rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7569–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W.; Fuss, I.J.; Blumberg, R.S. The immunology of mucosal models of inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 495–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.S.; Steinman, L.; Zamvil, S.S. Statins—Treatment option for central nervous system autoimmune disease? Neurotherapeutics 2007, 4, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward-Tharp, S.M.; Song, Y.J.; Siegel, R.M.; O’Shea, J.J. New insights into T cell biology and T cell-directed therapy for autoimmunity, inflammation, and immunosuppression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1183, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Leypoldt, F.; Kaya, Z.; Bieber, K.; McLachlan, S.M.; Komorowski, L.; Luo, J.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Hammers, C.M.; et al. Mechanisms of Autoantibody-Induced Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longobardi, T.; Jacobs, P.; Bernstein, C.N. Utilization of health care resources by individuals with inflammatory bowel disease in the United States: A profile of time since diagnosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, E.A.; Asch, S.M.; Adams, J.; Keesey, J.; Hicks, J.; DeCristofaro, A.; Kerr, E.A. The quality of health care delivered to adults in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappelman, M.D.; Dorn, S.D.; Peterson, E.; Runge, T.; Allen, J.I. Quality of care for gastrointestinal conditions: A primer for gastroenterologists. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crandall, W.V.; Margolis, P.A.; Kappelman, M.D.; King, E.C.; Pratt, J.M.; Boyle, B.M.; Duffy, L.F.; Grunow, J.E.; Kim, S.C.; Leibowitz, I.; et al. Improved Outcomes in a Quality Improvement Collaborative for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e1030–e1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogler, G.; Bernstein, C.N.; Sood, A.; Goh, K.L.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K.; Abbas, Z.; Fried, M. Role of biological therapy for inflammatory bowel disease in developing countries. Gut 2012, 61, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.M.; Hawkins, A.T.; James, S.D.; Ballard, B.R.; M’Koma, A.E. Inflammatory Bowel Disease On-Line Web-Based Guide to Health Professionals and Patients in Developing and African Nations. Jpn. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Threshold Values for Intervention Cost-Effectiveness by Region; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Cost Effectiveness and Strategic Planning (WHO-CHOICE); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bodger, K. Cost effectiveness of treatments for inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmacoeconomics 2011, 29, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryszyn, P.W.; Witczak, I. Costs in inflammatory bowel diseases. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2016, 11, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Papineau, N.; Zajaczkowski, J.; Rawsthorne, P.; Okrusko, G.; Blanchard, J.F. Direct hospital costs for patients with inflammatory bowel disease in a Canadian tertiary care university hospital. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzig, M.E.; Benchimol, E.I.; Lee, L.; Targownik, L.E.; Singh, H.; Kaplan, G.G.; Bernstein, C.N.; Bitton, A.; Nguyen, G.C.; Lee, K.; et al. The Impact of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Canada 2018: Direct Costs and Health Services Utilization. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2019, 2 (Suppl. 1), S17–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadstrup, K.; Alulis, S.; Borsi, A.; Elkjaer Stallknecht, S.; Nielsen, A.; Rikke Jorgensen, T.; Wennerstrom, C.; Qvist, N.; Munkholm, P. Societal costs attributable to Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis within the first 5 years after diagnosis: A Danish nationwide cost-of-illness study 2002–2016. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, S. Quantitative methods in the review of epidemiologic literature. Epidemiol. Rev. 1987, 9, 965–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loginov, A.S.; Parfenov, A.I.; Sivash, E.S.; Tsvetkov, V.F.; Zinov’ev, O.I. Crohn’s disease. The problem of early diagnosis. Ter. Arkh. 1992, 64, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, A.M. Challenging question: Can we diagnose Crohn’s disease without histology? Dig. Dis. 2013, 31, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, G.; Dignass, A.; Bokemeyer, B.; Danese, S.; Gionchetti, P.; Moser, G.; Beaugerie, L.; Gomollon, F.; Hauser, W.; Herrlinger, K.; et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis part 3: Special situations. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- M’Koma, A.E. Diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease: Potential role of molecular biometrics. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 6, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burakoff, R. Indeterminate colitis: Clinical spectrum of disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 38 (Suppl. 1), S41–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaine, W.J. Is indeterminate colitis determinable? Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2012, 14, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.D.; Hawkins, A.; Um, J.W.; Ballard, B.R.; Smoot, D.T.; M’Koma, A.E. The MYTHS of de novo Crohn’s Disease after Restorative Proctocolectomy with Ileal Pouch-anal Anastomosis for Ulcerative Colitis. Jpn. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jarchin, L.; Spencer, E.A.; Khaitov, S.; Greenstein, A.; Jossen, J.; Lai, J.; Dunkin, D.; Pittman, N.; Benkov, K.; Dubinsky, M.C. De Novo Crohn’s Disease of the Pouch in Children Undergoing Ileal Pouch-Anal Anastomosis for Ulcerative Colitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.D.; Hawkins, A.T.; M’Koma, A.E. Adenocarcinoma at the Ileostomy Site after a Proctocolectomy for Ulcerative Colitis and/or Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: An Overview. Ostomy/Wound Manag. 2018, 64, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Maclean, A.R.; Cohen, Z.; Macrae, H.M.; O’Connor, B.I.; McLeod, R.S. Crohn’s disease and indeterminate colitis and the ileal pouch-anal anastomosis: Outcomes and patterns of failure. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2005, 48, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumery, M.; Singh, S.; Dulai, P.S.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Sandborn, W.J. Natural History of Adult Ulcerative Colitis in Population-based Cohorts: A Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 343–356.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narula, N.; Kim, B.J.; Davis, C.H.; Dewhurst, W.L.; Samp, L.A.; Aloia, T.A. A proactive outreach intervention that decreases readmission after hepatectomy. Surgery 2018, 163, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodossi, A.; Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Jass, J.; Firth, J.; Dixon, M.; Leader, M.; Levison, D.A.; Lindley, R.; Filipe, I.; Price, A.; et al. Observer variation and discriminatory value of biopsy features in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1994, 35, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seldenrijk, C.A.; Morson, B.C.; Meuwissen, S.G.; Schipper, N.W.; Lindeman, J.; Meijer, C.J. Histopathological evaluation of colonic mucosal biopsy specimens in chronic inflammatory bowel disease: Diagnostic implications. Gut 1991, 32, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzardi, A.E.; Johnson, A.T.; Vogel, R.I.; Pambuccian, S.E.; Henriksen, J.; Skubitz, A.P.; Metzger, G.J.; Schmechel, S.C. Quantitative comparison of immunohistochemical staining measured by digital image analysis versus pathologist visual scoring. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavrielides, M.A.; Gallas, B.D.; Lenz, P.; Badano, A.; Hewitt, S.M. Observer variability in the interpretation of HER2/neu immunohistochemical expression with unaided and computer-aided digital microscopy. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.M.; Suarez, K.; Lim, E.; Singh, S.; Pereira, M.; Ibeawuchi, S.R.; Katkar, G.; Dunkel, Y.; Mittal, Y.; Chattopadhyay, R.; et al. Host engulfment pathway controls inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3967–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosli, M.; Sabbahi, H.; Alyousef, H.; Abdulhaq, M.; Hadadi, A.; Aljahdali, E.; Jawa, H.; Bazarah, S.; Qari, Y. Risk Stratification of Patients with Crohn’s Disease: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Decision Making and Its Impact on Long-Term Outcome. Dig. Dis. 2018, 36, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staradub, V.L.; Messenger, K.A.; Hao, N.; Wiley, E.L.; Morrow, M. Changes in breast cancer therapy because of pathology second opinions. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 9, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassopoulos, T.; Cohen, R.D.; Scherl, E.J.; Schwartz, R.M.; Kosinski, L.; Regueiro, M.D. Ulcerative Colitis Care Pathway. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truelove, S.C.; Horler, A.R.; Richards, W.C. Serial biopsy in ulcerative colitis. Br. Med. J. 1955, 2, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pabla, B.S.; Schwartz, D.A. Assessing Severity of Disease in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’Koma, A.E. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Expanding Global Health Problem. Clin. Med. Insights Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burisch, J.; Munkholm, P. Inflammatory bowel disease epidemiology. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 29, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molodecky, N.A.; Soon, I.S.; Rabi, D.M.; Ghali, W.A.; Ferris, M.; Chernoff, G.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Barkema, H.W.; et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 46–54.e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, N.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Sandborn, W.J. Recent advances in the management of perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease: Lessons for the clinic. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajendran, M.; Loganathan, P.; Catinella, A.P.; Hashash, J.G. A comprehensive review and update on Crohn’s disease. Dis. Mon. 2018, 64, 20–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajendran, M.; Bauer, A.J.; Buchholz, B.M.; Watson, A.R.; Koutroubakis, I.E.; Hashash, J.G.; Ramos-Rivers, C.; Shah, N.; Lee, K.K.; Cruz, R.J.; et al. Ileocecal Anastomosis Type Significantly Influences Long-Term Functional Status, Quality of Life, and Healthcare Utilization in Postoperative Crohn’s Disease Patients Independent of Inflammation Recurrence. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geboes, K.; Van Eyken, P. Inflammatory bowel disease unclassified and indeterminate colitis: The role of the pathologist. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Rabau, M.Y.; Haboubi, N.Y. Indeterminate colitis. Tech. Coloproctol. 2007, 11, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousvaros, A.; Antonioli, D.A.; Colletti, R.B.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Glickman, J.N.; Gold, B.D.; Griffiths, A.M.; Jevon, G.P.; et al.; North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition; Colitis Foundation of America Differentiating ulcerative colitis from Crohn disease in children and young adults: Report of a working group of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 44, 653–674. [Google Scholar]
- Adamina, M.; Bonovas, S.; Raine, T.; Spinelli, A.; Warusavitarne, J.; Armuzzi, A.; Bachmann, O.; Bager, P.; Biancone, L.; Bokemeyer, B.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; Hudesman, D. First-Line Biologics or Small Molecules in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Practical Guide for the Clinician. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Escher, J.; Hebuterne, X.; Klek, S.; Krznaric, Z.; Schneider, S.; Shamir, R.; Stardelova, K.; Wierdsma, N.; Wiskin, A.E.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical Nutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 632–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lega, S.; Pin, A.; Arrigo, S.; Cifaldi, C.; Girardelli, M.; Bianco, A.M.; Malamisura, M.; Angelino, G.; Faraci, S.; Rea, F.; et al. Diagnostic Approach to Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Clinical Practice: A Ten-Year Multicentric Experience. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, T.K.O.; Rachakonda, G.; Williams, A.D.; Hawkins, A.T.; James, S.D.; Sakwe, A.M.; Hui, N.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Goodwin, J.S.; et al. Linking bacterial enterotoxins and alpha Defensin 5 expansion in the Crohn’s colitis: A new insight into the etiopathogenetic and differentiation triggers driving colonic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2021, in press. [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, D.K. Inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyams, J.S.; Davis, P.; Grancher, K.; Lerer, T.; Justinich, C.J.; Markowitz, J. Clinical outcome of ulcerative colitis in children. J. Pediatr. 1996, 129, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, J.; Oota, M.; Iwama, T. Recent trends in ileoanal anastomosis. Ann. Chir. Gynaecol. 