Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Current Recommendations for Salt Intake
3.1.1. Salt Requirement Recommendations for the General Population
3.1.2. Salt Restriction Recommendations in Particular Situations: HF and CKD
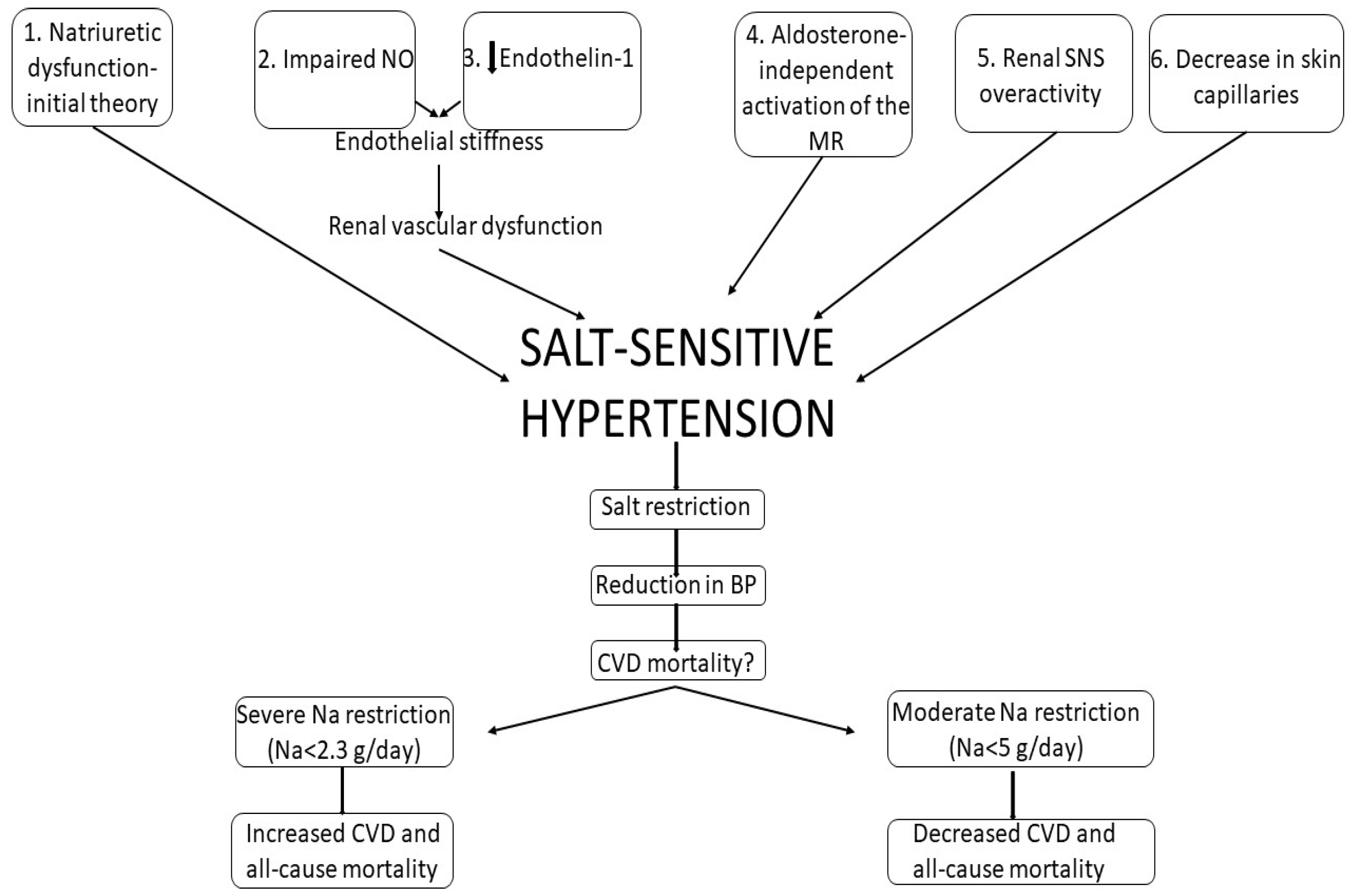
3.2. Salt-Sensitive versus Salt-Resistant Hypertension
3.3. Salt and Cardiovascular Events
3.4. Low-Salt Diet—Advantages
3.4.1. Low-Salt Diet and BP
| Outcome | Evidence from Meta-Analyses |
|---|---|
| BP | Dose-response relationship between salt reduction and BP decrease (He 2013 [47], Taylor 2011 [48], Graudal 2020 [32], Aburto 2013 [49]) |
| CV events |
|
| HF | Severe salt restriction: |
| Lipids | Salt restriction: |
| Kidney function | Salt reduction:
|
3.4.2. Salt Intake and CKD
3.4.3. Salt Intake and Stroke
3.4.4. Salt Intake and HF
3.5. “Salt Not Always an Enemy”: The Deleterious Effects of Salt Restriction
3.5.1. CVD and All-Cause Mortality
3.5.2. HF
3.5.3. Metabolic Parameters
3.5.4. Hypotension
4. Conclusions
Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, R.; Sutradhar, R.; Yao, Z.; Wodchis, W.P.; Rosella, L.C. Smoking, drinking, diet and physical activity—Modifiable lifestyle risk factors and their associations with age to first chronic disease. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. A comprehensive review on salt and health and current experience of worldwide salt reduction programmes. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2008, 23, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Ippolito, R.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Strazzullo, P. Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suckling, R.J.; Swift, P.A. The health impacts of dietary sodium and a low-salt diet. Clin. Med. (Northfield Il) 2015, 15, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.A.; Tekle, D.; Rosewarne, E.; Flexner, N.; Cobb, L.; Al-Jawaldeh, A.; Kim, W.J.; Breda, J.; Whiting, S.; Campbell, N.; et al. A Systematic Review of Salt Reduction Initiatives Around the World: A Midterm Evaluation of Progress Towards the 2025 Global Non-Communicable Diseases Salt Reduction Target. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1768–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.R.; Cutler, J.A.; Obarzanek, E.; Buring, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Kumanyika, S.K.; Appel, L.J.; Whelton, P.K. Long term effects of dietary sodium reduction on cardiovascular disease outcomes: Observational follow-up of the trials of hypertension prevention (TOHP). BMJ 2007, 334, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, D.S.A.; Prieto, M.C.; Navar, L.G. Salt-Sensitive Hypertension: Perspectives on Intrarenal Mechanisms. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2015, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Ingole, S.; Jain, R. Salt sensitivity and its implication in clinical practice. Indian Heart J. 2018, 70, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T. Mechanism of Salt-Sensitive Hypertension: Focus on Adrenal and Sympathetic Nervous Systems. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Alderman, M.H.; Brady, A.J.B.; Diaz, R.; Gupta, R.; López-Jaramillo, P.; Luft, F.C.; Lüscher, T.F.; Mancia, G.; et al. Salt and cardiovascular disease: Insufficient evidence to recommend low sodium intake. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3363–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Sodium Intake for Adults and Children. In Guidel Sodium Intake Adults Child; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, e13–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, e895–e1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Outcomes Blood Pressure Work Group I; Disease, K.; Cheung, A.K.; Chang, T.I.; Cushman, W.C.; Furth, S.L.; Hou, F.F.; Ix, J.H.; Knoll, G.A.; Muntner, P.; et al. