Prediction of Heart Function and Volume Status in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients through N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Laboratory Measures
2.3. Measurement of Echocardiographic Parameters
2.4. Definition of Diastolic Dysfunction
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Patients
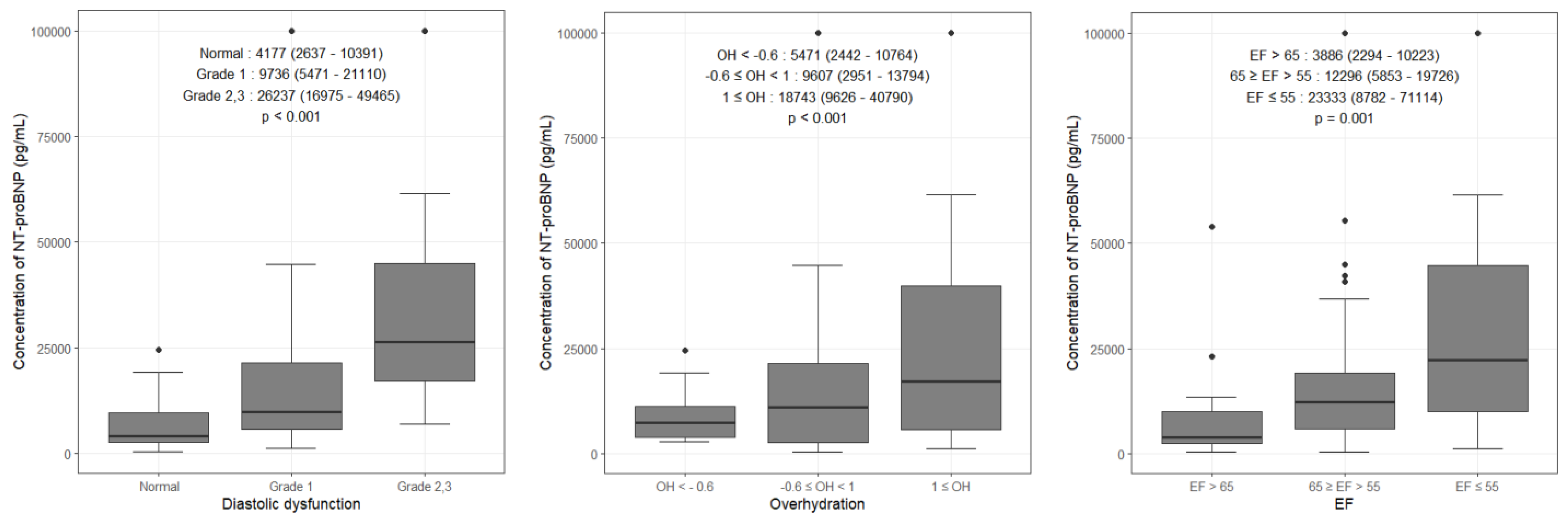
3.2. Comparison of NT-proBNP Levels According to Variables
3.3. Risk Factors for Higher NT-proBNP Level
3.4. Cutoff Level of NT-proBNP for HF
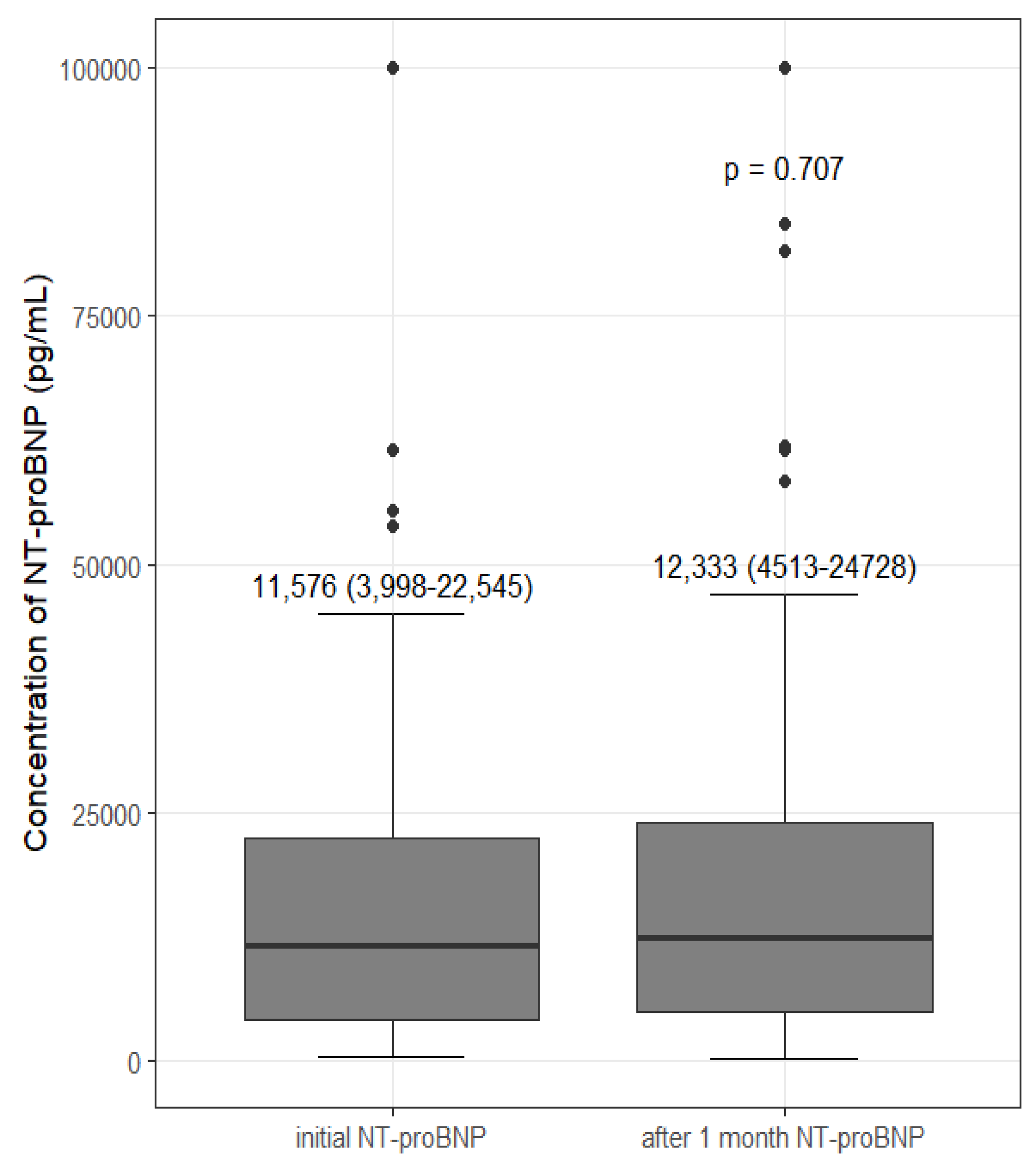
3.5. Change in NT-proBNP after Intervention
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review and Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, R.N.; Parfrey, P.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, S16–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trespalacios, F.C.; Taylor, A.J.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Bakris, G.L.; Abbott, K.C. Heart failure as a cause for hospitalization in chronic dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.H.; Ladefoged, S.; Corell, P.; Schou, M.; Hildebrandt, P.R.; Atar, D. N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide predicts mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease in hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.H.; Park, J.J.; Choi, D.J.; Yoon, C.H.; Oh, I.Y.; Kang, S.M.; Yoo, B.S.; Jeon, E.S.; Kim, J.J.; Cho, M.C.; et al. Prognostic value of NT-proBNP in heart failure with preserved versus reduced EF. Heart 2015, 101, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaphiriou, A.; Robb, S.; Murray-Thomas, T.; Mendez, G.; Fox, K.; McDonagh, T.; Hardman, S.M.; Dargie, H.J.; Cowie, M.R. The diagnostic accuracy of plasma BNP and NTproBNP in patients referred from primary care with suspected heart failure: Results of the UK natriuretic peptide study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2005, 7, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Shan, L.; Wei, M. NT-proBNP test with improved accuracy for the diagnosis of chronic heart failure. Medicine 2017, 96, e9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Kümpers, P.; Seidler, V.; Biertz, F.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D. Diagnostic value of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) for left ventricular dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5 on haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2008, 23, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyan, S.; Light, R.P.; Agarwal, R. Relationships of N-terminal pro-B-natriuretic peptide and cardiac troponin T to left ventricular mass and function and mortality in asymptomatic hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 50, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flythe, J.E.; Bansal, N. The relationship of volume overload and its control to hypertension in hemodialysis patients. Semin. Dial. 2019, 32, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, J.; Pinney, J.; Davenport, A. N-terminal proBNP—Marker of cardiac dysfunction, fluid overload, or malnutrition in hemodialysis patients? Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Zou, J.; Shen, B.; Ding, X. Association of N-Terminal Pro-brain Natriuretic Peptide With Volume Status and Cardiac Function in Hemodialysis Patients. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 646402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.Y.