1986, 75, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parks, A.G.; Nicholls, R.J.; Belliveau, P. Proctocolectomy with ileal reservoir and anal anastomosis. Br. J. Surg. 1980, 67, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’Koma, A.; Wise, P.E.; Seeley, E.H.; Washington, M.K.; Schwartz, D.A.; Muldoon, R.L.; Herline, A.J.; Caprioli, R.M. Human Alpha Defensins are Differentially Expressed Between the Inflammatory Colitides. Gastroenterology 2010, 138 (Suppl. 1), S525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, E.H.; Washington, M.K.; Caprioli, R.M.; M’Koma, A.E. Proteomic patterns of colonic mucosal tissues delineate Crohn’s colitis and ulcerative colitis. Proteomics. Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narula, N.; Cooray, M.; Anglin, R.; Muqtadir, Z.; Narula, A.; Marshall, J.K. Impact of High-Dose Vitamin D3 Supplementation in Patients with Crohn’s Disease in Remission: A Pilot Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, N.; Kainz, S.; Petritsch, W.; Haas, T.; Feichtenschlager, T.; Novacek, G.; Eser, A.; Vogelsang, H.; Reinisch, W.; Papay, P. The efficacy and safety of either infliximab or adalimumab in 362 patients with anti-TNF-alpha naive Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narula, N.; Reinisch, W. Letter: Comparative safety and efficacy of infliximab vs. adalimumab in Crohn’s disease-should one consider disease location? Authors’ reply. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkins, A.T.; Um, J.W.; M’Koma, A.E. Adaptive Returns of Deficient Systemic Plasma Immunoglobulin G Levels as Rehabilitation Biomarker after Emergency Colectomy for Fulminant Ulcerative Colitis. Clin. Med. Insights Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 1179552217746692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.A.; Kennedy, N.A.; Raine, T.; Hendy, P.A.; Smith, P.J.; Limdi, J.K.; Hayee, B.; Lomer, M.C.E.; Parkes, G.C.; Selinger, C.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut 2019, 68 (Suppl. 3), s1–s106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.K.; Ali, M.S.; Manohar, D.B., Sr.; Sethi, M., Jr. A Challenging Case of Ileosigmoid Knotting in an Elderly. Cureus 2020, 12, e9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Williams, G.; Stephenson, B.M. The lateral rectus abdominis positioned stoma (LRAPS) trephine: The hope in Pandora’s box. Hernia 2020, 24, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Allegretti, J.R.; Siddique, S.M.; Terdiman, J.P. AGA Technical Review on the Management of Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1465–1496.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, C.; McLean, M.H.; Durum, S.K. Interleukin-27 as a Novel Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Critical Review of the Literature. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, J.M. How to fund IBD nurses. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31 (Suppl. 1), 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stange, E.F.; Schroeder, B.O. Microbiota and mucosal defense in IBD: An update. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahadevan, U.; Sandborn, W.J. Diagnosis and management of pouchitis. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1636–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B. Diagnosis and management of postoperative ileal pouch disorders. Clin. Colon. Rectal. Surg. 2010, 23, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.M.; Qiu, S.; M’Koma, A.E.; Powel, D.W.; Cohn, S.; Shi, X.Z. Sa130 Mechanical stress plays a critical role in intestinal fibrosis and smooth muscle hyperplasia in rodent model of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, S-431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geesala, R.L.Y.; Zhang, K.; M’Koma, A.E.; Cohn, S.; Shi, X.Z.P. Novel insights into the mechanism of action of exclusive enteral nutrition in Crohn’s disease: Pre-clinical study in a rodent model of Crohn’s-like colitis. Inflamm. Bowe. Dis. 2022, 28, S27–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacucci, M.; Cannatelli, R.; Labarile, N.; Mao, R.; Panaccione, R.; Danese, S.; Kochhar, G.S.; Ghosh, S.; Shen, B. Endoscopy in inflammatory bowel diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic and post-pandemic period. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, G.R.; Rubin, D.T. Coronavirus and Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Management Strategies for the Practicing Clinician. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajendran, M.; Perisetti, A.; Aziz, M.; Raghavapuram, S.; Bansal, P.; Tharian, B.; Goyal, H. Inflammatory bowel disease amid the COVID-19 pandemic: Impact, management strategies, and lessons learned. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2020, 33, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, O.M.; Rispo, A.; Testa, A.; Imperatore, N.; Pellegrini, L.; Guarino, A.D.; Ricciolino, S.; Patturelli, M.; De Palma, G.; Castiglione, F. The impact of a dedicated contact centre on the clinical outcome of patients with inflammatory bowel disease during the COVID-19 outbreak. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820959586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebli, J.M.F.; Queiroz, N.S.F.; Damiao, A.; Chebli, L.A.; Costa, M.H.M.; Parra, R.S. How to manage inflammatory bowel disease during the COVID-19 pandemic: A guide for the practicing clinician. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1022–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, C.W.; Irving, P.M.; Beaugerie, L. COVID-19 and IBD drugs: Should we change anything at the moment? Gut 2021, 70, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxonera, C.; Alba, C.; Olivares, D.; Martin, M.; Ventero, A.; Canas, M. Innovation in IBD Care during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Results of a Cross-Sectional Survey on Patient-Reported Experience Measures. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 27, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, O.M.; Rispo, A.; Castiglione, F. Noninvasive monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease in the post COVID-19 era. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2020, 52, 1236–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysha, A.A.; Rentsch, C.; Prentice, R.; Johnson, D.; Bryant, R.V.; Ward, M.G.; Costello, S.P.; Lewindon, P.; Ghaly, S.; Connor, S.J.; et al. Practical management of inflammatory bowel disease patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: Expert commentary from the Gastroenterological Society of Australia Inflammatory Bowel Disease faculty. Intern. Med. J. 2020, 50, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Lim, J.K.; Altayar, O.; Davitkov, P.; Feuerstein, J.D.; Siddique, S.M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; El-Serag, H.B. AGA Rapid Recommendations for Gastrointestinal Procedures during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 739–758.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH; CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19); CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Truelove and Witts Criteria | |||||
| Variable | Mild | Severe | Fulminant | ||
| No. of stools/day | <4 | >6 | >10 | ||
| Blood in stool | Intermittent | Frequent | Continuous | ||
| Temperature, °C | Normal | >37.5 | >37.5 | ||
| Pulse rates/min | Normal | >90 | >90 | ||
| Hemoglobin | Normal | <75% normal | Transfusion required | ||
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, mm/h | ≤30 | >30 | >30 | ||
| Colonic features on radiograph/imaging | None | Air, edematous wall, thumbprinting | Colonic dilatation | ||
| Clinical signs | None | Abdominal tenderness | Abdominal distension and tenderness | ||
| Mayo Score for Ulcerative Colitis | |||||
| Variable | Definition | Score | Variable | Definition | Score |
| Stool pattern | Normal no. of daily bowel movement | 0 | Endoscopic finding | Inactive colitis | 0 |
| 1–2 more bowel movement than normal | 1 | Erythema, vascularity | 1 | ||
| 3–4 more bowel movement than normal | 2 | Friability, marked erythema, erosions | 2 | ||
| 5 or more bowel movement than normal | 3 | Ulceration, severe friability spontaneous bleeding | 3 | ||
| Most severe rectal | None | 0 | Physician Global | Normal | 0 |
| bleeding of the day | Bollo streaks seen in the stool less than | 1 | Assessment | Mild colitis | |
| half of the time | 1 | ||||
| Blood in most stool | 2 | Moderate colitis | 2 | ||
| Pure blood passed | 3 | Severe colitis | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
M’Koma, A.E. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment-Overview. Medicina 2022, 58, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050567
M’Koma AE. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment-Overview. Medicina. 2022; 58(5):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050567
Chicago/Turabian StyleM’Koma, Amosy Ephreim. 2022. "Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment-Overview" Medicina 58, no. 5: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050567
APA StyleM’Koma, A. E. (2022). Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment-Overview. Medicina, 58(5), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58050567