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Pract. Guidel. 2021, 99, S1–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C.; Coleman, T.G.; Granger, H.J. Circulation: Overall Regulation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1972, 34, 13–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, T.W.; DiCarlo, S.E.; Pravenec, M.; Morris, R.C. The pivotal role of renal vasodysfunction in salt sensitivity and the initiation of salt-induced hypertension. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, T.W.; DiCarlo, S.E.; Pravenec, M.; Morris, R.C. Changing views on the common physiologic abnormality that mediates salt sensitivity and initiation of salt-induced hypertension: Japanese research underpinning the vasodysfunction theory of salt sensitivity. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, I.S.; Tavares-Mordwinkin, R.; Castejon, A.M.; Alfieri, A.B.; Cubeddu, L.X. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphism, nitric oxide production, salt sensitivity and cardiovascular risk factors in Hispanics. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 19, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Vos, I.; Shaw, S.; Boer, P.; D’Uscio, L.V.; Gröne, H.J.; Rabelink, T.J.; Lattmann, T.; Moreau, P.; Lüscher, T.F. Dysfunctional renal nitric oxide synthase as a determinant of salt-sensitive hypertension: Mechanisms of renal artery endothelial dysfunction and role of endothelin for vascular hypertrophy and Glomerulosclerosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnock, D.G.; Kusche-Vihrog, K.; Tarjus, A.; Sheng, S.; Oberleithner, H.; Kleyman, T.R.; Jaisser, F. Blood pressure and amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in vascular and renal cells. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusche-Vihrog, K.; Tarjus, A.; Fels, J.; Jaisser, F. The epithelial Na+ channel. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertuglu, L.A.; Elijovich, F.; Laffer, C.L.; Kirabo, A. Salt-Sensitivity of Blood Pressure and Insulin Resistance. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPont, J.J.; Greaney, J.L.; Wenner, M.M.; Lennon-Edwards, S.L.; Sanders, P.W.; Farquhar, W.B.; Edwards, D.G. High Dietary Sodium Intake Impairs Endothelium-Dependent Dilation in Healthy Salt-Resistant Humans. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, P.W. Vascular consequences of dietary salt intake. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, L.; Galletti, F.; Fata ELa Sabino, P.; Strazzullo, P. Effect of dietary sodium restriction on arterial stiffness: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarazaki, H.; Ando, K.; Fujita, M.; Matsui, H.; Nagae, A.; Muraoka, K.; Kawarasaki, C.; Fujita, T. Mineralocorticoid receptor activation: A major contributor to salt-induced renal injury and hypertension in young rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 300, F1402–F1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodeo, C. Salt Appetite and Aging. Arq. Bras. De Cardiol. 2019, 113, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, W.M.; Sacks, F.M.; Ard, J.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; Conlin, P.R.; Svetkey, L.P.; Erlinger, T.P.; Moore, T.J.; et al. Effects of diet and sodium intake on blood pressure: Subgroup analysis of the DASH-sodium trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Oniki, H. High salt intake promotes a decline in renal function in hypertensive patients: A 10-year observational study. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 36, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Di Cola, M.S.; Savino, I.; Galletti, F.; Strazzullo, P. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Dietary Sodium Restriction with or without Concomitant Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System-Inhibiting Treatment on Albuminuria. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graudal, N.A.; Hubeck-Graudal, T.; Jurgens, G. Effects of low sodium diet versus high sodium diet on blood pressure, renin, aldosterone, catecholamines, cholesterol, and triglyceride. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison-Bernard, L.M. The renal renin-angiotensin system. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2009, 33, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, M.; Matsui, H.; Shibata, S.; Gotoda, T.; Fujita, T. Salt-induced nephropathy in obese spontaneously hypertensive rats via paradoxical activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor: Role of oxidative stress. Hypertens 2007, 50, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, S.; Nagase, M.; Yoshida, S.; Kawarazaki, W.; Kurihara, H.; Tanaka, H.; Miyoshi, J.; Takai, Y.; Fujita, T. Modification of mineralocorticoid receptor function by Rac1 GTPase: Implication in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohama, D.; Nishimoto, M.; Ayuzawa, N.; Kawarazaki, W.; Fujii, W.; Oba, S.; Shibata, S.; Marumo, T.; Fujita, T. Activation of Rac1-Mineralocorticoid Receptor Pathway Contributes to Renal Injury in Salt-Loaded db/db Mice. Hypertens 2021, 78, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonios, T.F.T.; Singer, D.R.J.; Markandu, N.D.; Mortimer, P.S.; MacGregor, G.A. Structural skin capillary rarefaction in essential hypertension. Hypertens 1999, 33, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze, J.; Dahlmann, A.; Lerchl, K.; Kopp, C.; Rakova, N.; Schrö Der, A.; Luft, F.C. Spooky sodium balance. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajah, V.; Connolly, K.; McEniery, C.; Wilkinson, I. Skin Sodium and Hypertension: A Paradigm Shift? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; D’Elia, L.; Kandala, N.B.; Cappuccio, F.P. Salt intake, stroke, and cardiovascular disease: Meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ 2009, 339, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto, N.J.; Ziolkovska, A.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Meerpohl, J.J. Effect of lower sodium intake on health: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 346, f1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graudal, N.; Jürgens, G.; Baslund, B.; Alderman, M.H. Compared with usual sodium intake, low- and excessive-sodium diets are associated with increased mortality: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Hypertens. 2014, 27, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, H.; Lee, S.F.; Mony, P.; Devanath, A.; et al. Urinary Sodium and Potassium Excretion, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Yusuf, S.; Mente, A.; Gao, P.; Mann, J.F.; Teo, K.; Sleight, P.; Sharma, A.M.; Dans, A.; Probstfield, J.; et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion and risk of cardiovascular events. JAMA 2011, 306, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayedi, A.; Ghomashi, F.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary sodium, sodium-to-potassium ratio, and risk of stroke: A systematic review and nonlinear dose-response meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. Intersalt: An international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24 hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. BMJ 1988, 297, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Li, J.; MacGregor, G.A. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2013, 346, f1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.S.; Ashton, K.E.; Moxham, T.; Hooper, L.; Ebrahim, S. Reduced dietary salt for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (cochrane review). Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, A.; O’Donnell, M.; Yusuf, S. Sodium Intake and Health: What Should We Recommend Based on the Current Evidence? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.U.; Riaz, H.; Valavoor, S.; Zhao, D.; Vaughan, L.; Okunrintemi, V.; Riaz, I.B.; Khan, M.S.; Kaluski, E.; et al. Effects of Nutritional Supplements and Dietary Interventions on Cardiovascular Outcomes An Umbrella Review and Evidence Map: An Umbrella Review and Evidence Map. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtani, K.R.; Heneghan, C.; Onakpoya, I.; Tierney, S.; Aronson, J.K.; Roberts, N.; Hobbs, F.D.R.; Nunan, D. Reduced Salt Intake for Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, E.J.; Campbell, K.L.; Bauer, J.D.; Mudge, D.W.; Kelly, J.T. Altered dietary salt intake for people with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 6, CD010070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Borrelli, S.; Provenzano, M.; De Stefano, T.; Vita, C.; Chiodini, P.; Minutolo, R.; de Nicola, L.; Conte, G. Dietary Salt Restriction in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Zou, M.; Zhen, Z.; Xue, Y. Effect of a sodium restriction diet on albuminuria and blood pressure in diabetic kidney disease patients: A meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Woodward, M.; Sacks, F.M.; Carey, V.J.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J. Time Course of Change in Blood Pressure from Sodium Reduction and the DASH Diet. Hypertension 2017, 70, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerbass, F.B.; Morais, J.G.; dos Santos, R.G.; Kruger, T.S.; Sczip, A.C.; da Luz Filho, H.A. Factors associated to salt intake in chronic hemodialysis patients. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2013, 35, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.F.F.; Peixoto, A.J. Sodium balance in maintenance hemodialysis. Semin. Dial. 2010, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze, J.; Krause, H.; Hecht, H.; Dietsch, P.; Rittweger, J.; Lang, R.; Kirsch, K.A.; Hilgers, K.F. Reduced osmotically inactive Na storage capacity and hypertension in the Dahl model. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2002, 283, F134–F141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitiyakara, C.; Chabrashvili, T.; Chen, Y.; Blau, J.; Karber, A.; Aslam, S.; Welch, W.J.; Wilcox, C.S. Salt intake, oxidative stress, and renal expression of NADPH oxidase and superoxide dismutase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketonen, J.; Merasto, S.; Paakkari, I.; Mervaala, E.M.A. High sodium intake increases vascular superoxide formation and promotes atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Blood Press. 2005, 14, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, C.K.; Michellazzo, S.M.; De Nucci, G.; Zatz, R. Sodium excess aggravates hypertension and renal parenchymal injury in rats with chronic NO inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, F697–F705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.M.; Burrell, L.M.; Black, M.J.; Wu, L.L.; Dilley, R.J.; Cooper, M.E.; Johnston, C.I. Salt induces myocardial and renal fibrosis in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circulation 1998, 98, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, M.E.; Temmar, M.; Kakou, A.; Lacolley, P.; Thornton, S.N. Sodium intake and vascular stiffness in hypertension. Hypertension 2009, 54, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, Y.; Joseph, J. Sodium Intake and Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.W.; Huang, L.H.; Ku, C.H. Use of dietary sodium intervention effect on neurohormonal and fluid overload in heart failure patients: Review of select research based literature. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2018, 42, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Yusuf, S. Sodium Intake and Cardiovascular Health. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.W.; Hailpern, S.M.; Fang, J.; Alderman, M.H. Sodium intake and mortality in the NHANES II follow-up study. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 275.e1–275.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, T.; Kuklina, E.V.; Flanders, W.D.; Hong, Y.; Gillespie, C.; Chang, M.; Gwinn, M.; Dowling, N.; Khoury, M.J.; et al. Sodium and potassium intake and mortality among US adults: Prospective data from the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterna, S.; Gaspare, P.; Fasullo, S.; Sarullo, F.M.; Di Pasquale, P. Normal-sodium diet compared with low-sodium diet in compensated congestive heart failure: Is sodium an old enemy or a new friend? Clin. Sci. 2008, 114, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado d’Almeida, K.S.; Rabelo-Silva, E.R.; Souza, G.C.; Trojahn, M.M.; Santin Barilli, S.L.; Aliti, G.; EduardoRohde, L.; Biolo, A.; Beck-da-Silv, L. Aggressive fluid and sodium restriction in decompensated heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Results from a randomized clinical trial. Nutrition 2018, 54, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricio, C.G.; Tanaka, D.M.; de Souza Gentil, J.R.; Ferreira Amato, C.A.; Marques, F.; Schwartzmann, P.V.; Schmidt, A.; Simões, M.V. A normal sodium diet preserves serum sodium levels during treatment of acute decompensated heart failure: A prospective, blind and randomized trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 32, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyas, E.; Jeitler, K.; Horvath, K.; Semlitsch, T.; Hemkens, L.G.; Pignitter, N.; Siebenhofer, A. Benefit assessment of salt reduction in patients with hypertension: Systematic overview. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulowicz, W.; Radziszewski, A. Pathogenesis and treatment of dialysis hypotension. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, S36–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kilpatrick, R.D.; McAllister, C.J.; Greenland, S.; Kopple, J.D. Reverse epidemiology of hypertension and cardiovascular death in the hemodialysis population: The 58th annual fall conference and scientific sessions. Hypertension 2005, 45, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hogas, M.; Statescu, C.; Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Bilha, S.C.; Haisan, A.; Timofte, D.; Hogas, S. Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective. Medicina 2022, 58, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175
Hogas M, Statescu C, Padurariu M, Ciobica A, Bilha SC, Haisan A, Timofte D, Hogas S. Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective. Medicina. 2022; 58(9):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175
Chicago/Turabian StyleHogas, Mihai, Cristian Statescu, Manuela Padurariu, Alin Ciobica, Stefana Catalina Bilha, Anca Haisan, Daniel Timofte, and Simona Hogas. 2022. "Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective" Medicina 58, no. 9: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175
APA StyleHogas, M., Statescu, C., Padurariu, M., Ciobica, A., Bilha, S. C., Haisan, A., Timofte, D., & Hogas, S. (2022). Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective. Medicina, 58(9), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175