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.W.; Jin, K. Clinical efficacy of biomarkers for evaluation of volume status in dialysis patients. Medicine 2020, 99, e21460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, S.; Price, C.P.; John, R.I.; Abbas, N.A.; Webb, M.C.; Kempson, M.E.; Lamb, E.J. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and amino-terminal proBNP in patients with CKD: Relationship to renal function and left ventricular hypertrophy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchner, A.; Hengstenberg, C.; Löwel, H.; Riegger, G.A.; Schunkert, H.; Holmer, S. Effect of compensated renal dysfunction on approved heart failure markers: Direct comparison of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP. Hypertension 2005, 46, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, T.G.; Shukalek, C.B.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Zarnke, K.B.; Ronksley, P.E.; Iragorri, N.; Graham, M.M.; James, M.T. Association of NT-proBNP and BNP With Future Clinical Outcomes in Patients With ESKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemodialysis Adequacy 2006 Work Group. Clinical practice guidelines for hemodialysis adequacy, update 2006. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48 (Suppl. S1), S2–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedberg, K.; Cleland, J.; Dargie, H.; Drexler, H.; Follath, F.; Komajda, M.; Tavazzi, L.; Smiseth, O.A.; Gavazzi, A.; Haverich, A.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic heart failure: Executive summary (update 2005): The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 1115–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1–39.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Smiseth, O.A.; Appleton, C.P.; Byrd, B.F., III; Dokainish, H.; Edvardsen, T.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Gillebert, T.C.; Klein, A.L.; Lancellotti, P.; et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016, 29, 277–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasue, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Sumida, H.; Kikuta, K.; Kugiyama, K.; Jougasaki, M.; Ogawa, H.; Okumura, K.; Mukoyama, M.; Nakao, K. Localization and mechanism of secretion of B-type natriuretic peptide in comparison with those of A-type natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and patients with heart failure. Circulation 1994, 90, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayés-Genís, A. The circulating NTproBNP level, a new biomarker for the diagnosis of heart failure in patients with acute shortness of breath. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2005, 58, 1142–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoits-Filho, R.; Bucharles, S.; Barberato, S.H. Diastolic heart failure in dialysis patients: Mechanisms, diagnostic approach, and treatment. Semin. Dial. 2012, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, J.; McKelvie, R.; Lonn, E.; Tait, P.; Carlsson, J.; Gianni, M.; Jarnert, C.; Persson, H. BNP and NT-proBNP predict echocardiographic severity of diastolic dysfunction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.N.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Paul, G.K.; Debnath, R.C.; Shakil, S.S. Association of Diastolic Dysfunction with N-terminal Pro-B-type Natriuretic Peptide Level in Heart Failure Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Mymensingh Med. J. 2019, 28, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.A.; Kim, D.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Oh, D.J.; Yu, S.H.; Kang, E.T. Association between serum n-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide concentration and left ventricular dysfunction and extracellular water in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Perit. Dial. Int. 2006, 26, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Yang, J.W.; Yoo, J.S.; Choi, S.O.; Han, B.G. Association between E/e ratio and fluid overload in patients with predialysis chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.G.; Song, S.H.; Yoo, J.S.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, E. Association between OH/ECW and echocardiographic parameters in CKD5 patients not undergoing dialysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, B.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.O.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, J.S. Relative overhydration is independently associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in dialysis naive patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Yilmaz, B.; Küçükseymen, S.; Özpelit, E.; Pekel, N. Association of overhydration and cardiac dysfunction in patients have chronic kidney disease but not yet dialysis. Nephrol. Ther. 2016, 12, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, M.J.; Marcelli, D.; Canaud, B.; Konings, C.J.; Leunissen, K.M.; Levin, N.W.; Carioni, P.; Maheshwari, V.; Raimann, J.G.; van der Sande, F.M.; et al. Unraveling the relationship between mortality, hyponatremia, inflammation and malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: Results from the international MONDO initiative. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Chiu, Y.W.; Kuo, H.T.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, T.H.; Lin, M.Y.; Hwang, S.J.; Kuo, M.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; et al. The interaction between fluid status and angiopoietin-2 in adverse renal outcomes of chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.; Talens-Visconti, R.; Salvador, A.; Bertomeu, V.; Miro, V.; Garcia de Burgos, F.; Climent, V.; Cortes, R.; Paya, R.; Perez-Bosca, J.L.; et al. NT-proBNP levels and hypertension. Their importance in the diagnosis of heart failure. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2004, 57, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Values |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60.8 ± 11.7 |
| Sex (M/F) | 49/47 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.42 ± 3.77 |
| Duration of dialysis treatment (months) | 86 (4–352) |
| History of hypertension (%) | 91.7 |
| History of diabetes (%) | 42.7 |
| History of IHD (%) | 19.8 |
| History of CHF (%) | 26 |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 2.1 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 155 ± 18 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 72 ± 13 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 77 ± 9 |
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 10.7 ± 0.8 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.0 ± 0.4 |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 4.8 ± 1.0 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 11,576 (4058–22,460) |
| Kt/V | 1.65 ± 0.2 |
| BIS-OH (L) | 0.4 (−0.7–1.5) |
| EF (%) | 59.2 ± 8.2 |
| Wall motion abnormality (%) | 12.5 |
| LVH (%) | 42.7 |
| Diastolic dysfunction (%) | 63.2 |
| Variable | Yes | No | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 12,261 (3939–22,631) | 9736 (3599–22,744) | 0.565 |
| History of hypertension | 12,274 (4179–23,698) | 7724.5 (3886–9348.5) | 0.118 |
| History of diabetes | 12,261 (2879–24,378) | 9736 (4177–18,563) | 0.897 |
| History of IHD | 17,033 (3017–24,378) | 9736 (4058–21,967) | 0.448 |
| History of CHF | 18,743 (12,385–50,154) | 8931 (3170–17,413) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 64,716 (29,432–100,000) | 10,794.5 (3939–21,304) | 0.045 |
| Wall motion abnormality | 29,027 (13,550–100,000) | 9673 (38,41–18,698) | 0.001 |
| LVH | 21,110 (12,665–40,790) | 6006 (2637–11,955) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic dysfunction | 17,129 (7771–29,075) | 4177 (2637–10,391) | <0.001 |
| Independent Variable | p-Value | β |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.827 | −0.021 |
| Sex | 0.007 | 0.350 |
| Body mass index | 0.377 | −0.104 |
| History of diabetes | 0.695 | −0.040 |
| Duration of dialysis treatment | 0.265 | −0.110 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.778 | 0.027 |
| Kt/V | 0.104 | −0.234 |
| BIS-OH | 0.001 | 0.331 |
| EF | 0.001 | −0.340 |
| Diastolic dysfunction | 0.027 | 0.226 |
| Variable | NT-ProBNP | p-Value | NT-ProBNP | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <4058 (n = 24) | ≥4058 (n = 72) | <11,576 (n = 48) | ≥11,576 (n = 48) | |||
| Age (years) | 0.827 | −0.021 | ||||
| EF (%) | 0.174 | 0.070 | ||||
| <55 | 1 (4.2) | 12 (16.7) | 3 (6.3) | 10 (20.8) | ||
| ≥55 | 23 (95.8) | 60 (83.3) | 45 (93.8) | 38 (79.2) | ||
| Diastolic dysfunction | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 7 (29.2) | 53 (73.6) | 20 (41.7) | 40 (83.3) | ||
| No | 17 (70.8) | 18 (25.0) | 28 (58.3) | 7 (14.6) | ||
| Wall motion abnormality | 0.284 | 0.027 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (4.2) | 11 (15.3) | 2 (4.2) | 10 (20.8) | ||
| No | 23 (95.8) | 61 (84.7) | 46 (95.8) | 38 (79.2) | ||
| LVH | 0.004 | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 4 (16.7) | 37 (51.4) | 7 (14.6) | 34 (70.8) | ||
| No | 20 (83.3) | 35 (48.6) | 41 (85.4) | 14 (29.2) | ||
| Total (n = 96) | Group 1 (n = 17) a | Group 2 (n = 11) b | Group 3 (n = 23) c | Group 4 (n = 45) d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔNT-proBNP e | 306 (−1341–3662) | −210 (−12,899–3142) | −887 (−6739–2925) | 1575 (−113–6439) | 330 (−1090–3585) |
| p-Value | 0.016 | 0.104 f | 0.007 g | 0.118 h | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.H.; Moon, I.; Oh, Y.S.; Yu, B.C.; Park, M.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Choi, S.J. Prediction of Heart Function and Volume Status in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients through N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide. Medicina 2022, 58, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080975
Lee KH, Moon I, Oh YS, Yu BC, Park MY, Kim JK, Choi SJ. Prediction of Heart Function and Volume Status in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients through N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide. Medicina. 2022; 58(8):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080975
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kyung Ho, Inki Moon, Young Seung Oh, Byung Chul Yu, Moo Yong Park, Jin Kuk Kim, and Soo Jeong Choi. 2022. "Prediction of Heart Function and Volume Status in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients through N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide" Medicina 58, no. 8: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080975
APA StyleLee, K. H., Moon, I., Oh, Y. S., Yu, B. C., Park, M. Y., Kim, J. K., & Choi, S. J. (2022). Prediction of Heart Function and Volume Status in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients through N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide. Medicina, 58(8), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58080975






